Seismogenic structure analysis of the MS5.7 Songyuan,Jilin,earthquake on May 28,2018
-
摘要:
利用黑龙江、吉林、内蒙古三省数字地震台网的三分量宽频带波形资料对2018年5月28日吉林省松原市宁江区发生的MS5.7地震进行了全波形矩张量反演,获取了此次地震的震源机制解和矩心位置;并使用震源-矩心方法讨论了该地震的发震断层。研究结果显示:松原MS5.7地震的矩震级为MW5.2,矩心位置为(45.225°N,124.685°E),矩心深度为7 km。震源机制解参数显示:该地震为走滑型;节面Ⅰ的走向、倾角和滑动角分别为217°,82°和164°;节面Ⅱ的走向、倾角和滑动角分别为309°,74°和8°;双力偶成分占96.4%,方差减少为93%。震源−矩心图显示震源更接近节面Ⅰ,与北东向的扶余—肇东断裂走向及倾角一致,因此,推测扶余—肇东断裂为发震断层。
Abstract:Based on the three-component waveform data of regional broadband stations of Heilongjiang, Jilin and Inner Mongolia digital seismic networks, the full waveform moment tensor inversion for the MS5.7 earthquake occurred in Ningjiang district of Songyuan, Jilin Province, on May 28, 2018 is carried out, and the focal mechanism solution and centroid position of the earthquake are obtained. And then the hypocenter-centroid method is used to determine the actual seismogenic fault. The results show that the moment magnitude is MW5.2, centroid position is (45.225°N, 124.685°E), and centroid depth is 7 km. The mechanism parameters of the earthquake are: strike 217°, dip 82°, rake 164° for the nodal planeⅠ , strike 309°, dip 74°, rake 8° for the nodal planeⅡ , and the event is of strike-slip type. Moreover, double-couple component is 96.4%, and variance reduction is 93%. The hypocenter-centroid plot indicates that the hypocenter is close to nodal plane Ⅰ , which is consistent with the strike and dip angle of the Fuyu-Zhaodong fault. Therefore, it is indicated that the Fuyu-Zhaodong fault is the real fault plane.
-
① 刘俊清等。2018。2018年5月28日松原宁江MS5.7地震序列及后续地震趋势分析报告。吉林省地震局内部资料。② 个人交流。
-
表 1 反演使用的宽频带台站仪器
Table 1 Broadband station instruments for inversion
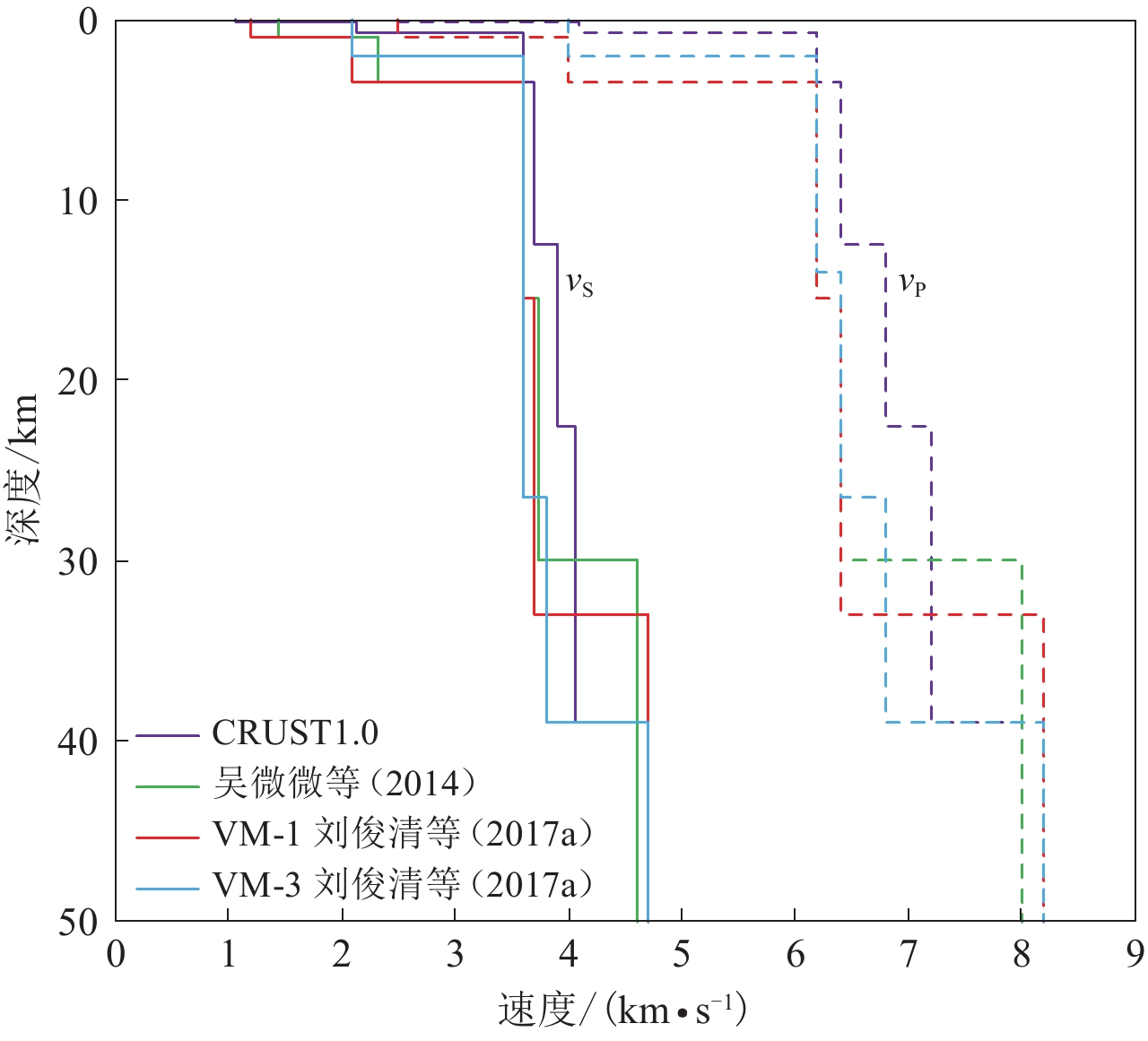
序号 台站名 采样率/Hz 地震计 数采 震中距/km 1 IDR 100 BBVS-60 EDAS-24IP 216 2 QAN 100 BBVS-60 EDAS-24IP 269 3 NEH 100 Guralp CMG-3ESPC EDAS-24IP 358 4 NZN 100 CIS-1H/VBB EDAS-24IP 290 5 WLT 100 CIS-1H/VBB EDAS-24L 226 6 GAN 100 CIS-1H/VBB EDAS-24IP 313 7 WAK 100 BBVS-60 EDAS-24IP 222 8 BNX 100 CIS-1H/VBB EDAS-24IP 217 9 WUC 100 Guralp CMG-3ESPC EDAS-24IP 187 10 YST 100 BBVS-60 EDAS-24GN 170 11 FMT 100 BBVS-60 EDAS-24IP 231 表 2 不同速度模型计算出的地震矩张量结果对比
Table 2 Comparison of moment tensor solutions calculated by different velocity models
速度模型 节面 走向/° 倾角/° 滑动角/° VR DC MW 矩心深度/km CRUST1.0 Ⅰ 217 77 162 64% 60.8% 5.1 6 Ⅱ 311 73 14 吴微微等(2014) Ⅰ 216 75 159 74% 73.3% 5.1 6 Ⅱ 312 70 16 刘俊清等(2017a)VM-1 Ⅰ 216 77 160 70% 70.4% 5.1 6 Ⅱ 311 71 13 刘俊清等(2017a)VM-3 Ⅰ 219 85 171 56% 53.9% 5.2 6 Ⅱ 310 81 5 表 3 不同震源机制计算结果对比
Table 3 Comparison of focal mechanisms from different agency or researchers
来源 MW 矩心深度/km 节面Ⅰ 节面Ⅱ DC VR 走向/° 倾角/° 滑动角/° 走向/° 倾角/° 滑动角/° 测试1 5.1 6 216 75 159 312 70 16 73.3% 74% 测试2 5.2 6 214 69 154 313 66 23 93.5% 88% 李君等(2019) − 6 220 79 162 314 72 12 − − GFZ (2018) 5.2 14 223 77 180 313 90 13 − − USGS (2018) 5.3 12 47 68 −169 313 80 −22 64% − 注:测试1为利用本文选择的全部11个宽频带台站反演的结果,测试2为利用NZN,IDR,WLT,WAK,BNX,YST和FMT等7个
宽频带台站反演结果表 4 松原MS5.7地震基本参数
Table 4 Basic parameters of Songyuan MS5.7 event
编号 发震时间 震中位置 MS 震源深度/km 震中位置 结果来源 年-月-日 时: 分: 秒 北纬/° 东经/° 1 2018-05-28 01: 50: 52.5 45.31 124.69 5.7 10 松原市宁江区 中国地震台网(2018) 2 2018-05-28 01: 50: 52.6 45.27 124.71 5.7 10 松原市宁江区 刘俊清等① 3 2018-05-28 01: 50: 52.6 45.24 124.64 5.3 10 扶余 USGS(2018) 4 2018-05-28 01: 50: 53.9 45.33 124.42 5.2 (MW) 10 东北 GFZ(2018) 5 2018-05-28 01: 50: 52.5 45.27 124.77 5.7 8.1 松原市宁江区 本文 -
李传友,汪一鹏,张良怀,李志田,李春风. 1999. 吉林省松原地区1119年6¾级地震的发震构造条件[J]. 中国地震,15(3):237–246. Li C Y,Wang Y P,Zhang L H,Li Z T,Li C F. 1999. Causative tectonic conditions of the historic earthquake (M=6¾) in 1119 in Songyuan area[J]. Earthquake Research in China,15(3):237–246 (in Chinese).
李君,王勤彩. 2018. 2013年松原5级震群序列精定位、震源机制解及发震构造特征[J]. 地震,38(4):62–73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3274.2018.04.006 Li J,Wang Q C. 2018. Relocation and focal mechanism of the Songyuan earthquake swarm sequence in 2013[J]. Earthquake,38(4):62–73 (in Chinese).
李君,王勤彩,郑国栋,刘庚,周辉,周聪. 2019. 2018年5月松原MS5.7地震序列发震断层及应力场特征[J]. 地震学报,41(2):207–218. doi: 10.11939/jass.20180101 Li J,Wang Q C,Zheng G D,Liu G,Zhou H,Zhou C. 2019. Characteristics of seismogenic faults and stress fields of the Song-yuan MS5.7 earthquake sequence in May 2018[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,41(2):207–218 (in Chinese).
刘俊清,刘财,雷建设,甘卫军,杨清福,张晨侠. 2017a. 2013年前郭MS5.8震群矩张量研究[J]. 地球物理学报,60(9):3418–3413. Liu J Q,Liu C,Lei J S,Gan W J,Yang Q F,Zhang C X. 2017a. The moment tensors of the 2013 Qianguo MS5.8 seismic swarm[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,60(9):3418–3431 (in Chinese).
刘俊清,甘卫军,刘财,张晨侠,高金哲,梁诗明. 2017b. 2013年吉林前郭MS5.5震群的双差法重新定位及震源机制[J]. 地震地质,39(5):981–993. Liu J Q,Gan W J,Liu C,Zhang C X,Gao J Z,Liang S M. 2017b. Relocations and focal mechanism solotions of MS5.5 Qianguo earthquake swarm in Jilin Province in 2013[J]. Seismology and Geology,39(5):981–993 (in Chinese).
刘俊清. 2018. 吉林省西部地区典型地震活动研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学: 17−22. Liu J Q. 2018. The Study of the Typical Seismicity in Western Region of Jilin Province[D]. Changchun: Jilin University: 17−22 (in Chinese).
刘权峰,盛俭,卢滔,张洪艳,盘晓东. 2017. 扶余/松原—肇东断裂研究综述[J]. 防灾科技学院学报,19(3):8–16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8047.2017.03.002 Liu Q F,Sheng J,Lu T,Zhang H Y,Pan X D. 2017. Research status of Fuyu/Songyuan-Zhaodong fault[J]. Journal of Institute of Disaster Prevention,19(3):8–16 (in Chinese).
刘双庆,薛艳,蔡宏雷,谢静. 2015. 利用重测定的震源深度特征探讨2013年吉林前郭5.8级震群发震因素[J]. 地震研究,38(2):211–220. Liu S Q,Xue Y,Cai H L,Xie J. 2015. Discussion on cause factor of Jilin Qianguo MS5.8 earthquake sequence in 2013 using focal depth characteristic of relocation[J]. Journal of Seismological Research,38(2):211–220 (in Chinese).
吕晗. 2017. 扶余/松原—肇东断层南段地震危险性分析[D]. 长春: 吉林大学: 2−20. Lü H. 2017. Risk Assessment of Southern Segment of Fuyu/Songyuan-Zhaodong Fault[D]. Changchun: Jilin University: 2−20 (in Chinese).
盘晓东,刘俊清,贾若,康建红,李婷,唐春呈. 2018. 2018年5月28日吉林松原宁江5.7级地震研究概述[J]. 国际地震动态,(8):151–152. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4975.2018.08.132 Pan X D,Liu J Q,Jia R,Kang J H,Li T,Tang C C. 2018. A summary of the study on the Ningjiang M5.7 earthquake in Songyuan,Jilin Province,May 28,2018[J]. Recent Developments in World Seismology,(8):151–152 (in Chinese).
盛书中,万永革,王晓山,黄骥超,徐志国,李静. 2017. 2013年吉林松原震群重定位及其发震构造[J]. 地学前缘,24(2):212–219. Sheng S Z,Wan Y G,Wang X S,Huang J C,Xu Z G,Li J. 2017. Relocation of the 2013 Songyuan earthquake swarm in Jilin Province and its seismogenic structure[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,24(2):212–219 (in Chinese).
唐雅芝. 1988. 1119年吉林省地震震中的确定[J]. 遥感信息,(1):27–29. Tang Y Z. 1988. Determination of location of epicenter of the 1119 earthquake in Jilin Province[J]. Remote Sensing Information,(1):27–29 (in Chinese).
唐雅芝. 1990. 公元1119年2月吉林省前郭强震三要素的确定[J]. 东北师大学报(自然科学版),(3):151–159. Tang Y Z. 1990. Three essential factor of a severe earthquake in Qianguo of Jilin Province on February,1119[J]. Journal of Northeast Normal University,(3):151–159 (in Chinese).
吴戈,房贺岩,李志田,方明远. 1988. 1119年前郭地震考察与研究[J]. 东北地震研究,4(1):67–76. Wu G,Fang H Y,Li Z T,Fang M Y. 1988. The investigation and study of Qianguo earthquake,1119[J]. Northeastern Seismological Research,4(1):67–76 (in Chinese).
吴微微,杨建思,苏金蓉,杜文康,高瑜,郑钰,田宝峰,刘莎,吴朋. 2014. 2013年吉林前郭一乾安震源区中强地震矩张量反演与区域孕震环境研究[J]. 地球物理学报,57(8):2541–2554. doi: 10.6038/cjg20140815 Wu W W,Yang J S,Su J R,Du W K,Gao Y,Zheng Y,Tian B F,Liu S,Wu P. 2014. Moment inversion of moderate earthquakes and seismogenic environment in Qianguo-Qian ’ an source region,2013,Jilin Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,57(8):2541–2554 (in Chinese).
杨文,薛艳,张小涛,韩颜颜,张雪梅. 2018. 2017年松原4.9级地震与2018年松原5.7级地震序列特征研究[J]. 国际地震动态,(8):77–78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4975.2018.08.068 Yang W,Xue Y,Zhang X T,Han Y Y,Zhang X M. 2018. Sequence characteristics of the 2017 Songyuan M4.9 earthquake and the 2018 Songyuan M5.7 earthquake[J]. Recent Developments in World Seismology,(8):77–78 (in Chinese).
于吉鹏,孟国杰,苏小宁,Shestakov N,Gerasimenko M,Takahashi H,Ohzono M,刘泰,李承涛. 2019. 基于GPS观测研究中国东北地区现今地壳形变特征[J]. 地震,39(3):11–27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3274.2019.03.002 Yu J P,Meng G J,Su X N,Shestakov N,Gerasimenko M,Takahashi H,Ohzono M,Liu T,Li C T. 2019. The current crustal deformation of Northeast China deduced from GPS observations[J]. Earthquake,39(3):11–27 (in Chinese).
中国地震台网中心. 2018. 吉林松原市宁江区5.7级地震[EB/OL]. [2018-12-20]. http://news.ceic.ac.cn/CC20180528015053.html. CENC. 2018. The MS5.7 earthquake in Ningjiang district of Songyuan, Jilin Province[EB/OL]. [2018-12-20]. http://news.ceic.ac.cn/CC20180528015053.html (in Chinese). 中国地震局第一监测中心. 2018. 水平应变率场[EB/OL]. [2018-12-20]. http://www.eqdsc.com/spyblc-1.html. First Crust Monitoring and Application Center, China Earthquake Administration. 2018. Horizontal strain rate field[EB/OL]. [2018-12-20]. http://www.eqdsc.com/spyblc-1.html (in Chinese).
Benetatos C,Málek J,Verga F. 2013. Moment tensor inversion for two micro-earthquakes occurring inside the Háje gas storage facilities,Czech republic[J]. J Seismol,17(2):557–577. doi: 10.1007/s10950-012-9337-0
GFZ. 2018. Earthquake info[EB/OL]. [2019-02-03].http://geofon.gfz-potsdam.de/eqinfo/event.php?id=gfz2018kict.
Bouchon M. 2003. A review of the discrete wavenumber method[J]. Pure Appl Geophys,160(3):445–465. doi: 10.1007/PL00012545
Fojtíková L,Zahradník J. 2014. A new strategy for weak events in sparse networks:The first-motion polarity solutions constrained by single-station waveform inversion[J]. Seismol Res Lett,85(6):1265–1274. doi: 10.1785/0220140072
Kikuchi M,Kanamori H. 1991. Inversion of complex body waves:Ⅲ[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,81(6):2335–2350.
Klein F W. 1989. User’s Guide to HYPOINVERSE: A Program for VAX Computers to Solve for Earthquake Locations and Magnitudes[R]. Virginia: U S Geological Survey: 89−314.
Krizova D,Zahradník J,Kiratzi A. 2013. Resolvability of isotropic component in regional seismic moment tensor inversion[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,103:2460–2473.
Sokos E N,Zahradnik J. 2008. ISOLA:A fortran code and a matlab GUI to perform multiple-point source inversion of seismic data[J]. Comput Geosci,34(8):967–977. doi: 10.1016/j.cageo.2007.07.005
Sokos E,Zahradník J. 2013. Evaluating centroid-moment-tensor uncertainty in the new version of ISOLA software[J]. Seismol Res Lett,84(4):656–665. doi: 10.1785/0220130002
USGS.2018. M5.3-14 km WNW of Fuyu, China[EB/OL]. [2019-02-03]. https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/eventpage/us1000eczp/executive.
Zahradník J,Serpetsidaki A,Sokos E,Tselentis G A. 2005. Iterative deconvolution of regional waveforms and a double-event interpretation of the 2003 Lefkada earthquake,Greece[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,95(1):159–172. doi: 10.1785/0120040035
Zahradník J,Gallovic F,Sokos E,Serpetsidaki A,Tselentis A. 2008a. Quick fault-plane identification by a geometrical method:Application to the MW6.2 Leonidio earthquake,6 January 2008,Greece[J]. Seismol Res Lett,79(5):653–662. doi: 10.1785/gssrl.79.5.653
Zahradník J,Jansky J,Plicka J. 2008b. Detailed waveform inversion for moment tensors of M~4 events:Examples from the Corinth gulf,Greece[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,98(6):2756–2771. doi: 10.1785/0120080124
Zahradník J,Custódio S. 2012. Moment tensor resolvability:Application to southwest Iberia[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,102(3):1235–1254. doi: 10.1785/0120110216





 下载:
下载: