Reconstruction method for diurnal variations ofthe geomagnetic field by XGBoost machine learning
-
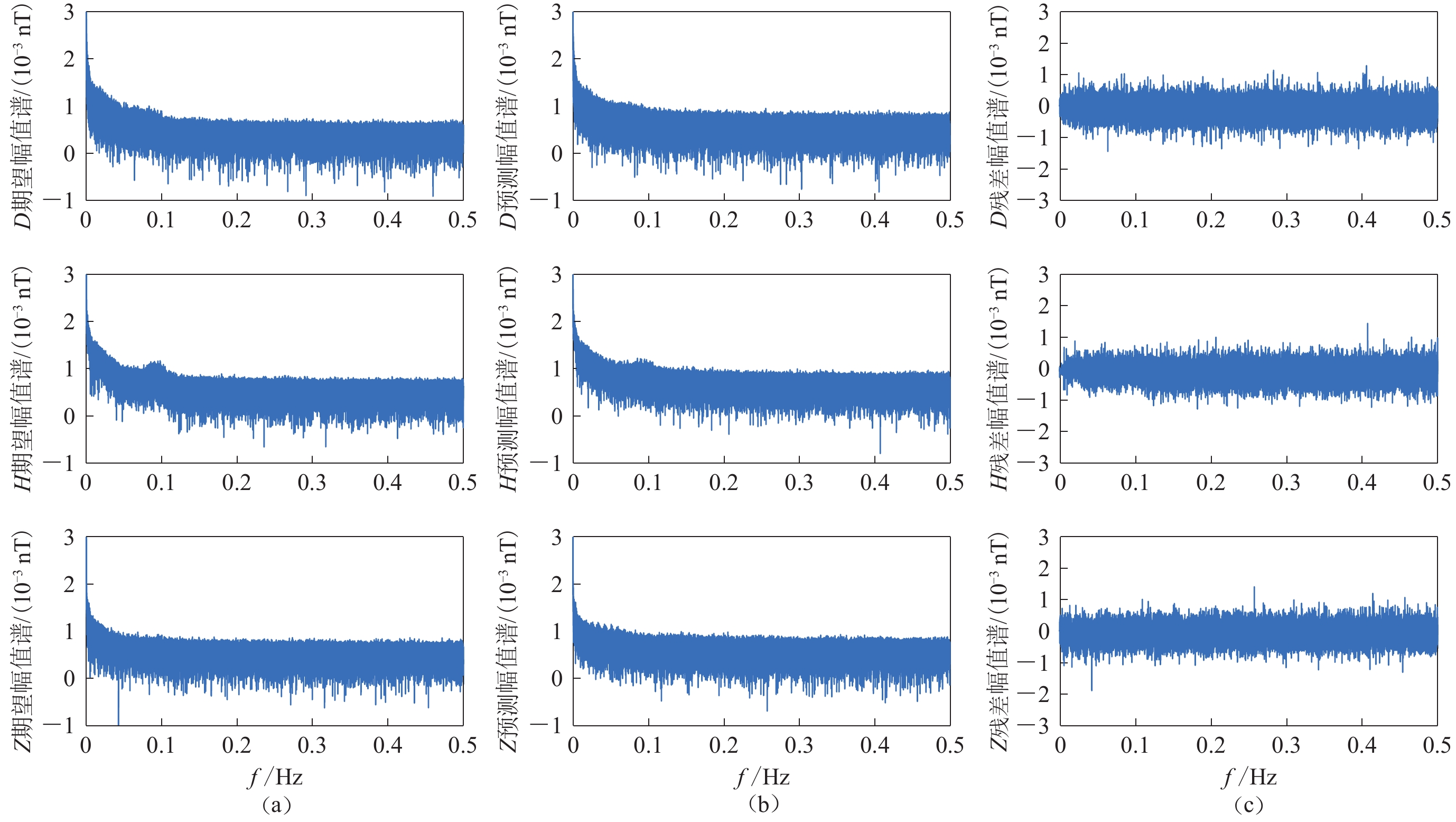
摘要: 为了重构或恢复存在严重干扰或数据缺失的台站观测数据,本文基于周边已有台站的高质量观测数据采用XGBoost机器学习方法重构地磁日变数据。仿真试验结果显示,无论是磁静日还是磁扰日,地磁场分量的绝对残差均值均低于0.1 nT。试验统计数据及重构结果残差曲线的对比分析表明,地磁日变重构精度与地磁活动性和待重构信号的时变剧烈程度有关;相较于反向传播神经网络,XGBoost方法对地磁场日变数据的重构精度更高。本文研究表明,基于XGBoost机器学习的重构方法在处理非线性复杂问题方面具有优势,能够用于高精度重构存在严重干扰或数据缺失的地磁台站观测数据的重构。Abstract: The long-term observation data of the geomagnetic field based on the geomagnetic stations (networks) are of great value for studying the spatio-temporal variation rules, characteristics, also and the field source information of the geomagnetic field. However, due to infrastructure and human activities (such as high-speed rail, highways, power grids, etc) as well as sudden instrument failures, there are interferences and missing observation data in some time periods for some observation stations. Therefore, this paper utilizes the XGBoost machine learning method to reconstruct the observation data of some stations with severe interference and missing data based on the high-quality observation data of existing stations in their surrounding areas. The results of simulation experiments show that the reconstruction residuals of geomagnetic field components are lower than 0.1 nT whether in magnetically quiet days or in disturbed days. Further comparative analysis of the experimental statistics and residual curve illustrates that the reconstruction accuracy mainly depends on the geomagnetic activity and the time-variable complexity of the signals to be reconstructed, and in addition the reconstruction accuracy by XGBoost method is higher than that by the BP neural network. This research suggests that, the reconstruction method by XGBoost machine learning has an advantage in dealing with nonlinear complex signals, and thus can be effectively applied to reconstruct the observation data of some stations with severe interference and missing data.
-
Keywords:
- data reconstruction /
- geomagnetic field /
- diurnal variations /
- XGBoost /
- machine learning
-
-
表 1 采用XGBoost方法与BP神经网络方法对2013年不同季节磁静日和磁扰日地磁场日变的绝对残差均值
Table 1 Mean absolute residual of geomagnetic daily variation on the magnetically quiet and disturbed days of different seasons in 2013 by XGBoost method and BP neural network method
季节 月-日 磁静/扰日 XGBoost BP神经网络 ∆D/nT ∆H/nT ∆Z/nT ∆D/nT ∆H/nT ∆Z/nT 春秋季 03-16 静日 0.067 0.160 0.082 0.370 0.480 0.390 03-25 扰日 0.074 0.103 0.094 0.980 1.120 1.020 04-05 扰日 0.125 0.164 0.066 1.340 2.070 1.510 04-19 静日 0.068 0.122 0.062 0.880 0.940 0.910 09-19 扰日 0.072 0.078 0.138 0.950 1.030 1.110 09-28 静日 0.045 0.058 0.130 0.260 0.420 0.340 10-02 扰日 0.136 0.152 0.143 0.860 0.910 0.890 10-10 静日 0.067 0.075 0.054 0.350 0.550 0.510 夏季 05-01 扰日 0.127 0.142 0.102 2.890 3.010 2.970 05-30 静日 0.105 0.128 0.046 1.550 1.860 1.900 06-02 扰日 0.072 0.122 0.055 3.570 1.050 2.330 06-25 静日 0.068 0.113 0.128 2.010 2.560 1.980 07-02 静日 0.087 0.105 0.134 1.970 2.310 2.220 07-07 扰日 0.098 0.129 0.240 4.010 3.540 3.040 08-15 扰日 0.077 0.127 0.083 2.510 2.010 1.030 08-29 静日 0.063 0.096 0.076 0.980 2.680 1.870 冬季 01-22 静日 0.056 0.043 0.057 0.530 0.750 0.420 01-26 扰日 0.063 0.048 0.049 0.640 1.050 0.990 02-06 静日 0.049 0.077 0.041 0.320 0.910 0.880 02-16 扰日 0.078 0.200 0.043 1.130 1.640 1.370 11-11 扰日 0.113 0.102 0.120 0.760 0.980 0.820 11-24 静日 0.089 0.095 0.107 0.220 0.350 0.290 12-02 静日 0.035 0.043 0.068 0.270 0.480 0.330 12-09 扰日 0.098 0.126 0.137 1.210 1.590 1.460 静日均值 0.072 0.089 0.082 0.809 1.191 1.003 扰日均值 0.094 0.119 0.106 1.738 1.667 1.545 总均值 0.083 0.106 0.094 1.273 1.429 1.274 -
安振昌. 1999. 1950—2000年中国地磁测量地磁图与地磁研究[J]. 地球物理学进展,14(4):75–88. An Z C. 1999. Geomagnetic surveys and geomagnetic charts and geomagnetic studies in China for 1950−2000[J]. Progress in Geophysics,14(4):75–88 (in Chinese).
安振昌,彭丰林,刘少华,王广福. 2014. 1683—1949年中国地磁测量、地磁图和地磁模型的总考评与研究[J]. 地球物理学报,57(11):3795–3803. An Z C,Peng F L,Liu S H,Wang G F. 2014. Inspection and study on the geomagnetic survey, charts and models during 1683−1949 in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,57(11):3795–3803 (in Chinese).
边刚,刘雁春,卞光浪,于波. 2009. 海洋磁力测量中多站地磁日变改正值计算方法研究[J]. 地球物理学报,52(10):2613–2618. Bian G,Liu Y C,Bian G L,Yu B. 2009. Research on computation method of multi-station diurnal variation correction in marine magnetic surveys[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,52(10):2613–2618 (in Chinese).
卞光浪,刘雁春,翟国君,边刚,于波. 2010. 基于纬差加权法的海洋磁力测量多站地磁日变改正值计算[J]. 测绘科学,35(3):118–120. Bian G L,Liu Y C,Zhai G J,Bian G,Yu B. 2010. Diurnal geomagnetic correction with multi-observatories in marine magnetic surveying[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping,35(3):118–120 (in Chinese).
冯志生,梅卫萍,张苏平,杜斌,居海华,杨从杰,张秀霞. 2005. FHD磁力仪Z分量分钟值日变化空间相关性的初步应用[J]. 华南地震,25(3):1–7. Feng Z S,Mei W P,Zhang S P,Du B,Ju H H,Yang C J,Zhang X X. 2005. Preliminary application of the daily-variation spatial correlation method of vertical component’s minutely value of FHD magnetometer[J]. South China Journal of Seismology,25(3):1–7 (in Chinese).
管志宁. 2005. 地磁场与磁力勘探[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 257–294. Guan Z N. 2005. Geomagnetic Field and Magnetic Exploration[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 257–294 (in Chinese).
郭建华,薛典军. 1999. 多台站磁日变校正方法研究及应用[J]. 地球学报,20(增刊):932–937. Guo J H,Xue D J. 1999. The application and method research of magnetic diurnal calibration based on multi-station[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica,20(S):932–937 (in Chinese).
李超,张文辉,林基明. 2019. 基于XGBoost算法的恒星/星系分类研究[J]. 天文学报,60(2):71–80. Li C,Zhang W H,Lin J M. 2019. Research on star/galaxy classification based on XGBoost algorithm[J]. Acta Astronomica Sinica,60(2):71–80 (in Chinese).
潘星辰,姚长利,郑元满,石磊,张素琴. 2020. 海洋磁测日变校正的纬度改正方法研究[J]. 地球物理学报,63(8):3025–3026. Pan X C,Yao C L,Zheng Y M,Shi L,Zhang S Q. 2020. Study on latitude correction method of diurnal variation correction for marine magnetic survey[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,63(8):3025–3026 (in Chinese).
单汝俭,金国,曾志成. 1990. 局部地区地磁日变及拟合方法研究[J]. 长春地质学院学报,20(3):315–322. Shan R J,Jin G,Zeng Z C. 1990. Study on geomagnetic diurnal variation and its fitting methods in local area[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Earth Science,20(3):315–322 (in Chinese).
吴琼,余文铖,洪海生,喻蕾,段炼,尚明远,刘哲. 2020. 基于XGBoost算法的配网台区低压跳闸概率预测[J]. 中国电力,53(4):105–113. Wu Q,Yu W C,Hong H S,Yu L,Duan L,Shang M Y,Liu Z. 2020. Probability prediction of low-voltage tripping failures in distribution transformer station areas based on XGBoost algorithm[J]. Electric Power,53(4):105–113 (in Chinese).
吴双,石宇强. 2019. 基于BP网络与XGBoost的质量控制方法研究[J]. 制造业自动化,41(12):12–17. Wu S,Shi Y Q. 2019. Research on quality control method based on BP network and XGBoost[J]. Manufacturing Automation,41(12):12–17 (in Chinese).
徐文耀. 2003. 地磁学[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 1–45. Xu W Y. 2003. Geomagnetism[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press: 1–45 (in Chinese).
徐行,廖开训,陈邦彦,王建革. 2007. 多台站地磁日变观测数据对远海磁测精度的影响分析[J]. 海洋测绘,27(1):38–40. Xu X,Liao K X,Chen B Y,Wang J G. 2007. The effect analysis of the observed diurnal magnetic variation from multi-stations on the accuracy of marine magnetic survey[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting,27(1):38–40 (in Chinese).
姚法章. 1988. 订正法在地磁绝对观测中的应用[J]. 地震地磁观测与研究,(6):35–38. Yao F Z. 1988. The application of correction method in geomagnetic absolute observation[J]. Seismological and Geomagnetic Observation and Research,(6):35–38 (in Chinese).
姚休义. 2015. 地磁台站观测异常识别与数据重构技术研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地球物理研究所: 88–99. Yao X Y. 2015. Method of Artificial Electromagnetic Disturbances Identification and Data Reconstruction[D]. Beijing: Institute of Geophysics, China Earthquake Administration: 88–99 (in Chinese).
姚休义,滕云田,杨冬梅,姚远,陈俊. 2016. 地磁观测数据重构技术研究[J]. 地震学报,38(6):878–888. Yao X Y,Teng Y T,Yang D M,Yao Y,Chen J. 2016. On reconstruction technique of geomagnetic observation data[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,38(6):878–888 (in Chinese).
姚休义,滕云田,杨冬梅,姚远. 2018. 基于神经网络的地磁观测数据重构研究[J]. 地球物理学报,61(6):2358–2368. Yao X Y,Teng Y T,Yang D M,Yao Y. 2018. Reconstruction of geomagnetic data based on artificial neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,61(6):2358–2368 (in Chinese).
张向宇,关永贤,张锡林. 2016. 回归分析法在日变数据推算中的应用[J]. 物探与化探,40(3):603–608. Zhang X Y,Guan Y X,Zhang X L. 2016. The application of regression to estimating geomagnetic data[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration,40(3):603–608 (in Chinese).
朱兆才. 1989. 空间相关性分析在地磁观测研究中的应用[J]. 地震地磁观测与研究,(5):44–49. Zhu Z C. 1989. Spatial correlation analysis in the application of the geomagnetic observational studies[J]. Seismological and Geomagnetic Observation and Research,(5):44–49 (in Chinese).
Bergen K J,Johnson P A,de Hoop M V,Beroza G C. 2019. Machine learning for data-driven discovery in solid earth geoscience[J]. Science,363(6433):1–10. doi: 10.1126/science.aau0323
Chen T Q, Guestrin C. 2016. XGBoost: A scalable tree boosting system[C]//Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York: Association for Computing Machinery: 785.
Friedman J H. 2001. Greedy function approximation:A gradient boosting machine[J]. Ann Stat,29(5):1189–1232.
Hajian A, Styles P. 2018. Application of Soft Computing and Intelligent Methods in Geophysics[M]. Switzerland: Springer International Publishing: 3–193.
Kohavi R. 1995. A study of cross-validation and bootstrap for accuracy estimation and model selection[C]//Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc: 1137–1143.
Pelikan M,Sastry K,Goldberg D E. 2002. Scalability of the Bayesian optimization algorithm[J]. Int J Approxim Reason,31(3):221–258. doi: 10.1016/S0888-613X(02)00095-6
Xia Y F,Liu C Z,Li Y Y,Liu N N. 2017. A boosted decision tree approach using Bayesian hyper-parameter optimization for credit scoring[J]. Exp Syst Appl,78:225–241. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2017.02.017
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 陈宝魁,王博为,王东升. 海底强震观测记录与地震动特性研究进展. 世界地震工程. 2023(01): 200-208 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)





 下载:
下载: