Numerical simulation of earthquake-induced loess landslides based on particle flow method
-
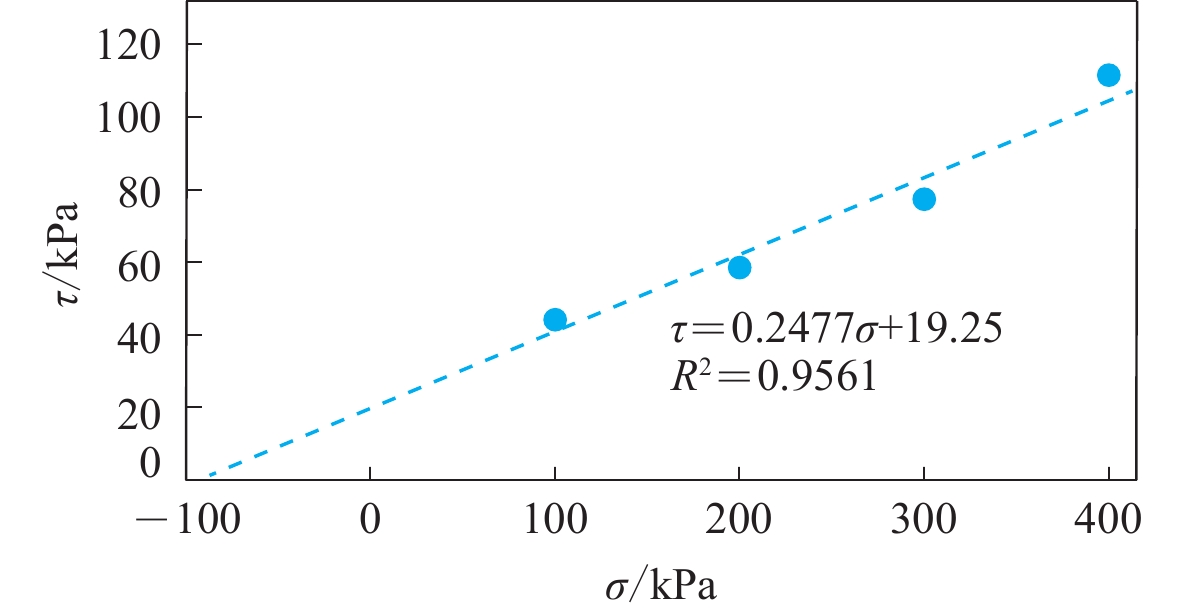
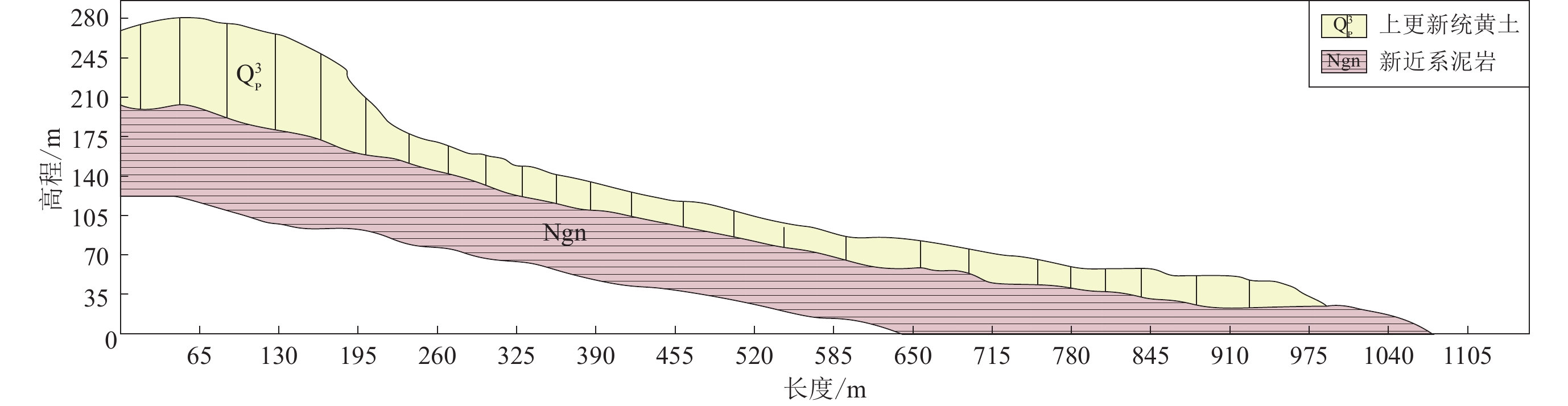
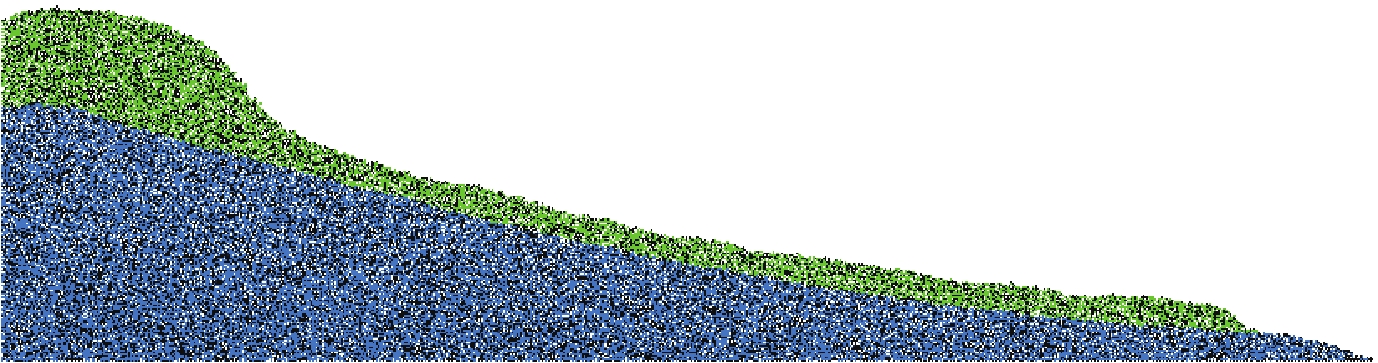
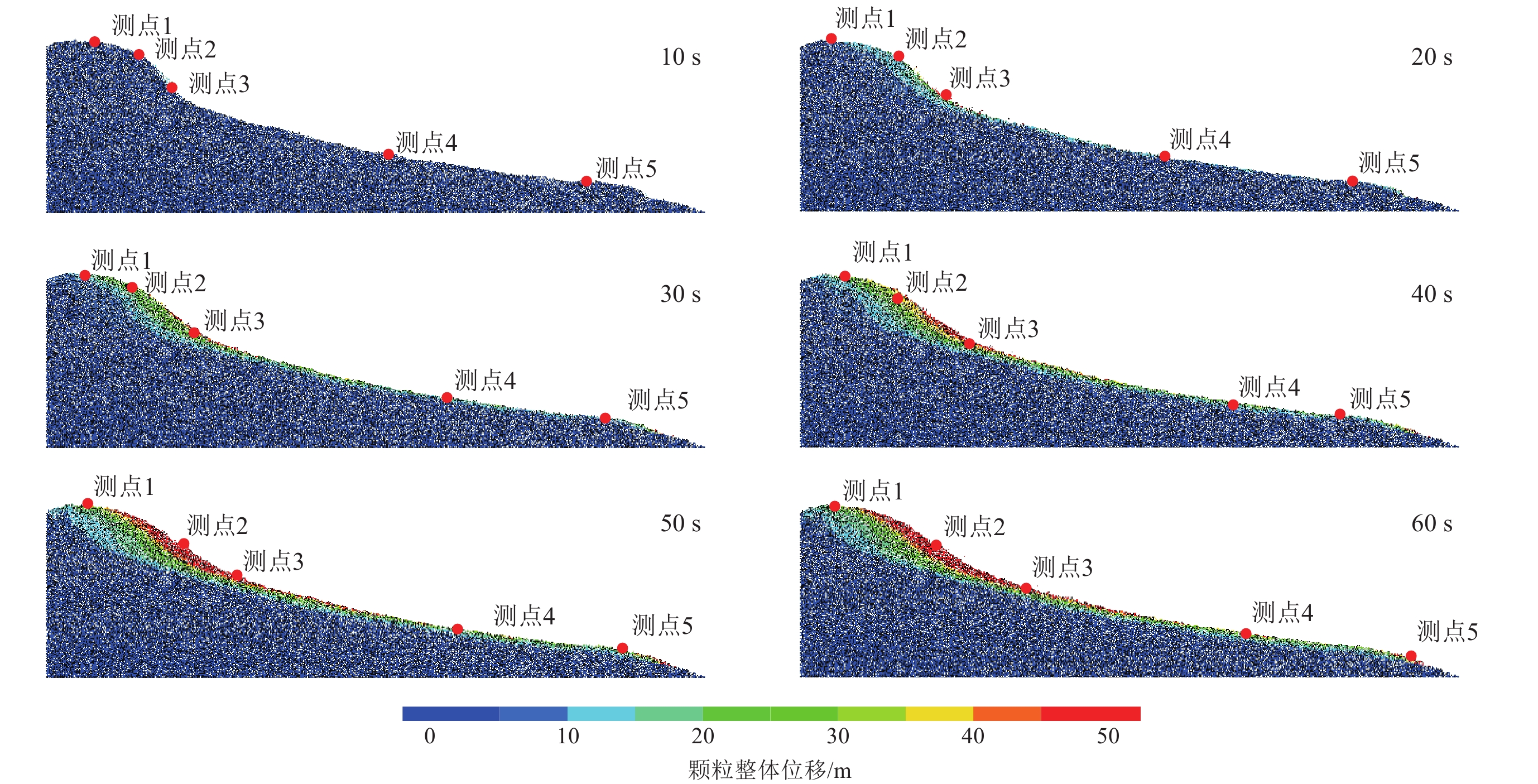
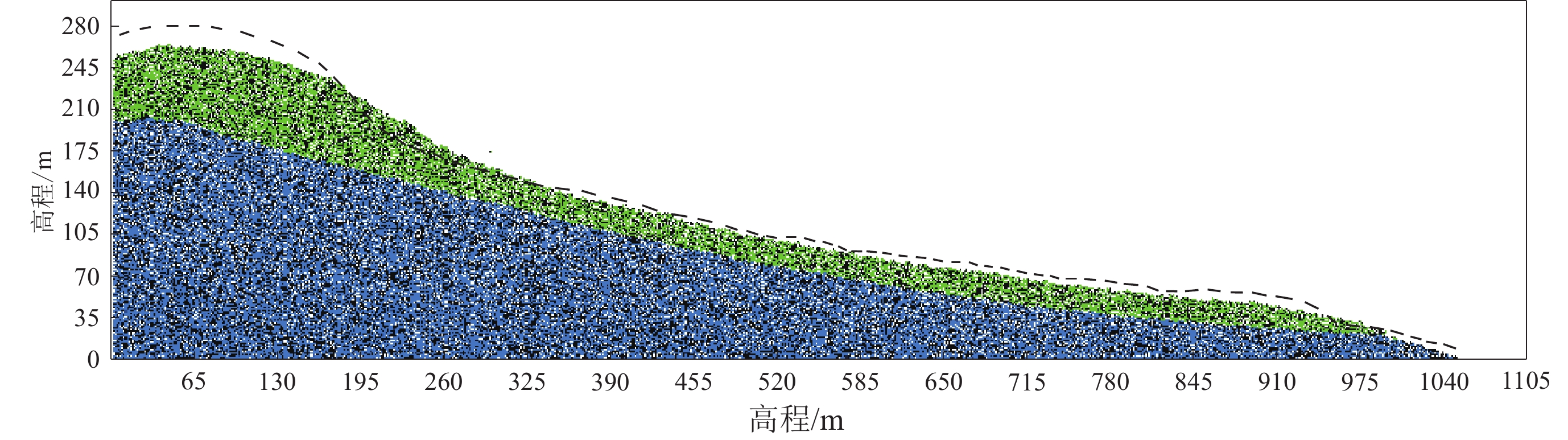
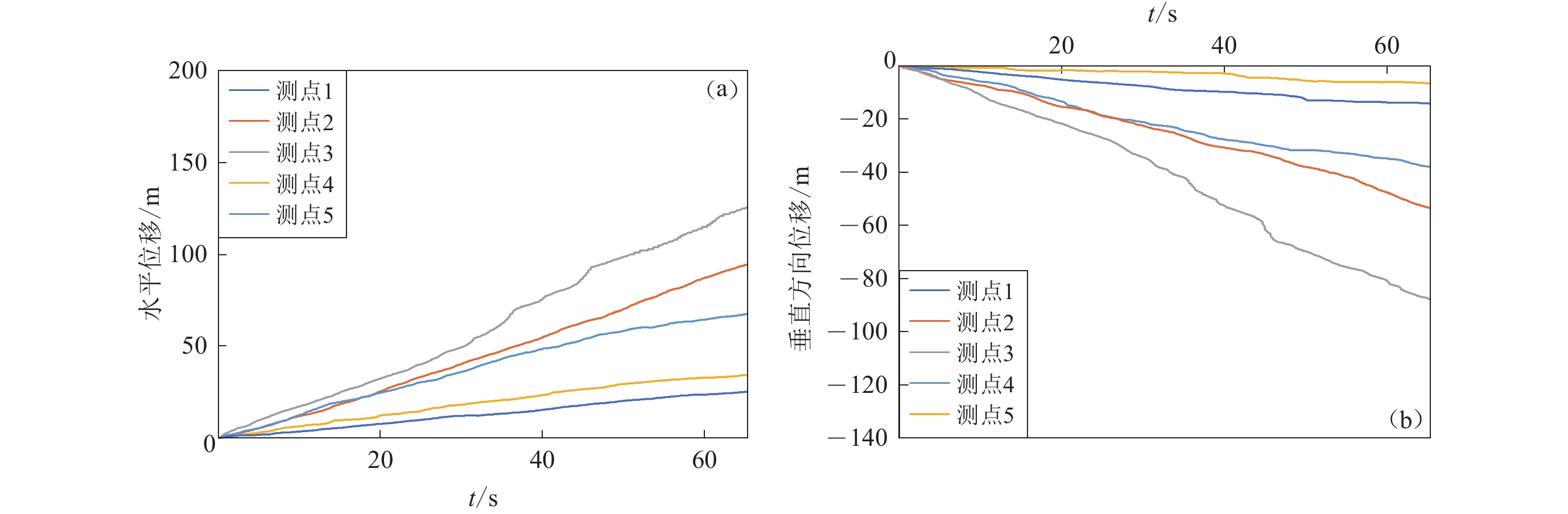
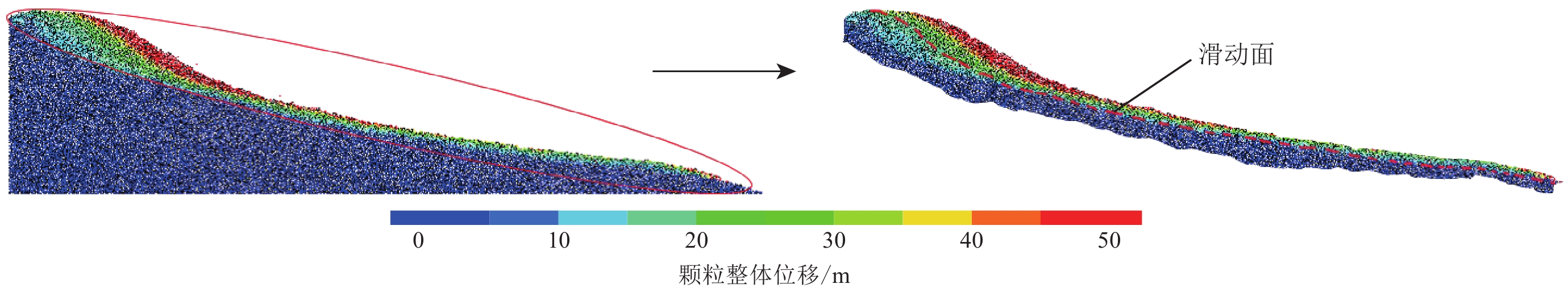
摘要: 基于颗粒流理论研究土质边坡动力稳定性及其滑动过程是近年来滑坡研究的一个新热点。在野外调查和室内试验的基础上,通过标定土体细观参数、模型建立、动力输入、动态监测等过程,利用PFC2D程序模拟了西吉县兴平乡堡湾村下马达子滑坡的失稳破坏运动过程,得到了该滑坡的破坏运动机理。得到如下结论:① 下马达子滑坡的失稳机制是在地震作用下斜坡前缘牵引、后缘推挤,使得坡肩受拉发生破坏,失稳后坡肩位置较大的速度和位移是地震滑坡破坏力强、致灾范围大的主要原因;② 黄土地震滑坡的滑坡后壁相对平缓,这是区别于重力滑坡的重要特征之一;③ 颗粒流模拟得到的滑坡前后相对高差和长度与实际情况较为吻合,因此,颗粒流方法可以用于地震滑坡滑距的预测。Abstract: Research on the dynamic stability and sliding process of soil slopes based on particle flow theory is a new hot spot in landslide research in recent years. On the basis of field investigation and indoor experiment, the PFC2D program was used to simulate the instability failure movement process of the Xiamadazi landslide in Baowan village, Xingping township, Xiji county through the process of calibrating soil parameters, model establishment, power input, dynamic monitoring, etc., and the failure movement mechanism of the landslide is obtained. The following conclusions are obtained: ① The instability mechanism of the Xiamadazi landslide is that under the action of the earthquake, the leading edge of the slope is pulled and the trailing edge is pushed, causing the shoulder to be pulled and damaged. The larger velocity and displacement at the shoulder position after the instability is the main reason for the strong destructive force and the large disaster range of the earthquake landslide; ② The back wall of the earthquake-induced loess landslides is relatively flat, which is one of the important characteristics different from gravity landslides; ③ The relative altitude difference and length before and after the landslide obtained by particle flow simulation is more consistent with the actual situation. Therefore, the particle flow method can be used to predict the slip distance of earthquake landslides.
-
-
表 1 土工试验参数
Table 1 Geotechnical test parameters
岩性 饱和密度/(g·cm−3) 孔隙比 含水率 饱和度 液限 塑限 压缩模量/MPa 黏聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/° 黄土 2.00 0.62 19.6% 86% 29.4% 18.5% 9.59 18.9 14 表 2 细观试验参数
Table 2 Micro-scale test parameters
颗粒半径
/m颗粒密度
/(g·cm−3)阻尼比 摩擦系数 法向刚度
/MPa切向刚度
/MPa平行黏结参数 抗拉强度/Pa 黏聚力/Pa 摩擦角/° 摩擦系数 0.01—0.05 2 400 0.5 0.5 50 70 4×105 2×105 45 0.5 -
薄景山,段玉石,常晁瑜,李孝波,彭达,闫东晗. 2019. 斜坡地震稳定性研究的若干问题[J]. 自然灾害学报,28(1):1–8. Bo J S,Duan Y S,Chang C Y,Li X B,Peng D,Yan D H. 2019. Some problems of study on slope stability under earthquake[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,28(1):1–8 (in Chinese).
曹文,李维朝,唐斌,邓刚,李俊峰. 2017. PFC滑坡模拟二、三维建模方法研究[J]. 工程地质学报,25(2):455–462. Cao W,Li W C,Tang B,Deng G,Li J F. 2017. PFC study on building of 2D and 3D landslide models[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,25(2):455–462 (in Chinese).
常晁瑜,杨顺,焦淙湃,彭达. 2019. 1920年海原特大地震诱发黄土滑坡滑距统计与预测分析[J]. 防灾科技学院学报,21(2):36–43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8047.2019.02.006 Chang C Y,Yang S,Jiao C P,Peng D. 2019. Sliding distance statistics and prediction of the loess landslide triggered by the 1920 Haiyuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Institute of Disaster Prevention,21(2):36–43 (in Chinese).
常晁瑜,薄景山,李孝波,乔峰,闫东晗. 2020. 地震黄土滑坡滑距预测的BP神经网络模型[J]. 地震工程学报,42(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2020.06.1609 Chang C Y,Bo J S,Li X B,Qiao F,Yan D H. 2020. A BP neural network model for forecasting sliding distance of seismic loess landslides[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal,42(6):1609–1614 (in Chinese).
陈达,薛喜成,魏江波. 2018. 基于PFC2D的刘涧滑坡破坏运动过程模拟[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,46(4):115–121. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2018.04.019 Chen D,Xue X C,Wei J B. 2018. Simulation of failure process of Liujian landslide based on PFC2D[J]. Coal Geology and Exploration,46(4):115–121 (in Chinese).
贺续文,刘忠,廖彪,王翠翠. 2011. 基于离散元法的节理岩体边坡稳定性分析[J]. 岩土力学,32(7):2199–2204. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2011.07.046 He X W,Liu Z,Liao B,Wang C C. 2011. Stability analysis of jointed rock slopes based on discrete element method[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,32(7):2199–2204 (in Chinese).
李新坡,何思明. 2010. 节理岩质边坡破坏过程的PFC2D数值模拟分析[J]. 四川大学学报(工程科学版),42(增刊):70–75. Li X P,He S M. 2010. Numerical analysis of the failure of heavily jointed rock slopes using PFC2D[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition)
,42(S1):70–75 (in Chinese). 刘红帅,薄景山,刘德东. 2007. 岩土边坡地震稳定性评价方法研究进展[J]. 防灾科技学院学报,9(3):20–27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8047.2007.03.006 Liu H S,Bo J S,Liu D D. 2007. Development on study of seismic stability evaluation methods of rock-soil slopes[J]. Journal of Institute of Disaster-Prevention Science and Technology,9(3):20–27 (in Chinese).
石崇,张强,王盛年. 2018. 颗粒流(PFC5.0)数值模拟技术及应用[J]. 岩土力学,39(增刊):36. Shi C,Zhang Q,Wang S N. 2018. Numerical simulation technology and application of particle flow (PFC5.0)[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,39(S2):36 (in Chinese).
王光谦,倪晋仁. 1992. 颗粒流研究评述[J]. 力学与实践,14(1):7–19. Wang G Q,Ni J R. 1992. A review of research on particle flow[J]. Mechanics and Practice,14(1):7–19 (in Chinese).
许冲,田颖颖,马思远,徐锡伟,周本刚,吴熙彦,庄建琦,高玉欣,吴玮莹,黄学强. 2018. 1920年海原8.5级地震高烈度区滑坡编录与分布规律[J]. 工程地质学报,26(5):1188–1195. Xu C,Tian Y Y,Ma S Y,Xu X W,Zhou B G,Wu X Y,Zhuang J Q,Gao Y X,Wu W Y,Huang X Q. 2018. Inventory and spatial distribution of landslides in Ⅸ-Ⅺ high intensity areas of 1920 Haiyuan (China) M8.5 earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,26(5):1188–1195 (in Chinese).
徐张建,林在贯,张茂省. 2007. 中国黄土与黄土滑坡[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,26(7):1297–1312. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.07.001 Xu Z J,Lin Z G,Zhang M S. 2007. Loess in China and Loess landslides[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,26(7):1297–1312 (in Chinese).
张江伟. 2016. 土质边坡地震动力响应特性分析及稳定性评价[J]. 国际地震动态,(1):44–45. Zhang J W. 2016. Seismic dynamic response characteristics and stability evaluation of soil slopes[J]. Recent Developments in International Seismology,(1):44–45 (in Chinese).
周健,池永. 2003. 砂土力学性质的细观模拟[J]. 岩土力学,24(6):901–906. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2003.06.006 Zhou J,Chi Y. 2003. Mesomechanical simulation of sand mechanical properties[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,24(6):901–906 (in Chinese).
周健,池永,池毓蔚,徐建平. 2000. 颗粒流方法及PFC2D程序[J]. 岩土力学,21(3):271–274. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2000.03.020 Zhou J,Chi Y,Chi Y W,Xu J P. 2000. The method of particle flow and PFC2D Code[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,21(3):271–274 (in Chinese).
周喻,韩光,吴顺川,胡乃联. 2016. 断续节理岩体及岩质边坡破坏的细观机制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,35(增刊):3878–3889. Zhou Y,Han G,Wu S C,Hu N L. 2016. Meso mechanical failure mechanism of rock mass and slope with intermittent joints[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,35(S2):3878–3889 (in Chinese).
Behbahani S S,Moarefvand P,Ahangari K,Goshtasbi K. 2013. Pomiary przemieszczeń i sił kontaktu pomiędzy cząstkami materialnymi w trakcie wybierania wyrobiska pochyłego przy pomocy programu PFC2D[J]. Arch Min Sci,58(2):495–504.
Cundall P A,Strack O D L. 1979. A discrete numerical model for granular assemblies[J]. Geotechnique,29(1):47–65.
Hadjigeorgiou J,Esmaieli K,Grenon M. 2009. Stability analysis of vertical excavations in hard rock by integrating a fracture system into a PFC model[J]. Tunn Undergr Space Technol,24(3):296–308. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2008.10.002
Härtl J,Ooi J Y. 2008. Experiments and simulations of direct shear tests:Porosity,contact friction and bulk friction[J]. Granular Matter,10(4):263–271. doi: 10.1007/s10035-008-0085-3
Park J W,Song J J. 2009. Numerical simulation of a direct shear test on a rock joint using a bonded-particle model[J]. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci,46(8):1315–1328. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2009.03.007
Scholtès L,Donzé F V. 2012. Modelling progressive failure in fractured rock masses using a 3D discrete element method[J]. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci,52:18–30. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2012.02.009
Tang C L,Hu J C,Lin M L,Angelier J,Lu C Y,Chan Y C,Chu H T. 2009. The Tsaoling landslide triggered by the Chi-Chi earthquake,Taiwan:Insights from a discrete element simulation[J]. Eng Geol,106(1/2):1–19.
Wang C,Tannant D D,Lilly P A. 2003. Numerical analysis of the stability of heavily jointed rock slopes using PFC2D[J]. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci,40(3):415–424. doi: 10.1016/S1365-1609(03)00004-2
Zhou J X,Zhu C Y,Zheng J M,Wang X H,Liu Z H. 2002. Landslide disaster in the loess area of China[J]. J Forestry Res,13(2):157–161. doi: 10.1007/BF02857244
Zhou X P,Qian Q H,Cheng H,Zhang H P. 2015. Stability analysis of two-dimensional landslides subjected to seismic loads[J]. Acta Mech Solida Sin,28(3):262–276. doi: 10.1016/S0894-9166(15)30013-6
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 张研,邝贺伟. 地震震级预测的相关向量机模型. 世界地震工程. 2020(01): 212-221 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 汪小厉,李玲利,杨源源. 金寨震群震源深度确定及成因初步分析. 中国地震. 2017(02): 269-279 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: