Response of the topography of Laixihe drainage to the structural deformation induced by MS6.0 Luxian earthquake and its indication
-
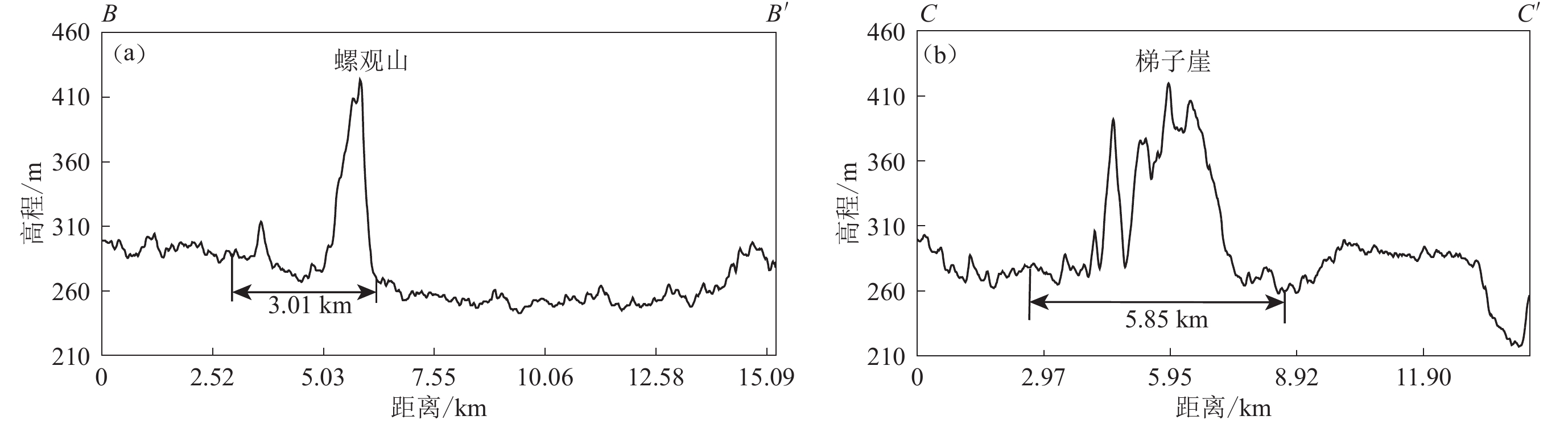
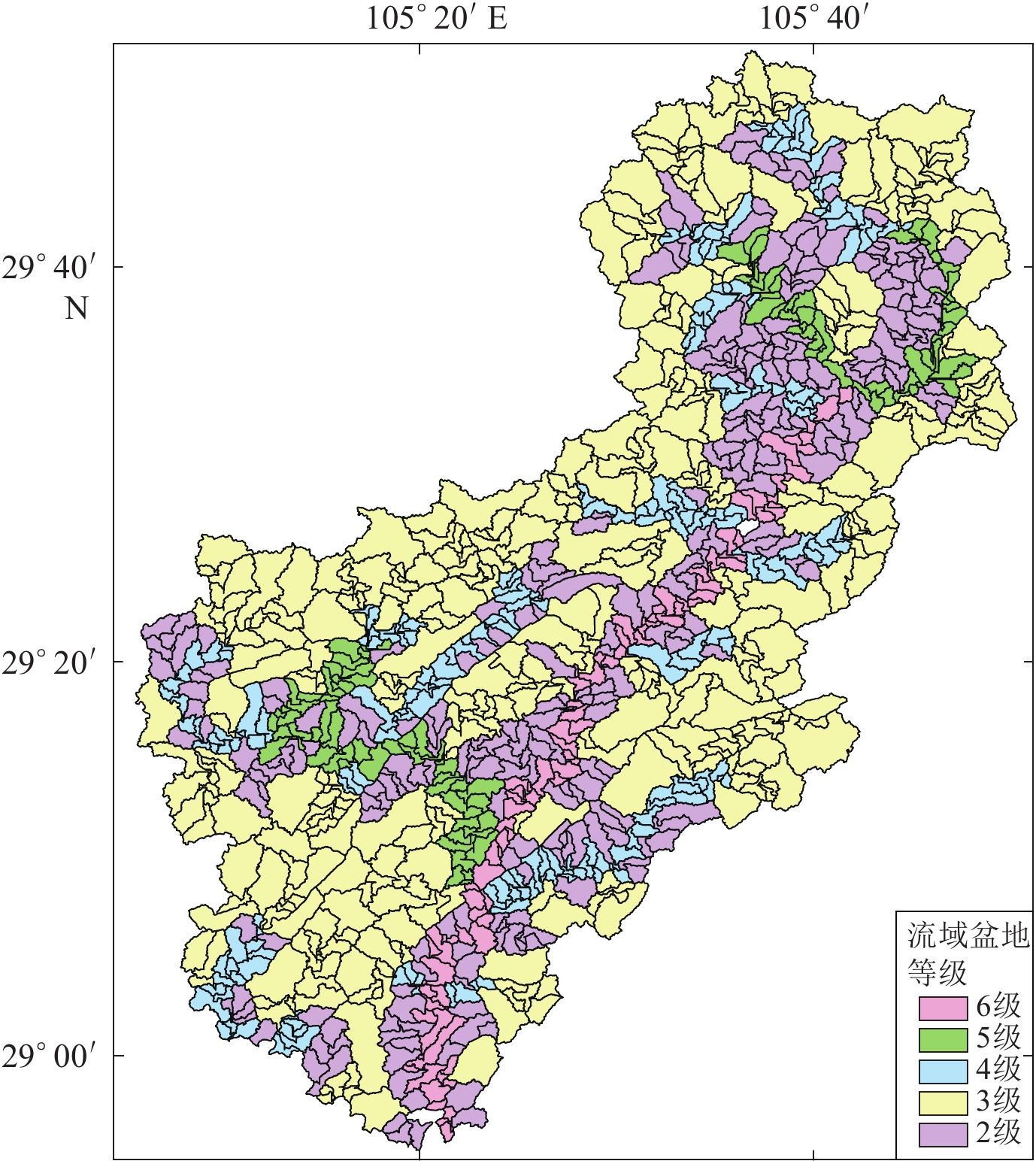
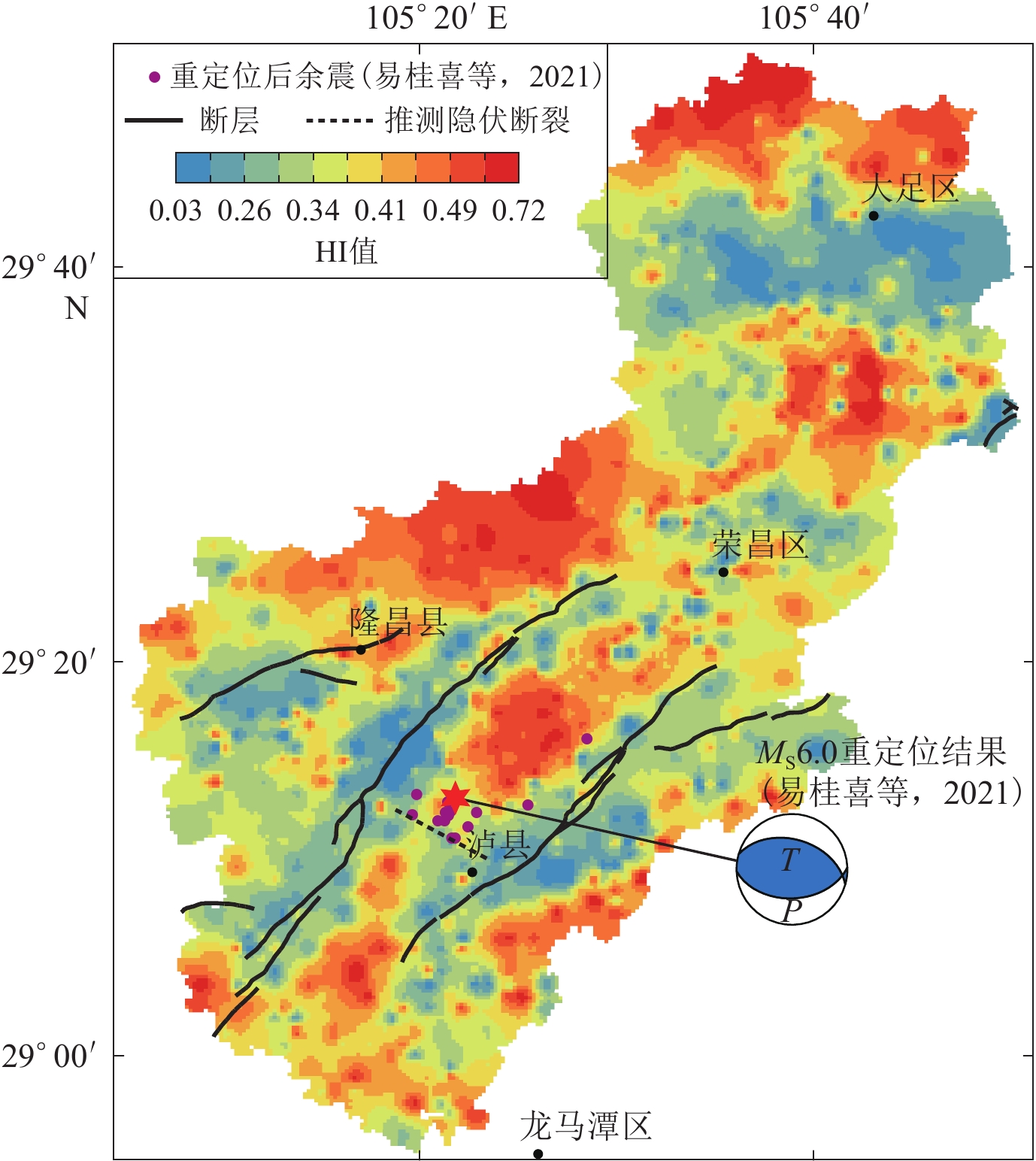
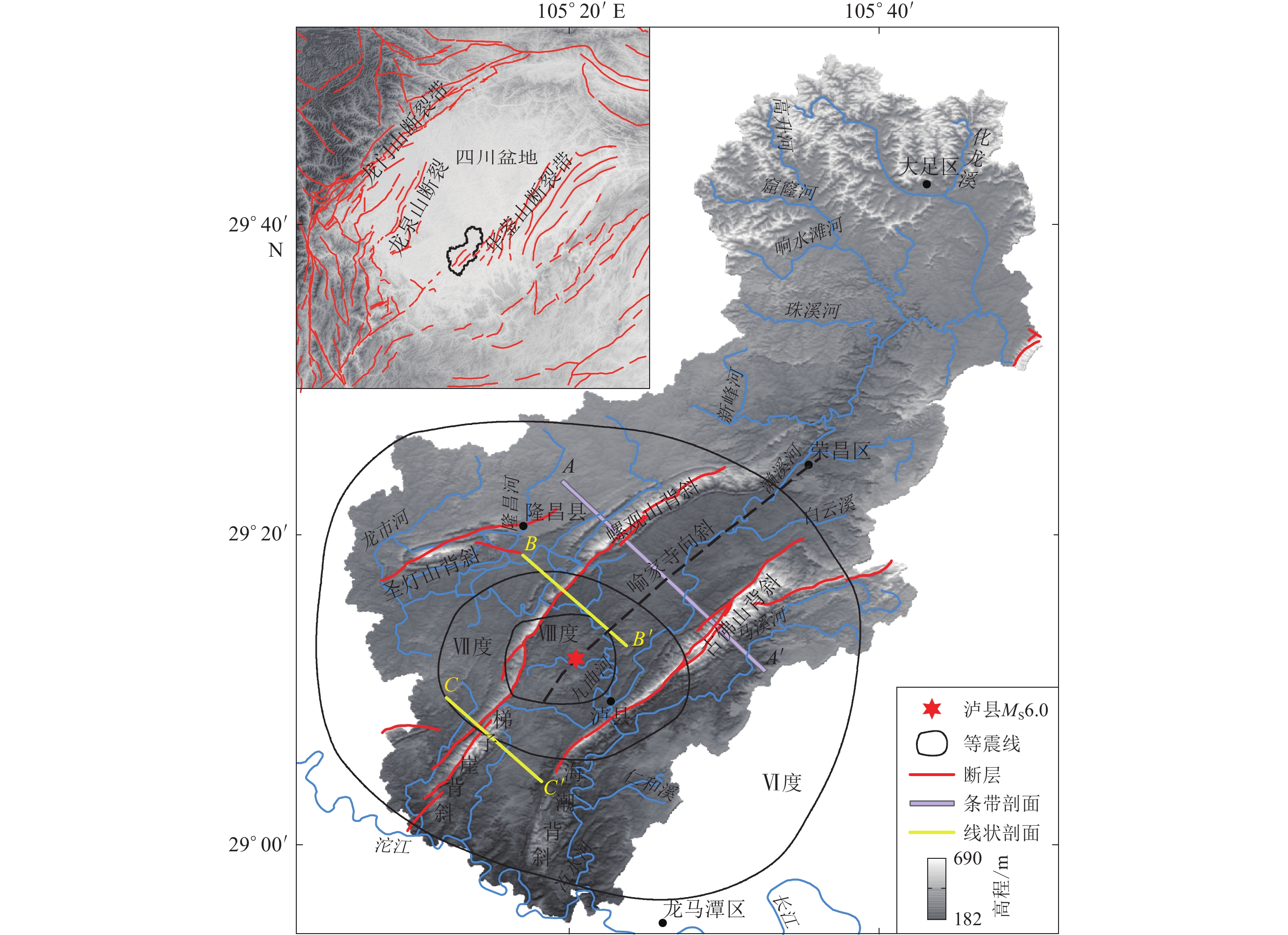
摘要: 以12.5 m 数字高程模型数据为基础,采用数字地貌分析方法提取了濑溪河流域的高程剖面和面积-高程积分(HI)等地貌参数,分析了2021年9月16日四川盆地东南部泸县MS6.0地震震中附近区域地貌与构造活动的响应关系。结果显示:震中西侧的螺观山和梯子崖背斜在震中的南北两端存在明显的缩短量差异;HI条带状低值区的展布方向与流域内构造的方向一致,HI高值区位于华蓥山两条断裂夹持的谷地,但在震中附近存在WNW向的HI低值带。综合分析认为,泸县地震震中附近应存在一走向为WNW的隐伏构造,它不仅调节了螺观山和梯子崖背斜在震中南北两端的缩短量差异,也使得HI值受其影响呈低值特征,该结果与震源机制解结果、等震线长轴走向以及余震空间展布的优势方向相一致。Abstract: Based on 12.5 m DEM data, the elevation profile and hypsometric integral (HI) of Laixihe drainage are extracted by digital geomorphological analysis method, and the response relationship between geomorphology and tectonic activity in the areas near the epicenter of Luxian MS6.0 earthquake is analyzed. The results show that the Luoguanshan and Tiziya anticlines have obvious shortening differences between the north and south ends of the epicenter. The low HI value zone is consistent with the direction of the structure in the basin. The high HI value zone is located between the valleys clamped by the two faults of Huayingshan, but there is a low value zone in WNW direction near the epicenter. The comprehensive analysis shows that there should be a WNW-trending buried structure near the epicenter, which not only regulates the shortening difference between the north and south ends of the epicenter for the Luoguanshan and Tiziya anticlines, but also makes the HI value being a low value characteristic affected by it. The WNW direction of the buried structure is consistent with the results of the focal mechanism solution, major axis strike of isoseismal line, and the dominant predirection of spatial distribution of aftershocks.
-
-
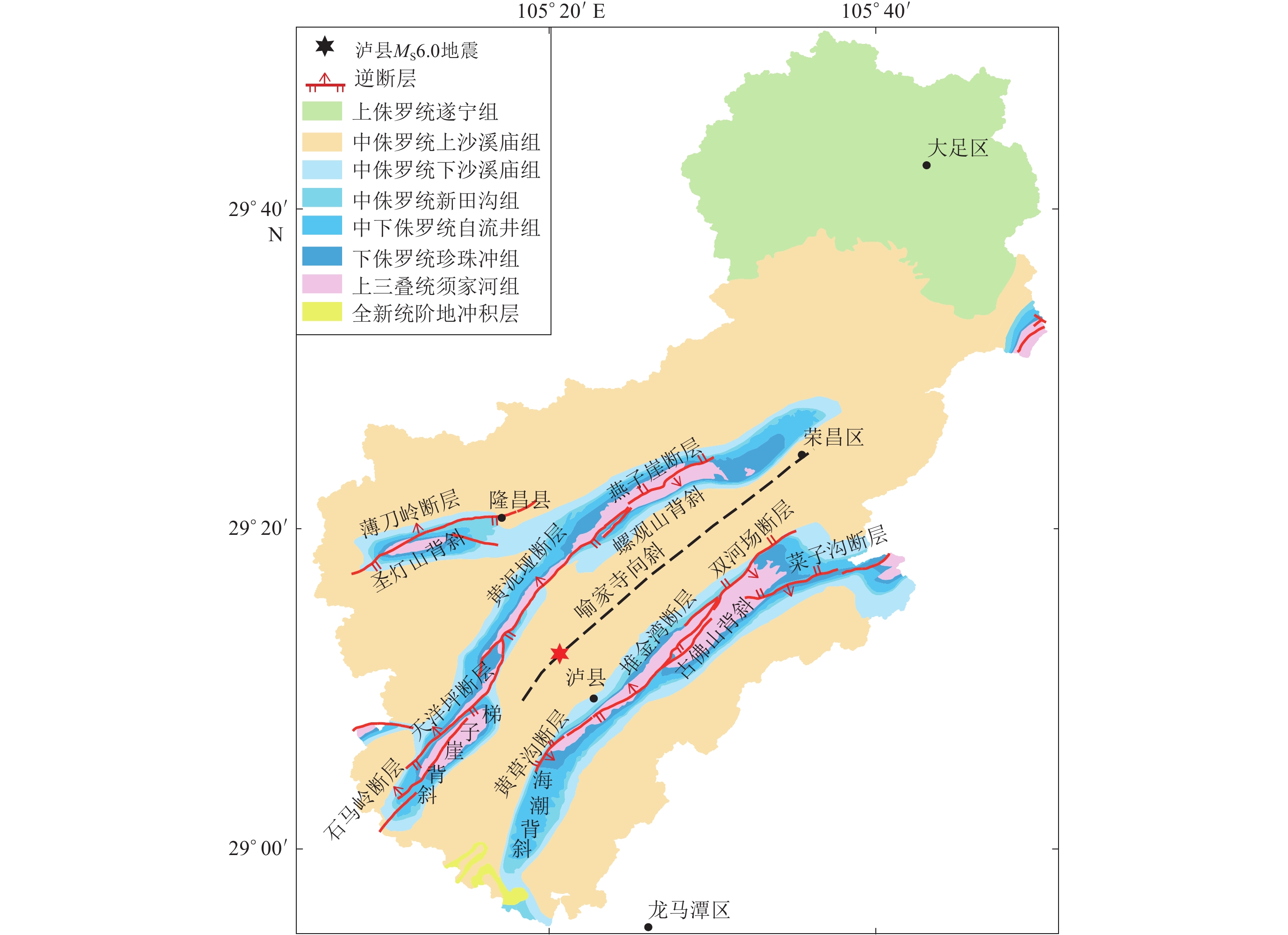
表 1 泸县MS6.0地震震中附近区域断层(引自四川省地质局,1980)
Table 1 Faults information of Luxian MS6.0 earthquake area (after Sichuan Geology Bureau,1980)
名称 构造部位 走向 倾向 倾角/° 长度/km 性质 薄刀岭断层 圣灯山背斜北翼 N60°E NW 30—42 18.0 压性逆断层 石马岭断层 梯子崖背斜北西翼 N40°E SE 28—43 5.6 压性逆断层 天洋坪断层 梯子崖背斜北西翼 N45°E NW 30—63 18.0 压性逆断层 燕子崖断层 螺观山背斜近核部 N60°E SE 26—57 10.0 压性逆断层 黄泥垭断层 梯子崖背斜核部北段 N40°E NW 30—70 25.0 压性逆断层 堆金湾断层 海潮背斜及古佛山背斜近核部 N40°E NW 50—75 22.4 压性逆断层 黄草沟断层 海潮背斜北西翼 NE SE 35 4.4 压性逆断层 双河场断层 古佛山背斜北西翼 N40°—50°E SE 30—40 12.0 压性逆断层 菜子沟断层 古佛山背斜南东翼 N70°E S 28—37 10.0 压性逆断层 -
邓宾. 2013. 四川盆地中-新生代盆-山结构与油气分布[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学: 17–18. Deng B. 2013. Meso-Cenozoic Architecture of Basin-Mountain System in the Sichuan Basin and Its Gas Distribution[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology: 17–18 (in Chinese).
贺鸿冰. 2012. 华蓥山构造带的构造几何学与运动学及其对川东与川中地块作用关系的启示[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学: 1–2. He H B. 2012. Geometry and Kinematics Structures of the Huayingshan Mountains: Implications to Relationship Between Central Sichuan and East Sichuan Block[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences: 1–2 (in Chinese). 李奋生,赵国华,李勇,颜照坤,梁明剑,闫亮,李敬波,邵崇建,郑立龙. 2015. 龙门山地区水系发育特征及其对青藏高原东缘隆升的指示[J]. 地质论评,61(2):345–355. Li F S,Zhao G H,Li Y,Yan Z K,Liang M J,Yan L,Li J B,Shao C J,Zheng L L. 2015. The characteristics of drainage development in Longmen mountains area and its indication to the uplift of the eastern margin of Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Plateau[J]. Geological Review,61(2):345–355 (in Chinese).
李伟,谢超,程宏宾,冯兵. 2021. 利用水系方位角和GPS数据研究龙门山后山断裂运动模式[J]. 四川地震,(2):7–10. Li W,Xie C,Cheng H B,Feng B. 2021. Study on the fault movement model of the backmountain of Longmen mountain based on the azimuth angle and GPS data[J]. Earthquake Research in Sichuan,(2):7–10 (in Chinese).
梁明剑,李大虎,郭红梅,王世元. 2014a. 成都盆地南缘第四纪构造变形及地貌响应特征[J]. 地震工程学报,36(1):98–106. Liang M J,Li D H,Guo H M,Wang S Y. 2014a. Quaternary tectonic deformation and geomorphologic response characteristics in the southern margin of Chengdu basin[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal,36(1):98–106 (in Chinese).
梁明剑,周荣军,闫亮,赵国华,郭红梅. 2014b. 青海达日断裂中段构造活动与地貌发育的响应关系探讨[J]. 地震地质,36(1):28–38. Liang M J,Zhou R J,Yan L,Zhao G H,Guo H M. 2014b. The relationships between neotectonic activity of the middle segment of Dari fault and its geomorphological response,Qinghai Province,China[J]. Seismology and Geology,36(1):28–38 (in Chinese).
刘静,曾令森,丁林,Tapponnier P,Gaudemer Y,文力,谢克家. 2009. 青藏高原东南缘构造地貌、活动构造和下地壳流动假说[J]. 地质科学,44(4):1227–1255. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2009.04.014 Liu J,Zeng L S,Ding L,Tapponnier P,Gaudemer Y,Wen L,Xie K J. 2009. Tectonic geomorphology,active tectonics and lower crustal channel flow hypothesis of the southeastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology,44(4):1227–1255 (in Chinese).
刘静,张金玉,葛玉魁,王伟,曾令森,李根,林旭. 2018. 构造地貌学:构造-气候-地表过程相互作用的交叉研究[J]. 科学通报,63(30):3070–3088. Liu J,Zhang J Y,Ge Y K,Wang W,Zeng L S,Li G,Lin X. 2018. Tectonic geomorphology:An interdisciplinary study of the interaction among tectonic climatic and surface processes[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,63(30):3070–3088 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/N972018-00498
四川省地质局. 1980. 中华人民共和国区域地质调查报告(遂宁幅、自贡幅、内江幅、宜宾幅、泸州幅)[M]. 成都: 四川省地质局: 153. Sichuan Geology Bureau. 1980. Reginal Geological Survey Report of People’s Republic of China (Suining, Zigong, Neijiang, Yibin and Luzhou Geological Map Sheet)[M]. Chengdu: Sichuan Geology Bureau: 153 (in Chinese).
四川省地震局. 2021. 四川泸县6.0级地震烈度图发布[EB/OL]. [2021-12-24]. http://www.scdzj.gov.cn/xwzx/fzjzyw/202109/t20210920_50114.html. Sichuan Earthquake Agency. 2021. Intensity map of the MS6.0 Sichuan Luxian earthquake on September 16, 2021[EB/OL]. [2021-12-24]. http://www.scdzj.gov.cn/xwzx/fzjzyw/202109/t20210920_50114.html (in Chinese).
苏琦. 2015. 青藏高原东北缘典型流域地貌参数分析与构造变形探讨[D]. 兰州: 中国地震局兰州地震研究所: 69–70. Su Q. 2015. Study on Typical Drainage Basins Along Northeastern Tibetan Plateau and Its Tectonic Deformation[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou Institute of Seismology, China Earthquake Administration: 69–70 (in Chinese).
王丹, 董有浦, 焦骞骞, 张东越, 段佳鑫, 余华玉. 2021. 滇中地块新生代晚期的变形机制: 基于构造地貌学分析[J/OL]. [2021-12-24].地球科学. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1874.P.20211118.1549.004.html. Wang D, Dong Y P, Jiao Q Q, Zhang D Y, Duan J X, Yu H Y. 2021. The mechanism of tectonic deformation of the central Yunnan terrane in the Late Cenozoic based on tectonic geomorphology[J/OL].[2021-12-24]. Earth Science. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1874.P.20211118.1549.004.html (in Chinese).
易桂喜,赵敏,龙锋,梁明剑,王明明,周荣军,王思维. 2021. 2021年9月16日四川泸县MS6.0地震序列特征及孕震构造环境[J]. 地球物理学报,64(12):4449–4461. doi: 10.6038/cjg2021O0533 Yi G X,Zhao M,Long F,Liang M J,Wang M M,Zhou R J,Wang S W. 2021. Characteristics of the seismic sequence and seismogenic environment of the MS6.0 Sichuan Luxian earthquake on September 16,2021[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,64(12):4449–4461 (in Chinese).
于洋,王先彦,李一泉,戴岩,鹿化煜. 2018. 长江源地区通天河段水系格局演化与构造活动的关系[J]. 地理学报,73(7):1338–1351. doi: 10.11821/dlxb201807012 Yu Y,Wang X Y,Li Y Q,Dai Y,Lu H Y. 2018. The evolution of drainage pattern and its relation to tectonic movement in the upstream Yangtze catchment[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica,73(7):1338–1351 (in Chinese).
张会平,刘少峰. 2004. 利用DEM进行地形高程剖面分析的新方法[J]. 地学前缘,11(3):226. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.03.036 Zhang H P,Liu S F. 2004. A new method for elevation profile analysis using DEM[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,11(3):226 (in Chinese).
张会平,杨农,刘少峰,张岳桥. 2006. 数字高程模型(DEM)在构造地貌研究中的应用新进展[J]. 地质通报,25(6):660–669. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2006.06.002 Zhang H P,Yang N,Liu S F,Zhang Y Q. 2006. Recent progress in the DEM-based tectonogeomorphic study[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,25(6):660–669 (in Chinese).
张世民,谢富仁. 2001. 鲜水河—小江断裂带7级以上强震构造区的划分及其构造地貌特征[J]. 地震学报,23(1):36–44. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3782.2001.01.005 Zhang S M,Xie F R. 2001. Seismo-tectonic divisions of strong earthquakes (M≥7.0) and their tectonic geomorphology along Xianshuihe-Xiaojiang fault zone[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,23(1):36–44 (in Chinese).
赵正望. 2005. 川东南地区构造特征及其对油气成藏的控制作用[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学: 33. Zhao Z W. 2005. The Regional Tectonic Characteristic of Southeast Sichuan Basin and Its Control to Oil and Gas Reservoir[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences: 33 (in Chinese).
周荣军,唐荣昌,钱洪,文德华,马声浩,何玉林,蒲晓虹. 1997. 地震构造类比法的应用:以川东地区华蓥山断裂带为例[J]. 地震研究,20(3):316–322. Zhou R J,Tang R C,Qian H,Wen D H,Ma S H,He Y L,Pu X H. 1997. An application of seismotectonic analogy to the Huayingshan fault zone in east Sichuan[J]. Journal of Seismological Research,20(3):316–322 (in Chinese).
Chen Y C,Sung Q,Cheng K Y. 2003. Along-strike variations of morphotectonic features in the western foothills of Taiwan:Tectonic implications based on stream-gradient and hypsometric analysis[J]. Geomorphology,56(1/2):109–137.
Clark M K,Royden L H. 2000. Topographic ooze:Building the eastern margin of Tibet by lower crustal flow[J]. Geology,28(8):703–706. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2000)28<703:TOBTEM>2.0.CO;2
Langbein W B. 1947. Topographic Characteristics of Drainage Basins[R/OL]. [2021-11-04]. https://pubs.usgs.gov/wsp/0968c/report.pdf.
Liu-Zeng J,Tapponnier P,Gaudemer Y,Ding L. 2008. Quantifying landscape differences across the Tibetan Plateau:Implications for topographic relief evolution[J]. J Geophys Res,113(F4):F04018.
Pike R J,Wilson S E. 1971. Elevation-relief ratio,hypsometric integral,and geomorphic area-altitude analysis[J]. GSA Bull,82(4):1079–1084. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1971)82[1079:ERHIAG]2.0.CO;2
Whipple K X,Tucker G E. 1999. Dynamics of the stream-power river incision model:Implications for height limits of mountain ranges,landscape response timescales,and research needs[J]. J Geophys Res:Solid Earth,104(B8):17661–17674. doi: 10.1029/1999JB900120
Willett S D, Hovius N, Brandon M T, Fisher D M. 2006. Tectonics, Climate, and Landscape Evolution[M/OL]. [2021-11-04]. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Sean-Willett/publication/235431560_Tectonics_Climate_and_Landscape_Evolution/links/00b4951932ecc71355000000/Tectonics-Climate-and-Landscape-Evolution.pdf.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 莫丽桦,储日升,谷旺旺,盛敏汉,马海超,李雪垒. 2021年四川泸县M_S6.0地震震源参数研究. 地球物理学报. 2024(04): 1487-1500 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 易子韩,肖瑞卿,匡野,王刚,李峰,李洪奎,孙玮,杨渊宇,马理论,胡俊晨,孙昭杰,胡锦荣. 川东南侏罗山式构造与泸县地区活动构造研究. 矿物岩石. 2024(03): 105-122 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 周文英,梁明剑,魏娅玲,宫悦,廖程,左洪,杨力,薛莲,毛泽斌. 四川马尔康6.0级震群区流域地貌特征与控制因素研究. 震灾防御技术. 2023(04): 745-756 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: