Crustal structure in the Dasanjiang basin and its adjacent areas
-
摘要: 收集了大三江盆地及其邻区区域地震台网及多个流动台阵的连续波形及远震事件资料,采用背景噪声层析成像和接收函数叠加方法,分别获得了研究区三维S波速度结构、基底及莫霍面深度和泊松比。结果显示:浅层速度结构较好地反映了地表地形及地质特征,三江盆地呈明显的低速,虎林和勃利等小型盆地的S波速度也相对较低,而小兴安岭、张广才岭等则呈高速;到中下地壳层,盆地区则表现为明显的高速,表明到该深度层盆地已趋于稳定;依兰—伊通断裂下的低速异常延伸较深,表明它是一条较深的区域性断裂。接收函数结果显示:区内莫霍面的深度大约为30—36 km,整体较为平缓;在三江盆地内,前进坳陷的沉积层最厚,可达5.4 km,最薄处位于富锦隆起,为2.7 km,到西部绥滨断陷内沉积层又变厚,这与该盆地已知的两坳夹一隆的构造相一致。Abstract: We collected continuous waveforms and teleseismic events both from the regional permanent seismic network and several temporary seismic arrays in the Dasanjiang basin and its adjacent areas and obtained the 3D S-wave velocity structure, basement depth, Moho depth and Poisson’s ratio by using the ambient noise tomography and receiver function methods. Our results show that the shallow velocity structure corresponds well to the surface topography and geological features. The Sanjiang basin shows obvious low-velocity and small basins such as Hulin and Boli basins are also imaged as relatively low velocities, while the Xiaoxing’anling and Zhangguangcailing are characterized by high velocities. In the mid-lower crust, all basins show obvious high velocities, which indicates that they are stable at this depth. The low-velocity anomaly beneath the Yilan-Yitong fault extends down to deep, indicating that it is a regional deep fault. The results of the receiver function show that the Moho depth varies gently in the range of 30 km to 36 km. In the Sanjiang basin, the sedimentary thickness beneath Qianjin depression is the thickest, which could reach 5.4 km. While the sedimentary thickness beneath Fujin uplift is the thinnest, which could be 2.7 km. Beneath the western Suibin depression, sedimentary layer becomes thick again. The above features are consistent with the known tectonics of two depressions sandwiching one uplift.
-
-
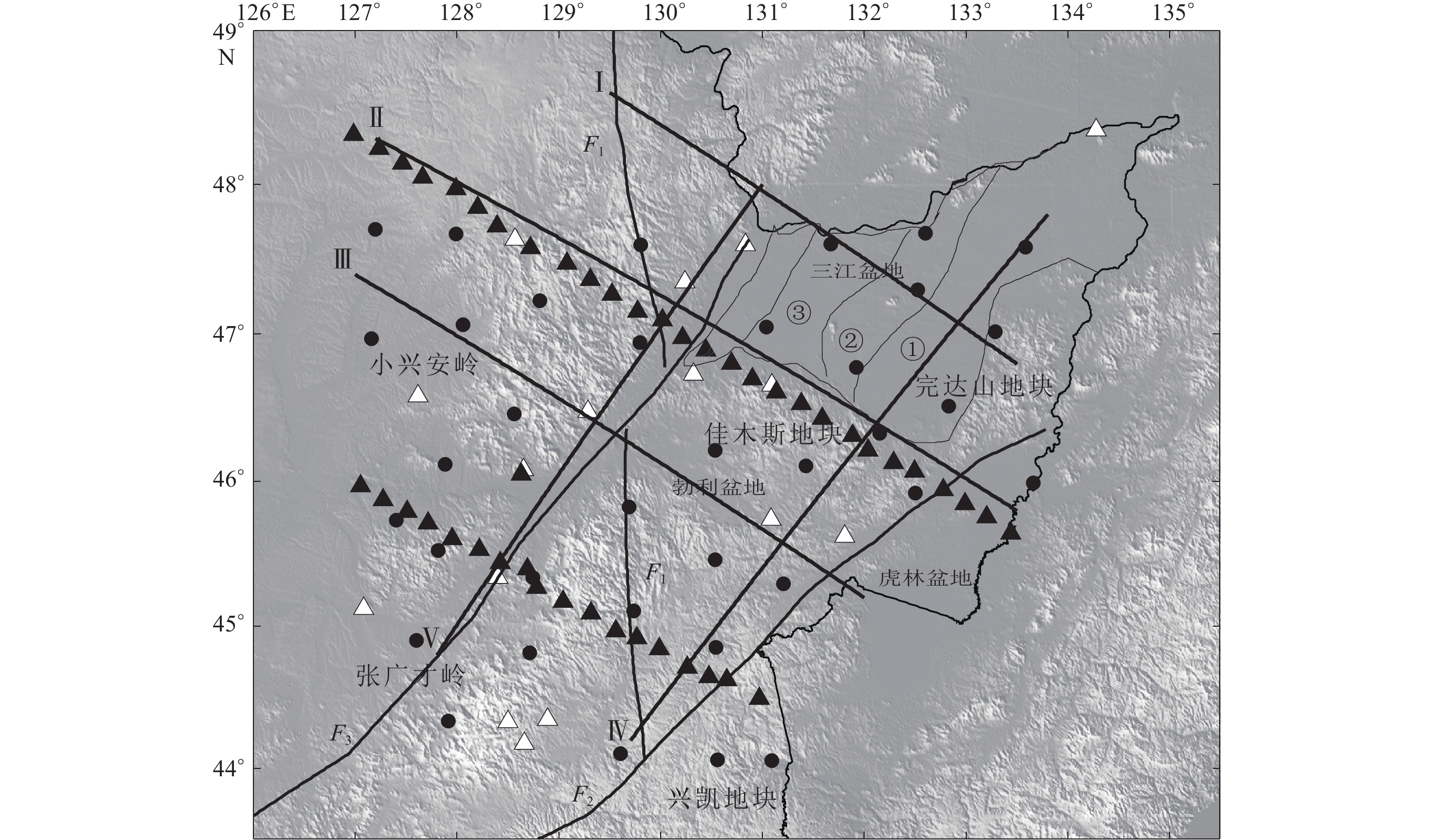
图 1 研究区主要构造背景及所用地震台站分布
图中白色三角形为中国数字地震台网固定台站,黑色圆点为多国合作布设的东北流动台阵(NECESSArray)的流动台站,黑色三角形为中国地震局地球物理研究所布设的五大连池—虎林和满洲里—绥芬河宽频带地震测线的流动台站;黑色粗线为图4中5条S波速度剖面Ⅰ −Ⅴ。灰色线为三江盆地内的次级构造单元边界,其中① 前进坳陷,② 富锦隆起,③ 绥滨断陷. 黑线代表区域主要断裂,F1:牡丹江断裂;F2:敦密断裂;F3:依兰—伊通断裂,下同
Figure 1. Map showing the major geological features of the studied area and distribution of seismic stations used in the study
White triangles represent permanent stations from China digital seismic network,black dots represent temporary stations from the NECESSArray,the black triangles represent temporary stations of Wudalianchi-Hulin and Manzhouli-Suifenhe broadband seismic survey lines which were performed by Institute of Geophysics,China Earthquake Administration. The thick black lines are the location of five profiles,the serial numbers of which are marked at the left end of the profile. The gray lines are the boundary of secondary tectonic units in Sanjiang basin,① Qianjin depression;② Fujin uplift;③ Suibin depression. The black lines represent major faults in the region,F1:Mudanjiang fault; F2:Dunmi fault;F3:Yilan-Yitong fault,the same below
图 6 不同深度层上的S波速度平面图
每层的深度标在各子图的右上角,蓝色三角形为中国数字地震台网固定台站,红色三角形为多国合作布设的东北台阵(NECESSArray)的流动台站,黑色三角形为中国地震局地球物理所布设的五大连池—虎林和满洲里—绥芬河宽频带地震测线的流动台站。其它标识同图1
Figure 6. S-wave velocity map at each depth slice
The depth of each layer is shown at the upper right corner of each panel. Blue triangles represent permanent stations from China digital seismic network,red triangles represent temporary stations from the NECESSArray,the black triangles represent temporary stations of Wudalianchi-Hulin and Manzhouli-Suifenhe broadband seismic survey lines. Other labels are the same as those in Fig. 1 (a) 3 km;(b) 5 km;(c) 10 km;(d) 15 km;(e) 20 km;(f) 25 km
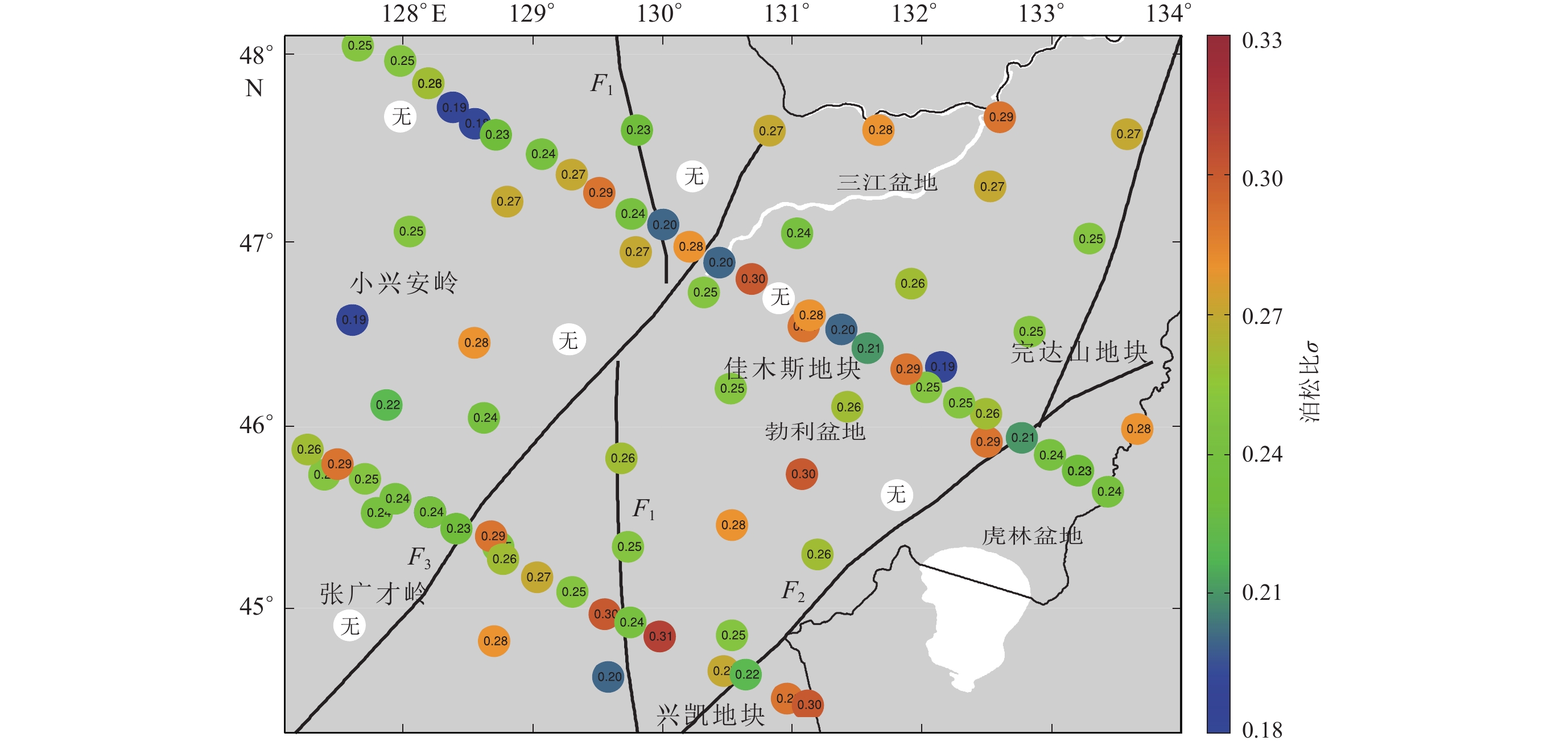
图 8 研究区地震台站下方沉积层厚度图
白色圆点表示计算后得到的台站下方沉积层厚度为零或者小于1.5 km,接收函数不能分辨;“无”表示该台站的数据质量较差,未得到计算结果,下同
Figure 8. Distribution of the sedimentary depth beneath the stations in the studied area
The white dot indicates the station beneath which the thickness of the sedimentary layer is zero or less than 1.5 km,which are not resolved by the receiver function. “None” indicates that the data quality of the station is poor and the calculation result is not obtained,the same below
-
高东辉,陈永顺,孟宪森,张永刚,唐有彩. 2011. 黑龙江地区背景噪声面波群速度层析成像[J]. 地球物理学报,54(4):1043–1051. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.04.019 Gao D H,Chen Y J,Meng X S,Zhang Y G,Tang Y C. 2011. Crustal and uppermost mantle structure of the Heilongjiang region from ambient noise tomography[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,54(4):1043–1051 (in Chinese).
葛肖虹,刘俊来,任收麦,袁四化. 2014. 中国东部中—新生代大陆构造的形成与演化[J]. 中国地质,41(1):19–38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.01.002 Ge X H,Liu J L,Ren S M,Yuan S H. 2014. The formation and evolution of Mesozoic-Cenozoic continental tectonic in eastern China[J]. Geology in China,41(1):19–38 (in Chinese).
和钟铧,刘招君,张晓冬,陈永成,董林森. 2009. 黑龙江东部晚中生代盆地群构造层划分及构造沉积演化[J]. 世界地质,28(1):20–27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2009.01.003 He Z H,Liu Z J,Zhang X D,Chen Y C,Dong L S. 2009. Subdivisions of structural layers and tectonic-sedimentary evolution of eastern basin in Heilongjiang in Late Mesozoic[J]. Global Geology,28(1):20–27 (in Chinese).
贾承造,郑民. 2010. 东北白垩纪大三江盆地沉积构造演化及其残留盆地群的油气勘探意义[J]. 大庆石油学院学报,34(6):1–12. Jia C Z,Zheng M. 2010. Sedimentary history,tectonic evolution of Cretaceous Dasanjiang basin in Northeast China and the significance of oil and gas exploration of its residual basin[J]. Journal of Daqing Petroleum Institute,34(6):1–12 (in Chinese).
李天觉,陈棋福. 2019. 利用接收函数方法研究中国东北东南部地区不同构造体的地壳特征[J]. 地球物理学报,62(8):2899–2917. doi: 10.6038/cjg2019M0379 Li T J,Chen Q F. 2019. Crustal structure of different tectonic units in southeastern part of Northeast China using receiver functions[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,62(8):2899–2917 (in Chinese).
刘国兴,张兴洲,杨宝俊,翁爱华,唐君辉,李雪森. 2006. 佳木斯地块及东缘岩石圈电性结构特征[J]. 地球物理学报,49(2):598–603. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2006.02.037 Liu G X,Zhang X Z,Yang B J,Weng A H,Tang J H,Li X S. 2006. Electrical structures of the lithosphere along the Jiamusi massif and its eastern edge[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,49(2):598–603 (in Chinese).
卢造勋,夏怀宽. 1993. 内蒙古东乌珠穆沁旗至辽宁东沟地学断面[J]. 地球物理学报,36(6):765–772. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.1993.06.008 Lu Z X,Xia H K. 1993. Geoscience transect from Dong Ujimqinqi of Inner Mongolia to Donggou of Liaoning,China[J]. Acta Geophysica Sinica,36(6):765–772 (in Chinese).
孙斌. 2013. 东北盆地群重磁特征与深部结构研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学: 52–60. Sun B. 2013. A Study of Gravity-Magnetic Features and Deep Tectonics of the NE China Basin Groups[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University: 52–60 (in Chinese).
王枫. 2010. 黑龙江省东部张广才岭群新兴组: 岩石组合、时代及其构造意义[D]. 长春: 吉林大学: 3–5. Wang F. 2010. The Xinxing Formation From Zhangguangcai Range Group in Eastern Heilongjiang Province: Rock Association, Geochronology and Tectonic Implications[D]. Changchun: Jilin University: 3–5 (in Chinese).
危自根,陈凌. 2012. 东北地区至华北北缘地壳结构的区域差异:地壳厚度与波速比的联合约束[J]. 地球物理学报,55(11):3601–3614. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.11.009 Wei Z G,Chen L. 2012. Regional differences in crustal structure beneath northeastern China and northern North China Craton:Constrains from crustal thickness and vP/vS ratio[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,55(11):3601–3614 (in Chinese).
危自根,储日升,陈凌,崇加军,李志伟. 2016. 复杂地壳接收函数H-κ叠加:以安纳托利亚板块为例[J]. 地球物理学报,59(11):4048–4062. doi: 10.6038/cjg20161110 Wei Z G, Chu R S, Chen L, Chong J J, Li Z W. 2016. Analysis of H-κ and vP/vS receiver function beneath crust with complex structure: Taking the Anatolia Plate as an example[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 59(11): 4048–4062 (in Chinese).
许卫卫,郑天愉. 2005. 渤海湾盆地北西盆山边界地区泊松比分布[J]. 地球物理学报,48(5):1077–1084. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2005.05.014 Xu W W,Zheng T Y. 2005. Distribution of Poisson’s ratios in the northwestern basin-mountain boundary of the Bohai Bay basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,48(5):1077–1084 (in Chinese).
许英才,王琼,曾宪伟,马禾青,许文俊,金涛. 2018. 鄂尔多斯地块西缘莫霍面起伏及泊松比分布[J]. 地震学报,40(5):563–581. Xu Y C,Wang Q,Zeng X W,Ma H Q,Xu W J,Jin T. 2018. Moho depth and Poisson’s ratio distribution in the western edge of Ordos block[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,40(5):563–581 (in Chinese).
杨宝俊,穆石敏,金旭,刘财. 1996. 中国满洲里—绥芬河地学断面地球物理综合研究[J]. 地球物理学报,39(6):772–782. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.1996.06.007 Yang B J,Mu S M,Jin X,Liu C. 1996. Synthesized study on the geophysics of Manzhouli-Suifenhe geoscience transect,China[J]. Acta Geophysica Sinica,39(6):772–782 (in Chinese).
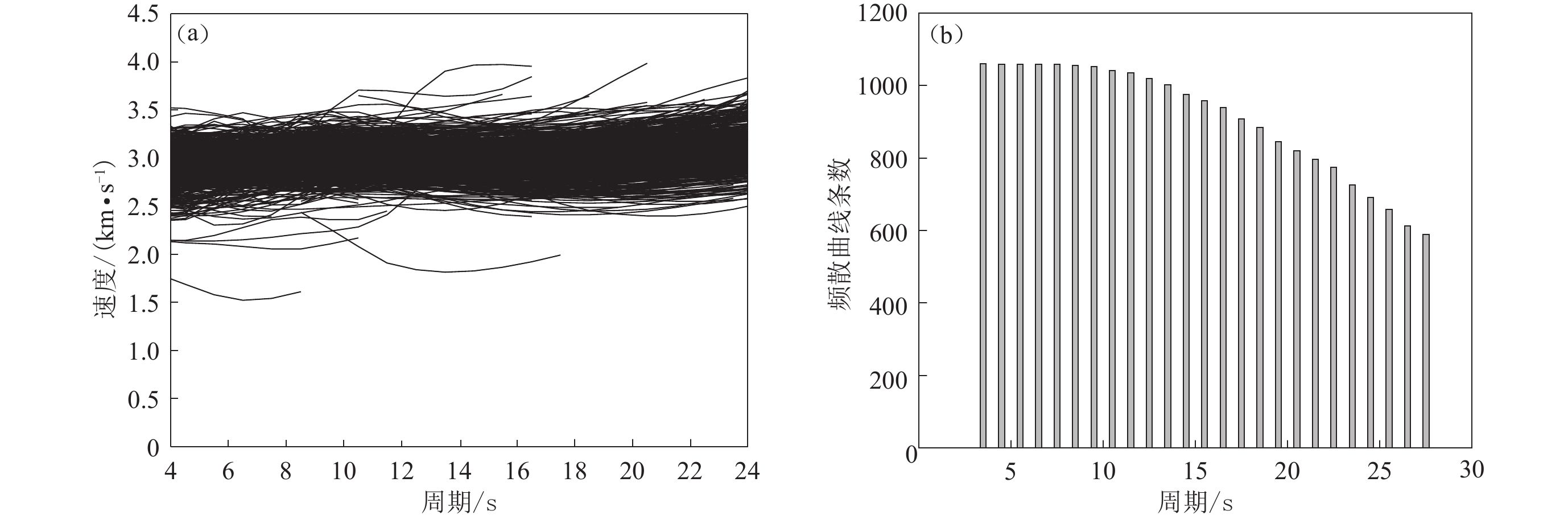
姚华建,徐果明,肖翔,朱良保. 2004. 基于图像分析的双台面波相速度频散曲线快速提取方法[J]. 地震地磁观测与研究,25(1):1–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3246.2004.01.001 Yao H J,Xu G M,Xiao X,Zhu L B. 2004. A quick tracing method based on image analysis technique for the determination of dual stations phase velocities dispersion curve of surface wave[J]. Seismological and Geomagnetic Observation and Research,25(1):1–8 (in Chinese).
曾正彬. 2012. 分析三江盆地石油地质条件与勘探前景[J]. 中国石油和化工标准与质量,33(9):140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4076.2012.10.115 Zeng Z B. 2012. Analysis of petroleum geological conditions and exploration prospects in Sanjiang basin[J]. China Petroleum and Chemical Standard and Quality,33(9):140 (in Chinese).
张风雪,吴庆举,李永华. 2014. 中国东北地区远震S波走时层析成像研究[J]. 地球物理学报,57(1):88–101. Zhang F X,Wu Q J,Li Y H. 2014. A traveltime tomography study by teleseismic S wave data in the Northeast China area[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,57(1):88–101 (in Chinese).
张广成,吴庆举,潘佳铁,张风雪,余大新. 2013a. 利用H-κ叠加方法和CCP叠加方法研究中国东北地区地壳结构与泊松比[J]. 地球物理学报,56(12):4084–4094. doi: 10.6038/cjg20131213 Zhang G C,Wu Q J,Pan J T,Zhang F X,Yu D X. 2013a. Study of crustal structure and Poisson ratio of NE China by H-κ stack and CCP stack methods[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,56(12):4084–4094 (in Chinese).
张广成,吴庆举,李永华,潘佳铁,张风雪,管见. 2013b. 利用莫霍面Ps震相研究中国东北地区地壳各向异性[J]. 地震学报,35(4):485–497. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-3782.2013.04.004 Zhang G C,Wu Q J,Li Y H,Pan J T,Zhang F X,Guan J. 2013b. An investigation on crustal anisotropy of Northeast China using Moho Ps converted phase[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,35(4):485–497 (in Chinese).
章倩倩. 2012. 三江盆地演化与沉积充填特征[D]. 荆州: 长江大学: 5–20. Zhang Q Q. 2012. The Structural Characteristics and Depositional Filling in the Sanjiang Basin[D]. Jingzhou: Yangtze University: 5–20 (in Chinese).
张云鹏,任建业,王珊,赵学钦. 2016. 东北大三江盆地群早白垩世存在统一湖盆的沉积学证据[J]. 中国地质,43(4):1280–1290. Zhang Y P,Ren J Y,Wang S,Zhao X Q. 2016. The sedimentary evidence for the existence of unified basin in Early Cretaceous in Dasanjiang basin group,Northeast China[J]. Geology in China,43(4):1280–1290 (in Chinese).
张兴洲,郭冶,曾振,付秋林,蒲建彬. 2015. 东北地区中—新生代盆地群形成演化的动力学背景[J]. 地学前缘,22(3):88–98. Zhang X Z,Guo Y,Zeng Z,Fu Q L,Pu J B. 2015. Dynamic evolution of the Mesozoic-Cenozoic basins in the northeastern China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,22(3):88–98 (in Chinese).
张毅. 2019. 应用接收函数方法研究中国东部壳幔间断面结构[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京): 18–28. Zhang Y. 2019. Study of the Crust-Mantle Discontinuity Structure in Eastern China With Receiver Function Method[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing): 18–28 (in Chinese).
郑秀芬,欧阳飚,张东宁,姚志祥,梁建宏,郑洁. 2009. “国家数字测震台网数据备份中心”技术系统建设及其对汶川大地震研究的数据支撑[J]. 地球物理学报,52(5):1412–1417. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.05.031 Zheng X F,Ouyang B,Zhang D N,Yao Z X,Liang J H,Zheng J. 2009. Technical system construction of Data Backup Centre for China Seismograph Network and the data support to researches on the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,52(5):1412–1417 (in Chinese).
周建波,张兴洲,马志红,刘立,金魏,张梅生,王成文,迟效果. 2009. 中国东北地区的构造格局与盆地演化[J]. 石油与天然气地质,30(5):530–538. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2009.05.002 Zhou J B,Zhang X Z,Ma Z H,Liu L,Jin W,Zhang M S,Wang C W,Chi X G. 2009. Tectonic framework and basin evolution in Northeast China[J]. Oil &Gas Geology,30(5):530–538 (in Chinese).
周荔青. 2005. 深大断裂与中国东部新生代盆地油气资源分布[D]. 西安: 西北大学: 5–9. Zhou L Q. 2005. Oil And Gas Distribution in Deep Fault Rupture And Cenozoic Basin in Eastern Part of China[D]. Xi’an: Northwest University: 5–9 (in Chinese).
朱洪翔,田有,刘财,冯晅,杨宝俊,刘才华,刘廷,马锦程. 2017. 中国东北地区高分辨率地壳结构:远震接收函数[J]. 地球物理学报,60(5):1676–1689. doi: 10.6038/cjg20170506 Zhu H X,Tian Y,Liu C,Feng X,Yang B J,Liu C H,Liu T,Ma J C. 2017. High-resolution crustal structure of Northeast China revealed by teleseismic receiver functions[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,60(5):1676–1689 (in Chinese).
朱洪翔. 2020. 接收函数与噪声频散联合反演东北典型构造区S波速度结构[D]. 吉林: 吉林大学: 16–40. Zhu H X. 2020. Shear Wave Structure of Typical Regions in NE China From Joint Inversion of Receiver Function and Ambient Noise Dispersion[D]. Jilin: Jilin University: 16–40 (in Chinese).
Barmin M P,Ritzwoller M H,Levshin A L. 2001. A fast and reliable method for surface wave tomography[J]. Pure Appl Geophys,158(8):1351–1375. doi: 10.1007/PL00001225
Bensen G D,Ritzwoller M H,Barmin M P,Levshin A L,Lin F,Moschetti M P,Shapiro N M,Yang Y. 2007. Processing seismic ambient noise data to obtain reliable broad-band surface wave dispersion measurements[J]. Geophys J Int,169(3):1239–1260. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2007.03374.x
Chen L,Wen L X,Zheng T Y. 2005. A wave equation migration method for receiver function imaging:1. Theory[J]. J Geophys Res,110(B11):B11309. doi: 10.1029/2005JB0003665
Guo Z,Chen Y J,Ning J Y,Feng Y G,Grand S P,Niu F L,Kawakatsu H,Tanaka S,Obayashi M,Ni J. 2015. High resolution 3-D crustal structure beneath NE China from joint inversion of ambient noise and receiver functions using NECESSArray data[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett,416:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2015.01.044
Herrmann R B, Ammon C J. 2004. Surface waves, receiver functions and crustal structure, computer programs in seismology, version 3.30[CP/OL]. [2021-09-20]. http://www.eas.slu.edu/People/RBHerrmann/CPS330.html.
He R Z,Shang X F,Yu C Q,Zhang H J,van der Hilst R D. 2014. A unified map of Moho depth and vP/vS ratio of continental China by receiver function analysis[J]. Geophys J Int,199:1910–1918. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggu365
Huang J L,Zhao D P. 2006. High-resolution mantle tomography of China and surrounding regions[J]. J Geophys Res,111(B9):B09305. doi: 10.1029/2005JB004066
Kang D,Shen W S,Ning J Y,Ritzwoller M H. 2016. Seismic evidence for lithospheric modification associated with intracontinental volcanism in northeastern China[J]. Geophys J Int,204(1):215–235. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggv441
Ligorría J P,Ammon C J. 1999. Iterative deconvolution and receiver-function estimation[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,89(5):1395–1400. doi: 10.1785/BSSA0890051395
Schimmel M,Stutzmann E,Gallart J. 2011. Using instantaneous phase coherence for signal extraction from ambient noise data at a local to a global scale[J]. Geophys J Int,184(1):494–506. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2010.04861.x
Stockwell R G,Mansinha L,Lowe R P. 1996. Localization of the complex spectrum:The S transform[J]. IEEE Trans Signal Process,44(4):998–1001. doi: 10.1109/78.492555
Tang Y C,Obayashi M,Niu F L,Grand S P,Chen Y J,Kawakatsu H,Tanaka S,Ning J Y,Ni J F. 2014. Changbaishan volcanism in Northeast China linked to subduction-induced mantle upwelling[J]. Nat Geosci,7(6):470–475. doi: 10.1038/ngeo2166
Tao K,Niu F L,Ning J Y,Chen Y J,Steve G,Kawakatsu H,Tanaka S,Obayashi M,Ni J. 2014. Crustal structure beneath NE China imaged by NECESSArray receiver function data[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett,398:48–57. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2014.04.043
Zhang Y,Huang J L. 2019. Structure of the sediment and crust in the Northeast North China Craton from improved sequential H-κ stacking method[J]. Open Geosci,11:682–696.
Zheng Y,Shen W S,Zhou L Q,Yang Y J,Xie Z J,Ritzwoller M H. 2011. Crust and uppermost mantle beneath the North China Craton,northeastern China,and the Sea of Japan from ambient noise tomography[J]. J Geophys Res,116(B12):B12312. doi: 10.1029/2011JB008637
Zhu L P,Kanamori H. 2000. Moho depth variation in southern California from teleseismic receiver functions[J]. J Geophys Res,105(B2):2969–2980.




 下载:
下载: