Removing tilt noise from the vertical component data of ocean bottom seismograph:A case study on the data from the Pankun test in the South China Sea
-
摘要:
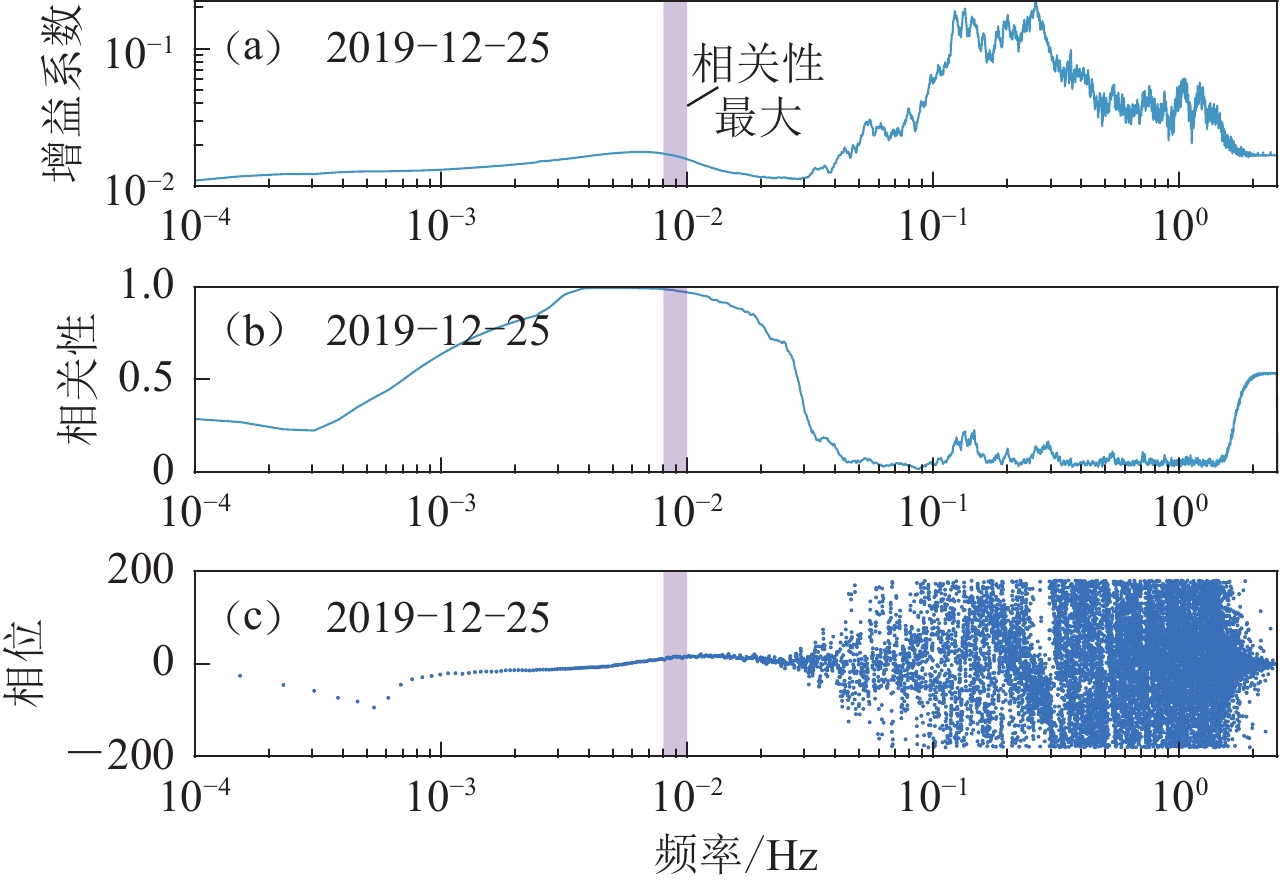
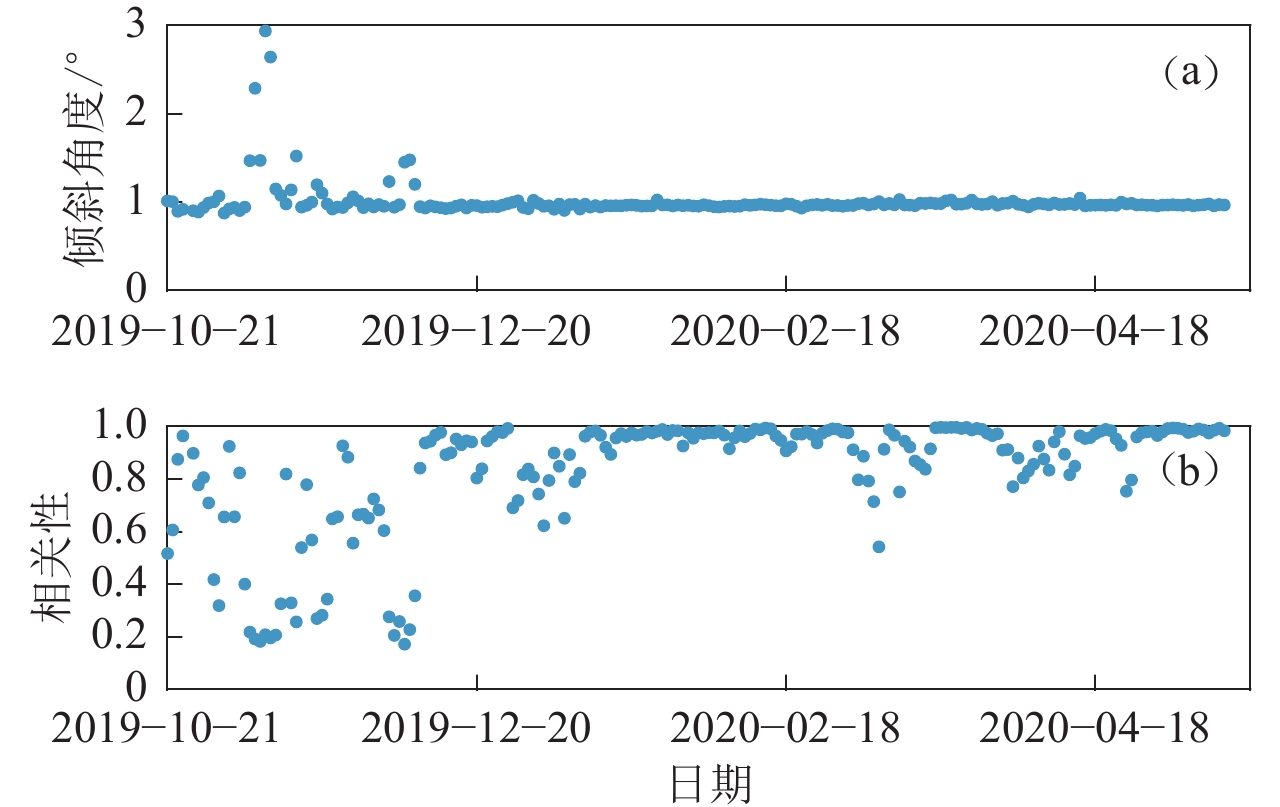
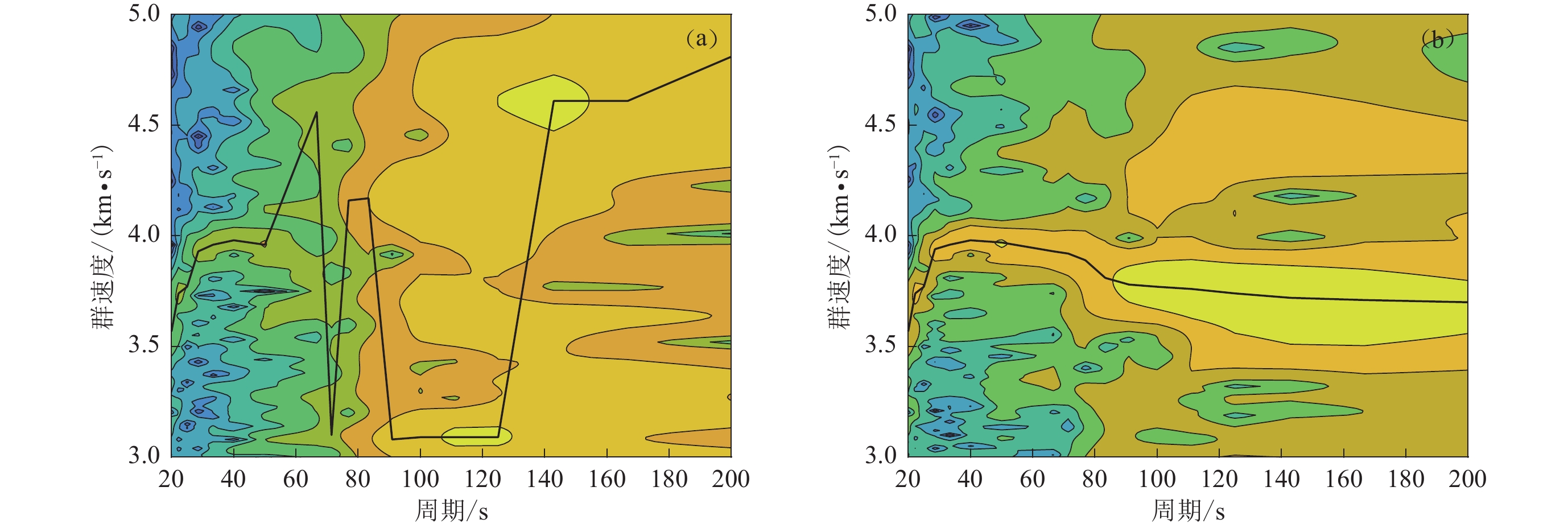
基于水平分量和垂直分量噪声数据之间的相关性,可以通过水平到垂直分量的传递函数去除垂直分量的倾斜噪声。本文以2019—2020年磐鲲海底地震仪南海测试的数据为例,描述了该方法的原理和过程,并对比了去除倾斜噪声前后的地震波形以及瑞雷波的频散特征。结果表明:倾斜噪声的去除明显提高了海底地震仪的低频段地震波形的信噪比,使得地震面波更有利于海洋岩石圈深部结构成像;此外,尽管磐鲲海底地震仪的调平系统使地震计的倾角(1.0°)远小于其容倾角(2.5°),在底流作用下,海底地震仪还是产生了明显的倾斜噪声。因此,地震仪调平系统的性能对海底地震仪的数据质量有着非常重要的影响。
Abstract:Based on the correlations between the noise data of the horizontal and the vertical components, we can remove the tilt noise from the vertical component by using the transfer function of the horizontal-to-vertical component. Using the data from the 2019−2020 Pankun OBS South China Sea test, this paper describes the theory and process of this method. It compares the seismograms before and after removing the tilt noise and highlights the improvement of the dispersions of Rayleigh surface waves. The results show that removing tilt noise can improve the signal-to-noise ratio of seismograms for the OBS data in the low-frequency range, resulting in surface waves more conducive to imaging the deep structure of the oceanic lithosphere. This study also shows that although the tilt angle (1.0°) of the seismometer of Pankun OBS is much smaller than the tolerance of the tilt angle of the instrument (2.5°), the bottom currents still generate a significant level of tilt noise on OBS data. Therefore, the leveling system of the instrument is a crucial component affecting the OBS data quality.
-
Keywords:
- ocean bottom seismograph (OBS) /
- seismic noise /
- tilt noise /
- removing noise
-
-
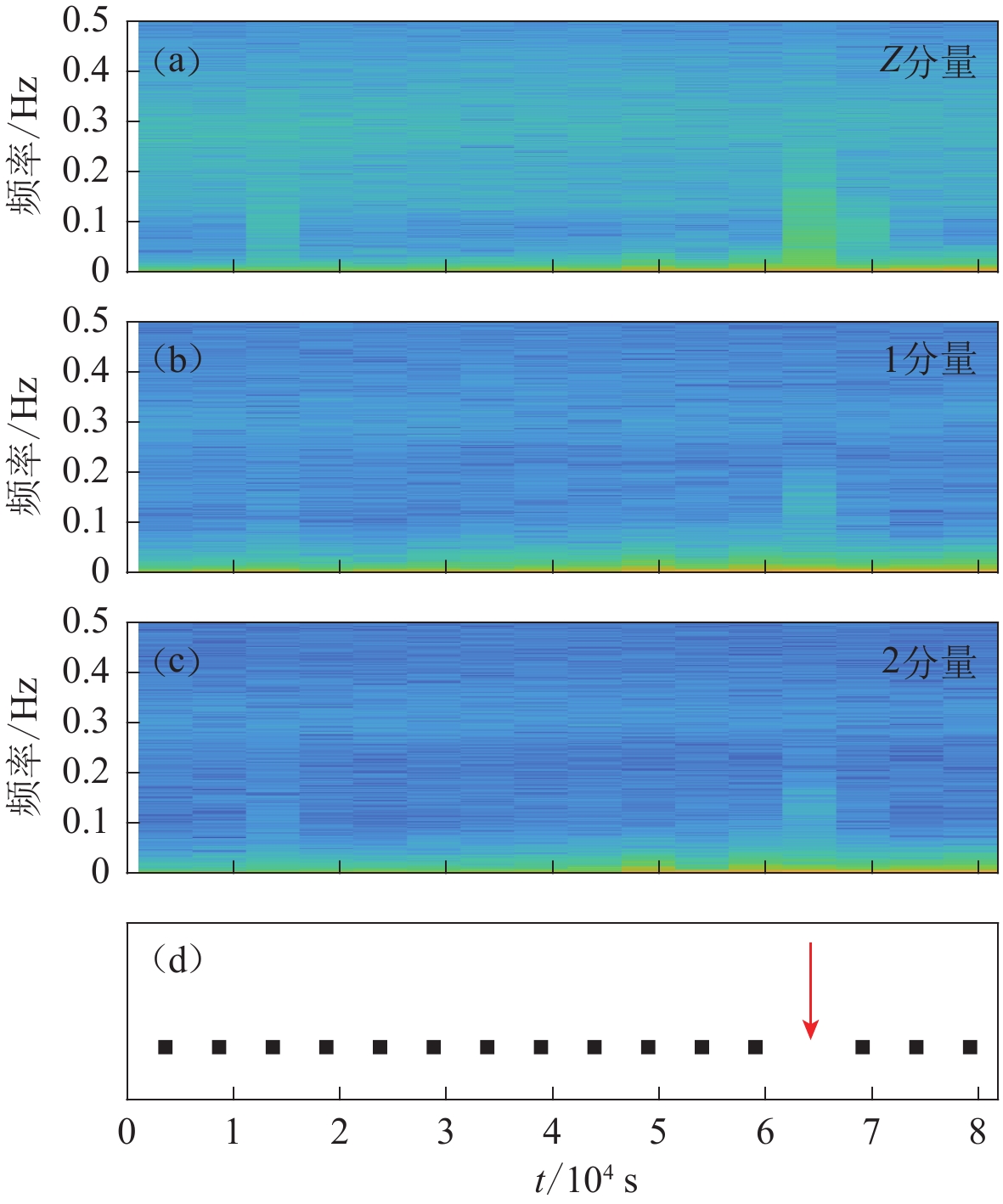
图 2 2020年3月18日垂直(a)和水平(b,c)分量的频谱及噪声时间窗选择(d)
图(d)中的方块表示窗口被接受,而方块的缺失(箭头所示)表示窗口未通过基于日平均值设置的阈值
Figure 2. Spectrogram for the vertical (a) and horizontal (b,c) components,and the noise time windows selection (d) on 18th March,2020
A square in fig. (d) indicates that the window is accepted, while the absence of a square (indicated by the arrow) indicates that the window does not pass the threshold set based on the daily average
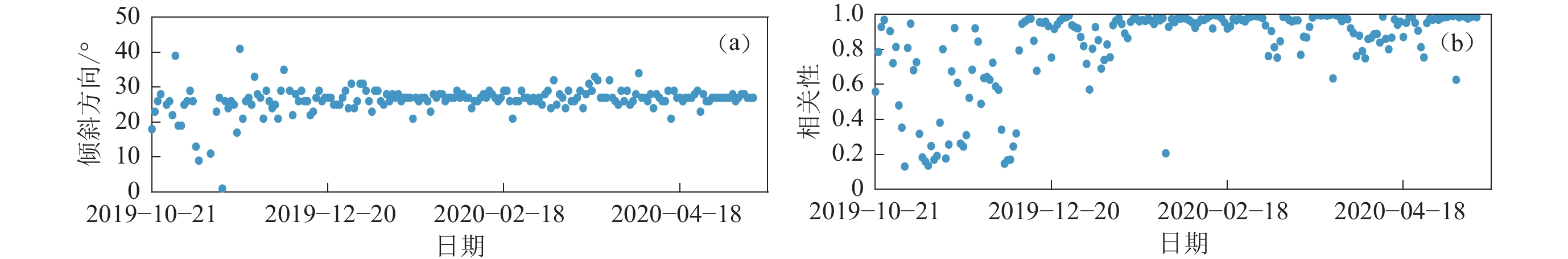
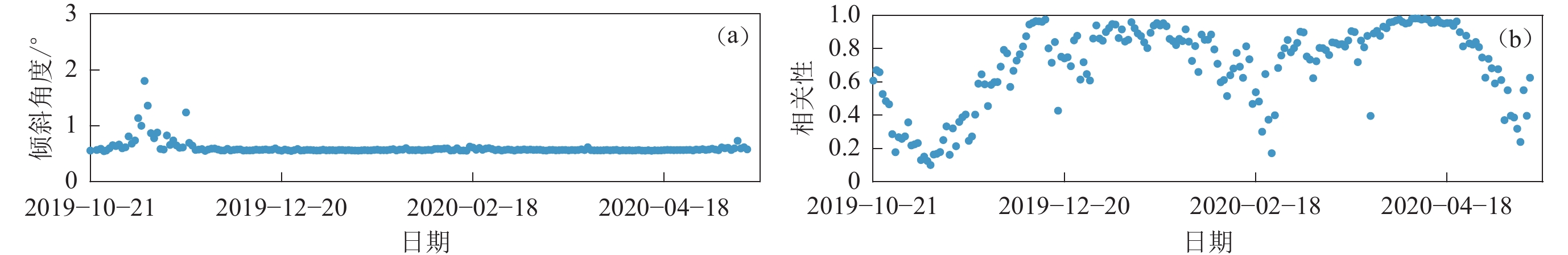
图 3 台站K02布设期间水平与垂直分量的最大相关性方向(a)和对应的相关大小(b)
图(a)中的倾斜方向为相对水平分量1顺时针转过的角度
Figure 3. Maximum coherence direction (a) and corresponding coherence value (b) of the horizontal to vertical component during station K02 deployment
The tilt direction in fig.(a) represents the degrees turned clockwise relative to the horizontal component 1
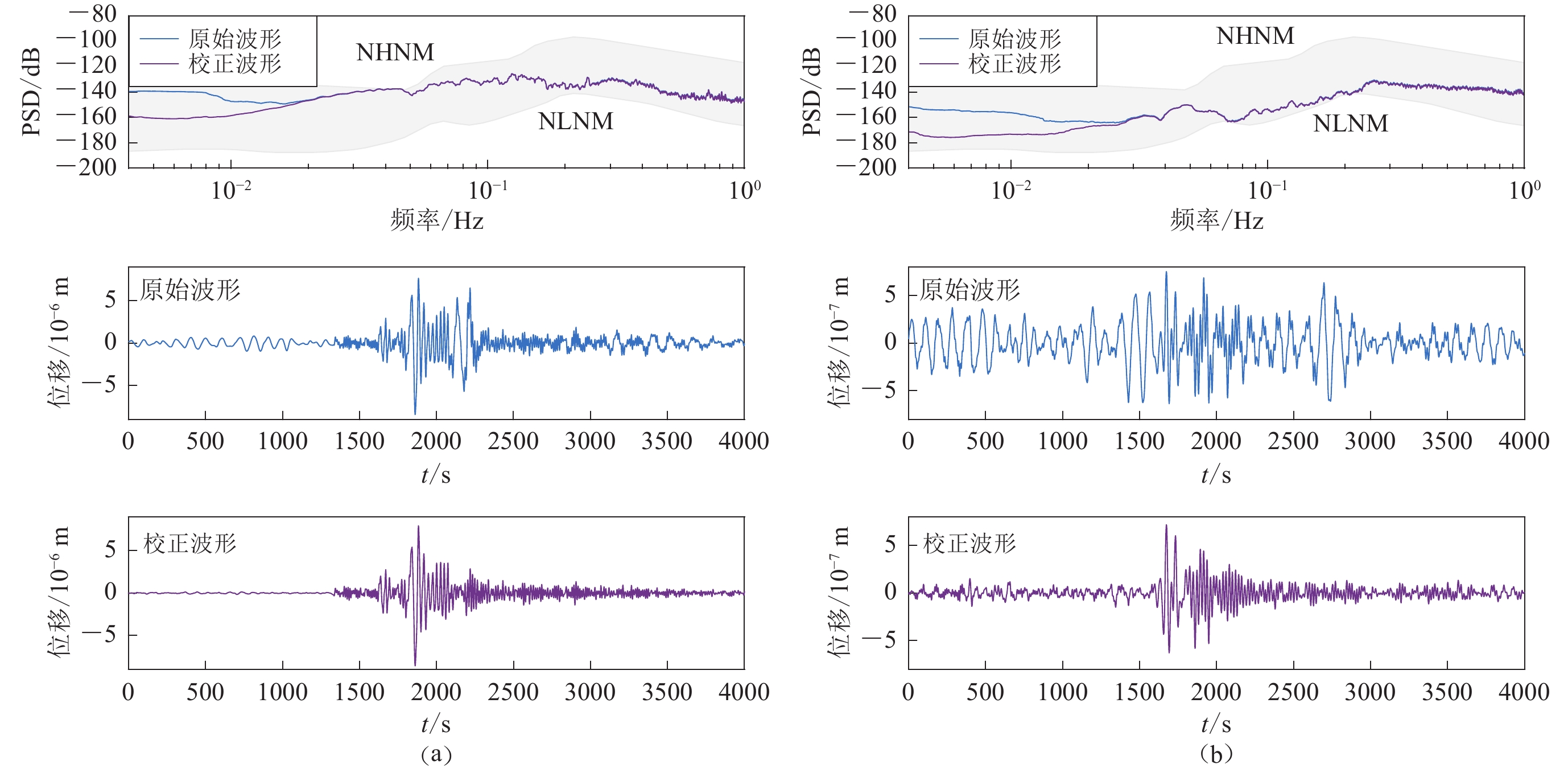
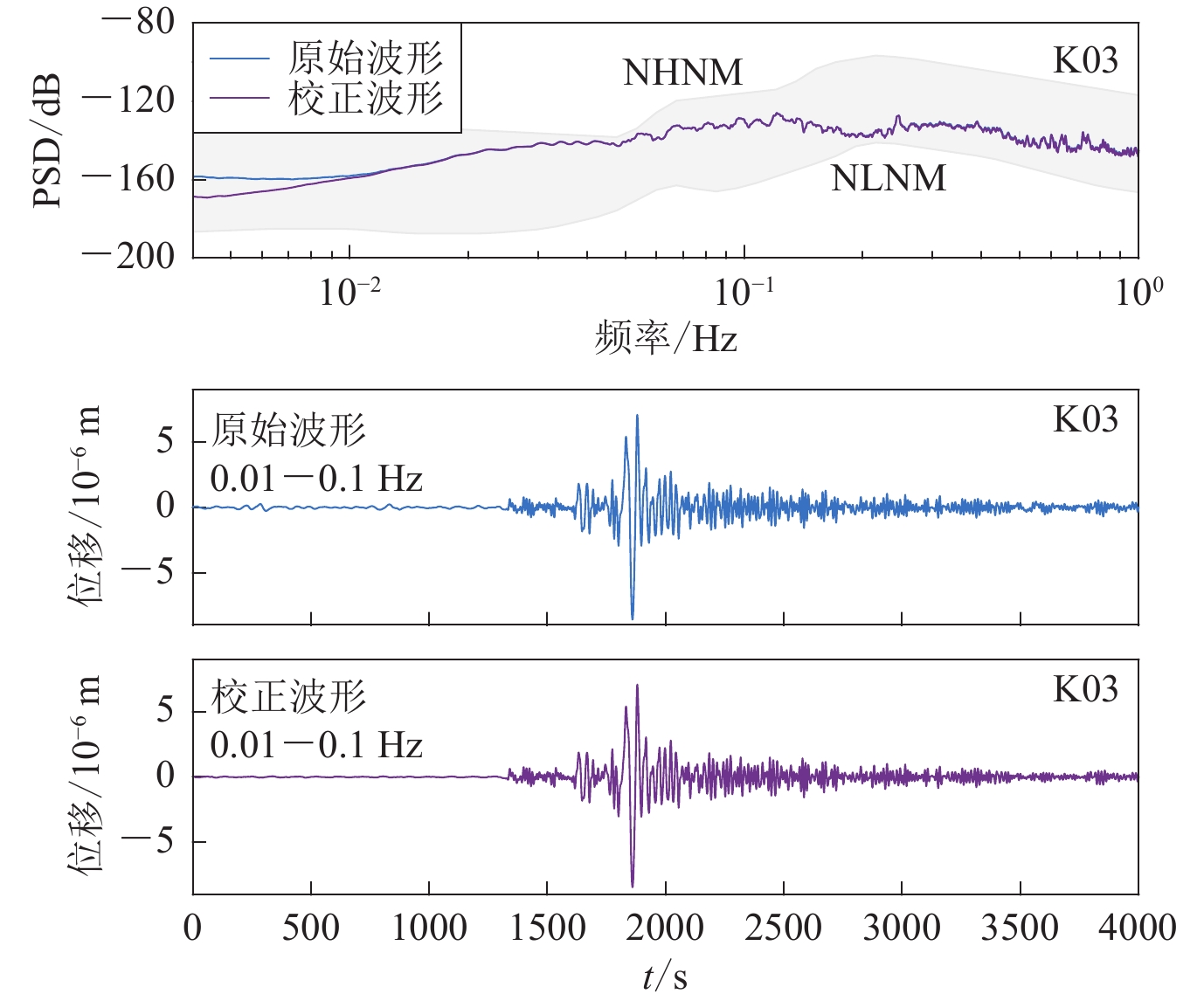
图 6 去除倾斜噪声前后波形(滤波至0.01—0.1 Hz)及其功率谱密度 (PSD) 对比
(a) 2020年3月18日巴厘岛南部附近发生的MW6.2地震;(b) 2019年12月25日东太平洋海隆南部附近发生的MW6.1地震
Figure 6. Comparison of waveforms (filtered at 0.01−0.1 Hz) and its PSDs before and after tilt noise removed
(a) MW6.2 earthquake occurred near the south of Bali on March 18,2020;(b) MW6.1 earthquake occurred near the southern East Pacific Rise on December 25,2019
-
刘丹,杨挺,黎伯孟,吴越楚,王宜志,黄信锋,杜浩然,王建,陈永顺. 2022. 分体式宽频带海底地震仪的研制、测试和数据质量分析[J]. 地球物理学报,65(7):2560–2572. Liu D,Yang T,Le B M,Wu Y C,Wang Y Z,Huang X F,Du H R,Wang J,Chen Y S. 2022. Seismometer-detached broadband ocean bottom seismograph (OBS):Development,test,and data quality analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,65(7):2560–2572 (in Chinese).
Agius M R,Rychert C A,Harmon N,Laske G. 2017. Mapping the mantle transition zone beneath Hawaii from PS receiver functions:Evidence for a hot plume and cold mantle downwellings[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett,474:226–236. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2017.06.033
An C,Cai C,Zhou L,Yang T. 2021. Characteristics of low-frequency horizontal noise of ocean-bottom seismic data[J]. Seismol Res Lett,93(1):257–267. doi: 10.1785/0220200349
Bell S W,Forsyth D W,Ruan Y Y. 2015. Removing noise from the vertical component records of ocean-bottom seismometers:Results from year one of the Cascadia Initiative[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,105(1):300–313. doi: 10.1785/0120140054
Bell S,Ruan Y Y,Forsyth D W. 2016. Ridge asymmetry and deep aqueous alteration at the trench observed from Rayleigh wave tomography of the Juan de Fuca plate[J]. J Geophys Res:Solid Earth,121(10):7298–7321. doi: 10.1002/2016JB012990
Bendat J S, Piersol A G. 1986. Random Data: Analysis and Measurement Procedures[M]. 2nd ed. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley and Sons.
Bowden D C,Kohler M D,Tsai V C,Weeraratne D S. 2016. Offshore southern California lithospheric velocity structure from noise cross-correlation functions[J]. J Geophys Res:Solid Earth,121(5):3415–3427. doi: 10.1002/2016JB012919
Cai C,Wiens D A,Shen W S,Eimer M. 2018. Water input into the Mariana subduction zone estimated from ocean-bottom seismic data[J]. Nature,563(7731):389–392. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0655-4
Collins J A,Vernon F L,Orcutt J A,Stephen R A,Peal K R,Wooding F B,Spiess F N,Hildebrand J A. 2001. Broadband seismology in the oceans:Lessons from the ocean seismic network pilot experiment[J]. Geophys Res Lett,28(1):49–52. doi: 10.1029/2000GL011638
Crawford W C,Webb S C. 2000. Identifying and removing tilt noise from low-frequency (<0.1 Hz) seafloor vertical seismic data[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,90(4):952–963. doi: 10.1785/0119990121
Doran A K,Laske G. 2019. Seismic structure of marine sediments and upper oceanic crust surrounding Hawaii[J]. J Geophys Res:Solid Earth,124(2):2038–2056. doi: 10.1029/2018JB016548
Duennebier F K,Blackinton G,Sutton G H. 1981. Current-generated noise recorded on ocean bottom seismometers[J]. Mar Geophys Res,5(1):109–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00310316
Eilon Z C,Gaherty J B,Zhang L,Russell J,McPeak S,Phillips J,Forsyth D W,Ekström G. 2022. The Pacific OBS research into convecting asthenosphere (ORCA) experiment[J]. Seismol Res Lett,93(1):477–493. doi: 10.1785/0220210173
Hung T D,Yang T,Le B M,Yu Y Q. 2019. Effects of failure of the ocean-bottom seismograph leveling system on receiver function analysis[J]. Seismol Res Lett,90(3):1191–1199. doi: 10.1785/0220180276
Janiszewski H A,Gaherty J B,Abers G A,Gao H,Eilon Z C. 2019. Amphibious surface-wave phase-velocity measurements of the Cascadia subduction zone[J]. Geophys J Int,217(3):1929–1948. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggz051
Liu C G,Hua Q F,Pei Y L,Yang T,Xia S H,Xue M,Le B M,Huo D,Liu F,Huang H B. 2014. Passive-source ocean bottom seismograph (OBS) array experiment in South China Sea and data quality analyses[J]. Chinese Science Bull,59(33):4524–4535. doi: 10.1007/s11434-014-0369-4
Liu D,Yang T,Wang Y,Wu Y,Huang X. 2023. Pankun:A New Generation of Broadband Ocean Bottom Seismograph[J]. Sensors,23(11):4995. doi: 10.3390/s23114995
Lin P Y P,Gaherty J B,Jin G,Collins J A,Lizarralde D,Evans R L,Hirth G. 2016. High-resolution seismic constraints on flow dynamics in the oceanic asthenosphere[J]. Nature,535(7613):538–541. doi: 10.1038/nature18012
Moore R D,Dorman L M,Huang C Y,Berliner D L. 1981. An ocean bottom,microprocessor based seismometer[J]. Mar Geophys Res,4(4):451–477. doi: 10.1007/BF00286039
Peterson J R. 1993. Observations and Modeling of Seismic Background Noise[R]. Albuquerque: U. S. Geological Survey.
Shiobara H,Kanazawa T,Isse T. 2013. New step for broadband seismic observation on the seafloor:BBOBS-NX[J]. IEEE J Oceanic Eng,38(2):396–405. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2012.2222792
Stähler S C,Sigloch K,Hosseini K,Crawford W C,Barruol G,Schmidt-Aursch M C,Tsekhmistrenko M,Scholz J R,Mazzullo A,Deen M. 2016. Performance report of the RHUM-RUM ocean bottom seismometer network around La Réunion,western Indian Ocean[J]. Adv Geosci,41:43–63. doi: 10.5194/adgeo-41-43-2016
Stephen R A, Spiess F N, Collins J A, Hildebrand J A, Orcutt J A, Peal K R, Vernon F L, Wooding F B. 2003. Ocean seismic network pilot experiment[J]. Geochem Geophys Geosyst, 4(10). doi: 10.1029/2002gc000485.
Tian Y,Ritzwoller M H. 2017. Improving ambient noise cross-correlations in the noisy ocean bottom environment of the Juan de Fuca plate[J]. Geophys J Int,210(3):1787–1805. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggx281
Toomey D R,Allen R M,Barclay A H,Bell S W,Bromirski P D,Carlson R L,Chen X W,Collins J A,Dziak R P,Evers B,Forsyth DW,Gerstoft P,Hooft E E E,Livelybrooks D,Lodewyk J A,Luther D S,McGuire J J,Schwartz S Y,Tolstoy M,Tréhu A M,Weirathmueller M,Wilcock W S D. 2014. The Cascadia initiative:A sea change in seismological studies of subduction zones[J]. Oceanography,27(2):138–150. doi: 10.5670/oceanog.2014.49
Wang Y Z,Yang T,Wu Y C,Liu D,Huang X F,Wang J,Zhong W X,Shou H T,Zhou Y,Chen Y S. 2022. A new broad-band ocean bottom seismograph and characteristics of the seismic ambient noise on the South China Sea seafloor based on its recordings[J]. Geophys J Int,230(1):684–695. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggac092
Webb S C. 1988. Long-period acoustic and seismic measurements and ocean floor currents[J]. IEEE J Oceanic Eng,13(4):263–270. doi: 10.1109/48.9239
Webb S C. 1998. Broadband seismology and noise under the ocean[J]. Rev Geophys,36(1):105–142. doi: 10.1029/97RG02287
Webb S C,Crawford W C. 1999. Long-period seafloor seismology and deformation under ocean waves[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,89(6):1535–1542. doi: 10.1785/BSSA0890061535
Wooding F B,Peal K R,Collins J A. 2001. Seafloor seismometer burial[J]. Sea Technol,42(8):10–13.
Yang Z H, Sheehan A F, Collins J A, Laske G. 2012. The character of seafloor ambient noise recorded offshore New Zealand: Results from the MOANA ocean bottom seismic experiment[J]. Geochem Geophys Geosyst, 13(10). doi: 10.1029/2012gc004201.
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(4)





 下载:
下载: