Research on daily variation of vertical component of geomagnetic field in China
-
摘要:
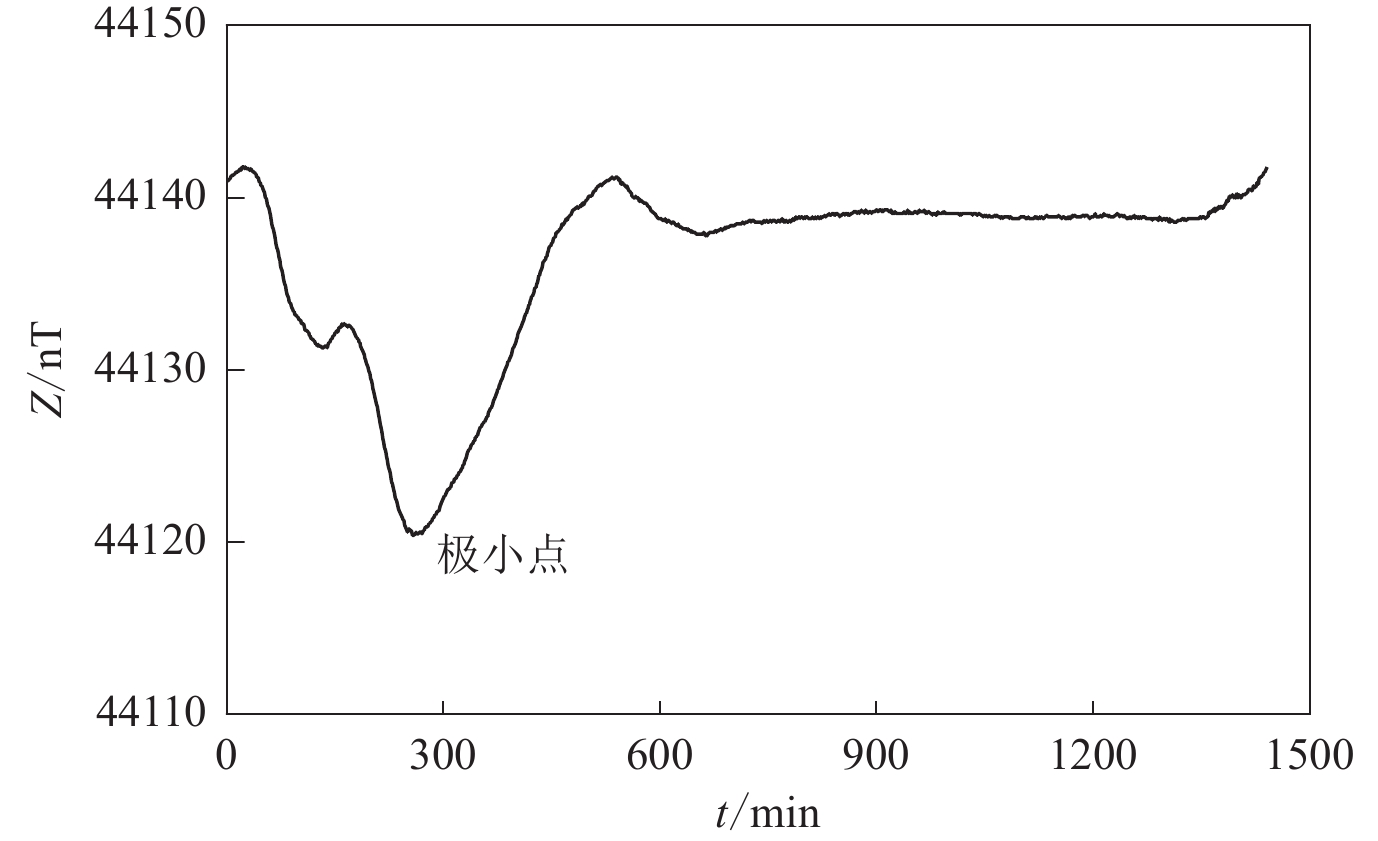
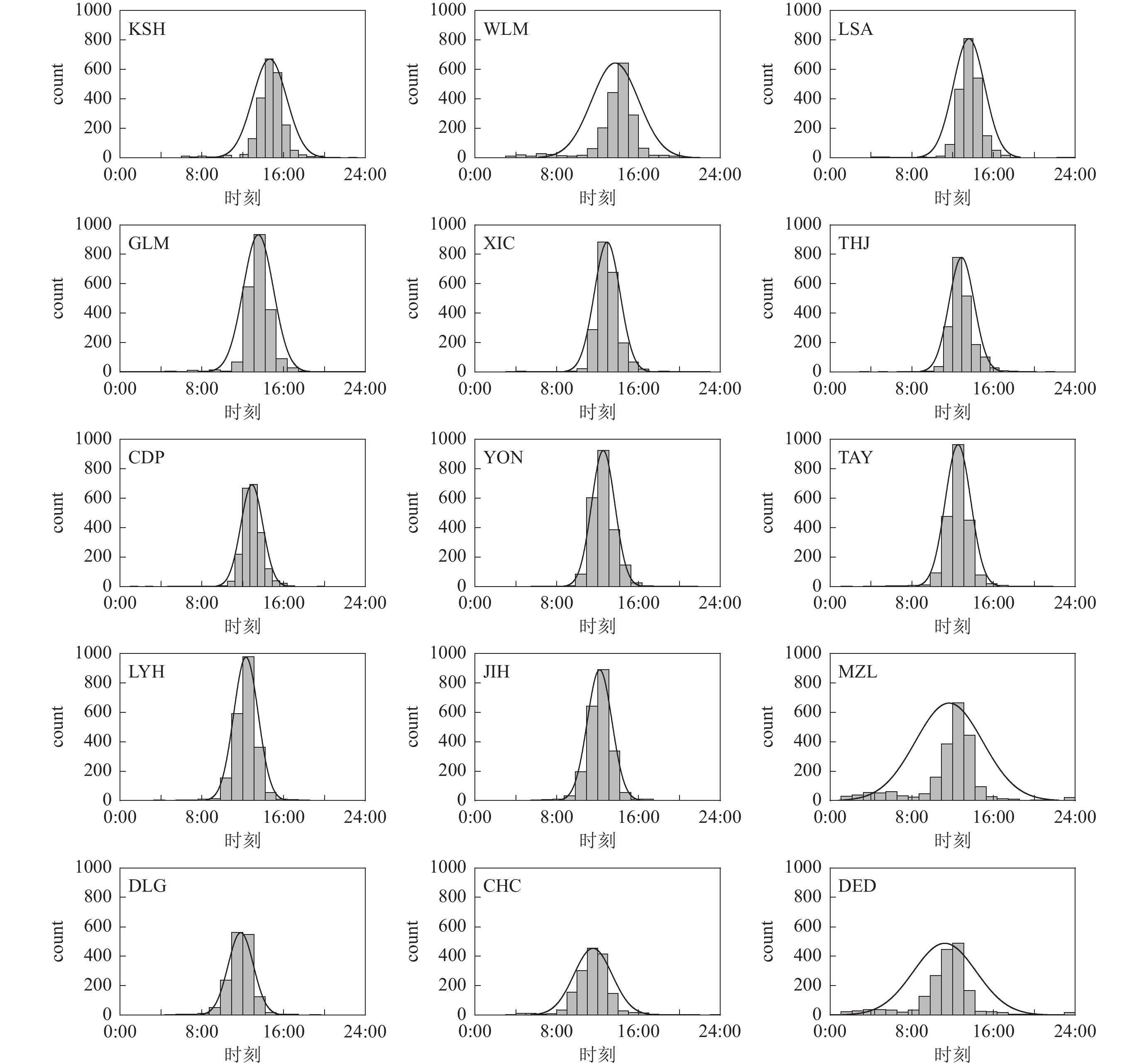
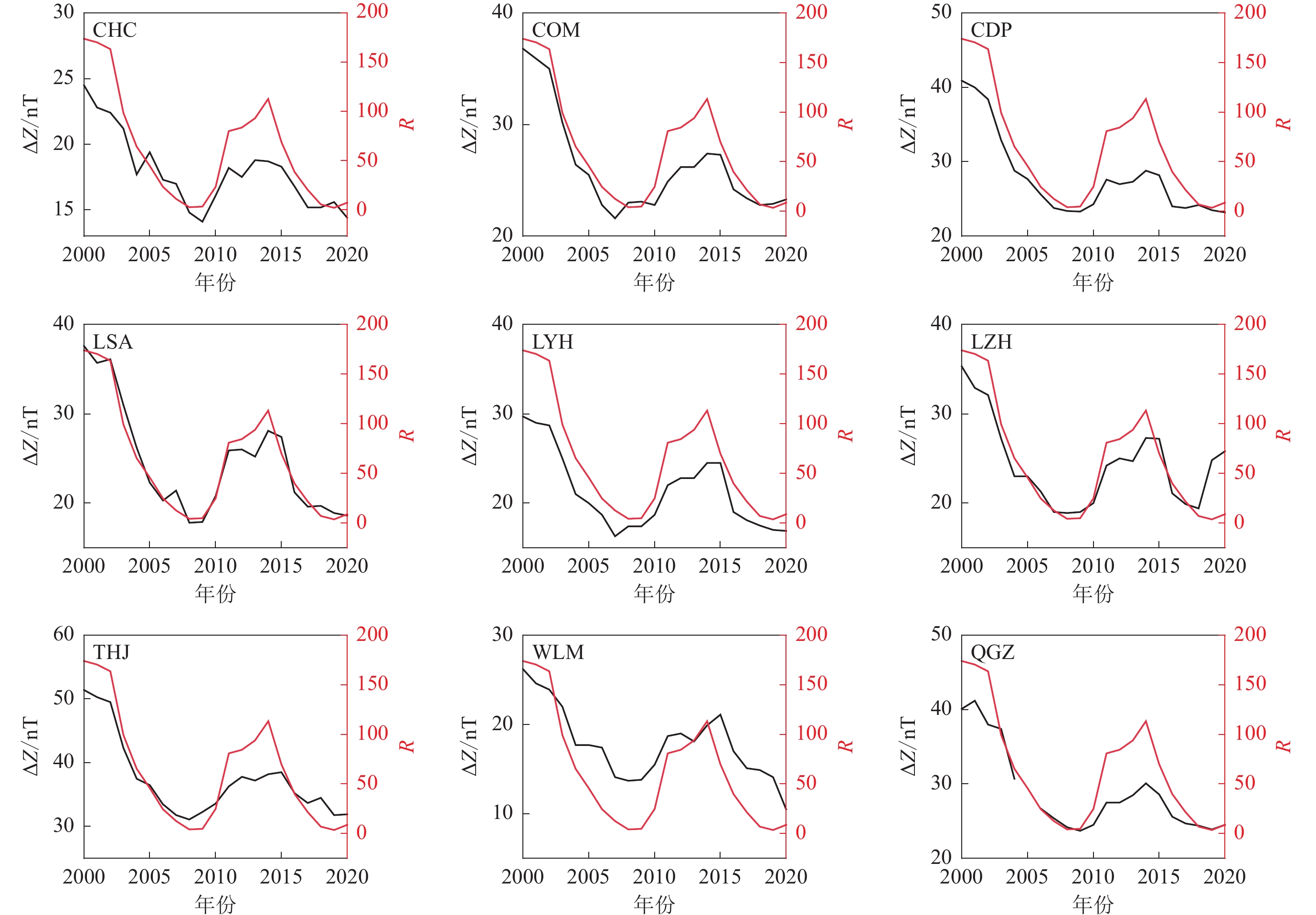
基于我国地磁台站的观测数据,首先根据地磁台垂直分量日变化曲线的形态特征,统计了15个地磁台站垂直分量的极小时间(地方时),并重点探讨了这些极小时间在我国区域内的分布特性及其与台站经度的关系。其次选取27个地磁台垂直分量太阳活动高年与太阳活动低年年均值日变幅,分析垂直分量日变幅与太阳黑子活动之间的关系,并按照劳埃德季节划分的分点月份,夏至点月份、冬至点月份等不同季节及太阳活动高低年分别探讨垂直分量日变幅在不同季节和太阳活动高低年的变化规律及特性。研究结果表明:① 我国区域内地磁场垂直分量的极小时间主要集中在当地正午附近,与台站的经度呈显著负相关关系,并且该时间分布符合正态分布模式;② 地磁场垂直分量的日变幅显著受太阳黑子活动的影响,与太阳黑子数的相关系数为0.929,二者存在高度正相关性,垂直分量的日变幅显示出约11年的周期性变化;③ 垂直分量的日变幅变化受季节影响,表现出明显的季节性差异,地磁场日变幅在夏至点月份比冬至点月份更为活跃,在不同季节产生不同影响。研究结果为了解地磁场日变化特征和规律及地球内部活动提供了依据和参考。
Abstract:Based on the observation data from geomagnetic stations in China, we first statistically analyzed the minimum time (local time) of the vertical component at 15 geomagnetic stations based on its morphological characteristics of the daily variation curves. We then focused on the distribution characteristics of these minimum times within the Chinese region and their relationship with the longitude of the stations. Secondly, we selected 27 geomagnetic stations to analyze the annual average daily variation amplitudes of the vertical component during periods of high and low solar activity, aiming to achieve the relationship between the daily variation amplitudes of the vertical component and sunspot activity. This analysis was conducted for different seasons, including the months around the equinoxes, summer solstice, and winter solstice, as well as for years with high and low solar activity. The results show that: ① The minimum time of the vertical component of the geomagnetic field in China is mainly concentrated around local noon, showing a significant negative correlation with the longitude of the stations, and this time distribution follows a normal distribution pattern. ② The daily variation amplitude of the vertical component of the geomagnetic field is significantly influenced by sunspot activity, by a correlation coefficient of 0.929 with the number of sunspots, indicating a strong positive correlation. The daily variation amplitude of the vertical component exhibits a cyclic change of about 11 years. ③ The daily variation amplitude of the vertical component shows seasonal differences, being more active in the months around the summer solstice compared to the months around the winter solstice, indicating distinct seasonal impacts. These findings provide insights into the daily variation characteristics and patterns of the geomagnetic field and offer references for understanding Earth's internal activities.
-
Keywords:
- minimal time /
- normal distribution /
- daily range /
- sunspot index /
- correlation
-
-
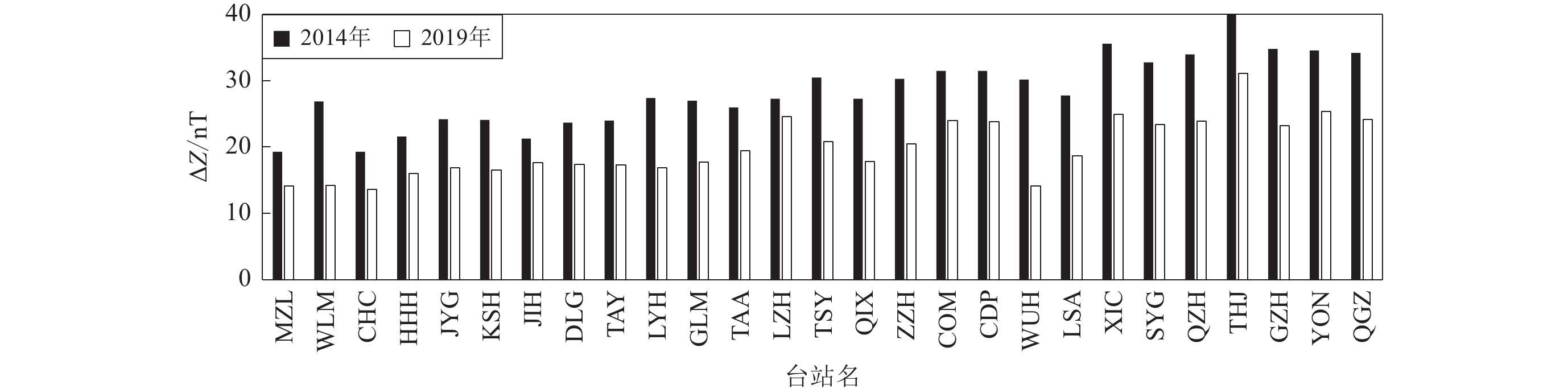
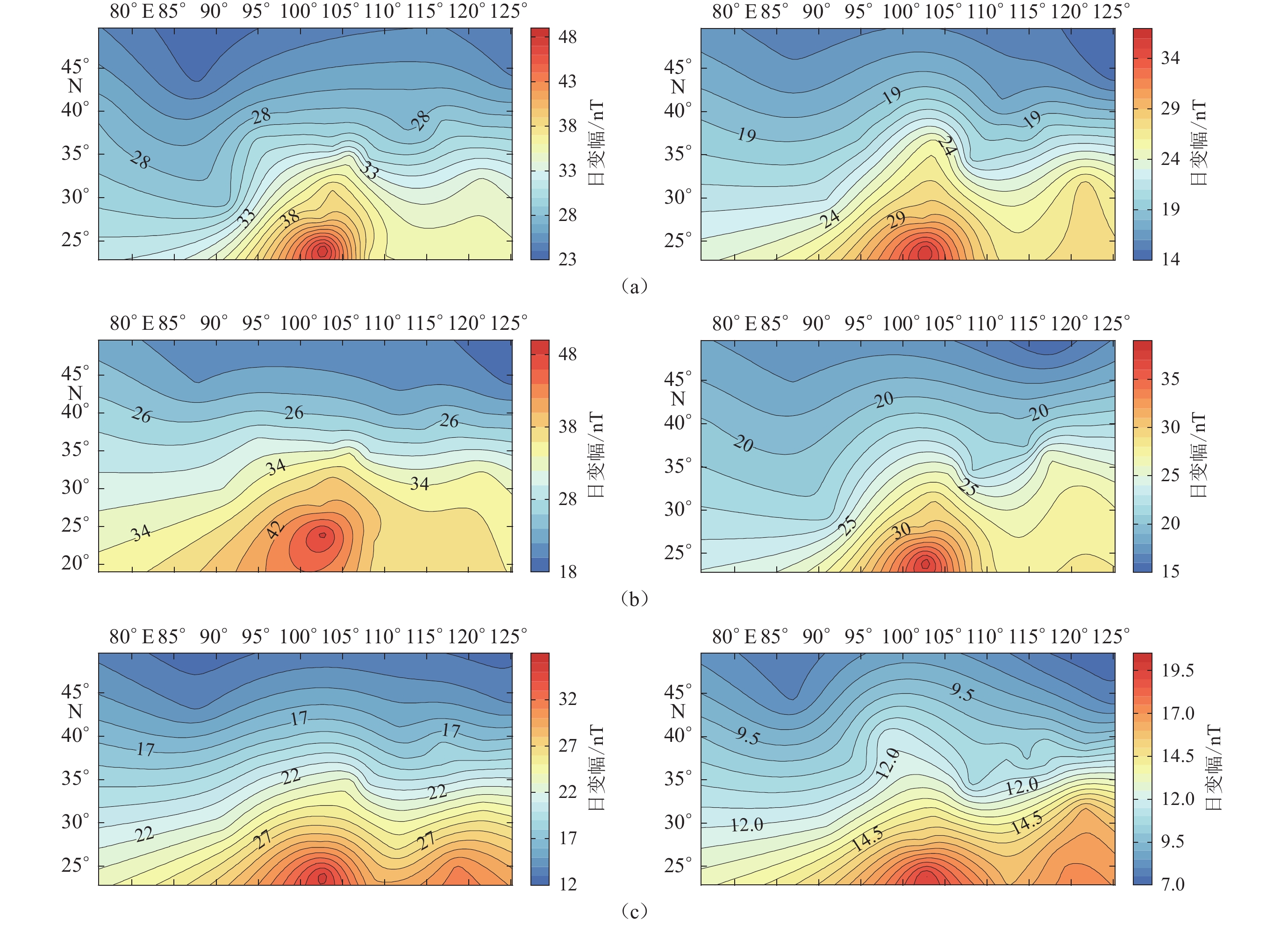
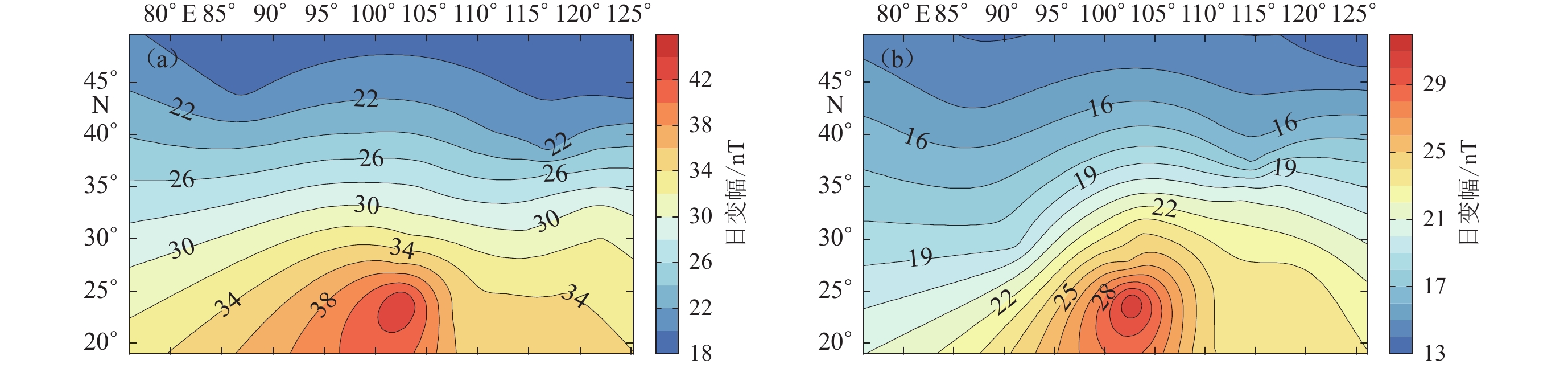
图 6 地磁场垂直分量在太阳活动高年(2014年)(左)和太阳活动低年(2019年)(右)不同季节的日变幅等值线图
(a) 分点月份;(b) 夏至点月份;(c) 冬至点月份
Figure 6. Contour map of daily variation amplitude of vertical component in geomagnetic field in different seasons in high solar year (2014)(left) and low solar year (2019) (right)
(a) Equinox month;(b) Summer solstice month;(c) Winter solstice month
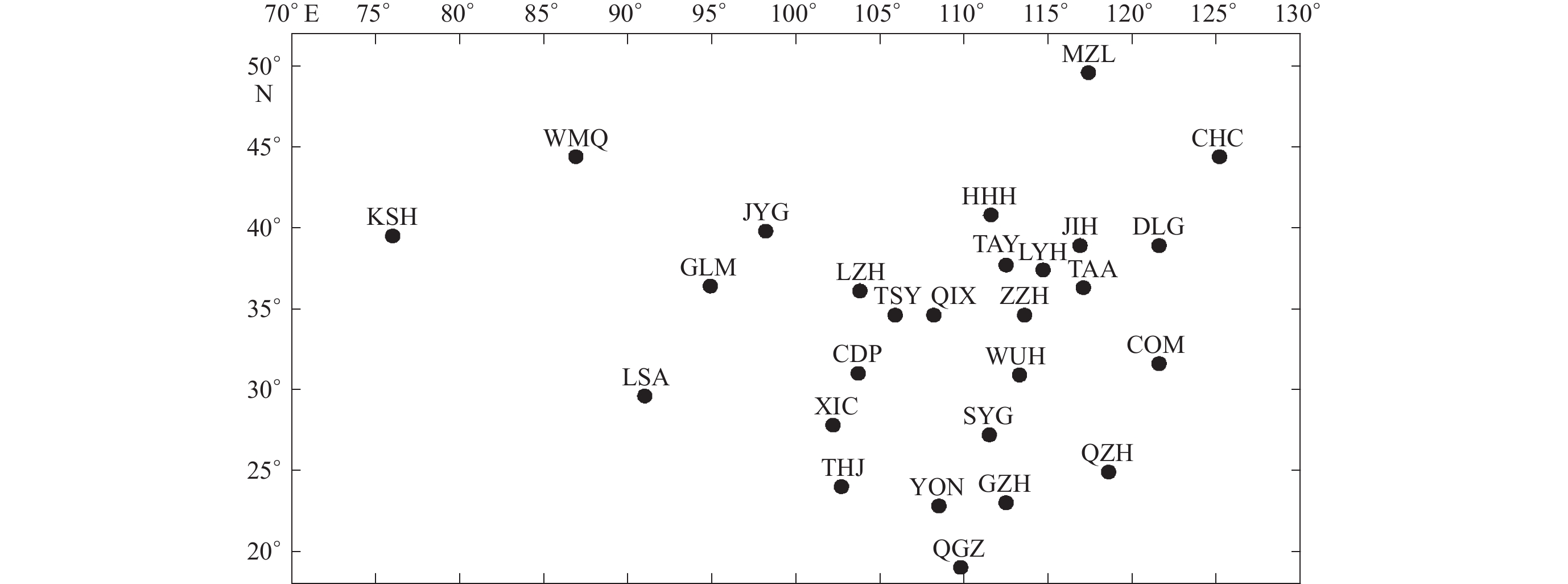
表 1 2014年我国Z分量极小值时间统计表
Table 1 The minimum time statistics of Z-component in China in 2014
序号 台站名 简称 极小值时间 序号 台站名 简称 极小值时间 1 喀 什 KSH 14:13 9 太 原 TAY 12:36 2 乌鲁木齐 WMQ 13:58 10 红 山 LYH 12:25 3 拉 萨 LSA 13:46 11 静 海 JIH 12:19 4 格尔木 GLM 13:41 12 满洲里 MZL 11:51 5 西 昌 XIC 12:58 13 大 连 DLG 11:50 6 通 海 THJ 12:58 14 长 春 CHC 11:42 7 成 都 CDP 12:58 15 德 都 DED 11:10 8 邕 宁 YON 12:40 表 2 2000—2020年地磁场垂直分量日变幅与太阳黑子数量间的相关系数
Table 2 Correlation coefficients between daily variation amplitude and sunspot number during 2000−2020
地磁台站 相关系数 地磁台站 相关系数 CHC 0.932 LZH 0.843 COM 0.925 THJ 0.855 CDP 0.987 WLM 0.937 LSA 0.968 QGZ 0.912 LYH 0.977 -
陈斌,顾左文,高金田,袁洁浩,狄传芝. 2010. 中国地区地磁长期变化研究[J]. 地球物理学报,53(9):2144–2154. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2010.09.014 Chen B,Gu Z W,Gao J T,Yuan J H,Di C Z. 2010. Study of geomagnetic secular variation in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,53(9):2144–2154 (in Chinese).
陈伯舫. 1974. 渤海西岸的电导率异常[J]. 地球物理学报,17(3):169–172. Chen P F. 1974. Conductivity anomaly in west coast of Po Hai (渤海)[J]. Acta Geophysica Sinica,17(3):169–172 (in Chinese). 丁鉴海,余素荣,肖武军. 2003. 地磁“低点位移”现象与昆仑山口西8.1级地震[J]. 西北地震学报,25(1):16–21. Ding J H,Yu S R,Xiao W J. 2003. Geomagnetic low-point displacement phenomena and west to Kunlun mountain pass MS8.1 earthquake[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal,25(1):16–21 (in Chinese).
丁鉴海,刘杰,余素荣,肖武军. 2004. 地磁日变化异常与强震的关系[J]. 地震学报,26(增刊):79–87. Ding J H,Liu J,Yu S R,Xiao W J. 2004. Geomagnetic diurnal-variation anomalies and their relation to strong earthquakes[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,26(S1):79–87 (in Chinese).
冯志生,梅卫萍,张苏平,杜斌,居海华,杨从杰,张秀霞. 2005. FHD磁力仪Z分量分钟值日变化空间相关性的初步应用[J]. 华南地震,25(3):1–7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8662.2005.03.001 Feng Z S,Mei W P,Zhang S P,Du B,Ju H H,Yang C J,Zhang X X. 2005. Preliminary application of the daily-variation spatial correlation method of vertical component’s minutely value of FHD magnetometer[J]. South China Journal of Seismology,25(3):1–7 (in Chinese).
乐贵明,王家龙. 2004. 太阳黑子相对数最强周期的小波分析[J]. 地球物理学报,47(5):743–746. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2004.05.002 Le G M,Wang J L. 2004. Wavelet analysis of the periods with relatively most sunspot numbers[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,47(5):743–746 (in Chinese).
王庆玺,欧阳小龙. 2001. 利用地磁场总强度预测地震三要素初探[J]. 西北地震学报,23(2):131–136. Wang Q X,Ouyang X L. 2001. A preliminary study on prediction of epicenter,magnitude and original time by using geomagnetic total intensity[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal,23(2):131–136 (in Chinese).
王亚丽,吴迎燕,卢军,余素荣,黎明晓. 2009. 中国大陆地区地磁场Z分量日变化相位的空间分布特征研究[J]. 地球物理学报,52(4):1033–1040. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.04.020 Wang Y L,Wu Y Y,Lu J,Yu S R,Li M X. 2009. Spatial distribution characteristics of geomagnetic Z component phase variation in Chinese mainland[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,52(4):1033–1040 (in Chinese).
徐文耀. 2009. 地磁活动指数的过去、现在和未来[J]. 地球物理学进展,24(3):830–841. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2009.03.002 Xu W Y. 2009. Yesterday,today and tomorrow of geomagnetic indices[J]. Progress in Geophysics,24(3):830–841 (in Chinese).
叶式辉. 1978. 天体的磁场[M]. 北京:科学出版社:10−100. Ye S H. 1978. Celestial Magnetic Field[M]. Beijing:China Science Publishing & Media Ltd (CSPM):10−100 (in Chinese).
袁桂平,李鸿宇,张贵霞,潘颖. 2018. 地磁垂直分量Z日变幅逐日比及其与磁暴和地震的关系[J]. 地震,38(1):139–146. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3274.2018.01.013 Yuan G P,Li H Y,Zhang G X,Pan Y. 2018. Daily variation ratio of geomagnetic Z component and its relationship with magnetic storms and earthquakes[J]. Earthquake,38(1):139–146 (in Chinese).
张永忠,康国发. 1995. 中国低纬地区地磁场Z分量日变特征[J]. 地震地磁观测与研究,16(2):19–23. Zhang Y Z,Kang G F. 1995. Daily variation characteristic of Z component of geomagnetic field at low latitudes of China[J]. Seismological and Geomagnetic Observation and Research,16(2):19–23 (in Chinese).
赵旭东,何宇飞,李琪,刘晓灿. 2022. 基于中国地磁台网数据的太阳静日期间地磁场Z分量日变化幅度分析[J]. 地球物理学报,65(10):3728–3742. doi: 10.6038/cjg2022P0628 Zhao X D,He Y F,Li Q,Liu X C. 2022. Analysis of the geomagnetic component Z daily variation amplitude based on the Geomagnetic Network of China during solar quiet days[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,65(10):3728–3742 (in Chinese).




 下载:
下载: