Three-dimensional seismic velocity structure beneath the M6.4 Yangbi,Yunnan earthquake region
-
摘要: 利用2015年1月至2021年5月28日期间我国云南省漾濞县及周边地区固定台站和漾濞地震后布设的流动台站所记录到的近震资料,使用双差层析成像方法获得了该地震震区的高分辨率地壳三维速度结构和震源位置。重定位结果显示,漾濞M6.4地震序列主要沿NW−SE向展布,与维西—乔后—巍山断裂走向一致,地震主要集中在4—10 km的深度范围,呈约80°高倾角分布。结合定位结果与三维速度结构显示:漾濞M6.4地震序列的空间分布与速度结构变化具有相关性,主震位于P波、S波高低速异常交界处,这种介质物性变化的交界地带可能有利于中强地震的孕育和发生,余震主要分布在低P波速度、高S波速度和低波速比的脆性区域;沿漾濞地震序列的分布走向,主震两侧呈现完全不同的速度结构,其西北部具有明显的高P波速度、低S波速度特征,该地区高密度、强韧性的地层可能是阻挡漾濞地震的NW向破裂而呈单向破裂特征的原因。Abstract: This paper collected the seismic travel-time data both from temporary stations employed after Yangbi M6.4 earthquake and the seismic networks in Yangbi region and its vicinity from January of 2015 to 28 May, 2021 and performed the high-resolution inversion for three-dimensional velocity structure and accurate hypocentral locations by using double-difference seismic tomography method. The relocation results show that the sequence spread in the NW−SE direction along the Weixi-Qiaohou-Weishan fault. The focal depth in the area is generally in the range of 2−5 km with high dip angle of 80°. The three-dimensional velocity structure shows that the spatial distribution characteristics of the Yangbi M6.4 earthquake sequence are closely related to the velocity structure. The epicenter of the Yangbi M6.4 main shock was located near the P- and S-wave high-to-low-velocity anomaly transitional zones, which are favorable for occurrence of moderate-strong earthquakes, and the aftershocks are mainly distributed in the brittle region with low vP, high vS and low vP/vS. In addition, along the strike of Yangbi earthquake sequence, there are totally different velocity structures on both sides of main earthquake, and significant higher vP and lower vS anomalies are observed in the northwest of the Yangbi M6.4 main shock compared with the southeast part, which may obstruct the northwestward slipping of the seismogenic fault of Yangbi M6.4 earthquake, leading to the striking unilateral source rupture.
-
引言
据中国地震台网测定,北京时间2021年5月21日21时48分,云南省大理州漾濞县(25.67°N,99.87°E)发生M6.4地震,该地震造成3人死亡,32人受伤,部分房屋和多项基础设施受到不同程度损坏。该地震前27分钟在其东南侧有M5.6强震发生,震后1小时内又陆续发生M5.0和M5.2强震及多次M4.0以上地震,本次漾濞地震序列较为活跃。
漾濞地震发生后,云南省地震局现场工作队通过对灾区218个调查点的震害调查,参照震区地震的构造背景、余震分布、震源机制、仪器烈度等科技支撑成果,结合强震动观测记录,确定了此次地震的烈度图(云南省地震局,2021),此次地震极震区烈度达Ⅷ度,面积约170平方千米,主要涉及漾濞县苍山西镇、漾江镇和太平乡等三个乡镇,等震线呈椭圆状,长轴走向为NW向。
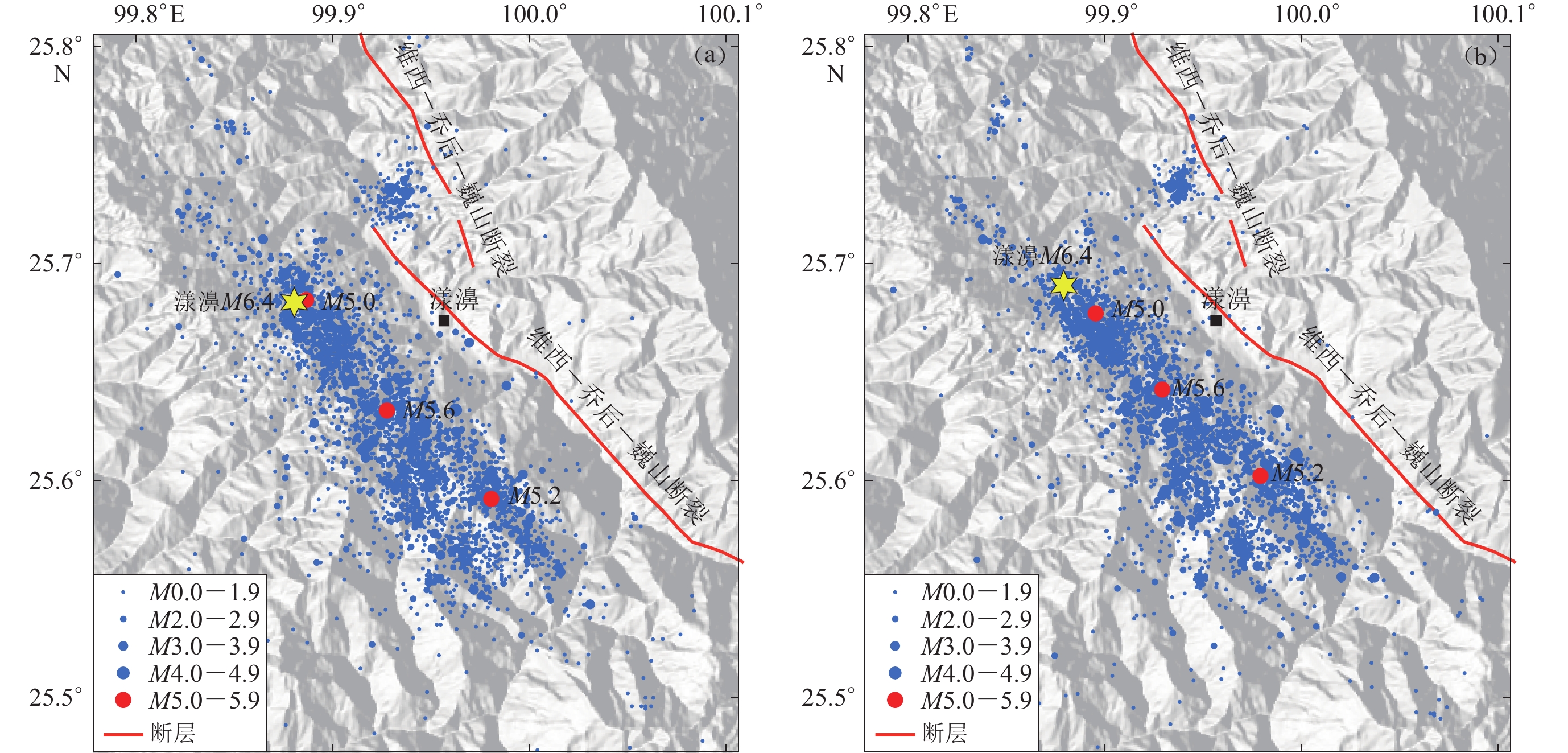
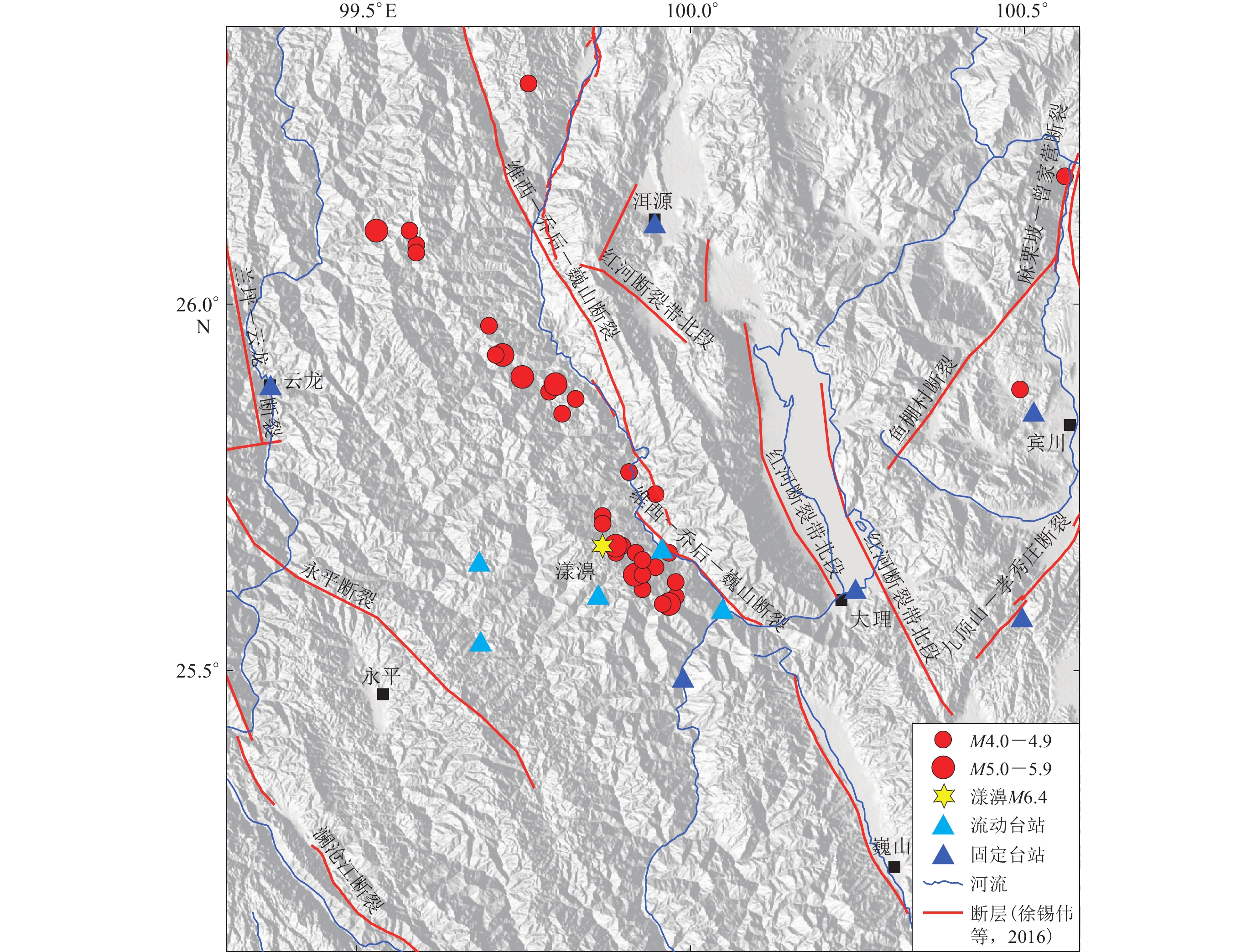
漾濞M6.4地震发生在川滇菱形地块西缘,该区域的构造背景极其复杂。区内同时发育NW向和NE向的断裂构造(常祖峰等,2014),主要断裂有澜沧江断裂、永平断裂、维西—乔后—巍山断裂、红河断裂带等,其中维西—乔后—巍山断裂近年来的活动性较强,主要表现为右旋走滑为主兼具正断的运动性质(常祖峰等,2016),2013年洱源M5.5地震(常祖峰等,2014)和2017年漾濞M4.8和M5.1地震(李姣等,2020)均发生在这条断裂上,此次漾濞M6.4地震的震源位于维西—乔后—巍山断裂的上盘(图1)。
前人在研究区开展的速度结构研究以大尺度居多,例如:王椿镛等(2002)、吴建平等(2006)分别对川滇地区地壳上地幔P波、S波速度结构进行了研究;马宏生等(2008)利用区域台站记录资料反演了川滇地区地壳上地幔三维P波速度结构;Lei等(2009)获得了云南地区地壳和上地幔高分辨率成像结果;胥颐等(2013)反演了云南地区的P波速度结构;Liu等(2021)通过体波和面波的联合反演得到了中国西南部的高分辨率速度结构。此外,多项研究(李永华等,2006;韦伟等,2010;Lei,Zhao,2016;胡亚平等,2017;刘伟等,2019;Lei et al,2019;Zheng et al,2019)对青藏高原东缘的速度结构进行了分析。但由于以上结果的尺度较大,未能很好地揭示出漾濞及周边地区的精细速度结构。
鉴于此,为进一步研究漾濞及周边地区的地震时空分布特征和相对准确的震源深度,探讨地震活动与速度结构之间的关系,本文收集了2015年以来漾濞及周边地区固定台站及流动台站观测数据(图1),拟采用双差层析成像方法(Zhang,Thurber,2003,2006)对漾濞及邻近地区地震事件的震源位置和地壳速度结构进行联合反演,并在此基础上深入探讨该区域内所发生的中强地震的深部结构特征,以期为减轻研究区地震灾害风险提供一定的参考。
1. 数据与方法
1.1 数据
本文的研究区范围为(99.4ºE—100.4ºE,25.2ºN—26.2ºN),为保证足够的射线覆盖,将该范围向四周各扩展0.5º (98.9ºE—100.9ºE,24.7ºN—26.7ºN)作为反演范围(图2)。2021年5月21日漾濞M6.4地震后,在震源区周围布设了5个流动台站,平均台间距为12 km,最小间距约11 km (图1)。此外,本文还收集了2015年1月至2021年5月28日期间漾濞及周边地区固定台站所记录到的P波和S波震相数据。
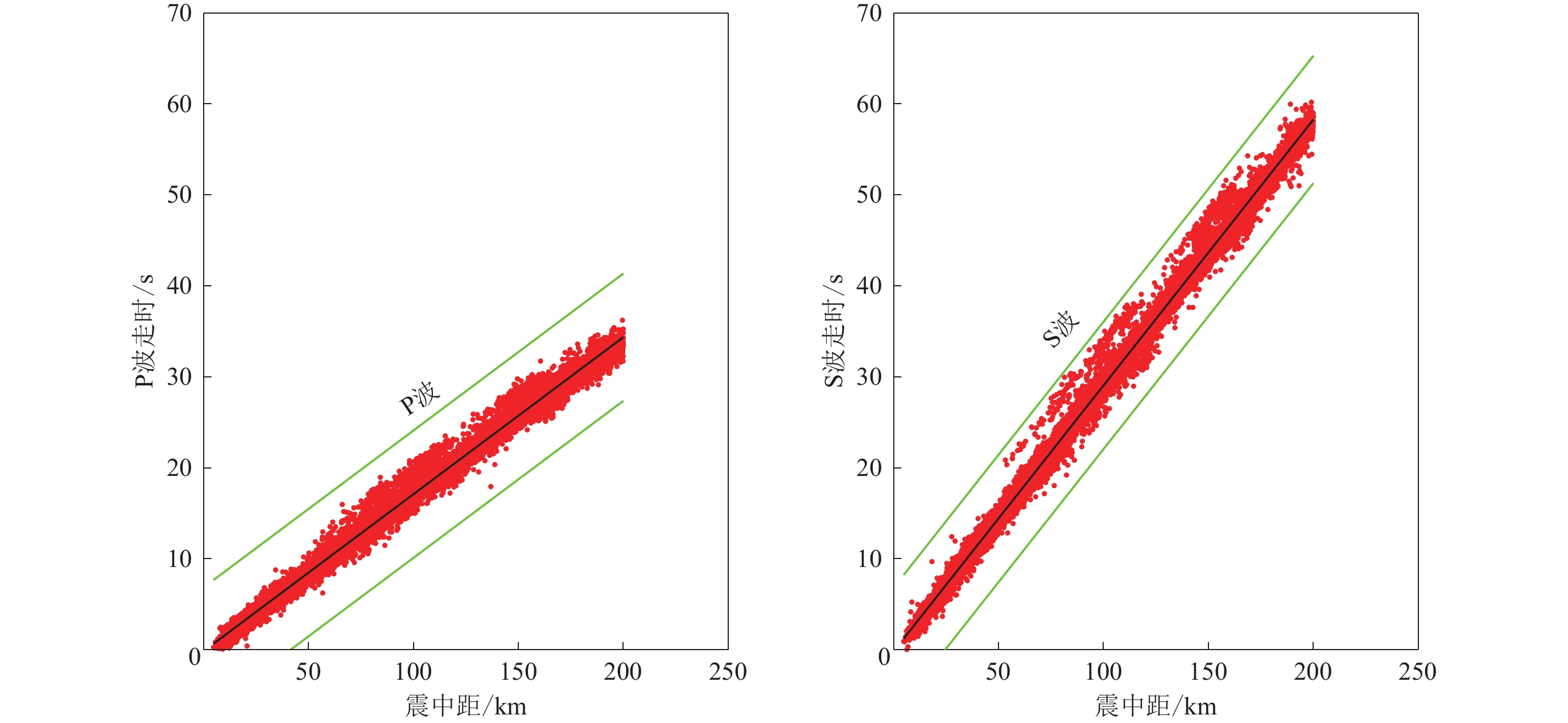
为保证观测数据的定位精度和可靠性,我们按照以下标准进行筛选:震中距小于200 km;地震对间距小于10 km;每个地震事件至少被4个台站记录到,P波和S波的时距曲线如图3所示。这样,最终筛选出用于反演的台站21个,地震事件10 439个,P波、S波绝对走时分别为7万3 005条和5万9 026条,P波、S波相对走时分别为30万8 551条和23万3 748条。
1.2 双差层析成像方法
双差层析成像方法TomoDD是Zhang和Thurber (2003)在双差定位方法(Waldhauser,Ellsworth,2000)的基础上发展而来。该方法利用绝对走时数据与每个台站记录的邻近事件之间的走时差数据进行三维速度结构与震源位置的联合反演,其基本思路为:假设相邻两个地震事件到达同一台站有相似路径,对其到时残差作差,得到双差数据,将其作为反演中的观测数据来反演速度结构。采用阻尼最小二乘法求解,使得由双差和绝对走时数据残差的2范数系统构成的目标函数最小化,同时反演P波和S波速度结构,从而获取最优的震源位置和三维速度结构(Zhang,Thurber,2006)。该方法自提出以来,由于其在地震定位和速度结构反演精度上的优势得以广泛应用于地壳结构精细分析中(王伟平,2016;肖卓,高原,2017;李敏娟等,2018;刘伟等,2019;缪思钰等,2019;李大虎等,2021;孙权等,2021)。
1.3 初始模型和参数的选择
本文参考Shen等(2016)的背景噪声成像结果以及Xiao等(2021)综合P波偏振、瑞雷波和接收函数所得到的中国大陆三维速度结构结果,并根据数据的残差分布进行适当调整,最终选用的初始模型列于表1。通过和达法拟合研究区的纵横波波速比为1.71;水平方向上采用0.1º×0.1º的网格间隔,垂直方向上的网格节点分别为−10,0,5,10,15,20,25,30,50 km。
表 1 本文所用的P波初始速度模型Table 1. Initial P wave velocity model used in this study深度/km vP/(km·s−1) 深度/km vP/(km·s−1) 0 4.4 20 6.0 5 5.6 25 6.1 10 5.8 30 6.3 15 5.9 50 8.0 双差层析成像方法采用带阻尼的最小二乘正交分解(least squares QR factorization,简写为LSQR)算法,进行迭代求解(Zhang,Thurber,2003)。反演中使用的最佳阻尼因子和平滑权重通过构建数据方差和模型方差间的折中曲线来确定(Eberhart-Phillips,1986),本文最终选取的最佳阻尼因子和平滑因子分别为300和40,如图4所示。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 分辨率测试
为验证反演结果的稳定性和可靠性,本文采用测试板方法以0.1º×0.1º网格和±5%异常相间的棋盘模型作为理论模型进行分辨率测试。图5给出了不同深度的检测板结果,可以看出:在5—15 km的深度范围内,P波和S波的速度模型分辨效果较好,基本可以达到0.1°,且P波的恢复度优于S波。
2.2 漾濞M6.4地震序列重定位结果
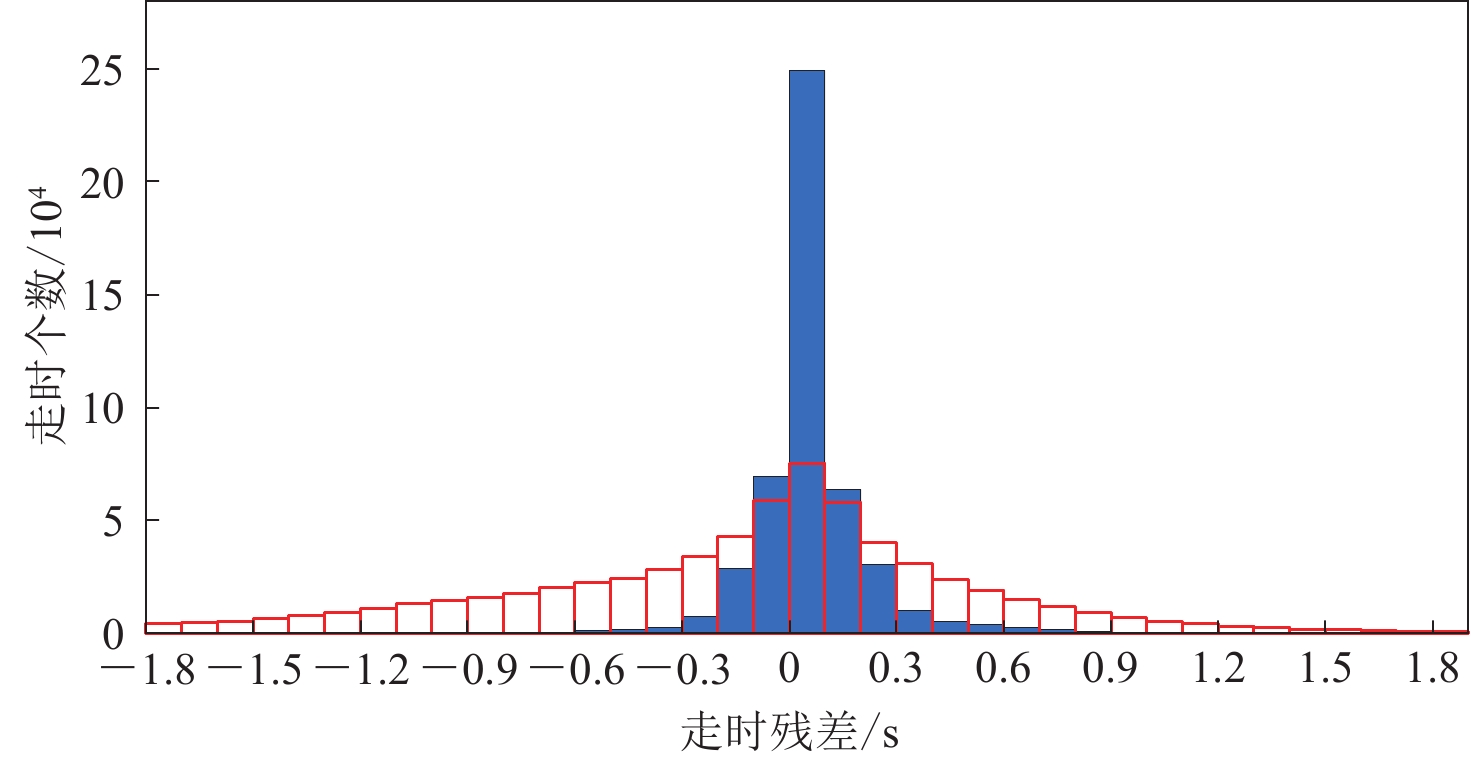
图6给出了漾濞M6.4地震序列重定位前后的地震空间分布变化,可以看出:重定位后漾濞地震序列分布更加聚集;重定位后地震的位置发生了变化,以M6.4和M5.0地震最为明显,重定位前二者基本处于同一位置,重定位后M5.0地震位于M6.4沿地震序列走向的东南部。在震源深度方面,重定位后的地震集中分布在4—10 km深度(图7);重定位后走时残差显著减小,由0.78 s降至0.15 s (图8)。
本文重定位结果显示,漾濞地震序列主要呈NW−SE向展布,平行于维西—乔后—巍山断裂走向(图6),M6.4主震位于地震序列的西北部,除其东北部有一小簇地震分布外,整体呈单向破裂特征。值得注意的是,部分余震在M5.6地震处分叉,呈NNW向分布。从中强地震的发震时间来看,2021年5月21日21时21分M5.6地震先发生,其后依次发生21时48分M6.4地震、21时55分M5.0地震和22时31分M5.2地震。据此我们推测M5.6地震发生后,断层在NNW和NW两个方向上均发生破裂,其中主震发生在NW向破裂上。
2.3 三维速度结构
本文利用双差层析成像方法同时反演了P波和S波速度,其不同深度的水平切片如图9所示。可以看出,研究区P波和S波速度结构具有明显的横向不均匀性,其分布特征与区域内的断裂带相关,总体上维西—乔后—巍山断裂表现为高速异常,红河断裂带北段为低速异常,这与Liu等(2021)的研究结果较为一致。
![]() 图 9 不同深度z的vP (左)和vS (右)分布黑色圆圈代表地震, 图(b)中AA′和BB′分别为平行、垂直于漾濞地震序列走向的剖面Figure 9. vP (left) and vS (right) distribution at the depth z of 5,10 and 15 kmThe circles represent earthquakes,and in Fig. (b) AA′ and BB′ are the two profiles parallel to and perpendicular with the strike of the Yangbi sequence,respectively
图 9 不同深度z的vP (左)和vS (右)分布黑色圆圈代表地震, 图(b)中AA′和BB′分别为平行、垂直于漾濞地震序列走向的剖面Figure 9. vP (left) and vS (right) distribution at the depth z of 5,10 and 15 kmThe circles represent earthquakes,and in Fig. (b) AA′ and BB′ are the two profiles parallel to and perpendicular with the strike of the Yangbi sequence,respectively5 km深度上,维西—乔后—巍山断裂为P波、S波高速异常,其两侧的红河断裂带北段和永平断裂为低速异常区。在该深度上,地震主要分布在P波高低速异常过渡地区,且偏向高速一侧,以及S波高速异常地区。10 km深度上,在S波速度切片上,红河断裂带北段依旧表现为低速异常,维西—乔后—巍山断裂北部为低速、南部为高速,永平断裂为弱高速,其两侧为低速异常;P波速度切片上,维西—乔后—巍山断裂和永平断裂均为高速异常,低速异常位于两断裂之间。在该深度上,研究区地震依旧多发生在P波高、低速异常交界带和S波高速异常地区。15 km深度上,P波高速异常主要分布在永平断裂北部,而其南部和红河断裂带北段及维西—乔后—巍山断裂为P波低速异常,S波高速异常位于漾濞地区,其周边为低速异常。该深度上,地震相对较少,分布情况与前面类似。
此外,利用vP/vS本文还获得了研究区不同深度的波速比分布,如图10所示。一般来说,相对于P波,S波到时拾取误差较大,速度分辨率较低,因此直接通过P波和S波速度相除得到的波速比会存在一定误差(孙权等,2021),但是如果两者速度分辨率足够高且相差不大,速度结构的空间不均匀性尺度远大于波长,vP/vS则可以在一定程度上反映真实的波速比(Nakajima et al,2001)。本文获得的P波和S波速度分辨率达到0.1º,因此得到的波速比较为可信,整体上波速比随深度的增加而增大。由图10可知,在5 km和10 km深度上,地震多位于低波速比地区,而在15 km深度上,地震主要位于高波速比地区。
2.4 漾濞M6.4地震序列分布与速度结构关系
为讨论地震分布与速度结构的关系,我们将重定位后的震源位置分别投影到不同深度的剖面上,即将震源深度在0—7.5 km之间的地震投影至5 km深度剖面,7.5—12.5 km之间的地震投影至10 km深度剖面,大于12.5 km的地震投影至15 km深度剖面,结果如图9和图10所示,可见漾濞M6.4地震序列分布与速度结构变化具有明显的相关性,即地震总体上发生在中上地壳P波、S波高低速异常过渡地区,且偏向P波低速和S波高速一侧。
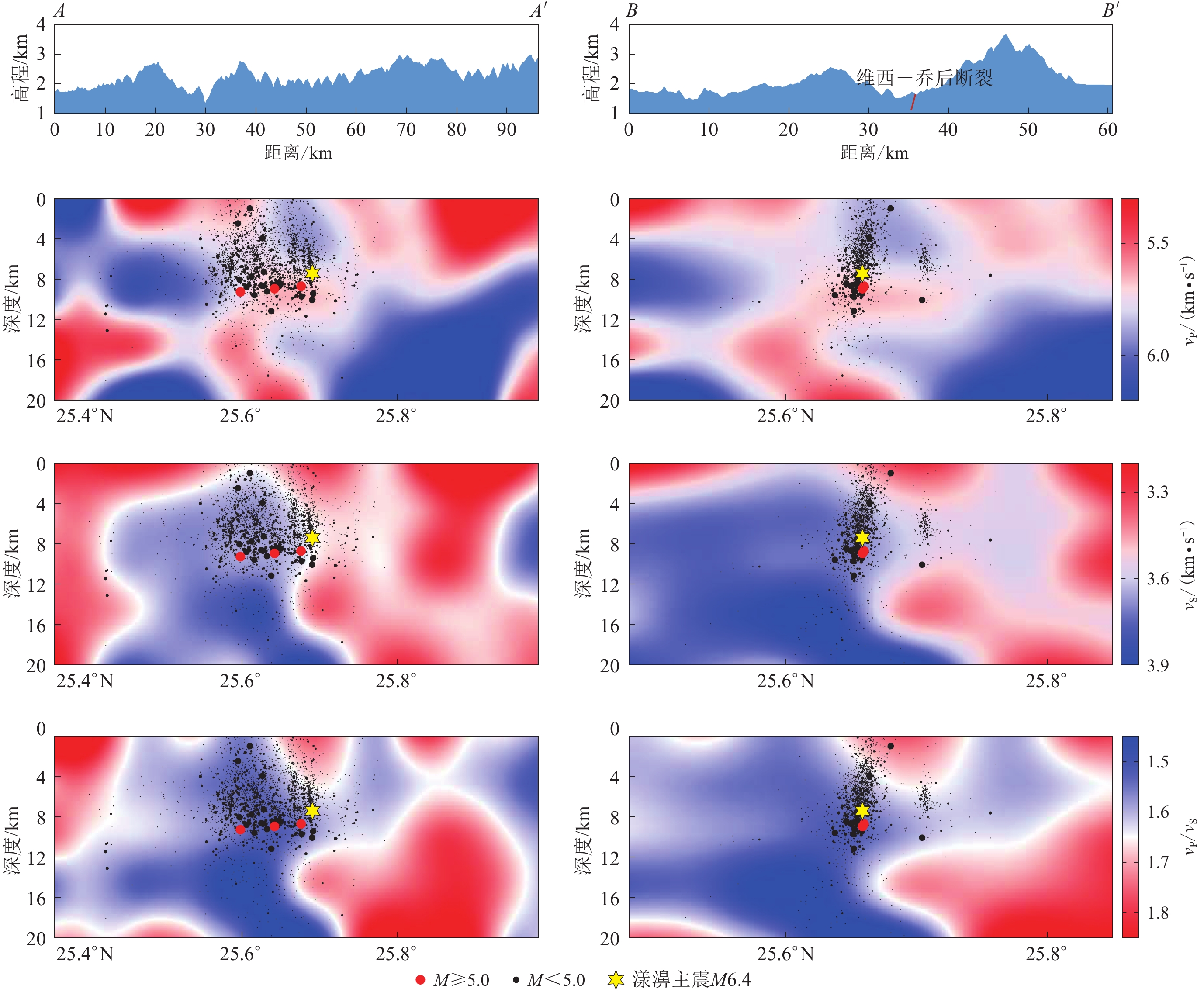
为进一步探讨其分布关系我们沿地震分布走向和垂向(图9b)分别给出了AA′和BB′纵剖面的vP,vS和vP/vS分布,如图11所示,并将剖面两侧的漾濞地震序列震中投影至速度图像上。结果显示,漾濞M6.4地震位于P波、S波高低速异常交界带,此类区域往往是介质物性发生变化的地区,由于结构和应力场的变化,这些区域相对脆弱,更利于能量的积累与释放进而引发地震(刘伟等,2019),这可能是主震发生于此的原因。漾濞地震余震主要分布在低P波速度、高S波速度和低波速比区域,此类区域通常为脆性易碎的介质,在初始破裂发生以后,可能会相继破裂,余震频发。据中国地震台网中心发布的漾濞M6.4地震序列统计,从主震发生前1小时至主震发生后12小时内共发生M3.0—3.9地震17次,M4.0—4.9地震9次,M5.0—5.9地震3次。
地震重定位结果显示,漾濞序列地震主要位于4—10 km的深度范围内,有感及破坏性地震(M≥3.0)的震源深度明显要深,如剖面AA′所示,M6.4地震及三个M≥5地震的震源深度均在8 km左右,其中主震略浅,而其它小震的震源深度相对要浅。剖面BB′显示,漾濞地震序列呈约80º的高倾角分布,这与中国地震台网中心震后发布的震源机制结果一致,说明维西—乔后—巍山断裂在该段的倾角约80º,与常祖峰等(2016)的研究结果一致。
本次漾濞地震呈明显的单向破裂特征,余震集中分布在主震的东南部,而其西北部余震则极少(图6)。从速度和波速比结构(图9,10,11)来看,沿余震分布走向,主震两侧呈现完全不同的速度结构,主震西北部具有明显的高P波速度、低S波速度的特征,表示该区域具有高密度、强韧性的特征,因此不易发生破裂。这可能是此次漾濞地震西北部未发生较大破裂而呈现单向破裂特征的原因所在。
3. 讨论与结论
本文利用2015年1月至2021年5月28日期间漾濞及周边地区固定台站,以及漾濞地震发生后所布设的流动台站所记录的P波和S波震相到时数据,采用双差层析成像方法,获得了漾濞及周边地区的高分辨率三维地壳速度结构及地震重定位结果,主要结论如下:
1) 漾濞M6.4地震序列主要沿NW−SE向展布,走向平行于维西—乔后—巍山断裂,沿地震序列方向在M5.6地震处出现沿NNW向分布的分支。在深度上,地震主要集中在4—10 km的深度范围,呈约80º 高倾角分布,且中强地震分布相对较深。
2) 研究区速度结构存在明显的横向不均匀性,速度分布特征与地质构造相关,主要受区域断层控制。
3) 漾濞M6.4地震序列的震中分布与速度结构变化具有相关性。漾濞主震位于P波、S波高低速异常交界地区,余震主要分布于低P波速度、高S波速度和低波速比的脆性区域。主震的西北部具有明显的高P波速度、低S波速度的特征,高密度、强韧性的地层可能阻挡了漾濞地震的NW向破裂,从而呈单向破裂特征。
漾濞M6.4地震发生后,余震不断,后期仍有大量余震。本文仅收集到主震后7天的数据,获得了研究区基本的上地壳速度结构,随着时间的延长和更多成果的积累,对发震区的孕震环境和应力状态将会有更深入的认识。
中国科学技术大学张海江教授提供了双差层析成像(Tomodd)程序,两位审稿专家提出了宝贵的修改意见和建议,云南省地震局地震监测人员为地震编目付出了辛勤工作,作者在此一并表示感谢。
-
图 9 不同深度z的vP (左)和vS (右)分布
黑色圆圈代表地震, 图(b)中AA′和BB′分别为平行、垂直于漾濞地震序列走向的剖面
Figure 9. vP (left) and vS (right) distribution at the depth z of 5,10 and 15 km
The circles represent earthquakes,and in Fig. (b) AA′ and BB′ are the two profiles parallel to and perpendicular with the strike of the Yangbi sequence,respectively
表 1 本文所用的P波初始速度模型
Table 1 Initial P wave velocity model used in this study
深度/km vP/(km·s−1) 深度/km vP/(km·s−1) 0 4.4 20 6.0 5 5.6 25 6.1 10 5.8 30 6.3 15 5.9 50 8.0 -
常祖峰,张艳凤,周青云,虎雄林,臧阳. 2014. 2013年洱源MS5.5地震烈度分布及震区活动构造背景研究[J]. 中国地震,30(4):560–570. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4683.2014.04.009 Chang Z F,Zhang Y F,Zhou Q Y,Hu X L,Zang Y. 2014. Intensity distribution characteristics and active tectonic background in area of the 2013 Eryuan MS5.5 earthquake[J]. Earthquake Research in China,30(4):560–570 (in Chinese).
常祖峰,常昊,臧阳,代博洋. 2016. 维西—乔后断裂新活动特征及其与红河断裂的关系[J]. 地质力学学报,22(3):517–530. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2016.03.009 Chang Z F,Chang H,Zang Y,Dai B Y. 2016. Recent active features of Weixi-Qiaohou fault and its relationship with the Honghe fault[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,22(3):517–530 (in Chinese).
胡亚平,王志,刘冠男,柳存喜,伏毅. 2017. 南北地震带地壳结构多参数成像及强震触发机制研究[J]. 地球物理学报,60(6):2113–2129. doi: 10.6038/cjg20170608 Hu Y P,Wang Z,Liu G N,Liu C X,Fu Y. 2017. Crustal structure imaging of multi-geophysical parameters and generating mechanisms of large earthquakes in North-South Seismic Zone[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,60(6):2113–2129 (in Chinese).
李大虎,詹艳,丁志峰,高家乙,吴萍萍,孟令媛,孙翔宇,张旭. 2021. 四川长宁MS6.0地震震区上地壳速度结构特征与孕震环境[J]. 地球物理学报,64(1):18–35. doi: 10.6038/cjg2021O0241 Li D H,Zhan Y,Ding Z F,Gao J Y,Wu P P,Meng L Y,Sun X Y,Zhang X. 2021. Upper crustal velocity and seismogenic environment of the Changning MS6.0 earthquake region in Sichuan,China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,64(1):18–35 (in Chinese).
李姣,姜金钟,杨晶琼. 2020. 2017年漾濞MS4.8和MS5.1地震序列的微震检测及重定位[J]. 地震学报,42(5):527–542. doi: 10.11939/jass.20190161 Li J,Jiang J Z,Yang J Q. 2020. Microseismic detection and relocation of the 2017 MS4.8 and MS5.1 Yangbi earthquake sequence,Yunnan[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,42(5):527–542 (in Chinese).
李敏娟,沈旭章,张元生,刘旭宙,梅秀苹. 2018. 基于密集台阵的青藏高原东北缘地壳精细结构及九寨沟地震震源区结构特征分析[J]. 地球物理学报,61(5):2075–2087. doi: 10.6038/cjg2018L0720 Li M J,Shen X Z,Zhang Y S,Liu X Z,Mei X P. 2018. Fine crustal structures of northeast margin of the Tibetan Plateau and structural features of Jiuzhaigou earthquake focal area constrained by the data from a high-density seismic array[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,61(5):2075–2087 (in Chinese).
李永华,吴庆举,安张辉,田小波,曾融生,张瑞青,李红光. 2006. 青藏高原东北缘地壳S波速度结构与泊松比及其意义[J]. 地球物理学报,49(5):1359–1368. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2006.05.015 Li Y H,Wu Q J,An Z H,Tian X B,Zeng R S,Zhang R Q,Li H G. 2006. The Poisson ratio and crustal structure across the NE Tibetan Plateau determined from receiver functions[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,49(5):1359–1368 (in Chinese).
刘伟,吴庆举,张风雪. 2019. 利用双差层析成像方法反演青藏高原东南缘地壳速度结构[J]. 地震学报,41(2):155–168. doi: 10.11939/jass.20180083 Liu W,Wu Q J,Zhang F X. 2019. Crustal structure of southeastern Tibetan Plateau inferred from double-difference tomography[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,41(2):155–168 (in Chinese).
马宏生,张国民,闻学泽,周龙泉,邵志刚. 2008. 川滇地区三维P波速度结构反演与构造分析[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报,33(5):591–602. Ma H S,Zhang G M,Wen X Z,Zhou L Q,Shao Z G. 2008. 3-D P wave velocity structure tomographic inversion and its tectonic interpretation in Southwest China[J]. Earth Science:Journal of China University of Geosciences,33(5):591–602 (in Chinese).
缪思钰,张海江,陈余宽,谭玉阳,苗园园,黄振华,王飞,谢庆明. 2019. 基于微地震定位和速度成像的页岩气水力压裂地面微地震监测[J]. 石油物探,58(2):262–271. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2019.02.012 Miao S Y,Zhang H J,Chen Y K,Tan Y Y,Miao Y Y,Huang Z H,Wang F,Xie Q M. 2019. Surface microseismic monitoring of shale gas hydraulic fracturing based on microseismic location and tomography[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum,58(2):262–271 (in Chinese).
孙权,裴顺平,苏金蓉,刘雁冰,薛晓添,李佳蔚,李磊,左洪. 2021. 2019年6月17日四川长宁MS6.0地震震源区三维速度结构[J]. 地球物理学报,64(1):36–53. doi: 10.6038/cjg2021O0246 Sun Q,Pei S P,Su J R,Liu Y B,Xue X T,Li J W,Li L,Zuo H. 2021. Three-dimensional seismic velocity structure across the 17 June 2019 Changning MS6.0 earthquake,Sichuan,China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,64(1):36–53 (in Chinese).
王椿镛,Mooney W D,王溪莉,吴建平,楼海,王飞. 2002. 川滇地区地壳上地幔三维速度结构研究[J]. 地震学报,24(1):1–16. Wang C Y,Mooney W D,Wang X L,Wu J P,Lou H,Wang F. 2002. Study on 3-D velocity structure of crust and upper mantle in Sichuan-Yunnan region,China[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,24(1):1–16 (in Chinese).
王伟平. 2016. 鲜水河、安宁河和龙门山断裂带交汇区双差层析成像研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地球物理研究所: 39−70. Wang W P. 2016. The Application of Double-Difference Tomography Method in the Intersection Zone of Xianshuihe Fault, Anninghe Fault and Longmenshan Fault[D]. Beijing: Institute of Geophysics, China Earthquake Administration: 39−70 (in Chinese).
韦伟,孙若昧,石耀霖. 2010. 青藏高原东南缘地震层析成像及汶川地震成因探讨[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,40(7):831–839. Wei W,Shi R M,Shi Y L. 2010. P-wave tomographic images beneath southeastern Tibet:Investigating the mechanism of the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Science China Earth Science,53(9):1252–1259.
吴建平,明跃红,王椿镛. 2006. 川滇地区速度结构的区域地震波形反演研究[J]. 地球物理学报,49(5):1369–1376. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2006.05.016 Wu J P,Ming Y H,Wang C Y. 2006. Regional waveform inversion for crustal and upper mantle velocity structure below Chuan-Dian region[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,49(5):1369–1376 (in Chinese).
肖卓,高原. 2017. 利用双差成像方法反演青藏高原东北缘及其邻区地壳速度结构[J]. 地球物理学报,60(6):2213–2225. doi: 10.6038/cjg20170615 Xiao Z,Gao Y. 2017. Crustal velocity structure beneath the northeastern Tibetan Plateau and adjacent regions derived from double difference tomography[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,60(6):2213–2225 (in Chinese).
徐锡伟, 韩竹军, 杨晓平, 张世民, 于贵华, 周本刚, 李峰, 马保起, 陈桂华, 冉永康. 2016. 中国及邻区地震构造图[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 1. Xu X W, Han Z J, Yang X P, Zhang S M, Yu G H, Zhou B G, Li F, Ma B Q, Chen G H, Ran Y K. 2016. Seismotectonic Map in China and Its Adjacent Regions[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press: 1 (in Chinese).
胥颐,杨晓涛,刘建华. 2013. 云南地区地壳速度结构的层析成像研究[J]. 地球物理学报,56(6):1904–1914. doi: 10.6038/cjg20130613 Xu Y,Yang X T,Liu J H. 2013. Tomographic study of crustal velocity structures in the Yunnan region southwest China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,56(6):1904–1914 (in Chinese).
云南省地震局. 2021. 云南漾濞6.4级地震烈度图发布[EB/OL]. [2021-05-25]. http://yndzj.gov.cn/yndzj/_300559/_300651/629959/index.html. Yunnan Earthquake Agency. 2021. Seismic intensity map of the M6.4 Yangbi earthquake[EB/OL]. [2021-05-25]. http://yndzj.gov.cn/yndzj/_300559/_300651/629959/index.html (in Chinese).
Eberhart-Phillips D. 1986. Three-dimensional velocity structure in northern California Coast Ranges from inversion of local earthquake arrival times[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,76(4):1025–1052.
Lei J S,Zhao D P,Su Y J. 2009. Insight into the origin of the Tengchong intraplate volcano and seismotectonics in Southwest China from local and teleseismic data[J]. J Geophys Res:Solid Earth,114(B5):B05302. doi: 10.1029/2008JB005881
Lei J S,Zhao D P. 2016. Teleseismic P-wave tomography and mantle dynamics beneath eastern Tibet[J]. Geochem Geophys Geosyst,17(5):1861–1884. doi: 10.1002/2016gc006262
Lei J S,Zhao D P,Xu X W,Xu Y G,Du M F. 2019. Is there a big mantle wedge under eastern Tibet?[J]. Phys Earth Planet Inter,292:100–113.
Liu Y, Yao H J, Zhang H J, Fang H J. 2021. The community velocity model V.1.0 of Southwest China, constructed from joint body- and surface-wave travel-time tomography[J]. Seismol Res Lett: 1–16. doi: 10.1785/0220200318.
Nakajima J,Matsuzawa T,Hasegawa A,Zhao D P. 2001. Three-dimensional structure of vP,vS and vP/vS beneath northeastern Japan:Implications for arc magmatism and fluids[J]. J Geophys Res:Solid Earth,106(B10):21843–21857. doi: 10.1029/2000JB000008
Shen W S,Ritzwoller M H,Kang D,Kim Y H,Lin F C,Ning J Y,Wang W T,Zhang Y,Zhou L Q. 2016. A seismic reference model for the crust and uppermost mantle beneath China from surface wave dispersion[J]. Geophys J Int,206(2):954–979. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggw175
Waldhauser F,Ellsworth W. 2000. A double-difference earthquake location algorithm:Method and application to the northern Hayward fault,California[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,90(6):1353–1368. doi: 10.1785/0120000006
Xiao X,Cheng S H,Wu J P,Wang W L,Sun L,Wang X X,Wen L X. 2021. Shallow seismic structure beneath the continental China revealed by P-wave polarization,Rayleigh wave ellipticity and receiver function[J]. Geophys J Int,225(2):998–1019. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggab022
Zhang H J,Thurber C H. 2003. Double-difference tomography:The method and its application to the Hayward fault,California[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,93(5):1875–1889. doi: 10.1785/0120020190
Zhang H J,Thurber C H. 2006. Development and applications of double-difference seismic tomography[J]. Pure Appl Geophys,163(2/3):373–403. doi: 10.1007/s00024-005-0021-y
Zheng C,Zhang R Q,Wu Q J. 2019. Variations in crustal and uppermost mantle structures across eastern Tibet and adjacent regions:Implications of crustal flow and asthenospheric upwelling combined for expansions of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Tectonics,38(8):3167–3181. doi: 10.1029/2018TC005276
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 蔡剑锋,张煜,张双喜,叶泵,韦瑜. 维西—乔后断裂带上连续地震的应力降和两种不同的孕震机制. 地球物理学报. 2023(02): 602-615 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. Mengqiao Duan,Kezhen Zuo,Cuiping Zhao,Lianqing Zhou. Seismogenic environment and mechanism of the Yangbi M_S6.4 earthquake in Yunnan, China. Earthquake Science. 2022(04): 297-310 .  必应学术
必应学术
3. 张丽娟,万永革,王福昌,靳志同,崔华伟. 采用模糊聚类算法确定2021年漾濞地震序列的断层结构. 地震地质. 2022(06): 1634-1647 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: