Effects of the groundwater level variation on earthquake ground motions
-
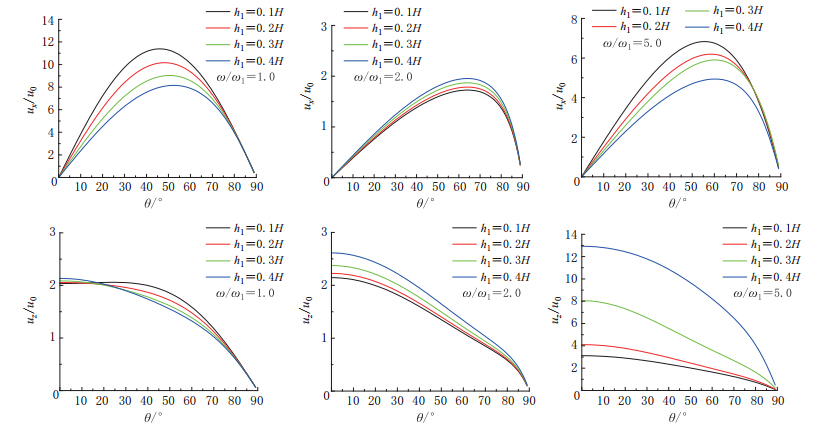
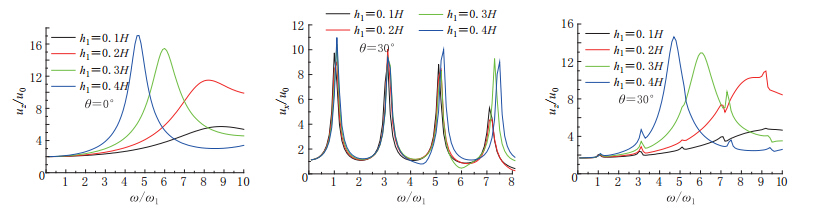
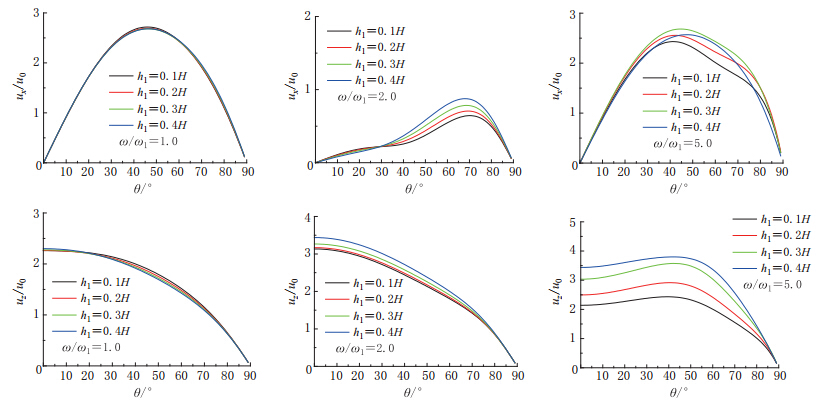
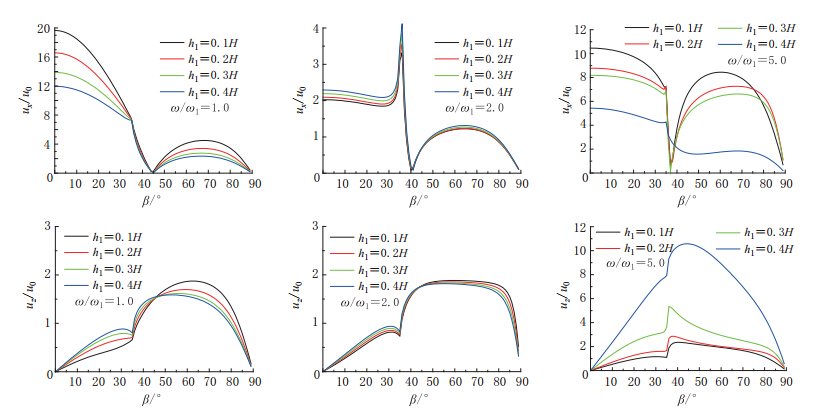
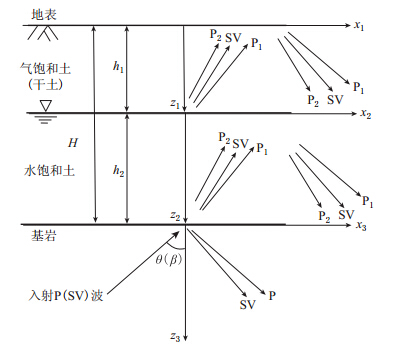
摘要: 本文以Biot提出的流体饱和多孔介质波动理论为基础, 建立了成层地基模型, 把地下水位以下的饱和土层用水饱和多孔介质模拟, 地下水位以上土层用气饱和多孔介质模拟. 通过研究入射平面简谐波在成层地基中的传播, 分析了地下水位变化对地震地面运动的影响. 结果表明: P波入射下, 当土体骨架相对刚度较小时, 地下水位变化对地表位移尤其是竖向地表位移幅值影响较大, 随着地下水位的下降, 竖向位移逐渐增加, 相对应的峰值频率逐渐减小; 当土体骨架相对刚度较大时, 地下水位变化对地面运动影响不大.Abstract: Based on Biot’s theory of fluid-saturated porous media, this paper presents the effects of groundwater level variation on earthquake ground motions through the analyses of wave propagation in layered foundation. In this analysis, a layered foundation model is built, assuming the saturated soil layer below the groundwater level as water-saturated porous soil, and the soil layer above the groundwater level as air-saturated porous soil. Numerical results show that under the incident P wave, the groundwater level variation has larger effect on the amplitudes of ground surface displacement, especially on the amplitudes of vertical surface displacement when the relative stiffness of soil skeleton is small. With the decline of the groundwater level, the vertical surface displacements increase, and the frequencies at the resonance peaks decrease correspondingly. But when the relative stiffness of soil skeleton becomes large, the variation of groundwater level has little effect on earthquake ground motions.
-
-
表 1 上覆土层的材料参数
Table 1 The material parameters of the overlying soil
土层 材料参数 ρf
/(kg·m-3)μ
/MPaKs
/MPaKb
/GPaKf
/MPan k
/pm2η
/(μPa·s)cP1
/(m·s-1)cP2
/(m·s-1)cS
/(m·s-1)第一组 水饱和层 1000 66 110 36 2200 0.47 100 1000 1558.3 48.6 187.7 气饱和层 1.2 66 110 36 0.1 0.47 100 18.7 375.6 12.0 216.7 第二组 水饱和层 1000 1100 1630 36 2200 0.47 100 1000 1969.2 157.7 766.1 气饱和层 1.2 1100 1630 36 0.1 0.47 100 18.7 1532.6 11.9 884.8 -
李伟华. 2004. 含饱和土的复杂局部场地波动散射问题的解析解和显式有限元数值模拟[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学土木建筑工程学院: 230-233. Li W H. 2004. Analytical Solutions and Numerical Simulation of the Scattering of Plane Waves by Local Sites with Saturated Soil[D]. Beijing: School of Civil Engineering and Architecture,Beijing Jiaotong University: 230-233 (in Chinese).
刘晶波. 1989. 波动的有限元模拟及复杂场地对地震动的影响[D]. 哈尔滨: 国家地震局工程力学研究所: 181-266. Liu J B. 1989. Finite Element Simulation of Wave Motion and Effect of Complex Site on Seismic Wave Motion[D]. Harbin: Institute of Engineering Mechanics,China Earthquake Administration: 181-266 (in Chinese).
Eringen A C,Suhubi E S. 1975. Elastodynamics,Vol.2: Linear Theory[M]. New York: Academic Press: 1-14




 下载:
下载: