Coseismic slip distribution of the 2011 Tohoku MW9.0 earthquake inferred from GPS and InSAR data
-
摘要: 本文首先对Envisat/ASAR数据进行干涉处理, 获取2011年日本东北MW9.0地震的地表InSAR同震形变场; 然后通过对InSAR同震形变数据重采样方法的深入分析, 选择条纹率法结合干涉图的空间相干性对InSAR同震形变数据进行重采样; 最后基于弹性半空间位错模型, 联合InSAR与GPS形变数据, 采用最小二乘法反演发震断层的滑动分布. 研究结果表明: 考虑相干性的条纹率重采样方法, 更适用于形变场中存在除断层外的有限边界、 且形变场范围较大的InSAR数据重采样处理; 断层滑动主要发生在地表以下50 km范围内, 最大滑动量为49.9 m, 矩张量为4.89×1022 N·m, 所对应的矩震级为MW9.1, 与地震学反演的结果比较吻合.
-
关键词:
- 日本东北MW9.0地震 /
- 合成孔径雷达干涉测量 /
- 数据重采样 /
- 同震滑动分布
Abstract: To determine the causative fault slip distribution of the Tohoku MW9.0 earthquake in Japan, the coseismic deformation field of this earthquake was obtained with synthetic aperture radar interferometry (InSAR) technique based on Envisat/ASAR data. With detailed analysis and comparison of different methods used to resample InSAR deformation data, the fringe rate method taking into account spatial coherence of the interferogram was chosen for data resampling. Based on the elastic half-space dislocation model, the slip distribution of causative fault was inverted from InSAR and GPS data using the least squares method. The research results show that the fringe rate with coherence method is more suitable for data resampling of wider range InSAR deformation field, within which there are finite boundaries except fault. The majority of the fault slips occurred mainly in the range of 50 km below the surface, and the maximal slip on the fault is 49.9 m, meanwhile, the moment tensor is 4.89×1022 N·m, the corresponding moment magnitude is MW9.1. All these are consistent well with the results from seismological inversion, suggesting this inversion result in this study is reliable. -
引言
日本位于欧亚、 菲律宾、 太平洋和北美等四大板块交汇处,太平洋板块向北美板块移动形成俯冲带,并以80—90 mm/a的速率向西北部的北美板块俯冲(Sella et al,2002),导致两大板块边界应力不断积累.虽然地震在该板块边界经常发生并释放出一定能量,但更大的能量于2011年3月11日以日本东北MW9.0地震的形式得到了释放.此次地震不仅直接造成了人员伤亡和财产损失,而且还引发了巨大的海啸及其它次生灾害,给日本带来了巨大的灾难.
对断层滑动分布的研究可以进一步为日本东北MW9.0地震的研究提供依据.该地震发生后,不同研究者分别利用不同数据对此次地震发震断层的滑动分布进行了反演研究.例如:Ozawa等(2011)利用GPS数据确定了同震和余震的滑动分布,并对滑动分布结果进行了分析,其中同震滑动分布显示最大滑动量集中在近震区,达到27 m,释放的矩张量为3.43×1022 N·m;Zhang等(2012)利用GPS形变数据和远震数据分别反演了断层的同震滑动分布,并联合反演了断层的破裂过程,认为日本东北MW9.0地震为双侧破裂事件;Yagi和Fukhata(2011)通过远震P波数据反演了断层的破裂过程,得到总滑动量的最大值为50 m,地震矩张量为5.7×1022N·m;许才军等(2012)通过GPS形变数据对PALSAR和ASAR的干涉测量结果进行轨道误差校正后,对InSAR数据进行均匀采样,然后联合PALSAR、 ASAR的干涉测量数据和GPS数据反演了断层的滑动分布,反演的最大滑动量为50.3 m,震级为MW8.9;刁法启等(2012)基于分层模型,利用陆上GPS数据并加入海底GPS/声波资料反演了断层的滑动分布,结果显示最大滑动量为45.8 m,震级为MW9.0;Wang等(2012a)利用ASAR的干涉测量数据与GPS数据观测时间段的不同,分别确定了该地震同震和余震的断层滑动分布,认为InSAR数据可以对断层的滑动量提供更丰富的约束;Feng等(2012)以及Feng和Jónsson(2012)先利用GPS数据对InSAR形变结果进行校正,以消除大气和轨道的影响,再通过不同的数据组合对断层的同震滑动分布进行反演和比较分析.由于不同研究者所选用数据以及使用方法的不同,导致出现了不同的结果.
通过上述研究可知,虽然陆上GPS观测资料数量不少,但InSAR仍然可以弥补GPS在空间约束上的不足.同时,由于海底GPS/声波测站目前只有几个,相对于陆地上的GPS和InSAR观测资料来讲,其对断层滑动量的约束能力很难体现.另外,日本东北MW9.0地震所引起的地表破坏范围较大,几乎包括了整个日本主岛,且所能观测到的地表形变只位于断层的一侧,因此,利用InSAR数据进行反演时,只采用单纯的均匀采样或者四叉树采样(Jónsson et al,2002)方法并不合适,而选择更为合适的数据点重采样方法就显得尤为重要.本文首先对Envisat/ASAR数据进行干涉处理,得到地震同震形变场;然后对InSAR同震形变数据重采样的方法进行深入分析,选择条纹率结合相干性的方法对InSAR数据进行重采样;最后基于弹性半空间位错模型(Okada,1985),用重采样后的InSAR和GPS数据对发震断层的滑动分布进行联合反演,并对反演结果进行分析.
1. GPS和InSAR同震形变场
1.1 GPS同震形变场
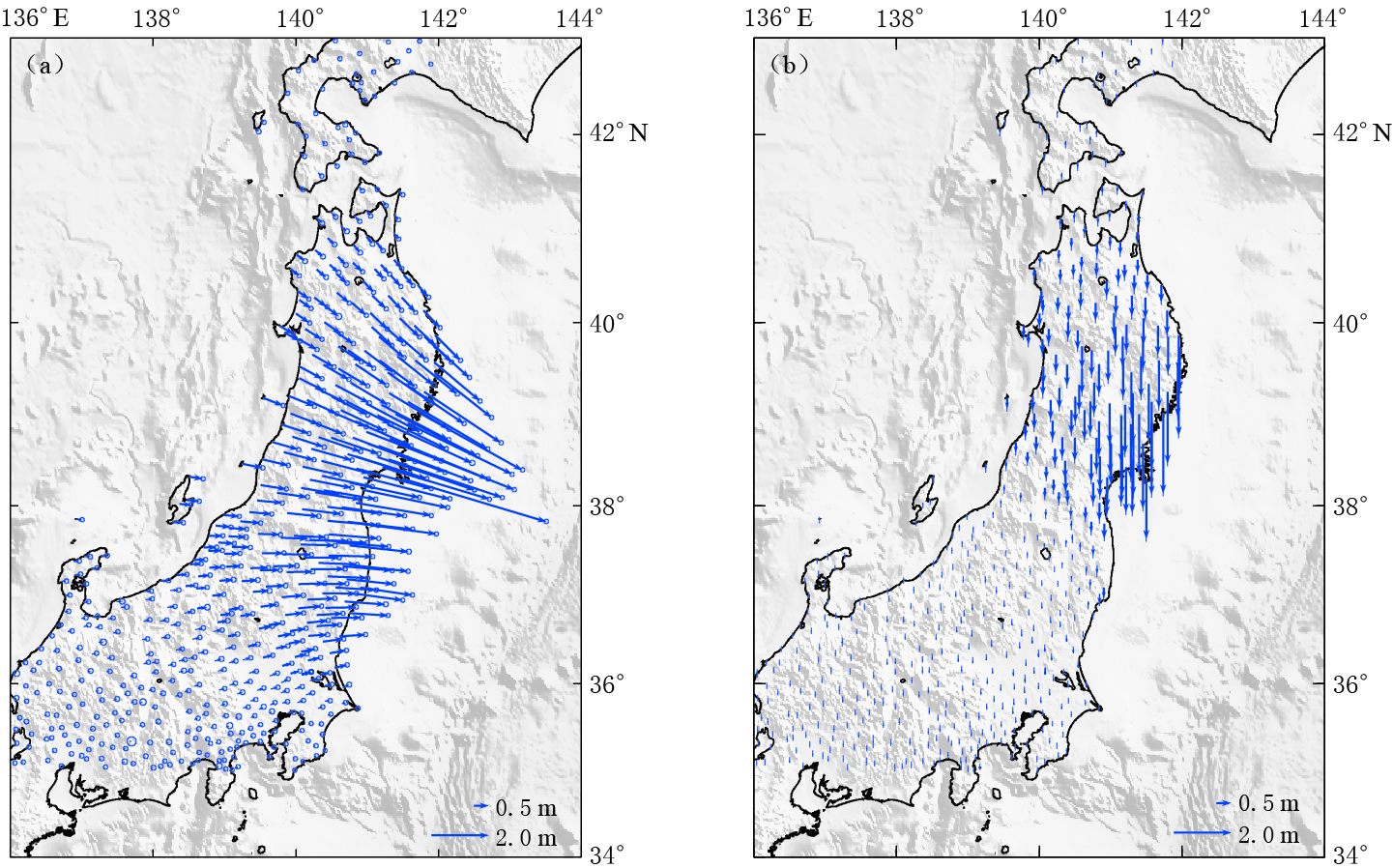
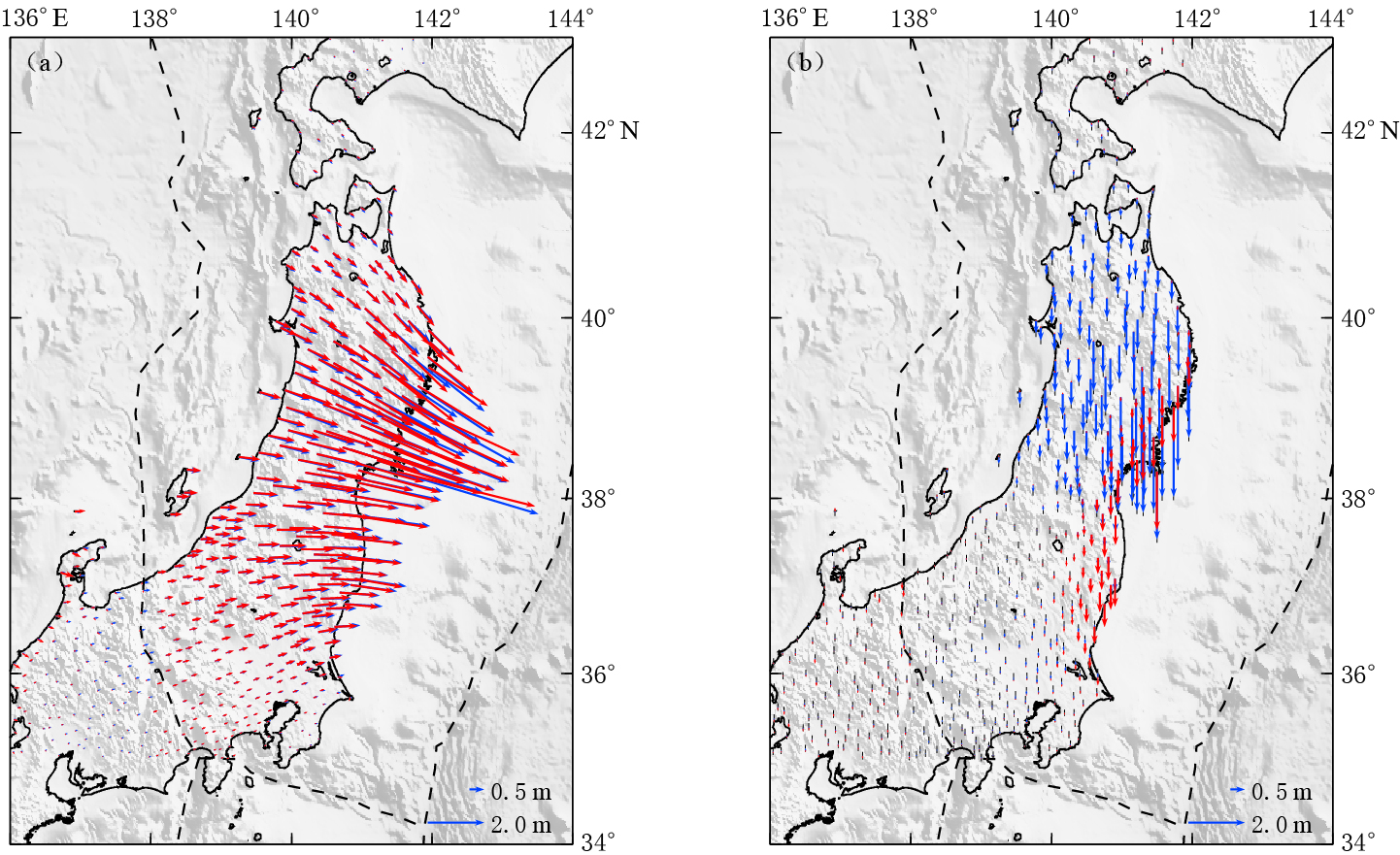
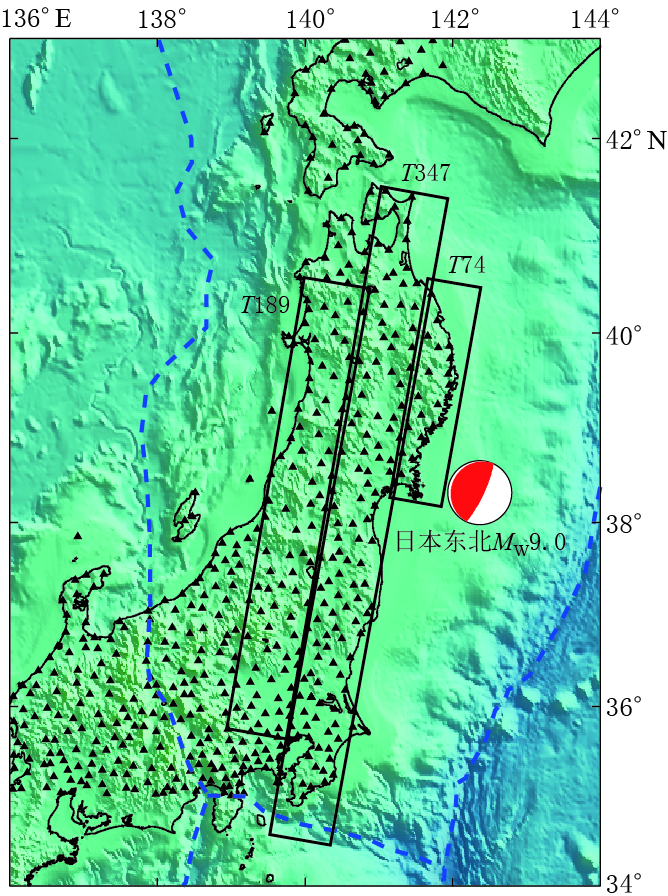
日本在其大陆布设了“地球观测网络”,并于2011年3月11日在日本东北MW9.0地震前后分别进行了观测.美国喷气推进实验室的“先进的快速成像和分析”(ARIA)团队及加利福尼亚理工学院对日本地球空间信息局的“地球观测网络”的GPS数据进行了处理,得到并发布了GPS同震形变数据(ARIA,2011).本文考虑到InSAR覆盖范围以及对断层滑动分布反演的需要,只选取了35°N—43°N、 136°E—142°E范围内的GPS点进行分析. GPS测站分布如图 1所示. 可以看出,GPS测站覆盖了整个日本主岛且分布比较均匀,平均间距为20—30 km.图 2给出了GPS测定的水平及垂直同震位移场.可以看出,水平方向形变集中在36°N—40°N范围内的陆地地区,位移方向指向震源方向,最大水平形变量为4—5 m;垂直方向形变集中在38°N—40°N范围内的陆地地区,并呈现出下降的趋势,垂直方向形变量相对于水平方向较弱,但也达到了1—2 m.单从GPS测量结果来看,此次地震释放了非常大的能量,对地面造成了巨大影响.
1.2 InSAR形变数据处理及分析
日本东北MW9.0地震发生前后,日本宇航局ALOS卫星L波段的PALSAR传感器以及欧洲空间局Envisat卫星C波段的ASAR传感器对地震区进行了观测.根据本文研究区域,通过各空间局的数据获取计划获取了一定的SAR数据,同时又通过Supersites网站(Supersites,2011)下载了部分SAR数据. 由于PALSAR数据存在较显著的轨道误差及大气电离层误差,因此,本文只选用ASAR数据进行干涉处理及作为滑动分布的约束.
本文所获取的SAR数据均为原始数据,这些数据不能直接用于干涉处理. 因此,在SAR数据获取后,首先要对原始数据进行处理,主要包括:原始数据参数文件的生成,原始数据拼接,以及距离向压缩和方位向压缩等.从GPS数据可以发现,日本东北MW9.0地震震区范围较大,单景影像只能覆盖小部分震区,因此在生成原始数据的参数文件后,必须对同一轨道的多景影像进行拼接处理.经过拼接以及后续的SLC数据生成后,根据InSAR形变测量的要求,从众多ASAR数据中选取表 1中的数据进行干涉处理. 该数据的覆盖范围如图 1中矩形框所示.
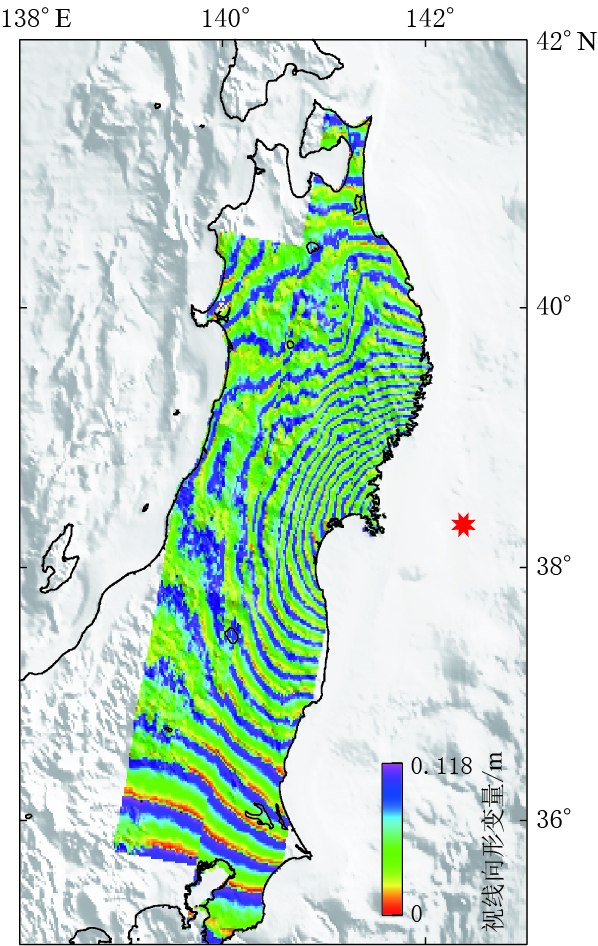
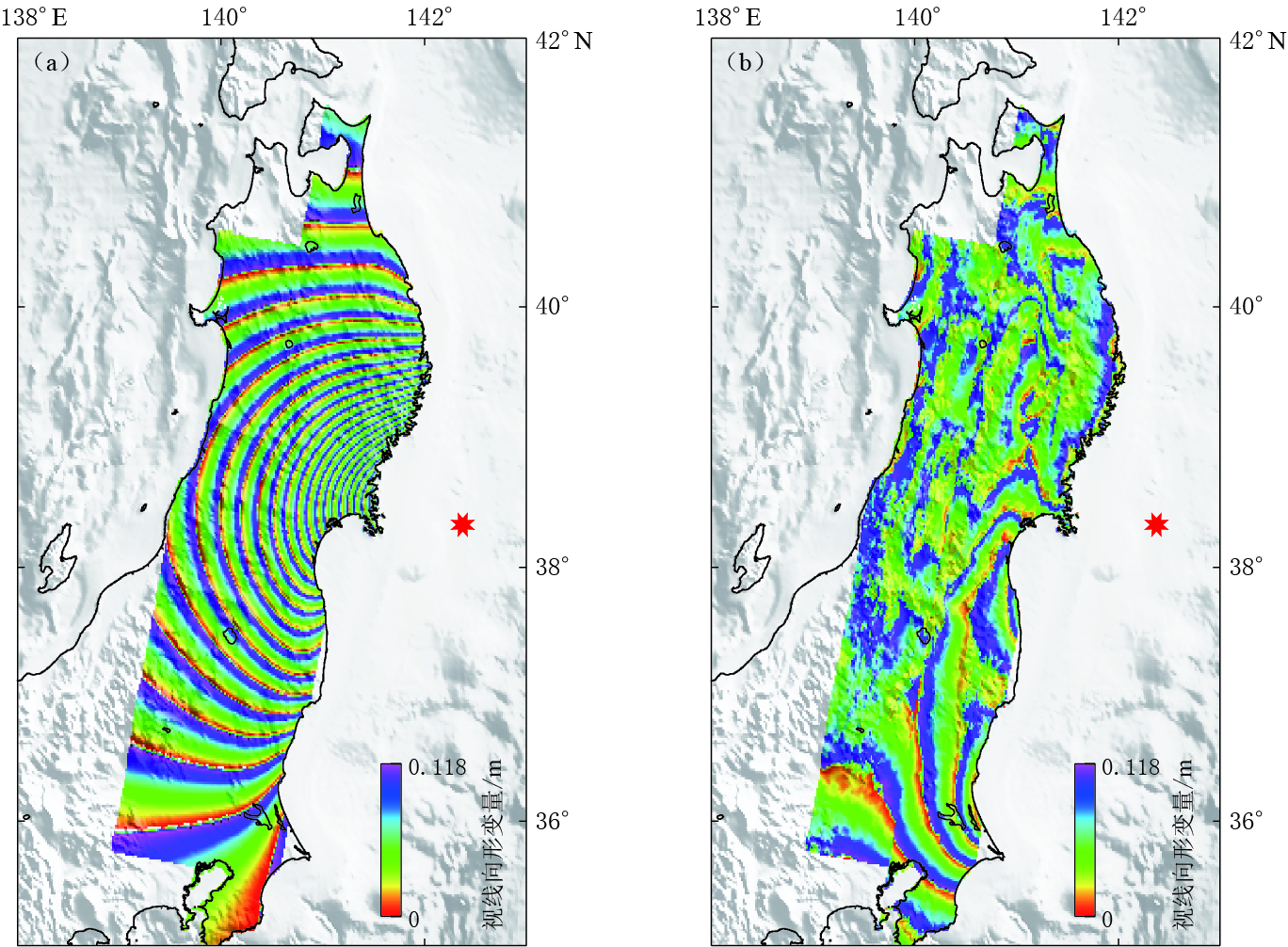
表 1 Envisat/ASAR数据信息Table 1. Details of Envisat/ASAR data数据名称 轨迹 主影像时间 辅影像时间 时间基线/d 垂直基线/m T189 2011-03-10 2011-04-09 30 -315 Envisat/ASAR T347 2011-02-19 2011-03-21 30 -174 T74 2011-03-02 2011-04-01 30 -120 对于经过干涉处理生成的初始干涉图,采用二轨差分干涉测量方法去除地形相位的影响,使用的外部地形数据来自“航天飞机雷达地形测绘任务”(shuttle radar topography mission,简写为SRTM)的90米分辨率的数字高程模型(Farr et al,2007). 将研究区域的SRTM数据投影到干涉图所对应的雷达坐标系下,然后根据高程与相位的转换关系模拟地形相位,再将地形相位部分从干涉相位中去除,生成差分干涉图(D-InSAR).为获取地表的视线向真实形变,需要对差分干涉图进行解缠处理. 在解缠之前首先采用改进的Goldstein滤波方法(Li et al,2008)对差分干涉图进行去噪处理,以减小噪声的影响;然后采用最小费用流和不规则三角网的方法对差分干涉图进行解缠,去除大气影响后得到了仅包含形变相位的差分干涉图;最后再将干涉图转化为形变图.由于该形变图为雷达坐标系下的视线向形变图,经过地理编码的处理后便得到了WGS-84坐标系下的形变图. ASAR同震形变干涉图如图 3所示.通常ASAR形变干涉图中每个条纹代表 0.028 m的形变值,但由于日本东北MW9.0地震所引起的地表形变非常大,使得形变干涉条纹非常密集,不便显示,因此图 3中形变以每个条纹0.118 m进行显示.
从图 3可以看出,大部分地区的干涉相干性较高,相位条纹保持着比较好的连续性,并未出现由于形变梯度过大而引起的条纹混叠现象. 图中东北地区及最南部地区相干性比较好,条纹也很连续;但在中间的西部地区存在比较严重的相位失相干,使得噪声相对比较明显. 失相干可能是由地表植被或者冰雪覆盖所引起的.可见,日本本土绝大部分地区均受到了地震的严重影响,产生了大的形变,在37°N—40°N之间地区的干涉条纹比较密集,在其南部及北部地区条纹相对较稀疏,故此次地震对日本北部地区的影响要比南部大.本文的形变干涉结果与已有研究结果(许才军等,2012; Feng,Jónsson,2012;Wang et al,2012a)具有很好的一致性,与GPS所测得的形变特征(图 2)也比较吻合.
2. InSAR形变场重采样方法
由于InSAR数据具有高空间分辨率的特点,决定了利用该数据获取同震形变场的数据量相当大. 如果将所有的形变数据点均用作反演,不但影响计算效率,而且有可能超出计算机的计算能力.因此,如何选择合理的数据点进行反演就显得尤为重要.本文首先对常用的平均选点法(许才军等,2012)、 四叉树法(Jónsson et al,2002)和条纹率法(Feng,Jónsson,2012)进行分析和比较,分析不同方法的适用性及各自特点,确定最终用于反演的选点方法并进行数据采样.
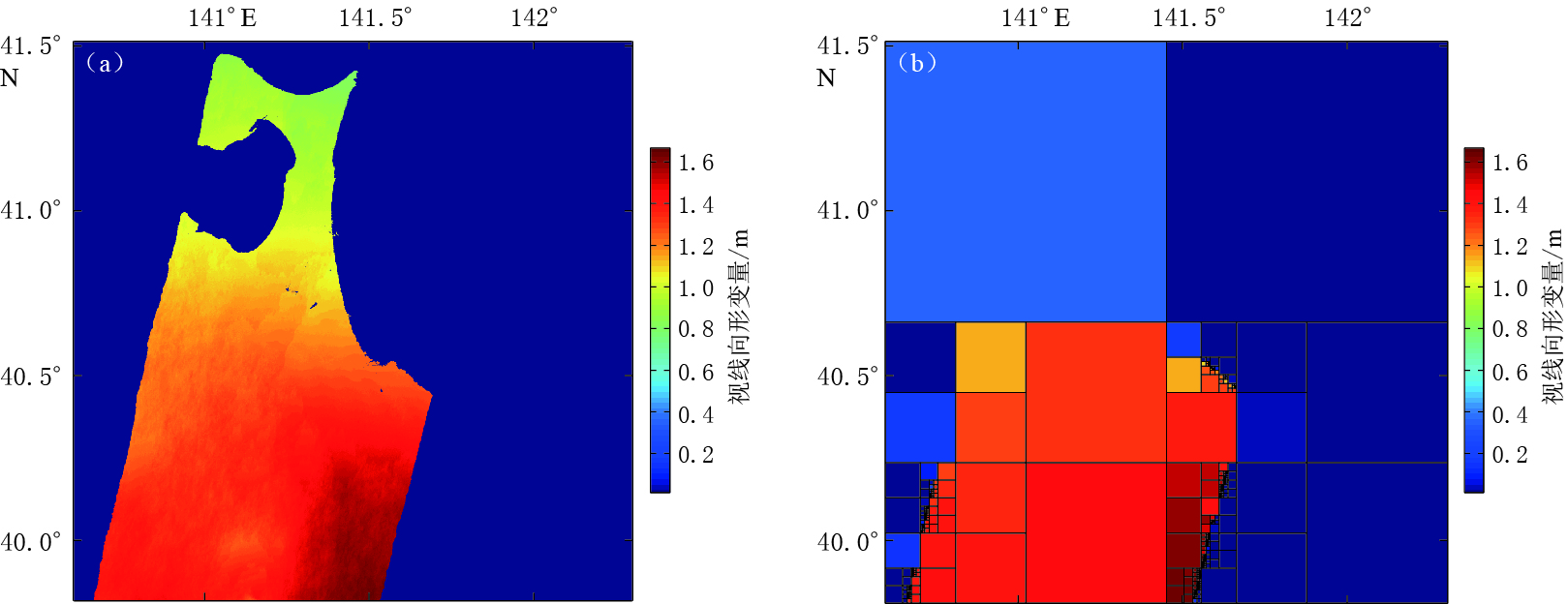
考虑到日本东北MW9.0地震的数据量非常大,为便于计算,本文在进行四叉树选点试验时,只对T347形变场的部分(图 4)进行了选点分析.从InSAR结果已知此次地震产生了很大的形变,形变梯度较大. 从四叉树选点方法的特点来看,该方法适用于此次地震InSAR结果的选点.本文采用四叉树选点的方法,将所选部分区域的均方根差阈值设为0.5 m,选到的点数为9628个,所选的采样点多集中在陆地边界以及不同InSAR条带边界处.由于此次地震形变范围广,整个形变场中存在陆地边界及不同条带间的边界,因此无论阈值选择大与小,按照四叉树方法进行处理时,在边界处的数据点更容易被选中,而在边界内部的数据点则不容易被选中,从而使边界内部被选中的数据点明显少于边界处的数据点.从四叉树方法提出的初衷以及用于反演的思路来看,靠近震源的地方受地震影响更大,应采样更多的点用于约束震源模型;而远离震源的地方则影响较小,应采样较少的点.由此可知,通过四叉树方法很难实现合理的数据点采样,即整个InSAR形变场采样数据点数由右向左递减,故该方法并不适用于日本东北MW9.0地震InSAR数据点的重采样工作.
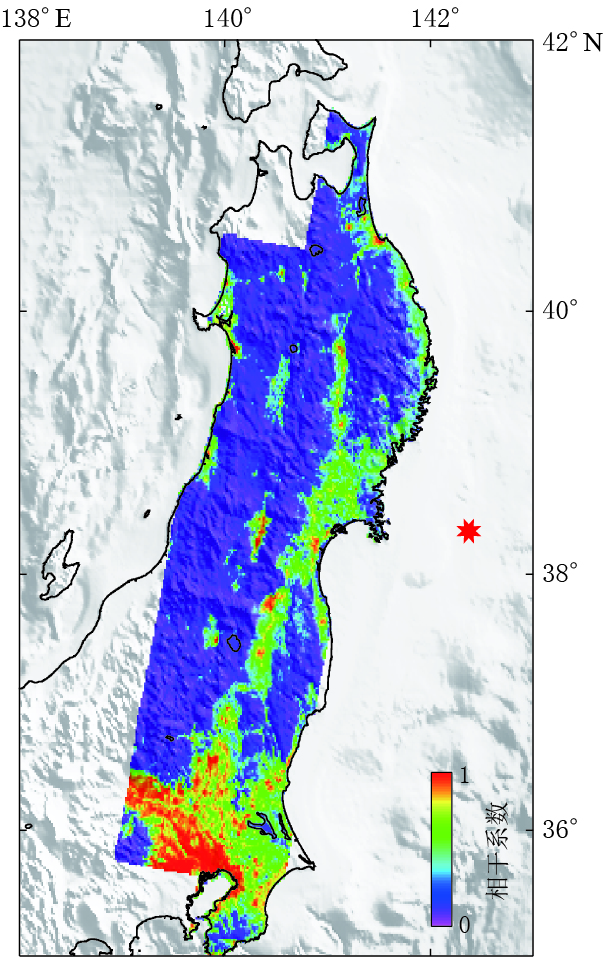
本文同样也对平均选点法及条纹率法进行了试验和分析,并结合干涉图的相干性(图 5)对数据进行重采样.可以看出,高相干区域主要集中在T347中部以及整个形变场的南部地区. 为保证数据质量,在采用条纹率法和平均选点法进行数据采样处理时,根据经验将相干性小于0.3的点剔除,最终的采样结果如图 6所示.条纹率法共采样数据点3 473个(其中T347条带2393个,T74条带158个,T189条带922个),平均选点法共采样数据点3467个(其中T347条带2401个,T74条带163个,T189条带903个). 采样点个数上有所差异,但总数相当.从两种采样方法的采样数据点分布(图 6)可知:平均选点法的结果对相干性的依赖性较高,在高相干地区选择的点较多,即在整个干涉图的下部,所采样数据点相对较多;条纹率法对相干性的依赖性则相对较低,所选数据点分布主要依赖于条纹分布.利用形变数据点进行反演时,点位梯度分布越好,对断层模型的约束越合理. 由此可知,条纹率采样法更适用于日本东北MW9.0地震,采样数据点不至于全部集中在高相干点处,这样既保证了数据的质量,也保证了能全面反映形变信息.因此,本文最终将条纹率法所采样的数据作为断层同震滑动分布反演的观测数据.
3. 断层滑动分布反演及分析
在得到日本东北MW9.0地震的同震形变之后,联合GPS和InSAR数据对断层的同震滑动分布进行反演.
3.1 滑动分布反演
本文反演所用的断层几何参数采用Zhang等(2012)确定的结果.在进行反演前,将断层分成若干个小的断层单元,根据确定的断层几何参数,将断层沿走向方向划分为31列,深度方向划分为20行,断层单元总数为620个.反演模型采用均匀介质弹性半空间位错模型(Okada,1985),介质的泊松比定为0.25.在确定断层几何参数后,形变数据与滑动量之间变为线性关系,于是可以构建观测数据d与地震断层滑动量s之间的关系,即

式中,D为拉普拉斯平滑算子,k2为平滑因子,W为数据权比参数,G为格林函数.该式可利用线性反演方法求解.
利用最小二乘法对GPS和InSAR形变数据进行联合反演计算,得到了日本东北MW9.0地震的断层滑动分布.在进行GPS和InSAR联合反演时,通过经验定权(Feng et al,2010;Wang et al,2012b)确定权比参数的大小.反演结果如图 7所示.
3.2 反演结果分析
从反演滑动分布(图 7a)可知,断层滑动主要集中在断层中上部,最大滑动量为49.9 m.根据该反演结果获得的矩张量为M0=4.89×1022 N·m,所对应的矩震级为MW9.1. 该结果与Yagi和Fukhata(2011)通过远震P波数据反演的结果较吻合.本文还对反演结果的误差进行了计算,结果表明滑动量越大的地方误差也越大,计算结果如图 7b所示.
最后利用反演结果正演模拟了InSAR形变场(图 8)和GPS形变场(图 9),并对InSAR与GPS观测结果进行了对比(图 8、 图 9).可以看出,模拟形变场的结果与观测数据较接近.从InSAR残差干涉图(图 8b)可以看出,大部分区域的形变拟合较好,只能看到少量的干涉条纹,南部地区的干涉条纹拟合较差.通过分析InSAR形变场和GPS形变场可知,由于InSAR形变结果覆盖整个区域,南北跨度较大,而本文所采用反演模型为简单的均匀半空间弹性位错模型,并未考虑介质的非均匀变化以及地球曲率的影响,这势必会造成反演结果存在一定程度的偏差.
4. 讨论与结论
本文通过对InSAR形变数据重采样方法的比较和分析,并联合GPS反演得到了日本东北MW9.0地震的断层同震滑动分布,得出如下结论:
1)所得差分干涉图的相位条纹保持了比较好的连续性,并未出现由于形变梯度过大而引起的条纹混叠现象,较好地反映了此次地震对日本陆上地区地表所造成的影响,即绝大部分地区均受到了该地震的严重影响,在地表产生了很大的形变,并以震中为中心由东向西逐渐减小.在37°N—40°N之间的陆上区域,条纹比较密集,形变较大;在37°N以南地区条纹相对较稀疏,形变较小,这与GPS所测的形变特征较吻合.
2)利用InSAR技术能够检测高空间分辨率的同震地表形变,利用该数据可进行断层滑动量反演,但在反演数据量过大时需进行重采样处理.日本东北MW9.0地震所引起的地表形变范围及梯度均较大,且在地震影响区域内存在除断层外的有限边界(如陆地边界),所以采用考虑相干性的条纹率法对InSAR形变数据进行重采样是比较合理的.
3)利用GPS和InSAR同震形变数据可以联合反演断层的滑动分布,InSAR数据可以很好地弥补GPS数据空间分辨率的不足.联合反演得到的滑动量主要分布在地表以下50 km范围内,最大滑动量为49.9 m,矩张量为4.89×1022 N·m,所对应的矩震级为MW9.1. 该结果与Yagi和Fukhata(2011)通过远震P波数据反演的结果比较吻合,与其他研究者(刁法启等,2012;许才军等,2012;Feng,Jónsson,2012)所得到的滑动分布稍有差异,最大滑动量也存在一定的差异. 造成这些差异的原因,主要是所采用的数据、 反演方法以及模型不同所造成的.
欧洲空间局提供了部分ASAR数据(项目CIP.14439),北京大学张勇研究员和中国科学院测量与地球物理研究所刁法启博士对本研究给予了帮助,在此一并表示感谢.
-
表 1 Envisat/ASAR数据信息
Table 1 Details of Envisat/ASAR data
数据名称 轨迹 主影像时间 辅影像时间 时间基线/d 垂直基线/m T189 2011-03-10 2011-04-09 30 -315 Envisat/ASAR T347 2011-02-19 2011-03-21 30 -174 T74 2011-03-02 2011-04-01 30 -120 -
ARIA. 2011. ARIA GPS displacement data provided by JPL and Caltech[EB/OL]. [2011-08-01]. ftp://sideshow.jpl.nasa.gov/pub/usrs/ARIA/.
doi: 10.1029/2005RG000183 doi: 10.1029/2009GL041213 doi: 10.1029/2012GL051628 Supersites. 2011. Supersites Tohoku-Oki: GEO's Tohoku-Oki event Supersite website[EB/OL]. [2013-07-31]. http://supersites.earthobservations.org/sendai.php.
doi: 10.1029/2011GL048701 -
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 孙云强,邱鑫鹏,陈常勇,赵卓,林君祺,龚炜程. GNSS和InSAR约束的2023积石山M_S6.2地震同震滑动分布. 地震工程学报. 2024(04): 867-879 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 黎朕灵,金明培,缪素秋. 2021年云南漾濞M_S6.4地震同震位移场和震源滑动模型反演. 地震研究. 2021(03): 330-337 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 云烨,吕孝雷,付希凯,薛飞扬. 星载InSAR技术在地质灾害监测领域的应用. 雷达学报. 2020(01): 73-85 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 武晔,万永革,武巴特尔,石砚斌. 数字信号处理课程“地震数据重采样”综合性实验设计. 实验室研究与探索. 2018(02): 178-182+192 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: