Using the electron-hole theory to estimate the “energy” magnitude related to the electromagnetic abnormities before the Wenchuan MS8.0 earthquake
-
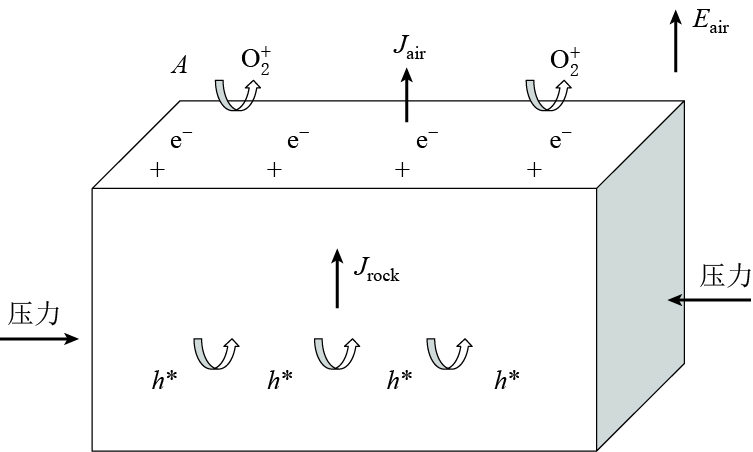
摘要: 基于汶川MS8.0地震前3天记录到的强空间电磁异常的观测事实, 引用岩石压电效应模型和岩石受压产生的电子-空穴理论, 尝试推算和解释汶川地震前产生的显著空间电磁异常现象的“能量源”问题. 结果显示: 在设定汶川MS8.0地震发震主断层所受最大水平主应力和断层表面积的情况下, 根据理论模型模拟计算得出, 当发震主断层在强压力作用下形成微破裂至宏观破裂发育产生主破裂前, 断层表面积累的电荷带电量为106—107 C, 产生的垂直地-气界面附加电场为107—108 V/m; 主破裂发生时, 断层表面电量可达108 C, 电场强度高达109 V/m, 断层输出电流量级达105 A. 震源区地-气界面电磁场的增强, 一方面引起地面附近大范围电磁观测参数的大幅度突变异常, 另一方面加速震源区上空的气体分子电离, 空气电离增强空气的电导率, 促使电荷快速扩散至电离层高度, 直接引起高空电离层参数的短时突变异常并经空间地震监测卫星记录到.Abstract: On the base of the electron-hole theory stated by Freund et al, this paper attempts to deduce and interpret the energy of the obvious lithosphere-atmosphere-ionosphere coupling observed on May 9, 2008, three days before the Wenchuan MS8.0 earthquake. During the process, we set the largest horizontal principal stress and the earthquake plate area of the main fault. The simulation results show, during the period of the micro-cracks developing into the macro-cracks before the main rupture occurs, the total surface charge range of the main fault falls in 106—107 C and the related upward electric field, which is perpendicular to the interface between the Earth surface and the atmosphere, is 107—108 V/m. The corresponding parameters are up to 108 C and 109 V/m when the main rupture happens, and the output current is up to 105 A in order. On one hand, the electric field increasing in the interface between the Earth surface and the atmosphere, can cause electromagnetic parameter abnormities of the ground-based observation, with the range beyond 1000 km; on the other hand, it can accumulate air ionization above pre-earthquake zone, leading to ionospheric parameters short-time sudden changes recorded by some spatial seismic monitoring satellites.
-
-
-
徐锡伟.2009.5·12汶川8.0级地震地表破裂图集[M].北京: 地震出版社: 17. Xu X W.2009.Album of 5·12 Wenchuan 8.0 Earthquake Surface Ruptures,China[M].Beijing: Seismological Press: 17 (in Chinese).




 下载:
下载: