Dynamic characteristics analysis of moistening loess tunnel of Yintao water supply main channel
-
摘要: 为了得到增湿后黄土围岩隧洞在地震作用下的动力特性, 基于初始弹性模量和抗剪强度指标与含水量的关系, 采用时程分析法, 对增湿情况下的黄土围岩-隧洞结构进行地震动力分析. 数值计算结果表明: 随着含水量的增加, 隧洞衬砌各部位主应力绝对值减小, 自振圆频率减小, 自振周期相应增大; 与输入的地震加速度峰值相比, 当黄土隧洞围岩含水量小于临界含水量时, 隧洞顶部加速度峰值大于输入地震加速度峰值, 大于临界含水量时则出现相反的结果; 同一含水量下, 隧洞衬砌对称部位最大、 最小主应力交替出现, 使隧洞衬砌材料发生疲劳损伤, 是隧洞衬砌破坏的主要原因. 本文研究结果可以为在不同含水量情况下黄土围岩-隧洞结构的抗震分析提供参考.Abstract: In order to obtain the dynamic characteristics of tunnel in loess surrounding rock under seismic action after moistening, the seismic dynamics of the loess surrounding rock with moistening and tunnel structure had been analyzed with the time-history method, basing on the relationship between initial elastic modulus, the shear strength parameters and the water content. The numerical computation results showed that, with the water content of the loess surrounding rock increasing, the absolute value of principal stress and the autooscillation circular frequency all decreased relatively, while the period of free vibration increased correspondingly. When the water content was less than its critical value, the peak acceleration of the tunnel roof was larger than the original seismic peak acceleration. Otherwise, it was opposite. Under the same water content, the maximum and minimum principal stress appeared alterna-tely, making the tunnel lining material fatigue damage, which was the main reason for the tunnel lining damage. The results can provide a reference for the seismic analysis on the different water content conditions of loess surrounding rock and tunnel structure.
-
Keywords:
- moistening /
- the loess tunnel /
- time-history analysis /
- water content /
- peak acceleration /
- principal stress
-
引言
黄土是一种第四纪沉积物,广泛分布于世界各个国家,其面积约占陆地总面积的9.3%.我国是黄土占地面积最大的国家,约占国土面积的6%.甘肃引洮供水一期工程中10#—15#隧洞为黄土隧洞,场地黄土分为两层,上部为上更新统风积马兰黄土(eolQ23),下部为冲洪积粉质壤土(al-plQ13),两者的工程地质性状基本相似,分析时统称为Q3黄土.黄土材料在干燥状态下具有较高的强度,黄土隧洞也具有较好的稳定性,然而黄土遇水后强度降低,从而导致隧洞结构破坏而发生坍塌等事故.研究人员对黄土围岩地下结构在地震作用下的破坏情况进行了研究分析. 例如:郑颖人等(2010)为了得到地震作用下无衬砌隧洞的力学规律,利用有限差分程序,同时考虑隧洞的拉破坏和剪破坏,得出了隧洞顶部首先出现局部拉破坏,然后出现侧边整体破坏的破坏机制;陈立伟等(2007)将黄土视为理想弹塑性材料,采用Druke-Prager破坏准则,分析黄土暗穴在地震作用下的稳定性; 邓国华等(2007)基于已提出的Q3黄土初始切线模量与含水量的关系,对一典型的黄土隧洞进行增湿变形分析,得到了典型黄土隧洞在围岩增湿情况下围岩的变形、地面沉降和衬砌受力等结果.
本文以前人研究为基础,结合黄土抗剪强度指标和初始弹性模量的变化,模拟了增湿条件下黄土隧洞在水平地震作用下,自振圆频率、质量阻尼系数、刚度阻尼系数和隧洞顶部地震加速度时程的变化规律,以及衬砌的薄弱位置及其主应力和最大位移变化等规律.
1. 动力分析模型及计算参数
1.1 动力分析模型
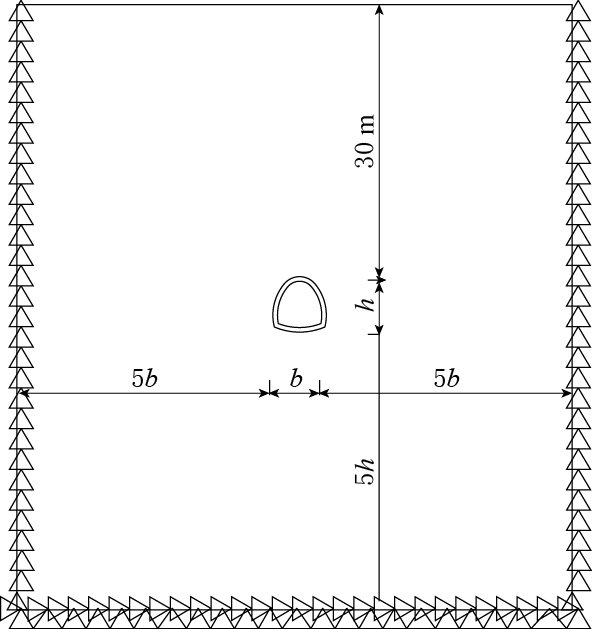
隧洞横断面形状为类马蹄形,宽×高为5.5 m×6 m,衬砌厚度为0.5 m.为了减少计算时间,左右边界及底部边界计算范围分别取隧洞宽和高的5倍,上部边界至隧洞顶部为30 m,隧洞上部边界为自由边界,左右边界为竖向约束,底部为固定绞支座(高峰,任侠,2001;程选生,郑颖人,2011).由于沿隧洞长度方向尺寸远比隧洞横向宽度大,故按照平面应变问题计算.计算模型如图 1所示.
1.2 计算参数选取
1.2.1 工程概况
引洮一期总干渠黄土主要分布在内官香泉盆地南部的黄土梁峁地貌区,10#—15#隧洞均有分布.该土层分为两层,上层为厚度5—25 m的马兰黄土(eolQ23),下层为粉质壤土(al-plQ13),两者的工程地质性状相似,在分析时统称为Q3黄土.该黄土液限为28%—31.6%,塑限为16.9%—22.1%,黏聚力为18.7—31.1 kPa,内摩擦角为22.7°—28.6°,压缩模量为5.56—14.93 MPa,弹性模量为36.6—142.3 MPa.
1.2.2 计算参数
工程中能使黄土含水量增加的原因主要为降雨和地下水位的上升,黄土增湿后的一个显著特点就是其抗剪强度指标发生巨大变化.随着含水量的增加,其黏聚力骤减,但内摩擦角的变化并不是很显著.Drucker-Prager屈服准则能准确描述岩石、土壤等材料,在有限元分析中可得到较为精确的结果.黄土的塑性行为被假定为理想弹塑性. 因此本文假设黄土为理想弹塑性材料,利用Drucker-Prager屈服准则,采用有效应力的变化来描述黄土强度的变化. 增湿黄土的有效黏聚力与含水量的关系为(张茂花等,2006)

式中:c′为有效黏聚力,单位为kPa;w为含水量.
弹性模量是黄土隧洞抗震分析最主要的参数之一,其变化与黄土损伤有很大的关系. 基于已提出的Q3黄土初始弹性模量与含水量的关系(林斌,2005),可以初步判断Q3黄土在不同含水量情况下的初始弹性模量为

式中:E为Q3黄土初始弹性模量,单位为MPa;w为黄土初始含水量.
根据已有理论公式,结合引洮隧洞黄土的特有性质,取黄土塑限范围内含水量分别为7.42%、9.36%、11.95%、13.25%和15.10%(对超出塑限含水量的黄土围岩隧洞作了相同的分析,其数值结果不收敛,说明黄土围岩含水量超过其塑限后的时程反应并不稳定而发生破坏)的黄土围岩隧洞进行地震时程分析.据陈存礼等(2006)研究结果,可以不考虑含水量对黄土阻尼比的影响.计算中假定阻尼比和泊松比均为常数,隧洞衬砌为C30混凝土,容量为2.5 kN/m3,弹性模量为30 GPa,泊松比为0.20.黄土围岩部分计算参数张茂花等(2006)结果(表 1),其中含水量9.36%和13.25%为其它含水量参数的线性内插值.
表 1 黄土隧洞围岩计算参数Table 1. The calculation parameters of tunnel in loess surrounding rockw γ/(kN·m-3) E/MPa c/kPa φ/° μ ξ 7.42% 1.64 130 57.8 24.1 0.3 0.12 9.36% 1.61 118 39.5 25.2 0.3 0.12 11.95% 1.59 100 31.0 26.0 0.3 0.12 13.25% 1.56 97 20.2 26.5 0.3 0.12 15.10% 1.54 93 17.2 27.1 0.3 0.12 注: w为含水量(下同), γ为容量, E为初始弹性模量, c为黏聚力, φ为内摩擦角, μ为泊松比, ξ为阻尼比. 2. 地震波选取
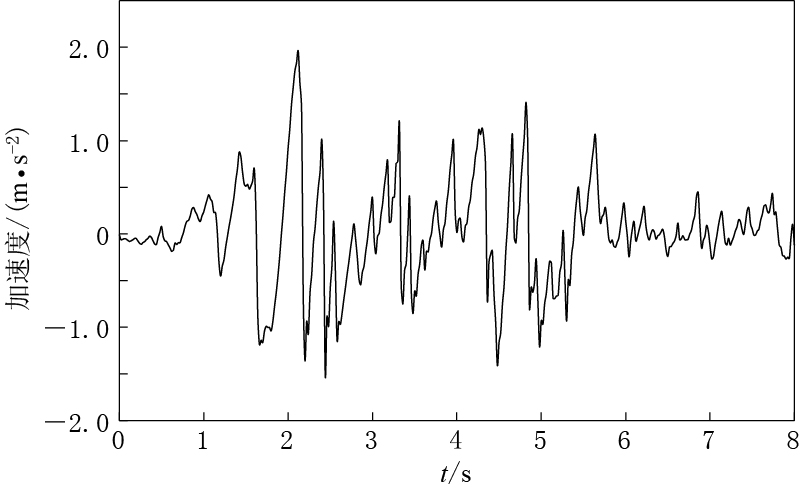
在进行地震加速度时程分析时,应考虑场地特征和近、远震情况,合理选用输入模型的地震加速度.地下工程的抗震问题实际上是非常复杂的,应考虑基岩深度以及基岩面上的实际地震波等情况. 为简单起见,本文选取能代表Ⅱ,Ⅲ类场地的El-Centro地震波NS向量,其峰值加速度出现在2.12 s,为3.418 m/s2. 本文按照烈度为Ⅷ度的地震(峰值加速度为1.96 m/s2)进行计算,如图 2所示.对其原始数据波进行调整,使其峰值加速度为1.96 m/s2. 参考翁祝梅和毛丽华(2006)的研究结果,地下结构抗震验算只考虑水平向地震波即可.
3. 黄土隧洞动力特性分析
地震时程分析过程为非线性求解,在水平地震作用下,黄土隧洞在(t+Δt)时刻的动力平衡方程为

式中:at+Δt,åt+Δt和ät+Δt分别为黄土隧洞在(t+Δt)时刻的位移向量、速度向量和加速度向量;M,C和K分别为黄土隧洞的质量矩阵、阻尼矩阵和刚度矩阵;(äg)t+Δt为外部输入的黄土隧洞的地震加速度时程.采用Newmark隐式积分法,假设


将式(4)、(5)带入式(3),简化后得

由式(6)解出at+Δt后,代入式(4)解出ät+Δt,最后代入式(5)解出åt+Δt.
黄土隧洞隔离体的总阻尼矩阵采用瑞雷阻尼矩阵,即

式中,η为质量阻尼系数,λ为刚度阻尼系数.η和λ可分别由下式求解:


式中:ξi和ξj分别为第i阶和第j阶对应的阻尼比. 为分析简单,假定阻尼比ξi=ξj=ξ;ωi和ωj分别为由模态分析得到的第i阶和第j阶的自振圆频率.
4. 数值分析结果
4.1 自振圆频率变化规律
首先对黄土隧洞模型隔离体进行模态分析,分析其前8阶自振圆频率.增湿后各含水量所对应的圆频率如表 2所示. 随着含水量的增加,同一阶的圆频率呈减小的趋势,且减小的趋势在含水量w≥11.95%时变慢.自振周期与自振圆频率的关系为
表 2 黄土隧洞围岩含水量与圆频率关系表Table 2. The relationship between water content and circular frequency of tunnel in loess surrounding rockw ω1 ω2 ω3 ω4 ω5 ω6 ω7 ω8 7.42% 0.68998 1.5569 2.0702 2.4639 2.7083 3.3117 3.4490 3.4992 9.36% 0.66358 1.4974 1.9908 2.3695 2.6048 3.1851 3.3172 3.3648 11.95% 0.61490 1.3876 1.8446 2.1955 2.4139 2.9514 3.0741 3.1172 13.25% 0.61142 1.3798 1.8341 2.1831 2.4003 2.9348 3.0568 3.0994 15.10% 0.60259 1.3599 1.8076 2.1516 2.3657 2.8925 3.0128 3.0545 注: ω1—ω8分别为第1—8阶圆频率. 
可以看出,随着含水量的增加,自振圆频率ω的减小,自振周期T相应增大.
4.2 阻尼系数变化规律
由表 2可以看出,ω1和ω2变化最大,而ω6以后的圆频率变化则变小,故本文选取ω1和ω6. 根据式(8)和式(9)求出增湿后各含水量下的质量阻尼系数η和刚度阻尼系数λ(表 3),然后根据式(7)计算瑞雷阻尼矩阵.
表 3 黄土隧洞围岩含水量与阻尼系数关系表Table 3. The relationship between water content and damping coefficients of tunnel in loess surrounding rockw η λ 7.42% 0.137 0.060 9.36% 0.132 0.062 11.95% 0.122 0.067 13.25% 0.121 0.068 15.10% 0.120 0.069 注: η为质量阻尼系数, λ为刚度阻尼系数. 由表 3可以看出,随着含水量的增加,质量阻尼系数减小,刚度阻尼系数变大,且均在含水量w≥11.95%后变化减缓.
4.3 隧洞顶部加速度变化规律
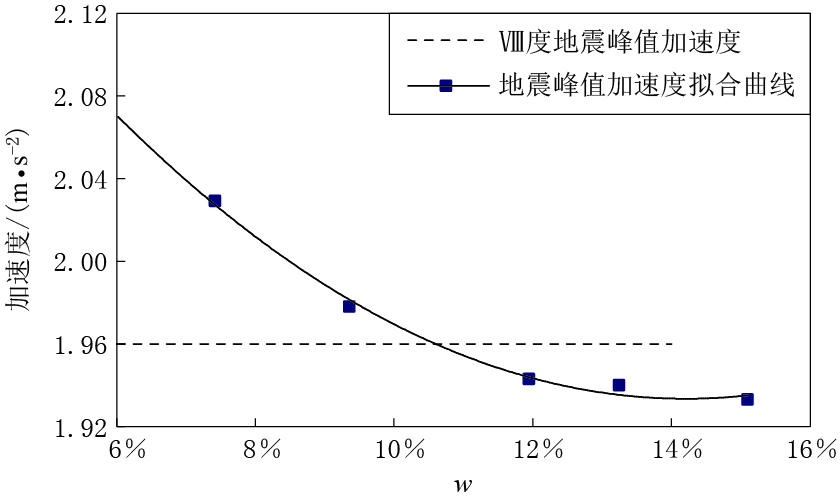
输入水平向El-Centro地震波加速度后,得到不同含水量情况下黄土隧洞顶部的地震峰值加速度,如表 4所示.可以看出:在Ⅷ度地震下,各含水量情况下黄土隧洞顶部峰值加速度发生时间均为2.22 s,相比输入加速度发生时间出现了滞后现象;在含水量为7.42%和9.36%情况下,地震加速度出现了放大现象; 而后3组含水量情况下,峰值加速度均比输入加速度小.根据表 4数据可以拟合出一条关于含水量w2多项式的加速度-含水量曲线,如图 3所示. 由图中曲线得出临界含水量为10.12%,即在此含水量下黄土隧洞顶部地震加速度不会出现增大或减小的现象.
表 4 黄土隧洞顶部含水量与地震峰值加速度关系表Table 4. The relationship between water content and seismic peak acceleration of the loess tunnel roofw t/s A/(m·s-2) 7.42% 2.22 2.029 9.36% 2.22 1.978 11.95% 2.22 1.943 13.25% 2.22 1.940 15.10% 2.22 1.933 注: A为地震峰值加速度. 根据所得的各含水量所对应的黄土隧洞顶部峰值加速度拟合曲线,可得到拟合方程为

式中,w为黄土围岩含水量,A为地震峰值加速度.
4.4 隧洞薄弱位置及其应力变化规律
高波等(2009)研究发现,隧洞的拱肩处出现几乎贯通整条隧洞的纵向裂缝;由田瑞瑞(2012)研究结果可知,有衬砌隧洞的塑性区域出现在两拱肩和拱脚位置,隧洞的最大、最小主应力及最大位移均出现在拱肩和拱脚处,该结果与实际工程发生地震破坏时的情况和数值模拟结果相似.由此可以看出,隧洞的薄弱位置在隧洞左右拱肩及左右拱脚位置.表 5给出了各含水量情况下,左、右拱肩和拱脚处的主应力及最大位移.
表 5 黄土隧洞衬砌主应力及最大位移Table 5. The principal stress and maximum displacement of the loess tunnel liningw 衬砌位置 σmax/MPa σmin/MPa s/cm 7.42% 左拱肩 3.02 -2.64 2.72 右拱肩 2.64 -3.02 2.70 左拱脚 2.60 -2.97 2.69 右拱脚 2.96 -2.61 2.67 9.36% 左拱肩 2.97 -2.63 2.95 右拱肩 2.62 -3.00 2.92 左拱脚 2.58 -2.94 2.91 右拱脚 2.92 -2.58 2.89 11.95% 左拱肩 2.75 -2.55 3.52 右拱肩 2.52 -2.82 3.50 左拱脚 2.46 -2.57 3.48 右拱脚 2.56 -2.47 3.46 13.25% 左拱肩 2.09 -1.88 3.90 右拱肩 1.80 -2.16 3.87 左拱脚 1.73 -2.10 3.85 右拱脚 2.02 -1.83 3.83 15.10% 左拱肩 1.92 -1.67 4.12 右拱肩 1.58 -1.99 4.10 左拱脚 1.51 -1.84 4.08 右拱脚 1.84 -1.62 4.06 注:σmax为最大主应力,σmin为最小主应力,s为最大位移. 在水平地震加速度作用下,随着含水量的增加,左、右拱肩处主应力绝对值减小,但各位置处最大位移值增大.当黄土围岩含水量增湿到塑性范围时,黄土隧洞在地震作用下表现为塑性破坏而发生数值模拟不收敛.取左、右拱肩处的位置为黄土隧洞分析点,发现当左拱肩出现最大主应力时,右拱肩出现最小主应力,且其绝对值大小基本相等,发生时间也相同.
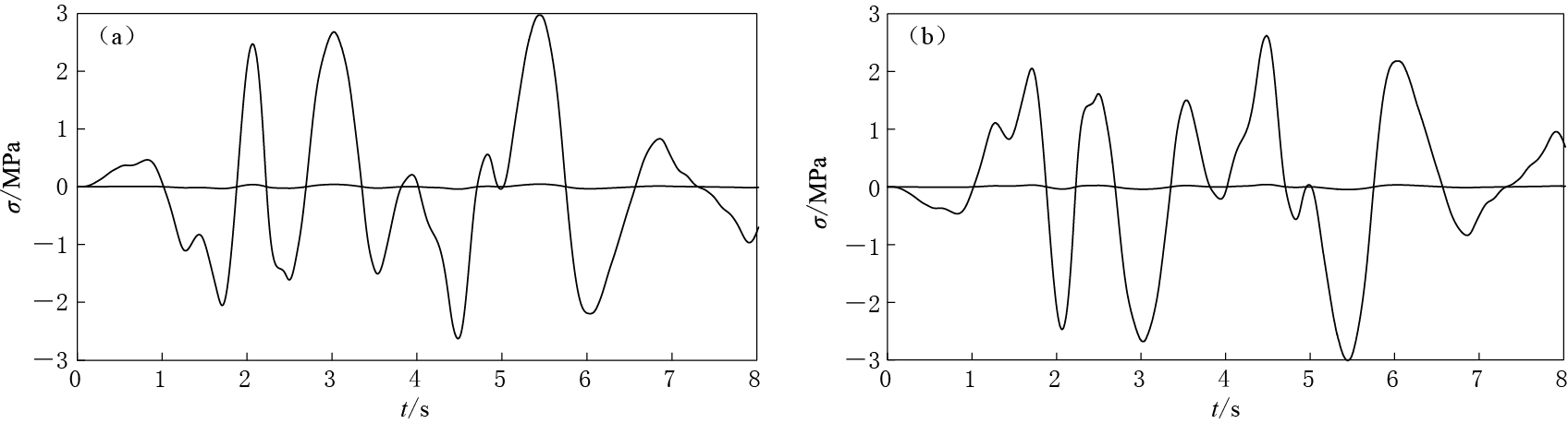
图 4给出了含水量w=9.36%时隧洞左、右拱肩的主应力图. 图中纵轴上部为正向主应力,下部为负向主应力. 可以看出,在同一含水量情况下,随着时间的递增,左拱肩首先出现正向的主应力峰值,同时右拱肩出现负向的主应力峰值,左右拱肩主应力关于σ=0对称相等.由此可以得出,黄土隧洞衬砌材料的破坏原因是由于地震作用下,最大、最小主应力交替出现而使材料发生疲劳损伤所造成的.
5. 讨论与结论
本文采用地震动力时程分析法,基于初始弹性模量和抗剪强度指标的变化,模拟了黄土围岩增湿后隧洞一系列的动力特性.数值模拟结果显示:
1)随着含水量的增加,同一阶的自振圆频率呈减小的趋势,且减小的趋势在含水量w≥11.95%时变慢,相应的自振周期随着含水量的增加而增大;
2)随着含水量的增加,质量阻尼系数η减小,刚度阻尼系数λ变大;
3)随着含水量的增加,相对于输入地震加速度,数值模拟分析得到的隧洞顶部加速度先大于输入地震加速度,随后又小于输入地震加速度;
4)衬砌拱肩和拱脚位置为抗震薄弱位置,与汶川地震后公路隧道震害结果相类似,且随着含水量的增加,拱肩和拱脚处主应力绝对值呈减小而最大位移呈增大趋势.
基于上述分析结果,本文提出了黄土围岩增湿后隧洞顶部加速度临界含水量概念,并求得引洮总干渠黄土隧洞顶部加速度临界含水量为10.12%;以含水量w=9.36%时左、右拱肩主应力图为例,分析了衬砌破坏的原因是由于水平地震作用下衬砌拱肩最大、最小主应力交替出现而使材料发生疲劳损伤造成的.因此,加强黄土隧洞拱肩和拱脚位置的支护对于其抗震性能的提升是必不可少的.此外,还应避免在隧洞施工及运营过程中,黄土围岩因外界因素使其含水量增大而导致其抗震性能降低.
-
表 1 黄土隧洞围岩计算参数
Table 1 The calculation parameters of tunnel in loess surrounding rock
w γ/(kN·m-3) E/MPa c/kPa φ/° μ ξ 7.42% 1.64 130 57.8 24.1 0.3 0.12 9.36% 1.61 118 39.5 25.2 0.3 0.12 11.95% 1.59 100 31.0 26.0 0.3 0.12 13.25% 1.56 97 20.2 26.5 0.3 0.12 15.10% 1.54 93 17.2 27.1 0.3 0.12 注: w为含水量(下同), γ为容量, E为初始弹性模量, c为黏聚力, φ为内摩擦角, μ为泊松比, ξ为阻尼比. 表 2 黄土隧洞围岩含水量与圆频率关系表
Table 2 The relationship between water content and circular frequency of tunnel in loess surrounding rock
w ω1 ω2 ω3 ω4 ω5 ω6 ω7 ω8 7.42% 0.68998 1.5569 2.0702 2.4639 2.7083 3.3117 3.4490 3.4992 9.36% 0.66358 1.4974 1.9908 2.3695 2.6048 3.1851 3.3172 3.3648 11.95% 0.61490 1.3876 1.8446 2.1955 2.4139 2.9514 3.0741 3.1172 13.25% 0.61142 1.3798 1.8341 2.1831 2.4003 2.9348 3.0568 3.0994 15.10% 0.60259 1.3599 1.8076 2.1516 2.3657 2.8925 3.0128 3.0545 注: ω1—ω8分别为第1—8阶圆频率. 表 3 黄土隧洞围岩含水量与阻尼系数关系表
Table 3 The relationship between water content and damping coefficients of tunnel in loess surrounding rock
w η λ 7.42% 0.137 0.060 9.36% 0.132 0.062 11.95% 0.122 0.067 13.25% 0.121 0.068 15.10% 0.120 0.069 注: η为质量阻尼系数, λ为刚度阻尼系数. 表 4 黄土隧洞顶部含水量与地震峰值加速度关系表
Table 4 The relationship between water content and seismic peak acceleration of the loess tunnel roof
w t/s A/(m·s-2) 7.42% 2.22 2.029 9.36% 2.22 1.978 11.95% 2.22 1.943 13.25% 2.22 1.940 15.10% 2.22 1.933 注: A为地震峰值加速度. 表 5 黄土隧洞衬砌主应力及最大位移
Table 5 The principal stress and maximum displacement of the loess tunnel lining
w 衬砌位置 σmax/MPa σmin/MPa s/cm 7.42% 左拱肩 3.02 -2.64 2.72 右拱肩 2.64 -3.02 2.70 左拱脚 2.60 -2.97 2.69 右拱脚 2.96 -2.61 2.67 9.36% 左拱肩 2.97 -2.63 2.95 右拱肩 2.62 -3.00 2.92 左拱脚 2.58 -2.94 2.91 右拱脚 2.92 -2.58 2.89 11.95% 左拱肩 2.75 -2.55 3.52 右拱肩 2.52 -2.82 3.50 左拱脚 2.46 -2.57 3.48 右拱脚 2.56 -2.47 3.46 13.25% 左拱肩 2.09 -1.88 3.90 右拱肩 1.80 -2.16 3.87 左拱脚 1.73 -2.10 3.85 右拱脚 2.02 -1.83 3.83 15.10% 左拱肩 1.92 -1.67 4.12 右拱肩 1.58 -1.99 4.10 左拱脚 1.51 -1.84 4.08 右拱脚 1.84 -1.62 4.06 注:σmax为最大主应力,σmin为最小主应力,s为最大位移. -
林斌. 2005. 考虑损伤效应的黄土流变模型研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学地质工程与测绘学院: 22-45. Lin B. 2005. Research on Rheological Model of Loess in Considering of Damage Effect[D]. Xi’an: School of Geology Engineering and Geomatics, Chang’an University: 22-45 (in Chinese).
田瑞瑞. 2012. 粘弹性边界条件下方家湾黄土隧道结构的地震动稳定研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州理工大学土木工程学院: 19-38. Tian R R. 2012. The Study on Seismic Stability of Fangjiawan Loess Tunnel Structure Under Viscoelastic Boundary Condition[D]. Lanzhou: School of Civil Engineering, Lanzhou University of Technology: 19-38 (in Chinese).
翁祝梅, 毛丽华. 2006. 抗震[M]. 北京: 知识产权出版社: 204-222. Weng Z M, Mao L H. 2006. Anti-Seismic[M]. Beijing: Intellectual Property Publishing House: 204-222 (in Chinese).




 下载:
下载: