Focal mechanisms and seismic anisotropy analysis of local earthquakes at the Cove Fort-Sulphurdale geothermal site, United States.
-
摘要: Cove Fort-Sulphurdale位于美国犹他州中西部, 是一个地质特征独特的地热资源富集区. 为了有效开发地热资源, 有必要了解该地区的应力分布和裂缝分布. 本文在前人工作的基础上使用地震资料, 利用波形匹配、 P波极性和横纵波振幅比联合约束反演的方法, 研究该地区地震的震源机制解; 同时结合该地区的横波分裂分析研究, 确定该地区的应力分布和断层/裂隙走向. 波形反演结果显示, 实际数据与模拟数据的波形匹配度非常高, 且二者的P波初动极性和横纵波振幅比也都非常相近. 由震源机制分析得出的断层面走向大部分趋于南北向, 与美国区域应力图显示的最大水平主应力指向(南北方向), 具有较好的一致性, 符合目前研究对该地区的构造认知. 横波分裂分析结果也表明如果各向异性主要是由该地区的断裂构造所引起, 那么该地区的主要断层或裂缝的方向可能为南北向.
-
关键词:
- Cove Fort-Sulphurdale /
- 震源机制 /
- 波形匹配 /
- 区域地震 /
- 横纵波振幅比 /
- 地热横波分裂 /
- 各向异性 /
- anisotropy
Abstract: Cove Fort-Sulphurdale is located in central-western Utah, which is characterized by its unique geologic features and rich geothermal resources. For better development of geothermal reservoirs, it is necessary to have the know-ledge of stress and fracture distribution of the region. Based on the previous work, we use the waveform matching method to invert the focal mechanisms of local earthquakes collected in Cove Fort-Sulphurdale, constrained by first arrival P wave polarities and S/P amplitude ratios. Furthermore, we also use the shear wave splitting analysis method to study the anisotropy in this region. Combining both focal mechanism and anisotropy results, we can determine the stress distribution and fault/fracture directions. The results show that the waveforms of synthetic data match real data very well, and the first arrival P wave polarities and S/P amplitude ratios are close. Fault plane solutions have strikes trending in approximately N-S direction, which is consistent with the maximum horizontal principle stress indicated by the stress map of America and our current understanding of the tectonics in this region. Shear wave-splitting analysis results also show that if the anisotropy is mainly caused by the fault structure in this region, the strikes of the main faults/fractures should be in the N--S direction. -
-
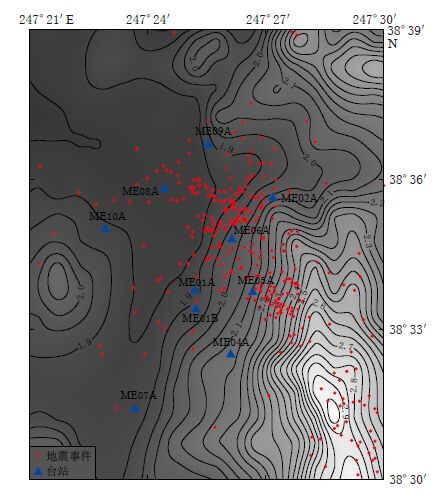
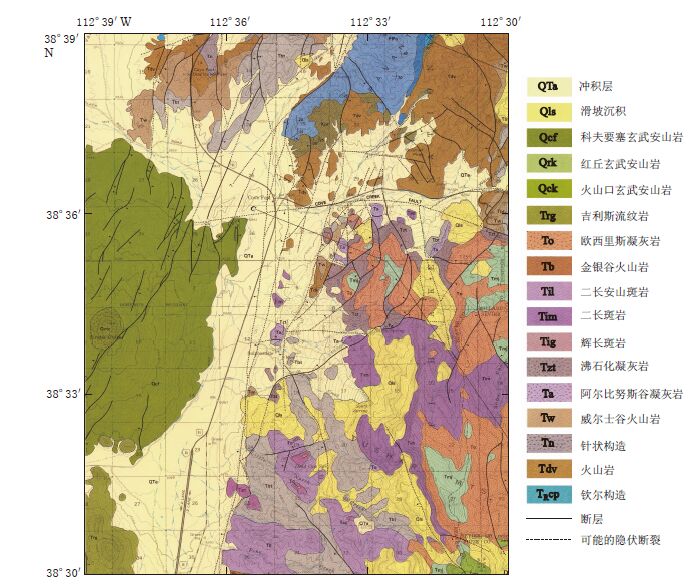
图 1 Cove Fort-Sulphurdale地热区域的地质图(引自Steven,Morris,1983)
Solid lines represent faults,dashed lines represent concealed faults that may exist, and rocks of different geological times are indicated in different colors
Figure 1. Regional geological map for the Cove Fort-Sulphurdale geothermal area(after Steven,Morris,1983)
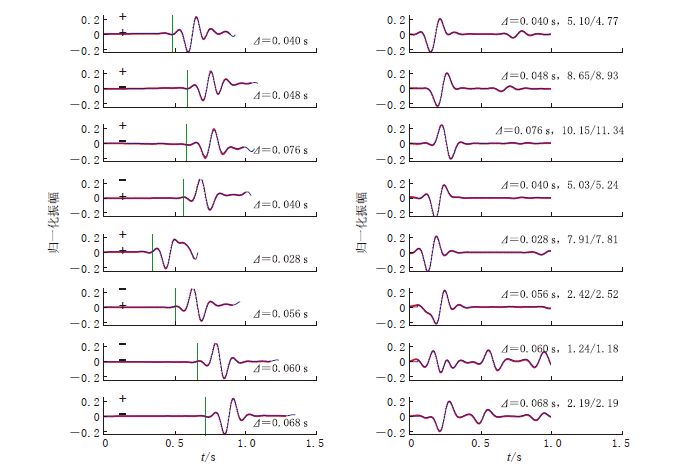
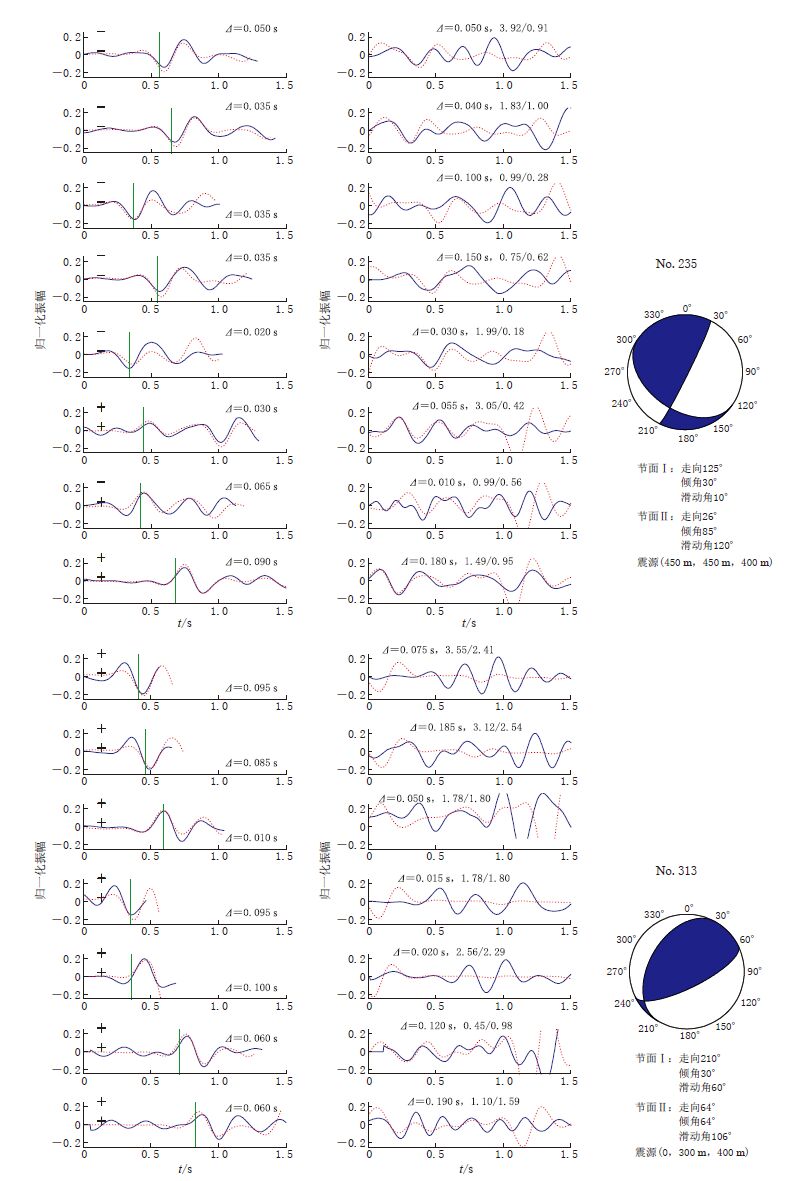
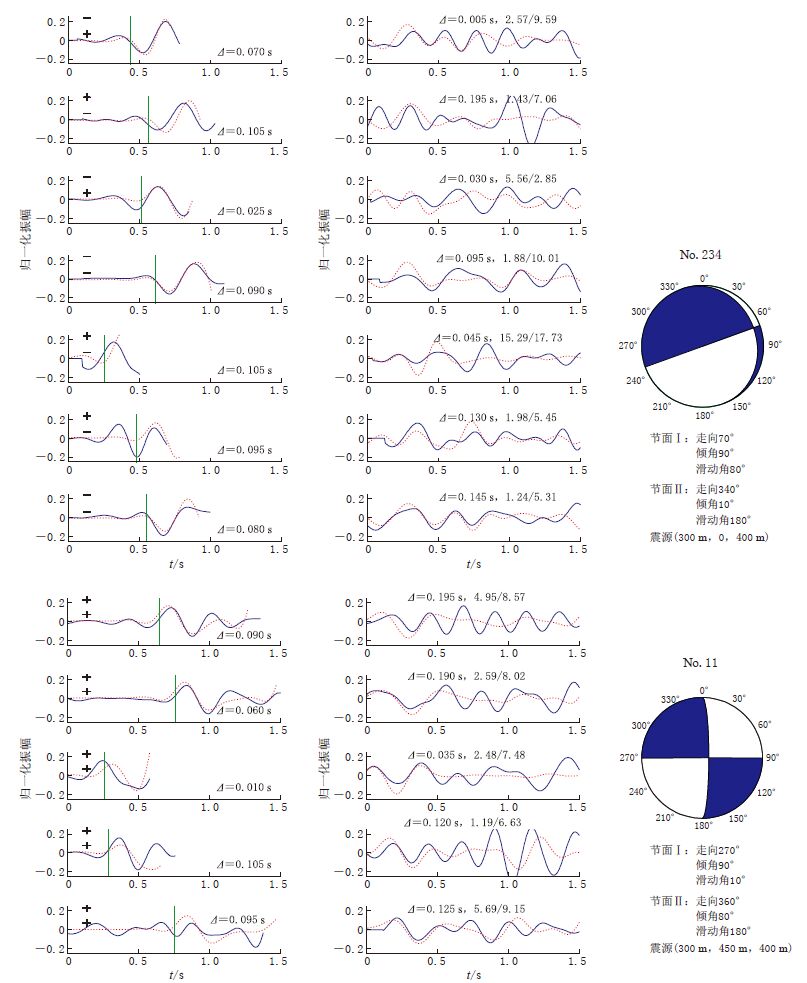
图 4 8个台站的模拟数据(红色点线)与合成数据(蓝色实线)的波形匹配图 左图为P波匹配结果,图中绿色竖线表示P波理论初至时间,零时刻代表记录开始时刻,上、下两个“+”或“-”分别表示合成数据和模拟数据的P波初动极性;右图为S波匹配结果,零时刻表示计算得到的S波开始时刻,最右侧数值表示横纵波振幅比信息,斜杠左边为合成数据的横纵波振幅比值,斜杠右边为相应的模拟数据的横纵波振幅比值.Δ 表示时移
Figure 4. Wave form matching between modelled (reddottedlines) and synthetic(bluesolidlines)waveforms at eight stations The left column shows P waves and right column shows S waves.The green lines indicate the calculated first P arrival times.For P waves,zero time means the origin time,“+"or“-"signs indicate the first arrival polarities of P waves inthedata(upper)and those in the synthetics(lower).For the S waves,zero time means the S-wave arrival time predicted by the calculated travel time,the number to the left of the slash denotes the S/P ratio for the data,the number to the right of the slash denotes the ratio for the modelled waveform.Δ indicates the time shift
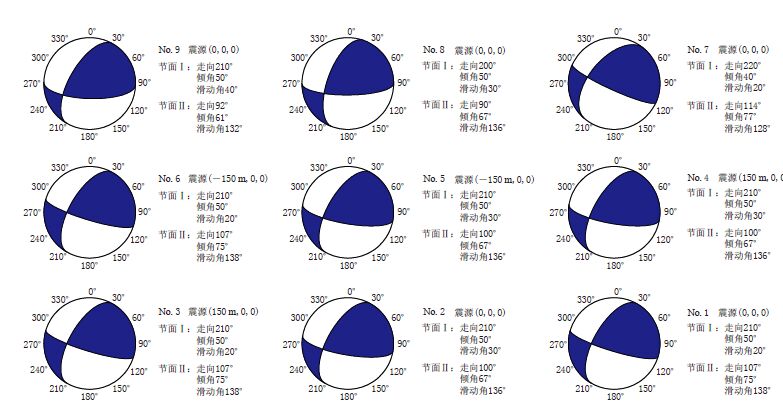
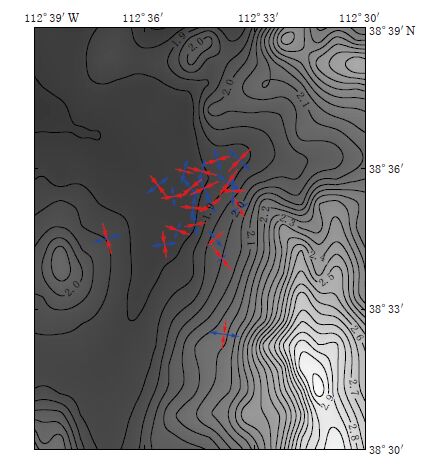
图 10 Cove Fort-Sulphurdale地区20个地震事件的P轴(红色)和T轴(蓝色)分布 轴线长短表示倾角大小,线段越短表示倾角越大
Figure 10. Distribution of P(red) and T(blue)axes determined from focal mechanisms of 20 seismic events in the Cove Fort-Sulphurdale area The length of axis indicates inclination with the shorter line representing greater inclination angle
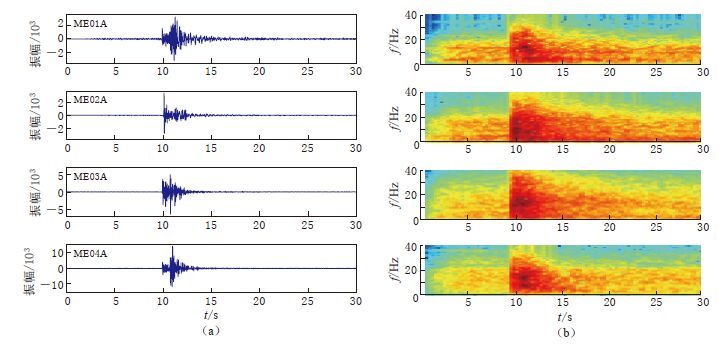
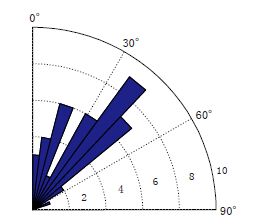
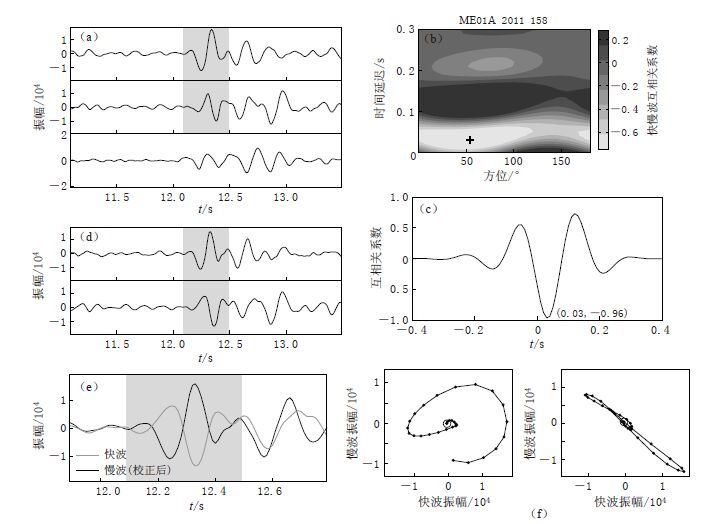
图 12 CDP方法横波分裂分析流程图 (a)ME01A台站的部分原始三分量记录,阴影部分表示用于横波分裂分析的窗口长度;(b)互相关函数值关于快波极化方向和慢波时间延迟的分布图. “+”表示最大互相关函数值,其对应的快波极化方向和慢波时间延迟分别为54°和0.03 s;(c)极化方向确定后,互相关函数值随慢波时间延迟的分布图;(d)旋转到快、 慢波极化方向后的水平分量波形图;(e)经时间延迟校正后的快慢波波形图;(f)慢波时间延迟校正前(左)、 后(右)的质点运动轨迹图
Figure 12. Shear wave splitting analysis flow chart using CDP method (a)Original three-component seismograms recorded on the station ME01A with the shadow part indicating the length of time window used in the shear wave-splitting analysis.(b)A contour plot of the cross-correlation coefficient values.The maximum cross-correlation coefficient value is indicated by the cross at the fast polarization direction(PD)54° and time delay(TD)0.03 s.(c)A plot of the cross-correlation coefficient values at the measured PD.(d)Seismograms rotated to the estimated fast and slow PDs.(e)Waveforms of the fast and slow components shifted with the measured TD.(f)The horizontal particle motion of the original seismogram(left panel) and that of the fast and slow components shifted with the measured TD(right panel)
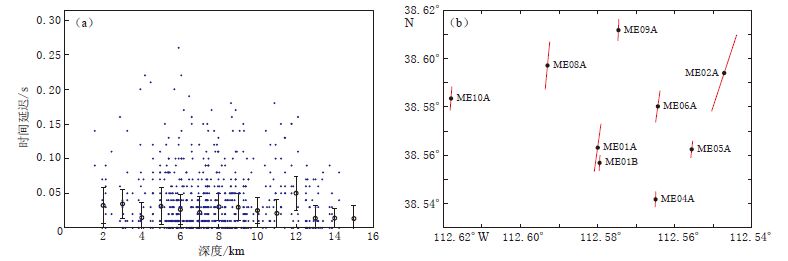
表 1 20个地震事件的震源参数
Table 1 Source parameters of 20 seismic events determined by the waveform matching method
事件序号 节面Ⅰ 节面Ⅱ P轴 T轴 走向/° 倾角/° 滑动角/° 走向/° 倾角/° 滑动角/° 方位/° 倾角/° 方位/° 倾角/° 11 270 90 -10 360 80 -180 -135.4 7.1 -44.6 7.1 116 10 90 120 100 30 10 73.4 37.8 -53.4 37.8 230 0 85 99 120 10 30 81.8 39.4 -80.2 49.2 234 160 90 80 340 10 180 -100.1 44.1 60.1 44.1 235 155 85 99 185 10 30 -123.2 39.4 74.8 49.2 259 140 90 -90 320 0 90 50.0 45.0 -130.0 45.0 267 290 70 10 197 81 160 -115.4 7.3 151.8 20.9 280 250 87 99 360 10 20 -28.5 41.3 169.4 47.3 285 200 80 -95 50 10 -60 103.9 54.7 -65.7 34.8 286 352 84 130 90 40 10 51.1 27.7 -62.9 37.8 299 20 80 90 200 10 90 110.0 35.0 -70.0 55.0 311 268 84 -130 170 40 -10 142.6 38.4 28.2 27.6 313 210 30 60 64 64 106 141.8 17.8 3.4 66.7 333 210 70 10 117 81 160 164.6 7.3 71.8 20.9 360 160 80 40 62 51 167 -75.1 19.0 28.7 34.8 402 260 80 10 168 80 170 -145.9 0.1 124.1 14.1 693 230 90 50 140 40 180 -7.3 32.8 107.3 32.8 761 340 90 60 250 30 180 96.6 37.8 -136.6 37.8 781 230 70 -10 323 81 -160 -171.8 20.9 95.4 7.3 841 140 80 -40 238 51 -167 91.3 34.8 -164.9 19.0 -
张欣, 张海江, Toksöz M N. 2012. 美国Utah州Cove Fort-Sulphurdale地区三维衰减层析成像研究[C]//中国地球物理学会第二十八届年会会议文集. 北京: 中国地球物理学会: 242. Zhang X,Zhang Haijiang, Toksöz M N. 2012. Three-dimensional seismic attenuation structure of the Cove Fort-Sulphurdale, Utah[C]//Proceeding of Chinese Geophysical Annual Meeting 2012. Beijing: Chinese Geophysical Society: 242 (in Chinese).
Moore J N, Samberg S M. 1979. Geology of the Cove Fort-Sulphurdale KGRA[R]. Utah: Univ Utah Res Inst, Earth Sci Lab, ESL-18: 44.
Nolet G, Dahlen F A, Montelli R. 2005. Traveltimes and amplitudes of seismic waves: A Reassessment[G]//Seismic Earth: Analysis of Broadband Seismograms. AGU Monograph Series, 157: 37-48.
Ross H P, Moore J N, Christensen O D. 1982. The Cove Fort-Sulphurdale KGRA: A Geologic and Geophysical Case Study[R]. Utah: Univ Utah Res Inst, Earth Sci Lab, ESL-90: 47.
Rutledge J T, Phillips W S. 2002. A comparison of microseismicity induced by gel-proppant-and water-injected hydraulic fractures, Carthage Cotton Valley gas field, East Texas[C]//72nd Annual International Meeting, SEG, Expanded Abstracts. Salt Lake: SEG: 2393-2396.
Steven T A, Morris H T. 1983. Geologic map of the Cove Fort quadrangle, west-central, Utah[EB/OL]. [2014-08-09]. http://ngmdb.usgs.gov/Prodesc/proddesc_9256.htm.
-
期刊类型引用(46)
1. 李皎皎,张永军,何怡原,李逸川,李诗珺,陈瑶. 基于航磁与小震精定位结果研究断裂构造特征——以攀西地区为例. 物探与化探. 2025(01): 206-214 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 吉宇,张广伟,任俊杰,何静,王肖薇. 基于背景噪声成像研究北京地区三维S波速度结构. 地震地质. 2025(01): 306-324 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 许永强,雷建设. 大同火山群及邻区中小地震重定位. 地震地质. 2024(02): 336-356 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 董春丽,张广伟,李欣蔚,王跃杰,丁大业,宫卓宏. 基于震源机制和地震定位研究2022年山西古交M_L4.1地震的发震构造. 地震地质. 2024(02): 414-432 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. Jinxin Hou,Yunpeng Zhang,Liwei Wang,Zhirong Zhao. Earthquake relocation using a 3D velocity model and implications on seismogenic faults in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Earthquake Research Advances. 2024(02): 55-64 .  必应学术
必应学术
6. 李佺洪,万永革. 采用模糊聚类算法确定2021年玛多地震序列的断层结构. 地球科学. 2024(09): 3363-3376 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 董春丽,王霞,李玉铰,梁永烨,丁大业,李云. 山西襄垣-潞城M_L2.8有感震动事件类型判别. 华北地震科学. 2023(03): 80-90 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 刘亢,杨婷,李红光,房立华,宋键. 小地震精定位与层析成像揭示的邢台地震区深部构造特征. 地震地质. 2023(06): 1328-1348 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 李玉丽,李启雷. 2021年西藏比如M_S6.1地震序列发震构造分析. 地震研究. 2022(01): 54-65 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 张丽娟,万永革,王福昌,靳志同,崔华伟. 采用模糊聚类算法确定2021年漾濞地震序列的断层结构. 地震地质. 2022(06): 1634-1647 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 钟世军,王治国,司政亚,孙海霞,岳晓媛,武敏捷. 北京地区小震精定位结果初步探讨. 中国地震. 2022(03): 513-525 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 潘黎黎,凌铭,李细光. 广西苍梧贺街-夏郢断裂遥感影像和小震分布. 华北地震科学. 2021(01): 32-41 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 徐志国,梁姗姗,郭铁龙,史健宇,李旭茂. 2020年7月12日唐山古冶M_(S)5.1地震震源参数. 地震地磁观测与研究. 2021(03): 25-33 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 陈晓,凌铭,邵金全,王欲成,彭爽. 河池-宜州-柳城断裂带小震精定位前后结果对比分析. 冶金管理. 2021(23): 25-26 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 梁姗姗,邹立晔,赵博,刘敬光,刘艳琼,姬运达,李旭茂,翟璐媛. 中国测震台网地震监测能力初步分析. 地震地磁观测与研究. 2021(06): 68-75 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 赵红坤,王万丽,周晓成,石宏宇,孙玉涛,刘永梅. 山西地震带北段与张家口——渤海地震带不同深度CO_2和Rn气体通量的差异性. 地震地磁观测与研究. 2020(02): 113-122 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 陈瑛,梁晓峰,闫宏芳,姜明明,艾印双. 郯庐断裂渤海湾北段地震活动及其指示意义. 地球物理学报. 2020(07): 2566-2578 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 李炎臻,李红谊,张力方,黄雅芬,刘敏,葛慧颖,吕悦军. 基于模板匹配定位法的江苏盐城附近微震检测和构造分析. 中国地震. 2020(03): 581-593 .  百度学术
百度学术
19. 葛慧颖,李红谊,黄雅芬,王同利,刘敏,李炎臻. 波形模板匹配定位方法在北京地区的应用. 震灾防御技术. 2020(04): 788-801 .  百度学术
百度学术
20. 谢张迪,韩竹军. 2014年云南景谷M_S6.6地震发震断层及其动力学参数. 地震地质. 2019(04): 887-912 .  百度学术
百度学术
21. 杨宇,雷建设,张广伟,梁姗姗,孙长青,米琦,鲁明文,杜沫霏,张冰,田凡凡,何静,王健,吴宝峰,马晨,刘泽民. 前郭M_S5.8和松原M_S5.7地震震源区地壳速度结构与孕震环境. 地球物理学报. 2019(11): 4259-4278 .  百度学术
百度学术
22. 段虎荣,闫全超,李闰,陈胜雷. 基于随机抽样一致性-网格搜索方法反演断层面倾角. 地震学报. 2019(05): 585-599+680 .  本站查看
本站查看
23. 曲中党,张训华,贺日政,吴志强,张洪双,吴蔚. 华北盆地边缘及邻区地壳S波速度结构及其地震孕育机制. 地球物理学进展. 2018(03): 957-968 .  百度学术
百度学术
24. 谢卓娟,吕悦军,方怡,史丙新. 京津冀地区地震重新定位及其与活动断裂的关系. 地震. 2017(03): 72-83 .  百度学术
百度学术
25. 陈成沟,邢成起,胡乐银,武敏捷,岳晓媛. 北京及其邻区小震重定位与活动构造分析. 地震. 2017(03): 84-94 .  百度学术
百度学术
26. 梁姗姗,徐志国,杜广宝,刘敬光,张广伟. 2013年甘肃岷县—漳县M 6.6地震序列精定位研究. 地震地磁观测与研究. 2017(02): 12-16 .  百度学术
百度学术
27. 蔡玲玲,李冬圣,孟立朋,常亮,温超,王宁. 京西北地区地震重定位分析. 地震地磁观测与研究. 2017(03): 47-52 .  百度学术
百度学术
28. 王喜龙,李营,杜建国,陈志,周晓成,李新艳,崔月菊,王海燕,张志宏. 首都圈地区土壤气Rn, Hg, CO_2地球化学特征及其成因. 地震学报. 2017(01): 85-101+155 .  本站查看
本站查看
29. 陈佳维,崔效锋,胡幸平. 唐山及周边地区中小地震重定位及其构造特征. 华北地震科学. 2017(01): 1-9 .  百度学术
百度学术
30. 张洪艳,马铭志,刘轶男,卢燕红,陈聪. 吉林前郭地区一维P波速度模型研究. 防灾减灾学报. 2016(03): 19-24 .  百度学术
百度学术
31. 王健,李春峰,雷建设,张广伟. 华北地区地震活动与地壳热结构关系研究. 地震学报. 2016(04): 618-631+658 .  本站查看
本站查看
32. 郑培玲,邢康,王明亮,贾漯昭,何重阳,高家乙. 河南范县及邻区地震精定位及震源机制解分析. 中国地震. 2016(04): 710-717 .  百度学术
百度学术
33. 魏红梅,王同军. 重庆及邻区地震精定位研究. 地震地磁观测与研究. 2015(01): 55-59 .  百度学术
百度学术
34. 孙晴,李守勇. 利用小震震源机制解反演濮阳地区应力场. 华北地震科学. 2015(04): 14-19 .  百度学术
百度学术
35. 张洪艳,张广伟,王晓山,盛俭,卢燕红,张宇. 2013年吉林前郭5.8级震群精定位及发震构造分析. 中国地震. 2015(03): 518-528 .  百度学术
百度学术
36. 陈筱青,于湘伟. 联合多种定位方法对华北地区地震重定位研究. 中国科学院大学学报. 2015(02): 243-251+280 .  百度学术
百度学术
37. 魏红梅,许顺洪. 基于Matlab的震中及深度分布绘制软件编制. 防灾减灾学报. 2014(04): 62-65 .  百度学术
百度学术
38. 蔡妍,吴建平,房立华,王未来,黄静. 鄂尔多斯东缘地震重定位及拉张盆地过渡区的地震分布特征. 地球物理学报. 2014(04): 1079-1090 .  百度学术
百度学术
39. 魏红梅,黄世源,许顺洪. 基于Matlab的震中分布图绘制软件应用. 地震地磁观测与研究. 2014(Z3): 299-302 .  百度学术
百度学术
40. Jianshe Lei,Guangwei Zhang,Furen Xie. The 20 April 2013 Lushan, Sichuan, mainshock, and its aftershock sequence: tectonic implications. Earthquake Science. 2014(01): 15-25 .  必应学术
必应学术
41. 王福昌,万永革,钱小仕,张丽娟,张梅东. 由地震分布丛集性给出断层参数的一种新方法. 地球物理学报. 2013(02): 522-530 .  百度学术
百度学术
42. 张广伟,雷建设. 四川芦山7.0级强震及其余震序列重定位. 地球物理学报. 2013(05): 1764-1771 .  百度学术
百度学术
43. 汪锐,谭成轩,安美建,冯梅,卢君,张劲松,毛星. 结合波形互相关的双差定位在北京西北地区地震活动性研究中的应用. 地学前缘. 2013(04): 115-124 .  百度学术
百度学术
44. 胡幸平,崔效锋. 华北地区中部地震精定位与构造应力场研究. 震灾防御技术. 2013(04): 351-360 .  百度学术
百度学术
45. 王福昌,靳志同,钱小仕,任晴晴,霍振香. 由余震分布确定大地震子断层及其参数的模糊聚类方法. 地震学报. 2012(06): 793-803+879 .  本站查看
本站查看
46. Relocation of the 10 March 2011 Yingjiang, China, earthquake sequence and its tectonic implications. Earthquake Science. 2012(01): 103-110 .  必应学术
必应学术
其他类型引用(17)




 下载:
下载: