Medium inhomogeneity of mid-upper crust beneath the middle segment of Tancheng-Lujiang fault zone
-
摘要: 利用山东省和江苏省数字地震台网24个台站的269个小震记录, 采用散射S波包络展宽法对郯庐断裂带中段中上地壳小尺度介质非均匀性进行了研究. 结果表明: 郯庐断裂带中段中上地壳介质呈现强烈的横向非均匀性, 该断裂带为不同强度、 不同尺度介质非均匀体分布的边界; 强弱介质非均匀性边界往往与深部构造发育具有较强的相关性; 中强震孕育与强弱非均匀体的分布有关, 地震多发生在强弱非均匀体的过渡带上. 郯庐断裂带中上地壳介质非均匀分布特征可能与苏鲁超高压变质带、 深部构造及岩浆活动有关.Abstract: On the basis of 269 small earthquakes recorded by the 24 stations of Jiangsu and Shandong digital seismograph networks, this paper studies the small-scale medium inhomogeneity of mid-upper crust beneath the middle segment of Tancheng-Lujiang fault zone by using the scattering S-wave envelope broadening method. The results reveal that strong inhomogeneity exists in the mid-upper crust beneath the middle segment of Tancheng-Lujiang fault zone, and the Tancheng-Lujiang fault zone is the boundary of the medium with different inhomogeneity strength and different inhomogeneity scale. The deep structures are strongly correlative with the boundary of the strong and the weak inhomogeneity. The results also show that the developments of the moderate-strong earthquakes are related with the distribution of the strong and the weak inhomogeneity bodies, and moderate-strong earthquakes generally occur at the transitional zone of the strong and the weak inhomogeneity bodies. The distribution characteristics of medium inhomogeneity in the mid-upper crust beneath the middle segment of Tancheng-Lujiang fault zone maybe relate with ultra-high pressure metamorphic belt, deep structures and magma activity.
-
-
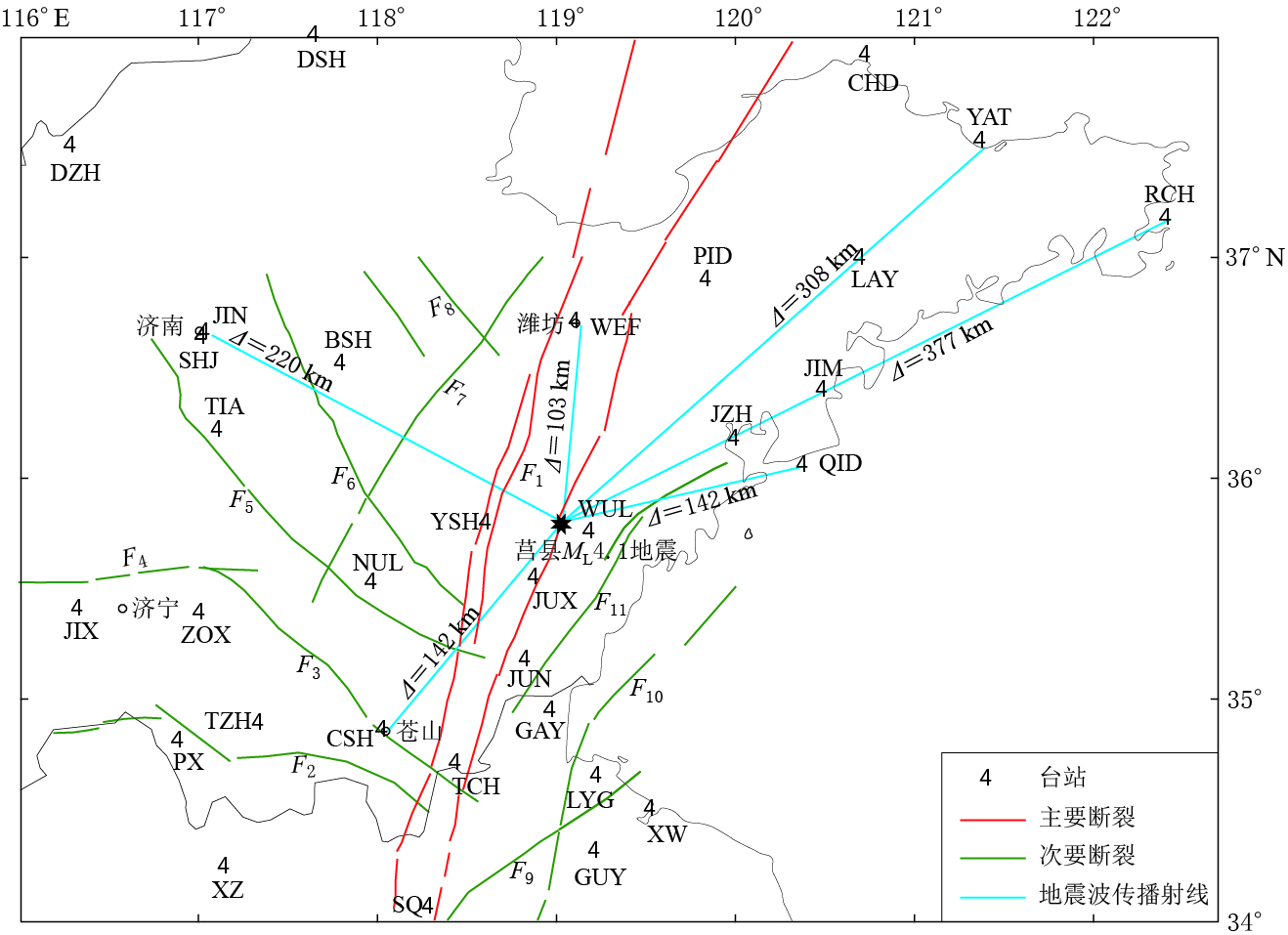
图 1 研究区主要断裂及观测台站分布
F1: 郯庐断裂带; F2: 韩庄断裂; F3: 苍尼断裂; F4: 郓城断裂; F5: 蒙山山前断裂; F6: 莱芜断裂; F7: 上五井断裂;F8: 益都断裂 ; F9: 邵店—桑墟断裂 ; F10: 海泗断裂; F11: 五莲—荣城断裂 F1: Tancheng-Lujiang fault zone; F2: Hanzhuang fault; F3: Cangni fault; F4: Yuncheng fault;F5: Mengshan piedmont fault; F6: Laiwu fault; F7: Shangwujing fault; F8: Yidu fault; F9: Shaodian-Sangxu fault; F10: Haisi fault; F11: Wulian-Rongcheng fault
Figure 1. Distribution of main faults and observation stations (triangles) in the studied area
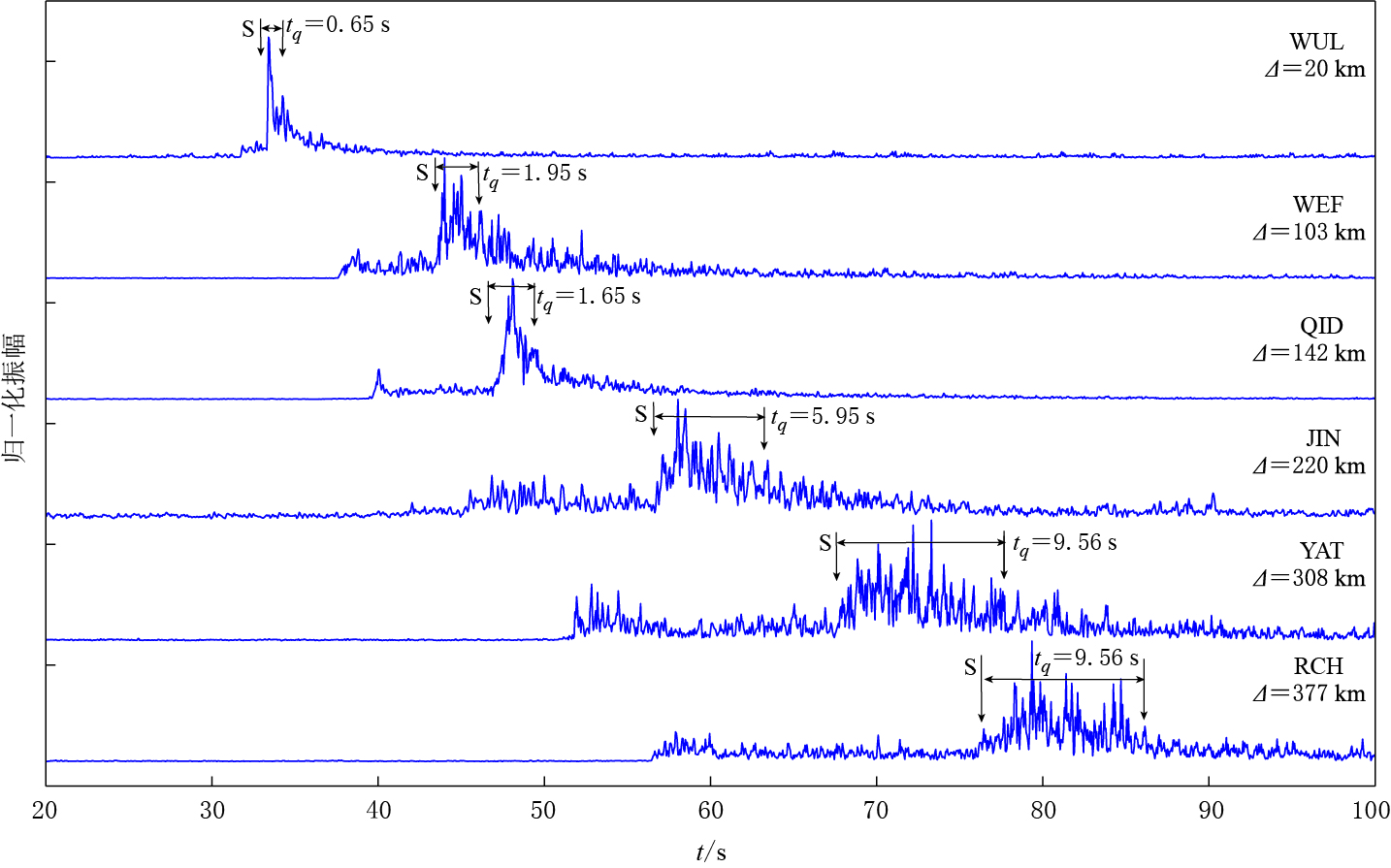
表 1 不同震中距的散射S波包络宽度
Table 1 Time lag of scattering S-wave envelope of different epicentral distances
台站 Δ/km tq/s tqu/(s·km-1)
WUL20 0.65 0.325 WEF 103 1.95 0.019 QID 142 1.65 0.012 JIN 220 5.95 0.027 YAT 308 9.56 0.031 RCH 377 10.67 0.028 表 2 相近震中距散射S波包络宽度
Table 2 Time lag of scattering S-wave envelope for the stations with similar epicentral distances
台站 Δ/km tq/s tqu/(s·km-1)
WEF103 1.95 0.019 QID 142 1.65 0.012 CSH 142 9.75 0.069 -




 下载:
下载: