Precise earthquake relocation of double seismic zone beneath Tohoku region in Japan
-
摘要: 日本所在的西太平洋地区是世界上中深源地震发生最为频繁的地区. 早期研究已表明, 日本东北地区下方的中深源地震呈双层分布. 为进一步分析该双震带的空间分布特征, 本文通过方法测试证明了采用球坐标系下的三维射线追踪法改进后的双差定位法进行地震重定位的精确性和有效性, 对使用该方法进行重定位前、 后各方向上的误差进行了分析, 并确定了最佳的定位参数. 在此基础上, 对日本东北地区的中深源地震进行了高精度重定位, 并对重定位得到的震源位置进行了空间拟合, 其结果表明地震呈明显的双层分布, 且与西太平洋俯冲板块几近平行. 本文研究结果对揭示双震带中地震的发震机理以及俯冲板块内的精细结构均具有重要意义.Abstract: Japan is located in western Pacific, where the intermediate-deep earthquakes occur frequently. Early researches indicate that the intermediate-deep earthquakes beneath Tohoku region in Japan constitute a double seismic zone. In order to analyze the spatial distribution characteristics of the double seismic zone in Tohoku region, we use a method test to show the precision and validity of the double-difference location algorithm, which has been improved by 3-D ray tracing method in spherical coordinate system. We analyse the errors before and after relocation along different directions, and determine the most suitable parameters for relocation. Then we obtain the precise relocated earthquakes in the double seismic zone beneath Tohoku region, and fit the relocated hypocenters in three-dimensional space. The relocation results of intermediate-deep earthquakes in Tohoku region indicate that the earthquakes in the seismic zone are distributed obviously in double layers, which are approximately parallel to the subducting western Pacific Plate. The results of this paper are significant to reveal the mechanisms of earthquakes in double seismic zone and the fine structures in the deep subduction zones.
-
引言
俯冲带的俯冲形态是地球科学的研究热点之一,是板块构造研究的基础问题. 日本列岛周围存在着4大板块: 东部的太平洋板块,西部的欧亚板块,南部的菲律宾海板块和北部的北美板块(鄂霍次克板块). 其中,太平洋板块年龄最老,约为170 Ma(Bartolini,Larson,2001),且较为活跃,以10 cm/a的平均速度俯冲至日本列岛下方,直接导致日本成为地震多发地区. 环太平洋俯冲带内的中深源地震,在空间上呈明显的分层分布,且各层的地震具有不同的震源机制,即双震带现象. 日本双震带充分证明了西太平洋板块的深俯冲现象. 江国明等(2008)指出,日本地区太平洋俯冲板块的平均厚度为85 km,日本东北地区和北海道地区下方洋壳深度均为110 km,洋壳平均厚度分别为7.5 km和5.0 km,平均速度变化幅度分别为1%和3%. 洋壳俯冲至110 km深处时,由于受温度和压力的影响,洋壳逐渐脱水、 变质,直至与上地幔顶部融合. 还有研究者针对环太平洋俯冲带内的双震带,提出了抗弯作用(Kawakatsu,1986)、 脱水作用(Seno et al,2001; Dobson et al,2002; Perrillat et al,2005)和相变断层(Kirby et al,1991; Kirby,1996; Shiro,Sadaki,2002)等模型来解释地震的成因,这些模型均反映了板块内应力状态在某种因素作用下的重新分布,并能解释不同深度双震带应力分布的成因,但也不同程度地显示了各自的缺陷和不足. 事实上,迄今为止尚无一种双震带应力模型可以完全解释深度大于30 km的地震成因(张克亮,魏东平,2008). 所以,对双震带类型的判断尤为重要,只有准确判断出双震带形态,才能选取合适的模型进行研究. 而地震定位或重定位的精度,对于判断地震带形态最为关键.
地震定位是地震学中的基础研究问题,其对地震活动特性、 地球内部结构、 震源的几何构造等研究均具有重要意义(田玥,陈晓非,2002). 早期的地震定位方法以几何作图法为主(如交切圆法等),后续的地震常规定位方法多源于Geiger(1912)提出的方法,即以走时残差为观测数据反演震源的4个参数. 诸多研究者对该方法进行了改进,例如: Klein(1978)提出了HYPO-INVERSE算法; Nelson和Vidale(1990)改进了该算法,提出三维速度模型中的QUAKE3D法; 赵仲和(1983)采用改进后的常规方法编写了HYPO81BJ程序; 吴明熙等(1990)对常规方法进行改进,提出了“合成法”. 这些方法均使得定位精度不断提高.
为了降低或消除地层速度结构对地震定位的影响,Waldhauser和Ellsworth(2000)提出了双差定位法,是目前公认的一种较好的定位方法. 其基本思想为,在两个震源间的距离相对于震源中心到观测台站的距离和两震源周围速度变化均较小的情况下,这两个震源到同一观测台站的射线路径基本相同,使得两震源在该台站上的走时残差与两震源间的距 离密切相关,而与射线经过地层的速度关系不大,故双差定位法能够降低地层速度结构对定位结果的影响,从而提高定位精度. 国内研究者曾用Waldhauser和Ellsworth(2000)编写的hypoDD程序对我国不同地区的地震进行了重定位,均取得了较好的结果(荣代潞,李亚荣,2004; 王小平等,2005; 李永红等,2006; 杨中书,曾文敬,2007; 于湘伟等,2010; 刘文邦等,2011; 莘海亮等,2011; Yu et al,2011; 赵博等,2013; 王未来等,2014; 李红光等,2015).
江国明等(2009)研究显示Waldhauser和Ellsworth(2000)提出的双差定位法在较早的研究中(杨智娴等,2003; 杨智娴,陈运泰,2004; Yang et al,2005),由于采用一维射线追踪法和直角坐标系,故不适合复杂速度模型中的地震定位,且深源地震定位时须考虑地球为球体而不能简单地使用直角坐标系,于是提出了采用球坐标系下的三维射线追踪法改进后的双差定位法. 该方法扩大了双差定位法的应用范围,提高了深震定位精度,为利用深源地震研究地球深部构造奠定了基础.
本文将采用江国明等(2009)提出的改进后的双差定位法,在使用绝对定位法得到的原始数据基础上,对日本东北地区双震带进行了高精度重定位,并通过定位结果分析震源位置与板块俯冲形态之间的关系,以加深对日本东北地区双震带的认识.
1. 数据
本文选用日本气象厅和Hi-net台网记录的2002年6月—2009年7月的深源地震P波到时数据,共22万8337条,误差不超过0.1 s; 具体地震台站分布如图 1所示.
根据本文研究需要,按照以下条件对所选的数据进行筛选: ① 地震震级无限制; ② 震源所在纬度为38°N—40°N; ③ 震源深度为80—200 km; ④ 地震数据同时被至少20个台站接收. 由此得到了5340次地震事件,其震中分布如图 2所示.
2. 方法测试
为验证改进后的双差定位法(江国明等,2009)的有效性和精确性,在实际地震定位前进行了方法测试,其具体步骤为: ① 对原始震源位置在水平方向和深度方向上分别加入均方差为5 km和3 km的随机误差,将所形成的新的震源位置作为“真实震源位置”; ② 根据全球一维速度模型IASP91,使用走时正演模拟法所得到的速度结构构建三维速度模型(江国明等,2008),即板块内速度变化幅度为5%(高速),地幔楔内为-3%(低速),地壳内为1%(低速); ③ 在所构建的三维速度模型中,根据“真实震源位置”和原始台站分布,利用三维射线追踪法获得理论到时数据,并在其中加入方差为0.1 s的随机误差,形成“观测数据”; ④ 以原始震源位置为初始位置,以IASP91模型为定位时的速度模型,利用改进的双差定位法对“观测数据”进行反演,并将重定位的震源位置与“真实震源位置”进行对比,以验证该定位方法的可靠性,并由此确定最佳的定位参数. 通过调试迭代次数i、 最大成对距离smax和阻尼系数d,将不同参数得到的定位结果与“真实震源位置”进行比较,以确定理论上的最佳设置参数.
使用双差定位法时,仍采用hypoDD定位程序双重循环的迭代思想,即外循环和内循环. 每次外循环包含若干次内循环; 每次内循环时,所用的定位参数均相同; 但每次外循环时,这些参数可以发生改变. 此外,外循环与内循环最大的区别是: 每次外循环时需要重新成对,而内循环时则无需此步骤.
方法测试过程中发现,如果阻尼系数较小,定位后结果与真实值偏差极大. 因此需要通过调整阻尼系数,并增加迭代次数,以期获得更好的定位结果.
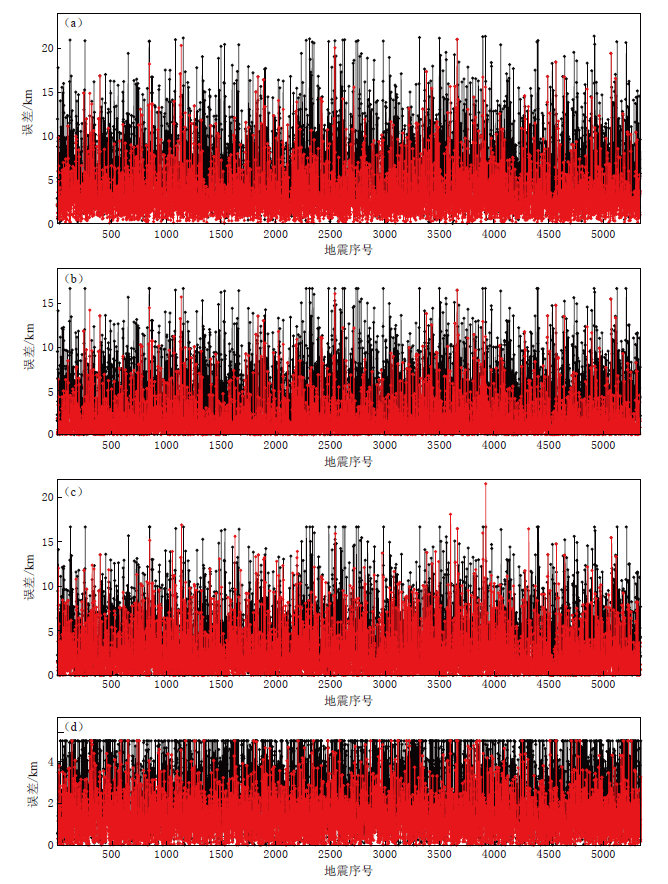
图 3为方法测试时初始震源位置与“真实震源位置”之间的距离(黑色直线)以及重定位后震源位置与“真实震源位置”之间的距离(红色直线). 双差法的定位参数为外循环lout为3次,每次外循环中内循环linn为2次,最大成对距离smax为5 km,阻尼系数d为50. 可以看出,原始震源位置与“真实震源位置”间的误差比较大,而重定位后误差则较小. 通过计算可得,原始定位数据的均方根误差为7.5 km,而采用上述双差定位法重定位后的均方根误差为4.1 km; 与其它定位参数的结果相比(表 1),该参数设置下的均方根误差最小.
![]() 图 3 方法测试中重定位前、 后误差的对比 (a) 总误差; (b) 纬度方向误差; (c) 经度方向误差; (d) 深度方向误差 黑色点线表示重定位前误差, 红色点线表示重定位后误差Figure 3. Comparison of errors before relocation with those after relocation in method test (a) Total errors; (b) Errors along latitude direction; (c) Errors along longitude direction; (d) Errors along depth direction. The black and red dotted lines represent the errors before and after relocation, respectively表 1 不同迭代次数i, 最大成对距离smax和阻尼系数d下的重定位后的均方根误差Table 1. RMS errors of relocated results in different iteration i, maximum pairwise distance smax and damping coefficient d
图 3 方法测试中重定位前、 后误差的对比 (a) 总误差; (b) 纬度方向误差; (c) 经度方向误差; (d) 深度方向误差 黑色点线表示重定位前误差, 红色点线表示重定位后误差Figure 3. Comparison of errors before relocation with those after relocation in method test (a) Total errors; (b) Errors along latitude direction; (c) Errors along longitude direction; (d) Errors along depth direction. The black and red dotted lines represent the errors before and after relocation, respectively表 1 不同迭代次数i, 最大成对距离smax和阻尼系数d下的重定位后的均方根误差Table 1. RMS errors of relocated results in different iteration i, maximum pairwise distance smax and damping coefficient di smax/km d RMS/km 3×1 2 50 7.0 3×1 5 45 4.3 3×2 5 45 4.3 3×1 5 50 4.3 3×1 5 100 5.1 3×2 5 50 4.1 使用上述最佳参数设置对“观测数据”进行重定位前、 后,震源在纬度、 经度和深度3个方向上的误差分布如图 4所示. 可以看出,“观测数据”中的大部分地震经过重新定位后3个方向上的误差均小于2 km,这表明改进后的双差法有效地减小了定位误差,适用于中深源地震的高精度定位. 需要特别说明的是,这里所说的初始震源位置与“真实震源位置”之间的距离减小是由于提高了定位的精确度所致,而不是由于改善了准确度.
![]() 图 4 方法测试中重定位前(上)、 后(下)的误差分布对比 (a) 总误差; (b) 纬度方向误差; (c) 经度方向误差; (d) 深度方向误差Figure 4. Comparison of errors before relocation (upper panels) with those after relocation (lower panels) in method test (a) Total errors; (b) Errors along latitude direction; (c) Errors along longitude direction; (d) Errors along depth direction
图 4 方法测试中重定位前(上)、 后(下)的误差分布对比 (a) 总误差; (b) 纬度方向误差; (c) 经度方向误差; (d) 深度方向误差Figure 4. Comparison of errors before relocation (upper panels) with those after relocation (lower panels) in method test (a) Total errors; (b) Errors along latitude direction; (c) Errors along longitude direction; (d) Errors along depth direction此外,纬度、 经度和深度方向上重定位后误差在2 km范围内的样本占总体比值分别 为75%,61%和77%,表明深度方向上的重定位效果最好,可能是由于震源位于台站下方使得深度方向比水平方向上的约束强所致.
3. 日本东北地区双震带重定位
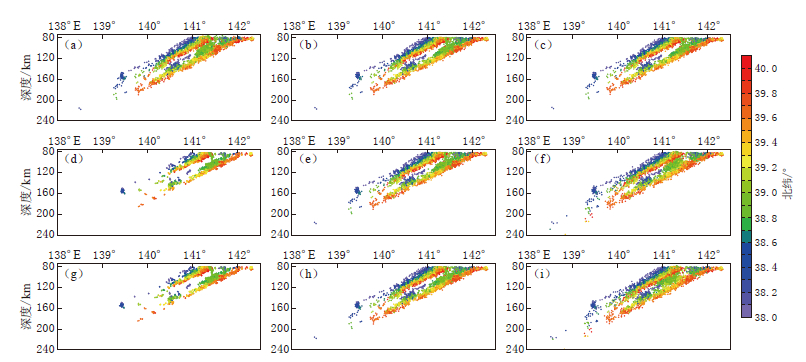
在方法测试的基础上,本文采用球坐标系下的三维射线追踪法改进后的双差定位法对日本东北地区的中深源地震进行重定位. 选取不同的定位参数,外循环次数lout为1—3,最大成对距离smax为1—10 km(步长为1 km),阻尼系数d为0—100(步长为5),共计630种参数组合,运行定位程序得到了相应的定位结果. 对630种重定位结果进行抽样,采用Surfer软件绘制出重定位后的震源位置剖面投影图,如图 5所示.
![]() 图 5 采用不同迭代次数i, 最大成对距离smax和阻尼系数d所得到的重定位后的震源位置剖面投影图 (a) i=1, smax=5 km, d=5; (b) i=1, smax=5 km, d=50; (c) i=1, smax=5 km, d=100; (d) i=2, smax=2 km, d=50; (e) i=2, smax=5 km, d=50; (f) i=2, smax=8 km, d=50; (g) i=3, smax=2 km, d=50; (h) i=3, smax=5 km, d=50; (i) i=3, smax=8 km, d=50Figure 5. Projections of relocated epicenters using different iteration i, maximum pairwise distance smax and damping coefficient d (a) i=1, smax=5 km, d=5; (b) i=1, smax=5 km, d=50; (c) i=1, smax=5 km, d=100; (d) i=2, smax=2 km, d=50; (e) i=2, smax=5 km, d=50; (f) i=2, smax=8 km, d=50; (g) i=3, smax=2 km, d=50; (h) i=3, smax=5 km, d=50; (i) i=3, smax=8 km, d=50
图 5 采用不同迭代次数i, 最大成对距离smax和阻尼系数d所得到的重定位后的震源位置剖面投影图 (a) i=1, smax=5 km, d=5; (b) i=1, smax=5 km, d=50; (c) i=1, smax=5 km, d=100; (d) i=2, smax=2 km, d=50; (e) i=2, smax=5 km, d=50; (f) i=2, smax=8 km, d=50; (g) i=3, smax=2 km, d=50; (h) i=3, smax=5 km, d=50; (i) i=3, smax=8 km, d=50Figure 5. Projections of relocated epicenters using different iteration i, maximum pairwise distance smax and damping coefficient d (a) i=1, smax=5 km, d=5; (b) i=1, smax=5 km, d=50; (c) i=1, smax=5 km, d=100; (d) i=2, smax=2 km, d=50; (e) i=2, smax=5 km, d=50; (f) i=2, smax=8 km, d=50; (g) i=3, smax=2 km, d=50; (h) i=3, smax=5 km, d=50; (i) i=3, smax=8 km, d=50由图 5可以看出: 当最大成对距离设置得较小时(如图 5d,g),满足条件的原始地震数目变少,因此得到的结果中样本点也较少,虽然也能反映出双震带的基本形态,但却丢失了较多的地震事件; 而如果将最大成对距离设置过大,又会造成组内两个震源到同一台站间的速度结构存在较大差异,增大系统误差,导致双差法定位失去优势. 经过反复测试,本文最终选择5 km作为最大成对距离.
当阻尼系数较小时(图 5a),重定位时每一次迭代都会造成定位结果偏离原始值较大距离,增加迭代次数后误差也增大; 而当阻尼系数较大时(图 5c),每次迭代求解后,新结果与原始位置偏离较小,多次迭代后系统不能保持稳定. 结合方法测试时的结果确定最佳阻尼系数为50.
从图 5b,e,h可以看出,最大成对距离为5 km,阻尼系数为50,分别迭代1,2,3次时,相对于重定位前震源位置,重定位后震源的分布成层性较好,相近震源更加集中. 我们将该组参数迭代3次的重定位结果与原始震源位置绘制成剖面投影图(图 6). 考虑到图 5跨越了2°的纬度范围,不同纬度线剖面上的地震分布会发生重叠,从而导致层面判别不清,且不便于分析其空间形态,故将研究区域分为38°N—39°N和39°N—40°N两个剖面进行分别绘制(图 7c,d),并以同样方法对原始震源位置进行绘制(图 7a,b). 可以看出,重定位后地震更加集中,成层性更好.
![]() 图 7 不同纬度范围内重定位前、 后震源位置剖面投影图 (a) 重定位前, 纬度为38°N—39°N; (b) 重定位前, 纬度为39°N—40°N;(c) 重定位后, 纬度为38°N—39°N; (d) 重定位后, 纬度为39°N—40°NFigure 7. Projections of epicenters of different latitude ranges before and after relocation (a) Before relocation, latitude range is 38°N--39°N; (b) Before relocation, latitude range is 39°N--40°N; (c) After relocation, latitude range is 38°N--39°N; (d) After relocation, latitude range is 39°N--40°N
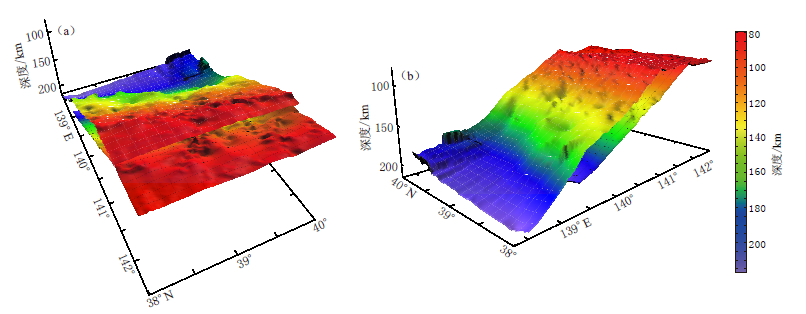
图 7 不同纬度范围内重定位前、 后震源位置剖面投影图 (a) 重定位前, 纬度为38°N—39°N; (b) 重定位前, 纬度为39°N—40°N;(c) 重定位后, 纬度为38°N—39°N; (d) 重定位后, 纬度为39°N—40°NFigure 7. Projections of epicenters of different latitude ranges before and after relocation (a) Before relocation, latitude range is 38°N--39°N; (b) Before relocation, latitude range is 39°N--40°N; (c) After relocation, latitude range is 38°N--39°N; (d) After relocation, latitude range is 39°N--40°N为了更清楚地了解地震带的空间分布形态和产状特征,我们对重定位后的数据进行了空间拟合,并绘制出三维图像,用两个曲面拟合双震带每一层的上表面,如图 8所示. 可以看出,双震带分布于两个倾斜曲面,在深部(180 km附近)两曲面倾角略微变缓,并呈现出逐渐汇合的趋势,宏观上双震带走向均为NNE向. 我们还将重定位后的数据用两个平面进行拟合,得到上、 下层的倾角分别为28.8°和26.4°. 而Zhao等(1997)的研究已表明,日本东北地区50 km深度以下的板块俯冲倾角约为30°,且38°N以北区域俯冲板块为NNE走向,可见双震带与俯冲板块近于平行分布.
4. 讨论与结论
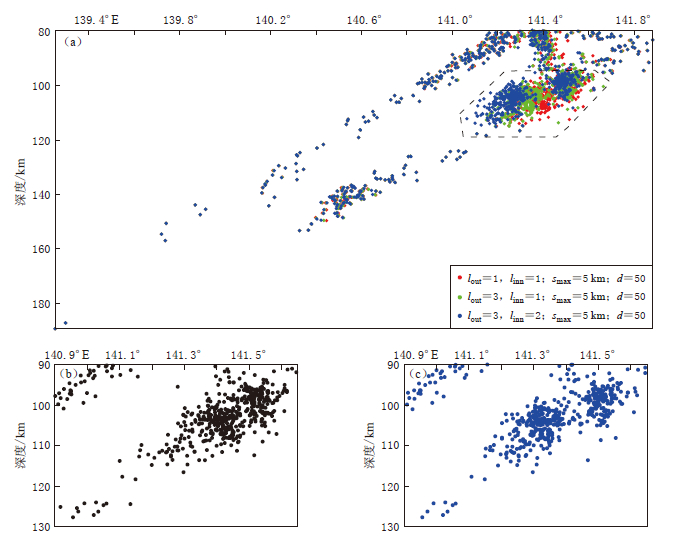
本文采用改进后的双差定位法(江国明等,2009),对日本东北地区双震带进行了高精度重定位,证实了日本东北地区在70—250 km深度存在平行分布的双震带. 在研究中我们还通过观察重定位后的剖面图像,在38.8°N—39°N范围内位于双震带下层的地震出现位置上移的情况,且上移幅度随最大成对距离的增大和迭代次数的增加而增大. 选取该纬度范围内的所有地震使用双差法单独进行了重定位,经过对比3种参数设置下的重定位结果(图 9a),发现100—200 km深度范围内处于下层地震带的地震(虚线框内)随着迭代次数的增多,由原先较为散乱的分布(图 9b)集中到两个区域(图 9c),造成了上述“位置上移”的假象. 由于重定位后震源位置并未变得更加散乱,而是集中在各区域内,结合方法测试得到的重定位后误差减小的结论,本文认为该现象是合理的. 尽管如此,Michelini和Lomax(2004)研究也指出在确定地震相对位置时,采用一个不正确的速度模型能够导致震源位置产生明显的偏差; Thurber和Zhang(2004)研究结果则进一步说明,即使使用比一维射线追踪更为有效的三维射线追踪法,由于不能得到绝对准确的三维速度模型,也会不可避免地出现定位结果的误差. 故综合考虑,不能排除产生“位置上移”这一现象是由于受到速度模型影响的可能性.
![]() 图 9 不同迭代次数下38.8°N—39°N范围内地震重定位结果的对比 (a) 不同迭代次数下38.8°N—39°N范围内所有地震重定位结果; (b) 重定位前 虚线框内震源分布; (c) 重定位后虚线框内震源分布Figure 9. Comparison of earthquakes relocation results in 38.8°N--39°N with different iterations (a) Relocation results of all of the earthquakes in 38.8°N--39°N with different iterations; (b) Epicenters distribution before relocation in the dashed box; (c) Epicenters distribution after relocation in the dashed box
图 9 不同迭代次数下38.8°N—39°N范围内地震重定位结果的对比 (a) 不同迭代次数下38.8°N—39°N范围内所有地震重定位结果; (b) 重定位前 虚线框内震源分布; (c) 重定位后虚线框内震源分布Figure 9. Comparison of earthquakes relocation results in 38.8°N--39°N with different iterations (a) Relocation results of all of the earthquakes in 38.8°N--39°N with different iterations; (b) Epicenters distribution before relocation in the dashed box; (c) Epicenters distribution after relocation in the dashed box综上,本文得到如下结论:
1)为了提高定位效率和定位精度,重定位前需对震源进行分组,并通过调整最大成对距离来控制分组情况. 通过方法测试证明了定位方法的有效性和可行性,并确定了合适的阻尼系数和迭代次数. 本文最终选定的最佳阻尼系数为50,迭代次数为3.
2)在方法测试中发现,使用双差法的重定位效果在不同方向上亦不同,且深度方向上效果更好. 因此在进一步研究中,将考虑对不同方向上的定位结果进行加权处理,从而得到更为可信的结果.
3)在方法测试基础上,本文采用改进的双差定位法对日本东北地区的中深源地震进行了重定位. 结果显示,重定位后的日本东北地区深发地震呈明显的双层分布,并与西太平洋俯冲板块几近平行,分层双震带形态比较清晰.
4)利用高精度的重定位结果,拟合了双震带的空间分布形态和产状特征,有助于后续的研究.
中国地质大学(北京)大学生创新创业训练计划提供资助,日本气象厅提供地震数据,中国地质大学(北京)信息工程学院范峥同学对本文测试程序提供帮助,作者在此一并表示谢意.
-
图 3 方法测试中重定位前、 后误差的对比 (a) 总误差; (b) 纬度方向误差; (c) 经度方向误差; (d) 深度方向误差 黑色点线表示重定位前误差, 红色点线表示重定位后误差
Figure 3. Comparison of errors before relocation with those after relocation in method test (a) Total errors; (b) Errors along latitude direction; (c) Errors along longitude direction; (d) Errors along depth direction. The black and red dotted lines represent the errors before and after relocation, respectively
图 4 方法测试中重定位前(上)、 后(下)的误差分布对比 (a) 总误差; (b) 纬度方向误差; (c) 经度方向误差; (d) 深度方向误差
Figure 4. Comparison of errors before relocation (upper panels) with those after relocation (lower panels) in method test (a) Total errors; (b) Errors along latitude direction; (c) Errors along longitude direction; (d) Errors along depth direction
图 5 采用不同迭代次数i, 最大成对距离smax和阻尼系数d所得到的重定位后的震源位置剖面投影图 (a) i=1, smax=5 km, d=5; (b) i=1, smax=5 km, d=50; (c) i=1, smax=5 km, d=100; (d) i=2, smax=2 km, d=50; (e) i=2, smax=5 km, d=50; (f) i=2, smax=8 km, d=50; (g) i=3, smax=2 km, d=50; (h) i=3, smax=5 km, d=50; (i) i=3, smax=8 km, d=50
Figure 5. Projections of relocated epicenters using different iteration i, maximum pairwise distance smax and damping coefficient d (a) i=1, smax=5 km, d=5; (b) i=1, smax=5 km, d=50; (c) i=1, smax=5 km, d=100; (d) i=2, smax=2 km, d=50; (e) i=2, smax=5 km, d=50; (f) i=2, smax=8 km, d=50; (g) i=3, smax=2 km, d=50; (h) i=3, smax=5 km, d=50; (i) i=3, smax=8 km, d=50
图 7 不同纬度范围内重定位前、 后震源位置剖面投影图 (a) 重定位前, 纬度为38°N—39°N; (b) 重定位前, 纬度为39°N—40°N;(c) 重定位后, 纬度为38°N—39°N; (d) 重定位后, 纬度为39°N—40°N
Figure 7. Projections of epicenters of different latitude ranges before and after relocation (a) Before relocation, latitude range is 38°N--39°N; (b) Before relocation, latitude range is 39°N--40°N; (c) After relocation, latitude range is 38°N--39°N; (d) After relocation, latitude range is 39°N--40°N
图 9 不同迭代次数下38.8°N—39°N范围内地震重定位结果的对比 (a) 不同迭代次数下38.8°N—39°N范围内所有地震重定位结果; (b) 重定位前 虚线框内震源分布; (c) 重定位后虚线框内震源分布
Figure 9. Comparison of earthquakes relocation results in 38.8°N--39°N with different iterations (a) Relocation results of all of the earthquakes in 38.8°N--39°N with different iterations; (b) Epicenters distribution before relocation in the dashed box; (c) Epicenters distribution after relocation in the dashed box
表 1 不同迭代次数i, 最大成对距离smax和阻尼系数d下的重定位后的均方根误差
Table 1 RMS errors of relocated results in different iteration i, maximum pairwise distance smax and damping coefficient d
i smax/km d RMS/km 3×1 2 50 7.0 3×1 5 45 4.3 3×2 5 45 4.3 3×1 5 50 4.3 3×1 5 100 5.1 3×2 5 50 4.1 -
Klein F W. 1978. Hypocenter Location Program Hypoinverse: Part Ⅰ. Users Guide to Versions 1, 2, 3, and 4. Part Ⅱ. Source Listings and Notes[R]. USGS Open-File Report: 78-694.
Yu X W, Zhang W B, Chen Y T. 2011. Seismic imaging and seismicity analysis in Beijing-Tianjin-Tangshan region[EB/OL]. [2015-04-15]. http://www.hindawi.com/journals/ijge/2011/216315/.
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载: