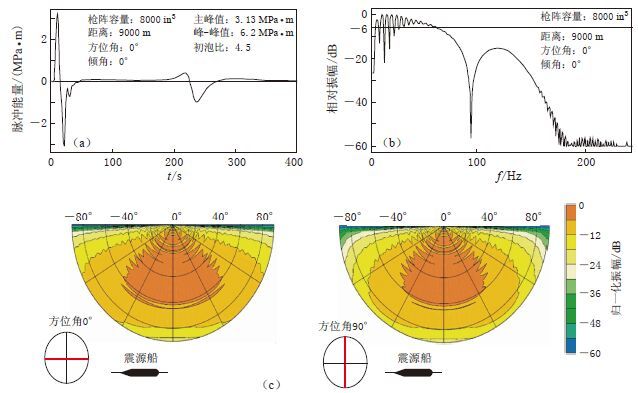
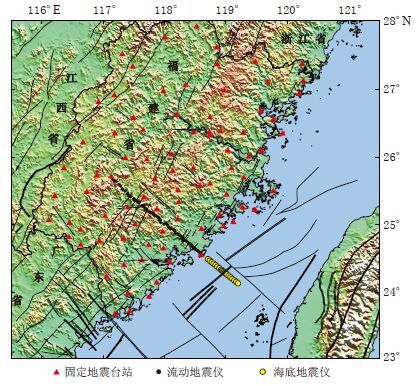
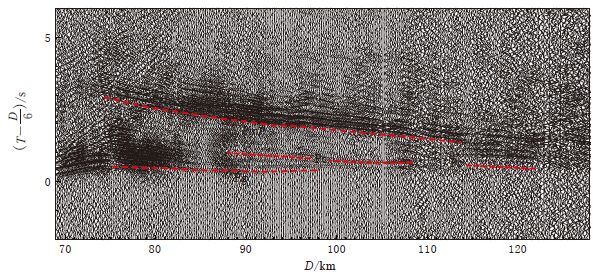
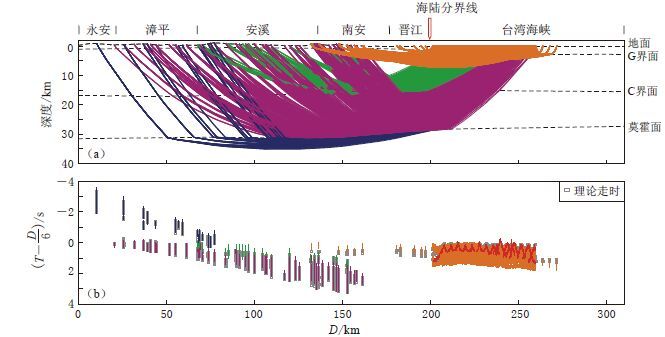
A preliminary exploration into onshore-offshore seismic experiment by using large volume air-gun source in Taiwan Strait
-
摘要: 本文利用在我国台湾海峡采用大容量气枪震源开展海陆联测获得的广角地震测线HX9, 采用二维射线追踪法反演得到了HX9剖面的地壳二维速度结构和地壳界面形态, 初步探明了福建—台湾海峡海陆过渡带的深部构造. 结果表明: HX9剖面的地壳内存在两个速度间断面, 即C界面和莫霍面, 其中: C界面为上、 下地壳的分界面, 是一个小的速度不连续面, 速度变化值达0.08—0.16 km/s; 而地壳底部的莫霍面则有较大的速度反差, 变化值达1.02—1.29 km/s, 莫霍面上、 下的速度分别为6.75—6.97 km/s和8.00—8.07 km/s. 沿剖面的地壳界面形态总体起伏不大, 陆域上、 下地壳的厚度和界面变化趋势均相似, 从陆域到海域呈微倾斜变化趋势, 表现为减薄陆壳的特征. 莫霍面陆域埋深约为31.6 km, 向福建东南沿海逐渐减薄至27.4 km左右.Abstract: This paper revealed the 2-D crustal velocity structure and interface morphology by inversion of the 2-D ray tracing method along the survey line HX9 conducted by onshore-offshore seismic experiment using the large volume air-gun source in Taiwan Strait, preliminary ascertaining the deep crustal structures of the sea-land transition zone between Fujian land and Taiwan Strait. The results show that there are two velocity discontinuities in the earth’s crust, i.e., C and Moho interfaces. C interface, as a demarcation between the upper crust and lower crust, is a small velocity discontinuity, with the velocity rang-ing 0.08--0.16 km/s; whereas for the Moho interface at the bottom of crust, there is a large velocity difference being 1.02--1.29 km/s. The velocity above the Moho interface is 6.75--6.97 km/s, and that beneath the Moho interface is 8.00--8.07 km/s. Along the profile, the overall crustal interface morphology is less volatile. The thickness and its variation tendency in the upper crust are similar to those lower crust of continental area. However, the crustal interface has slightly tilted trends from land to sea, suggesting the characteristic of thinned continental crust. The Moho interface is about 31.6 km deep in the continental area, and gradually thins to about 27.4 km in the southeast coast of Fujian.
-
2021年5月21日21时48分(北京时间)云南省大理白族自治州漾濞县(99.87°E,25.67°N)发生MS6.4地震。该地震发生后,我们对震中附近的地下流体观测资料进行了系统的总结,结果显示云南省地震台在2021年2月24日提出洱源井水温异常,该井水温在漾濞MS6.4地震前呈现明显的异常现象。
洱源水温观测井位于云南省大理白族自治州洱源县玉湖镇,地理坐标为(99.95°E,26.11°N),地处洱源盆地,位于红河断裂带与维西—巍山断裂之间(图1)。该井建成于1984年,井深266.56 m,套管下至165.56 m,其中80.22—144.02 m为滤水管,165.56—266.56 m为裸孔。0—73.16 m的岩性为冲积湖积层,其中上部为黏土及砂土层、下部为石英质、石英颗粒砂土及碎石砾石层;73.16—170.3 m为千枚岩及粉砂质千枚岩,中间夹有变质砾岩、片岩;170.3—175.1 m为千枚岩破碎带;175.1—202.4 m为砂质千枚岩及少量变粒片岩;202.4—266.56 m以变质泥岩为主,中间为片岩及角砾(云南省地震局,2005)。
![]() 图 1 洱源井的构造位置及附近的地震分布断层数据据中国活动构造图(邓起东等,2007)修改补充;地震目录引自中国地震台网中心;震源机制解源于哈佛大学(Dziewonski,Ekström,2021);地质单元和河流数据源于MapSIS软件(蒋骏等,2000)Figure 1. Tectonic position of the Eryuan well and the distribution of nearby earthquakesThe fault data are revised from China ative tectonic map (Deng et al,2007),earthquake catalogue are from China Earthquake Networks Center,focal mechanisms are from Harvard University (Dziewonski,Ekström,2021),and geological units and rivers refer to MapSIS (Jiang et al,2000)
图 1 洱源井的构造位置及附近的地震分布断层数据据中国活动构造图(邓起东等,2007)修改补充;地震目录引自中国地震台网中心;震源机制解源于哈佛大学(Dziewonski,Ekström,2021);地质单元和河流数据源于MapSIS软件(蒋骏等,2000)Figure 1. Tectonic position of the Eryuan well and the distribution of nearby earthquakesThe fault data are revised from China ative tectonic map (Deng et al,2007),earthquake catalogue are from China Earthquake Networks Center,focal mechanisms are from Harvard University (Dziewonski,Ekström,2021),and geological units and rivers refer to MapSIS (Jiang et al,2000)洱源井从1991年开始观测水温,观测仪器为中国地震局地壳应力研究所(现应急管理部国家自然灾害防治研究院)研制的SZW-1A水温仪,温度探头放置在井下190 m。2015年10月SZW-1A水温仪器发生故障,10月13日更换为中科光大公司研制的ZKGD3000-NT水温仪,温度探头置于90 m处,该水温仪的观测精度优于0.05 ℃,1分钟采样1次。
洱源井距离漾濞MS6.4地震仅50 km,洱源井水温在漾濞地震前的变化如图2所示,可见:2020年10月3日水温开始下降,2021年4月中旬下降速率减缓,至2021年5月21日下降幅值约0.15 ℃,下降持续230天;漾濞地震发生时,洱源井水温出现显著的同震上升,上升幅值为0.018 ℃,之后持续上升。
针对洱源井水温的下降异常,云南省地震台于2021年3月1日开展了异常核实。通过观测系统检查、环境因素调查及气象因素分析,认为洱源井水温的下降异常不存在人为、仪器和环境等干扰因素(高文斐,胡小静,2021)。
为分析洱源井水温下降异常与漾濞MS6.4地震的关系,将洱源井水温历史观测资料与周围地震的对应情况进行对比。图3a为洱源观测井自采用中科光大水温仪以来的观测曲线,可见洱源井水温共出现过两次与漾濞MS6.4地震前类似的下降异常。一次为2015年10月至2016年4月出现的持续下降,2016年4月底下降转缓,下降幅值约0.19 ℃,转缓1个月后发生2016年5月18日云龙MS5.0地震,该地震与洱源井相距42 km,地震发生时记录到显著的水温同震响应,响应幅值为0.013 ℃,地震后水温回升。另一次为2016年12月初至2017年3月中旬出现的水温持续下降,降幅为0.11 ℃,下降有所转缓后发生2017年3月27日漾濞MS5.1地震,该地震与洱源井相距29 km,地震发生时同样记录到显著的水温同震响应,响应幅值为0.024 ℃,地震后水温回升。图4为三次MS≥5.0地震前洱源井水温下降变化的对比曲线,可见,2015年观测以来,洱源井水温共出现三次显著下降异常现象,之后周边均发生了MS5.0以上地震,地震发生时均记录到显著的同震响应,震后转折回升,因此三次地震前水温下降异常具有一定的重复性。
将洱源井水温异常与地震的对应情况进行统计检验,图3b为洱源井100 km范围内2015年10月13日至2021年8月21日期间MS5.0以上地震的M-t图,可见该时段内共发生6次MS5.0以上地震,因为2021年5月21日发生在漾濞县的四次地震为前震-主震-余震型地震事件(龙锋等,2021),本文将其视为一个地震序列,即洱源井水温自2015年观测以来在三次地震事件前均出现重复性下降异常。洱源井水温异常与地震一一对应,通过统计检验。
综合洱源井水温历史资料对比分析和统计检验的结果,本文认为洱源井水温2020年10月至2021年5月的异常变化与2021年5月21日漾濞MS6.4地震有关,为水温地震前兆观测积累了一次震例。洱源井水温异常的机理可能与震源断层及外围区域的应力演化有关,尚待进一步研究。
-
-
孟祥丽. 2012. 琼北地区地壳速度结构与构造特征[D] . 南昌: 东华理工大学核工程与地球物理学院: 22-48. MengX L. 2012. The Velocity Structure and Structural Feature of Crust in the Northern Hainan Region[D]. Nanchang: School of Nuclear Engineering and Geophysics, East China University of Technology: 22-48 (in Chinese) .





 下载:
下载: