Upper crustal structure of Haiyuan tectonic zone and its surrounding areas
-
摘要: 基于甘肃省夏河县—陕西省靖边县剖面的8次人工地震初至波数据, 利用有限差分走时方法反演得到了沿该剖面长约650 km的上部地壳速度结构和结晶基底的深度分布. 反演结果显示: 海原构造区西侧的西秦岭—祁连山褶皱区上部地壳的横向非均匀性明显, 基底深度从1 km到5 km不等, 反映了褶皱区改造变形强烈的构造特征; 其东侧的鄂尔多斯盆地基底深度约为5—6 km, 其速度均匀、 稳定, 上地壳呈弱速度梯度特征; 海原构造区及海原弧形断裂带附近上部地壳的破坏变形最严重, 区内横向高低速相间分布. 综上可知, 海原构造区东西两侧上地壳结构的显著差异揭示了其结构复杂性的成因及其与地震活动性的关系.Abstract: By using the eight-shots of deep seismic sounding records from the Xiahe (Gansu Province) to Jingbian (Shaanxi Province) section, we get the upper crustal structure and basement depth of Haiyuan tectonic zone and its surrounding areas, which is a 650 km long profile. The result shows that, Qinling-Qilianshan folding zone in the west of Haiyuan tectonic zone has an obviously lateral heterogeneity in upper crust, the basement depth ranges from 1 to 5 km, which reveals that the zone has been destructed and deformed strongly. Whereas on the east side of Haiyuan tectonic zone, the Ordos block exhibits a homogeneous and stable upper crust, which has a 5-6 km depth crystalline basement and a relative low velocity gradient. Moreover, the upper crust of Haiyuan tectonic zone and the Haiyuan arcuate fault zone are the most strongly destructed and deformed areas along the profile. Therefore, the distinct difference in upper crust structure between the east and west side of Haiyuan tectonic zone reveals the cause of structural complexity and its relation with seismic activities.
-
Keywords:
- crustal structure /
- finite difference /
- northeast Tibetan Plateau /
- Ordos /
- Haiyuan fault
-
引言
海原构造区位于我国南北地震带的北段,青藏高原东北缘的秦岭—祁连褶皱区、 鄂尔多斯地块与阿拉善地块的拼合处. 该区地壳结构复杂,地震频发,自有记载以来的强震有1879年武都MS8.0,1920年海原MS8.5及1927年古浪MS8.0大地震. 大量的研究结果表明,该区域的地壳厚度自西向东逐渐减薄,由西部祁连山褶皱带的51 km,减薄至东部鄂尔多斯盆地区的44 km(张少泉等,1985; 李松林等,2002). 该区断裂广泛发育,自西向东依次分布着西秦岭北缘断裂、 南西华山南麓断裂、 香山北麓—桃山—李旺堡断裂、 青铜峡—固原断裂等大型断裂.
国内研究人员对海原构造区和海原断裂带开展了大量的研究工作. 詹艳等(2004)关于穿越海原震区的大地电磁测深剖面的解释结果显示,海原震区正好位于其西南侧的高阻区与东北侧低阻区的过渡带上,电阻率在该剖面上的剧烈横向变化揭示了该区地壳结构复杂的总体特征. 滕吉文等(2008)利用鄂尔多斯盆地内部的深地震测深资料,提出鄂尔多斯盆地的上地壳为双层结构,且上下层的速度梯度差异显著. 施炜等(2013)根据野外构造测量,提出了海原断裂带的新生代构造演化序列,认为该区自新生代以来受多期构造应力场的控制,特别是全新世以来在NE向构造挤压作用下,断裂左行走滑活动剧烈. 王伟涛等(2014)根据该区的磷灰石裂变径迹年代学结果及地震反射剖面结果,揭示了晚新生代以来海原断裂带经历了先逆冲、 后走滑的两阶段变形过程. 上述研究结果为认识海原构造区和海原断裂带提供了大量的资料,但并未给出该区东西两侧上地壳结构的差异对比.
鉴于此,本文首先使用中国地震局地球物理勘探中心分别于1999年、 2014年和2015年在海原构造区获取的8炮深地震测深资料,形成长约650 km的甘肃省夏河县—陕西省靖边县的深地震测深二维剖面; 然后利用有限差分地震走时层析成像得到夏河—靖边剖面上部地壳的P波速度结构; 最后通过比较沿该剖面不同构造单元的上部地壳的结构特征,分析海原构造区活动断裂的深部构造形态、 上地壳变形特征及其与强震孕育的关系.
1. 地质构造背景
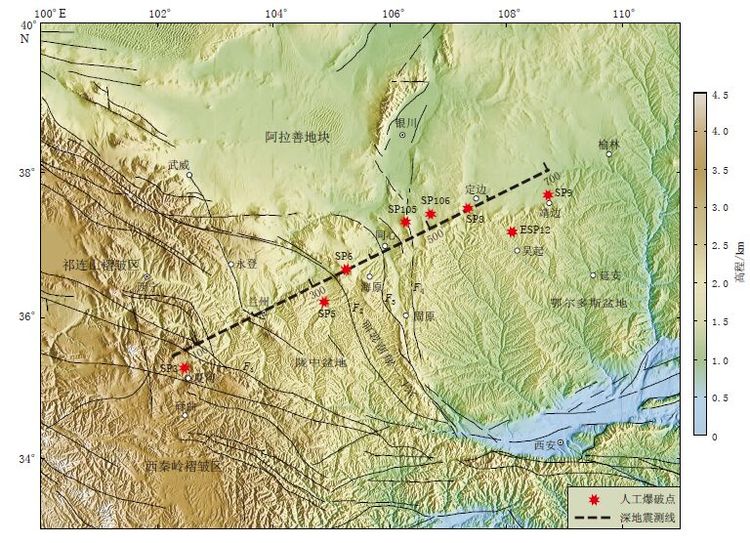
夏河—靖边剖面自西向东分成4个构造单元: 陇中盆地、 兴仁—海原盆地、 鄂尔多斯西缘褶皱带和鄂尔多斯盆地,如图 1所示. 陇中盆地是祁连山褶皱系东延的一个大型山间盆地,地表广泛覆盖第三系和第四系沉积,在构造运动上主要受到以ENE--WSW向挤压为特征的现代应力场控制; 其西侧的西秦岭北缘断裂是一个近NW走向的大型断裂,且很可能是一个超壳断裂(李清河等,1991). 兴仁—海原盆地与陇中盆地之间以ENE向的毛毛山—南西华山断裂为界,历史上有名的“西海固多震区”(西吉、 海原、 固原)位于该区. 由于青藏高原ENE向的持续挤压作用,发育一系列弧形断裂,其中海原弧形断裂带成为青藏高原东北缘活动性最强的断裂构造带. 香山北麓—桃山—李旺堡断裂是西秦岭—祁连山褶皱区向华北地台区的过渡带,将兴仁—海原盆地与鄂尔多斯西缘褶皱带隔开. 兴仁—海原盆地和鄂尔多斯西缘褶皱带构造复杂、 横向变化显著,一系列NW向的弧形断裂把盆地内部分成若干隆起和凹陷构造. 夏河—靖边剖面最东端的鄂尔多斯地块是一个大型的中生代盆地,在新生代隆升成高原,是我国华北地区最稳定的构造单元,其内部几乎未发生过地震. 嘉世旭和张先康(2005)的研究显示,鄂尔多斯地块内部地壳结构简单、 地壳平均速度较高,反映了其内部变形弱的稳定构造特征.
![]() 图 1 研究区构造分布图及测线位置F1: 西秦岭北缘断裂; F2: 南西华山南麓断裂; F3: 香山北麓—桃山—李旺堡断裂; F4: 青铜峡—固原断裂Figure 1. Tectonic settings and position of the survey line in the studied areaF1:North margin fault of west Qinling; F2: South margin fault of South-West Huashan; F3:Xiangshan-Taoshan-Liwangbu fault; F4: Qingtongxia-Guyuan fault
图 1 研究区构造分布图及测线位置F1: 西秦岭北缘断裂; F2: 南西华山南麓断裂; F3: 香山北麓—桃山—李旺堡断裂; F4: 青铜峡—固原断裂Figure 1. Tectonic settings and position of the survey line in the studied areaF1:North margin fault of west Qinling; F2: South margin fault of South-West Huashan; F3:Xiangshan-Taoshan-Liwangbu fault; F4: Qingtongxia-Guyuan fault2. 有限差分成像方法和数据
有限差分层析成像方法最初由Vidale(1988)提出,随后Hole(1992)将其进行了改进,使它更有效地应用于速度变化剧烈的模型中. 该方法正演时采用地震走时程函方程的有限差分解法,对模型进行正方形网格剖分,计算速度快,算法稳定; 相比于射线追踪方法,该方法对复杂结构中的地震走时计算更为有效. 反演过程采用反投影的方法,在迭代反演过程中,不断修改模型网格的慢度,避免了矩阵运算,大大提高了计算速度. 但是,该方法本身并不能给出模型参数的分辨率,可以通过射线的分布情况判断模型各区域的可信程度,对于没有射线覆盖的区域,模型参数值与初始模型一致,不具有参考价值.
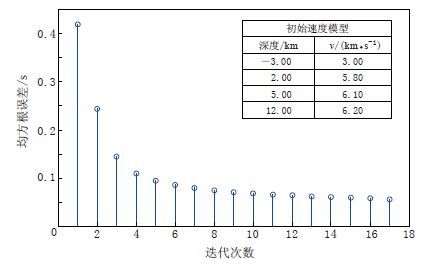
夏河—靖边剖面全长650 km,共进行了8次爆破激发(图 1),其中包含1999年的5炮,2014年的1炮和2015年的2炮,炮间距从35 km 到240 km 不等,接收点距为2—3 km. 为了减少炮点相对测线横向偏差对走时的影响,数据处理时去掉近炮点10 km以内的初至波数据,参与计算的初至波共349个,走时拾取精度为0.05—0.10 s. 本文模型横向长度为650 km,纵向深度为15 km,计算时横向和纵向网格间距均设为0.5 km,共包含3万9000个网格. 基于一维试错法走时拟合,综合区域大地构造信息,得到反演所用的初始模型如图 2所示. 可以看出,对初至走时进行15次迭代反演后,走时均方根误差从初始的0.419 s下降至0.058 s,趋于稳定.
3. 初至震相走时特征
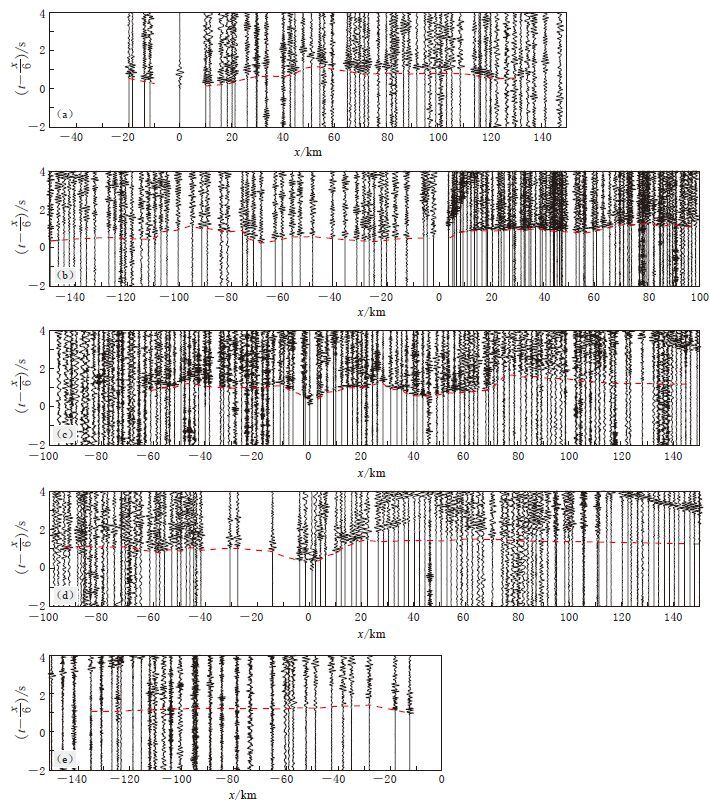
图 3分别给出了SP3炮、 SP5炮、 SP105炮、 SP106炮和SP9炮的深地震测深记录. 由图 3a给出的SP3炮东支记录可以看出初至波可连续追踪约120 km. 当偏移距在50 km以内时,折合到时约为0.3—0.7 s,视速度约为5.5 km/s,反映出西秦岭北缘断裂以南地表高速的特征; 当偏移距为50 km左右时,初至波有一个明显的错动,分析是由于断裂引起的初至波滞后所致; 当偏移距大于50 km时,初至波折合走时约为0.8—1.0 s,视速度约为6.0 km/s; 当偏移距达到120 km附近,走时提前约0.3 s,反映出陇中盆地盖层相对厚、 速度相对低的特征.
SP5炮(图 3b)西支记录的初至波可连续追踪约170 km. 由图 3b可以看出: 偏移距-75 km处有一个比较明显的分界线,东侧走时平稳,折合到时约为0.3—0.5 s,视速度约为5.95 km/s,反映了陇中盆地东部盖层偏薄、 速度偏高的特征; 当偏移距为-75—-110 km时,初至波折合走时明显滞后,最大滞后可达0.8 s,显示了陇中盆地内部存在一个相对低速的构造.
SP5炮(图 3b)东支和SP105炮(图 3c)西支记录反映了海原构造区的上地壳结构. SP5炮东支记录的初至波追踪距离约110 km,自西向东存在走时先超前再滞后的特征,显示了海原构造区内横向速度变化明显的特征. SP105西支记录也显示了类似的走时特征,该记录的初至波走时在偏移距-45 km处有一个明显的滞后,其位置大致与香山北麓—桃山—李旺堡断裂相对应,故推测很可能是该断裂引起的走时滞后.
SP106炮(图 3d)东支和SP9炮(图 3e)西支的记录则反映了鄂尔多斯块体上部地壳的结构. SP106炮东支记录的初至波走时相对西支走时明显滞后,反映出东西两侧的上地壳结构差异很大. 东支记录在偏移距30 km以内,折合到时从0.9 s 增加至1.3 s,视速度约为5.0 km/s,显示了盖层速度相对低、 基底相对深的结构特征; 偏移距大于30 km后,初至波折合走时约为1.4—1.2 s,视速度约为6.06 km/s,显示了鄂尔多斯盆地上地壳结构简单、 稳定的特征. 该盆地内其余炮的资料也显示了相似的走时特征.
4. 上地壳速度结构特征
海原构造区的上地壳结构反演结果如图 4所示,可以看出其东西两侧的上地壳结构存在显著差异,以下按照夏河—靖边剖面自西向东的3个分段依次阐述.
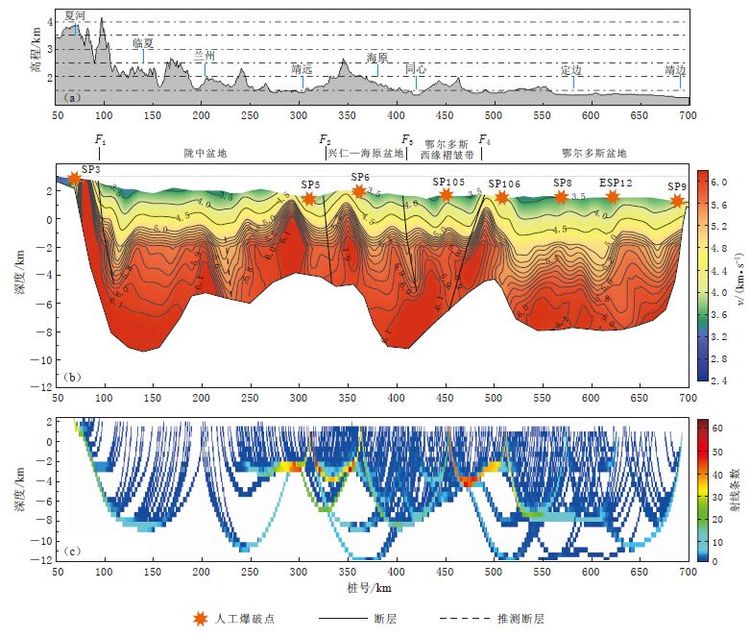
![]() 图 4 夏河—靖边剖面上地壳速度结构与射线分布图(a)地表高程;(b)速度结构;(c)射线分布. F1: 西秦岭北缘断裂; F2: 南西华山南麓断裂; F3: 香山北麓—桃山—李旺堡断裂; F4: 青铜峡—固原断裂Figure 4. Upper crust velocity and ray coverage of Xiahe-Jingbian section(a)Elevation;(b)Velocity structure;(c)Ray coverage F1: North margin fault of west Qinling; F2: South margin fault of South-West Huashan; F3: Xiangshan-Taoshan-Liwangbu fault; F4: Qingtongxia-Guyuan fault
图 4 夏河—靖边剖面上地壳速度结构与射线分布图(a)地表高程;(b)速度结构;(c)射线分布. F1: 西秦岭北缘断裂; F2: 南西华山南麓断裂; F3: 香山北麓—桃山—李旺堡断裂; F4: 青铜峡—固原断裂Figure 4. Upper crust velocity and ray coverage of Xiahe-Jingbian section(a)Elevation;(b)Velocity structure;(c)Ray coverage F1: North margin fault of west Qinling; F2: South margin fault of South-West Huashan; F3: Xiangshan-Taoshan-Liwangbu fault; F4: Qingtongxia-Guyuan fault夏河—靖边剖面西段100—330 km桩号段为陇中盆地. 由图 4b可以看出,陇中盆地内部西侧速度较东侧速度低; 陇中盆地盖层的速度约为3.5—5.0 km/s,西侧盖层较东侧偏厚. 若将5.9 km/s的速度等值线作为结晶基底面,陇中盆地结晶基底埋深约为2—4 km,西部深东部浅. 还可以看到,模型桩号100 km和240 km处有两个明显的低速结构向下延伸,西侧低速可能是西秦岭北缘断裂在深部的体现,而东侧的低速在地表并未体现,可能是由于隐伏断裂或者盆地内部的凹陷构造所致. 西秦岭北缘断裂形成历史悠久,经历过多期构造运动,新生代以前经历了自北向南的推挤,自第四纪以来演变为左旋走滑断层(腾瑞增等,1994; 孟秀军等,2014),图 4b中给出了该断层在深部的延伸趋势. 值得注意的是,由于SP3炮点与SP5炮点之间间距较大,射线覆盖几乎无交叉,故该桩号段的模型分辨率较其它分段偏低,所得结果仅供参考.
夏河—靖边剖面中段330—490 km桩号段属于兴仁—海原盆地和鄂尔多斯西缘褶皱带. 由图 4b可以看出,该分段上地壳结构呈现出明显的横向非均匀特征,高低速结构相间排列,反映了该分段上地壳强烈的改造变形. 南西华山南麓断裂把陇中盆地与兴仁—海原盆地隔开,在330 km桩号处上地壳速度显示较周围地区偏低. 海原县西南的南华山和西华山是六盘山的余脉,其中南华山主峰海拔为2955 m,为宁夏第二高峰,该区地表速度偏高、 基底隆升,这是由于地壳经历强烈的NE向挤压作用而隆升所致(施炜等,2013). 270—350 km桩号段,两侧基底上隆,中间呈低速下凹的结构特征,其中290 km和350 km桩号附近结晶基底埋深仅1 km,推测该区为先隆起、 后断裂破坏的构造运动特征. 鄂尔多斯西缘褶皱带与兴仁—海原盆地大体上被香山北麓—桃山—李旺堡断裂分隔,这与模型420 km处的狭窄舌状低速带对应,基底埋深约为6 km,造成了SP105炮西侧-45 km处初至波的明显滞后(图 3c). 香山北麓—桃山—李旺堡断裂是一条以左旋走滑为主兼具倾向滑动的全新世活动断裂(李海峰等,2014),图 4中给出的断裂分布显示了该断裂在横向上分布较窄,与其西侧的南西华山南麓断裂相比,其对上部地壳的改造有限.
夏河—靖边剖面东段的490—700 km桩号段属于鄂尔多斯盆地,上地壳显示了相对简单、 稳定的速度结构,结晶基底埋深约为5—6 km,盖层速度为3.0—5.0 km/s. 由图 4b可以看出,速度值为5.0—6.0 km/s、 间隔为0.1 km/s的等值线均匀分布于地下2—6 km的深度范围内,与其西侧的褶皱区形成较明显的对比,显示出该段上地壳弱速度梯度特征. 青铜峡—固原断裂总体呈N--S向延伸,断层面向W倾斜,浅部较陡,断裂在地表多处出露(张进等,2004),图 4b中480 km桩号附近绘制的断裂显示了青铜峡—固原断裂在深部的延伸趋势,该断裂有可能延伸至上地壳深部. 在该断裂的东侧(约490 km桩号处),模型显示出一个较高的速度异常和基底相对隆起,这导致了SP105炮东侧40 km处的初至波走时超前(图 3c),故推测在祁连褶皱系NE方向挤压的过程中,鄂尔多斯盆地边缘被迫隆升,这一结果尚待日后作进一步研究.
5. 讨论与结论
青藏高原东北缘的海原构造区及其周缘区域由于所处的特殊地理位置,一直是地学界关注的热点区域. 本文使用该区8次人工地震测深所获取的初至波数据,通过基于有限差分走时反演方法得到了夏河—靖边剖面的上地壳速度结构.
夏河—靖边剖面西侧的西秦岭—祁连山褶皱区上地壳横向非均匀性明显,横向速度差异约为10%—20%,基底深度在南、 西华山地区及鄂尔多斯西缘约为1—2 km,而在其它区域约为4—5 km. 该区域内横向高低速相间分布,显示了褶皱区经多期改造后的变形特征. 海原构造区所在的兴仁—海原盆地及鄂尔多斯西缘褶皱区显然比其西侧的陇中盆地的横向非均匀性要明显,这可能与该区一系列断裂带的走滑特征有关. 受到NE向的挤压推覆兼走滑运动,断裂带附近区域内部破碎并逐渐加宽,而断裂带与断裂带之间的盆地区域受到的破坏相对较小.
夏河—靖边剖面东侧的鄂尔多斯盆地呈现未受破坏的稳定沉积构造特征,结晶基底深度约为5—6 km,上地壳速度为5.0—6.0 km/s,呈弱速度梯度特征,速度变化梯度约为0.25/s. 而在该剖面的几个基底相对隆起区域,速度等值线则非常密集,速度变化梯度约为0.55/s. 结晶基底一般被认为是大陆地壳沉积盖层的底界面,该界面以下为结晶程度较好的太古代变质岩,速度通常约为6.0 km/s,因地区不同稍有不同(段永红等,2003; 曹令敏,赖晓玲,2012). 王夫运等(2008)认为可以通过盖层与基底之间速度等值线的疏密变化来判断结晶基底的深度,盖层速度等值线较密集而基底以下相对稀疏. 综合以上观点,本文选取5.9 km/s的速度等值线作为结晶基底的参考深度.
有限差分走时层析成像方法在反演过程中采用了反投影算法,无法给出模型参数的分辨率,但可根据射线在地下介质中的覆盖程度来定性地评价反演的可信程度. 由射线分布(图 4c)可以看出: 100—300 km桩号段,射线覆盖深度达6—8 km,但射线交叉程度不高,对速度值的约束一般; 300—500 km桩号段,射线覆盖深度达4—6 km,不同炮点之间的射线相互交叉多次,反演速度值的可信度最高; 500—700 km桩号段,射线覆盖深度约为8 km,射线虽有交叉,但速度值的精度不及300—500 km桩号段.
夏河—靖边剖面上地壳初至波反演结果可为更好地认识海原构造区及其周缘地区的上地壳结构提供参考. 海原震区上地壳局部地区发生的挤压褶皱、 隆升变形、 破碎及一系列弧形断裂带的发育,均与青藏高原NE向的持续挤压运动及刚性的鄂尔多斯块体阻挡有关.
-
图 1 研究区构造分布图及测线位置
F1: 西秦岭北缘断裂; F2: 南西华山南麓断裂; F3: 香山北麓—桃山—李旺堡断裂; F4: 青铜峡—固原断裂
Figure 1. Tectonic settings and position of the survey line in the studied area
F1:North margin fault of west Qinling; F2: South margin fault of South-West Huashan; F3:Xiangshan-Taoshan-Liwangbu fault; F4: Qingtongxia-Guyuan fault
图 4 夏河—靖边剖面上地壳速度结构与射线分布图
(a)地表高程;(b)速度结构;(c)射线分布. F1: 西秦岭北缘断裂; F2: 南西华山南麓断裂; F3: 香山北麓—桃山—李旺堡断裂; F4: 青铜峡—固原断裂
Figure 4. Upper crust velocity and ray coverage of Xiahe-Jingbian section
(a)Elevation;(b)Velocity structure;(c)Ray coverage F1: North margin fault of west Qinling; F2: South margin fault of South-West Huashan; F3: Xiangshan-Taoshan-Liwangbu fault; F4: Qingtongxia-Guyuan fault
-
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 车子强,吴忠良,高原. 利用背景噪声资料研究海原断裂带及邻区Rayleigh波相速度和方位各向异性. 地震. 2023(01): 105-123 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 吴国炜,熊小松,高锐,陈宣华,李英康,王冠,王小成,任海东. 北山构造带南部上地壳二维初至波层析成像. 地学前缘. 2022(02): 402-415 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 吴国炜,熊小松,高锐,陈宣华,李英康,叶卓,王冠,吴鸿梅. 二维初至波层析成像揭示的北祁连—阿拉善南缘浅层地壳结构. 地球学报. 2022(06): 843-857 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 莘海亮,曾宪伟,康敏,高级. 海原弧形构造区地壳三维精细速度结构成像. 地球物理学报. 2020(03): 897-914 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 林吉焱,唐国彬,徐涛,蔡辉腾,吕庆田,白志明,邓阳凡,黄敏夫,金星. 钦杭—武夷山成矿带上地壳速度结构与基底特征:万载—惠安宽角反射/折射地震剖面约束. 地球物理学报. 2020(12): 4396-4409 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 滕吉文,宋鹏汉,刘有山. 汶川-映秀M_S8.0地震的地球物理场与动力过程. 科学通报. 2018(19): 1882-1905 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 许英才,曾宪伟,许文俊,马禾青,金涛,任家琪. 基于台阵的青藏高原东北缘海原-六盘山断裂带及邻区地壳结构研究. 中国地震. 2018(03): 484-497 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 赵金仁,范振宇,刘保金,马策军,邓晓果,宋向辉,刘宝峰,王帅军,海燕,李怡青. 爆破地震揭示的华北西部高分辨基底速度结构. 科学通报. 2017(36): 4294-4307 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)




 下载:
下载: