Tomography of the S wave attenuation in the upper crust of Three Gorges Reservoir region
-
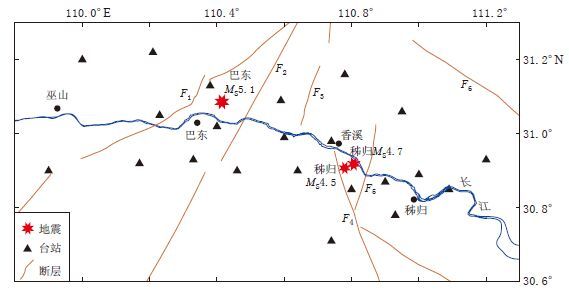
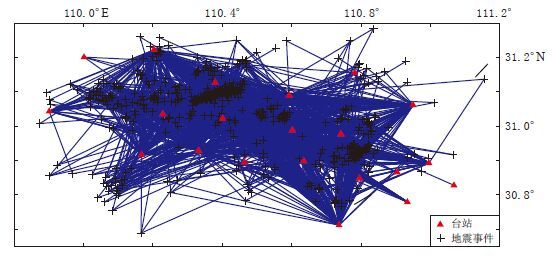
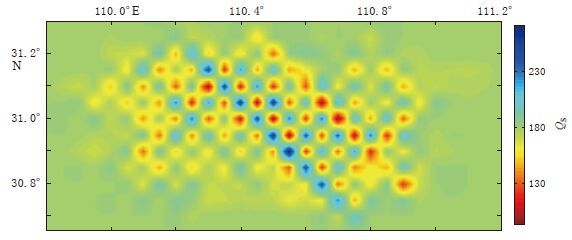
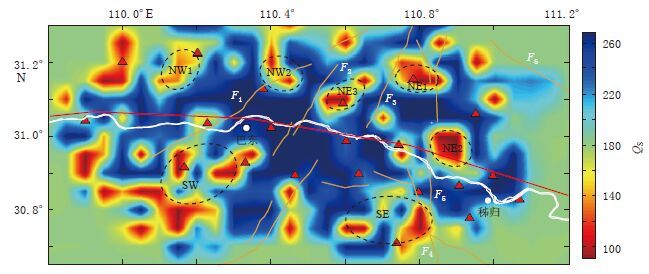
摘要: 利用三峡数字地震台网2009年1月—2015年2月记录的1300多次ML>1.5小震事件6000多条射线的S波数据, 利用S波衰减层析成像技术获得了三峡库区秭归—巴东段上地壳QS成像分布图. 结果显示, 三峡库区上地壳QS值存在明显的横向不均匀性, 沿水库近岸区主要为QS高值区, 外围NE, NW, SW和SE 等4个方向上均存在QS低值异常区, 这是由于这些异常区位于不同地层转换带, 岩层较易破碎, 易于库水渗流所致. 在巫山—秭归段剖面上, 本文QS成像结果与人工地震测深剖面上基底至上地壳底部之间岩层的Q值变化形态基本一致, 前者均值比后者低, 反映了上地壳深部介质对地震波衰减特性的影响. 2013年巴东MS5.1震群活动和2014年秭归MS4.5, MS4.7震群活动均分布在QS高值与低值过渡区, 这种区域的地下介质位于“软”、 “硬”转换带上, 岩层易破碎, 应力和能量易集聚, Q值易受水的渗透引起变化, 从而降低发震断层抗剪切强度而诱发地震.Abstract: A 2-D S-wave QS values of the upper crust of Zigui-Badong segment beneath the Three Gorges Reservoir region are estimated by means of S wave attenuation tomography based on more than 6000 S wave-rays of 1300 small seismic events with ML>1.5 recorded by digital seismic network of Three Gorges from January 2009 to February 2015. The results show that QS exhibits a significantly lateral heterogeneity distribution in Three Gorges Reservoir region, with high QS value mainly in the nearby riversides and low QS value in the surrounding area in the northeast, northwest, southwest and southeast directions. Particularly, the low QS value is closely related to seepage of reservoir water due to the conversion and fragment of rock stratum. The variation of QS value in this paper is in accord with Q value of rock stratum from rock-basement to the bottom of the upper crust from the Wushan-Zigui deep seismic sounding (DSS) profile, which reflects that the deep media of upper crust have influence on the seismic wave attenuation. The MS5.1 Badong earthquake swarm in 2013 and the MS4.5, MS4.7 Zigui earthquake swarms in 2014 were basically converged to transitional edge regions of high and low QS values. That is because that, the physical property of the crustal medium is located on the weak-soft transitional region, strain energy is prone to accumulate, and QS value also decreses due to the permeation of the water, furthermore, the shear strength of the seismogenic fault is reduced so as to induce earthquakes.
-
引言
在均匀水平层状介质中,面波具有多模特征,即在相同频率下存在多个传播速度。传统上将这些传播速度从低到高排列,速度最低的模式称为基阶模式,也称为零阶模式,向上依次称为一阶、二阶等高阶模式(夏江海,2015)。对于速度递增的均匀水平层状介质,通常基阶模式能量占据主导地位,观测频散曲线通常对应基阶模式(Socco et al,2010)。在反演时,基于理论预测模型计算出频散曲线后,可以直接取速度最小的模式与观测频散曲线进行拟合。如果基于观测数据得到分离的高阶模式的频散曲线,也可以在反演时同时拟合高阶模式的频散曲线。只要将同一频率计算的速度由低到高排列,依次与基阶、一阶和二阶等模式频散曲线进行拟合即可。反演时考虑高阶模式瑞雷面波具有两个明显的优势:① 相同频率下,高阶模式面波比基阶模式具有更深的穿透深度,可以约束更深层的S波速度(Gabriels et al,1987;Socco et al,2010);② 同时考虑基阶和高阶模式频散曲线可以提高反演的稳定性(Xu et al,2006)和准确性(Maraschini et al,2010)。
然而在浅地表地球物理研究领域,由于沉积环境不同或经过人为改造或其它自然条件,会形成存在低速夹层的介质。根据频散曲线的形态和分布,可以将低速层存在时的频散曲线简单地分为两类。其中一类为含低速层模型的频散曲线,在低频段,基阶模式瑞雷面波在某个频率处表现出明显的低速特征;在高频段,频散曲线存在视觉上的交叉现象,观测到的频散曲线在各个模式之间跳跃,或许是不同模式共同作用的结果。Foti (2000)称此时的频散曲线为有效频散曲线(effective dispersion curve),凡友华等(2009)将其称之为能量最大模。此时,很难精确地将频散曲线与具体的模式对应。如果按照速度递增正频散介质的反演方法,无法根据相速度的大小选择合适的模式进行拟合,即存在模式误判(mode-misidentified)现象(Zhang,Chan,2003;Gao et al,2014)。对于此类情形,可以采用Foti (2000)的方式,对预测的理论模型计算时域观测记录,采用与实际记录相同的处理方式,获得有效的相速度并与观测的有效相速度进行拟合,或者直接拟合观测与理论波场(Forbriger,2003a,b)。通过理论和实验模拟,多名研究人员提出一种考虑高阶模式频散曲线的反演方法(鲁来玉等,2006;Lu,Zhang ,2006;Lu et al,2007),该方法通过计算各个模式能量的大小,选取各频段能量最大的模式,与观测的频散曲线进行拟合。上述所列方法需要计算预测模型的波场记录,比计算频散曲线需要更多的计算时间,但相对于反演精度的提高,这种代价是值得的(Maraschini,Foti,2010;Soccoet al,2010;Ikeda et al,2012)。
很多研究者开展了基于高阶瑞雷面波模式的反演研究(Xia et al,2003;鲁来玉等,2006;Luo et al,2007;罗银河等,2008;李建平,2018;Matsuzawa,Yoshizawa,2019;Wang et al,2019)。本文主要讨论另一类含低速层介质模型的高阶模式面波反演问题。对于这类模型,频散曲线在低频段与前述的低速层模型类似,基阶模式在某些频段表现出明显的低速特征;但在实际能提取到的频段范围,即我们感兴趣的范围内,各个模式的频散曲线仍然是明显分离的,视觉上不存在交叉现象。限于激发源和复杂介质模型的原因,实际观测到的基阶模式频散曲线并不包含明显低速特征的频段,在有效的频段内,观测频散曲线与速度递增介质的频散曲线的介质类似,正如下文第二节中所讲的实例。即便如此,通过考虑高阶模式的反演,依然可以基于观测频散曲线重建介质的低速特征,而仅考虑基阶模式反演时则无法重建介质的低速层特征。鉴于此,本文拟通过实例分析和数值模拟,研究高阶模式频散信息对此类模型低速层的约束作用。在案例分析中,我们选择浅层地震反射勘探中被视作干扰的面波信号作为处理对象,联合基阶和高阶面波频散曲线反演浅地表S波速度,为浅层地震反射资料解释提供额外的约束。因此,本文的研究目的是双重的:一是讨论高阶模式瑞雷面波的频散对低速层的约束;二是通过案例分析证明,浅层地震反射数据中的面波可以被重新利用,在不增加经济成本的情况下,通过多模式面波反演为反射资料解释提供独立的信息约束。
1. 数据采集和处理
本文采用的实例分析数据来自“天津活断层探测与地震危险性评价”项目实施的浅层地震反射勘探的数据(王辉,丁志峰,2006)。如图1所示,该地震测线(L02)近垂直于天津北断裂布设。沿测线布设TN4,TN5,TN6,TN7共四个钻孔,钻孔间距分别为50,65,50 m,孔深分别为200,100,100,200 m。地震勘探数据采用可控源车激发能量,扫描频率为20—120 Hz,扫描时间长度为8 s,探测方向由北西至南东,数据采集系统采用德国DMT公司生产的SUMMIT高分辨率遥测地震仪。测线总长度为2.0 km,共采集103个点,炮点每次沿测线移动18 m;1—92号炮点由120道检波器接收,93号炮点接收道数为116道,此后每移动一次炮点记录减少6道,到103号炮点时记录为56道;设置偏移距为24 m,道间距为3 m,采样间隔取0.5 ms,记录长度为1 024 ms,采用三次震源叠加以增加信噪比。
![]() 图 1 跨天津北断裂的地震勘探测线及钻孔位置示意图(陈宇坤等,2013)Figure 1. Schematic diagram of seismic survey line and borehole location across the north fault of Tianjin (Chen et al,2013)
图 1 跨天津北断裂的地震勘探测线及钻孔位置示意图(陈宇坤等,2013)Figure 1. Schematic diagram of seismic survey line and borehole location across the north fault of Tianjin (Chen et al,2013)图2给出了沿测线第41个炮点的时域记录,可以看出:体波信号主要集中在前200 ms,200 ms之后可以看到较强的面波信号;由于面波传播速度较慢,在第64道记录之后,面波能量的主要到时在1 024 ms之后,超过了当初主要研究体波反射设置的记录长度。对各炮点的多道记录,采用二维傅里叶变换(Mcmechan,Yedlin,1981;Gabriels et al,1987;Alleyne,Cawley,1991;Forchap,Schmid,1998;Lu,Zhang,2004),将其变换到频率-波数域内。如图3a所示,在频率-波数域中,体波能量在整个扫频范围20—120 Hz内均有分布;面波能量主要集中在20—60 Hz之间,表现为斜率不同的近似直线,斜率的大小取决于波的传播速度。将体波剔除后的结果如图3b所示,可以明显观察到不同模式的瑞雷面波相速度,其中基阶、一阶及二阶频散能量均较为明显。
![]() 图 3 图2所示时间序列在频率-波数域和频率-相速度域中的能量分布(a) 未剔除体波的结果;(b) 剔除体波后的结果;(c) 提取的三个模式的频散点Figure 3. The energy distribution in the frequency-wavenumber and frequency-phase velocity domains for the time series shown in Fig.2(a) The result before removing body waves;(b) The result after removing body waves; (c) The extraction of surface-wave dispersion curves for three modes
图 3 图2所示时间序列在频率-波数域和频率-相速度域中的能量分布(a) 未剔除体波的结果;(b) 剔除体波后的结果;(c) 提取的三个模式的频散点Figure 3. The energy distribution in the frequency-wavenumber and frequency-phase velocity domains for the time series shown in Fig.2(a) The result before removing body waves;(b) The result after removing body waves; (c) The extraction of surface-wave dispersion curves for three modes根据相速度vR、频率f和波数k之间的关系,可将频率-波数域变换到频率-相速度域。如图3c所示,在频率-相速度域中,面波能量的极大值点对应面波频散方程的解,即面波的特征值。根据能量极大值对应的频率和相速度的连线,可以提取观测的不同模式的相速度频散。如图3c中的圆点所示,这些频散曲线根据相速度由低到高依次称为基阶模式、一阶模式和二阶模式。可以看出,基阶、一阶和二阶模式的能量较强,三阶模式之后能量逐渐减弱。因此,我们在后面的反演中将主要考虑前三阶模式。
2. 基阶及多阶面波反演:实例分析
图3c显示,基阶、一阶和二阶模式的频散曲线是相互分离的,不存在实际勘探中复杂地质条件下可能会出现的模式跳跃或“之”字形回折现象。因此,在反演时不考虑激发强度,只考虑振型相速度的大小。在相同频率下,通过相速度的大小判断该速度属于基阶、一阶或二阶等模式,从而与相应模式的观测频散曲线拟合。
反演采用地震学计算机程序(computer programs in seismology,缩写为CPS)中的surf96 (Herrmann,2013),由于该程序的反演方法基于线性最小二乘原理,对初始模型的依赖性较高。因此我们根据早期面波勘探解释频散曲线时相速度与深度的对应关系经验公式:
$$ {v}_{{\rm{S}}}=1.1{v}_{{\rm{R}}} \qquad {\textit{z}}=\frac{\lambda}{3} \text{,} $$ (1) 式中,vS为深度z处的S波速度,vR为波长λ对应的相速度(Foti,2000)。根据频率、相速度、波长的关系,计算出提取的基阶模式频散点在此经验公式中对应深度的S波速度;然后依据钻孔岩土介质性质给出了此文反演的初始模型。由于瑞雷面波相速度对密度和纵波速度的敏感度远远不及S波速度(Xia et al,1999;鲁来玉等,2011),本文仅反演S波速度。密度和P波速度根据场地条件给出,完整的初始模型参数如表1所示。
表 1 初始模型参数和各模式频散曲线联合反演的S波速度Table 1. The parameters of the initial model and the S-wave velocities inverted from multi-mode dispersion curves层序 层厚/m 深度/m ρ/(g·cm−3) vP/(m·s−1) 初始vS/(m·s−1) 反演vS/(m·s−1) 1 1.0 1.0 1.60 300 152 135.4 2 1.0 2.0 1.73 400 156 145.3 3 1.0 3.0 1.77 470 163 200.8 4 1.0 4.0 1.79 550 165 221.5 5 1.0 5.0 1.79 570 170 195.4 6 1.0 6.0 1.79 590 180 169.6 7 1.0 7.0 1.79 600 185 155.3 8 1.0 8.0 1.79 700 190 102.4 9 2.0 10.0 1.79 800 200 152.8 10 3.0 13.0 1.79 900 210 254.6 11 4.0 17.0 1.80 1 100 220 259.3 半空间 $ \infty $ $ \infty $ 1.80 1 200 230 250.1 首先仅考虑基阶面波模式的反演,结果如图4a所示,S波速度模型随迭代次数的变化如图4a左所示,将30次迭代之后的结果作为最终模型。可观察到迭代进行到15次左右时已经基本收敛,反演得到的模型是一个速度递增的S波速度剖面。图4a右中反演模型的理论频散曲线很好地拟合了观测的基阶模式频散曲线(图中红色误差棒),而反演模型的理论频散曲线与观测的一阶和二阶模式频散曲线(灰色误差棒)没有拟合。
![]() 图 4 基于多模式瑞雷面波频散曲线的反演(左)及其最终模型理论频散曲线与观测频散曲线的拟合(右)(a) 仅用基阶模式;(b) 基阶、一阶模式联合;(c) 基阶、一阶和二阶模式联合Figure 4. The inversion based on multi-mode Rayleigh-wave dispersion curves (left) and the fitting between the theoretical and observed dispersion curves (right)(a) Using only the fundamental mode;(b) Using the fundamental and the first modes;(c) Using the fundamental,the first and the second modes
图 4 基于多模式瑞雷面波频散曲线的反演(左)及其最终模型理论频散曲线与观测频散曲线的拟合(右)(a) 仅用基阶模式;(b) 基阶、一阶模式联合;(c) 基阶、一阶和二阶模式联合Figure 4. The inversion based on multi-mode Rayleigh-wave dispersion curves (left) and the fitting between the theoretical and observed dispersion curves (right)(a) Using only the fundamental mode;(b) Using the fundamental and the first modes;(c) Using the fundamental,the first and the second modes图4b左是使用基阶和一阶模式频散曲线联合反演的结果,为了增加收敛速度,反演时将基阶模式反演的结果作为初始模型。与图4a相比,加入一阶模式之后,反演的S波速度剖面出现明显的低速层,深度在4—10 m之间。此时,如图4b右所示,该模型的频散曲线很好地拟合了观测的基阶(红色误差棒)和一阶模式(绿色误差棒)频散曲线;二阶观测频散曲线拟合情况较之前稍好,但仍有偏差。
图4c左是使用三个模式的观测频散曲线联合反演的结果,使用的初始模型是基阶和一阶模式联合反演的结果,即图4b左中的反演结果。可以看出,基阶、一阶和二阶模式的联合反演结果与基阶、一阶模式的联合反演结果相近,但拟合效果更佳。如图4c右所示,反演模型的理论频散曲线很好地拟合了各阶模式的观测频散曲线。
上述过程体现了高阶模式面波反演对反演多解性的约束。在只考虑基阶模式的情况下,得到的地下S波速度是递增的,加入高阶模式之后,在4—10 m左右出现明显的低速层。这一方面表明,此频带范围的基阶模式可能对5 m以下深度的约束不够;另一方面说明,在实际应用时,由于频散数据的限制,仅仅考虑基阶模式可能无法获得真实的S波速度。
通常,对于介质存在低速夹层的情形,其频散曲线形态可简单分为两类。第一类为含低速层模型的频散曲线,基阶模式的瑞雷面波在某个反映低速层深度的频率附近表现出明显的低速特征;在高频段,频散曲线存在视觉上的交叉现象,观测的频散曲线,在各个模式之间跳跃或呈现“之”字形的回折。另一类低速层介质,即如图4c右模型的频散曲线所示,各个模式的频散曲线是明显分离的,视觉上不存在交叉现象。图4c右中,观测的多模式频散曲线呈现分离的状态,在有效的频带范围(23—40 Hz)内,并没有明显的低速指示(比如类似10 Hz附近基阶模式的相速度极小值点),其形态和速度递增的模型频散曲线类似。对于这样的频散曲线形态,图4c左的结果表明,考虑三个模式的最终反演结果具有明显的低速层。由于每次考虑更高一阶的模式反演时,都是利用前一次的反演结果作为初始模型,最终的低速层结果是否可信?反演结果是否与初始模型的选择有关?为了回答这些问题,并验证反演结果的可信度,我们将通过速度递增和含有低速层的两个模型进行数值模拟,以研究高阶模式对低速层的约束。
3. 高阶模式瑞雷面波对低速层的约束:数值模拟
反演结果会受到两类因素影响:一类是比较稳定的因素,如反演方法本身带来的影响等;另一类是不稳定的因素,如实际数据提取产生的误差、频带范围限制和初始模型等先验信息的影响。为了判定前述反演结果的可靠性,我们选取两个模型进行数值模拟研究。模型参数如表2所示,其中:模型1是由图4a中仅采用基阶模式反演得到的模型再按速度大小构建的正频散介质模型;模型2是含有低速层的模型,即图4c中的最终反演模型。两个模型的理论频散曲线如图5所示。将图5中的理论频散曲线作为观测数据,采用与第二节不同的初始模型、不同的频带范围并考虑不同模式的频散曲线,讨论这些因素对反演结果的影响。在实际应用中,频散曲线的提取误差总是存在的,这是面波频散曲线反演的一般性问题。这里我们不考虑对频散曲线进行加噪处理,原因在于:① 频散曲线的提取误差即使在实际应用中,通常是利用频率-速度域的能量分布给出的,也不是统计意义上的误差;② 在反演中,如果要考虑频散曲线提取误差的影响,可以通过多次测量的标准差作为误差,直接作为输入。因此,本文将聚焦于初始模型和观测频段以及高阶模式面波对低速层的约束。本节将分作三个部分,前两小节分别介绍模型1和模型2的情况,最后进行分析讨论。
表 2 模型1和模型2的模型参数Table 2. The parameters of models 1 and 2层序 层厚/m 深度/m 模型1 模型2 $\mathrm{\rho }/ ( \mathrm{g}\cdot {\mathrm{c}\mathrm{m} }^{-3} ) $ ${v}_{{\rm{P}}}/ ( {\rm{m}}\cdot {{\rm{s}}}^{-1} ) $ ${{v} }_{{{\rm{S}}} }/ ( \mathrm{m}\cdot {\mathrm{s} }^{-1} ) $ $\mathrm{\rho }/ ( \mathrm{g}\cdot {\mathrm{c}\mathrm{m} }^{-3} ) $ ${v}_{{\rm{P}}}/ ( {\rm{m}}\cdot {{\rm{s}}}^{-1} ) $ ${{v} }_{{{\rm{S}}} }/ ( \mathrm{m}\cdot {\mathrm{s} }^{-1} ) $ 1 1.0 1.0 1.581 7 249.1 126.5 1.605 3 266.2 135.4 2 1.0 2.0 1.654 6 399.7 156.0 1.629 7 373.2 145.3 3 1.0 3.0 1.728 3 556.2 192.9 1.724 1 580.1 200.8 4 1.0 4.0 1.735 2 659.8 196.8 1.776 2 738.1 221.5 5 1.0 5.0 1.739 5 646.0 199.2 1.732 7 654.9 195.4 6 1.0 6.0 1.739 5 664.8 199.3 1.683 6 554.8 169.6 7 1.0 7.0 1.739 7 653.0 199.4 1.653 0 505.1 155.3 8 1.0 8.0 1.742 1 739.8 200.8 1.508 2 376.8 102.4 9 2.0 10.0 1.754 8 832.9 208.2 1.647 2 611.3 152.8 10 3.0 13.0 1.767 5 926.3 216.0 1.824 7 1 089.9 254.6 11 4.0 17.0 1.780 3 1 120.5 224.1 1.831 0 1 297.7 259.3 半空间 $ \infty $ $ \infty $ 1.792 9 1 210.7 232.3 1.818 5 1 303.7 250.1 ![]() 图 5 表2中两个模型的理论频散曲线红点表示的频率范围与本文实际数据采集得到的观测频散曲线的频带范围相同,如图3c所示(a) 模型1:速度递增模型;(b) 模型2:含有低速层的模型Figure 5. The theoretical dispersion curves calculated from two models 1 and 2 listed in Table 2The red dots indicate the theoretical dispersion curves with the same frequency range as the observed dispersion curves shown in Fig. 3c (a) Model 1:A normal layered model with S-wave velocity increasing with depth; (b) Model 2:A model with a low-velocity layer
图 5 表2中两个模型的理论频散曲线红点表示的频率范围与本文实际数据采集得到的观测频散曲线的频带范围相同,如图3c所示(a) 模型1:速度递增模型;(b) 模型2:含有低速层的模型Figure 5. The theoretical dispersion curves calculated from two models 1 and 2 listed in Table 2The red dots indicate the theoretical dispersion curves with the same frequency range as the observed dispersion curves shown in Fig. 3c (a) Model 1:A normal layered model with S-wave velocity increasing with depth; (b) Model 2:A model with a low-velocity layer3.1 模型1
图6是利用较宽频带范围的频散数据进行反演的结果,观测到的频散点是模型1正演计算得到的1—60 Hz (间隔为1 Hz)的数据。依旧采用表1中的初始模型参数,但区别于第二节在加入新的一阶进行反演时用前一次反演的最终结果更新初始模型以加快收敛速度的做法,本节在反演时均使用同一个初始模型。图6左列分别表示仅使用基阶(图6a)、基阶和一阶(图6b)以及基阶、一阶和二阶(图6c)模式反演的结果。灰色实线表示初始模型,红色到蓝色表示不同迭代次数的结果,蓝色实线是30次迭代最终得到的结果,黑色虚线表示理论模型;右列对应左侧同一行反演所得最终模型计算的理论频散曲线与所使用的观测频散点的拟合情况。
![]() 图 6 基于模型1多模式瑞雷面波频散曲线的反演(左)及其最终模型理论频散曲线与观测频散曲线的拟合(右)(a) 仅用基阶模式;(b) 基阶和一阶模式联合;(c) 基阶、一阶和二阶模式联合Figure 6. The inversion based on multi-mode Rayleigh-wave dispersion curves of model 1 (left) and the fitting between the theoretical and observed dispersion curves (right)(a) Using only the fundamental mode;(b) Using the fundamental and the first modes;(c) Using the fundamental,the first and the second modes
图 6 基于模型1多模式瑞雷面波频散曲线的反演(左)及其最终模型理论频散曲线与观测频散曲线的拟合(右)(a) 仅用基阶模式;(b) 基阶和一阶模式联合;(c) 基阶、一阶和二阶模式联合Figure 6. The inversion based on multi-mode Rayleigh-wave dispersion curves of model 1 (left) and the fitting between the theoretical and observed dispersion curves (right)(a) Using only the fundamental mode;(b) Using the fundamental and the first modes;(c) Using the fundamental,the first and the second modes对比图6中利用不同模式频散曲线的反演结果,可以看出,对于正频散的介质模型(模型1),如果观测频散曲线的频段较宽,仅利用基阶模式的信息就能很好地拟合理论频散曲线,而且仅利用基阶模式反演得到的模型,对高阶模式的观测频散曲线也有很好的拟合。与加入高阶信息反演的结果相对比,唯一能分辨的区别可能在于在反演迭代过程中收敛速度上的微小差异。对比图6a,6b和6c中的反演迭代次数可知,增加高阶模式频散信息联合反演迭代过程的收敛速度相对于仅使用基阶反演时稍快。
图7是基于图5a中红色圆点所示的23—40 Hz之间的频散点进行反演的结果,其中基阶、一阶和二阶模式的频散曲线与实例分析中的观测频散曲线频带范围一致。图7中左列分别表示仅使用基阶(图7a)、基阶和一阶(图7b)以及基阶、一阶和二阶(图7c)模式反演的结果。灰色实线表示初始模型,红色到蓝色表示不同迭代次数的结果,蓝色实线是30次迭代最终得到的结果,黑色虚线表示的是理论模型;右列分别对应左列最终模型计算的频散曲线与所使用的频散点的拟合情况。
观察图7可以发现,即使观测频带范围较窄,对于速度递增的正频散介质(模型1),仅用基阶反演与加入高阶信息反演的结果都能很好地收敛于理论模型。但是,随着高阶模式信息的加入,反演的收敛速度明显加快。此外,与图6对比发现,仅使用基阶频散信息反演时,频带范围也会影响反演的收敛速度。图6a显示迭代小于5次就基本收敛于理论模型,图7a经过了更多次的迭代才达到与其相当的收敛效果。此时,加入高阶模式反演能缩小甚至消除这种差距(如图7b和图7c)。上述结果表明,仅使用基阶频散数据进行反演时,提取的数据的频段范围会影响反演的收敛速度,加入高阶信息可以减小对反演收敛速度的影响。因此,在实际运用中,加入高阶模式信息可以加快反演收敛速度,使反演更加稳定。
在第二节的实例分析中,为了加快收敛速度,我们通常采用低阶模式反演的最终模型作为考虑更高阶模式反演的初始模型。在图6和图7中,仅考虑基阶模式的反演结果已相当接近理论的模型。三种反演情况的初始模型是相同的,考虑不同模式不同频带范围的反演结果都未出现低速层。因此这个结果说明,在实例分析中,加入高阶模式之后,反演得到的低速特征并非初始模型选择的原因,而是实际介质的真实反映,这一点从下文对含有低速层的模型2的模拟结果可得到进一步印证。
3.2 模型2
图8、图9和图10给出了包含低速层的模型2的数值模拟结果。图8是基于较宽频带的数据反演的结果,左侧分别是利用基阶模式(图8a左)、基阶和一阶(图8b左)以及基阶、一阶和二阶(图8c左)模式反演的模型随迭代次数的变化,图中灰色实线表示初始模型,红色到蓝色实线代表不同迭代次数的结果,蓝色实线是30次迭代的最终结果,黑色虚线表示理论模型;图8c和图8d的区别在于后者反演使用的初始模型为基阶和一阶的反演结果。图8右侧分别对应左侧最终模型计算的理论频散曲线与所使用的观测频散点的拟合情况。图9将二阶观测模式频散曲线截掉几个高频点并采用三种模式共同反演,图9b与图9a的区别是前者将基阶和一阶的反演结果作为初始模型。图10与图8类似,差别是图10各模式的频带范围较窄,在23—40 Hz之间。
![]() 图 8 基于模型2多模式瑞雷面波频散曲线的反演(左)及其最终模型理论频散曲线与观测频散曲线的拟合 (右)(a) 仅用基阶模式;(b) 基阶和一阶模式联合Figure 8. The inversion based on multi-mode Rayleigh-wave dispersion curves of model 2 (left) and the fitting between the theoretical and observed dispersion curves (right)(a) Using only the fundamental mode;(b) Using the fundamental and the first modes
图 8 基于模型2多模式瑞雷面波频散曲线的反演(左)及其最终模型理论频散曲线与观测频散曲线的拟合 (右)(a) 仅用基阶模式;(b) 基阶和一阶模式联合Figure 8. The inversion based on multi-mode Rayleigh-wave dispersion curves of model 2 (left) and the fitting between the theoretical and observed dispersion curves (right)(a) Using only the fundamental mode;(b) Using the fundamental and the first modes![]() 图 8 基于模型2多模式瑞雷面波频散曲线的反演(左)及其最终模型理论频散曲线与观测频散曲线的拟合 (右)(c) 基阶、一阶和二阶模式联合;(d) 基阶、一阶和二阶模式联合,其中初始模型为图(c)的最终模型Figure 8. The inversion based on multimode Rayleigh-wave dispersion curves of model 2 (left) and the fitting between the theoretical and observed dispersion curves (right)(c) Using the fundamental,the first and the second modes;(d) Using the fundamental, the first and the second modes,and the initial model is the final model of Fig.c;
图 8 基于模型2多模式瑞雷面波频散曲线的反演(左)及其最终模型理论频散曲线与观测频散曲线的拟合 (右)(c) 基阶、一阶和二阶模式联合;(d) 基阶、一阶和二阶模式联合,其中初始模型为图(c)的最终模型Figure 8. The inversion based on multimode Rayleigh-wave dispersion curves of model 2 (left) and the fitting between the theoretical and observed dispersion curves (right)(c) Using the fundamental,the first and the second modes;(d) Using the fundamental, the first and the second modes,and the initial model is the final model of Fig.c;![]() 图 9 基于模型2多模式瑞雷面波频散曲线的反演 (左) 及其最终模型理论频散曲线与观测频散曲线的拟合 (右)(a) 基阶、一阶和二阶模式联合(仅使用部分二阶频散数据);(b) 基阶、一阶和二阶模式联合,其中初始模型为图8b的最终模型(仅使用部分二阶频散数据)Figure 9. The inversion based on multi-mode Rayleigh-wave dispersion curves of model 2 (left) and the fitting between the theoretical and observed dispersion curves (right)(a) Using the fundamental,the first higher and the second higher modes (only part of the second higher mode dispersion data are used);(b) Using the fundamental,the first and the second modes,and the initial model is the final model of Fig.8b (only part of the second mode dispersion data are used)
图 9 基于模型2多模式瑞雷面波频散曲线的反演 (左) 及其最终模型理论频散曲线与观测频散曲线的拟合 (右)(a) 基阶、一阶和二阶模式联合(仅使用部分二阶频散数据);(b) 基阶、一阶和二阶模式联合,其中初始模型为图8b的最终模型(仅使用部分二阶频散数据)Figure 9. The inversion based on multi-mode Rayleigh-wave dispersion curves of model 2 (left) and the fitting between the theoretical and observed dispersion curves (right)(a) Using the fundamental,the first higher and the second higher modes (only part of the second higher mode dispersion data are used);(b) Using the fundamental,the first and the second modes,and the initial model is the final model of Fig.8b (only part of the second mode dispersion data are used)由于模型2的反演结果差异较大,因此只讨论结果好坏,不再讨论收敛速度。从图8中可观察到:① 仅利用基阶反演的结果在5 m内是很理想的,但在5—13 m与理论模型有所偏差,特别是在6—8 m和10—13 m处(图8a左),此时,理论频散曲线与基阶观测频散点拟合很好,但并没有拟合上(图8a右);② 加入一阶进行反演的结果明显好很多,所得结果与理论模型相当接近,理论频散曲线与基阶、一阶拟合很好,与二阶在相对低频部分拟合很好,高频部分仅有微小偏差(图8b左);③ 图8c左在加入二阶信息后,结果却与理论模型有了很大偏差;观测频散点与理论频散曲线拟合也不好(图8c右);④ 图8d左是利用基阶和一阶的反演结果作为初始模型,加入二阶信息反演的结果,对比前面三种情况,此时得到的结果是最好的,其频散点拟合情况也很好。
如图9,截去二阶54—60 Hz范围内的七个观测频散点,然后利用基阶、一阶和二阶联合反演的结果(图9a)相较图8b左的结果在2—10 m深度更好;而以基阶、一阶反演结果作为初始模型反演(图9b左)的结果较此还要更好一些,与图8d左的结果基本一致。
图10a仅考虑基阶模式的反演结果显示,4—10 m的低速层未能很好地恢复,反演模型的频散曲线在10 Hz左右的极小值也不够明显,最终结果与真实模型尽管相差较大,但所表现出的高速层和低速层深度基本一致。随着加入高阶信息反演,得到的反演模型的低速层逐渐接近真实模型,且反演模型的基阶模式频散曲线中10 Hz处的极小值也越来越明显。
图8a中的基阶模式频散曲线具有较宽的频带范围,在整个频段上,频散曲线的变化特征就指示了低速层的存在,比如图8b中基阶模式频散曲线在10 Hz左右具有速度的极小值。因此,仅利用基阶模式的反演结果,虽然与真实模型有一定的差距,但反演模型表现出明显的低速特征。正因为如此,在实际应用中,如果观测的频散曲线不含明显的低速特征,经验会使人们以为反演的模型不应具有明显的低速特征,这种经验并不总是有用的。如图10所示,如果观测的频散曲线只是整个频段的一部分,且不具有明显的低速特征,按照经验,其反演模型应该不具有明显的低速特征。但图10的结果表明,虽然仅考虑基阶模式时,反演模型频散曲线的低速层特征并不明显;但加入模式之后,反演模型频散曲线的低速特征相当接近真实模型,如图10b和10c所示。这里对于仅考虑基阶和模式的反演,采用了同样的初始模型,且给定的初始模型不具有明显的低速特征,因此可以排除低速层的存在是初始模型造成的。对比图10b与图10c,可以看出基阶、一阶联合反演结果与基阶、一阶及二阶的联合反演结果相比并不能确切地说哪个更好。具体来说,前者对5 m以上的层约束更好,后者对5 m以下的约束更好;且二者的结果均比仅使用基阶反演的结果要好。在图10d中,采用基阶和一阶反演的结果作为考虑更多模式反演时的初始模型,其反演结果与理论模型基本一致。图10的模拟结果表明,图4中反演得到的低速层特征,并不是初始模型选择的原因。处理实际数据时,用前一次的反演结果作为考虑更反演时的初始模型也是合理的。
3.3 讨论
Liang等(2008)的研究认为低速层以下的相速度具有很低的敏感度。对于相速度对S波速度敏感度很低的地层,其反演结果具有较强的不确定性,需慎重对待(尹晓菲等,2020)。基于这个观点,我们计算了频率为30,35和40 Hz在不同深度的瑞雷面波相速度对S波速度的敏感度(图11)。整体而言,两个模型的基阶模式敏感度主要集中在浅地表4 m之内,4 m以下敏感度迅速衰减为0,这佐证了第二节我们推测实际提取的基阶频散数据对5 mm以下的深度约束不够的观点。对于速度递增的模型1,随着阶数的增加,相同频率下,阶数越高,其敏感度反映的深度越深,如图11所示,模型1的一阶模式敏感度主要集中在0—12 m以内,二阶模式在0—17 m均有敏感度。对含有低速层的模型2,基阶模式的敏感度特征与速度递增的模型1类似,但是高阶模式的敏感度表现出明显不同的特征,其敏感度的最大值集中在4—10 m,即模型2的低速层之内,这是典型的能陷模式的导波特征(张碧星,鲁来玉,2002),与包含低速层的多层介质高阶模式面波产生的机理相关,一阶和二阶模式对应在低速层内来回反射,能量陷于低速层内的能陷模式,因此一阶和二阶模式对低速层更为敏感,即使观测频散曲线不包含明显指示低速特征的频段,也可以通过一阶和二阶模式的加入反演约束模型的低速层。这也证明,图4的实例分析中反演得到的低速层,是实际介质模型的反映,与初始模型的选择无关。
如Liang等(2008)所说,模型2的1阶高阶灵敏度在低速层4—10 m下确实逐渐衰减为0,但二阶在16 m深度以上仍有一定敏感度,且两种模式在低速层均有较高的敏感度。在4 m以内,基阶的灵敏度高出一阶和二阶很多。因此,在加入二阶反演时出现无法收敛的原因可能是由于反演具有多解性,基阶和高阶都对此范围有约束,反而影响了反演结果。加入二阶数据反演时出现的情况说明反演算法的局限性限制了数据利用的最大化,因此反演并非利用越多的观测数据越好,应根据实际情况使用数据。实际应用中,最可靠的标准应该是各阶观测频散数据的拟合情况,拟合好的情况下,加入高阶信息进行反演的结果明显更准确,即加入高阶信息可以提高反演准确性;而由于反演的多解性及反演算法对初始模型的依赖性,在观测数据拟合不好的情况下,不能盲目加入高阶信息,可以尝试对高阶信息先筛选后使用,或将未加入更高阶信息时拟合情况较好的反演结果作为初始模型,再进行反演从而得到更准确的结果。
为了更直观地观察考虑不同模式的反演结果,图12给出了模型1和模型2考虑不同模式、基于不同频段频散曲线的反演结果。图12a为速度递增的模型1的反演结果,左侧为较窄频段的频散曲线反演结果,右侧为较宽频段的频散曲线反演的结果。整体而言,仅用基阶模式与加入高阶模式的反演结果差异较小,仅用基阶模式反演也能较好地恢复真实模型。
图12b为包含低速层的模型2的反演结果,左侧为窄频段的频散曲线反演结果,右侧为较宽频段的频散曲线反演的结果。观察图12b可以发现,仅使用基阶及使用基阶和一阶反演时,宽频带范围的结果明显更好;但加入二阶后,窄、宽频段的反演结果相差无几。这一点并不奇怪,在图12b右中,反演所用的频带包含了高频和低频段数据,相应地提供了更多地约束。因此,如果能获取感兴趣的深度范围对应频率范围完整的基阶频散数据,那此时仅用基阶反演得到的结果相对来说也是比较可靠的。另外,与模型1相比,此时高阶模式对低速层的约束更为显著,仅考虑基阶模式时,如果频带较窄,反演模型低速特征并不明显(图12b左灰色实线);如果频带范围较宽,反演的模型包含低速特征(图12b右灰色实线),但与真实模型也相差较远;对于窄频段情况,仅考虑基阶模式则难以恢复模型的低速特征(图12b左灰色实线)。这与之前众多学者研究多模式瑞雷面波频散反演得出的观点—高阶模式对地下介质分析有着重要作用,尤其是存在低速层时作用更为显著相契合(如Tokimatsu et al,1992)。
通过以上数值模拟,我们论证了:① 对于本文所考虑的这类包含低速层的介质模型,仅从观测的基阶模式无法准确地重建介质的低速特征,高阶模式瑞雷面波对低速层具有重要的约束作用;② 相对于基阶模式,包含低速层的高阶模式对应着时域多径在低速夹层中来回反射、能量陷于低速层内部的能陷导波,因此其灵敏度主要集中在低速层区域;③ 在第二节中,由实际观测数据反演得到的低速层并不是初始模型选取的原因,而是实际介质的真实反应。
4. 沿测线的二维S波速度剖面
通过理论分析,我们论证了基于实际观测的多模面波反演的可靠性。将第二节中单个阵列的反演结果作为阵列中心位置下方的速度结构,然后移动阵列,对各个炮点的数据进行类似处理,再将不同阵列的一维S波速度剖面拼合得到拟二维S波速度剖面。
按照上述方法,我们对测线上103个炮点的排列都进行处理,得到了各阵列下方的一维S波速度结构,再通过插值构建出沿测线的拟二维S波速度剖面,如图13所示。由于缺乏该区的钻孔波速资料,我们只能结合该区的第四纪地层特征对所得结果进行定性分析。前人利用基于天津地区钻孔资料开展的古地磁与磁性地层的研究所得结果,并结合钻孔资料,给出的天津地区的第四纪地层剖面(如陈宇坤等,2008)显示,天津地区的第四纪地层全新统(Qh)底板埋深约为18.6 m。该深度范围正是我们反演的有效深度范围,顶部多有人工填土,底部常含有泥炭层和咸、淡水化合物,为海侵前的海相沉积。沿测线的钻孔TN7,TN6,TN5及TN4的结果显示,第一海相层的深度约在2—18 m之间(陈宇坤等,2013),其图层性质如图13右所示(陈宇坤等,2013)。反演的整个剖面显示,在浅地表2 m之内,有一个低速层,对应地表的杂填土;在2—5 m范围,对应第一海相层的顶层;其土层性质为黏土,相对地表的杂填土和下面的海相沉积,表现为高速特征,速度范围为200—300 m/s;在5—10 m范围出现了一个低速层,其速度范围在100—200 m/s,推测是粉砂和细粉砂海相沉积层的反映。在此低速层之后速度逐渐增加至12 m深度的200—300 m/s。
5. 讨论与结论
在实际应用中,存在一类包含低速层的介质模型,在感兴趣的频率范围内,瑞雷面波各模式频散曲线并无视觉上的交叉现象,各个模式的观测频散曲线也无明显的低速特征指示。针对这类包含低速层的介质模型,本文通过对天津某地一条测线的浅层地震反射勘探资料进行二次处理提取出其中的面波信息,结合数值模拟,研究了高阶瑞雷面波对低速层的约束作用。研究结果表明:① 对于该类包含低速层的介质模型,仅仅由频散点数较少的基阶模式的频散曲线无法反演重建介质的低速特征,想要约束模型的低速层需要加入高阶模式的频散曲线;② 这类含低速层的模型,其观测频散曲线在感兴趣的频段可能无明显的低速特征指示,如果同时考虑高阶模式反演,反演模型的低速特征可能是真实模型的体现,并不是由初始模型的选择或其它原因引起;③ 这类模型的存在表明,观测的基阶模式无低速特征指示,并不意味着真实模型不含低速层,因此在实际应用中,仅由观测曲线的速度变化特征定性判定模型是否具有低速特征,具有一定局限性,尤其是观测频段较窄时;④ 验证了传统高阶模式反演的两个优势,即相同频率下,高阶模式面波比基阶模式具有更深的穿透深度,以及同时考虑基阶和高阶模式频散曲线可以加快收敛速度,增加反演的稳定性;⑤ 浅层地震反射中的勘探数据,经过一定处理,可以对之前被视为干扰的面波信号进行二次利用;且由于此类数据能提取到的频散数据频率覆盖范围较窄,此时高阶模式反演很适用。就本文考虑的实例而言,利用较少模式反演的结果作为增加更多模式反演时的初始模型是合理的选择,反演模型中低速层的出现并非出于初始模型选择。
天津市地震局高武平高级工程师在资料处理和论文撰写过程中提供了帮助,两位审稿专家为文章的完善提出了宝贵意见,作者在此一并表示感谢!
-
图 8 三峡库区上地壳S波QS值分布图
三角形为台站,红线为剖面测线Ⅰ,椭圆为QS低值区,白线为长江三峡,棕线为断裂
Figure 8. Distribution of QS values in the upper crust of Three Gorges Reservoir region
Red triangles represent stations,red line represents the profile Ⅰ,ellipses represent the areas with low QS value,white line represents Three Gorges of the Yangtze River,brown lines represent faults
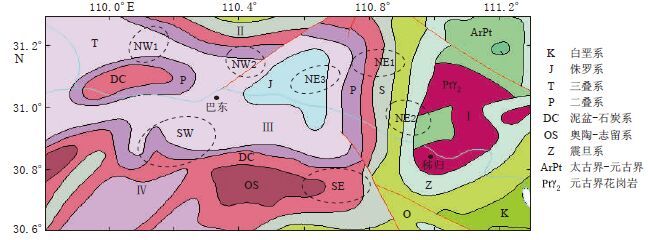
图 9 三峡库区地质构造简图(黄崇轲等,2002)
Ⅰ: 黄陵背斜; Ⅱ: 神农架穹窿; Ⅲ: 秭归向斜; Ⅳ: 八面山褶皱区
Figure 9. Sketch map showing geological tectonic of Three Gorges Reservoir region(after Huang et al,2002)
Ⅰ: Huangling anticline; Ⅱ: Shennongjia dome; Ⅲ: Zigui syncline; Ⅳ: Bamianshan fold area
表 1 三峡库区人工测深剖面不同段的平均Q值与QS值比较
Table 1 Comparison of average Q value with QS value for the different segments on the deep seismic sounding(DSS)profile in Three Gorges Reservoir region
距剖面西端(奉节)距离/km Q值 QS值 基底以上 基底至上地壳底部 25—60 110 308 160—220 60—90 65 345 240—260 90—100 93 345 240-260 100—150 74 291 120—200 平均Q值 85 322 约180 -
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 刘朝阳. 基于光纤微动的泉水敏感区不良地质探查方法研究. 铁道建筑技术. 2024(10): 184-187+203 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载: