High resolution remote sensing application research in active fault surveying
-
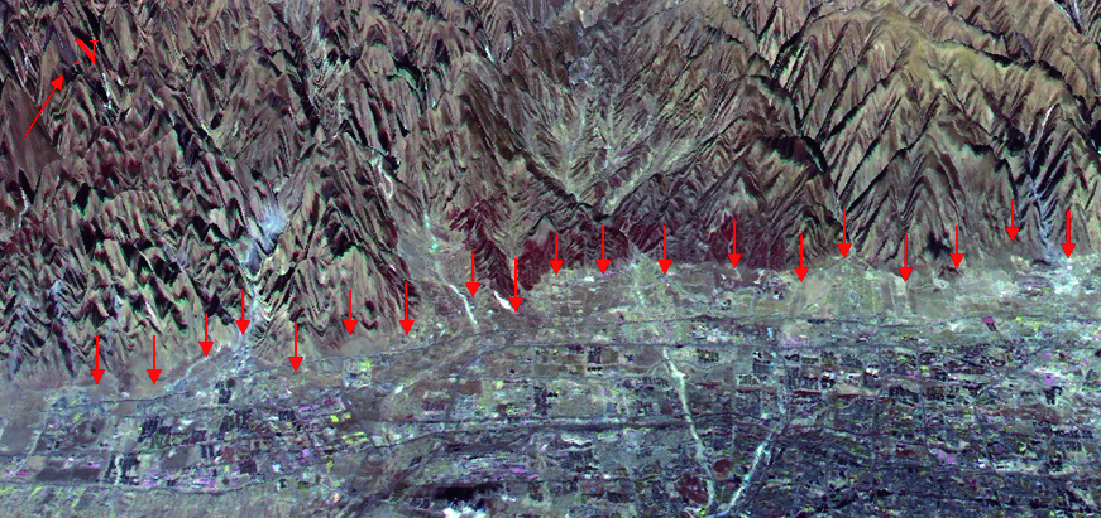
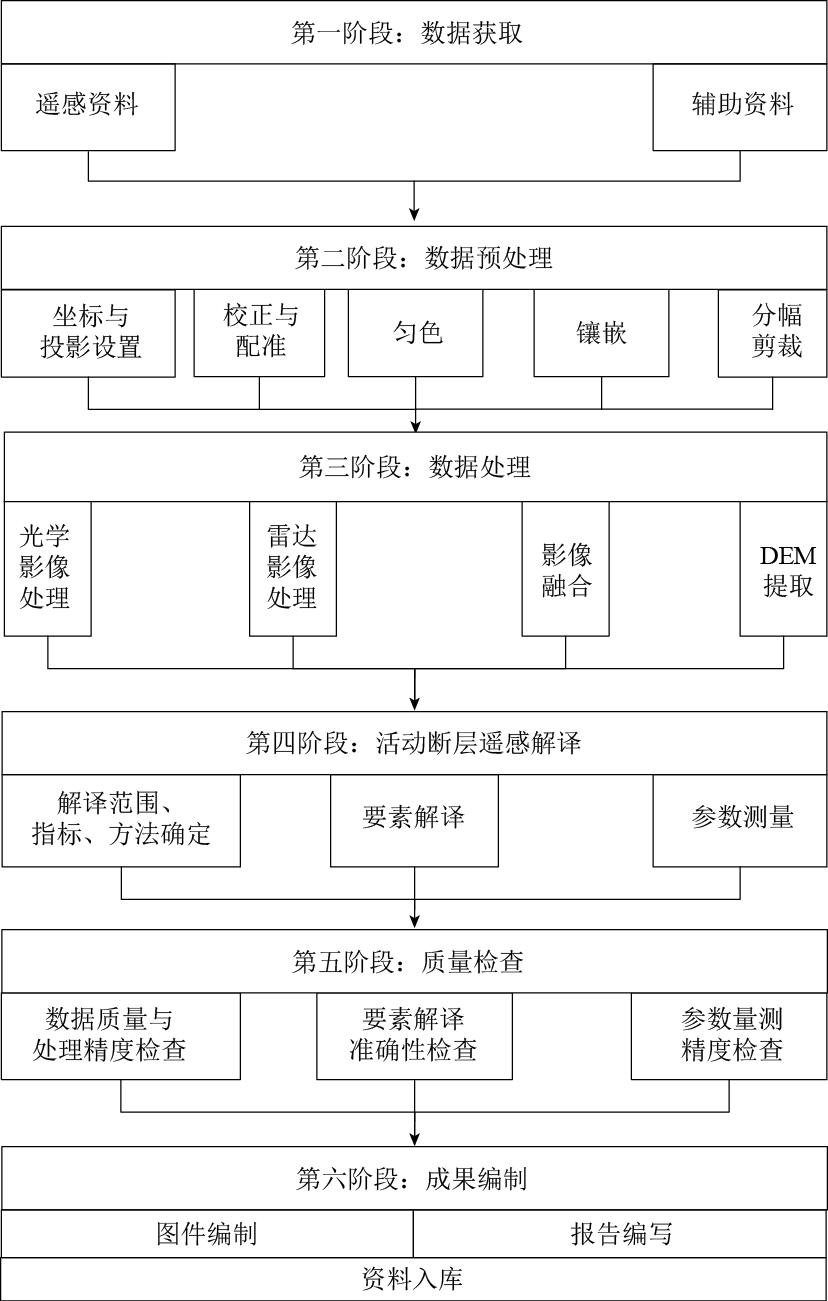
摘要: 本文系统分析了高分辨率遥感在活动断裂调查中应用的技术现状、工作流程,梳理了各类遥感数据的要求、适用条件和处理方法,总结了活动断裂的遥感解译方法、解译要素和测量参数,并通过实例解析了一些典型的断错地貌,给出了相应的遥感特征. 基于资源三号卫星的立体像对和影像,判读了大青山活动断裂的几何特征和活动特性. 结果表明: 人工改造较大的地区宜收集早期遥感影像,利用不同波段间地物光谱的差异来增强隐伏活动断裂的信息,使用空间增强方法来识别断层陡坎等线性构造;雷达数据多极化分解是检测隐伏构造信息的有效方法;由宏观信息向局部信息追踪是活动断裂解译的有效途径;将遥感影像与数字高程模型(DEM)联合可进行活动断层参数的高精度测量. 本文结果可为活动断裂大比例尺、定量调查提供参考.Abstract: This paper analyzes systematically the technology status-quo and work flow of high resolution remote sensing in application of the active fault investigation,combing with the various of remote sensing data requirements,applicable conditions and processing methods,and summarizes the interpretation method,interpretation elements and measurement parameters of remote sensing for active faults. Furthermore,some typical features of faulted geomorphologies are analyzed,and the corresponding remote sensing characteristics are described. Taking the Daqingshan as a test,the geometric features and activity characteristics of the active faults in the area are interpreted by using the stereoscopic image and image of ZY3,meeting the needs of quantitative research on the active structure. The results suggest that the old remote sensing image should be collected in the surfaces deeply changed by city development,and the spectral differences in different bands can be adopted to enhance the information of buried faults,meanwhile, the spatial enhancement methods can be used to identify fault scarp. Multi-polarization radar data decomposition is an effective method for the detection of buried structure features,and tracking from the macro information to the local information is also an effective way to make active faults interpretation. The combination of remote sensing images with DEM will improve the measurement precise of active fault parameters. The results provide reference for the large-scale and quantitative investigation of active faults,and for the researchers to grasp the relevant technology of remote sensing application as soon as possible.
-
-
表 1 遥感解译各波段所探测的地物特征
Table 1 Remote sensing spectrum and its surface features
编号 波段范围/μm 波段名称 波段优势 1 0.45—0.52 蓝绿色波段 对水体有一定的透视能力,适用于浅水水下地形和构造的研究 2 0.52—0.60 绿色波段 位于植物的反射峰附近,适用于探测植被的反射率,可反映水下地形和构造特征 3 0.63—0.69 红波段 位于叶绿色的主要吸收带,可提供丰富的裸露地表、岩性、地层、构造、地貌等特征 4 0.76—0.90 近红外波段 是植物的高反射区,可反映植被信息;也是水体的强吸收区,用于含水的地质构造、地貌等的识别 5 1.55—1.75 短波红外波段 对植物和土壤的水分含量敏感,可用于隐伏构造的识别 6 10.4—12.5 热红外波段 对地物热辐射敏感,可根据热辐射差异进行热分布制图、岩石识别与地质探矿 7 2.08—2.35 短波红外波段 对岩石、矿物反应敏感,可用于地质调查、 岩石类型及岩石蚀变带区分 表 2 遥感影像分类、解译要素及应用范围
Table 2 Classification,interpretation element and application range of remote sensing image
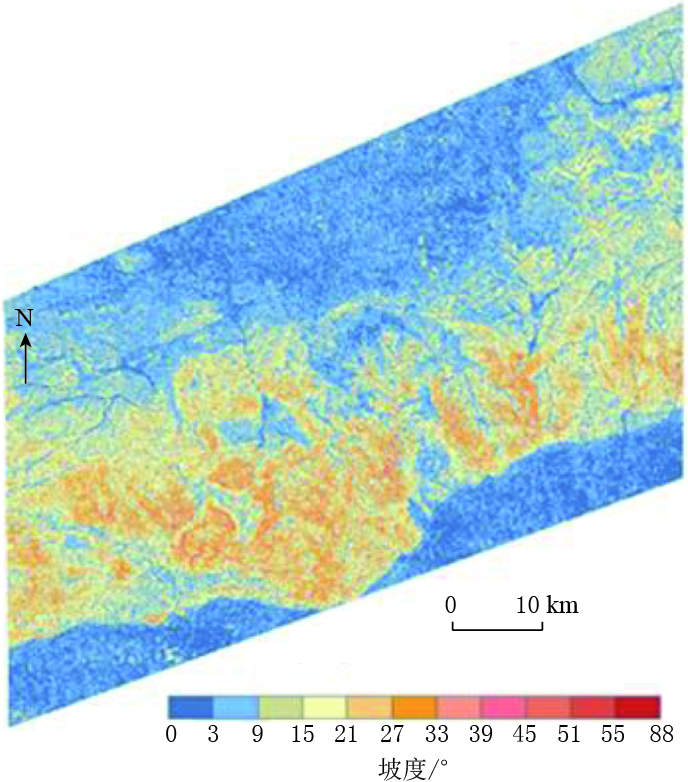
影像分类 空间分辨率/m 解译目标尺度 遥感解译要素 应用阶段 低分辨率影像 < 20 单体尺度约10倍像元大小 单体尺度在大于或等于500 m的地貌单元,连续 class="table_top_border2"或断续状线性特征,大尺度面状构造地貌要素 初察阶段,为宏观掌握活动断裂和地貌发育信息 中等分辨率影像 20—2 单体尺度约5—10倍像元大小 单体尺度大于或等于200 m的地质、地貌、断层迹线或线性构造,位移值大于等于50 m的断错地貌单元 中间阶段,可控制地质地貌边界,把握活动断裂的基本信息 高分辨率影像 < 2 单体尺度约5—10倍像元大小 单体尺度大于或等于30 m的地质、地貌、断层迹线或线性构造,位移值不小于5 m的断错地貌单元 用于详察阶段的图件产品编制和报告编写 表 3 各类各级识别要素
Table 3 All kinds of recognition elements at all levels
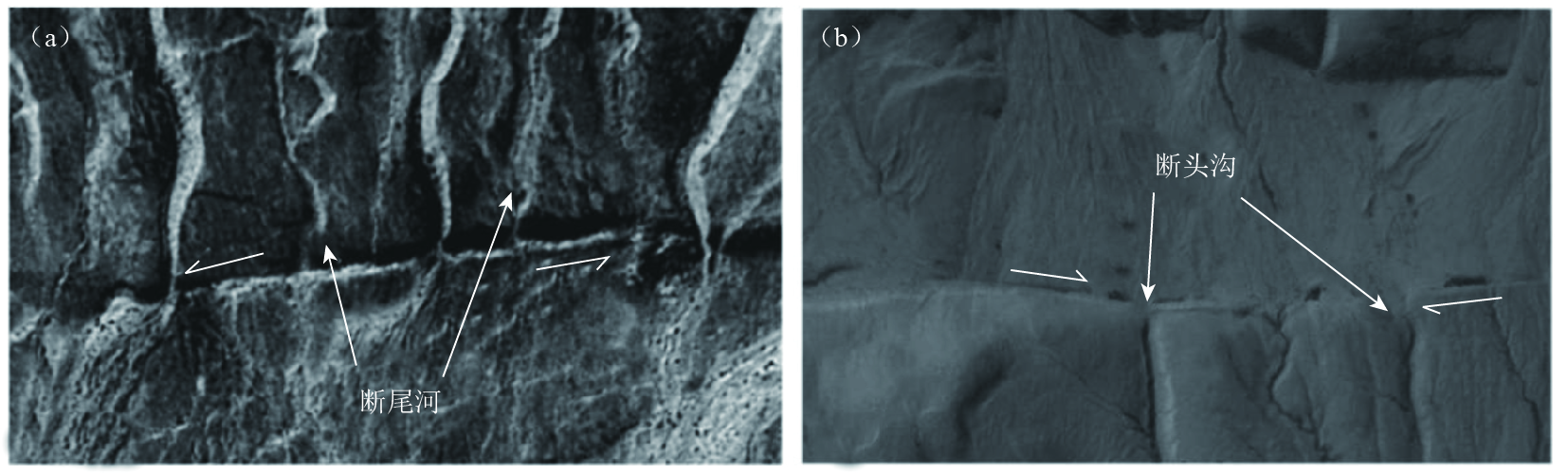
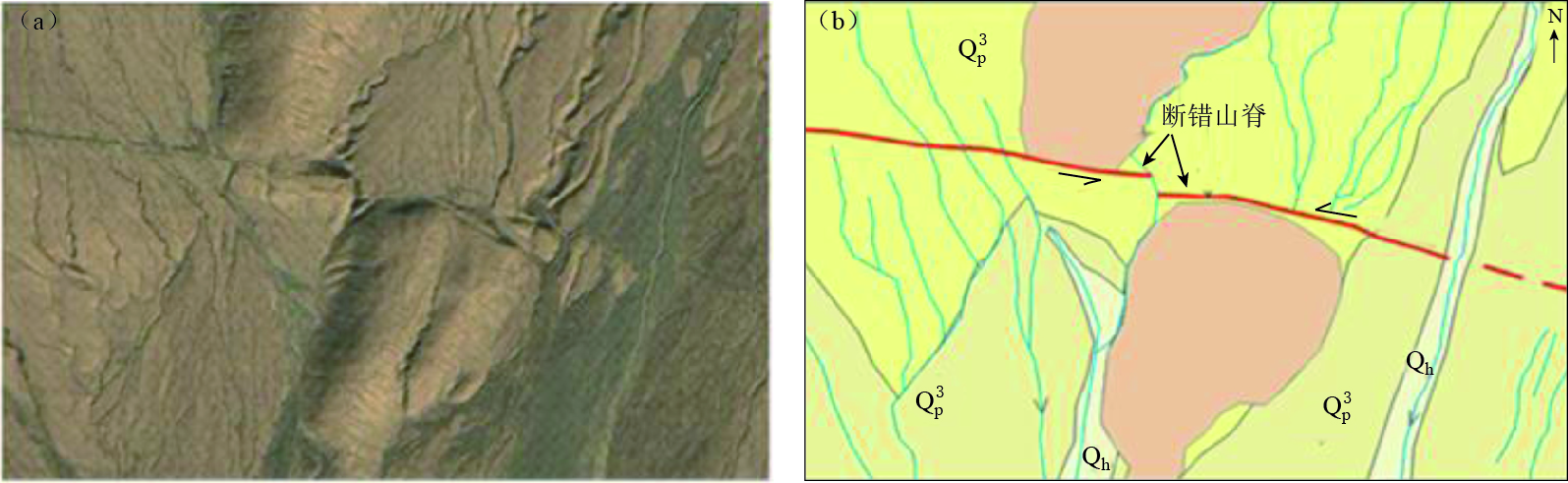
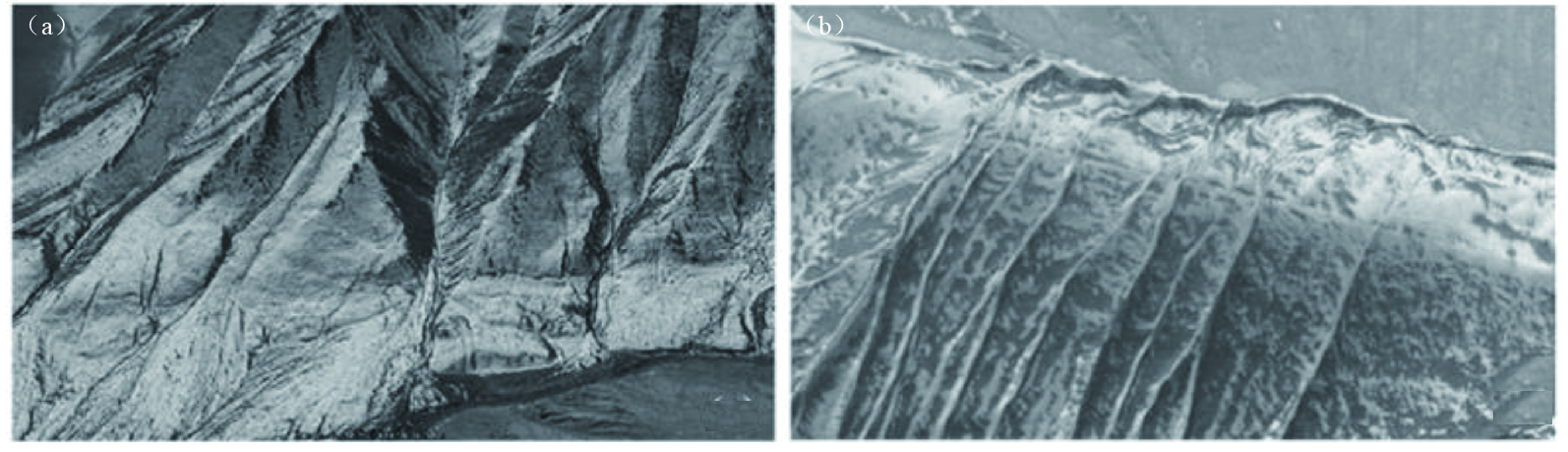
一级要素类别 二级要素类别 具体要素 地层要素 松散沉积层和基岩,第四纪地层及其类型,基岩区宜解译岩浆岩 地貌要素 阶地识别与分级,冲(洪)积扇的识别与分期;水系、冲沟、裂点提取,夷平面、基岩残山、古滑坡体、岗地等 构造地貌要素 正断层 断层陡坎、断错阶地、断层崖、断错洪积扇、断塞塘等 逆断层 断层陡坎、断错阶地、反向陡坎、挤压脊、鼓包、褶皱等 走滑断层 地表破裂带、断塞塘、断层槽地、断错阶地、断错洪积扇、断头沟、断尾沟、挤压脊、闸门脊、鼓包、褶皱、雁行斜列式地表破裂、拉分盆地等线性标志的走滑位错 -




 下载:
下载: