Preliminary research on probing depth of borehole geoelectrical resistivity observation
-
摘要: 对井下地电阻率观测的探测深度进行了研究,计算了均匀半空间和给定结构参数的水平层状介质模型在不同装置电极埋深下的探测深度,分析了探测深度与装置电极埋深和介质电阻率结构之间的关系,得到如下结果:①与地表观测相比,在供电极距为1 km左右时,探测深度随装置电极埋深的增大而增大,且增大的速度与装置电极埋深密切相关;当装置电极埋深h < 100 m时,探测深度的增大速度远小于装置电极埋深h≥100 m时. ②当装置电极埋深h < 50 m时,与地表观测相比探测深度增加很小,不超过10 m;当装置电极埋深相同时,供电极距越大,与地表观测相比探测深度增加得越小. ③对于水平层状电阻率均匀分层结构,在装置电极埋深相同的情况下,下伏低阻结构的探测深度显著大于下伏高阻结构.本文的研究结果表明,为了观测到深部电阻率的变化情况,首先需要查明测区电性结构,再进行综合分析,以确定井下地电阻率观测的装置电极埋深,其结果为深部电阻率变化研究提供了理论基础.Abstract: In this paper, we studied probing depths of borehole geoelectrical resistivity observation by homogeneous half-space model and horizontally layered model with given structure parameters, and analyzed the relationship among probing depth, electrode buried depth of configuration and medium resistivity structure. The results are as follows: ① Compared with surface observation, when electrode distance is about 1 km, probing depth increases with electrode buried depth of configuration, and the increasing rate is closely related with electrode buried depth, as the increasing rate of electrode buried depth less than 100 m is much smaller than that greater than 100 m. ② When electrode buried depth of configuration is within 50 m, probing depth has a slow increase which is less than 10 m, compared with surface observation. For the same electrode buried depth, the greater electrode distance is, the smaller probing depth increases. ③ For the horizontally layered structure of homogeneous resistivity, probing depth in underlying low resistivity structure is significantly larger than that in underlying high resistivity structure under the condition of same electrode buried depth of configurations. Therefore, in order to observe the resistivity variations of deep medium, it is necessary to firstly identify the electrical structure parameters of observation area, and then determine electrode buried depth of borehole geoelectrical resistivity observation through comprehensive analyses.
-
引言
地电阻率前兆观测从物探电法移植而来,在我国已开展50余年.多年的监测结果表明,大震前在震源区及其附近一般均会出现视电阻率变化 (钱复业等, 1982, 1990;桂燮泰等,1989;Lu et al,1999;叶青等,2005;张学民等,2009;钱家栋等,2013),地电阻率是一种比较可靠的地震前兆观测方法 (张国民等,2001;杜学彬,2010).为了减小乃至消除来自表层的干扰以获得可能的深部地震或构造运动信息,研究人员已经逐渐认识到开展井下地电阻率前兆监测的必要性,并陆续开展了相关试验与理论研究 (苏鸾声等,1982;刘允秀等,1985;孟庆武,阎洪朋,1991;聂永安,姚兰予,2009;聂永安等,2010;解滔等,2012).近年来我国加快了井下地电阻率监测台站的建设并加强了观测数据的分析工作 (王兰炜等,2015),杨兴悦等 (2015)和张磊等 (2015)的研究表明,无论是获取强震前的视电阻率变化信息,还是压制表层干扰,井下地电阻率观测均优于传统的地表观测,是一种十分有发展前景的地震前兆观测方式.
目前在我国地电阻率井下观测台站建设中,关于装置电极布设深度对观测结果的影响仍缺乏深入研究,且观测井深和极距的设计缺乏合理性,因此应加快推动相关理论和技术研究,以保障此类观测系统建设的科学性和合理性 (王兰炜等,2015).以观测目的为出发点,装置电极的合理埋深取决于地电阻率的影响系数 (毛先进等,2014;解滔等,2016) 沿深度的分布和理论探测深度,二者均与地电结构密切相关,同时需要避开地表干扰源.物探中研究探测深度的目的是为了将观测值与某个深度相关联,通过选取最佳的电极距使观测数据与地质目标最相关 (霍军廷等,2011).在地震前兆监测方面,赵和云和钱家栋 (1982)研究了对称四极装置布置于地表时的勘探深度和探测范围,认为对于给定的电极距,勘探深度和探测范围与监测区电性结构密切相关;杜学彬等 (2008)分析了强震附近对称四极装置电阻率观测的探测深度,其结果显示对于各向异性介质,在强震孕震晚期和震中附近可检测到较深部地壳介质的电阻率变化.这些工作对台址选择及布极参数的确定均有很好的指导意义,但其仅针对观测装置位于地表的情况.
在井下电阻率观测方面, 毛先进等 (2014)和解滔等 (2016)从影响系数的角度, 研究了其在水平层状介质中的变化特征, 结果显示,不同地层地电阻率影响系数的大小与电阻率结构、装置电极埋深和供电极距等密切相关.本文则在此基础上,进一步研究井下地电阻率观测的探测深度,为确定井下地电阻率观测中最佳装置电极埋深等参数提供理论依据.
1. 探测深度计算方法
常规物探电法对探测深度的定义是,对于均匀半空间,在不同供电极距AB的情况下,AB中垂线上给定深度处的水平方向电流密度是随AB变化的,当水平方向电流密度达到最大时,该深度称为探测深度 (傅良魁,1983),这一定义给出了探测深度与供电极距AB的关系.由于地震前兆监测中实际台站的台址多为多层介质,电流密度的最大值可能存在多值性.为了克服该缺陷,赵和云和钱家栋 (1982)给出了新的探测深度的定义:设地表至深度z处测量电极M与N之间水平方向的面电流为IMN(z),全部面电流为IMN(∞),令二者的比值

(1) 则满足上式的z即为探测深度.比值取

在地电阻率前兆监测分析中,采用式 (1) 作为探测深度的定义更为合理,本文采用该式计算均匀半空间、水平层状介质地表及井下地电阻率观测的探测深度.
1.1 均匀半空间
若均匀半空间的电阻率为ρ,对称四极装置中供电极A,B与测量极M,N的埋深均为h(简称为装置电极埋深),AB=2L(L为半供电极距),MN=2a (a为半测量极距),供电电流强度为I,则深度z处分别与M,N水平坐标相同的两点间的电位差为

(2) 式中,Q=ρI/(2π),深度z处分别与M,N水平坐标相同的两点间的面电流密度为

(3) 地表至深度z处的面电流为

(4) 由式 (2),(3),(4) 计算得到

(5) 
(6) 式 (5) 与式 (6) 相除得

(7) 根据式 (1),求出使式 (7) 等于

1.2 水平层状结构
对于水平层状结构,当供电电极及测量电极位于地表或地下时,可用边界积分方程法或有限元法求得点电流源激励下的地下任意两点间的电位差.本文选用边界积分方程法,该方法能对任意层数的一维及二维介质进行模拟,且其在理论和数值模拟两方面的准确性已被证明 (毛先进,鲍光淑,1998).求得地下各层分界面上分别与M,N水平坐标相同的两个网格节点间的电位差后,根据式 (1),(3),(4) 计算得到探测深度.
2. 计算结果
2.1 均匀半空间
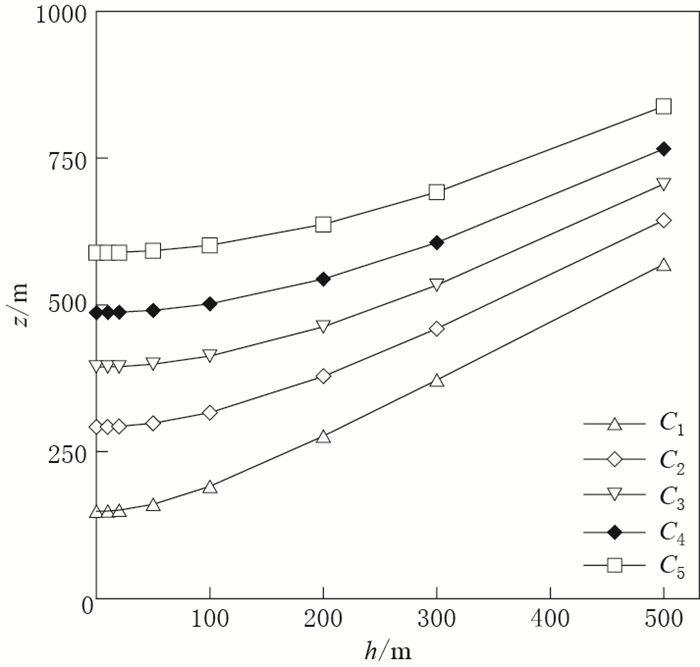
我国地电阻率观测中半供电极距L为500 m左右,表 1给出了目前常用装置 (装置参数分别用C1,C2,C3,C4,C5表示,下同) 在不同埋深时探测深度z的计算结果.探测深度随埋深的变化见图 1.
表 1 几种常用观测装置在井下的探测深度 (均匀半空间)Table 1. The borehole probing depths of several common observation configurations (homogeneous half-space)装置电极埋深
h/mC1
(L=150 m,
a=25 m)C2
(L=300 m,
a=75 m)C3
(L=400 m,
a=75 m)C4
(L=500 m,
a=125 m)C5
(L=600 m,
a=125 m)0 148.2 292.1 394.1 486.8 589.0 10 148.8 292.3 394.3 486.9 589.1 20 150.2 293.1 394.8 487.4 589.5 50 160.3 298.4 398.8 490.6 592.2 100 190.9 316.3 412.5 501.8 601.5 200 276.5 378.1 462.5 543.9 637.3 300 371.9 459.4 533.4 606.1 691.9 500 569.1 644.2 705.6 765.7 838.2 注:L=AB/2,a=MN/2,下同. 由表 1和图 1可知,与观测装置位于地表时 (h=0) 的探测深度z相比,h分别为10,20,50 m时探测深度的增加值依次为0.1—0.6 m,0.5—2.0 m,3.2—12.1 m;h < 100 m时探测深度随埋深的增加速度缓慢,且L越大这一现象越明显;h>100 m时探测深度随埋深的增加速度明显增大.
2.2 水平层状结构
水平层状结构的探测深度与地电阻率的结构有关 (赵和云,钱家栋,1982;霍军廷等,2011),实际地电阻率的结构因地而异.水平层状电阻率均匀分层结构可定性地分为下伏高阻与下伏低阻两种情形,本文则针对这两种情形分别进行研究.
2.2.1 下伏低阻结构计算结果
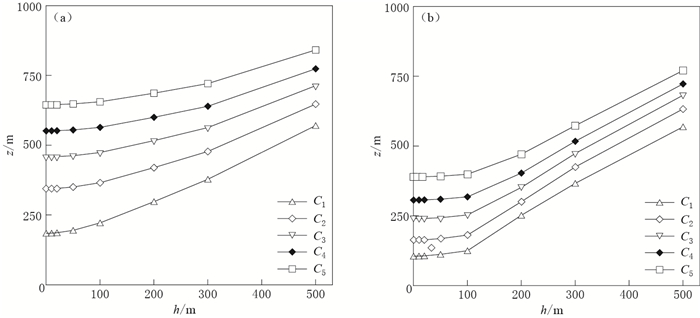
给定一个4层电阻率水平层状均匀分层结构,从上至下电阻率依次为80,40,90, 20 Ω·m,第1—3层厚度均为50 m,第4层厚度趋于∞.计算中设定对称四极装置中供电极A,B与测量极M,N在地表或地下同一深度,不同装置 (C1,C2,C3,C4,C5) 在不同埋深时探测深度z的计算结果见表 2,探测深度随埋深的变化情况如图 2a所示.
表 2 几种常见观测装置在井下的探测深度 (下伏低阻)Table 2. The borehole probing depths of several common observation configurations (underlying low resistivity structure)装置电极埋深
h/mC1
(L=150 m,
a=25 m)C2
(L=300 m,
a=75 m)C3
(L=400 m,
a=75 m)C4
(L=500 m,
a=125 m)C5
(L=600 m,
a=125 m)0 184.4 344.3 458.2 551.3 645.0 10 184.9 344.6 458.5 551.5 645.2 20 186.2 345.3 459.0 551.8 645.6 50 194.9 350.0 462.3 554.7 647.8 100 221.5 365.3 473.6 563.9 655.7 200 297.7 419.4 516.3 600.0 686.4 300 377.9 477.6 563.2 639.6 720.6 500 570.2 646.9 712.9 773.8 841.1 由表 2和图 2a可知,与观测装置位于地表时 (h=0) 的探测深度z相比,h分别为10,20,50 m时探测深度的增加值依次为0.2—0.5 m,0.6—1.8 m,2.8—10.5 m;h < 100 m时探测深度随埋深的增加速度缓慢,且L越大这一现象越明显;h>100 m时探测深度随埋深的增加速度明显增大.
2.2.2 下伏高阻结构计算结果
将上述下伏低阻结构中底层 (即第四层) 的电阻率改为200 Ω·m,其它各层电阻率及层厚保持不变,依然设定对称四极装置中供电极A,B与测量极M,N在地表或地下同一深度处,不同装置 (C1,C2,C3,C4,C5) 在不同埋深时探测深度z的计算结果见表 3,探测深度随埋深的变化见图 2b.
表 3 几种常见观测装置在井下的探测深度 (下伏高阻)Table 3. The borehole probing depths of several common observation configurations (underlying high resistivity structure)装置电极埋深
h/mC1
(L=150 m,
a=25 m)C2
(L=300 m,
a=75 m)C3
(L=400 m,
a=75 m)C4
(L=500 m,
a=125 m)C5
(L=600 m,
a=125 m)0 104.5 162.6 238.8 305.6 388.7 10 104.9 162.7 239.0 305.8 388.8 20 105.8 163.3 239.5 306.2 389.2 50 111.0 167.3 242.4 308.6 391.2 100 124.3 180.3 252.4 317.1 398.1 200 251.1 300.0 351.0 402.4 469.7 300 365.5 424.3 472.5 516.3 572.1 500 568.0 632.2 681.2 721.9 769.7 由表 3和图 2b可知,与观测装置位于地表时 (h=0) 的探测深度z相比,h分别为10,20,50 m时探测深度的增加值依次为0.1—0.4 m,0.5—1.3 m,2.5—6.5 m;h < 100 m时探测深度随埋深的增加速度缓慢,且L越大这一现象越明显;h>100 m时探测深度随埋深的增加速度明显增大.
3. 讨论与结论
本文以电流的主要分布范围为指标,讨论了均匀半空间和电阻率均匀分层模型中下伏低阻及下伏高阻两种典型结构,并通过模拟计算的方法对不同结构下地电阻率在井下前兆观测中的探测深度进行了初步研究.结果显示,在供电极距为数百米至上千米时,与地表观测相比,井下观测的探测深度的增加值具有如下特点:
1) 对于目前我国常用的观测装置和典型的地电阻率结构来说,当装置电极埋深h≤100 m时,与观测装置位于地表时相比,探测深度随埋深增加的速率比埋深h>100 m时小得多.作者此前对其影响系数的研究 (毛先进等,2014) 也得到相似的结论:对于均匀分层结构,在装置电极埋深h≤100 m时基底层 (最下层) 的影响系数随埋深的增加速率比埋深h>100 m时小得多,同时表层介质的影响系数还呈现“减小—增加—减小”起伏变化的现象.
2) 当供电极距在数百米至上千米、装置电极埋深在50 m以内时,与地表观测相比,其探测深度的增加很小,最大只有十余米,且当装置电极埋深相同时,供电极距越大,探测深度的增加值越小.这表明,虽然这样的装置电极埋深对减小来自地表的干扰是有利的,但从获得深部电阻率变化信息的角度来看,并不能达到井下观测的目的.
3) 当装置和电极埋深均相同时,下伏高阻结构的探测深度最小,下伏低阻结构的探测深度最大,均匀半空间的探测深度介于二者之间.比较表 2与表 3可知,按照本文选取的典型地电结构参数,在装置相同的情况下,下伏低阻结构中装置电极埋深为100 m时的探测深度与下伏高阻结构中装置电极埋深为200—300 m时的探测深度相当.实际上,下伏高阻结构是一种比较常见的情形,在这种情况下要增加探测深度就需要加大装置电极埋深.
根据上述特点,本文认为,为获得深部电阻率的变化信息,在井下观测中观测装置应达到一定的埋深,才能获得与地表观测相比更有意义的探测深度.为此,首先需要查明测区电性结构,然后通过计算分析,确定井下地电阻率观测的装置电极埋深.对于我国目前常用的观测装置 (供电极距为数百米至上千米),在均匀分层电性结构下:当观测区为下伏低阻结构时,装置电极埋深应不小于100 m;当观测区为下伏高阻结构时,装置电极埋深应不小于200 m.
需要指出的是,本文仅计算了给定分层参数时两种典型电性结构下 (高阻、低阻) 的装置电极埋深结果,并不能代表所有的高阻或低阻分层结构的情况.对于不同台址,由于电性分层结构存在差异,因此合理的装置电极埋深亦有所差异,应通过具体的计算分析而确定.
-
表 1 几种常用观测装置在井下的探测深度 (均匀半空间)
Table 1 The borehole probing depths of several common observation configurations (homogeneous half-space)
装置电极埋深
h/mC1
(L=150 m,
a=25 m)C2
(L=300 m,
a=75 m)C3
(L=400 m,
a=75 m)C4
(L=500 m,
a=125 m)C5
(L=600 m,
a=125 m)0 148.2 292.1 394.1 486.8 589.0 10 148.8 292.3 394.3 486.9 589.1 20 150.2 293.1 394.8 487.4 589.5 50 160.3 298.4 398.8 490.6 592.2 100 190.9 316.3 412.5 501.8 601.5 200 276.5 378.1 462.5 543.9 637.3 300 371.9 459.4 533.4 606.1 691.9 500 569.1 644.2 705.6 765.7 838.2 注:L=AB/2,a=MN/2,下同. 表 2 几种常见观测装置在井下的探测深度 (下伏低阻)
Table 2 The borehole probing depths of several common observation configurations (underlying low resistivity structure)
装置电极埋深
h/mC1
(L=150 m,
a=25 m)C2
(L=300 m,
a=75 m)C3
(L=400 m,
a=75 m)C4
(L=500 m,
a=125 m)C5
(L=600 m,
a=125 m)0 184.4 344.3 458.2 551.3 645.0 10 184.9 344.6 458.5 551.5 645.2 20 186.2 345.3 459.0 551.8 645.6 50 194.9 350.0 462.3 554.7 647.8 100 221.5 365.3 473.6 563.9 655.7 200 297.7 419.4 516.3 600.0 686.4 300 377.9 477.6 563.2 639.6 720.6 500 570.2 646.9 712.9 773.8 841.1 表 3 几种常见观测装置在井下的探测深度 (下伏高阻)
Table 3 The borehole probing depths of several common observation configurations (underlying high resistivity structure)
装置电极埋深
h/mC1
(L=150 m,
a=25 m)C2
(L=300 m,
a=75 m)C3
(L=400 m,
a=75 m)C4
(L=500 m,
a=125 m)C5
(L=600 m,
a=125 m)0 104.5 162.6 238.8 305.6 388.7 10 104.9 162.7 239.0 305.8 388.8 20 105.8 163.3 239.5 306.2 389.2 50 111.0 167.3 242.4 308.6 391.2 100 124.3 180.3 252.4 317.1 398.1 200 251.1 300.0 351.0 402.4 469.7 300 365.5 424.3 472.5 516.3 572.1 500 568.0 632.2 681.2 721.9 769.7 -
杜学彬, 叶青, 马占虎, 李宁, 陈军营, 谭大诚. 2008.强地震附近电阻率对称四极观测的探测深度[J].地球物理学报, 51(6): 1943-1949. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200806039.htm Du X B, Ye Q, Ma Z H, Li N, Chen J Y, Tan D C. 2008. The detection depth of symmetric four-electrode resistivity observation in/near the epicentral region of strong earthquakes[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 51(6): 1943-1949 (in Chinese). http://manu39.magtech.com.cn/Geophy/EN/abstract/abstract861.shtml
杜学彬. 2010.在地震预报中的两类视电阻率变化[J].中国科学:地球科学, 40(10): 1321-1330. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201010004.htm Du X B. 2011. Two types of changes in apparent resistivity in earthquake prediction[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 54(1): 145-156. doi: 10.1007/s11430-010-4031-y
傅良魁. 1983.电法勘探教程[M].北京:地质出版社: 18-19. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYQY201603027.htm Fu L K. 1983. Electrical Prospecting Tutorial [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 18-19 (in Chinese).
桂燮泰, 关华平, 戴经安. 1989.唐山、松潘地震前视电阻率短临异常图象重现性[J].西北地震学报, 11(4): 71-75. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZBDZ198904007.htm Gui X T, Guan H P, Dai J A. 1989. The short-term and immediate anomalous pattern recurrences of the apparent resistivity before the Tangshan and Songpan earthquakes of 1976[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal, 11(4): 71-75 (in Chinese).
霍军廷, 吴信民, 李乃民. 2011.电阻率剖面法探测深度的研究[J].物探化探计算技术, 33(4): 418-423. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTHT201104013.htm Huo J T, Wu X M, Li N M. 2011. Study of investigation depth of electrical resistivity profiling method[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 33(4): 418-423 (in Chinese). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-WTHT201104013.htm
刘允秀, 吴国有, 王蕃树, 王邦本. 1985. 深埋电极地电阻率观测的实验结果[G]//地震预测: 地电方法论文集. 福州: 福建科学技术出版社: 206-216. Liu Y X, Wu G Y, Wang F S, Wang B B. 1985. Study on experimental results of buried electrode resistivity monitoring system[G]// Earthquake Prediction: Collection of Papers on Georesistivity Method. Fuzhou: Fujian Science and Technology Press: 206-216 (in Chinese).
毛先进, 鲍光淑. 1998.一种适于电阻率成像的正演新方法[J].地球物理学报, 41(增刊): 385-393. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX1998S1040.htm Mao X J, Bao G S. 1998. A new modeling method for resistivity tomography[J]. Acta Geophysica Sinica, 41(Suppl): 385-393 (in Chinese). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX1998S1040.htm
毛先进, 杨玲英, 钱家栋. 2014.水平层状介质中深埋装置系统地电阻率影响系数特征研究[J].地震学报, 36(4): 678-685. http://www.dzxb.org/Magazine/Show?id=28994 Mao X J, Yang L Y, Qian J D. 2014. Characteristics of the influence coefficient in the cases of deeply-buried configurations for geoelectrical resistivity observation[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 36(4): 678-685 (in Chinese). http://www.dzxb.org/Magazine/Show?id=28994
孟庆武, 阎洪朋. 1991.临沂台深井电阻率异常变化与地震的关系[J].西北地震学报, 13(4): 70-74. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZBDZ199104010.htm Meng Q W, Yan H P. 1991. Anomalous changes of resistivity in deep wells observed at Linyi station and its relation to earthquakes[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal, 13(4): 70-74 (in Chinese). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZBDZ199104010.htm
聂永安, 姚兰予. 2009.成层半空间深埋电极产生的电位分布[J].中国地震, 25(3): 246-255. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZD200903002.htm Nie Y A, Yao L Y. 2009. Study on electrical potential by buried source electrode within horizontally layered half-space model[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 25(3): 246-255 (in Chinese). http://www.cqvip.com/QK/84216X/201002/34571089.html
聂永安, 巴振宁, 聂瑶. 2010.深埋电极的地电阻率观测研究[J].地震学报, 32(1): 33-40. http://www.dzxb.org/Magazine/Show?id=27252 Nie Y A, Ba Z N, Nie Y. 2010. Study on buried electrode resistivity monitoring system[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 32(1): 33-40 (in Chinese). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZXB201001005.htm
钱复业, 赵玉林, 于谋明, 王志贤, 刘小伟, 常思敏. 1982.地震前地电阻率的异常变化[J].中国科学:化学, 12(9): 831-839. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZBDZ198202004.htm Qian F Y, Zhao Y L, Yu M M, Wang Z X, Liu X W, Chang S M. 1983. Geoelectric resistivity anomalies before earthquakes[J]. Science in China: Chemistry, 26(3): 326-336. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-JBXG198303009.htm
钱复业, 赵玉林, 刘婕, 黄燕妮. 1990.唐山7.8级地震地电阻率临震功率谱异常[J].地震, 10(3): 33-39. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZN199003004.htm Qian F Y, Zhao Y L, Liu J, Huang Y N. 1990. Power spectrum anomaly of earth resistivity immediately before Tang-shan earthquake M 7.8[J]. Earthquake, 10(3): 33-39 (in Chinese).
钱家栋, 马钦忠, 李劭秾. 2013.汶川MS8.0地震前成都台NE测线地电阻率异常的进一步研究[J].地震学报, 35(1): 4-17. http://www.dzxb.org/Magazine/Show?id=28812 Qian J D, Ma Q Z, Li S N. 2013. Further study on the anomalies in apparent resistivity in the NE configuration at Chengdu station associated with Wenchuan MS8.0 earthquake[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 35(1): 4-17 (in Chinese).
苏鸾声, 王邦本, 夏良苗, 李验轩. 1982.井下电极观测地电阻率排除地面干扰的实验[J].地震学报, 4(3): 274-276. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXB198203005.htm Su L S, Wang B B, Xia L M, Li Y X. 1982. Elimination of surface disturbances in earth-resistivity measurement by lowering the electrodes in shallow wells[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 4(3): 274-276 (in Chinese). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZXB198203005.htm
王兰炜, 张宇, 张世中, 颜蕊, 王子影, 张兴国, 胡哲. 2015.我国井下地电阻率观测技术现状分析[J].地震地磁观测与研究, 36(2): 95-102. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZGJ201502019.htm Wang L W, Zhang Y, Zhang S Z, Yan R, Wang Z Y, Zhang X G, Hu Z. 2015. The status of deep-well geo-electrical resistivity observation in China[J]. Seismological and Geomagnetic Observation and Research, 36(2): 95-102 (in Chinese).
解滔, 杜学彬, 陈军营, 安张辉, 谭大诚, 范莹莹, 刘君. 2012.井下地电阻率观测中地表电流干扰影响计算[J].地球物理学进展, 27(1): 112-121. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.1004-2903.2012.01.013 Xie T, Du X B, Chen J Y, An Z H, Tan D C, Fan Y Y, Liu J. 2012. Calculation for the influence from the surface disturbance current in the deep-well geoelectrical resistivity observation[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 27(1): 112-121 (in Chinese). http://manu39.magtech.com.cn/Geoprog/EN/abstract/abstract8478.shtml
解滔, 杜学彬, 卢军. 2016.井下视电阻率观测影响系数分析[J].中国地震, 32(1): 40-53. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZD201601004.htm Xie T, Du X B, Lu J. 2016. Sensitivity coefficients analysis of deep-well apparent resistivity measurement[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 32(1): 40-53 (in Chinese).
杨兴悦, 王燕, 张立红, 张俏丽, 叶媛媛. 2015.天水井下地电阻率资料应用研究[J].震灾防御技术, 10(1): 173-183. doi: 10.11899/zzfy20150118 Yang X Y, Wang Y, Zhang L H, Zhang Q L, Ye Y Y. 2015. Analysis of geoelectrical resistivity data from underground well at Tianshui station[J]. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 10(1): 173-183 (in Chinese).
叶青, 杜学彬, 陈军营, 谭大成, 马占虎. 2005. 2003年大姚和民乐—山丹地震1年尺度预测[J].地震研究, 28(3): 226-230. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYJ200503003.htm Ye Q, Du X B, Chen J Y, Tan D C, Ma Z H. 2005. One-year prediction for the Dayao and Minle-Shandan earthquakes in 2003[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 28(3): 226-230 (in Chinese).
张国民, 傅征祥, 桂燮泰. 2001.地震预报引论[M].北京:科学出版社: 214-270. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYQY201603027.htm Zhang G M, Fu Z X, Gui X T. 2001. Introduction to Earthquake Prediction [M]. Beijing: Science Press: 214-270 (in Chinese).
张磊, 乔子云, 罗娜, 张国苓, 贾立峰, 白云刚, 张波. 2015.河北大柏舍台深井与浅层地电阻率观测对比分析[J].华北地震科学, 33(4): 49-53. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDKD201504010.htm Zhang L, Qiao Z Y, Luo N, Zhang G L, Jia L F, Bai Y G, Zhang B. 2015. Contrastive analysis of georesistivity in deep-well and on ground at Dabaishe station[J]. North China Earthquake Sciences, 33(4): 49-53 (in Chinese).
张学民, 李美, 关华平. 2009.汶川8.0级地震前的地电阻率异常分析[J].地震, 29(1): 108-115. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZN200901014.htm Zhang X M, Li M, Guan H P. 2009. Anomaly analysis of earth resistivity observations before the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Earthquake, 29(1): 108-115 (in Chinese). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DIZN200901014.htm
赵和云, 钱家栋. 1982.地电阻率法中勘探深度和探测范围的理论讨论和计算[J].西北地震学报, 4(1): 40-56. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZBDZ198201003.htm Zhao H Y, Qian J D. 1982. Theoretical discussion and calculation about detective depth and detective range in earth resistivity method[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal, 4(1): 40-56 (in Chinese). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZBDZ198201003.htm
Lu J, Qian F Y, Zhao Y L. 1999. Sensitivity analysis of the Schlumberger monitoring array: Application to changes of resistivity prior to the 1976 earthquake in Tangshan, China[J]. Tectonophysics, 307(3/4): 397-405. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/256860286_Sensitivity_analysis_of_the_Schlumberger_monitoring_array_Application_to_changes_of_resistivity_prior_to_the_1976_earthquake_in_Tangshan_China
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 叶青,王晓,杜学彬,解滔,范晔,周振贵,刘高川. 中国地震井下地电阻率研究进展. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版). 2022(03): 669-683 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. Guoze ZHAO,Xuemin ZHANG,Juntao CAI,Yan ZHAN,Qinzhong MA,Ji TANG,Xuebin DU,Bing HAN,Lifeng WANG,Xiaobin CHEN,Qibin XIAO,Xiangyu SUN,Zeyi DONG,Jijun WANG,Jihong ZHANG,Ye FAN,Tao YE. A review of seismo-electromagnetic research in China. Science China(Earth Sciences). 2022(07): 1229-1246 .  必应学术
必应学术
3. 赵国泽,张学民,蔡军涛,詹艳,马钦忠,汤吉,杜学彬,韩冰,王立凤,陈小斌,肖骑彬,孙翔宇,董泽义,王继军,张继红,范晔,叶涛. 中国地震电磁研究现状和发展趋势. 中国科学:地球科学. 2022(08): 1499-1515 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 鲍海英,夏忠,毕雪梅,李鸿宇,王昕. 江苏海安顾庄观测站井下地电阻率观测影响系数分析. 地震. 2022(03): 192-203 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 黄明威,张琪,李梦莹,杨牧萍. 新城子井下地电阻率观测影响系数分析. 防灾减灾学报. 2020(01): 49-56 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 高曙德,罗维斌,张博,武善艺,李娜,曹玲玲,窦喜英. 编码源地电观测对干扰信号的抑制试验——以通渭台观测为例. 地震工程学报. 2020(05): 1096-1103 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 毛先进,段炜,庄儒新,杨玲英,赵晋民. 井下地电阻率观测中布极参数的确定方法. 地震研究. 2019(01): 96-101 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 樊晓春,解滔,吴帆,袁慎杰. 井下地电阻率观测影响系数分析——以江宁地震台为例. 中国地震. 2019(02): 347-358 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: