Spatio-temporal revolution characteristics of methane emission before and after the 2013 Lushan MS7.0 earthquake
-
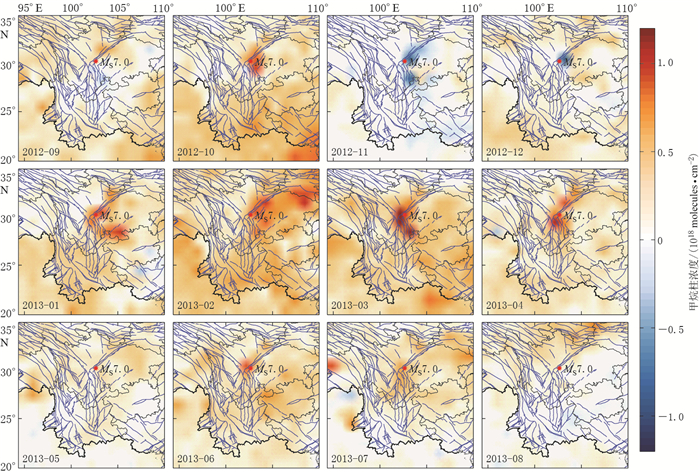
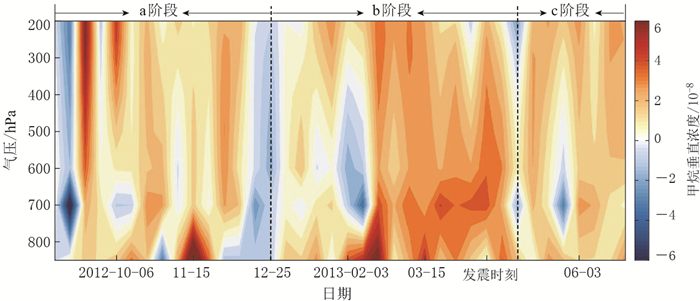
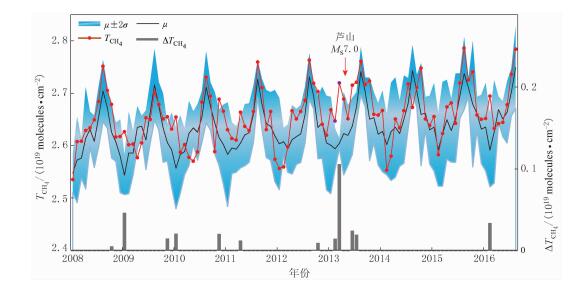
摘要: 为研究地震活动与大气甲烷浓度时空演变之间的关系,以芦山MS7.0地震为例,基于极轨卫星AQUA上搭载的卫星大气红外探测器(AIRS)获取的甲烷数据产品,通过背景值差值法对该地震前后甲烷柱浓度信息、垂直浓度廓线信息及长时间序列变化信息进行提取,挖掘芦山地震前后甲烷异常排放的时空演化特征.结果表明:2013年1—4月芦山震中区存在明显的甲烷浓度升高;甲烷浓度时空演化趋势为初始排放→激增扩散→聚敛加强→相对减弱→震后排放→回复平静;震前震中区甲烷柱浓度为该地区2008年1月—2016年8月异常最显著的时段.因此认为芦山MS7.0地震前甲烷排放浓度升高现象或为该地震的前兆信息.Abstract: Taking the case of Lushan MS7.0 earthquake, the spatio-temporal evolution characteristics of methane (CH4) before and after the earthquake were studied using CH4 data got from atmospheric infrared sounder (AIRS) instrument on AQUA satellite. Total volume of CH4, CH4 vertical profiles and long-time serial variation before and after the earthquake were analyzed by the background contents difference value method. The results showed that the CH4 concentration increased significantly in the epicentral area from January to April, 2013. The evolution trend of CH4 appeared as following: initially rose→increased abruptly and diffused→accumulated and reached to maximum→relatively attenuated→degassed after earthquake→returned to normal. The anomalies of CH4 concentration observed before the earthquake have reached the maximum in epicentral area during the period from January 2008 to August 2016. The increase of CH4 concentration before the earthquake was likely to be the precursor of MS7.0 Lushan earthquake.
-
Keywords:
- Lushan earthquake /
- anomaly /
- remote sensing /
- CH4
-
-
-
车用太, 刘耀炜, 何钄. 2015.断层带土壤气中H2观测:探索地震短临预报的新途径[J].地震, 35(4): 1-10. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/92280X/201504/666216943.html Che Y T, Liu Y W, He L. 2015. Hydrogen monitoring in fault zone soil gas: A new approach to short/immediate earthquake prediction[J]. Earthquake, 35(4): 1-10 (in Chinese). http://www.cqvip.com/QK/92280X/201504/666216943.html
陈运泰, 杨智娴, 张勇, 刘超. 2013.从汶川地震到芦山地震[J].中国科学:地球科学, 43(6): 1064-1072. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSCD201701022.htm Chen Y T, Yang Z X, Zhang Y, Liu C. 2013. From 2008 Wenchuan earthquake to 2013 Lushan earthquake[J]. Scientia Sinica Terrae, 43(6): 1064-1072 (in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSCD201701022.htm
崔月菊, 杜建国, 荆凤, 李新艳. 2016. 2008年汶川MS8.0地震前后川西含碳气体卫星高光谱特征[J].地震学报, 38(3): 448-457. http://www.dzxb.org/Magazine/Show?id=29203 Cui Y J, Du J G, Jing F, Li X Y. 2016. Mapping emission of carbon-bearing gases from the satellite hyperspectral data in western Sichuan before and after the 2008 Wenchuan MS8.0 earthquake[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 38(3): 448-457 (in Chinese). http://www.dzxb.org/Magazine/Show?id=29203
杜建国, 王先彬, 谢鸿森. 1994.深部物质运动的气体地球化学特征[J].地球科学进展, 9(3): 48-52. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ403.007.htm Du J G, Wang X B, Xie H S. 1994. Mantle degassing: A gasgeochemical feature of deep-earth-matter movement[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 9(3): 48-52 (in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ403.007.htm
杜乐天. 2005.地球排气作用的重大意义及研究进展[J].地质论评, 51(2): 174-180. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200502012.htm Du L T. 2005. Significance of earth degassing and its research progress[J]. Geological Review, 51(2): 174-180 (in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200502012.htm
方震, 刘耀炜, 杨选辉, 杨多兴, 张磊. 2012.地震断裂带中气体来源及运移机制研究进展[J].地球物理学进展, 27(2): 483-495. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201202012.htm Fang Z, Liu Y W, Yang X H, Yang D X, Zhang L. 2012. Advance in study on the source and migration mechanisms of gas in the seismic fault zone[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 27(2): 483-495 (in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201202012.htm
高清武. 1992.地震前H2、Hg等断层气的异常变化[J].中国地震, 8(3): 53-59. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=939212 Gao Q W. 1992. Anomalous change of H2, Hg et al. and fault soil gas before earthquakes[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 8(3): 53-59 (in Chinese). http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=939212
荆凤, 申旭辉, 王辉, 康春丽, 熊攀. 2016. 2015年尼泊尔MS8.1地震红外特征分析[J].地震学报, 38(3): 429-437. doi: 10.11939/jass.2016.03.010 Jing F, Shen X H, Wang H, Kang C L, Xiong P. 2016. Infrared characteristics analysis of the 2015 Nepal MS8.1 earthquake[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 38(3): 429-437 (in Chinese). doi: 10.11939/jass.2016.03.010
林依再. 2001.土壤氡气异常特征与台湾南投7.6级地震[J].地震研究, 24(4): 321-325. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYJ200104006.htm Lin Y Z. 2001. Anomaly characteristics of soil radon and Nantou earthquake M7.6 in Taiwan[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 24(4): 321-325 (in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYJ200104006.htm
秦凯. 2013. 基于GEOSS的地震遥感热异常时空分析方法与检验[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学(北京): 17-18. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11413-1013292579.htm Qin K. 2013. GEOSS-Based Thermal Anomalies Spatio-Temperal Analysis for Seismicity: Method and Verification[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology (Beijing): 17-18 (in Chinese). http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11413-1013292579.htm
上官志冠, 高松升. 1990.滇西地区二氧化碳的释放与地震[J].地震学报, 12(2): 186-193. http://www.dzxb.org/Magazine/Show?id=28332 Shangguan Z G, Gao S S. 1990. The CO2 discharges and earthquakes in western Yunnan[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 12(2): 186-193 (in Chinese). http://www.dzxb.org/Magazine/Show?id=28332
王杰, 张雄, 潘黎黎, 曾佐勋. 2013.芦山地震(MS7.0) 前甲烷释放与大气增温异常[J].地学前缘, 20(6): 29-35. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/DXQY201306005.htm Wang J, Zhang X, Pan L L, Zeng Z X. 2013. Anomalies of temperature increase and methane release before Lushan earthquake (MS7.0)[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 20(6): 29-35 (in Chinese). http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/DXQY201306005.htm
吴昊, 魏鸣, 管理, 史洋. 2014.甲烷含量对大气结构及暴雨的影响机理研究[J].科学技术与工程, 14(23): 153-157. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2014.23.028 Wu H, Wei M, Guan L, Shi Y. 2014. Mechanism analysis of the influence of methane content on the atmospheric structure and rainstorm[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 14(23): 153-157 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2014.23.028
徐常芳. 1997.壳内流体演化及地震成因(三)[J].地震学报, 19(2): 139-144. http://www.dzxb.org/Magazine/Show?id=27542 Xu C F. 1997. The crustal fluid evolution and the causes of earthquakes (Ⅲ)[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 19(2): 139-144 (in Chinese). http://www.dzxb.org/Magazine/Show?id=27542
岳中琦. 2013.汶川地震与山崩地裂的极高压甲烷天然气成因和机理[J].地学前缘, 20(6): 15-20. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201306003.htm Yue Z Q. 2013. Cause and mechanism of highly compressed and dense methane gas mass for Wenchuan earthquake and associated rock-avalanches and surface co-seismic ruptures[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 20(6): 15-20 (in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201306003.htm
张景廉, 杜乐天, 曹正林, 阎存凤, 王斌婷. 2011.再论汶川大地震与深部气体的关系[J].西北地震学报, 33(1): 96-101. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZBDZ201101019.htm Zhang J L, Du L T, Cao Z L, Yan C F, Wang B T. 2011. More discussion on the relationship between Wenchuan earthquake and deep gas[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal, 33(1): 96-101 (in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZBDZ201101019.htm
张培仁, 王基华, 孙凤民. 1993.氢:预报地震的灵敏元素[J].地震地质, 15(1): 69-77. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ199301010.htm Zhang P R, Wang J H, Sun F M. 1993. Hydrogen: A sensitive element to predictable earthquake[J]. Seismology and Geology, 15(1): 69-77 (in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ199301010.htm
朱宏任, 汪成民, 万登堡, 朱自强. 1991.地震烈度的气体地球化学标度初探[J].中国地震, 7(1): 59-64. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZD199101009.htm Zhu H R, Wang C M, Wan D B, Zhu Z Q. 1991. A preliminary study on the scale of gaseous geochemistry for determining seismic intensity[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 7(1): 59-64 (in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZD199101009.htm
朱永峰. 1998.地幔流体与地球的放气作用[J].地学前缘, 5(增刊): 71-75. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY8S1.007.htm Zhu Y F. 1998. Mantle fluid and earth degassing[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 5(S): 71-75 (in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY8S1.007.htm
Amani A, Mansor S, Pradhan B, Billa L, Pirasteh S. 2014. Coupling effect of ozone column and atmospheric infrared sounder data reveal evidence of earthquake precursor phenomena of Bam earthquake, Iran[J]. Arab J Geosci, 7(4): 1517-1527. doi: 10.1007/s12517-013-0877-6
Cui Y, Du J, Zhang D, Sun Y. 2013. Anomalies of total column CO and O3 associated with great earthquakes in recent years[J]. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci, 13(10): 2513-2519. doi: 10.5194/nhess-13-2513-2013
Famin V, Nakashima S, Boullier A M, Fujimoto K, Hirono T. 2008. Earthquakes produce carbon dioxide in crustal faults[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 265(3/4): 487-497. https://hal-insu.archives-ouvertes.fr/docs/00/19/71/97/PDF/EPSL2007_final.pdf
King C Y, Zhang W, Zhang Z C. 2006. Earthquake-induced groundwater and gas changes[J]. Pure Appl Geophys, 163(4): 633-645. doi: 10.1007/s00024-006-0049-7
Pulinets S A, Ouzounov D, Karelin A V, Boyarchuk K A, Pokhmelnykh L A. 2006. The physical nature of thermal anomalies observed before strong earthquakes[J]. Phys Chem Earth A B C, 31(4/5/6/7/8/9): 143-153. http://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/43c2303069eae009591bec43-3.html
Singh R P, Kumar J S, Zlotnicki J, Kafatos M. 2010. Satellite detection of carbon monoxide emission prior to the Gujarat earthquake of 26 January 2001[J]. Appl Geochem, 25(4): 580-585. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2010.01.014
Uysal I T, Feng Y X, Zhao J X, Isik V, Nuriel P, Golding S D. 2009. Hydrothermal CO2 degassing in seismically active zones during the late Quaternary[J]. Chem Geol, 265(3/4): 442-454. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Jian-xin_Zhao/publication/240614014_Hydrothermal_CO2_degassing_in_seismically_active_zones_during_the_Late_Quaternary/links/0912f50afc4e85ebc1000000.pdf?origin=publication_list
Voltattorni N, Quattrocchi F, Gasparini A, Sciarra A. 2012. Soil gas degassing during the 2009 L′Aquila earthquake: Study of the seismotectonic and fluid geochemistry relation[J]. Ital J Geosci, 131(3): 440-447. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/236875663_Soil_gas_degassing_during_the_2009_L%27Aquila_earthquake_Study_of_the_seismotectonic_and_fluid_geochemistry_relation
Xiong X Z, Barnet C, Maddy E, Sweeney C, Liu X P, Zhou L H, Goldberg M. 2008. Characterization and validation of methane products from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS)[J]. J Geophys Res, 113(G3): G00A01. doi: 10.1029/2007JG000500/full
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. XU Jixiang,XU Chong,HE Xiangli,WEN Boyu,GE Keshui,BAI Yuzhu. Spatial Distribution of Seismic Landslides in the Areas of 1927 Gulang M8. 0 Earthquake. Earthquake Research in China. 2020(01): 5-28 .  必应学术
必应学术
2. 曹颖,付虹,张海江,陈余宽,黄江培. 云南普洱糯扎渡水库蓄水前后P波速度结构变化特征. 地震学报. 2018(06): 701-718+831 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 曹颖,黄江培,付虹. 云南小湾水库蓄水后P波速度结构的双差地震层析成像研究. 中国地震. 2018(04): 652-666 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 刘白云,曾文浩,袁道阳,李秋红,陈文凯. 1927年古浪8级大地震断层面参数和滑动性质. 地震地质. 2015(03): 818-828 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(9)




 下载:
下载: