Love wave tomography in Sichuan-Yunnan area from ambient noise
-
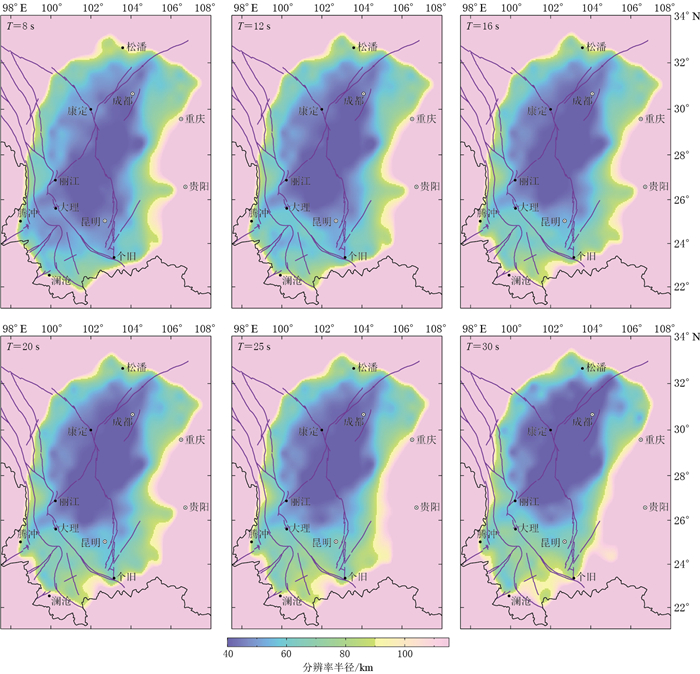
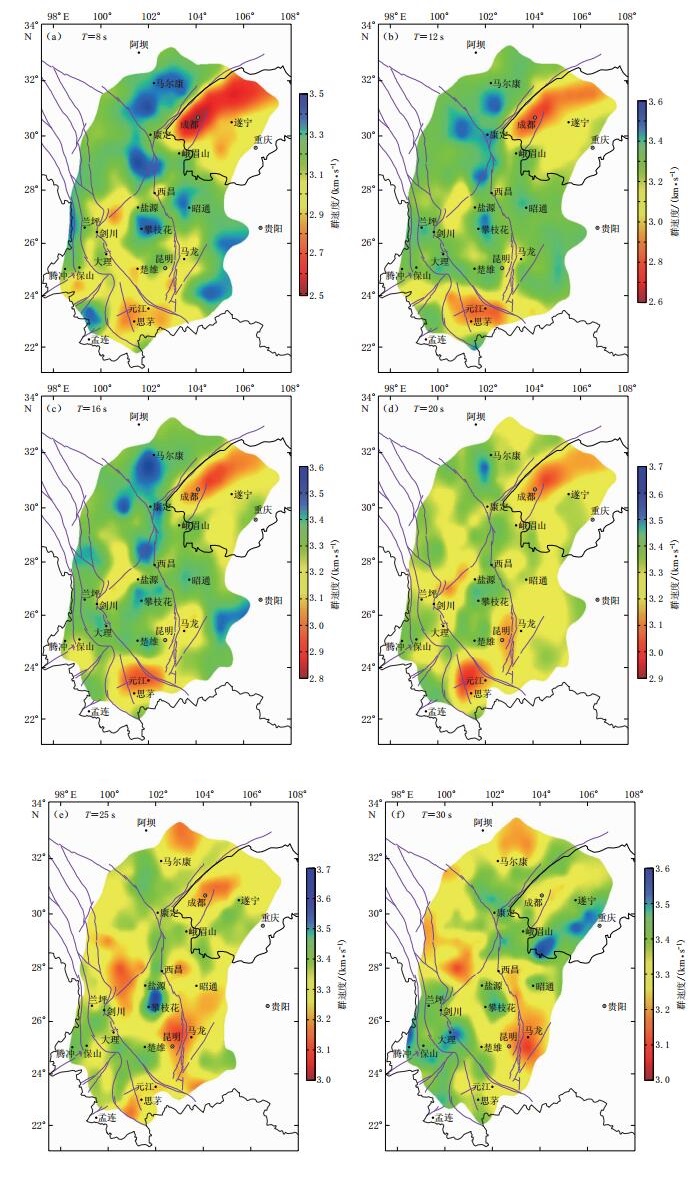
摘要: 本文选取了川滇地区98个固定台站记录到的三分量地震背景噪声数据,采用互相关方法提取了勒夫波互相关函数,并利用自适应时频分析方法获取了勒夫波群速度频散曲线,经反演得到周期为8—30 s的勒夫波群速度分布图像.层析成像结果显示:短周期的勒夫波群速度分布图像呈明显的横向不均匀性,且与地表地质和构造特征基本一致,其中四川盆地呈不均匀的低速异常,盆地内成都平原地区的群速度相对低于盆地中部的丘陵地区,速度分界线为遂宁与峨眉山之间的连线,四川盆地内的群速度变化反映出沉积层厚度的变化情况;攀枝花地区呈高速异常,可能与古地幔活动有关,幔源物质以侵入岩和底侵岩浆的形式停留在地壳的不同深度,从而形成高速异常的特征.本文结果为了解川滇地区的构造运动提供了地震学线索,并为下一步研究地壳径向各向异性奠定了基础.Abstract: We collected seismic ambient noise data recorded at 98 permanent seismic stations in Sichuan-Yunnan area to image crustal structure. The Love wave cross-correlation functions are obtained by cross-correlation of ambient noise. The group velocity dispersion curves for Love wave are measured by automated time-frequency analysis. Love wave group velocity is mapped in the periods between 8 s and 30 s. The tomographies show seismic images at short periods exhibit apparent horizontal heterogeneities, which is largely consistent with geological features and geophysical studies. The Sichuan basin appears as low group velocity anomaly, and the Chengdu plain shows lower group velocity relative to the hilly area in Sichuan basin, with the line connecting Suining with Emeishan being the boundary between higher velocity and lower one. The variation of group velocity anomalies in Sichuan basin reflects variable sedimentary thicknesses. The Panzhihua area appears as high velocity anomaly, which is associated with an ancient mantle plume. The materials from mantle is remained at the different depth in crust in the form of intrusive rocks and magmatic underplating, resulting in the characteristics of high velocity anomaly. These seismic images provide necessary information for the research on crustal radial anisotropy and understanding of tectonic process.
-
Keywords:
- ambient noise /
- tomography /
- Love wave /
- crustal structure /
- Sichuan-Yunnan area
-
审稿专家为本文提供了诸多宝贵的修改意见,闵照旭、杨润海和闻学泽为本研究收集并提供了云南省和四川省固定台网的连续波形资料,研究中使用了SEIZMO程序包、杨英杰博士的部分程序和Yanovskaya教授的面波层析成像计算程序,作者在此一并表示感谢.
-
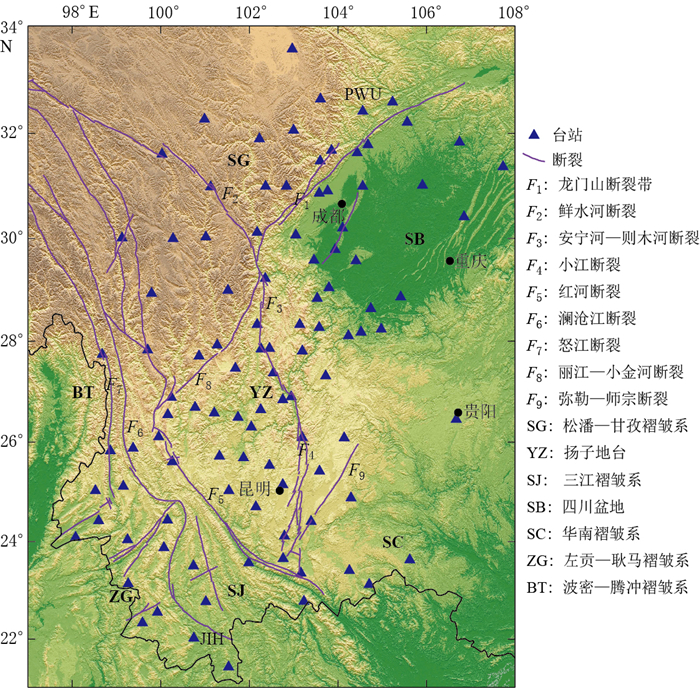
图 1 研究区区域地质构造简图(修改自Wang et al,2003)及台站分布
Figure 1. Location of the seismic stations (denoted by triangles) and major faults (modified from Wang et al, 2003) in the studied area
Purple lines are major faults. F1: Longmenshan fault; F2: Xianshuihe fault; F3: Anninghe-Zemuhe fault; F4: Xiaojiang fault; F5: Honghe fault; F6: Langcangjiang fault; F7: Nujiang fault; F8: Lijiang-Xiaojinhe fault; F9: Mile-Shizong fault. The main geological units are: SG: Songpan-Garze fold system; YZ: Yangtze platform; SJ: Sangjiang fold system; SB: Sichuan basin; SC: South China fold system; ZG: Zuogong-Gengma fold system; BT: Bomi-Tengchong fold system
-
程远志, 汤吉, 陈小斌, 董泽义, 肖骑彬, 汪利波. 2015.南北地震带南段川滇黔接壤区电性结构特征和孕震环境[J].地球物理学报, 58(11): 3965-3981. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dqwx201511008&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ Cheng Y Z, Tang J, Chen X B, Dong Z Y, Xiao Q B, Wang L B. 2015. Electrical structure and seismogenic environment along the border region of Yunnan, Sichuan and Guizhou in the south of the North-South Seismic Belt[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 58(11): 3965-3981 (in Chinese). http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dqwx201511008&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
范莉苹, 吴建平, 房立华, 王未来. 2015.青藏高原东南缘瑞利波群速度分布特征及其构造意义探讨[J].地球物理学报, 58(5): 1555-1567. doi: 10.6038/cjg20150509 Fan L P, Wu J P, Fang L H, Wang W L. 2015. The characteristic of Rayleigh wave group velocities in the southeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau and its tectonic implications[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 58(5): 1555-1567 (in Chinese). doi: 10.6038/cjg20150509
房立华, 吴建平, 吕作勇. 2009.华北地区基于噪声的瑞利面波群速度层析成像[J].地球物理学报, 52(3): 663-671. doi: 10.1002/cjg2.v52.3 Fang L H, Wu J P, Lü Z Y. 2009. Rayleigh wave group velocity tomography from ambient seismic noise in North China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 52(3): 663-671 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1002/cjg2.v52.3
房立华, 吴建平, 王未来, 王长在, 杨婷. 2013.华北地区勒夫波噪声层析成像研究[J].地球物理学报, 56(7): 2268-2279. doi: 10.6038/cjg20130714 Fang L H, Wu J P, Wang W L, Wang C Z, Yang T. 2013. Love wave tomography from ambient seismic noise in North-China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 56(7): 2268-2279 (in Chinese). doi: 10.6038/cjg20130714
付媛媛, 高原. 2016.东北地区背景噪声的Rayleigh和Love波相速度层析成像[J].地球物理学报, 59(2): 494-503. doi: 10.6038/cjg20160209 Fu Y Y, Gao Y. 2016. Phase velocity tomography of Rayleigh and Love waves using ambient noise in Northeast China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 59(2): 494-503 (in Chinese). doi: 10.6038/cjg20160209
嘉世旭, 刘保金, 徐朝繁, 刘志, 酆少英, 张建狮, 林吉焱, 田晓峰, 刘巧霞, 郭文斌. 2014.龙门山中段及两侧地壳结构与汶川地震构造[J].中国科学:地球科学, 44(3): 497-509. doi: 10.1007/s11430-013-4744-9 Jia S X, Liu B J, Xu Z F, Liu Z, Feng S Y, Zhang J S, Lin J Y, Tian X F, Liu Q X, Guo W B. 2014. The crustal structures of the central Longmenshan along and its margins as related to the seismotectonics of the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 57(4): 777-790. doi: 10.1007/s11430-013-4744-9
江为为, 刘伊克, 郝天珧, 宋海斌. 2001.四川盆地综合地质、地球物理研究[J].地球物理学进展, 16(1): 11-23. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqwlxjz200101002 Jiang W W, Liu Y K, Hao T Y, Song H B. 2001. Comprehensive study of geology and geophysics of Sichuan basin[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 16(1): 11-23 (in Chinese). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqwlxjz200101002
潘佳铁, 吴庆举, 李永华, 张风雪, 张广成. 2011.华北地区瑞雷面波相速度层析成像[J].地球物理学报, 54(1): 67-76. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqwlxb201101008 Pan J T, Wu Q J, Li Y H, Zhang F X, Zhang G C. 2011. Rayleigh wave tomography of the phase velocity in North China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(1): 67-76 (in Chinese). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqwlxb201101008
潘佳铁, 李永华, 吴庆举, 丁志峰. 2015.青藏高原东南部地区瑞雷波相速度层析成像[J].地球物理学报, 58(11): 3993-4006. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dqwx201511010&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ Pan J T, Li Y H, Wu Q J, Ding Z F. 2015. Phase velocity maps of Rayleigh waves in the southeast Tibetan Plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 58(11): 3993-4006 (in Chinese). http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dqwx201511010&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
唐有彩, 陈永顺, 杨英杰, 丁志峰, 刘瑞丰, 冯永革, 李鹏, 俞春泉, 魏松峤, 范文渊, 王海洋, 周仕勇, 宁杰远. 2011.华北克拉通中部地区背景噪声成像[J].地球物理学报, 54(8): 2011-2022. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ctta201401007 Tang Y C, Chen Y S, Yang Y J, Ding Z F, Liu R F, Feng Y G, Li P, YU C Q, Wei S Q, Fan W Y, Wang H Y, Zhou S Y, Ning J Y. 2011. Ambient noise tomography in North China craton[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(8): 2011-2022 (in Chinese). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ctta201401007
汪缉安, 徐青, 张文仁. 1990.云南大地热流及地热地质问题[J].地震地质, 12(4): 367-377. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dzdz199004012&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ Wang J A, Xu Q, Zhang W R. 1990. Heat flow data and some geologic-geothermal problems in Yunnan Province[J]. Seismology and Geology, 12(4): 367-377 (in Chinese). http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dzdz199004012&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
汪集旸, 黄少鹏. 1990.中国大陆地区大地热流数据汇编(第二版)[J].地震地质, 12(4): 351-363, 366. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqwlxb200105005 Wang J Y, Huang S P. 1990. Compilation of heat flow data in the China continental area (2nd edition)[J]. Seismology and Geology, 12(4): 351-363, 366 (in Chinese).
王二七, 尹纪云. 2009.川西南新生代构造作用以及四川原型盆地的破坏[J].西北大学学报:自然科学版, 39(3): 359-367. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbdxxb200903003 Wang E Q, Yin J Y. 2009. Cenozoic multi-stage deformation occurred in southwest Sichuan: Cause for the dismemberment of the proto-Sichuan basin[J]. Journal of Northwest University: Natural Science Edition, 39(3): 359-367 (in Chinese). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbdxxb200903003
吴建平, 杨婷, 王未来, 明跃红, 张天中. 2013.小江断裂带周边地区三维P波速度结构及其构造意义[J].地球物理学报, 56(7): 2257-2267. doi: 10.6038/cjg20130713 Wu J P, Yang T, Wang W L, Ming Y H, Zhang T Z. 2013. Three dimensional P-wave velocity structure around Xiaojiang fault system and its tectonic implications[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 56(7): 2257-2267 (in Chinese). doi: 10.6038/cjg20130713
熊绍柏, 郑晔, 尹周勋, 曾晓献, 全幼黎, 孙克忠. 1993.丽江—攀枝花—者海地带二维地壳结构及其构造意义[J].地球物理学报, 36(4): 434-444. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dqwx199304003&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ Xiong S B, Zheng Y, Yin Z X, Zeng X X, Quan Y L, Sun K Z. 1993. The 2-D structure and it's tectonic implications of the crust in the Lijiang-Panzhihua-Zhehai region[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 36(4): 434-444 (in Chinese). http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dqwx199304003&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
徐涛, 张忠杰, 刘宝峰, 陈赟, 张明辉, 田小波, 徐义刚, 滕吉文. 2015.峨眉山大火成岩省地壳速度结构与古地幔柱活动遗迹:来自丽江—清镇宽角地震资料的约束[J].中国科学:地球科学, 45(5): 561-576. doi: 10.1007/s11430-015-5094-6 Xu T, Zhang Z J, Liu B F, Chen Y, Zhang M H, Tian X B, Xu Y G, Teng J W. 2015. Crustal velocity structure in the Emeishan large igneous province and evidence of the Permian mantle plume activity[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 58(7): 1133-1147. doi: 10.1007/s11430-015-5094-6
徐义刚, 何斌, 罗震宇, 刘海泉. 2013.我国大火成岩省和地幔柱研究进展与展望[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 32(1): 25-39. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kwysdqhxtb201301002 Xu Y G, He B, Luo Z Y, Liu H Q. 2013. Study on mantle plume and large igneous provinces in China: An overview and perspectives[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 32(1): 25-39 (in Chinese). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kwysdqhxtb201301002
张乐天, 金胜, 魏文博, 叶高峰, 段书新, 董浩, 张帆, 谢成良. 2012.青藏高原东缘及四川盆地的壳幔导电性结构研究[J].地球物理学报, 55(12): 4126-4137. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.12.025 Zhang L T, Jin S, Wei W B, Ye G F, Duan S X, Dong H, Zhang F, Xie C L. 2012. Electrical structure of crust and upper mantle beneath the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau and the Sichuan basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 55(12): 4126-4137 (in Chinese). doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.12.025
张中杰, 白志明, 王椿镛, 吕庆田, 滕吉文, 李继亮, 孙善学, 王新征. 2005.冈瓦纳型和扬子型地块地壳结构:以滇西孟连—马龙宽角反射剖面为例[J].中国科学: D辑, 35(5): 387-392. doi: 10.1360/03yd0547 Zhang Z J, Bai Z M, Wang C Y, Lü Q T, Teng J W, Li J L, Sun S X, Wang X Z. 2005. Crustal structure of Gondwana-and Yangtze-typed blocks: An example by wide-angle seismic profile from Menglian to Malong in western Yunnan[J]. Science in China: Series D, 48(11): 1828-1836. doi: 10.1360/03yd0547
郑定昌, 盖增喜, 杨润海, 闵照旭, 唐有彩, 姜明明, 庞卫东. 2014.云南地区背景噪声层析成像[J].地震学报, 36(4): 602-614. http://www.dzxb.org/Magazine/Show?id=28988 Zheng D C, Ge Z X, Yang R H, Min Z X, Tang Y C, Jiang M M, Pang W D. 2014. Broadband ambient noise tomography in Yunnan Province[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 36(4): 602-614 (in Chinese). http://www.dzxb.org/Magazine/Show?id=28988
Bensen G D, Ritzwoller M H, Barmin M P, Levshin A L, Lin F, Moschetti M P, Shapiro N M, Yang Y. 2007. Processing seismic ambient noise data to obtain reliable broad-band surface wave dispersion measurements[J]. Geophys J Int, 169(3): 1239-1260. doi: 10.1111/gji.2007.169.issue-3
Burchfiel B C, Royden L H, van der Hilst R D, Hager B H, Chen Z, King R W, Li C, Lü J, Yao H J, Kirby E. 2008. A geological and geophysical context for the Wenchuan earthquake of 12 May 2008, Sichuan, People's Republic of China[J]. GSA Today, 18(7): 4-11. doi: 10.1130/GSATG18A.1
Clark M K, Royden L H. 2000. Topographic ooze: Building the eastern margin of Tibet by lower crustal flow[J]. Geology, 28(8): 703-706. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2000)28<703:TOBTEM>2.0.CO;2
Ditmar P G, Yanovskaya T B. 1987. A generalization of Backus-Gilbert method for estimation of lateral variations of surface wave velocity[J]. Phys Solid Earth, 23(6): 470-477.
Fang L H, Wu J P, Ding Z F, Panza G F. 2010. High resolution Rayleigh wave group velocity tomography in North China from ambient seismic noise[J]. Geophys J Int, 181(2): 1171-1182.
Guo Z, Gao X, Yao H J, Li J, Wang W M. 2009. Midcrustal low-velocity layer beneath the central Himalaya and southern Tibet revealed by ambient noise array tomography[J]. Geochem Geophys Geosys, 10(5): Q05007. doi: 10.1029/2009GC002458.
Guo Z, Gao X, Shi H, Wang W M. 2013. Crustal and uppermost mantle S-wave velocity structure beneath the Japanese islands from seismic ambient noise tomography[J]. Geophys J Int, 193(1): 394-406. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggs121
He B, Xu Y G, Chung S L, Xiao L, Wang Y M. 2003. Sedimentary evidence for a rapid, kilometer-scale crustal doming prior to the eruption of the Emeishan flood basalts[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 213(3/4): 389-405.
Kennett B L N, Engdahl E R, Buland R. 1995. Constraints on seismic velocities in the Earth from traveltimes[J]. Geophys J Int, 122(1): 108-124. doi: 10.1111/gji.1995.122.issue-1
Laske G, Masters G, Ma Z T, Pasyanos M. 2013. Update on CRUST1.0: A 1-degree global model of Earth's crust[J]. Geophys Res Abstr, 15: EGU2013-2658.
Levshin A L, Ritzwoller M H. 2001. Automated detection, extraction, and measurement of regional surface waves[J]. Pure Appl Geophys, 158(8): 1531-1545. doi: 10.1007/PL00001233
Li H Y, Su W, Wang C Y, Huang Z X. 2009. Ambient noise Rayleigh wave tomography in western Sichuan and eastern Tibet[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 282(1/4): 201-211.
Li H Y, Su W, Wang C Y, Huang Z X, Lü Z Y. 2010. Ambient noise Love wave tomography in the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Tectonophysics, 491(1/4): 194-204.
Lin F C, Moschetti M P, Ritzwoller M H. 2008. Surface wave tomography of the western United States from ambient seismic noise: Rayleigh and Love wave phase velocity maps[J]. Geophys J Int, 173(1): 281-298. doi: 10.1111/gji.2008.173.issue-1
Moschetti M P, Ritzwoller M H, Lin F, Yang Y. 2010. Seismic evidence for widespread western-US deep-crustal deformation caused by extension[J]. Nature, 464(7290): 885-889. doi: 10.1038/nature08951
Niu F L, Li J. 2011. Component azimuths of the CEArray stations estimated from P-wave particle motion[J]. Earthquake Science, 24(1): 3-13. doi: 10.1007/s11589-011-0764-8
Rodi W L, Glover P, Li T M C, Alexander S S. 1975. A fast, accurate method for computing group-velocity partial derivatives for Rayleigh and Love modes[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 65(5): 1105-1114.
Royden L H, Burchfiel B C, King R W, Wang E C, Chen Z L, Shen F, Liu Y P. 1997. Surface deformation and lower crustal flow in eastern Tibet[J]. Science, 276(5313): 788-790. doi: 10.1126/science.276.5313.788
Royden L H, Burchfiel B C, van der Hilst R D. 2008. The geological evolution of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Science, 321(5892): 1054-1058. doi: 10.1126/science.1155371
Saygin E, Kennett B L N. 2012. Crustal structure of Australia from ambient seismic noise tomography[J]. J Geophys Res, 117(B1): B01304.
Shapiro N M, Campillo M, Stehly L, Ritzwoller M H. 2005. High-resolution surface-wave tomography from ambient seismic noise[J]. Science, 307(5715): 1615-1618. doi: 10.1126/science.1108339
Suresh G, Bhattacharya S N, Teotia S S. 2015. Crust and upper mantle velocity structure of the northwestern Indian Peninsular shield from inter-station phase velocities of Rayleigh and Love waves[J]. Ann Geophys, 58(2): S0215.
Tang Y C, Chen Y J, Zhou S Y, Ning J Y, Ding Z F. 2013. Lithosphere structure and thickness beneath the North China Craton from joint inversion of ambient noise and surface wave tomography[J]. J Geophys Res, 118(5): 2333-2346.
Tapponnier P, Xu Z Q, Roger F, Meyer B, Arnaud N, Wittlinger G, Yang J S. 2001. Oblique stepwise rise and growth of the Tibet Plateau[J]. Science, 294(5547): 1671-1677. doi: 10.1126/science.105978
Wang C Y, Chan W W, Mooney W D. 2003. Three-dimensional velocity structure of crust and upper mantle in southwestern China and its tectonic implications[J]. J Geophys Res, 108(B9): ESE13-11.
Xie J Y, Ritzwoller M H, Shen W S, Yang Y J, Zheng Y, Zhou L Q. 2013. Crustal radial anisotropy across eastern Tibet and the western Yangtze craton[J]. J Geophys Res, 118(8): 4226-4252. doi: 10.1002/jgrb.50296
Yang Y J, Ritzwoller M H, Levshin A L, Shapiro N M. 2007. Ambient noise Rayleigh wave tomography across Europe[J]. Geophys J Int, 168(1): 259-274. doi: 10.1111/gji.2007.168.issue-1
Yang Y J, Zheng Y, Chen J, Zhou S Y, Celyan S, Sandvol E, Tilmann F, Priestley K, Hearn T M, Ni J F, Brown L D, Ritzwoller M H. 2010. Rayleigh wave phase velocity maps of Tibet and the surrounding regions from ambient seismic noise tomography[J]. Geochem Geophys Geosys, 11(8): Q08010. doi: 10.1029-2010GC003119/
Yang Y J, Ritzwoller M H, Zheng Y, Shen W S, Levshin A L, Xie Z J. 2012. A synoptic view of the distribution and connectivity of the mid-crustal low velocity zone beneath Tibet[J]. J Geophys Res, 117(B4): B04303.
Yanovskaya T B, Ditmar P G. 1990. Smoothness criteria in surface wave tomography[J]. Geophys J Int, 102(1): 63-72. doi: 10.1111/gji.1990.102.issue-1
Yao H J, van der Hilst R D, De Hoop M V. 2006. Surface-wave array tomography in SE Tibet from ambient seismic noise and two-station analysis: Ⅰ. Phase velocity maps[J]. Geophys J Int, 166(2): 732-744. doi: 10.1111/gji.2006.166.issue-2
Yao H J, Beghein C, van der Hilst R D. 2008. Surface wave array tomography in SE Tibet from ambient seismic noise and two-station analysis: Ⅱ. Crustal and upper-mantle structure[J]. Geophys J Int, 173(1): 205-219. doi: 10.1111/gji.2008.173.issue-1
Zhang Y, Ren Z Y, Xu Y G. 2013. Sulfur in olivine-hosted melt inclusions from the Emeishan picrites: Implications for S degassing and its impact on environment[J]. J Geophys Res, 118(8): 4063-4070. doi: 10.1002/jgrb.50324
Zhao G, Unsworth M J, Zhan Y, Wang L F, Chen X B, Jones A G, Tang J, Xiao Q B, Wang J J, Cai J T, Li T, Wang Y Z, Zhang J H. 2012. Crustal structure and rheology of the Longmenshan and Wenchuan MW7.9 earthquake epicentral area from magnetotelluric data[J]. Geology, 40(12): 1139-1142. doi: 10.1130/G33703.1
Zheng D C, Saygin E, Cummins P, Ge Z X, Min Z X, Cipta A, Yang R H. 2017. Transdimensional Bayesian seismic ambient noise tomography across SE Tibet[J]. J Asian Earth Sci, 134: 86-93. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.11.011
Zheng X, Zhao C P, Zhou L Q, Zheng S H. 2015. 3D shear-wave velocity structure beneath the southeastern Tibetan Plateau from ambient noise[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 105(3): 1371-1382. doi: 10.1785/0120140211
Zhou L Q, Xie J Y, Shen W S, Zheng Y, Yang Y J, Shi H X, Ritzwoller M H. 2012. The structure of the crust and uppermost mantle beneath South China from ambient noise and earthquake tomography[J]. Geophys J Int, 189(3): 1565-1583. doi: 10.1111/gji.2012.189.issue-3




 下载:
下载: