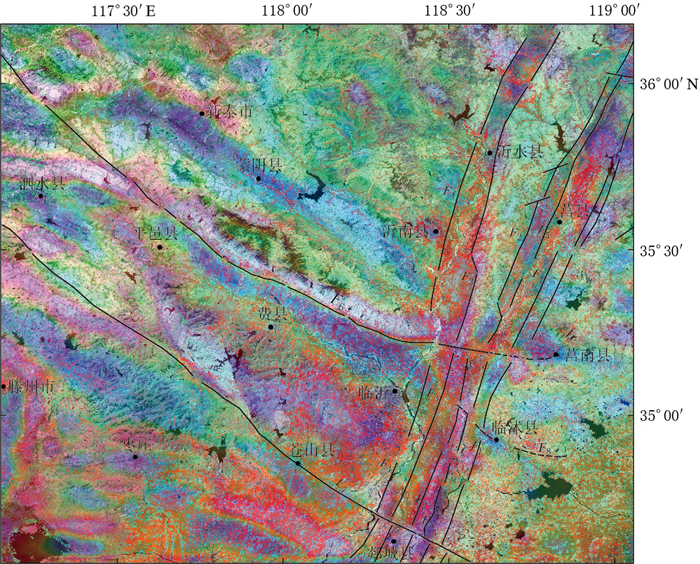
Intersection relationship between south segment of Yishu fault zone and surrounding faults derived from remote sensing and gravity multi-source data
-
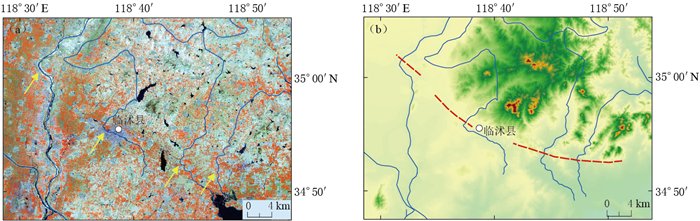
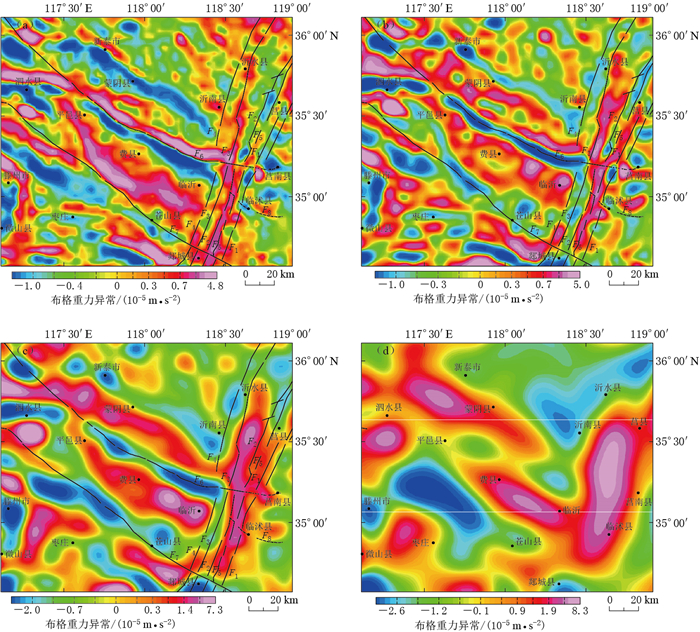
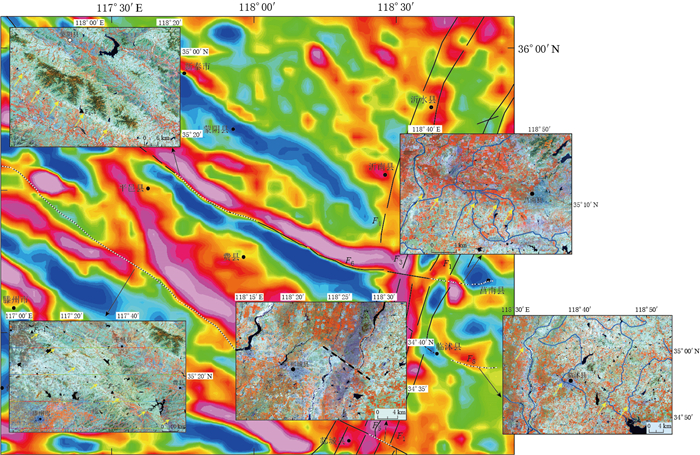
摘要: 以沂沭断裂带南段(沂水县—郯城县)及周边地区为研究对象,收集该地区的遥感影像、数字高程模型和布格重力数据,研究区域构造地貌和地壳深部构造特征,进一步对沂沭断裂带南段与周边断裂的交切关系予以分析.研究结果显示:在遥感影像中,蒙山山前断裂和苍尼断裂的构造地貌特征明显,断裂沿线发育水系转弯、河流错断、断层陡坎、断层崖、断层三角面等地貌现象,反映了两断裂正断兼左旋走滑的活动性质,其中蒙山山前断裂向东延伸至莒南县附近,苍尼断裂向东延至郯城一带,两条断裂在地貌上均截切了沂沭断裂带;在重力细节场中,两断裂形成了不同尺度上的重力梯度带,切割至下地壳深度,在地壳浅层至深层均交切于沂沭断裂带,且交切处出现扭曲、断折、串珠状等重力异常现象,证实其在地壳深部切穿沂沭断裂带.因此,两条断裂的遥感和重力场解译结果具有明显的一致性,在地貌及深部均截切沂沭断裂带南段,使其出现分段性特征.此外,在临沭县附近发现了一条新断裂,即相庄—沙岭断裂,该断裂在地貌上呈北高南低,沿线水系发生左旋同步转弯,且在1—3阶重力细节场中形成线性梯度条带,故推测该断裂下切至中地壳深度,在临沭县附近截切沂沭断裂带交切于东地堑,并未延伸至西地堑.Abstract: This paper collected remote sensing image, digital elevation model and Bouguer gravity data of the south segment of Yishu fault zone (namely the segment between Yishui county and Tancheng county) and its surrounding areas, and studied the regional tectonic landform and deep crustal structural characteristics so as to analyze the intersection relationships between south segment of Yishu fault zone and its surrounding faults. The research results indicate that Mengshan piedmont fault and Cangni fault exhibit obvious tectonic characteristics consisting of river bends, fault steep, gully leaps, fault scarps and fault facets in the remote sensing images. In detail, Mengshan piedmont fault extends eastward to Ju'nan county, while Cangni fault extends eastward to Tancheng. Both the faults crosscut Yishu fault zone on the geomorphology; in the gravity detail field, the two faults form a gravitational gradient zone on different scales, which extend down to the lower crust and appear as deep faults. Moreover, the lineaments intersect with Yishu fault zone and contribute to the distorted, broken, beaded gravity anomalies, confirming that Yishu fault zone has been cut through in the deep crust. Therefore, a great uniformity between the interpretation results of two faults in remote sensing and gravity field suggests that the two faults all crosscut south segment of Yishu fault zone in landform and deep crust, so that the segmentation characteristics occur. In addition, there is a new fault developed near Linshu county, namely Xiangzhuang-Shaling fault. The fault is higher in north and lower in south, along which the rivers left-hand bend synchronously, and in the 1-to-3-order gravity field there are linear gradient zones, so it is speculated that the fault extends down to the middle crust, and crosscuts the eastern graben of Yishu fault zone near Linshu county, but not extends to the western graben.
-
-
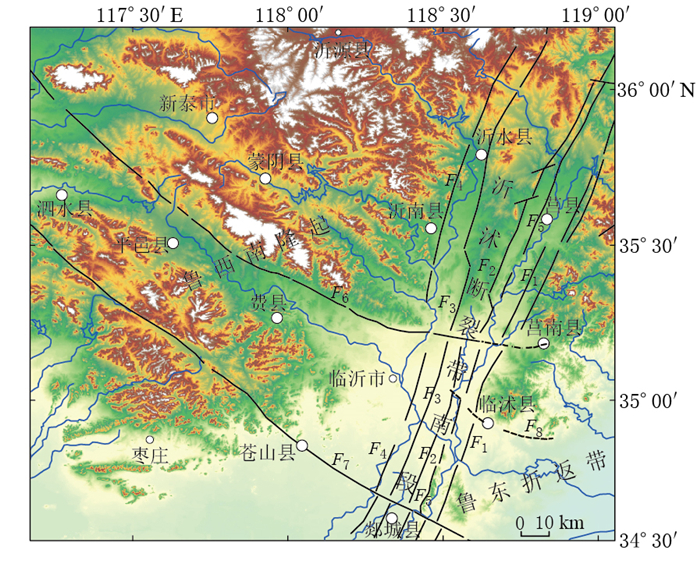
图 1 研究区地貌及主要断裂分布
图中主要断裂分布邓起东等(2007),并根据遥感和重力资料修正
F1:昌邑—大店断裂;F2:白芬子—浮来山断裂;F3:沂水—汤头断裂;F4:鄌郚—葛沟断裂;F5:安丘—莒县断裂;F6:蒙山山前断裂;F7:苍尼断裂;F8:相庄—沙岭断裂(推测断裂)Figure 1. Distribution of landscapes and active faults in the studied area
Main active faults refer to Deng et al (2007), and are modified based on remote sensing and gravity data F1: Changyi-Dadian fault; F2: Baifenzi-Fulaishan fault; F3: Yishui-Tangtou fault; F4: Tangwu-Gegou fault; F5: Anqiu-Juxian fault; F6: Mengshan piedmont fault; F7: Cangni fault; F8: Xiangzhuang-Shaling fault (inferred fault)
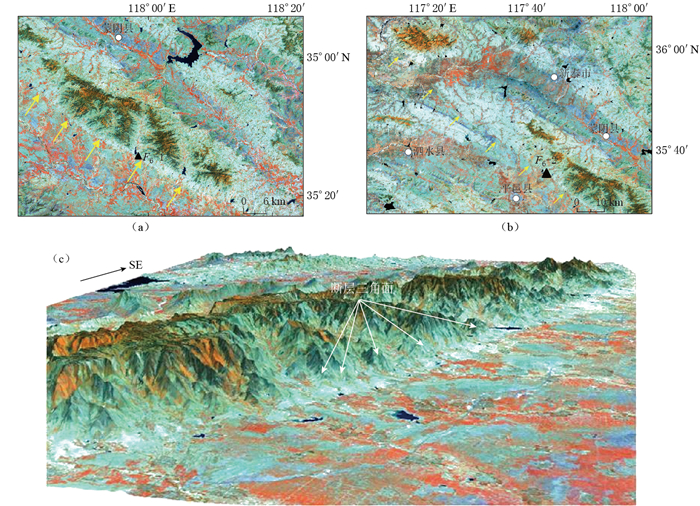
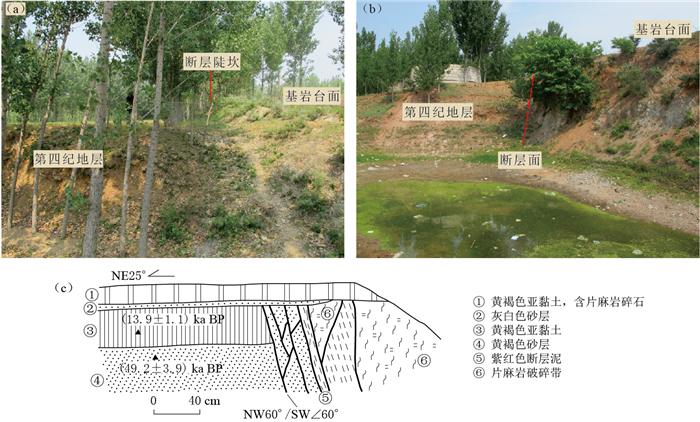
图 2 蒙山山前断裂遥感影像(F6-1, F6-2为野外考察点)
(a)铜石镇段断层崖、断层三角面;(b)邱阳—汪沟镇段断裂线性特征;(c)铜石镇段断层崖和断层三角面的三维图
Figure 2. Remote sensing images of Mengshan piedmont fault
(a) Fault scarp and fault triangular facet; (b) Fault linear feature of Qiuyang-Wanggou segment; (c) 3D model about fault scarp and fault triangular facet. F6-1 and F6-2 are field surveying sites
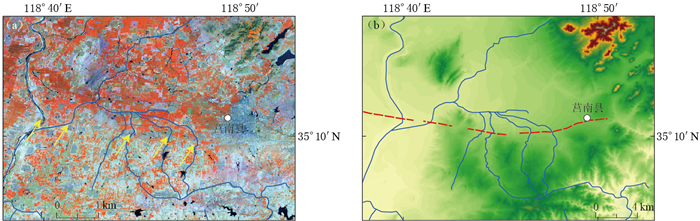
图 4 蒙山山前断裂野外实地考察及地质剖面
(a)铜石镇薛家村北的断层三角面(野外点F6-1位置见图 2a); (b)断面三角面近景;(c)大杨庄断层剖面(王志才等,2001)(野外点F6-2位置见图 2b)
Figure 4. Field investigation and previous profiles of Mengshan piedmont fault
(a) Fault triangular facet in the north of Xuejia village, Tongshi county (The field point F6-1 is shown in Fig. 2a); (b) Close shot of fault triangular facet; (c) The profile along the Dayangzhuang fault (after Wang et al, 2001)(The field point F6-2 is shown in Fig. 2b)
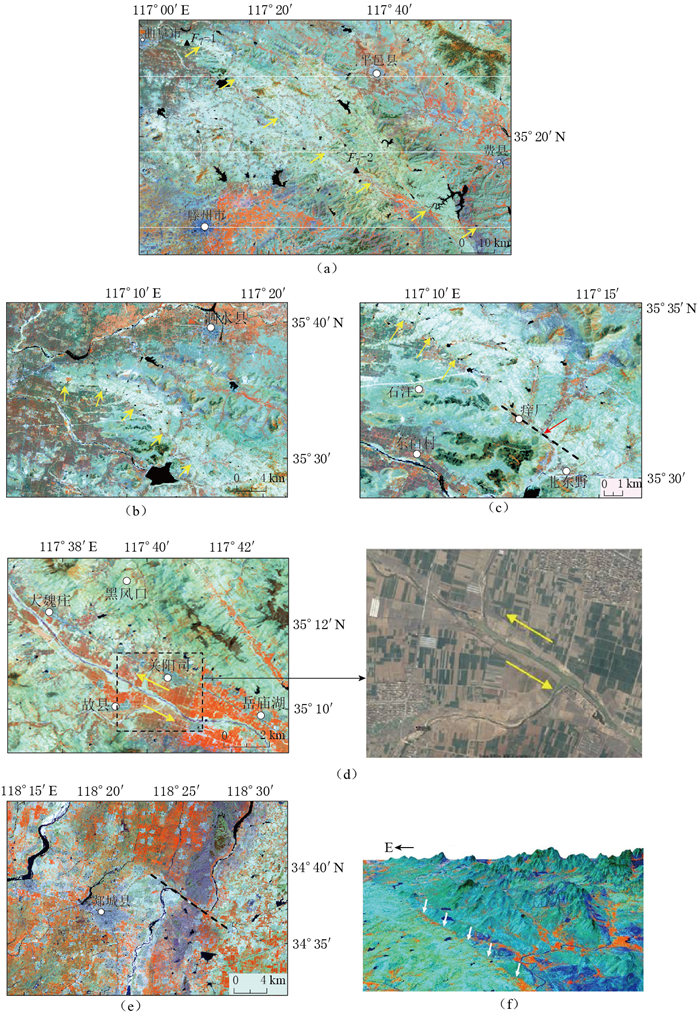
图 5 苍尼断裂遥感影像
(a)苍尼断裂西段线性特征,图中F7-1和F7-2为考察点;(b)断层陡坎; (c)痒厂—北东野的串珠状湖泊和河流转弯; (d)故县城附近河流左旋错动; (e)东段沭河大幅度转弯; (f)苍尼断裂三维立体图
Figure 5. Remote sensing image of Cangni fault
(a) Linear feature of west Cangni fault, where F7-1 and F7-2 are surveying sites; (b) Fault steep; (c) Bead-like lakes and turning of rivers from Yangchang to Beidongye; (d) River's sinistral dislocation near Guxian; (e) Shuhe's sharp turning of east Cangni fault; (f) 3D model of Cangni fault
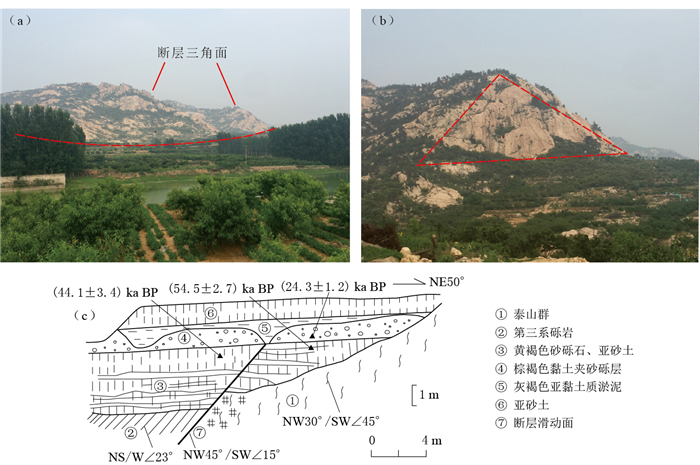
图 6 苍尼断裂野外实地考察及地质剖面
(a)基岩陡坎及冲沟剖面(野外点F7-1位置见图 5a); (b)水库断层剖面; (c)大杨庄断层剖面(王志才等,2001)(野外点F7-2位置见图 5a)
Figure 6. Field investigation and the profiles along Cangni fault
(a) Bedrock scarp and gully section (The field point F7-1 is shown in Fig. 5a); (b) Fault profile along the reservoir; (c) Fault profile of Dayangzhuang (The field point F7-2 is shown in Fig. 5a) (after Wang et al, 2001)
表 1 Landsat-7 ETM+波段参数
Table 1 Band parameter of Landsat-7 ETM+
波段号 波谱范围/μm 地面分辨率/m 波段名称 1 0.450—0.515 30 蓝绿色 2 0.525—0.605 30 绿色 3 0.630—0.690 30 红色 4 0.775—0.900 30 近红外 5 1.550—1.750 30 短波红外 6 10.40—12.50 60 热红外 7 2.090—2.350 30 短波红外 8 0.520—0.900 15 全色 表 2 1—4阶小波细节图反映的场源深度
Table 2 Source depth reflected by the first-to-fourth-order wavelet detailed images
阶次 近似场源深度/km 1阶细节 2—3 2阶细节 5—6 3阶细节 11—12 4阶细节 24—25 -
晁洪太, 崔昭文, 李家灵. 1992.鲁中地区北西向断裂及其第四纪晚期的活动特征[J].地震学刊, (2): 1-10. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dzxk199202000&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ Chao H T, Cui Z W, Li J L. 1992. The N-W trending faults in middle part of Shandong Province and their activities in the Late Quaternary[J]. Journal of Seismology, (2): 1-10 (in Chinese). http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dzxk199202000&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
晁洪太, 李家灵, 赵清玉, 崔昭文. 1998.沂沭断裂带活动褶皱及其与活动断层的关系[J].地震研究, 21(3): 261-267. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dzyj803.008&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ Chao H T, Li J L, Zhao Q Y, Cui Z W. 1998. Active folds in the Yishu fault zone and their relations to active faults[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 21(3): 261-267 (in Chinese). http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dzyj803.008&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
邓起东, 冉勇康, 杨晓平, 闵伟, 楚全芝. 2007.中国活动构造图[M].北京:地震出版社: 1. Deng Q D, Ran Y K, Yang X P, Min W, Chu Q Z. 2007. Map of Active Tectonics in China[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press: 1 (in Chinese).
方盛明, 张先康, 嘉世旭, 段永红, 杨卓欣, 邱淑燕. 2002.华北地区布格重力异常的多尺度分解特征与地震活动性[J].大地测量与地球动力学, 22(1): 34-39. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dkxbydz200201007 Fang S M, Zhang X K, Jia S X, Duan Y H, Yang Z Y, Qiu S Y. 2002. Multi-scale decomposition of Bouguer gravity anomaly and seismic activity in North China[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 22(1): 34-39 (in Chinese). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dkxbydz200201007
方仲景, 丁梦林, 向宏发, 计风桔, 李如成. 1986.郯庐断裂带的基本特征[J].科学通报, 31(1): 52-55. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlxxb201603001 Fang Z J, Ding M L, Xiang H F, Ji F J, Li R C. 1986. The basical feature of Tanlu fault zone[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 31(1): 52-55 (in Chinese). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlxxb201603001
高欣欣, 张步春, 沈梅琴. 1987.郯庐断裂带中段遥感信息的处理与识别[J].地震地质, 9(1): 27-34. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dzdz198701005&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ Gao X X, Zhang B C, Shen M Q. 1987. Processing and interpretation of remote sensing information for the middle of Tancheng-Lujiang fault zone[J]. Seismology and Geology, 9(1): 27-34 (in Chinese). http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dzdz198701005&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
郭慧, 江娃利, 谢新生. 2016. 1976年唐山MS7.8地震乐亭—滦南地区NW向地裂缝带赵滩点位调查[J].地震学报, 38(4): 644-655. doi:10.11939/jass.2016.04.010. Guo H, Jiang W L, Xie X S. 2016. Investigation on Zhaotan site in NW-trending ground fissure zone of 1976 MS7.8 Tangshan earthquake in Laoting-Luannan region[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 38(4): 644-655. doi:10.11939/jass.2016.04.010 (in Chinese).
何宏林. 2011.活动断层填图中的航片解译问题[J].地震地质, 33(4): 938-950. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzdz201104017 He H L. 2011. Some problems of aerial photo interpretation in active fault mapping[J]. Seismology and Geology, 33(4): 938-950 (in Chinese). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzdz201104017
侯遵泽, 杨文采. 1997.中国重力异常的小波变换与多尺度分析[J].地球物理学报, 40(1): 85-95. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqwlxb200104012 Hou Z Z, Yang W C. 1997. Wavelet transform and multi-scale analysis on gravity anomalies of China[J]. Acta Geophysica Sinica, 40(1): 85-95 (in Chinese). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqwlxb200104012
江娃利. 1991.航空像片在活断层研究中的应用[J].地震地质, 13(4): 323-331. Jiang W L. 1991. Application of aerophoto interpretation to study of active faults[J]. Seismology and Geology, 13(4): 323-331 (in Chinese).
姜文亮, 张景发, 陈丁, 路晓翠, 张鹏, 李丽梅. 2011.利用遥感、重力多源信息研究郯—庐断裂带苏—鲁段构造特征[J].地球学报, 32(2): 143-153. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dqxb201102005&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ Jiang W L, Zhang J F, Chen D, Lu X C, Zhang P, Li L M. 2011. Tectonic characteristics of Su-Lu segment of the Tan-Lu fault zone derived from RS and gravity multi-source information[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 32(2): 143-153 (in Chinese). http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dqxb201102005&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
李家灵, 晁洪太, 崔昭文, 赵清玉. 1994.郯庐活断层的分段及其大震危险性分析[J].地震地质, 16(2): 121-126. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dzdz402.003&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ Li J L, Chao H T, Cui Z W, Zhao Q Y. 1994. Segmentation of active fault along the Tancheng-Lujiang fault zone and evaluation of strong earthquake risk[J]. Seismology and Geology, 16(2): 121-126 (in Chinese). http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dzdz402.003&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
李善邦. 1980.我国早期地震工作发展概况[J].西北地震学报, 2(1): 1-5. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=zbdz198001000&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ Li S B. 1980. The development of Chinese early seismic work[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal, 2(1): 1-5 (in Chinese). http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=zbdz198001000&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
林爱明, 饶刚, 闫兵. 2013.从水系的分布形态探讨沂沭断裂带的运动特征[J].地学前缘, 20(4): 125-136. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201304010 Lin A M, Rao G, Yan B. 2013. Dynamic characteristics of the Yishu fault zone, central segment of the Tan-Lu fault zone, Shandong Province, China: Inferred from the distribution patterns of drainages[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 20(4): 125-136 (in Chinese). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201304010
林伟凡, 高维明. 1987.沂沭断裂带大地震复发周期[J].中国地震, 3(3): 36-42. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=zgzd198703005&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ Lin W F, Gao W M. 1987. The recurrence intervals of large earthquake in the Yishu fault zone[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 3(3): 36-42 (in Chinese). http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=zgzd198703005&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
刘玉刚, 陈涛, 闵伟, 周本刚. 2013.苍山—尼山断裂西段第四纪晚期活动性[J].地震地质, 35(4): 754-764. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=zgzd198703005&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ Liu Y G, Chen T, Min W, Zhou B G. 2013. Late Quaternary activities of the western segment of the Cangshan-Nishan fault[J]. Seismology and Geology, 35(4): 754-764 (in Chinese). http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=zgzd198703005&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
路晓翠, 张景发, 朱鲁, 陈丁, 张鹏, 李丽梅. 2012.利用小波多尺度分解研究郯庐断裂带苏鲁段构造[J].地球物理学进展, 27(1): 58-67. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.1004-2903.2012.01.007 Lu X C, Zhang J F, Zhu L, Chen D, Zhang P, Li L M. 2012. Study on the structure in the Sulu segment of Tan-Lu fault zone by wavelet multi-scale decomposition[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 27(1): 58-67 (in Chinese). doi: 10.6038/j.issn.1004-2903.2012.01.007
满洪敏. 2005.沂沭断裂带内部的差异活动及其成因分析[J].华北地震科学, 23(3): 13-21. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hbdzkx200503003 Man H M. 2005. Differential activity within Yishu fault zone and its causes of formation[J]. North China Earthquake Sciences, 23(3): 13-21 (in Chinese). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hbdzkx200503003
申宁华, 李春华, 张贵宾, 王华啸. 1986.用康滇大陆古裂谷带地区航磁异常计算居里深度[J].地球物理学报, 29(5): 496-502. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dqwx198605008&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ Shen N H, Li C H, Zhang G B, Wang H X. 1986. Curie isotherm depths calculation from aeromagnetic anomalies over Xikang and Yunnan continental paleorift zone[J]. Acta Geophysica Sinica, 29(5): 496-502 (in Chinese). http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dqwx198605008&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
施炜, 张岳桥, 董树文. 2003.郯庐断裂带中段第四纪活动及其分段特征[J].地球学报, 24(1): 11-18. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb200301003 Shi W, Zhang Y Q, Dong S W. 2003. Quaternary activity and segmentation behavior of the middle portion of the Tan-Lu fault zone[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 24(1): 11-18 (in Chinese). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb200301003
宋明春. 2008.山东省大地构造单元组成、背景和演化[J].地质调查与研究, 31(3): 165-175. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/qhwjyjjz200803003 Song M C. 2008. The composing, setting and evolution of tectonic units in Shandong Province[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 31(3): 165-175 (in Chinese). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/qhwjyjjz200803003
王华林. 1990.公元前70年诸城—昌乐地震发震构造的初步研究[J].地震学刊, (3): 100-103. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dzxk199003021&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ Wang H L. 1990. Preliminary researches on the seismogenic structure of the 70 BC Zhucheng-Changle earthquake[J]. Journal of Seismology, (3): 100-130 (in Chinese). http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dzxk199003021&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
王华林, 王纪强. 2012.沂沭断裂带北段活动构造遥感地质解译与检验[J].测绘通报, (增刊1): 276-280. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7982129 Wang H L, Wang J Q. 2012. Active tectonics remote sensing geological interpretation and inspection of the northern section of Yishu fault zone[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, (S1): 276-280 (in Chinese). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7982129
王文睿, 李斐, 鄢建国, 柯宝贵. 2009.月球重力异常的小波多尺度分析[J].地球物理学报, 52(7): 1693-1699. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqwlxb200907003 Wang W R, Li F, Yan J G, Ke B G. 2009. Wavelet multi-scale analysis on gravity anomaly and inner structure of the moon[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 52(7): 1693-1699 (in Chinese). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqwlxb200907003
王鑫, 张景发, 付萍杰, 高敏. 2015a.沂沭断裂带重力场及地壳结构特征[J].地震地质, 37(3): 731-747. doi:10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2015.03.006. Wang X, Zhang J F, Fu P J, Gao M. 2015a. Deep structures of Yishu fault zone derived from gravity data[J]. Seismology and Geology, 37(3): 731-747. doi:10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2015.03.006 (in Chinese).
王鑫, 张景发, 姜文亮, 高敏, 付萍杰. 2015b.基于布格重力数据研究郯庐断裂带江苏段深部构造[J].地球物理学进展, 30(4): 1516-1525. doi:10.6038/pg20150405. Wang X, Zhang J F, Jiang W L, Gao M, Fu P J. 2015b. Deep structures of Jiangsu segment of Tan-Lu fault zone derived from Bouguer gravity data[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 30(4): 1516-1525. doi:10.6038/pg20150405 (in Chinese).
王先美, 钟大赉, 李理, 丁增勇, 李松, 张荣强. 2010.鲁西北西向断裂系与沂沭断裂带晚中生代演化关系及其动力学背景探讨[J].地学前缘, 17(3): 166-190. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201003014 Wang X M, Zhong D L, Li L, Ding Z Y, Li S, Zhang R Q. 2010. Relationship between NW faults of west Shandong and Yi-Shu fault zone in Late Mesozoic and their geotectonic setting operations[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 17(3): 166-190 (in Chinese). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201003014
王志才, 石荣会, 晁洪太, 陶九庆, 韩延宏, 逄锦亮, 张春华. 2001.鲁中南隆起区第四纪晚期断裂活动特征[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 21(4): 95-102. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200104017 Wang Z C, Shi R H, Chao H T, Tao J Q, Han Y H, Pang J L, Zhang C H. 2001. Characteristics of the Quaternary fault activities in the middle and south region of Shandong Province[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 21(4): 95-102 (in Chinese). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200104017
徐嘉炜, 马国锋. 1992.郯庐断裂带研究的十年回顾[J].地质论评, 38(4): 316-324. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y987446 Xu J W, Ma G F. 1992. Review of ten years (1981—1991) of research on the Tancheng-Lujiang fault zone[J]. Geological Review, 38(4): 316-324 (in Chinese). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y987446
张鹏, 王良书, 钟锴, 丁增勇. 2007.郯庐断裂带的分段性研究[J].地质论评, 53(5): 586-591. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlp200705002 Zhang P, Wang L S, Zhong K, Ding Z Y. 2007. Research on the segmentation of Tancheng-Lujiang fault zone[J]. Geological Review, 53(5): 586-591 (in Chinese). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlp200705002
张鹏, 王良书, 石火生, 李丽梅, 谭慧明. 2010.郯庐断裂带山东段的中新生代构造演化特征[J].地质学报, 84(9): 1316-1323. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201009006 Zhang P, Wang L S, Shi H S, Li L M, Tan H M. 2010. The Mesozoic-Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the Shandong segment of the Tan-Lu fault zone[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 84(9): 1316-1323 (in Chinese). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201009006
张先, 赵丽. 2007.功率谱用于计算不同尺度磁性体场源深度的分析[J].物探与化探, 31(增刊1): 53-56. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wtyht2007z1014 Zhang X, Zhao L. 2007. An analysis of the power spectrum for computing field source depths of magnetic bodies of different scales[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 31(S1): 53-56 (in Chinese). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wtyht2007z1014
张岳桥, 董树文. 2008.郯庐断裂带中生代构造演化史:进展与新认识[J].地质通报, 27(9): 1371-1390. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=zqyd200809004&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ Zhang Y Q, Dong S W. 2008. Mesozoic tectonic evolution history of the Tan-Lu fault zone, China: Advances and new understanding[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 27(9): 1371-1390 (in Chinese). http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=zqyd200809004&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
郑朗荪, 高维明, 郑传贝. 1988.郯庐断裂带的分段与沂沭断裂的活动性[J].中国地震, 4(3): 123-129. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=zgzd198803022&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ Zheng L S, Gao W M, Zheng C B. 1988. Segmentation of Tancheng-Lujiang fault zone and activity of Yishu fault[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 4(3): 123-129 (in Chinese). http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=zgzd198803022&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
钟南才, 侯治华. 2005.安丘—莒县断裂莒县盆地段晚第四纪以来的活动特征[J].防灾技术高等专科学校学报, 7(4): 7-11. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=fzjs200504001&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ Zhong N C, Hou Z H. 2005. Active features of Anqiu to Juxian fault in the Juxian basin in Late Quaternary[J]. Journal of College of Disaster Prevention Techniques, 7(4): 7-11 (in Chinese). http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=fzjs200504001&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
朱书俊, 孙寿成. 1991. 1668年莒县—郯城大震研究综述[J].地震学刊, (4): 19-24. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dzxk199104003&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ Zhu S J, Sun S C. 1991. Review of Juxian-Tancheng earthquake in 1668[J]. Journal of Seismology, (4): 19-24 (in Chinese). http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dzxk199104003&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
Guo H, Jiang W L, Xie X S. 2011. Late-Quaternary strong earthquakes on the seismogenic fault of the 1976 MS7.8 Tangshan earthquake, Hebei, as revealed by drilling and trenching[J]. Science China Earth Science, 54(11): 1696-1715. doi: 10.1007/s11430-011-4218-x
Jackson J, Norris R, Youngson J. 1996. The structural evolution of active fault and fold systems in central Otago, New Zealand: Evidence revealed by drainage patterns[J]. J Struct Geol, 18(2/3): 217-234. doi: 10.1016-S0191-8141(96)80046-0/
Lacassin R, Replumaz A, Leloup P H. 1998. Hairpin river loops and slip-sense inversion on southeast Asian strike-slip faults[J]. Geology, 26(8): 703-706. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1998)026<0703:HRLASS>2.3.CO;2
Lin A, Miyata T, Wan T. 1998. Tectonic characteristics of the central segment of the Tancheng-Lujiang fault zone, Shandong Peninsula, eastern China[J]. Tectonophysics, 293: 85-104. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(98)00087-0
Lin A, Guo J, Kano K I, Awata Y. 2006. Average slip rate and recurrence interval of large-magnitude earthquakes on the western segment of the strike-slip Kunlun fault, northern Tibet[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 96(5): 1597-1611. doi: 10.1785/0120050051
Mallat S G. 1989. A theory for multi-resolution signal decomposition: The wavelet representation[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 11(7): 674-693. doi: 10.1109/34.192463
Maruyama T, Lin A M. 2004. Slip sense inversion on active strike-slip faults in southwest Japan and its implications for Cenozoic tectonic evolution[J]. Tectonophysics, 383(1/2): 45-70.
Wallace R E. 1968. Notes on stream channels offset by the San Andreas fault, southern coast ranges, California[C]//Proceedings of Conference on Geologic Problems of San Andreas Fault System. Palo Alto: Stanford University Publication in Geological Sciences: 6-21.




 下载:
下载: