Ability of decreasing noise and the characteristics of nearsurface wave field around Dazhai borehole in Pu'er
-
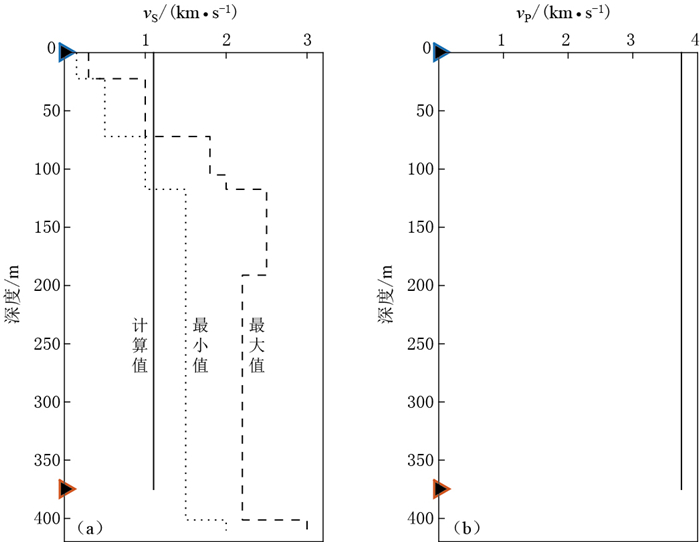
摘要: 基于2011年建立的云南普洱大寨深井台站,开展了噪声压制及附近波场特征研究.通过计算该台站的噪声功率谱概率密度函数,显示该井下台站对1 Hz以上的高频噪声具有明显的压制效果, 最高能降低40 dB,其降噪能力优于其它井下台阵,推断与该台站附近的场地条件有关.基于地表与井下地震记录的差异,应用正则化反卷积干涉方法进一步研究该台站附近的波场特征.以地表记录为参考,对井下记录进行反卷积,获取两台站之间的格林函数,直接识别出了原始记录上无法区分的上行入射波与下行地表反射波,然后利用两震相的到时差建立了一个浅层地震波速度模型,与理论模拟的结果一致.研究结果表明,相对于地表观测,井下台站在压制噪声和近地表地震波传播特征研究等方面具有很大的优势,同时该研究对其它地区开展深井观测具有参考意义.Abstract: In 2011, the Dazhai borebole station was established in Pu'er, Yunnan Province, to carry out some researches on noise suppression and the wavefield characteristics. We compute the power spectral density of continuous noise recordings within ten months to quantify the reduction in seismic noise with the station depth. The results demonstrate that the downhole station has obvious effect on decreasing noise up to 40 dB within the frequency band more than 1 Hz, which might be associated with the local site conditions. The Green's functions are then obtained between the two receivers by deconvoluting the down-hole recordings with the surface ones. From the deconvolution wavefield, the arrivals of up-going incident and down-going surface-reflection waves are directly identified that cannot be distinguished from the original seismic recordings. The two phases are utilized to set up a shallow seismic wave velocity model, which is consistent with the theoretical results. A comparison with the surface observation suggests that the borehole stations have great advantages in reducing noise and studying the propagation characteristics of near-surface seismic waves. The research here is of great significance for future down-hole observations in other sites.
-
Keywords:
- borehole /
- noise reduction /
- regularized deconvolution /
- incident wave /
- surface-reflected wave
-
引言
地震是构造应力作用下岩体突然断裂和错动所致。在这个过程中,随着应力的不断加载,地壳介质的物性参数也不断变化。及至孕震晚期,震源区应力相对集中的地壳介质的电性结构会发生变化,从而引起大地电场的变化(毛桐恩等,1999),这种地电场变化已在多次中强地震前观测到,属于中短期异常(Varotsos,Alexopoulos,1984;黄清华,刘涛,2006;马钦忠,2008;田山等,2009;安张辉等,2017;席继楼,2019)。但由于电磁环境复杂,有效的地震电信号经常被淹没在各种干扰中,使得震前异常电信号提取面临较大困难。目前常规使用的地震电信号提取方法有长短极距比值法(田山等,2009)、极化方位计算法(毛桐恩等,1999)、常规波形分析法(钱复业,赵玉林,2005)、频谱分析法(范莹莹等,2010)等,利用上述方法处理1975年海城MS7.3地震、2006年文安MS5.1地震、2008年汶川MS8.0地震、2013年芦山MS7.0地震和2017年九寨沟MS7.0地震等多次中强地震的观测资料时,均提取到与地震有关的地电场异常变化,但这些方法在异常提取、机理解释和抗干扰性方面还存在一定的局限。因此在复杂电磁环境中提取相对较弱的地震电磁信号,亟需将数学、信号处理与地震电磁物理过程相结合,才能更好地降低或消除地电场数据中干扰成分对预测的影响(黄清华,2005)。
近年来,相关学者对大地电场的机理、特征、数值模拟以及大地电场的物理解析等方面进行了深入的研究(黄清华,刘涛,2006;叶青等,2007),特别是谭大诚等(2010,2011,2012,2013,2019)基于大地电场的潮汐机理,将源于空间电流系和潮汐作用的大地电场与岩体裂隙结构联系起来(陈全等,2019),建立了大地电场的岩体裂隙水(电荷)渗流(移动)模型,并逐步发展出地电场优势方位角分析方法,藉此探寻震中附近的岩体裂隙结构变化。谭大诚等(2019)和艾萨等(2020)利用地电场优势方位角分析方法,在近几年的部分中强地震前也提取到了显著的异常信息。尤其是在部分地震前会出现多个场地的优势方位角变化在时间上出现了准同步的异常现象,这也加强了异常信息的信度。此外,地电场优势方位角分析方法机理解释明确,并对一般空间电磁干扰、附近电磁环境干扰等具有一定程度的抗干扰性(辛建村等,2017;张波等,2020),故该方法具有较高的可靠性和较好的应用前景。
2021年5月22日青海省果洛州玛多发生MS7.4地震(34.59°N,98.34°E),震源深度为17 km,震中位于巴颜喀拉地块内部,是一次典型的左旋走滑地震事件,局部兼有正断分量,在地表形成了走向北西—南东、长约70 km的破裂面。该地震是2008年汶川MS8.0地震以来中国大陆发生的震级最大的一次地震,打破了青海地区56个月的M6平静以及10年的M7平静。大武台地电场场地距本次地震震中约172 km,为距震中最近的地球物理场观测台站,但大武台的原始观测资料并未呈显著的地电异常现象。为了探究玛多MS7.4地震前大武台地电场是否存在地震电信号,本文拟利用大地电场优势方位角方法来提取玛多地震前大武台地电场的异常变化,对异常特征进行分析研究,并结合该方法在大武台记录的以往震例中的应用,梳理出强震前地电场优势方位角的异常变化特征,归纳总结该方法在青海地区强震前的异常判定指标,旨在为未来大震前后地电场的观测分析和跟踪研判提供参考依据。
1. 观测台站及数据分析方法
1.1 大武地震台
大武地震台位于青海省果洛藏族自治州玛沁县大武镇,海拔3 800 m,距离镇区3 km。目前大武台有新旧两个地电观测场地,相距约36 km。旧的大武台地电场(以下简称为大武台(旧))地位于台站院内,新的大武台地电场(以下简称为大武台(新))位于甘德县青珍乡的一个草滩,两套地电场台站周围均无高大建筑物、水库、湖泊、河流和大型厂矿等重大环境干扰源,且分别位于东昆仑断裂带两侧约10 km和25 km (图1),而东昆仑活动断裂带是一条规模巨大、构造活动十分强烈的全新世活动断裂,自1900年以来沿该断裂带已发生了10余次M7强震,最大地震为1947年3月果洛达日M7.7地震。
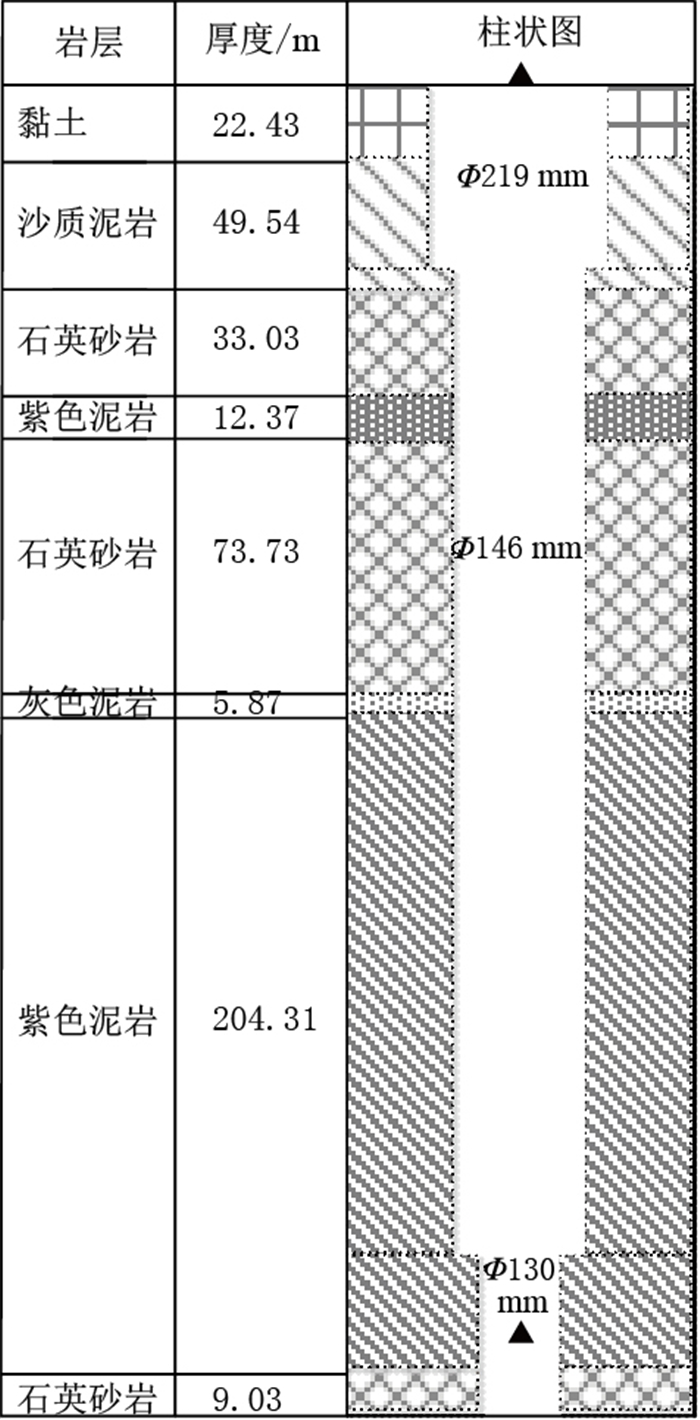
大武台地电场(旧)使用ZD9A-2B地电场仪,采用“多方向、多极距”方法进行观测,布极方式为“L”型,分别为NS,EW和NE三个测向的长、短极距共六道测线,线路采用绝缘铠装电缆以地埋的方式架设。电极装置采用固体不极化电极,深度为3.5 m,电极和铠装电缆均埋设在地表冻土层以下的潮湿土壤中,地电场布极装置方式如图2所示。
1.2 分析方法
大地电场具有日变波形特征,目前大地电场来源于地球日月潮汐作用和空间地球电离层两部分。而地壳中岩体内总存在含水裂隙,这些裂隙水或水中的电荷以日为周期沿裂隙往返渗流或移动,建立了大地电场的日变化的岩体裂隙水(电荷)渗流(移动)模型。即地下介质的应力积累会导致岩体裂隙结构的变化,从而使大地电场的强度或方位发生改变,因此岩体裂隙结构的优势方位基本就是大地电场的优势方位。
在实际地电场观测中,设潮汐地电场(大地电场主要成分)为ET,场地裂隙水主体渗流方向为α,也称为地电场优势方位角。当台站地电场的NS测向与NW测向之间的相关性最高时,大地电场ET的优势方位角α(北偏东)的计算公式如下(谭大诚等,2012,2013,2019):
$$ \alpha {\text{≈}} {180}- \frac{180}{\pi} {{\rm{arctan}}}\left(\sqrt{2}\frac{\displaystyle\sum\limits _{i=1}^{10}{A}_{{\rm{NW}} ( i ) }}{\displaystyle\sum\limits _{i=1}^{10}{A}_{{\rm{NS}} ( i ) }}-1\right) ,$$ (1) 式中ANW(i)和ANS(i)分别为NW测向和NS测向的第i阶潮汐谐波振幅。应用谐波分析法对地电场分钟值数据(每天1 440个)开展信号处理,即对这些数据进行快速傅里叶变换,得到周期为24,12,8,6,4.8,4,3.4,3,2.7和2.4 h谐波的振幅(谭大诚等,2019)。
此外,本文分析数据采用原始分钟值数据,减少了预处理造成的干扰,真实地反映异常的变化情况。
2. 异常特征
利用大地电场优势方位角方法,基于2020年以来大武台地电场(新旧两台)观测数据,得到地电场优势方位角随时间的变化曲线如图3所示。由图可见:大武台(旧)得到的观测数据其优势方位角在2020年1—5月中旬变化不大,即Δα在20°以内跳变,而在2020年5月中旬以后,方位角跳变范围出现快速、持续偏转的趋势,其偏转范围最大接近45° (图3a),持续至2021年4月方位角跳变出现快速偏转回升,随后发生玛多MS7.4地震;大武台(新)得到的观测数据其优势方位角在2020年1—5月跳变范围稳定,即Δα跳动范围在10°以内,而在2020年5月中旬以后,方位角跳变范围也同步出现缓慢、持续偏转的趋势,其偏转范围增大接近90° (图3b),随后发震。从整个演化过程来看,两套地电场台的地电场优势方位角于2020年5月中旬同步出现显著的快速偏转现象,随后在震前两个月再次出现快速偏转回升至正常跳变范围,随后发震。
3. 分析与讨论
为进一步探求玛多MS7.4地震前大地电场优势方位角异常的空间演化特征,选取2020年以来玛多地震震中500 km范围内的八个地电场台站的观测资料进行分析。首先查阅各观测台站的工作日志,对资料进行核实和排查,确保异常的可信度;然后使用地电场优势方位角方法得到这八个地电台的地电场优势方位角变化,详见表1,从表中可见四川省甘孜台、甘肃玛曲台同时期的地电场优势方位角均出现较为同步的异常变化,如图4所示。可见:甘孜台地电场优势方位角在2020年6月初开始出现显著、快速、持续偏转的现象,其偏转范围最大接近90°,收缩成近直线,随后在震前两个月出现跳变增大现象(图4a);玛曲台在震前同时期也出现了异常现象,但因环境干扰较为严重,异常形态不显著,主要以持续突跳为主(图4b)。
表 1 玛多MS7.4地震前震中500 km内地电场优势方位角的变化特征Table 1. Variation characteristic of the dominant azimuth based on geoelectric field before MS7.4 Maduo earthquake within 500 km地电场台站 震中距/km 异常形态 异常出现日期
年-月-日开始观测日期
年-月-日大武(旧) 170 快速偏转,Δα≈45° 2020-05-10 2014-12-12 大武(新) 169 Δα增大至90° 2020-05-08 2020-01-01 玛曲 335 Δα增大至60° 2020-05-04 2014-03-22 甘孜 360 快速偏转,Δα≈90° 2020-05-15 2017-12-01 都兰 190 无异常 无 2014-12-01 白水河 355 无异常 无 2015-01-01 金银滩 256 无异常 无 2019-06-04 门源地电场 433 无异常 无 2020-01-01 通过上述分析可以看出,地震前出现大地电场优势方位角异常现象是真实存在的,并且时间上具有一定准同步性,但场地具有选择性,例如:都兰台虽然距玛多地震震中仅190 km,但震前无异常现象,对该台有记录以来的数据分析也显示都兰台地电场使用该方法在以往地震前均无异常变化,目前认为这可能与其处于应力不敏感地区有关。根据詹艳(2008)利用大地电磁方法对巴颜喀拉地块探测的研究,大武台所处的巴颜喀拉地块内部的地壳上地幔电性结构具有成层性,中、强地震的震中多位于壳内低阻层的地层层段,埋深约20 km,这与本次地震的震源深度相似。此外,优势方位角未呈现异常现象的都兰台、白水河台、门源台和金银滩台处于柴达木地块以及祁连地块,而出现异常的玛曲台、甘孜台则与玛多地震共处于巴颜喀拉地块,可见,在玛多地震的孕育过程中,所处的巴颜喀拉地块存在电性结构的改变,而柴达木地块和祁连地块均未记录到明显的电性结构变化。综合分析认为,地电场优势方位角的变化显著受到构造的影响,异常响应多出现在同一地块内部或边缘。
大武台(旧)自2014年改造后,已经积累了近六年的地电场观测资料。通过梳理历史数据可知,大武台(旧)地电场对周边中强震以上的地震反应较为敏感,即在地震前出现明显的地电场优势方位角跳变异常现象。2015年以来,大武台(旧)500 km范围内共记录到MS5.5以上地震共四组,其相关的地电场优势方位角变化详见表2,可见:在四组中强地震前有三组出现了地电场优势方位角异常现象,异常比例为75%,说明大武地震台的地电场优势方位角预报效能较高。异常主要表现为方位角跳变范围出现准同步的大幅度突跳或收缩以及发生偏转等现象,且持续一段时间,在异常时间出现四个月或异常恢复后三个月内,震中附近500 km范围发生M6以上地震(或连续两次M5左右地震)的可能较大,若单台场地岩体出现剪裂(方位角跳变偏转45°或90°),异常信度则更高。
表 2 大武台周围500 km范围内MS5.5地震前地电场优势方位角的变化特征Table 2. Variation characteristic of dominant azimuth based on geoelectric field before MS5.5 earthquakes within 500 km of Dawu station台站 发震日期
年-月-日发震地点 MS 震中距/km 异常 异常出现月份
年-月备注 大武台 2016-01-21 门源 6.4 380 Δα增大 2015-10 多台同步 2016-10-17 杂多 6.2 500 震前2个月快速偏转恢复 2016-08 附近仅一台 2017-08-08 九寨沟 7.0 360 无 无 无 2019-10-28 夏河 5.7 240 快速偏转 2019-06 多台同步 2020-04-01 石渠县 5.6 200 震前3个月快速偏转恢复 2020-01 多台同步 孕震过程中应力不断变化,理论上岩体裂隙结构会因应力的变化而变化。在实际场地中,岩体结构差异会使其裂隙结构对应力变化的响应出现差异,这导致了不同场地裂隙优势方位角α异常具有场地选择性现象。在部分场地,应力积累过程会导致岩体裂隙结构发生剧烈变化,使得该场地的大地电场优势方位角α发生显著变化,例如:α出现大幅度持续突跳、范围收窄、偏转等,而当岩石受压破裂时,剪裂会导致Δα发生约45°的变化,共轭剪裂会导致Δα发生90°左右的变化。此次异常与以往异常特征相似,方位角跳变出现偏转45°或90°,且多台出现准同步异常现象。
4. 结论
通过大武台大地电场优势方位角计算和分析证实玛多MS7.4地震前多个场地出现准同步优势方位角跳变异常是真实存在的,真实反映了地下介质的变化,主要结论如下:
1) 大武台新、旧两套地电场在2020年1月至5月中旬大地电场优势方位角的跳变范围即Δα在10°—20°之内,至2020年5月中旬两套方位角出现或快或慢的持续偏转,其偏转范围最大接近45°或90°,2021年4月方位角跳变出现快速偏转回升过程。随后发生玛多MS7.4地震,两套资料的异常具有准同步性。
2) 对震中500 km范围内的八个地电场的优势方位角的计算表明,处于同一地块的甘孜台、玛曲台与大武台出现准同步异常现象,且异常形态相似,而其它地块的台站均无异常出现,说明地电场优势方位角异常受构造影响显著,异常响应多出现在同一地块内部或边缘。
3) 自2014年大武台地电场观测以来,台站周围500 km范围内共记录到MS5.5以上地震四组。地电场优势方位角计算显示,在四组中强地震前有三组出现了大武台地电场优势方位角异常现象,异常占比为75%,异常主要表现为方位角跳变范围出现准同步的大幅度突跳、或收缩以及发生偏转等现象。地震主要发生在异常出现后四个月或异常恢复后三个月内,台站附近400 km范围存在发生M6以上地震的可能(或连续两次M5地震)。
随着经济的发展和人类活动的加剧,地电场观测环境日益复杂,这使得从台站观测数据中识别相对较弱的地震电信号愈发困难,通过大地电场岩体裂隙水(电荷)渗流(移动)模型分析中强地震孕育前后附近场地岩体裂隙结构的变化特征,为异常提取提供了有效途径。但由于目前地电场场地稀疏且分布不均,导致样本量有限,不能完全真实地反映客观规律。今后随着地电观测的累积、震例的增加,应该加大对该方法的长期深入研究,从而更好地完善预测指标。
云南省普洱市地震局为本文提供了数据,德国地学研究中心Stefona Parolai教授和Bojana Petrovic博士为本文计算方法和程序提供了很多帮助,作者在此一并表示感谢. -
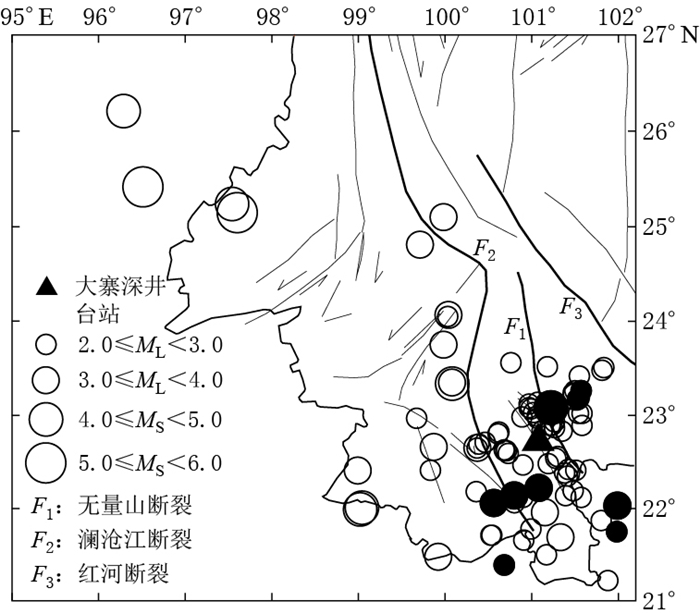
图 1 大寨深井台站位置及其记录到的地震分布
黑色圆圈为台站附近的地震分布,黑色实心圆圈为文中反卷积计算用到的地震事件
Figure 1. Location of the Dazhai borehole station (triangle) and distribution of local earthquakes Circles represent the location of local earthquakes and solid circles are the earthquakes used in this paper.
F1 : Wuliangshan fault; F2 : Lancangjiang fault; F3 : Honghe fault
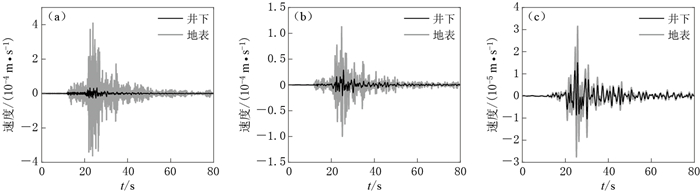
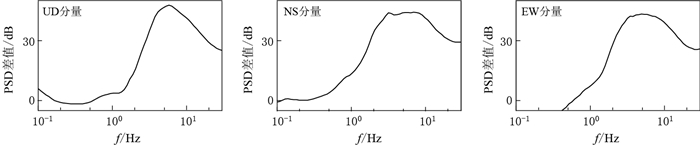
图 5 ML3.7地震事件南北向分量的原始波形(a)及其2.0 Hz(b)和1.0 Hz(c)低通滤波结果
Figure 5. Original waveforms (a) and low-pass filtered waveforms with the cut-off frequencies of 2.0 Hz (b) and 1.0 Hz (c) of the NS component of the ML3.7 event
Black lines indicate the borehole recordings, and grey lines indicate the surface recordings
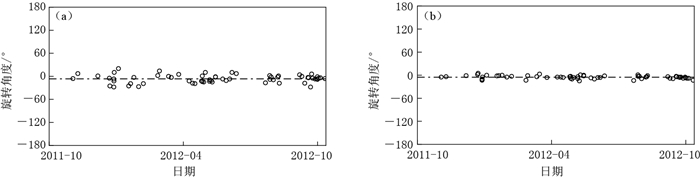
图 6 基于均方根误差方法(a)和互相关函数方法(b)得到的不同地震事件南北分裂的最佳旋转角度统计结果
黑色圆圈表示不同事件对应的角度,虚线表示不同角度的中值及均值
Figure 6. The optimal rotation angles corresponding to NS components of different events by RMS error (a) and cross-correlation (b)
Open circles indicate different angles corresponding to different events, and dashed lines indicate the median and mean value of all rotation angles
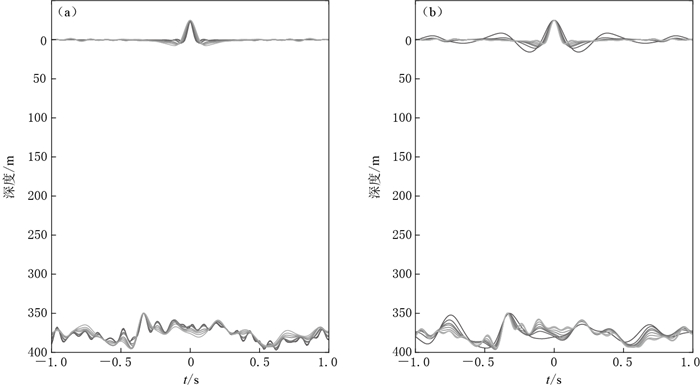
图 10 2011年11月9日ML3.2地震水平分量反卷积波场
(a)不同正则化参数ε下的反卷积波场, 线条颜色由浅变深,表示ε逐渐减小;
(b)不同迭代次数n下的反卷积波场, 线条颜色由深变浅,表示n逐渐增大Figure 10. Deconvolution wavefield of the event ML3.2 with different regularization parameters
(a) Deconvolution variation with regularization parameter ε decreasing from light to dark lines;
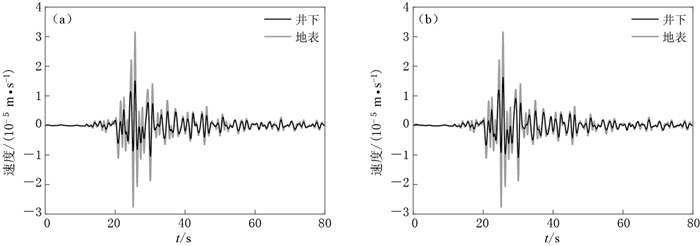
(b) Deconvolution variation with Landweber iterations n increasing from dark to light lines图 11 表 2中事件2(ML3.2)的原始记录(a)及其相应的反卷积波场(b)
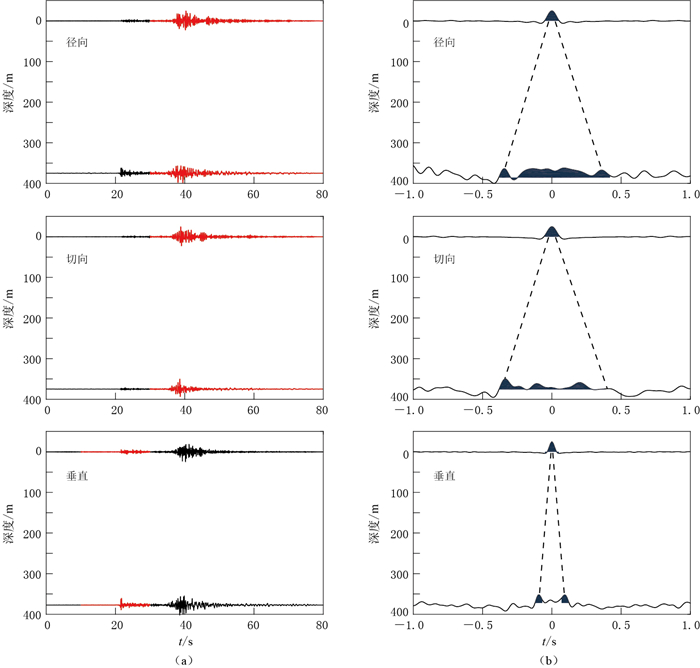
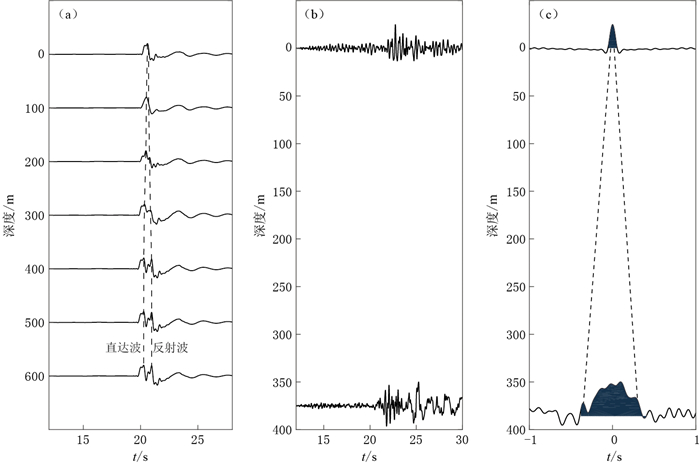
红线表示用于进行反卷积计算的时间窗口,黑色虚线是井下与地表之间相互对称的上行波和下行波
Figure 11. The deconvolution wavefield (b) from the original records (a) of No.2 event listed in Table 2
The red lines indicate the time window used for deconvolution, and the dashed lines show the up-going wave and down-going wave from bottom to surface
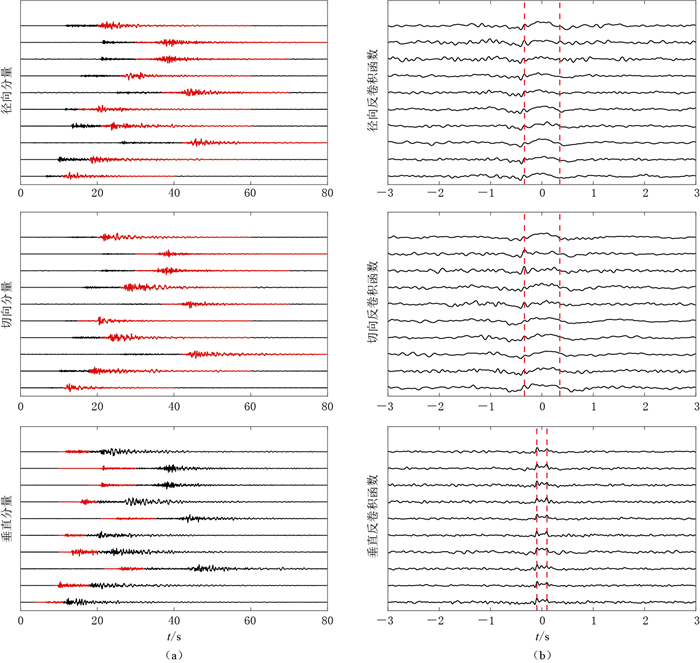
图 12 表 2中地震事件的原始井下记录(a)及其对应的反卷积波场(b)
(a)中红色实线表示用于反卷积计算的时间窗口, (b)中红色虚线分别表示入射波和地表反射波的位置
Figure 12. Aligned deconvolution wavefield (b) from the original borehole records (a) of all the events listed in Table 2
Red lines indicate the time window used for deconvolution, and vertical dashed red lines indicate the arrivals of incident and surface-reflected waves
表 1 最佳旋转角度的统计结果
Table 1 The statistics of optimal rotation angles
方法 均值 中值 两者平均值 均方根误差法 -6.66° -7° -6.83° 互相关函数法 -5.36° -5° -5.18° 表 2 用于反卷积计算的事件列表
Table 2 List of the events used for deconvolution
事件序号 发震时间 ML 震中距/km 年-月-日 时:分:秒 1 2011-11-02 19:33:05.1 3.7 71.21 2 2011-11-09 09:04:23.4 3.2 124.63 3 2011-11-16 23:47:37.5 2.6 121.54 4 2011-12-28 15:16:32.3 3.5 90.64 5 2012-02-22 00:41:39.7 2.3 145.54 6 2012-03-12 01:24:19.1 2.4 68.49 7 2012-04-13 23:06:45.7 2.7 78.48 8 2012-04-29 01:33:01.3 2.7 154.29 9 2012-07-28 08:16:15.5 3.2 57.63 10 2012-07-30 00:05:32.5 4.2(MS) 41.47 注:地震目录引自中国地震台网中心(2015). 表 3 合成理论地震图所用到的地壳模型
Table 3 Velocity model for calculating the synthetic seismograms
层数 vP/(km·s-1) vS/(km·s-1) 层厚/km QP QS 1 3.75 1.10 0.375 1000 500 2 6.10 3.55 13.85 1000 500 3 6.30 3.65 12.34 1000 500 注:QP,QS表示P波和S波的地下介质品质因子. -
冯德益, 张少泉, 卫鹏飞, 王俊国. 1990.深井观测地震波典型记录与分析应用[M].北京:地震出版社: 1-2. Feng D Y, Zhang S Q, Wei P F, Wang J G. 1990. Typical Records and Application of Deep Borehole Seismic Waves[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press: 1-2 (in Chinese).
葛洪魁, 陈海潮, 欧阳飚, 杨微, 张梅, 袁松湧, 王宝善. 2013.流动地震观测背景噪声的台基响应[J].地球物理学报, 56(3): 857-868. doi: 10.6038/cjg20130315 Ge H K, Chen H C, Ouyang B, Yang W, Zhang M, Yuan S Y, Wang B S. 2013. Transportable seismometer response to seismic noise in vault[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 56(3): 857-868 (in Chinese). doi: 10.6038/cjg20130315
《工程地质手册》编委会. 2007.工程地质手册[M].第4版.北京:中国建筑工业出版社: 1-1099. Editorial Committee of Engineering Geology Manual. 2007. Engineering Geology Manual[M]. 4th ed. Beijing: China Architecture and Building Press: 1-1099 (in Chinese).
李凤杰. 1989.深井地震波观测研究[M].北京:学术期刊出版社: 1-4. Li F J. 1989. Study on Deep Borehole Seismic Wave Observation[M]. Beijing: Academic Journal Press: 1-4 (in Chinese).
李少睿, 毛国良, 王党席, 罗治国. 2016.井下地震计方位角检测技术应用研究[J].地球物理学报, 59(1): 299-310. doi: 10.6038/cjg20160125 Li S R, Mao G L, Wang D X, Luo Z G. 2016. Research on the application of borehole seismometer azimuth detection technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 59(1): 299-310 (in Chinese). doi: 10.6038/cjg20160125
刘渊源, 崇加军, 倪四道. 2011.基于井下摆天然地震数据测量首都圈近地表波速结构[J].地震学报, 33(3): 342-350. http://www.dzxb.org/Magazine/Show?id=27826 Liu Y Y, Chong J J, Ni S D. 2011. Near surface wave velocity structure in Chinese capital region based on borehole seismic records[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 33(3): 342-350 (in Chinese). http://www.dzxb.org/Magazine/Show?id=27826
吕永清, 蔡亚先, 程骏玲. 2007.确定地震计安装方位的相干性分析法[J].大地测量与地球动力学, 27(4): 124-127. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/87801X/200801/26453603.html Lü Y Q, Cai Y X, Cheng J L. 2007. Orientation for seismometer with coherence analyzing method[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 27(4): 124-127 (in Chinese). http://www.cqvip.com/QK/87801X/200801/26453603.html
仝亚博, 杨振宇, 王恒, 张旭东, 安纯志, 徐颖超, 赵越. 2014.中国西南思茅地体中部白垩纪古地磁结果及陆内地壳变形特征[J].地球物理学报, 57(1): 179-198. doi: 10.6038/cjg20140116 Tong Y B, Yang Z Y, Wang H, Zhang X D, AnC Z, Xu Y C, Zhao Y. 2014. The Creatceous paleomagnetic results from the central part of the Simao terrane in the southwest part of China and its tectonic implication[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 57(1): 179-198 (in Chinese). doi: 10.6038/cjg20140116
王林瑛, 郭永霞, 刘芳, 蒋长胜. 2008.文安地震前后首都圈分区波速比时变特征[J].地震学报, 30(3): 240-253. http://www.dzxb.org/Magazine/Show?id=26581 Wang L Y, Guo Y X, Liu F, Jiang C S. 2008. Temporal vP/vS variation characteristics in different zones of China's capital area before and after 2006 Wen'an earthquake[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 30(3): 240-253 (in Chinese). http://www.dzxb.org/Magazine/Show?id=26581
谢剑波. 2014.地震记录的时间域反褶积、仿真及在地震计方位角相对测量中的应用[J].地球物理学报, 57(1): 167-178. doi: 10.6038/cjg20140115 Xie J B. 2014. Deconvolution, simulation of seismic records in the time domain and application in the relative measurements of seismometer orientation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 57(1): 167-178 (in Chinese). doi: 10.6038/cjg20140115
徐纪人, 赵志新. 2009.深井地球物理观测的最新进展与中国大陆科学钻探长期观测[J].地球物理学进展, 24(4): 1176-1182. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2009.04.003 Xu J R, Zhao Z X. 2009. Recent advance of borehole geophysical observation and Chinese continental scientific drilling long-term observatory at depth[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 24(4): 1176-1182 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2009.04.003
张尉, 陈棋福, 丘学林, 陈颙. 2009.首都圈数字地震台网对微弱爆破信号的检测能力[J].地球物理学报, 52(3): 681-690. http://www.irgrid.ac.cn/handle/1471x/197822 Zhang W, Chen Q F, Qiu X L, Chen Y. 2009. Weak explosion signal detection by the Beijing metropolitan digital seismic network[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 52(3): 681-690 (in Chinese). http://www.irgrid.ac.cn/handle/1471x/197822
中国地震台网中心. 2015. 历史查询[EB/OL]. [2015-08-07]. http://www.ceic.ac.cn/history. China Earthquake Network Center. 2017.History search[EB/OL]. [2015-08-07]. http://www.ceic.ac.cn/history (in Chinese).
Asai Y, Okubo M, Ishii H, Aoki H, Yamauchi T, Kitagawa Y, Koizumi N. 2005. Co-seismic strain-steps associated with the 2004 off the Kii Peninsula earthquakes-Observed with Ishii-type borehole strainmeters and quartz-tube extensometers[J]. Earth Planets Space, 57: BF03352568. doi: 10.1186/BF03352568.pdf
Aster R C, Shearer P M. 1991. High frequency borehole seismograms recorded in the San Jacinto fault zone, southern California, Part 1: Polarization[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 81(4): 1081-1100. https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/bssa/article-lookup/81/4/1057
Bertero M, Boccacci P. 1998. Introduction to Inverse Problems in Imaging[M]. Bristol: IOP Publishing: 1-347.
Bindi D, Parolai S, Spallarossa D, Catteneo M. 2000. Site effects by H/V ratio: Comparison of two different procedures[J]. J Earthq Eng, 4(1): 97-113. https://www.cambridge.org/core/books/the-italic-people-of-ancient...
Boese C, Wotherspoon L, Alvarez M, Malin P. 2015. Analysis of anthropogenic and natural noise from multilevel borehole seismometers in an urban environment, Auckland, New Zealand[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 105(1): 285-299. doi: 10.1785/0120130288
Chong J J, Ni S D. 2009. Near surface velocity and QS structure of the Quaternary sediment in Bohai basin, China[J]. Earthquake Science, 22(5): 451-458. doi: 10.1007/s11589-009-0451-1
Carter J A, Barstow N, Pomeroy P W, Chael E P, Leahy P J. 1991. High-frequency seismic noise as a function of depth[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 81(4): 1101-1114. https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/bssa/article-lookup/81/4/1101
Díaz J, Villaseor A, Morales J, Pazos A, Córdoba D, Pulgar J, García-Lobón J L, Harnafi M, Carbonell R, Gallart J, TopoIberia Seismic Working Group. 2010. Background noise characteristics at the IberArray broadband seismic network[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 100(2): 618-628. doi: 10.1785/0120090085
Fukao Y, Ishibashi K. 1996. Damages Caused by Osaka-Kobe-Awaji Large Earthquake and Earthquake Prediction[M]. Tokyo: Iwanami Press (in Japanese).
Fukushima Y, Kinoshita S, Sato H. 1992. Measurement of Q-1 for S waves in mudstone Chikura, Japan: Comparison of incident and reflected phases in borehole seismograms[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 82(1): 148-163.
Fukushima R, Nakahara H, Nishimura T. 2016. Estimating S-wave attenuation in sediments by deconvolution analysis of KiK-net borehole seismograms[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 106(2): 552-559. doi: 10.1785/0120150059
Grigoli F, Cesca S, Dahm T, Krieger L. 2012. A complex linear least-squares method to derive relative and absolute orientations of seismic sensors[J]. Geophys J Int, 188(3): 1243-1254. doi: 10.1111/gji.2012.188.issue-3
Hauksson E, Teng T L, Henyey T. 1987. Results from a 1500 m deep, three-level downhole seismometer array: Site response, low Q values, and fmax[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 77(6): 1883-1904. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/317931488_Hydraulic...
Ma K F, Lin Y Y, Lee S J, Mori J, Brodsky E E. 2012. Isotropic events observed with a borehole array in the Chelungpu fault zone, Taiwan[J]. Science, 337(6093): 459-463. doi: 10.1126/science.1222119
McNamara D E, Boaz R I. 2005. Seismic Noise Analysis System, Power Spectral Density Probability Density Function: Stand-Alone Software Package[R]. USGS Open-File Report: 2005-1438.
Mehta K, Snieder R, Grazier V. 2007a. Extraction of near-surface properties for a lossy layered medium using the propagator matrix[J]. Geophys J Int, 169(1): 271-280. doi: 10.1111/gji.2007.169.issue-1
Mehta K, Snieder R, Grazier V. 2007b. Downhole receiver function: A case study[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 97(5): 1396-1403. doi: 10.1785/0120060256
Nakata N, Snieder R. 2012. Estimating near-surface shear wave velocities in Japan by applying seismic interferometry to KiK-net data[J]. J Geophys Res, 177: B01308. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.705.4195
Nakata N. 2013. Combination of Hi-net and KiK-net data for deconvolution interferometry[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 103(6): 3073-3082. doi: 10.1785/0120130101
Nakata N, Snieder R, Behm M. 2014. Body-wave interferometry using regional earthquakes with multidimensional deconvolution after wavefield decomposition at free surface[J]. Geophys J Int, 199(2): 1125-1137. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggu316
Wang X, Chen Q F, Li J, Wei S J. 2016. Seismic sensor misorientation measurement using P-wave particle motion: An application to the NEC saids array[J]. Seismol Res Lett, 87(4): 901-911. doi: 10.1785/0220160005.
Okubo M, Asai Y, Aoki H, Ishii H. 2005. The seismological and geodetical roles of strain seismogram suggested from the 2004 off the Kii peninsula earthquakes[J]. Earth Planets Space, 57(4): 303-308. doi: 10.1186/BF03352567
Parolai S, Ansal A, Kurtulus A, Strollo A, Wang R J, Zschau J. 2009. The Ataky vertical array (Turkey): Insights into seismic wave propagation in the shallow-most crustal layers by waveform deconvolution[J]. Geophys J Int, 178(3): 1649-1662. doi: 10.1111/gji.2009.178.issue-3
Peterson J. 1993. Observations and Modeling of Seismic Background Noise[R]. USGS Open-File Report: 93-322.
Seale S H, Archuleta R J. 1989. Site amplification and attenuation of strong ground motion[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 79(6): 1673-1696.
Snieder R, Safak E. 2006. Extracting the building response using seismic interferometry: Theory and application to the Millikan library in Pasadena, California[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 96(2): 586-598. doi: 10.1785/0120050109
Tikhonov A N, Arsenin V Y. 1977. Solutions of Ill-Posed Problems[M]. WashingtonD C:V.H.Winston & Sons: 1-258.
Zhu L P, Rivera L A. 2002. A note on the dynamic and static displacements from a point source in multilayered media[J]. Geophys J Int, 148(3): 619-627. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-246X.2002.01610.x
Zoback M D, Hickman S H, Ellsworth W L. 2011. Scientific drilling into the San Andreas fault zone: An overview of SAFOD's first five years[J]. Scientific Drilling, 11: 14-28. doi: 10.5194/sd-11-14-2011
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 董博,纪春玲,张合,李姜,吕国军. 唐山区域概率地震危险性研究. 华北地震科学. 2020(01): 38-48 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 曹永兴,邓鹤鸣,蔡炜,刘衍宏,吴驰,邬雄. 电力设施应对地震及其次生灾害的研究进展. 高电压技术. 2019(06): 1962-1974 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 韩叶良,苏国锋,袁宏永,Rachel A. DAVIDSON. 基于概率情景的多场点系统地震风险分析方法. 清华大学学报(自然科学版). 2012(04): 540-543+549 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 雷建成,高孟潭,吴健,亢川川. 梯级电站系统的地震危险性评价方法初步研究. 地震学报. 2011(03): 373-385 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(9)





 下载:
下载: