Characteristics of crust vertical deformation and seismic risk analysis in Liaoning area
-
摘要: 利用辽宁地区三期复测水准资料,计算得出1988—1998年和1998—2016年两个时段的地壳垂直形变速率, 并绘制相应的地壳垂直形变速率矢量图和等值线图.结合辽宁地区的区域地质背景及构造断裂活动性,分析了区域地壳垂直形变特征与地震活动性之间的相关性,明确了该区域的整体地壳垂直形变趋势及需重点关注的区域.结果表明:海城MS7.3地震后较长时间内,辽宁地区整体以继承性运动为主,辽东隆起和辽西隆起以上升为主,下辽河断陷带下沉;1998年后,辽宁地区整体形变差异量减小,该地区垂直形变正趋于稳态,垂直形变速率梯度高值区仍集中于下辽河断陷带与辽东隆起、辽西隆起的交界地带,因此该区域的潜在危险性较高,需要持续并重点关注.Abstract: Based on the three-issue repeated measurement data of the Liaoning area, we calculate the vertical strain rate during 1988-1998 and 1998-2016, and draw the corresponding vector graph and isoline map of the vertical deformation rate. The correlation between vertical deformation characteristics and seismic activities is analyzed combining the geological background and tectonic activity in Liaoning area, thus to identify the overall trend of deformation and to require critical attention to the areas. The results showed that Liaoning region represents as inheritance movement, Liaodong and Liaoxi uplifts exhibit an upward trend, Liaohe down-faulted zone showed subsidence for a long time after MS7.3 Haicheng earthquake; the overall amount of difference of deformation in Liao-ning area decreased since 1998, the region's vertical deformation tends to be stable. The high gradient zone of deformation rate is still concentrated in the border of Liaohe down-faulted zone, Liaodong and Liaoxi area, and then these areas exist high potential risk and need sustained and focused attention.
-
Keywords:
- vertical deformation /
- tectonic activity /
- gradient /
- seismic activity
-
引言
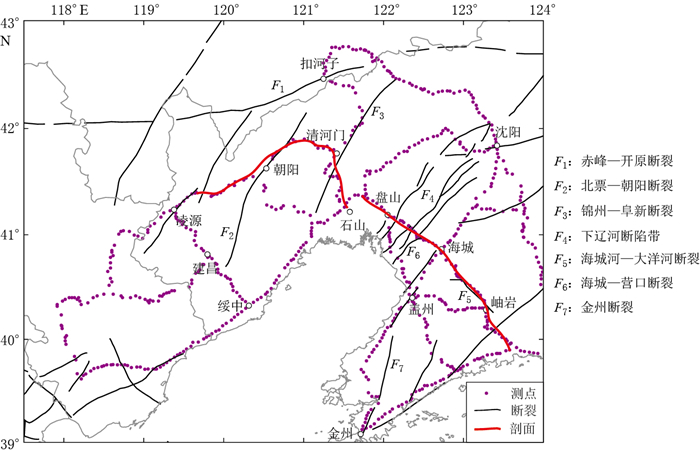
辽宁地区断裂构造十分发育,是现代构造活动相对强烈的地区(吴波,2015;姜岩,2016).中国大陆东部规模最大且活动性显著的断裂带郯庐断裂带通过本区,控制着本区域强震的孕育和发生.本区域地质构造总体呈北东向的条块状,东侧为辽东隆起,西侧为辽西隆起,中部为下辽河断陷带.区内活动断裂走向主要呈东西向、北东向和北西向分布, 其中:东西向断裂主要为赤峰—开原断裂,近东西向的张家口—北票断裂;北东向断裂是区内的主体构造.遍布整个辽宁地区,主要有下辽河断陷带(即郯庐断裂带的一部分)和北票—朝阳断裂;北西向断裂发育相对较少,多为一些截北东向的扭性断裂,如海城河—大洋河断裂.
地壳垂直形变速率能够直观地反映出地壳的垂向运动特征,继而反映出地壳构造活动的活跃与闭锁程度,结合地质背景及地震活动性,能为地震发生的研判提供参考.与其它手段相比,利用地壳垂直形变资料分析区域形变特征具有十分显著的优势(徐东卓等,2017). 20世纪70年代以来,区域精密水准资料已经广泛应用于地壳垂直运动研究,并在地震孕育理论、地震预报等研究中发挥了重要作用(应绍奋等,1988;黄立人等,1989;马文涛等,2004;王若柏等,2004).孔繁强和林玉祥(1991)、赖锡安等(2004)和郭良迁等(2012)已对辽宁地区垂直形变场的特征进行了分析,特别是1975年海城MS7.3地震之后,郭良迁等(2012)根据辽宁地区的地壳垂直形变场特征,分析了该地区未来的地震孕育发展趋势.
1975年海城MS7.3地震发生在下辽河断陷带东侧的海城—营口断裂带与北西向的海城河—大洋河断裂的交界部位(王若柏等,1995;高常波,钟以章,2000).海城MS7.3地震之后,地壳应力从地球动力学层面得以一定程度的释放,中短期内区域构造活动以继承性运动为主.而现今距海城大地震发生已有四十余年,且该时间段内未发生过MS≥6.0强震,未来几年内这种平衡是否被打破,地壳应力积累情况如何变化,这些均值得重点关注.本文拟利用2016年在辽宁地区开展的一系列精密水准复测工作所获取的最新一期资料,结合历史资料分析,以期获取该地区近期的垂直形变特征及地震活动性,为该区域地震危险性分析及强震预测提供依据.
1. 资料概况与数据处理
辽宁地区精密水准测点分布如图 1所示,水准资料西起河北遵化,东至辽宁丹东,北起内蒙古库伦旗,南到辽宁大连,覆盖了辽宁的大部分区域.水准资料时间跨度为1988—2016年,第一期施测时间为1988—1989年,第二期施测时间为1997—1998年,第三期施测时间为2013—2016年.其中,第一期与第二期的公共测点为480个,第二期与第三期的公共测点为267个.
首先,采用分段动态线性速率模型数进行据处理,以水准路线交会点为起算基准,平差计算得到1988—1998年和1998—2016年的地壳垂直形变速率,其动态平差结果中单位权中误差分别为0.87 mm/a,0.86 mm/a,均小于1 mm/a,表明本区域采用的数据整体实测精度较高;其次,对测点形变速率进行预处理,剔除个别量级过大或与相邻点差异过大的突变点;最后,采用多面函数法对计算结果进行格网化,并计算每个格网点的速率梯度模值, 绘制地壳垂直形变速率矢量图、等值线图与梯度图(Xu et al,2016).
2. 地壳垂直形变特征与区域地震活动性
2.1 地壳垂直形变特征分析
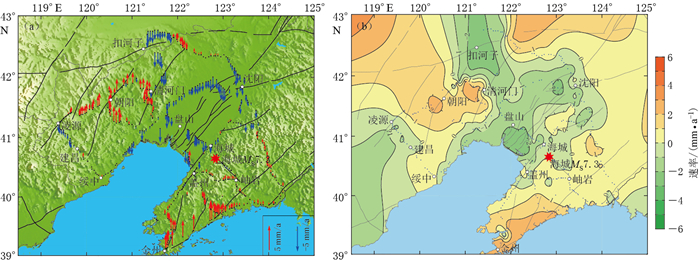
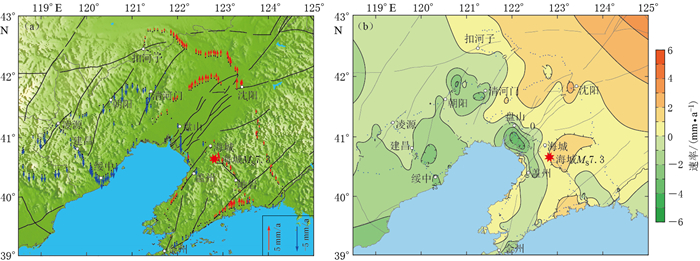
首先,采用连续曲率张力样条法对计算得到的地壳垂直形变速率值, 进行网格化处理,其原理是将张力参数引入最小曲率拟合曲面中,即在弹性薄板弯曲方程中加入张力参数,消除曲面中存在的无关变形点,张力参数的取值一般为0—1;其次,由于地壳变形的缓慢性和局部的一致性,同时为提高计算效率,选用Boxcar卷积滤波器进行平滑处理;最后,绘制出辽宁地区1988—1998年(图 2)和1998—2016年(图 3)两个时段的地壳垂直形变速率矢量图和等值线图.
由图 2a可以看出,1988—1998年期间辽东隆起和辽西隆起总体表现为上升趋势,下辽河断陷带则呈整体下降.辽东隆起由北向南上升速率逐步增大,尤其是大孤山—金州一线最大速率达2.5 mm/a;辽西隆起的上升区主要集中在凌源—朝阳—清河门、石山—清河门和锦州—朝阳这3个区域,速率为0—2.5 mm/a;下辽河断陷总体呈现较大幅度的下沉趋势,石山—盘山—海城和石山—沈阳一带最大下沉速率达2.5 mm/a.由图 2b可以看出:辽东隆起西南部的地壳垂直形变速率等值线走向为北东向,到岫岩—本溪一带转呈北西向,这种变化可能与海城河—大洋河隐伏断裂的构造活动有关;辽西隆起的地壳垂直形变速率等值线自西向东由北西向转呈北东走向,辽西隆起相对上升,上升条带北接赤峰—开原断裂,南邻北票—朝阳断裂,构造活动主要受这两条断裂控制;下辽河断陷带垂直形变速率等值线总体形态与下辽河断陷带走向一致,最大下沉速率出现在断裂带发育丰富的盘山地区,等值线形态在海城—岫岩一带发生微小转折,恰好是金州断裂与海城河—大洋河断裂的交会地段,说明该地区形变与构造活动关系密切.
1998—2016年辽宁地区的地壳垂直形变整体上呈现“东北升,西南降”的特征(图 3).从长期垂直形变速率(图 3a)来看,辽宁地区形变速率变化总体较为稳定,其中辽东隆起及下辽河断陷带北部以上升为主,最大上升速率为2 mm/a,辽西隆起以下沉为主,下沉速率约为0—2.5 mm/a.图 3b所示的等值线分布密集区域也是断裂发育分布较为集中的区域,主要是朝阳—清河门、石山—盘山—海城—岫岩和丹东—大孤山等3个区域.从盘山经海城、岫岩至大孤山一带垂直形变速率呈现出一个明显的转折过程,特别是在海城一带构造较为复杂的区域,垂直形变速率等值线由下降转为上升,由此推断海城河—大洋河隐伏断裂可能正处于强烈活动期,在其交界地带形成了一条北北西向的挤压条带,因此应予以重点关注.另外,清河门—盘山一带也经历了垂直形变速率等值线的转折变化,表明该时段内锦州—阜新断裂、下辽河断陷带可能也正处于活动期.
辽宁地区1988—1998年(图 2a)和1998—2016年(图 3a)两个时段的垂直形变速率矢量图显示:辽东隆起地块的形变演变过程为整体上升到北部上升南部下降,即金州—盖州一带地表由上升转为下降;下辽河断陷演化过程为整体下降到北部上升南部下沉,即盘山一带断陷发育丰富的地区仍然以下沉为主,但其东北端出现一定程度的隆升,与区域构造活动不完全一致;辽西隆起的演化进程为东北升西南降到整体微降.从较长时间尺度来看,近年来该区域的垂直形变速率整体变化不大.
2.2 地壳垂直形变剖面分析
根据辽宁地区断层及测线分布,选择跨区域内主要断裂带的两条水准剖面(位置见图 1),即朝阳—清河门—石山水准剖面和盘山—海城—岫岩—大孤山水准剖面,以分析断层两侧的形变特征及断层活动情况.
朝阳—清河门—石山水准剖面从西往东依次跨越北票—朝阳断裂和锦州—阜新断裂.北票—朝阳断裂走向为N45°E, 倾向为NW,早期以逆断层活动为主,上盘震旦系灰岩逆冲于下盘侏罗系砂砾岩之上,第四纪以来断层则转为以正断层活动为主.由图 4所示的1988—2016年该水准剖面的地壳垂直形变速率趋势可见,这两个时段内该断裂均呈现弱压性运动特征,即相对于上盘,下盘出现较小幅度的下沉.依据断层两侧水准测点的垂直形变速率估算断层的活动速率,两个时段内分别为-1.0 mm/a和-0.5 mm/a,断裂以逆冲活动为主.锦州—阜新断裂,倾向为NW,1988—1998年该断裂以压性活动为主,估算断层活动速率为-1.0 mm/a,而1998—2016年,断层活动性质发生转折,由压性转为张性活动,估算的断层形变速率为2.3 mm/a,这表明锦州—阜新断裂两侧的垂直形变活动速率差异较大.这两个时期形变速率反映出的断层张压活动性突变明显,显示了该区域内地壳垂直形变活动剧烈,需结合其它资料重点关注短期内的形变趋势.
盘山—海城—岫岩—大孤山水准剖面从北往南跨越下辽河断陷带和金州断裂.下辽河断陷带内发育有多条正断层,主要有台安—大洼断裂、牛居—油燕沟断裂、辽中断裂(又称为二界沟断裂)和海城—营口断裂.由图 5可知:1988—1998年,该断陷带总体以张性活动为主,断陷带内测点形变较为复杂,表明该时期内相应的断裂活动处于活跃期,断层活动速率约为3.1 mm/a;而从1998—2016年较长时段内的活动趋势来看,该区内测点的垂直形变速率变化不大,且速率值较小,维持在1.0 mm/a左右.金州断裂为正断层,倾向NW,1988—1998年,断层处于活跃期,以张性活动为主,估算断层活动速率为4.0 mm/a,1998—2016年,虽然该断层仍处于张性活动,但活动速率与前期相比明显变小,形变速率为0—1.0 mm/a.
2.3 地震危险性分析
利用辽宁地区形变速率值分别计算了1988—1998年和1998—2016年两个时间段内的垂直形变速率梯度并绘制梯度图.假定地壳垂直形变速率为V是平面坐标x,y的函数, 记为V (x, y), V的水平梯度即地壳垂直形变速率梯度G定义为
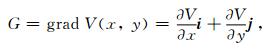
(1) 式中i,j表示x,y方向的单位矢量,则G的模为

(2) 形变速率梯度高值区即为|G|值较高的地区,也就是地壳垂直形变速率图上的等值线密集地区,编绘梯度图则为计算|G|值并编绘|G|值的等值线图.
对该区域两时段内发生的地震统计可知,1988—1998年辽宁地区发生MS≥4.5地震7次,1998—2016年15次,未发生较强地震.这些地震与该地区垂直形变速率梯度带分布的对应关系如图 6所示.可以看出:1988—1998年期间(图 6a)形变速率梯度高值区主要分布在朝阳—清河门、海城—盖州和沈阳一带,该时段内MS≥4.5地震发生频次较低,尤其是在海城一带频次更低,这可能与1975年海城MS7.3地震十几年后,地壳构造运动逐渐减弱有一定关系.图 6b与图 6a相比可知:总体上速率梯度高值区范围变小,这表明该地区垂直形变因受构造地块控制而减弱,反映了地壳应力相对较弱或松弛,但这也是应力积累的一个时期;从地震分布来看,速率梯度高值区所在的海城—盖州—岫岩一带近年来多次发生MS≥4.5地震,发震频次显著增大,故应持续关注该区域的形变趋势.
3. 讨论与结论
本文通过对辽宁地区近30年的多期复测精密水准资料的整理分析,总结了该区域的地壳垂直形变速率特征,结合地质背景及地震活动性,获得了以下认识:
1) 近年来辽宁地区的地壳垂直形变以继承性运动为主,断裂活动总体上较弱.研究期内,辽宁地区地壳垂直形变首先表现为明显的继承性运动,在运动形态上辽东隆起和辽西隆起以上升为主,下辽河断陷带呈下沉趋势,这种构造性运动非常明显,且与各主要断裂活动性质吻合得较好,如北票—朝阳断裂、锦州—阜新断裂均呈压性活动特征.近年数据表明辽宁地区的地壳垂直形变整体处于较为稳定阶段,形变值不大,但辽西隆起形变趋势有所转变,部分断裂活动性质变化尤为明显,例如锦州—阜新断裂活动性质由压性转为张性,表明辽西隆起的断裂活动具有增强的趋势.
2) 研究区内近年发生MS≥4.5地震22次,未发生MS≥6.0强震,从地震活动性来看,该区域处于一种相对较为平静的状态,值得持续跟踪关注.基于水准资料获取的地壳垂直形变速率梯度高值区与地震震中位置具有较好的对应关系.垂直形变速率梯度高值区大多是山地与平原的过渡地带,断裂发育丰富,例如金州断裂、下辽河断陷带等与北西、北西西向隐伏断裂的交会部位,赤峰—开原断裂与北票—朝阳断裂、锦州—阜新断裂的交会处,其相应的区域形变差异十分明显.
3) 综合研究期内垂直形变速率梯度与地震发生位置的关系,地壳垂直形变速率梯度高值区与地震的对应关系较为明显,因此认为形变速率梯度高值区带对地震危险区的判定具有较为积极的作用.从中长期趋势来看,辽宁地区的朝阳—清河门、海城—盖州—岫岩一带存在中强地震的孕育背景,这也是未来地壳形变监测的重点地带.
精密水准资料能够较为清晰地反映出了辽宁的区域垂直形变特征,结合地质构造背景等相关知识,可以用来判断地震危险区,但是,由于该区域其它观测资料相对缺乏,本文的研究手段较为单一, 下一步将结合全球卫星导航测量、重力测量等手段进行深层次的且更为精准的多数据融合分析研究.
-
-
高常波, 钟以章. 2000. 1999年辽宁海城—岫岩5.6级地震的地质构造背景和发震构造[J].地震地质, 22(4): 405-412. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Reference.aspx?id=Periodical... Gao C B, Zhong Y Z. 2000. Geological background and seismogenic fault of the Haicheng-Xiuyan M5.6 earthquake of November 29, 1999[J]. Seismology and Geology, 22(4): 405-412 (in Chinese). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Reference.aspx?id=Periodical...
郭良迁, 马青, 杜雪松, 陈聚忠, 张俊青, 郑智江. 2012.辽宁地区地壳垂直形变演化特征[J].大地测量与地球动力学, 32(3): 17-21. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/8a801c41c850ad02de804129... Guo L Q, Ma Q, Du X S, Chen J Z, Zhang J Q, Zheng Z J. 2012. Evolutional characteristics of vertical crustal deformation in Liaoning area[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 32(3): 17-21 (in Chinese). https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/8a801c41c850ad02de804129...
黄立人, 杨国华, 刘天奎. 1989.用速率面拟合法研究华北部分地区的现今地壳垂直运动[J].地震形变与地震, 9(3): 26-35. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYDZ603.003.htm Huang L R, Yang G H, Liu T K. 1989. The study of present vertical crustal movements in part of North China by the fitting method of velocity surface[J]. Crustal Deformation and Earthquake, 9(3): 26-35 (in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYDZ603.003.htm
姜岩. 2016. 辽东地区主干断裂的特征及三维地质模型[D]. 长春: 吉林大学: 5-10. Jiang Y. 2016. Geological Features of Main Faults and Three-Dimensional[D]. Changchun: Jilin University: 5-10 (in Chinese).
孔繁强, 林玉祥. 1991.辽宁地区垂直形变场特征再研究[J].东北地震研究, 7(1): 21-27. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DDYJ198601012.htm Kong F Q, Lin Y X. 1991. The further research on characteristics of the vertical deformation field in Liaoning area[J]. Northeastern Seismological Research, 7(1): 21-27 (in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DDYJ198601012.htm
赖锡安, 黄立人, 徐菊生. 2004.中国大陆现今地壳运动[M].北京:地震出版社: 4-15. Lai X A, Huang L R, Xu J S. 2004. Characteristics of Recent Crustal Movement of China Mainland[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press: 4-15 (in Chinese).
马文涛, 徐锡伟, 于贵华, 张兰凤. 2004.首都圈地区的地震活动性与断裂的关系[J].地震地质, 26(2): 293-304. http://www.doc88.com/p-130472880571.html Ma W T, Xu X W, Yu G H, Zhang L F. 2004. The relationship between seismic activity and fault activity in Beijing region[J]. Seismology and Geology, 26(2): 293-304 (in Chinese). http://www.doc88.com/p-130472880571.html
王若柏, 洪汉净, 许忠淮, 耿世昌, 孙东平, 韩月萍. 1995.华北地区地壳垂直形变场及动态演化特征[J].地震学报, 17(2): 148-155. http://www.dzxb.org/Magazine/Show?id=27760 Wang R B, Hong H J, Xu Z H, Geng S C, Sun D P, Han Y P. 1995. Field of vertical crustal deformation in North China and the feature of its dynamic evolution[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 8(2): 185-194. http://www.dzxb.org/Magazine/Show?id=27760
王若柏, 顾国华, 徐杰, 周伟. 2004.张家口—渤海地震构造带的地壳形变研究[J].地震地质, 26(4): 587-593. http://www.doc88.com/p-909961850761.html Wang R B, Guo G H, Xu J, Zhou W. 2004. Discussion on characteristics of crustal deformation along the Zhangjiakou-Bohai seismotectonic zone[J]. Seismology and Geology, 26(4): 587-593 (in Chinese). http://www.doc88.com/p-909961850761.html
吴波. 2015. 环渤海地区地壳形变特征研究[D]. 北京: 中国测绘科学研究院: 9-15. Wu B. 2016. Research on the Characteristics of Crustal Deformation in Bohai Rim Region[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Surveying and Mapping: 9-15 (in Chinese).
徐东卓, 焦守涛, 朱传宝, 孙非非, 管见, 尹海权. 2017.芦山MS7.0地震前龙门山断裂带西南段区域形变特征分析及发震模型探讨[J].地质学报, 91(10): 2175-2184. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.10.002 Xu D Z, Jiao S T, Zhu C B, Sun F F, Guan J, Yin H Q. 2017. Regional deformation characteristics in the southwest segment of Longmen mountain fault zone before Lushan MS7.0 earthquake and possibly induced earthquake model[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 91(10): 2175-2184 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.10.002
应绍奋, 张祖胜, 耿士昌, 陈德民, 王泽文, 何肇雄, 夏淑辉, 王纪尧. 1988.中国大陆垂直向现代运动基本特征[J].中国地震, 4(4): 1-8. Ying S F, Zhang Z S, Geng S C, Chen D M, Wang Z W, He Z X, Xia S H, Wang J Y. 1988. Basic characteristics of recent vertical crustal movement of China Mainland[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 4(4): 1-8 (in Chinese).
Xu D Z, Zhu C B, Meng X G, Li Y, Sun Q K, Zhang K. 2016. Analysis of fault activity characteristics in the northern margin of Tibetan Plateau before Qinghai Menyuan MS6.4 earthquake[J].Geodesy and Geodynamics, 7(4): 261-267. doi: 10.1016/j.geog.2016.07.001
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 王喜龙,罗银花,金秀英,杨梦尧,孔祥瑞. 辽南地区断裂带的断层土壤气地球化学特征及其对区域应力调整的指示. 地震地质. 2023(03): 710-734 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张占阳,杨国华,孙启凯,张俊青,何亚东. 一种基于变差系数与滑动时间窗的定量分析方法. 测绘与空间地理信息. 2021(07): 64-68+72 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王喜龙,贾晓东,杨梦尧. 辽宁金州断裂断层土壤气地球化学调查. 中国地震. 2021(04): 767-779 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 戴盈磊,万永革,梁永朵,张文静,惠杨. 基于震源机制解资料的辽宁地区现今构造应力场. 地震. 2020(03): 112-130 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 徐东卓,朱传宝,孟宪纲,尹海权,孙非非. 山西中北部地区地壳垂直形变时空演化特征及与强震的关系. 地震研究. 2018(03): 446-450+490 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: