Attenuation relationship of Arias intensity
-
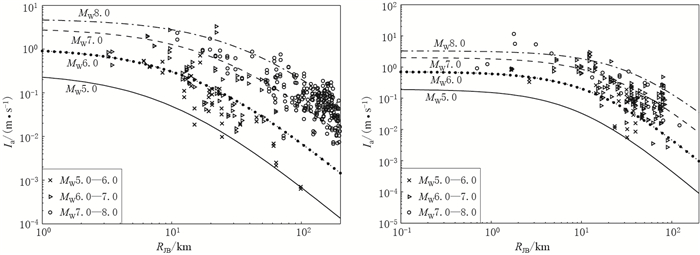
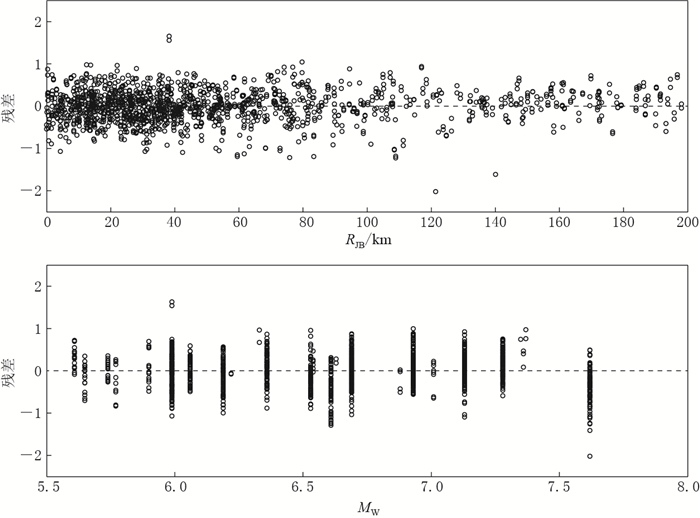
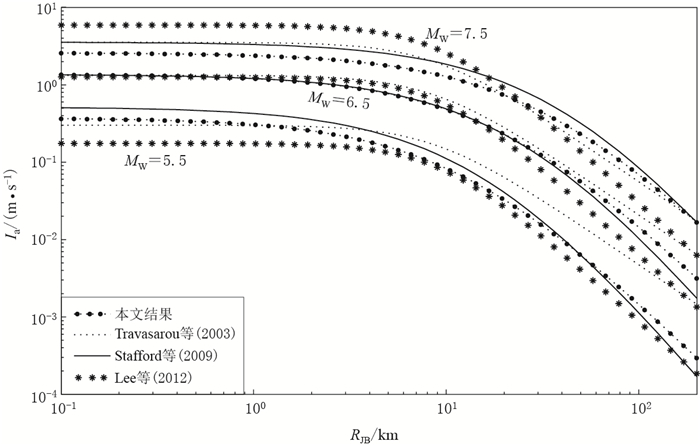
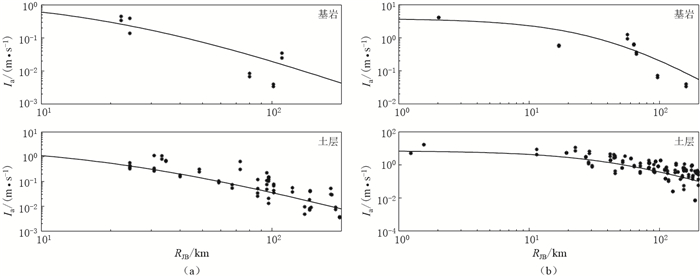
摘要: 本文选取美国NGA强震数据库中与我国大陆构造环境相近的美国西部、中亚和我国台湾地区的自由地表强震记录,计算其水平向阿里亚斯强度;采用分步回归法依次求取近场饱和项、距离衰减项、震级项、断层类型项和场地类别项的系数,得出衰减模型,并基于回归结果与实际数据的对比,分析了残差随距离或震级的分布.与前人工作得出的全球活动板块边界、新西兰和我国台湾地区的3种阿里亚斯强度衰减模型进行的比较显示,在MW6.5或远场区域4种模型的结果较接近,近场区域在高震级和低震级时有一定差异.最后,选取2008年汶川MW7.9和2013年芦山MW6.8两次地震的强震记录对模型进行检验,结果显示本文衰减关系均与实际数据拟合得很好,表明本文的模型适用于我国大陆地区的相关研究.Abstract: In this paper, the strong ground motion data recorded in earthquakes of western America, central Asia, and Taiwan area are selected from the Next Generation Attenuation strong motion database to develop the attenuation relationship of Arias intensity. A step-regression method is applied to obtain the coefficients of near-field saturation, distance, magnitude, fault type and site classification in the attenuation model. The distribution of residuals with distance and magnitude is analyzed by comparing the regression results with the actual data. The comparison of this attenuation model with those from previous studies shows that all these models are similar for MW6.5 or in the far field, but have some differences in the near field when the magnitude is higher or lower. Finally, the strong motion data of Wenchuan earthquake and Lushan earthquake are taken to verify the model, and the result show the attenuation relationship fits the data very well, suggesting that the obtained model in this paper be suitable for Chinese mainland.
-
审稿专家对本文提出了修改建议,国家强震动台网中心和美国NGA项目为本文提供了强震动数据,作者在此一并表示感谢.
-
表 1 本文场地分类标准
Table 1 Site classification standards in this study
场地类别 vS30/(m·s-1) 代码 基岩 >500 A 硬土 250-500 B 软土 <250 C 表 2 本文所用地震目录
Table 2 Catalog of earthquakes used in this study
序号 地震 发震时间 MW 记录条数 1 Kern County 1952-07-21 7.4 4 2 Parkfield 1966-06-28 6.2 10 3 Borrego Mountain 1968-04-09 6.6 2 4 San Fernando 1971-02-09 6.6 56 5 Tabas 1978-09-16 7.4 2 6 Coyote Lake 1979-08-06 5.7 18 7 Imperial Valley-06 1979-10-15 6.5 60 8 Victoria 1980-06-09 6.3 2 9 Westmorland 1981-04-26 5.9 12 10 Coalinga-01 1983-05-02 6.4 90 11 Borah Peak-01 1983-10-28 6.9 4 12 Morgan Hill 1984-04-24 6.2 46 13 North Palm Springs 1986-07-08 6.1 52 14 Chalfant Valley-01 1986-07-20 5.8 10 15 Chalfant Valley-02 1986-70-21 6.2 20 16 Whittier Narrows-01 1987-10-01 6.0 208 17 Superstition Hills-01 1987-11-24 6.2 2 18 Superstition Hills-02 1987-11-24 6.5 6 19 Loma Prieta 1989-10-18 6.9 146 20 Cape Mendocino 1992-04-25 7.0 8 21 Landers 1992-06-28 7.3 136 22 Northridge-01 1994-01-17 6.7 282 23 Double Springs 1994-09-12 5.9 2 24 Chi-Chi 1999-09-20 7.6 100 25 Manji-01 1990-06-20 7.4 2 26 Sierra Madre 1991-06-28 5.6 16 27 Little Skull Mountain 1992-06-29 5.7 16 28 Hector Mine 1999-10-16 7.1 158 表 3 阿里亚斯强度衰减关系系数
Table 3 Coefficients of attenuation relations of Arias intensity
震级 a b c d e m n f MW≤6.5 -3.407 1.065 2.494 0.956 0.462 -0.262 0.099 0.089 MW> 6.5 -1.073 0.715 2.494 0.956 0.462 -0.262 0.099 0.089 -
靳超宇, 俞言祥. 2009.欧洲中小震基岩水平向地震动衰减关系研究[J].中国地震, 25(2): 170-177. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y1778402 Jin C Y, Yu Y X. 2009. Attenuation relationships for horizontal ground motion on rock of small-moderate earthquakes in Europe[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 25(2): 170-177 (in Chinese). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZGZD200902008.htm
王秀英, 聂高众, 张玲. 2010.汶川地震触发崩滑与Arias强度关系研究[J].应用基础与工程科学学报, 18(4): 645-656. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/84465X/201004/35299625.html Wang X Y, Nie G Z, Zhang L. 2010. Relationship between landslides induced by the Wenchuan earthquake and Arias intensity[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 18(4): 645-656 (in Chinese). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-YJGX201004014.htm
肖亮, 俞言祥. 2010.一种新的拟合地震动衰减关系的分布回归法[J].地震学报, 32(6): 725-732. http://www.dzxb.org/Magazine/Show?id=27334 Xiao L, Yu Y X. 2010. A new step-regression approach for fitting ground motion data with attenuation relation[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 32(6): 725-732 (in Chinese). http://www.dzxb.org/Magazine/Show?id=27334
Abdrakhmatov K, Havenith H B, Delvaux D, Jongmans D, Trefois P. 2003. Probabilistic PGA and Arias intensity maps of Kyrgyzstan (Central Asia)[J]. J Seismol, 7(2): 203-220. doi: 10.1023/A:1023559932255
Akkar S, Bommer J J. 2007. Prediction of elastic displacement response spectra in Europe and the Middle East[J]. Earthq Eng Struct Dyn, 36(10): 1275-1301. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1096-9845
Ancheta T D, Darragh R B, Stewart J P, Seyhan E, Silva W J, Chiou B S J, Wooddell K E, Graves R W, Kottke A R, Boore D M, Kishida T, Donahue J L. 2014. NGA-west2 database[J]. Earthq Spectra, 30(3): 989-1005. doi: 10.1193/070913EQS197M
Arias A. 1970. A measure of earthquake intensity[G]//Seismic Design for Nuclear Power Plants. Cambridge: MIT Press: 438-483.
Boore D M, Atkinson G M. 2012. Ground-motion prediction equations for the average horizontal component of PGA, PGV, and 5%-damped PSA at spectral periods between 0.01 s and 10.0 s[J]. Earthq Spectra, 24(1): 99-138. doi: 10.1193/1.2830434
Cabanas L, Benito B, Herráiz M. 1997. An approach to the measurement of the potential structural damage of earthquake ground motions[J]. Earthq Eng Struct Dyn, 26(1): 79-92. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1096-9845
Campbell K W. 1981. Near-source attenuation of peak horizontal acceleration[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 71(6): 2039-2070. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/274955931_%27Near-Source_Attenuation_of_peak_horizontal_acceleration%27
Chen S Z, Atkinson G M. 2002. Global comparisons of earthquake source spectra[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 92(3): 885-895. doi: 10.1785/0120010152
Chiou B, Darragh R, Gregor N, Silva W. 2008. NGA project: Strong-motion database[J]. Earthq Spectra, 24(1): 23-44. doi: 10.1193/1.2894831
Douglas J. 2004. An investigation of analysis of variance as a tool for exploring regional differences in strong ground motions[J]. J Seismol, 8(4): 485-496. doi: 10.1007/s10950-004-3094-7
Jibson R W. 1993. Predicting earthquake-induced landslide displacements using Newmark's sliding block analysis[J]. Ransport Res Record, 1411: 9-17. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.733.2736
Lee C T, Hsieh B S, Sung C H, Lin P S. 2012. Regional Arias intensity attenuation relationship for Taiwan considering VS30[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 102(1): 129-142. doi: 10.1785/0120100268
Stafford P J, Berrill J B, Pettinga J R. 2009. New predictive equations for Arias intensity from crustal earthquakes in New Zealand[J]. J Seismol, 13(1): 31-52. doi: 10.1007/s10950-008-9114-2
Travasarou T, Bray J D, Abrahamson N A. 2003. Empirical attenuation relationship for Arias intensity[J]. Earthq EngStruct Dyn, 32(7): 1133-1155. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1096-9845




 下载:
下载: