Study on attenuation characteristics of seismic waves from small-moderate earthquakes in “Huoshan seismic window”, Anhui Province
-
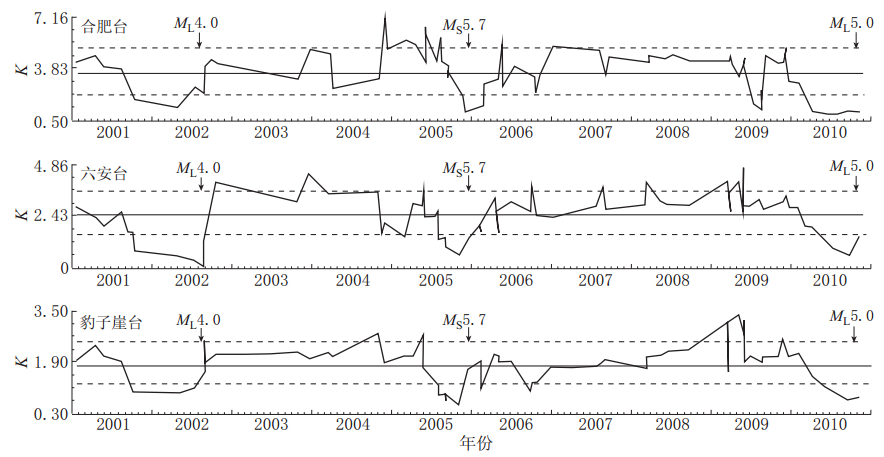
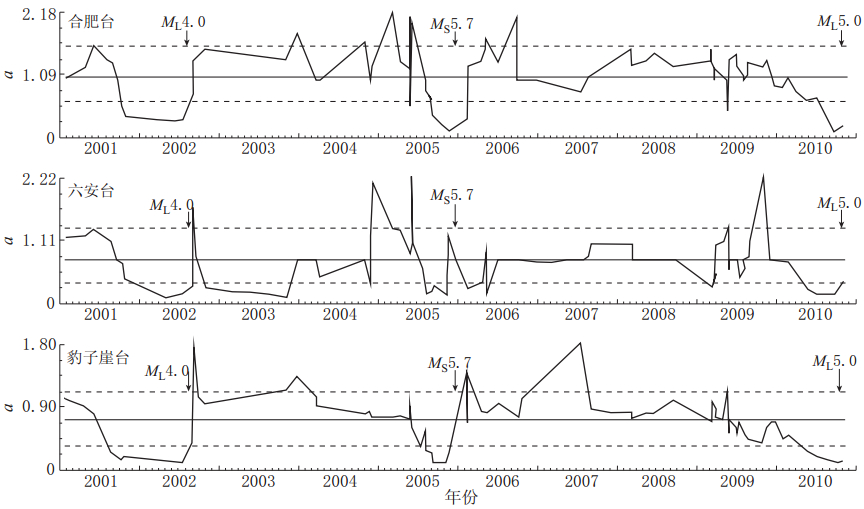
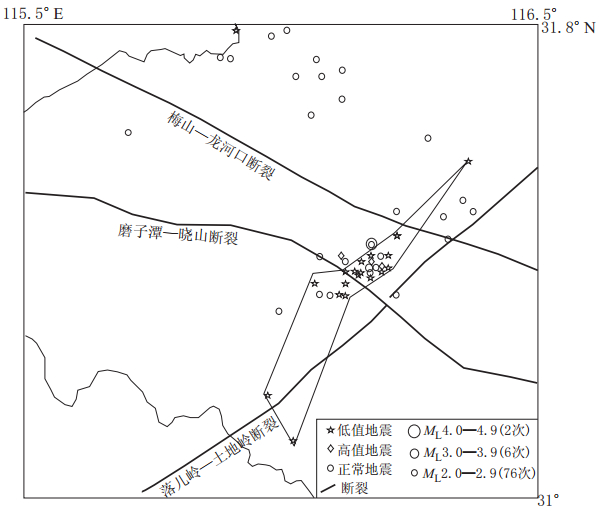
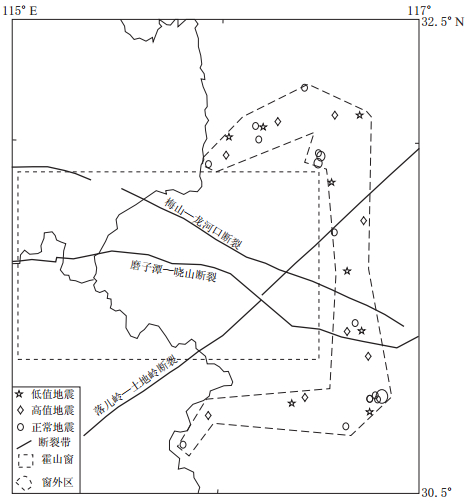
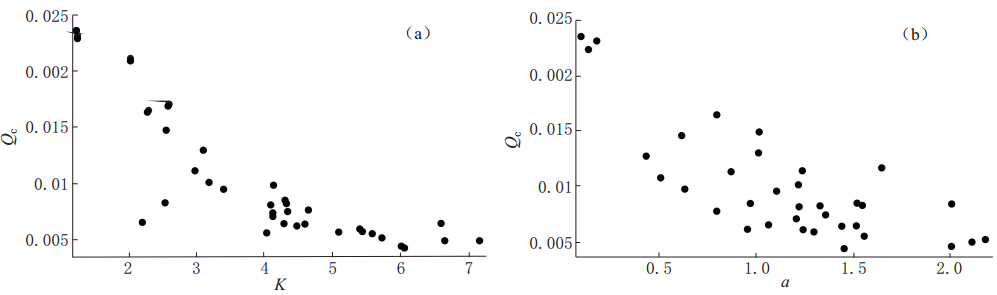
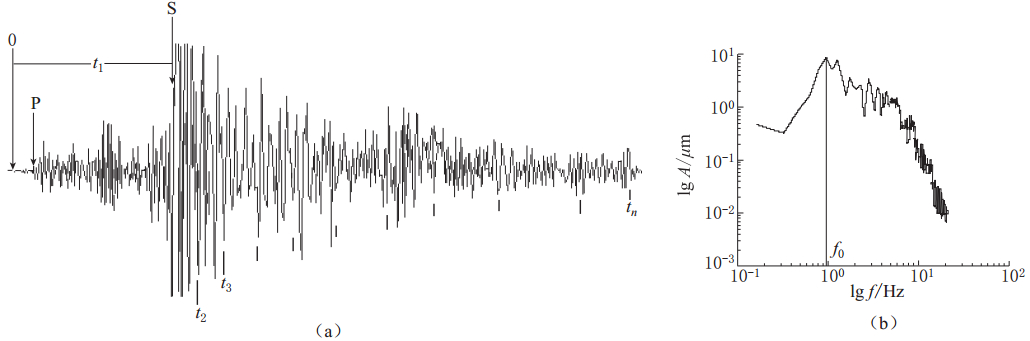
摘要: 利用安徽合肥台、 六安台和豹子崖台记录到的2001—2010年安徽“霍山窗”发生的ML≥2.0地震的波形资料, 计算了其振幅衰减系数K值和卓越频率衰减系数a值, 分析研究了K值和a值的时空变化特征, 并讨论了其与华东地区中强地震的对应关系及与Qc值的相关性. 结果表明, 3个台站均记录到了明显的变化特征: ① “霍山窗”ML4.0地震、 江西九江MS5.7地震及河南太康ML5.0地震前6个月左右时间内, K值和a值均呈现持续下降的异常低值状态, 平均下降幅度K值为20%—35%, a值为45%—51%, 并于上升的过程中发震, 震后趋于正常; ② K值的平面分布特征显示, K值异常地震主要位于断裂带交汇区附近, 并沿断裂带方向分布; ③ K值、 a值与Qc值基本呈负相关. 上述特征为进一步了解该区域的地壳介质状态和研究中强震前后Qc的变化特征提供了一定的依据. 该研究结果可能对中长期地震预报和震后趋势判断有一定的指示意义.Abstract: Based on the waveform data from ML≥2.0 earthquakes during 2001—2010 in Anhui “Huoshan seismic window” recorded by Hefei, Lu’an and Baoziya stations of Anhui Digital Seismic Network, the amplitude attenuation coefficient K and the predominant frequency attenuation coefficient a were calculated, their temporal and spatial variations were analyzed, and the possible relationship of the variations with moderate-strong earthquake occurrence in eastern China and coda Qc were discussed. The results indicate the following variation characteristics: ① In about six months before the ML4.0 earthquake in “Huoshan seismic window”, the MS5.7 Jiangxi Jiujiang earthquake and the ML5.0 Henan Taikang earthquake, K value and a value decreased continuously to an abnormally low state; the average rates of decrease for K and a are 20%—35% and 45%—51%, respectively; the earthquakes occurred during the rising process of K and a values. ② By inspecting the plane view of K variation, we found that earthquakes with abnormal K value are mainly located at or near the fault intersections and distributed along fault zones. ③ K and a values basically showed negative correlation with coda Qc value, providing certain basis for further studying Qc variation before and after moderate-strong earthquakes.
-
-
-
蔡静观, 许昭永, 李茜. 1985. 禄劝地震前后地震波的振幅衰减特征[J]. 地震研究, 8(增刊): 45-50. 陈宇卫, 张军, 庆梅, 王行舟, 章兵. 2007."霍山地震窗"小震序列运动学参数时变特征研究[J]. 地震, 27(1): 26-32. 李琼, 秦嘉政, 钱晓东. 2007. 2007年宁洱6.4级地震余震序列尾波Qc值研究[J]. 地震研究, 30(4): 337-343. 李琼, 钱晓东, 秦嘉政. 2008. 2005年云南文山地震余震序列尾波Qc值研究[J]. 地震研究, 29(3): 22-28. 秦嘉政, 钱晓东. 2002. 1993年中甸M5.8地震前后区域尾波衰减研究[J]. 地震研究, 25(3): 214-219. 宋永能. 1990. 霍山震群的时空分布特征及诱发因素探讨[J]. 西北地震学报, 12(3): 86. 许昭永, 蔡静观, 李茜. 1986. 地震前后地震波卓越频率的变化及多点滑移拟合法的应用[J]. 中国地震, 3(2): 69-74. 张帆, 姚立珣, 张震峰. 2005. 震后趋势判断中尾波振幅衰减特征K值的研究[J]. 地震地磁观测与研究, 26(4): 36-44. 郑兆苾, 庆梅, 李敏莉. 1999. 霍山窗与华东中强震关系研究[J]. 地震学刊, 19(2): 1-9. 郑先进, 刘东旺, 刘泽民, 沈小七. 2010. 安徽地区应力场分区特征及中强震前震源机制的一致性研究[J]. 华北地震科学, 28(1): 16-20. 朱新运, 刘杰, 张帆. 2006. 基于Aki模型的近震S波尾波Q值求解及分析软件研制[J]. 地震研究, 29(1): 76-80. Aki K, Chouet B. 1975. Origin of coda waves: Source, attenuation and scattering effects[J]. J Geophy Res, 80(85): 3322-3342.
Aki K. 1980. Attenuation of shear-waves in the lithosphere for frequencies from 0.05 to 25 Hz[J]. Phys Earth Plant Inter, 21(1): 50-60.
Herrmann R B. 1980. Q estimates using the coda of local earthquake[J]. Bull Seism Soc Amer, 70(2): 447-468.




 下载:
下载: