Numerical simulation on strong earthquake dynamic process of Bayan Har block
-
摘要: 以青藏高原为目标采用弹性体本构关系, 模拟印度板块持续向北推进、 挤压对巴颜喀拉块体及邻区的影响. 通过降低强震发生位置处单元弹性模量的方法, 模拟1900年以来发生在巴颜喀拉块体及周缘MS≥7.0强震, 计算序列中前面地震对后续强震的影响. 模拟结果表明: ① 巴颜喀拉块体背景场应力水平大致与块体西部等效应力同等大小, 自西向东逐渐递减, 巴颜喀拉块体西部和中部等效应力从南向北逐渐递减, 东部地区等效应力比较低; ② 模拟的14次地震序列中, 有8次发生在前面强震所引起的等效应力增大的区域内, 2次发生在等效应力增大和减小的过渡区域内, 3次发生在等效应力减小的区域内; ③ 从强震序列所引起的应力相互作用看, 历史地震对1970年以来发生的地震影响结果为: 历史地震加速了1973年亦基台错、 1997年玛尼和2001年昆仑山口西地震的发生, 昆仑山口西地震对汶川地震的影响较小, 汶川地震对玉树地震的发生不具有加速触发作用.Abstract: In this paper, we used the elastic constitutive relation to simulate the effect induced from the Indian plate everlasting northward collision on the Bayan Har block and surroundings on the Qinghai--Tibet plateau. By reducing the element elastic modulus at the earthquake location, a number of numerical simulations have been made for the strong earthquakes (MS≥7.0) since 1900, and also for the influence from the former earthquake on the latter. We obtained the following results: ① The background stress is higher in the west as expressed in equivalent stress, and decreases gradually to the east; in the middle-west of the block the stress level decreases gradually from south to north with equivalent stress obviously low in the east. ② In the strong earthquake series eight earthquakes were triggered before their occurrence and three were delayed, while other two were in the sress transition zone. ③ From the stress interaction between the strong earthquakes before and after 1970, we may conclud that the historic earthquakes triggered the 1973 Yijitaicuo earthquake, the 1997 Mani earthquake and the 2001 Kunlun Mountain Pass earthquake, while the influence of Kunlun Mountain Pass quake on the Wenchuan quake is insignificant, and the effect of Wenchuan quake on the Yushu earthquake is unobvious.
-
Keywords:
- Qinghai--Tibet plateau /
- Bayan Har block /
- shell element model /
- numerical simulation
-
-
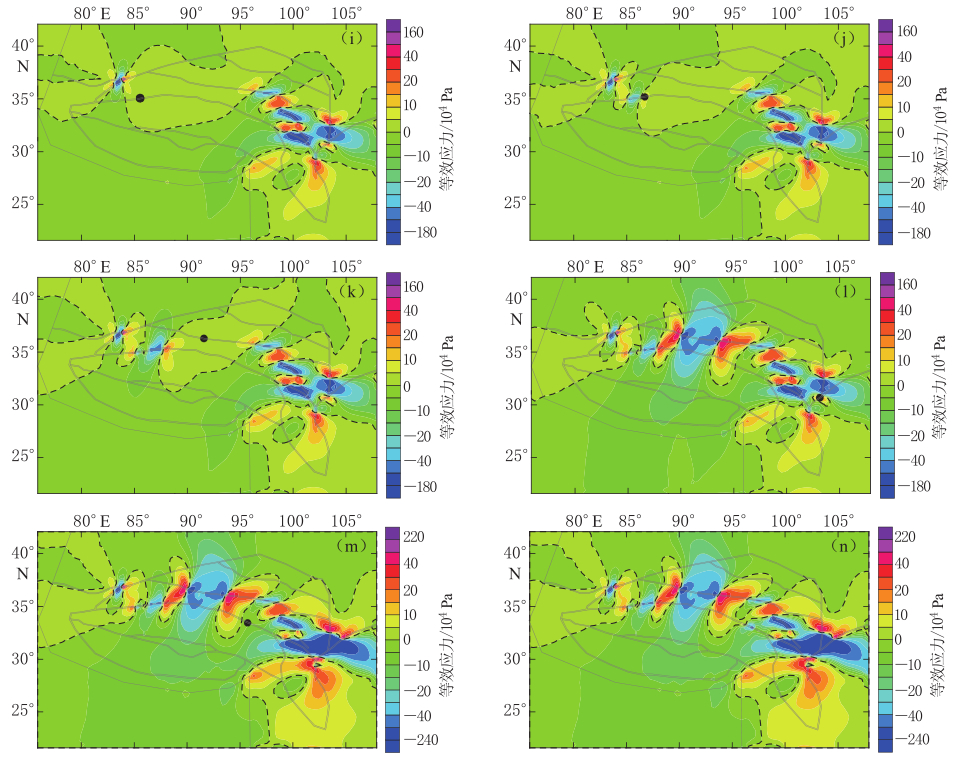
图 4 (a)-(h) 地震引起的等效应力变化图
(a)模拟第1次地震(道孚MS7.0);(b)模拟第2次地震(炉霍MS7.3);(c)模拟第3次地震(民丰MS7.3);(d)模拟第4次地震(叠溪MS7.5);(e)模拟第5次地震(阿兰湖MS7.5);(f)模拟第6次地震(达日MS7.7);(g)模拟第7次地震(康定MS7.5);(h)模拟第8次地震(阿兰湖MS7.0).图中虚线为0Pa线,图中黑色圆点表示下一次地震发生的位置
Figure 4. (a)-(h) Equivalent stress variation caused by earthquakes
(a)The first simulated earthquake(Daofu MS7 .0); (b)The second simulated earthquake (Luhuo MS7 .3);(c)T he third sim ulated earthquake (Minfeng MS7 .3); (d)T he fourth sim ulated earthquake (DiexiMS7 .5); (e)T he fifth sim ulated earthquake (Alan Lake MS7 .5); (f)T he sixth sim ulated earthquake(Dari MS7 .7); (g)T he seventh sim ulated earthquake (Kangding MS7 .5); (h)T he eighth sim ulatedearthquake(Alan Lake MS7 .0). Dashed lines for 0 Pa and black point stand for the location of nextearthquake in the figure
图 4 (i)-(n) 地震引起的等效应力变化图
(i)模拟第9次地震(炉霍MS7.6);(j)模拟第10次地震(亦基台错MS7.3);(k)模拟第11次地震(玛尼MS7.5);(l)模拟第12次地震(昆仑山口西MS8.1);(m)模拟第13次地震(汶川MS8.0);(n)模拟第14次地震(玉树MS7.1).图中虚线为0Pa线,黑色圆点表示下一次地震发生的位置
Figure 4. (i)-(n) Equivalent stress variation caused by earthquakes
(i)T he ninth sim ulated earthquake (Luhuo MS7 .6); (j)T he tenth sim ulated earthquake (Yijitaicuo MS7 .3);(k)T he eleventh sim ulated earthquake (M ani MS7 .5); (l) T he T welfth sim ulated earthquake (K nlunM ountains Pass MS8 .1); (m)T he thirteenth im ulated earthquake (W enchuan MS8 .0); (n)T he fourteenthsim ulated earthquake (Y ushu MS7 .1). Dashed lines for 0 Pa and black point stand for the location of nextearthquake in the figure
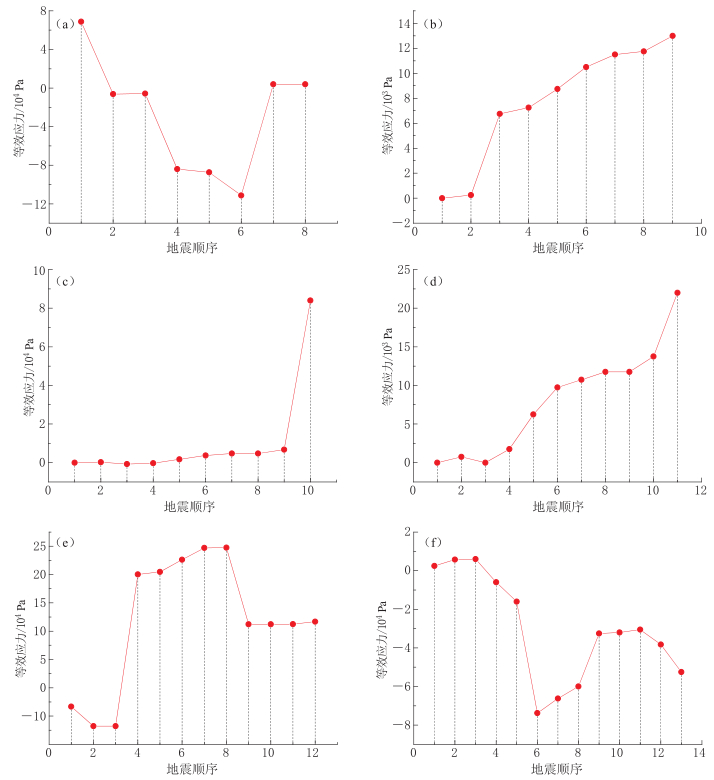
图 5 历史地震(地震顺序见表2)对1970年以来地震的影响
(a) 1973年炉霍地震前震源处应力变化曲线; (b) 1973年亦基台错地震前震源处应力变化曲线;(c) 1997年玛尼地震前震源处应力变化曲线; (d) 2001年昆仑山口西地震前震源处应力变化曲线;(e) 2008年汶川地震前震源处应力变化曲线; (f) 2010年玉树地震前震源处应力变化曲线
Figure 5. Influence of previous earthquakes on the earthquakes since 1970
(a) Stress change in the source region before 1973 Luhuo earthquake; (b) Stress change before 1973 Yijitaicuo earthquake; (c) Stress change before 1997 Mani earthquake; (d) Stress change before 2001 Kunlun Mountain Pass earthquake; (e) Stress change before 2008 Wenchuan earthquake; (f) Stress change before 2010 Yushu earthquake
表 1 青藏高原及邻区地壳介质物性参数
Table 1 Crustal physical properties in Qinghai Xizang plateau and surroundings

表 2 1900年以来巴颜喀拉块体内及周缘发生的MS≥7.0地震目录
Table 2 Earthquake catalogue(MS≥ 7.0)in the Bayan Har block and surroundings since 1900

-
陈兵, 江在森, 车时, 王庆良, 朱桂枝, 王继英. 2003. 玛尼7.9级地震对昆仑山口西8.1级地震的触发作用及动力背景初探[J]. 中国地震, 19(1): 1-7. 陈连旺, 詹自敏, 叶际阳, 李妍. 2010. 流变特性对青藏高原构造变形影响的数值模拟[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 31(3): 8-14. 陈宇坤, 陈杰. 2004. 2001年昆仑山口西MS8.1地震最大位移讨论[J]. 中国地震, 20(4): 380-387. 陈运泰. 2008. 汶川特大地震的震级和断层长度[J]. 科技导报, 26(10): 26-27. 程佳, 刘杰, 甘卫军, 余怀忠. 2011. 1997年以来巴颜喀拉块体周缘强震之间的黏弹性触发研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(8): 1997-2010. 戴黎明, 李三忠, 陶春辉, 李西双, 刘鑫, 索艳慧, 周淑惠, 周永刚, 高武斌. 2011. 印度板块挤压驱动龙门山断裂带活动的三维数值模型[J]. 地球物理学进展, 26(1): 41-51. 邓起东, 高翔, 陈桂华, 杨虎. 2010. 青藏高原昆仑-汶川地震系列与巴颜喀喇断块的最新活动[J]. 地学前缘, 17(5): 163-178. 邓起东, 于贵华, 叶文华. 1992. 地震地表破裂参数与震级关系的研究[M]//国家地震局地质研究所. 活动断裂研究(2). 北京: 地震出版社: 247-264. 李永华, 吴庆举, 安张辉, 田小波, 曾融生, 张瑞青, 李红光. 2006. 青藏高原东北缘地壳S波速度结构与泊松比及其意义[J]. 地球物理学报, 49(5): 1359-1368. 李永华, 吴庆举, 田小华, 张瑞青, 潘佳铁, 曾融生. 2009. 用接收函数方法研究云南及其邻区地壳上地幔结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 52(1): 67-80. 刘宝峰, 李松林, 张先康, 张成科, 赵金仁, 任青芳, 海燕. 2003. 玛沁-靖边剖面S波资料研究与探讨[J]. 地震学报, 25(1): 82-88. 苏伟, 彭艳菊, 郑月军, 黄忠贤. 2002. 青藏高原及其邻区地壳上地幔S波速度结构[J]. 地球学报, 23(3): 193-200. 王椿镛, 楼海, 吕智勇, 吴建平, 常利军, 戴仕贵, 尤惠川, 唐方头. 2008. 青藏高原东部地壳上地幔S波速度结构-下地壳流的深部环境[J]. 中国科学: D辑, 38(1): 22-32. 王连捷, 崔军文, 王薇, 乔子江, 孙东生, 赵卫华. 2010. 青海玉树MS7.1地震发震过程的数值模拟[J]. 地质力学学报, 16(2): 137-145. 王连捷, 崔军文, 周春景, 孙东生, 王薇, 唐哲民, 钱华山. 2009. 汶川5·12地震发震机理的数值模拟[J]. 地质力学学报, 15(2): 105-113. 闻学泽, 杜方, 张培震, 龙锋. 2011. 巴颜喀拉块体北和东边界大地震序列的关联性与2008年汶川地震[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(3): 706-716. 吴庆举, 曾融生. 1998. 用宽频带远震接收函数研究青藏高原的地壳结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 41(5): 669-679. 胥颐, 黄润秋, 李志伟, 徐亚, 刘劲松, 刘建华. 2009. 龙门山构造带及汶川震源区的S波速度结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 52(2): 329-338. 杨立明. 2009. 汶川地震发生的动力学过程及中强地震大尺度有序图像演化研究[J]. 国际地震动态, (4): 14-15. 杨树新, 陆远忠, 陈连旺, 叶际阳, 米琦. 2012. 用单元降刚法探索中国大陆强震远距离跳迁及主体活动区域转移[J]. 地球物理学报, 55(1): 105-116. 张东宁, 许忠淮. 1999. 中国大陆岩石层动力学数值模型的边界条件[J]. 地震学报, 21(2): 133-139. 张东宁, 高龙生. 1989. 东亚地区应力场的三维数值模拟[J]. 中国地震, 5(4): 24-33. 张桂芳, 屈春燕, 单新建, 刘云华, 宋小刚. 2011. 2010年青海玉树MS7.1级地震地表破裂带和形变特征分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(1): 121-127. 张培震, 王琪, 马宗晋. 2002. 中国大陆现今构造运动的GPS速度场与活动地块[J]. 地学前缘, 9(2): 430-441. 张培震, 邓起东, 张国民, 马瑾, 甘卫军, 闵伟, 毛凤英, 王琪. 2003a. 中国大陆的强震活动与活动块体[J]. 中国科学: D辑, 33(增刊): 12-20. 张培震, 王敏, 甘卫军, 邓起东. 2003b. GPS观测的活动断裂滑动速率及其对现今大陆动力作用的制约[J]. 地学前缘, 10(特刊): 81-92. 张晓亮, 江在森, 张希, 赵永年, 朱桂芝. 2007. 昆仑山口西MS8.1地震同震形变场的模拟分析[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 27(2): 16-21. 张中杰, 滕吉文, 李英康, Klemperer S, 杨立强. 2002. 藏南地壳速度结构与地壳物质东西向"逃逸": 以佩枯错-普莫雍错宽角反射剖面为例[J]. 中国科学: D辑, 32(10): 793-798. 郑勇, 傅容珊, 熊熊. 2006. 中国大陆及周边地区现代岩石圈演化动力学模型[J]. 地球物理学报, 49(2): 415-427. 周仕勇. 2008. 川西及邻近地区地震活动性模拟和断层间相互作用研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 51(1): 166-174. Banerjee P, Bürgmann R. 2002. Convergence across the northwest Himalaya from GPS measurement[J]. Geophys Res Lett, 29(13): 30-1-30-4.
Lu Y Z, Yang S X, Chen L W, Lei J S. 2011. Mechanism of the spatial distribution and migration of the strong earthquakes in China inferred from numerical simulation[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 40(4): 990-1001.
Paul J, Gaur V K, Bilham R, Larson K M, Ananda M B, Jade S, Mukal M, Anupama T S, Satyal G, Kumar D, Burgmann R. 2001. The motion and active deformation of India[J]. Geophys Res Lett, 28(4): 647-650.
Stein R S. 2003. Earthquake Conversations[J]. Scientific American, 288(1): 72-79.
-
期刊类型引用(17)
1. 刘博研,解孟雨,史保平. 青海玛多M_S7.4地震对周边活动断裂的库仑应力加载及发震概率增量的计算. 地球物理学报. 2022(02): 563-579 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 吴立新,卢菁琛,毛文飞,胡俊,周子龙,李志伟,齐源,姚汝冰. 基于断层倾角分段变化的玛多地震发震断层构造应力场演化数值模拟分析. 地球物理学报. 2022(10): 3844-3857 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 侯强,丁小军,赵宏,欧明霖,张博康. 青藏高原东南缘构造应力场重构. 大地测量与地球动力学. 2019(05): 458-463 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李江海,宋珏琛,毛翔. 二叠纪泛大陆球壳三维力学模拟及其构造意义. 地质论评. 2019(03): 551-557 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李平恩,廖力,奉建州,刘盼. 1900年以来巴颜喀拉块体应力演化与周缘强震关系的数值模拟研究. 地球物理学报. 2019(11): 4170-4188 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 廖力,李平恩,杨建思,刘盼,奉建州. 从应力演化角度讨论龙门山区域7级强震序列对芦山地震的影响. 地震地质. 2018(02): 450-464 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 石富强,朱琳,李玉江,丁晓光. 基于正交各向异性理论表征断层的变形行为. 地震研究. 2018(01): 64-72+157 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 侯强,邹文远,欧明霖,丁小军. 青藏高原东南缘壳幔力学耦合及其动力学意义. 大地测量与地球动力学. 2018(10): 991-1000 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 李术才,刘洪亮,李利平,石少帅,胡杰,孙尚渠. 隧道危石识别及防控研究现状与发展趋势. 中国公路学报. 2018(10): 1-18 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 武永彩,李昂,唐红涛. 滇西北地区近年来应力场的数值模拟研究. 大地测量与地球动力学. 2018(12): 1238-1240+1279 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 李平恩,廖力,刘盼. 太原盆地应力场演化与强震关系的数值模拟研究. 地球科学. 2017(09): 1623-1636 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 刘盼,马世虎,李平恩,韩晓飞. 龙门山地区历史强震数值模拟. 地震地磁观测与研究. 2017(06): 1-9 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 刘盼,李平恩,廖力. 从库仑破裂应力和余震分布角度探讨汶川地震和芦山地震的关系. 震灾防御技术. 2017(01): 40-55 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 廖思佩,侯强,杜永超. 基于GPS形变资料的川滇地区应力场数值模拟研究. 大地测量与地球动力学. 2016(07): 645-649 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 杨兴悦,曾文浩,王燕,李少华,孙召华. 甘东南及邻区7级以上强震数值模拟. 地球科学. 2016(07): 1238-1248 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 李惠娟,韩旭,吴欣,张妮华,申维娜. 巴颜喀拉山群重新划分. 现代矿业. 2016(09): 193-194+198 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 徐伟民,陈石,石磊. 新疆于田及周边地区地震活动性与重力异常特征. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报). 2014(12): 1831-1841 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(8)




 下载:
下载: