Recovery of co-seismic deformation from strong motion records during the Wenchuan earthquake
-
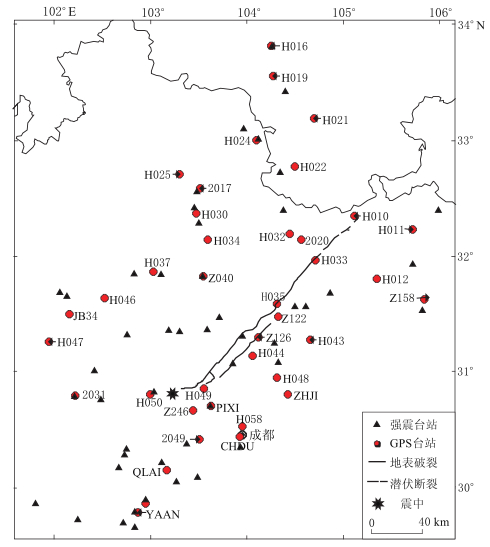
摘要: 利用汶川地震中得到的靠近映秀—北川主断裂的64个强震台站的三分量记录数据, 对加速度记录进行基线校正的基础上获取近断层地面运动的永久形变位移, 并将由强震记录获取到的地面位移结果与GPS观测到的同震位移进行对比分析, 研究汶川MS8.0地震的近断层地面运动的位移特征. 结果表明: ① 在靠近映秀—北川主断层的上盘和下盘, 东西相向的地面运动非常剧烈. 下盘的51SFB, 51MZQ和51JYH台东西向位移均为负(即地面运动向西), 其中51SFB台位移量最大, 达到1.49 m; 上盘的51WCW台位移向东, 位移量为1.26 m. ② 地面运动的位移分布主要表现为以龙门山断裂带的映秀—北川断裂为核心的相向运动, 东西方向上的永久位移要大于南北方向. 从断层机制上来讲, 断层的错动以逆冲运动为主(即逆冲位移要大于走滑分量的位移), 这与震源机制反演及地质考察的结果一致. ③ 大的地面永久位移集中分布在以龙门山断裂带为中心的狭长范围内, 离开发震断裂地面位移的衰减很快. 相比而言, 在发震断层的下盘一侧(即四川盆地)的地面位移的衰减比上盘一侧明显要快.Abstract: Records from 64 strong motion stations nearly along the Yingxiu--Beichuan fault in Wenchuan earthquake are used as database. Near fault permanent displacement were derived from acceleration records based on baseline correction, and were compared with GPS observation to investigate the ground motion displacement characteristics induced by Wenchuan MS8.0 earthquake. The following conclusions can be made from our study: ① The ground motion are significant as close to the Yingxiu--Beichuan fault both on the hanging wall and footwall. The permanent displacement from the 51SFB, 51MZQ and 51JYH record on the footwall is westward, with a largest displacement of 1.49 m from the 51SFB record, while the 51WCW record on the hanging wall is eastward with a displacement of 1.26 m. ② Distribution of permanent displacement shows that the movements of both hanging wall and footwall display a dominant direction toward the Yingxiu--Beichuan fault in the Longmen Shan zone, with east-west displacement being larger than north-south one. The fault mechanism is characterized mainly by a thrust motion, and the thrust motion component is much larger than the strike slip, being consistent with the results of seismic source inversion and field investigation. ③ The largest permanent displacements are limited in the narrow rupture zone along the Longmen Shan fault, and reduce rapidly away from the causative fault. It is noted that the permanent displacement in Sichuan basin on the footwall attenuates more rapidly with distance than that on the hanging wall.
-
Keywords:
- Wenchuan earthquake /
- ground motion /
- displacement /
- hanging wall /
- near fault
-
-
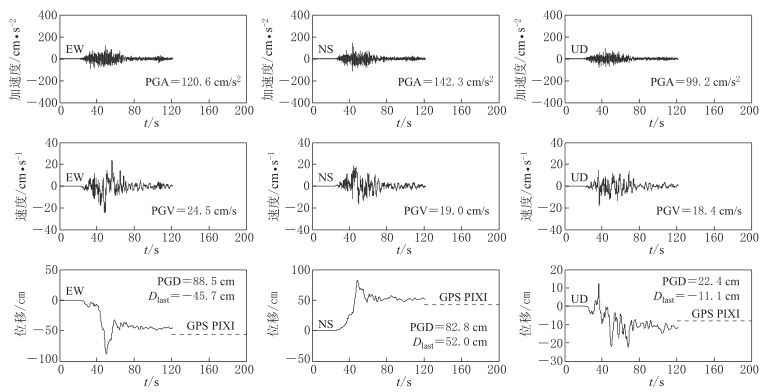
图 3 台站51PXZ记录校正后三分向的加速度、 速度和位移时程
图中Dlast为校正后获取到的永久位移; PGA,PGV,PGD分别为地面运动峰值加速度、 峰值速度和峰值位移
Figure 3. Three component acceleration,velocity and displacement time histories obtained from 51PXZ record after baseline correction
Dlast is the permanent displacement of strong ground motion; PGA,PGV and PGD are peak ground acceleration,velocity and displacement of strong motion data,respectively
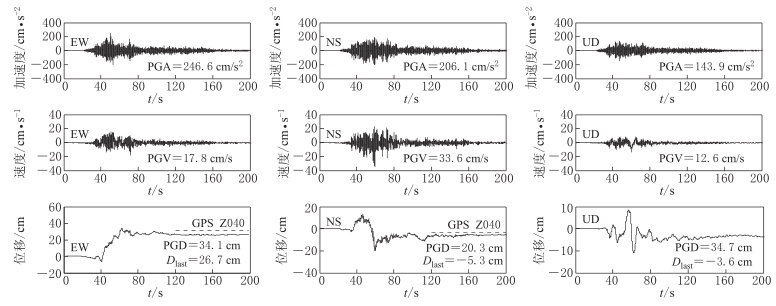
图 4 台站51MXD记录校正后三分向的加速度、 速度和位移时程
图中Dlast校正后获取到的永久位移; PGA,PGV,PGD分别为地面运动峰值加速度、 峰值速度和峰值位移
Figure 4. Three component acceleration,velocity and displacement time histories obtained from 51MXD record after baseline correction
Dlast is the permanent displacement of strong ground motion. PGA,PGV,PGD are peak ground acceleration,velocity and displacement of strong motion data,respectively
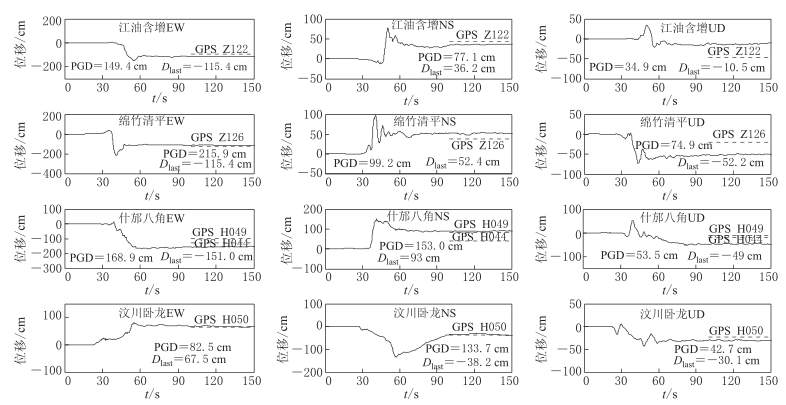
图 6 汶川卧龙(51WCW)、 什邡八角(51SFB)、 绵竹清平(51MZQ)、及江油含增(51JYH)台校正后的三分向的位移时程
图中Dlast为校正后获取到的永久位移,PGD为地面运动峰值位移
Figure 6. Three component displacement time histories obtained from 51WCW,51SFB,51MZQ and 51JYH record after baseline correction
Dlast is the permanent displacement of strong ground motion. PGD is peak ground displacement of strong motion data
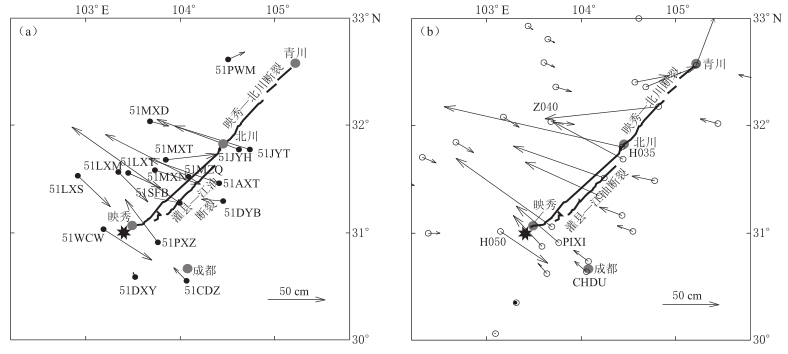
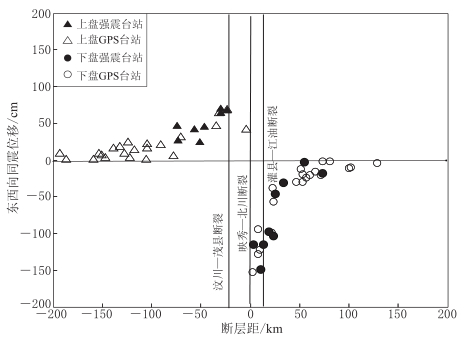
图 7 由强震记录获取到的汶川地震水平向永久位移(a)与GPS观测到的同震位移(b)的比较
实心圆表示强震台站,空心圆表示GPS观测台站
Figure 7. Comparison of obtained permanent horizontal displacement of Wenchuan earthquake from strong motion stations (a) with co-seismic displacement distribution observed by GPS stations (b)
Strong motion stations and GPS stations are shown as solid and open circles,respectively
-
陈桂华, 徐锡伟, 郑荣章, 于贵华, 李峰, 闻学泽, 何玉林, 叶友青, 陈献程, 王志才. 2008. 2008年汶川MS8.0地震地表破裂变形定量分析: 映秀-北川断裂地表破裂带[J]. 地震地质, 30(3): 723-738. 杜海林, 许力生, 陈运泰. 2009. 利用阿拉斯加台阵资料分析2008年汶川大地震的破裂过程[J]. 地球物理学报, 52(2): 372-378. 国家重大科学工程"中国地壳运动观测网络"项目组. 2008. GPS测定的2008年汶川MS8.0级地震的同震位移场[J]. 中国科学: D辑, 38(10): 1195-1206. 何宏林, 孙昭民, 王世元, 王纪强, 董绍鹏. 2008. 汶川MS8.0地震地表破裂带[J]. 地震地质, 30(3): 359-362. 彭小波, 李小军. 2012. 汶川地震强震动地面倾斜研究[J]. 地震学报, 34(1): 64-75. 王国权, 周锡元. 2004. 921台湾集集地震近断层强震记录的基线校正[J]. 地震地质, 26(1): 1-14. 王卫民, 赵连锋, 李娟, 姚振兴. 2008. 四川汶川8.0级地震震源过程[J]. 地球物理学报, 51(5): 1403-1410. 谢礼立, 周雍年, 胡成祥, 于海英. 1990. 地震动反应谱的长周期特性[J]. 地震工程与工程振动, 10(1): 1-19. 徐锡伟, 闻学泽, 叶建青, 马宝起, 陈杰, 周荣军, 何宏林. 2008. 汶川MS8.0地震地表破裂带及其发震构造[J]. 地震地质, 30(3): 597-629. 于海英, 王栋, 杨永强, 卢大伟, 解全才, 张明宇. 2008. 汶川8.0级地震强震动特征初步分析[J]. 震灾防御技术, 3(4): 321-336. 于海英, 江汶乡, 解全才, 杨永强, 程翔, 杨剑. 2009. 近场数字强震仪记录误差分析与零线校正方法[J]. 地震工程与工程振动, 29(6): 1-12. 张培震, 闻学泽, 徐锡伟, 甘卫军, 王敏, 沈正康, 王庆良, 黄媛, 郑勇, 李小军, 张竹琪, 马胜利, 冉勇康, 刘启元, 丁志峰, 吴建平. 2009. 2008年汶川8.0级特大地震孕育和发生的多单元组合模式[J]. 科学通报, 54(7): 944-953. 张勇, 冯万鹏, 许力生, 周成虎, 陈运泰. 2008. 2008年汶川大地震的时空破裂过程[J]. 中国科学: D辑, 37(10): 1186-1194. 赵翠萍, 陈章立, 周连庆, 李志雄, 康英. 2009. 汶川MW8.0级地震震源破裂过程研究: 分段特征[J]. 科学通报, 54(22): 3475-3482. 中国地震局震害防御司. 2008. 汶川8.0级地震未校正加速度记录[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 1-156. 周雍年, 章文波, 于海英. 1997. 数字强震仪记录的长周期误差分析[J]. 地震工程与工程振动, 17(2): 1-9. Chiu H C. 1997. Stable baseline correction of digital strongmotion data[J]. Bull Seism Soc Amer, 87(4): 932-944.
Bogdanov V I, Graizer V M. 1976. Determination of residual displacement of the ground from a seismogram[J]. Reports of the USSR Academy of Sciences, 229(1): 59-62.
Boore D M. 2001. Effect of baseline corrections on displacement and response spectra for several recordings of the 1999 Chi-Chi, Taiwan, earthquake[J]. Bull Seism Soc Amer, 91(5): 1199-1211.
Boore D M, Stephens C D, Joyner W B. 2002. Comments on baseline correction of digital strong-motion data: Examples from the 1999 Hector Mine, California, earthquake[J]. Bull Seism Soc Amer, 92(4): 1543-1560.
Graizer V M. 1979. Determination of the true displacement of the ground from strong-motion recordings[J]. Izv USSR Acad Sci Phys Solid Earth, 15(12): 875-885.
Graizer V M. 1987. Determination of the path of ground motion during seismic phenomena[J]. Izv USSR Acad Sci Phys Solid Earth, 22(10): 791-794.
Iwan W D, Moser M A, Peng C Y. 1985. Some observations on strong-motion earthquake measurement using a digital accelerograph[J]. Bull Seism Soc Amer, 75(5): 1225-1246.
Koketsu K, Hikima K, Miyake H, Maruyama T. 2008. The source process and strong ground motions of the 2008 Sichuan, China, Earthquake[C]//Proc, 14th World Conf on Earthquake Engineering. Beijing: International Association for Earthquake Engineering: 615-620.
Li X J, Zhou Z H, Moh Huang, Wen R Z, Yu H Y, Lu D W, Zhou Y N, Cui J W. 2008a. Preliminary analysis of strong-motion recordings from the magnitude 8.0 Wenchuan, China, earthquake of May 12[J]. Seism Res Lett, 79(6): 844-854.
Li X J, Zhou Z H, Yu H Y, Wen R Z, Lu D W, Huang M, Zhou Y N, Cui J W. 2008b. Strong motion observations and recordings from the great Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Earthq Eng and Eng Vib, 7(3): 235-246.
Parsons T, Chen J, Kirby E. 2008. Stress changes from the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake and increased hazard in the Sichuan basin[J]. Nature, 454(7203): 509-510.
Wu Y M, Wu C F. 2007. Approximate recovery of co-seismic deformation from Taiwan strong motion records[J]. J Seismol, 11(2): 159-170.




 下载:
下载: