Activity characteristics of faults in the triangle structure area in northern part of Longmenshan in the Shaanxi--Gansu--Sichuan junction
-
摘要: 龙门山北部3条不同走向的断裂带所围限的三角地区是我国陕甘川交界地区研究地震活动的重要场所.通过对区内秦岭南缘断裂、 平武—青川断裂、 岷江断裂及虎牙断裂活动特征研究和活动时代分析认为: 秦岭南缘断裂, 包括迭部—舟曲断裂、 武都—康县—略阳断裂及茶店—勉县断裂在晚更新世曾有过活动, 在全新世活动不明显; 龙门山断裂带东北段平武—青川断裂最后一次活动发生在晚更新世, 表现为右旋走滑的逆断裂, 全新世活动不明显; 岷江断裂和虎牙断裂不但在晚更新世活动强烈, 而且在全新世继续活动; 龙门山北部这个三角地区依然是未来地震活动关注的重点地区.Abstract: The triangle structure area surrounded by three different strike fault zones in northern part of Longmenshan is one of the important areas associated with earthquake activity in China. This paper studies the activity characteristics and active age of some primary fault zones, such as the southern margin fault zone of Qinling, Pingwu--Qingchuan fault, Minjiang fault and Huya fault. The conclusions are as follows: ① The southern margin fault zone of Qinling is composed of Diebu--Zhouqu fault, Wudu--Kangxian--Lüeyang fault and Chadian--Mianxian fault. The last fault activity was in Late Pleistocene and faults were steady in Holocene. ② Pingwu--Qingchuan fault in northeastern segment of Longmenshan fault zone is a thrust fault with dextral strike-slip component. The last fault activity was in Late Pleistocene and steady in Holocene. ③ Minjiang fault and Huya fault were strongly active from Pleistocene to Holocene. ④ This area is still one of important areas for studying earthquake activity in the future.
-
引言
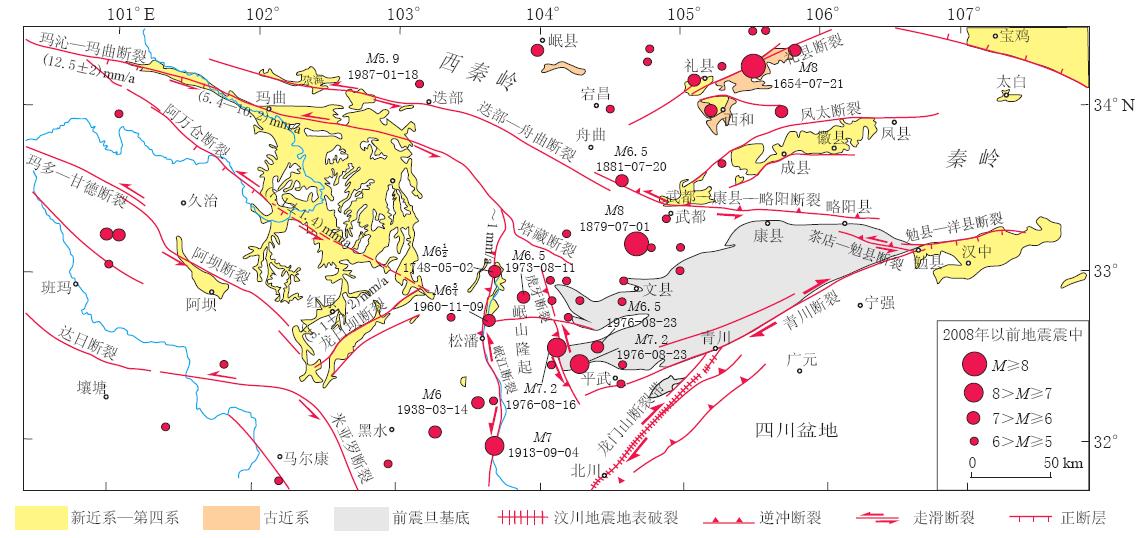
龙门山断裂带北部地区是由北东向的龙门山活动断裂带, 近东西向的东昆仑活动断裂带、 秦岭南缘活动断裂带, 以及近南北向的岷江活动断裂带、 虎牙活动断裂构成的倒三角形状的复杂的新构造活动区. 这一地区活动断裂分布较多, 新构造活动强烈, 是地震活动、 地质灾害频发的危险区域(图1).
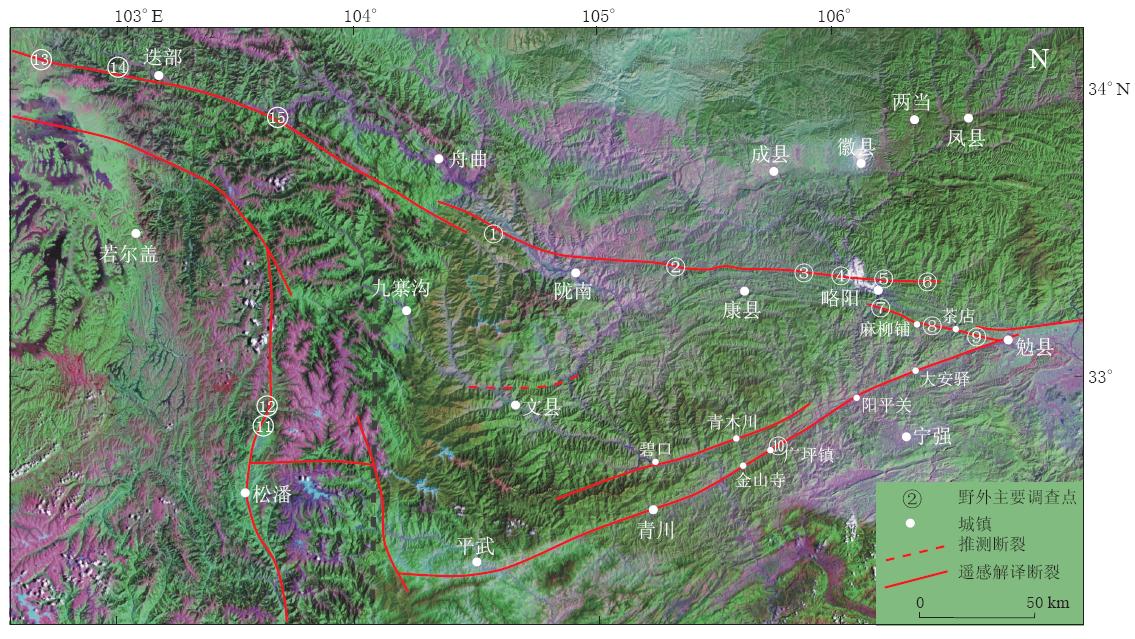
![]() 图 1 龙门山北部地区地质构造简图(据Zhang等(2009)图修改)Figure 1. Geology and structure in northern part of Longmenshan (revised after Zhang et al, 2009)
图 1 龙门山北部地区地质构造简图(据Zhang等(2009)图修改)Figure 1. Geology and structure in northern part of Longmenshan (revised after Zhang et al, 2009)研究区位于中国东西部一级构造地貌陡变的边界带上, 地形地貌的形成反映了区域上强烈的新构造活动. 唐荣昌和韩渭宾(1993)从构造地貌学角度认为存在3期4级夷平面; 刘树根等(1995)和Arne等(1997)通过磷灰石、 锆石裂变径迹测年, 认为川西高原在上新世—更新世为快速冷却时期; 杨农和张岳桥(2010)依据磷灰石裂变径迹测年年龄分析, 认为后龙门山逆冲推覆构造带在中新世晚期开始快速隆升, 而高原内部强烈隆升则发生在上新世末至中更新世; 高原隆升导致深切河谷地貌的形成和发育, 岷江深切河谷地貌是川西高原新近纪—第四纪快速隆升的响应(张岳桥等, 2005); 岷山的快速隆升和区内的差异性构造活动也导致了岷江水系东西两侧支流的不同程度发育(张会平等, 2006). 从深部地壳结构来看, 研究区也正好位于地壳厚度陡变带或南北地震带, 多条东西向构造与南北带相遇后, 或突然终止, 或突然改变方向.郭安宁和陈家超(2002)根据大地电磁测深的探测结果, 发现在南北地震带存在一个上地幔高导带; 人工地震探测表明, 在区内存在复合立交构造, 近东西向和北西向构造主要存在于地壳上部, 而南北向构造则同时位于地壳的上部和下部(李松林, 赖晓玲, 2010). 区域上强烈的新构造活动和频繁的地震活动, 吸引了众多学者对龙门山断裂带中部和南部、 岷江断裂以及虎牙断裂等历史强震活动明显的南北地震带上断裂的研究(Kirby et al, 2000, 2002; 周荣军等, 2000; 韩竹君等, 2001; 陈国光等, 2007; 唐方头等, 2008). 而对于强震分布较少的龙门山断裂带东北段和秦岭南缘断裂带, 则只是在汶川地震以后, 考虑到汶川地震对该区的影响, 才引起了一些学者对龙门山断裂带东北段的注意(陈立春等, 2008; 唐方头等, 2008; 杨晓平等, 2008).
从人口居住情况来看, 大多数城镇具有沿断裂带附近分布的特征. 特别是汶川MS8.0地震以后, 汶川地震地表破裂延入本区(徐锡伟等, 2008), 而且余震在区内分布较多, 给人民正常生活带来巨大的隐患. 显而易见, 本地区已成为汶川地震以后有待研究的重要区域(陈立春等, 2008; 杨晓平等, 2008; 彭华等, 2009).
考虑到研究区在大地构造位置、 地壳结构、 断裂延伸方向等方面的特殊特征, 本文提出了近南北向、 近东西向及北东向构造所围限的构造三角区, 通过区内断裂活动特征分析和相关样品测年(附表), 探讨汶川地震后在龙门山断裂带东北段及其周边地区的地震活动趋势, 为研究区的防震减灾提供科学依据.
1. 区域地质背景概况
研究区在地理位置上跨越陕川甘三省, 区内的几个主要城镇都沿断裂带分布. 在大地构造位置上, 研究区位于秦岭造山带、 扬子地块、 松潘—甘孜造山带及龙门山断裂带的结合部位. 复杂的大地构造背景造就了区域上复杂的构造特征.
自显生宙以来, 研究区经历了三叠纪晚期羌塘陆块与扬子板块的碰撞和早新生代的印藏碰撞两次重大的陆-陆碰撞事件, 造成了两次强烈的褶皱造山和两期前陆盆地, 具有典型的推覆构造特征(刘树根等, 1995; 许志琴等, 1999). 新生代以来, 印度板块与欧亚板块强 烈碰撞而产生的强大推挤力, 在龙门山以及北部地区又发生了大规模的逆掩推覆构造变形.
在新构造活动方面, 川西高原存在多期隆升剥蚀事件, 保留了3期4级夷平面, 分别 是新近纪末青海早期夷平面(海拔4 200—4 500 m)和青海晚期夷平面(海拔3 800—4 000 m)、 早更新世漳腊夷平面( 海拔3 500 m)、 中更新世涪江夷平面(海拔2 000—2 300 m)(刘树根等, 1995). 伴随着垂向上的新构造活动, 第四纪构造经历了早更新世末期从逆冲造山阶段向弱伸展阶段的转换和中更新世晚期或晚更新世初期从弱伸展阶段向走滑-逆冲阶段的两次构造体制的转换(张岳桥等, 2010). 晚新生代构造运动过程可细分为4个主要演化阶段: 中新世晚期—上新世早期, 上新世晚期—更新世早期, 晚更新世中期和晚更新世—全新世. 其中强烈的构造变动主要发生在中新世晚期—上新世早期和上新世晚期-更新世早期这两个时期, 分别导致了龙门山断裂带中、 南段冲断推覆系统以及龙门山北部地区东昆仑—西秦岭—岷山走滑-冲断系统的形成和发展(张岳桥等, 2003). 区内复杂的构造格局和构造活动, 特别是岷山断块在新生代的快速隆升, 使得龙门山断裂带处于构造屏蔽、 低应变、 高应力的环境下, 长期的应力-应变积累导致向西陡倾的断裂带向东逆冲运动而导致了汶川MS8.0地震的发生(张培震等, 2008).
在地震活动方面, 区内地震活动频繁. 1879年甘肃武都—文县发生M8大震(冯希杰等, 2005; 侯康明等; 2005; 袁道阳等, 2007), 死亡人数2万余人; 1976年四川松潘—平武地区连续发生M7.2地震, 使松潘、 平武、 南坪、 文县等县遭到破坏. 汶川MS8.0地震后, 区内连续发生M5.0以上余震18次. 此外,2010年断裂带附近的甘肃舟曲发生特大泥石流, 遇难人数1 434人. 这些灾害的发生, 与区内的构造活动是否有关, 值得关注.
2. 秦岭南缘断裂带
区内秦岭南缘断裂带是指西起甘肃玛曲西北部近WNW向, 过迭部、 武都后转为近EW向, 经甘肃康县北部、 陕西略阳、 勉县直至陕西洋县的这一段断裂, 长约600多千米. 该断裂带主要由迭部—舟曲断裂、 武都—康县—略阳断裂、 茶店—勉县断裂及勉县—洋县断裂(或称汉中盆地北缘断裂)组成(图1). 在遥感影像上, 区内主要断裂线性关系清楚, 依据影像特征并结合地质资料选择断裂出露较好的露头点进行了野外地质调查(图2).
![]() 图 2 位置① 舟曲县八楞乡西岔; ② 武都熊池坝; ③ 康县木瓜园; ④ 勉县徐家坪; ⑤ 勉县吴家营; ⑥ 略阳县两河口; ⑦ 略阳县夹门子村; ⑧ 宁强县麻柳铺; ⑨ 勉县艾叶口村; ⑩ 宁强县广坪乡院坝子村;⑪ 松潘县漳腊水晶乡; ⑫ 松潘县漳腊镇山巴乡尕米寺村;⑬ 若尔盖县热当坝;⑭ 若尔盖县热尔乡;⑮ 迭部县根古村Figure 2. Main faults deduced from remote sensing interpretation and field survey points in study area ① Xicha village, Baleng township, Zhouqu county; ② Xiongchiba township, Wudu city; ③ Muguayuan township, Kangxian county; ④ Xujiaping township, Mianxian county; ⑤ Wujiaying township, Mianxian county; ⑥ Lianghekou township, Lüeyang county; ⑦ Jiamenzi village of Lüeyang county; ⑧ Maliupu village of Ningqiang county; ⑨ Aiyekou village of Mianxian county; ⑩ Yuanbazi village, Guangping township, Ningqiang county;⑪ Shuijing township, Zhangla town, Songpan county;⑫ Gamisi village, Shanba township, Zhangla town, Songpan county;⑬ Xagdomba village of Zoige county; ⑭ Reer township, Zoige county;⑮ Gengu village of Diebu county
图 2 位置① 舟曲县八楞乡西岔; ② 武都熊池坝; ③ 康县木瓜园; ④ 勉县徐家坪; ⑤ 勉县吴家营; ⑥ 略阳县两河口; ⑦ 略阳县夹门子村; ⑧ 宁强县麻柳铺; ⑨ 勉县艾叶口村; ⑩ 宁强县广坪乡院坝子村;⑪ 松潘县漳腊水晶乡; ⑫ 松潘县漳腊镇山巴乡尕米寺村;⑬ 若尔盖县热当坝;⑭ 若尔盖县热尔乡;⑮ 迭部县根古村Figure 2. Main faults deduced from remote sensing interpretation and field survey points in study area ① Xicha village, Baleng township, Zhouqu county; ② Xiongchiba township, Wudu city; ③ Muguayuan township, Kangxian county; ④ Xujiaping township, Mianxian county; ⑤ Wujiaying township, Mianxian county; ⑥ Lianghekou township, Lüeyang county; ⑦ Jiamenzi village of Lüeyang county; ⑧ Maliupu village of Ningqiang county; ⑨ Aiyekou village of Mianxian county; ⑩ Yuanbazi village, Guangping township, Ningqiang county;⑪ Shuijing township, Zhangla town, Songpan county;⑫ Gamisi village, Shanba township, Zhangla town, Songpan county;⑬ Xagdomba village of Zoige county; ⑭ Reer township, Zoige county;⑮ Gengu village of Diebu county2.1 迭部—舟曲断裂
迭部—舟曲断裂(或称武都—玛曲断裂)位于玛曲活动断裂以北, 与玛曲活动断裂南北相距约20 km. 该断裂西自哈拉塘, 沿代桑曲南侧山前向东, 经尕海盆地南缘、 郎木寺盆地北缘、 热尔、 卡坝、 多儿、 插岗至武都, 沿秦岭南缘发育, 向东逐渐与武都—康县—略阳活 动断裂相连. 迭部—舟曲断裂走向NW—SE, 倾向SW, 长度约320 km. 1987年迭部M5.9 地震就发生这条断裂带上http://www.csi.ac.cn/manage/html/4028861611c5c2ba0111c5c558b00001/zhenli/zhwei/html/zhenli069.htm.
在构造地貌上, 迭部—舟曲断裂以左旋活动为主, 错断水系、 冲沟, 沿断裂发育断层崖、 断层陡坎、 断陷谷地等活动断裂地貌, 线性影像特征明显. 在尕海盆地南缘断裂表现为左旋走滑兼向北逆冲特征, 上盘古生界灰岩逆冲到下盘第四系冲积砂砾层之上, 控制着尕海盆地的南界(图3、 图4).
![]() 图 3 迭部—舟曲断裂的构造地貌特征(a) 甘肃碌曲尕海南部, 迭部—舟曲断裂控制新生代尕海盆地, 在盆地边缘形成陡坎地貌; (b) 若尔盖县热当坝, 迭部—舟曲断裂左旋走滑错断连续小山脊和小水沟; (c) 若尔盖县热当坝东,断裂活动形成的陡崖地貌; (d) 若尔盖县热尔乡附近, 形成的地貌陡坎;(e) 迭部县根古村附近, 断裂活动形成的现代开阔谷地Figure 3. Structural landform of Diebu- -Zhouqu fault(a) Diebu- -Zhouqu fault controling Cenozoic Gahai basin, forming fault scarp landform on basin margin in Gahai lake of Luqu county, Gansu province; (b) Diebu- -Zhouqu fault offsetting continuous small ridges and small water-ditches by left-lateral and strike-slip movement in Xagdomba village of Zoige county; (c) Cliff landform in Xagdomba village of Zoige county; (d) Fault scarp landform in Reer township, Zoige county; (e) Extensive valley in Gengu village of Diebu county
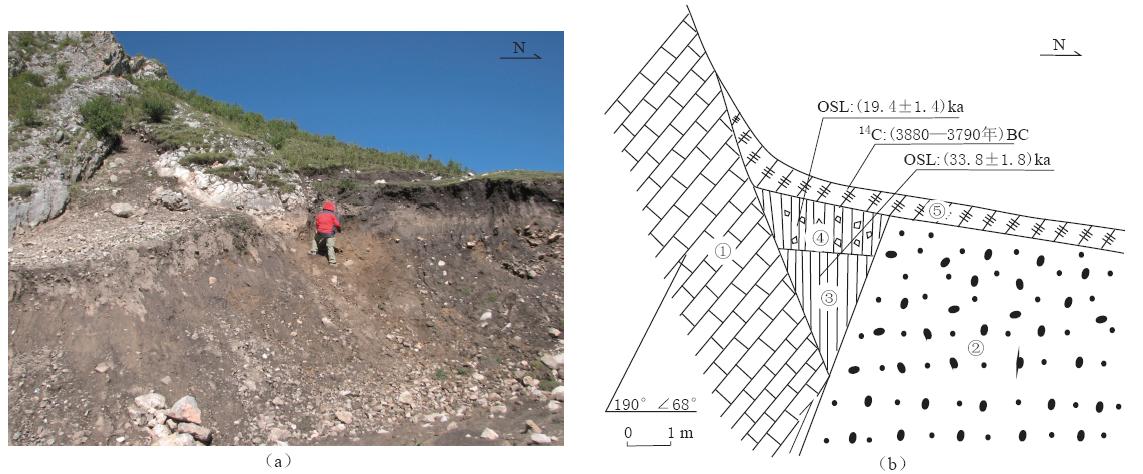
图 3 迭部—舟曲断裂的构造地貌特征(a) 甘肃碌曲尕海南部, 迭部—舟曲断裂控制新生代尕海盆地, 在盆地边缘形成陡坎地貌; (b) 若尔盖县热当坝, 迭部—舟曲断裂左旋走滑错断连续小山脊和小水沟; (c) 若尔盖县热当坝东,断裂活动形成的陡崖地貌; (d) 若尔盖县热尔乡附近, 形成的地貌陡坎;(e) 迭部县根古村附近, 断裂活动形成的现代开阔谷地Figure 3. Structural landform of Diebu- -Zhouqu fault(a) Diebu- -Zhouqu fault controling Cenozoic Gahai basin, forming fault scarp landform on basin margin in Gahai lake of Luqu county, Gansu province; (b) Diebu- -Zhouqu fault offsetting continuous small ridges and small water-ditches by left-lateral and strike-slip movement in Xagdomba village of Zoige county; (c) Cliff landform in Xagdomba village of Zoige county; (d) Fault scarp landform in Reer township, Zoige county; (e) Extensive valley in Gengu village of Diebu county![]() 图 4 甘肃碌曲县尕海附近古地震楔剖面图(a) 野外照片; (b) 素描图. ① 古生界灰岩; ② 第四纪冲积砂砾层; ③ 黄土状土; ④ 含角砾黄土状黄土; ⑤ 黑色腐殖土Figure 4. A section of ancient earthquake wedge in neighborhood of Gahai in Luqu county of Gansu (a) Photo of field; (b) Sketch picture. ① Paleozonic limestone; ② Quaternary alluvial sandy gravel;③ Loess-like soil; ④ Loess-like soil containing breccia; ⑤ Black humus soil
图 4 甘肃碌曲县尕海附近古地震楔剖面图(a) 野外照片; (b) 素描图. ① 古生界灰岩; ② 第四纪冲积砂砾层; ③ 黄土状土; ④ 含角砾黄土状黄土; ⑤ 黑色腐殖土Figure 4. A section of ancient earthquake wedge in neighborhood of Gahai in Luqu county of Gansu (a) Photo of field; (b) Sketch picture. ① Paleozonic limestone; ② Quaternary alluvial sandy gravel;③ Loess-like soil; ④ Loess-like soil containing breccia; ⑤ Black humus soil在尕海西还发现了迭部—舟曲断裂带上的古地震现象(图4). 选取地震楔中不同部位的3个样品分别进行光释光测年和14C测年, 结果为填充在地震楔中的样品的光释光年龄为(33.8±1.8)ka(样品编号: LM09-10)和(19.9±1.4)ka(样品编号: LM09-8). 覆盖在上 部的黑色腐殖土的样品经树轮校正后的14C年龄为(3 880—3 790年)BC(样品编号: LM09-9). 因此认为古地震发生的时间或断层活动的时间为(3 880—3 790年)BC以前, 上限时间为(19.9±1.4)ka.
2.2 武都—康县—略阳断裂
武都—略阳断裂东起略阳县城东北, 走向近EW, 经康县县城北部, 在武都附近向西北偏转, 止于舟曲东南部的三角坪乡. 在遥感影像图上, 该断裂的线性特征特别明显. 沿断层带两边地貌变化较大, 多处形成断层陡坎, 南部为地势较高的灰岩, 北部被第四系坡积物覆盖(图5).
![]() 图 5 武都—康县—略阳断裂的构造地貌特征(a) 舟曲三角坪乡插岗一带的断层崖地貌; (b) 武都(现陇南市)熊池坝古生代灰岩逆冲在中更新统之上, 形成地貌陡坎; (c) 略阳县城北部断裂活动形成的陡崖地貌; (d) 康县木瓜园断裂活动形成的陡坡地貌Figure 5. Structural landform of Wudu- -Kangxian- -Lüeyang fault(a) Landform of fault scarp in Chagang village, Sanjiaoping township, Zhouqu county; (b) Landform of fault scarp formed by thrust fault in Xiongchiba village of Wudu county; (c) Landform of fault scarp in the north of Lüeyang county; (d) Landform of fault scarp in Muguayuan township, Kangxian county
图 5 武都—康县—略阳断裂的构造地貌特征(a) 舟曲三角坪乡插岗一带的断层崖地貌; (b) 武都(现陇南市)熊池坝古生代灰岩逆冲在中更新统之上, 形成地貌陡坎; (c) 略阳县城北部断裂活动形成的陡崖地貌; (d) 康县木瓜园断裂活动形成的陡坡地貌Figure 5. Structural landform of Wudu- -Kangxian- -Lüeyang fault(a) Landform of fault scarp in Chagang village, Sanjiaoping township, Zhouqu county; (b) Landform of fault scarp formed by thrust fault in Xiongchiba village of Wudu county; (c) Landform of fault scarp in the north of Lüeyang county; (d) Landform of fault scarp in Muguayuan township, Kangxian county在三角坪乡插岗一带, 迭部—舟曲断裂和武都—康县—略阳断裂几乎衔接, 断裂活动明显, 地貌上形成断层崖. 在舟曲八楞乡西岔断裂带发育大套黑色断层泥(33°36′37.7″N, 104°28′28.8″E), 断裂带长达3—5 m左右(图6). 黑色断层泥的光释光年龄为(19.0±1.1)ka (样品编号: LB10-11). 虽然本样品计数点少, 但是其年龄数据基本复合本断裂活动规律, 说 明断裂最后一次活动在晚更新世. 断层泥内发育擦痕, 其倾向在10°左右, 倾伏角18°—20°, 揭示断裂为左旋的运动方式.
断裂带在武都东北部的熊池坝附近(33°24′23.9″N, 105°22′11.3″E), 断裂变为左旋逆冲断裂, 大套老地层左旋逆冲于中上更新统之上(图5b). 在下盘靠近坡积物底部的粘土层中采取粘土样品, 得到光释光年龄为(15.8±0.7)ka(样品编号: LB10-9). 这个年龄数据指示该断裂在晚更新世有过活动.
沿断裂带向东, 在多地表现为断面北倾的正断层, 倾角较陡, 为60°左右, 且局部发育断裂破碎带. 断层上盘为晚更新世黄土, 内含灰岩砾石和角砾; 下盘为地面表现陡峭的古生代灰岩(图5c, d). 黄土内部靠近灰岩里面发育近EW走向的水平擦痕, 根据擦痕特征指示断裂做左旋的走滑运动. 在陕西略阳的木瓜园(33°28′40.1″N, 105°50′ 50.2″E)、 徐家坪(33°22′13.0″N, 106°04′06″E)和陕西勉县吴家营(33°22′3.9″N, 106°9′28.8″E)选取上盘近地表黄土做光释光测年, 分别得到(35.2±1.4)ka(样品编号: LB10-8)、 (36.8±1.5)ka(样品编号: LB10-7)和(8.1±0.6)ka(样品编号: LB10-5)年龄数据. 所取黄土样品均覆盖于断裂面之上, 黄土的稳定沉积指示黄土堆积开始, 断裂活动趋于稳定. 前两个数据结果比较一致, 显示了断裂最后活动的时限发生在晚更新世后期; 后一个年龄活动时限的顶界年限为全新世活动, 结合区域分析得到的活动时代应该为晚更新世—全新世这一时间段.
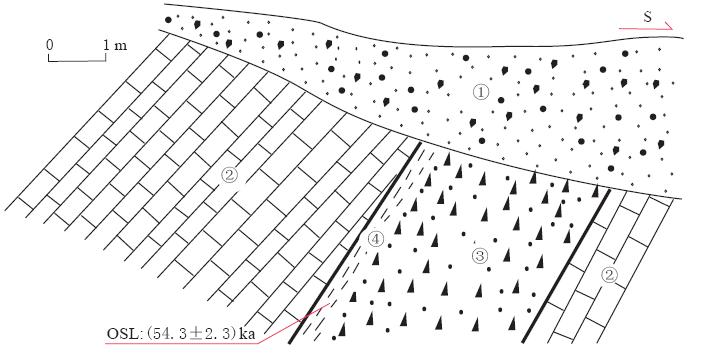
此外在陕西略阳两河口(33°21′44.1″N, 106°21′46.4″E)的断层带中发现有黑色断层泥, 断层泥夹于千枚岩与砂质板岩的混合地层之中(图7). 上盘岩层产状为325°∠45°, 下盘岩层产状为245°∠31°. 断裂破碎带中夹有石英脉透镜体, 在透镜体表面和断层泥中均发育明显的擦痕, 侧伏角45°左右向西, 指示断层为正断层兼有左旋活动. 选取黑色断层泥做光释光年龄测试, 得到了(40.4±1.0)ka(样品编号: LB10-6)的年龄, 揭示断层活动时限在晚更新世.
2.3 茶店—勉县断裂
茶店—勉县断裂东起陕西勉县县城西, 经勉县茶店、 宁强麻柳铺分水岭、 接官亭南邱家院子, 直到略阳县城南边的夹门子村, 穿过嘉陵江后消失. 该断裂走向为WNW- -ESE, 全长55 km左右. 在嘉陵江附近, 断裂活动有改变嘉陵江流向的特征.
在勉县城关镇的艾叶口村S309公路旁一民房建设工地(33°10′13.2″N, 106°33′14.5″E), 由于施工开挖, 断裂带出露出来, 原岩在断裂作用下已经泥化, 形成黑色断层泥, 断面北倾, 断面弯曲、 不平直. 在附近断裂带通过处, 由于原岩破碎, 多处发生小型滑坡现象. 对黑色断层泥取样进行光释光测年. 取了两个样品, 第一个样品(样品编号: LB10-1)由于释光计数少, 年龄不可靠; 另外一个样品得到(42.2±2.7)ka(样品编号: LB10-2)年龄. 同时在断裂带中发现擦痕, 侧伏角为8°—16°E, 指示断层具有走滑现象. 沿线在陕西勉县蒋台村(33°11′51.9″N, 106°34′17.9″E)发现断裂活动使河流左旋转向的现象.
在宁强县麻柳铺分水岭附近(33°12′53.3″N, 106°18′10.1″E), 断层带较窄, 断层泥有5 cm左右, 呈灰黑色, 断面北倾.
在接官亭邱家院子附近, 断裂作用在此处形成宽谷. 在厚层灰岩地层中, 活动断裂发育, 断层破碎带有黑色断层泥. 该断面南倾, 倾角为50°—60°, 断面比较平直.
在略阳县城以南夹门子村附近的嘉陵江东岸边(33°16′35.4″N, 106°7′54.2″E), 断裂发育于古生代灰岩地层中, 上被第四系覆盖(图8). 断层破碎带宽10 m左右, 在破碎带顶部发育黑黄相间的断层泥带, 宽约50 cm. 断层泥之下为含有角砾和砂粒的灰岩破碎带. 灰岩和断层带之上被第四系全新世含砾坡积物覆盖, 断层没有错断第四系全新世坡积物. 在靠近破碎带顶部的断层泥取样, 得到断层泥光释光年龄为(54.3±2.3)ka(样品编号: LB10-4).揭示断裂活动时限主要为晚更新世后期, 在全新世坡积物堆积以来未发生活动.
3. 青川—平武断裂带
青川—平武断裂(或称青川断裂)位于龙门山后山断裂的最北端, 是龙门山构造带中一条长期活动的逆断层. 青川断裂西起平武东部, 沿ENE方向过青川、 宁强县大安镇, 至勉县境内消失在新生代汉中盆地之中, 全长约210 km, 断裂带宽度一般在300—500 m. 断层两侧地层差异明显, 西北侧为深变质的前寒武系碧口群以及浅变质的志留系茂县群、 泥盆系危关群; 东南侧主要为志留系黄坪组. 西北盘出露岩体为印支期花岗岩, 东南盘出露的则是晋宁期花岗岩、 闪长岩. 青川断裂还是岩性的界限, 即前震旦纪石英岩与千枚岩的界限.
在汶川地震前, 沿青川断裂带地震活动强度较小, 其研究程度相对较低. 汶川地震以后, 余震发展抵达断裂带附近, 才引起一些学者的重视(樊春等, 2008; 江娃利等, 2009; 路静等, 2009; 彭华等, 2009).
樊春等(2008)根据遥感和地形地貌资料, 发现青川断裂在多处具有错断水系的特征, 结合区域背景分析认为青川断裂具有右旋走滑特征, 推测其活动始于距今(9—4)Ma, 缺少确切的年龄数据支持; 江娃利等(2009)利用雷达卫星影像资料分析研究, 认为青川断裂具有右旋走滑特征, 为晚更新世—全新世活动断裂, 但是缺乏年龄数据说明; 路静等(2009)也利用遥感资料对平武—青川断裂的右旋走滑活动特征进行了分析, 认为其活动时限为晚第四纪或晚更新世以来. 上述研究基本肯定了青川断裂的活动方式, 但缺少年龄数据支持.
本次考察在宁强县广坪乡院坝子村附近(32°46′51.7″N, 105°40′49.9″E)发现断裂错断二级河流阶地现象(图9). 断裂带为一平直沟谷, 走向N65°E. 经实地测量, 一级阶地拔河高3—5 m, 为种植农田; 二级阶地拔河高15—20 m, 被断裂右旋水平错断200 m左右, 阶地顶部为棕色网状黄土; 三级阶地拔河高30 m左右, 该阶地北侧为以千枚岩为基岩的山地. 在二级阶地顶部的网状黄土中取样, 得到黄土光释光年龄为(36±2.5)ka(样品编号: LM09-4).我们可以认为, 断裂的活动时限的上限为(36±2.5)ka, 只是由于一级阶地的人为活动影响, 没有取到下限年龄. 但是根据杨晓平等(2008)对龙门山断裂带北部地区的研究, 认为一级阶地为堆积阶地且形成于全新世. 由此推断青川断裂在此段的右旋活动时间为晚更新世—全新世.
4. 岷江断裂和虎牙断裂
岷江断裂和虎牙断裂为青藏高原东缘岷山隆起区的东西两侧的边界断裂, 也是研究区内地震活动最为频繁的一条近NS向活动构造带. 1933年四川叠溪M7.5地震、 1938年松潘南M6.0地震、 1960年漳腊M6.7地震均发生在岷江断裂带上(邓起东等, 1994; 钱洪等, 1999; 王康, 沈正康, 2011). 1976年的松潘—平武地区两次M7.2地震均发生在虎牙断裂带南段(邓起东等, 1994).
赵小麟等(1994)从沉积学和构造分析等方面对岷江断裂进行了研究, 认为岷江断裂北段第四纪活动始于距今2 Ma以前, 为一逆走滑断层, 其左旋位移量2.4 km, 左旋走滑速率1 mm/a. 岷江断裂南段的晚第四纪活动性表现为全新世洪积扇的断错, 晚更新世晚期湖相沉积层的变形, 断错冲沟, 以及全新世断塞塘等. 周荣军等(2000)通过对区域第四纪地貌发育过程及断错地貌研究, 得到岷江断裂晚第四纪以来的平均垂直滑动速率为0.37—0.53 mm/a, 岷山断块第四纪以来的平均隆起速率为1.5 mm/a 左右. 王康和沈正康(2011)根据跨岷山断块10 a尺度的GPS观测资料, 认为虎牙断裂具有2 mm/a的地壳缩短率. 岷江断裂具有明显的晚第四纪乃至全新世活动性. 岷江断裂和虎牙断裂在新构造时期的强烈活动造就了岷山断块的隆升(周荣军等, 2000; Kirby et al, 2000, 2002).
野外地质调查发现, 在松潘县漳腊水晶乡的岷江西岸坡上(N32°48′57.1″N, 103°37′47.4″E), 古生代灰岩逆冲于晚更新世钙质胶结的砾石层之上. 其断层面倾向274°, 倾角35°.
在松潘县漳腊镇山巴乡尕米寺村附近(32°53′52.2″N, 103°40′28.2″E), 发现在岷江沿岸发育3级河流阶地, 在三级阶地面上出现断裂沟槽和地震鼓包现象. 采样得到一级阶地顶部光释光年龄为(19.8±1.1)ka(样品编号: LM09-6), 二级阶地顶部光释光年龄为(35.3±2.6)ka(样品编号: LM09-7). 结合赵小麟等(1994)认为, 岷江流域三级阶地热释光年龄为(43.3±3.3)ka, 揭示断裂在晚更新世曾有过活动.
5. 讨论与结论
龙门山断裂带北部这一重要的被活动断裂夹持的三角地区是新构造研究和汶川地震以后地震潜在危险区研究的重要区域之一. 该三角区在几何特征上像楔子一样夹持于秦岭褶皱系与四川盆地之间. 通过前面对区内主要断裂活动特征分析, 可知其北侧边界的秦岭南缘断裂和东南边界龙门山断裂北东段平武—青川断裂, 最后一次的活动时间在晚更新世晚期4—2万年以后. 而这一三角区西部边界的岷江断裂带和虎牙断裂带不但在晚更新世有过强烈活动(Kirby et al, 2000), 而且在全新世以来继续活动, 使岷山断块成为我国著名南北地震带中段的强烈地震活动带(任治坤等, 2005; 马保起等, 2005).
为什么会形成这种构造格局和活动状态, 结合区域构造和大陆动力学研究, 认为是由于在晚更新世来自青藏块体的侧向挤压, 高原内部物质向东和向北扩展(Molnar et al, 1993; Molnar, 2005), 汇聚于岷山断块之上, 使岷山断块向东运动. 受四川盆地这一刚性块体和秦岭山体的阻挡, 这一三角区沿着北界断裂和东南边界断裂做走滑运动(张培震等, 2008; 齐少华等, 2009). 在晚更新世后期—全新世, 由于岷山的快速隆升, 对来自青藏块体的挤压在岷山块体进行了减缓, 由此使得秦岭南缘断裂和龙门山断裂带北东段的平武—青川断裂在全新世活动较弱.
汶川地震以后, 沿龙门山中央断裂带余震频发, 地震地表破裂和余震沿北东方向到达研究区内或附近.向该区域持续的挤压力, 会继续增加这一三角区能量的积累. 震后地应力测量也揭示该区内仍存在较高的应力(彭华等, 2009), 在这看似稳定的能量闭锁区块能量的积累(张希等, 2011), 而且在没有完全释放的背景下, 可成为汶川地震以后地震迁移的重要场所.
通过对龙门山断裂带北部三角区3条不同走向断裂带活动特征的分析, 得出以下结论:
1) 秦岭南缘断裂带, 包括迭部—舟曲断裂、 武都—康县—略阳断裂及茶店—勉县断裂, 在活动方式上有差别, 在西部尕海一带表现为明显的左旋走滑, 在舟曲向东逆冲作用明显. 在活动时限上, 秦岭南缘断裂带主要表现为晚更新世有过活动, 在全新世活动不明显.
2) 龙门山断裂带东北段平武—青川断裂最后一次活动在晚更新世, 表现为右旋走滑的逆断裂, 全新世活动不明显.
3) 岷江断裂和虎牙断裂在晚更新世活动强烈, 而且在全新世继续活动, 使夹持在两条断裂之间的岷山断块第四纪快速隆升, 成为我国南北地震带的重要组成部分.
4) 龙门山断裂带北部这一三角地区有能量持续积累的趋势, 依然是未来地震活动关注的重点区域.
-
图 1 龙门山北部地区地质构造简图(据Zhang等(2009)图修改)
Figure 1. Geology and structure in northern part of Longmenshan (revised after Zhang et al, 2009)
图 2 位置① 舟曲县八楞乡西岔; ② 武都熊池坝; ③ 康县木瓜园; ④ 勉县徐家坪; ⑤ 勉县吴家营; ⑥ 略阳县两河口; ⑦ 略阳县夹门子村; ⑧ 宁强县麻柳铺; ⑨ 勉县艾叶口村; ⑩ 宁强县广坪乡院坝子村;⑪ 松潘县漳腊水晶乡; ⑫ 松潘县漳腊镇山巴乡尕米寺村;⑬ 若尔盖县热当坝;⑭ 若尔盖县热尔乡;⑮ 迭部县根古村
Figure 2. Main faults deduced from remote sensing interpretation and field survey points in study area ① Xicha village, Baleng township, Zhouqu county; ② Xiongchiba township, Wudu city; ③ Muguayuan township, Kangxian county; ④ Xujiaping township, Mianxian county; ⑤ Wujiaying township, Mianxian county; ⑥ Lianghekou township, Lüeyang county; ⑦ Jiamenzi village of Lüeyang county; ⑧ Maliupu village of Ningqiang county; ⑨ Aiyekou village of Mianxian county; ⑩ Yuanbazi village, Guangping township, Ningqiang county;⑪ Shuijing township, Zhangla town, Songpan county;⑫ Gamisi village, Shanba township, Zhangla town, Songpan county;⑬ Xagdomba village of Zoige county; ⑭ Reer township, Zoige county;⑮ Gengu village of Diebu county
图 3 迭部—舟曲断裂的构造地貌特征(a) 甘肃碌曲尕海南部, 迭部—舟曲断裂控制新生代尕海盆地, 在盆地边缘形成陡坎地貌; (b) 若尔盖县热当坝, 迭部—舟曲断裂左旋走滑错断连续小山脊和小水沟; (c) 若尔盖县热当坝东,断裂活动形成的陡崖地貌; (d) 若尔盖县热尔乡附近, 形成的地貌陡坎;(e) 迭部县根古村附近, 断裂活动形成的现代开阔谷地
Figure 3. Structural landform of Diebu- -Zhouqu fault(a) Diebu- -Zhouqu fault controling Cenozoic Gahai basin, forming fault scarp landform on basin margin in Gahai lake of Luqu county, Gansu province; (b) Diebu- -Zhouqu fault offsetting continuous small ridges and small water-ditches by left-lateral and strike-slip movement in Xagdomba village of Zoige county; (c) Cliff landform in Xagdomba village of Zoige county; (d) Fault scarp landform in Reer township, Zoige county; (e) Extensive valley in Gengu village of Diebu county
图 4 甘肃碌曲县尕海附近古地震楔剖面图(a) 野外照片; (b) 素描图. ① 古生界灰岩; ② 第四纪冲积砂砾层; ③ 黄土状土; ④ 含角砾黄土状黄土; ⑤ 黑色腐殖土
Figure 4. A section of ancient earthquake wedge in neighborhood of Gahai in Luqu county of Gansu (a) Photo of field; (b) Sketch picture. ① Paleozonic limestone; ② Quaternary alluvial sandy gravel;③ Loess-like soil; ④ Loess-like soil containing breccia; ⑤ Black humus soil
图 5 武都—康县—略阳断裂的构造地貌特征(a) 舟曲三角坪乡插岗一带的断层崖地貌; (b) 武都(现陇南市)熊池坝古生代灰岩逆冲在中更新统之上, 形成地貌陡坎; (c) 略阳县城北部断裂活动形成的陡崖地貌; (d) 康县木瓜园断裂活动形成的陡坡地貌
Figure 5. Structural landform of Wudu- -Kangxian- -Lüeyang fault(a) Landform of fault scarp in Chagang village, Sanjiaoping township, Zhouqu county; (b) Landform of fault scarp formed by thrust fault in Xiongchiba village of Wudu county; (c) Landform of fault scarp in the north of Lüeyang county; (d) Landform of fault scarp in Muguayuan township, Kangxian county
-
陈国光, 计凤桔, 周荣军, 徐杰, 周本刚, 黎小刚, 叶友青. 2007. 龙门山断裂带晚第四纪活动性分段的初步研究[J]. 地震地质, 29(3): 657-673. 陈立春, 陈杰, 刘进峰, 李峰, 杨晓平, 冉勇康. 2008. 龙门山前山断裂北段晚第四纪活动性研究[J]. 地震地质, 30(3): 710-721. 邓起东, 陈社发, 赵小麟. 1994. 龙门山及邻区的构造和地震活动及动力学[J]. 地震地质, 16(4): 389-403. 樊春, 王二七, 王刚, 王世峰. 2008. 龙门山断裂带北段晚新近纪以来的右行走滑运动及其构造变换研究: 以青川断裂为例[J]. 地质科学, 43(3): 417-433. 冯希杰, 董星宏, 刘春, 李晋. 2005. 范家坝-临江断裂活动与1879年甘肃武都南8级地震的讨论[J]. 地震地质, 27(1): 155-163. 郭安宁, 陈家超. 2002. 中国大震问题[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 1-141. 韩竹君, 向宏发, 冉永康. 2001. 青藏高原东缘礼县-罗家堡断裂带晚更新世以来的活动性分析[J]. 地震地质, 23(1): 43-48. 侯康明, 雷中生, 万夫岭, 李丽梅, 熊振. 2005. 1879年甘肃武都南8级大地震及其同震破裂研究[J]. 中国地震, 21(3): 295-310. 江娃利, 张景发, 谢新生, 刘旭东, 龚丽霞, 姜文亮, 孙昌斌. 2009. 建立在雷达卫星影像判读基础上四川龙门山断裂带晚第四纪活动特征研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 29(3): 426-438. 李松林, 赖晓玲. 2010. 青藏高原东北缘和南北构造带中段地壳结构研究[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 1-130. 刘树根, 罗志立, 戴苏兰, Dennis A, Wilson C J L. 1995. 龙门山冲断带的隆升和川西前陆盆地的沉降[J]. 地质学报, 69(3): 205-214. 路静, 张景发, 姜文亮, 商晓青, 胡乐银. 2009. 龙门山断裂带北段活动特征的遥感地质解译研究[J]. 地震, 29(增刊): 164-172. 马保起, 苏刚, 侯治华, 舒赛兵. 2005. 利用岷江阶地的变形估算龙门山断裂带中段晚第四纪滑动速率[J]. 地震地质, 27(2): 234-242. 彭华, 马秀敏, 姜景捷. 2009. 龙门山北端青川断层附近应力测量与断层稳定性[J]. 地质力学学报, 15(2): 114-130. 齐少华, 刘启元, 陈九辉, 李昱, 李顺成, 郭飚, 王峻. 2009. 汶川MS8.0地震: 龙门山断裂两侧地壳各向异性的初步研究[J]. 地震地质, 31(3): 377-388. 钱洪, 周荣军, 马声浩, 黎小刚. 1999. 岷江断裂南段与1933年叠溪地震研究[J]. 中国地震, 15(4): 333-338. 任治坤, 田勤俭, 陈立泽. 2005. 南北地震带中段地震构造遥感解译[J]. 地震, 25(4): 127-132. 唐方头, 邓志辉, 梁小华, 蒋浦. 2008. 龙门山中段后山断裂带晚第四纪运动特征[J]. 地球物理学进展, 23(3): 710-716. 唐荣昌, 韩渭宾. 1993. 四川活动断裂与地震[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 1-368. 王康, 沈正康. 2011. 1933年叠溪地震的发震位置、 震源机制与区域构造[J]. 地震学报, 33(5): 557-567. 徐锡伟, 闻学泽, 叶建青, 马保起, 陈杰, 周荣军, 何宏林, 田勤俭, 何玉林, 王志才, 孙昭民, 冯希杰, 于贵华, 陈立春, 陈桂华, 于慎鄂, 冉勇康, 李细光, 李陈侠, 安艳芬. 2008. 汶川MS8.0地震地表破裂带及其发震构造[J]. 地震地质, 30(3): 597-629. 许志琴, 杨经绥, 姜枚, 李海兵. 1999. 大陆俯冲作用及青藏高原周缘造山带的崛起[J]. 地学前缘, 6(3): 139-151. 杨农, 张岳桥. 2010. 龙门山断裂活动和川西高原隆升历史的裂变径迹测年[J]. 地质力学学报, 16(4): 359-371. 杨晓平, 冯希杰, 戈天勇, 宋方敏, 师亚芹, 刘玉法. 2008. 龙门山断裂带北段第四纪活动的地质地貌证据[J]. 地震地质, 30(3): 644-657. 袁道阳, 雷中生, 何文贵, 熊振, 葛伟鹏, 刘兴旺, 刘百篪. 2007. 公元前186年甘肃武都地震考证与发震构造探讨[J]. 地震学报, 29(6): 654-663. 张会平, 杨农, 张岳桥, 孟晖. 2006. 岷江水系流域地貌特征及其构造指示意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 26(1): 126-135. 张培震, 徐锡伟, 闻学泽, 冉永康. 2008. 2008年汶川8.0级地震发震断裂的滑动速率、 复发周期和构造成因[J]. 地球物理学报, 51(4): 1066-1073. 张希, 王庆良, 唐红涛, 贾鹏. 2011. 汶川地震孕震背景与同震变化的铲形断层位错模拟[J]. 地球学报, 32(2): 189-194. 张岳桥, 李海龙, 李建华. 2010. 青藏高原东缘中更新世伸展作用及其新构造意义[J]. 地质论评, 56(6): 781-791. 张岳桥, 杨农, 陈文, 马寅生, 孟晖. 2003. 中国东西部地貌边界带晚新生代构造变形历史与青藏高原东缘隆升过程初步研究[J]. 地学前缘, 10(4): 599-612. 张岳桥, 杨农, 孟晖. 2005. 岷江上游深切河谷及其对川西高原隆升的响应[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 32(4): 331-339. 赵小麟, 邓起东, 陈社发. 1994. 岷山隆起的构造地貌学研究[J]. 地震地质, 16(4): 429-439. 周荣军, 蒲晓虹, 何玉林, 黎小刚, 戈天勇. 2000. 四川岷江断裂带北段的新活动、 岷山断块的隆起及其与地震活动的关系[J]. 地震地质, 22(3): 285-294. Arne D, Worley B, Wilson C, Chen S F, Foster D, Luo Z L, Liu S G, Dirks P. 1997. Differential exhumation in response to episodic thrusting along the eastern margin of the Tibetan plateau[J]. Tectonophysics, 280(3-4): 239-256.
Kirby E, Reiners P W, Krol M A, Whipple K X, Hodges K V, Farley K A, Tang W Q, Chen Z L. 2002. Late Cenozoic evolution of eastern margin of the Tibetan plateau: Inferences from 40Ar/39Ar and (U-Th)/He thermochronology[J]. Tectonics, 21(1): 1-20.
Kirby E, Whipple K X, Burchfiel B C, Tang W Q, Berger G, Sun Z M, Chen Z L. 2000. Neotectonics of the Min Shan, China: Implications for mechanisms driving quaternary deformation along the eastern margin of the Tibetan plateau[J]. Geol Soc Amer Bull, 112(3): 375-393.
Molnar P. 2005. Mio-pliocene growth of the Tibetan plateau and evolution of east Asian climate[J]. Palaeontol Electron, 8(1): 1-23.
Molnar P, England P, Martionod J. 1993. Mantle dynamics, uplift of Tibet plateau, and the Indian monsoon[J]. Rev Geophys, 31(4): 357-396.
Zhang Y Q, Dong S W, Yang N. 2009. Active faulting pattern, present-day tectonic stress field and block kinematics in the east Tibetan plateau[J]. Acta Geol Sin-Engl, 83(4): 694-712.
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 吴微微,梁明剑,龙锋,苏金蓉,陈学芬. 青川断裂及邻区现今地震活动性研究. 地震研究. 2023(02): 188-203 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 黄雄南,杨晓平,胡宗凯,杨海波. 白龙江断裂西段晚第四纪构造活动特征研究. 震灾防御技术. 2023(04): 701-717 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 靳志同,万永革,刘兆才,黄骥超,李瑶,杨帆. 2017年九寨沟M_S7.0地震对周围地区的静态应力影响. 地球物理学报. 2019(04): 1282-1299 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 程佳,姚生海,刘杰,姚琪,宫会玲,龙海云. 2017年九寨沟地震所受历史地震黏弹性库仑应力作用及其后续对周边断层地震危险性的影响. 地球物理学报. 2018(05): 2133-2151 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. ZHANG Chongyuan,WU Manlu,CHEN Qunce,LIAO Chunting. Piezomagnetic In-situ Stress Monitoring and its Application in the Longmenshan Fault Zone. Acta Geologica Sinica(English Edition). 2014(05): 1592-1602 .  必应学术
必应学术
其他类型引用(11)




 下载:
下载: