Source parameters of the 2013 Lushan MS7.0 earthquake and the characteristics of the near-fault strong ground motion
-
摘要: 2013年4月20日在我国四川省雅安市芦山县发生了MS7.0地震, 破坏最严重的宝兴、 芦山等极震区烈度达到Ⅷ—Ⅸ度. 该文针对芦山MS7.0地震震源参数的特征, 结合相关经验关系, 对本次地震的震源特征进行了初步分析. 结果表明, 芦山MS7.0地震为断层动态摩擦过程中的应力下调模式. 进一步应用Brune圆盘模型对芦山MS7.0地震近场强地面运动的理论值进行估算, 并基于加速度和速度的估算结果计算极震区的最大烈度, 约为Ⅷ—X度, 与实测的极震区最大烈度Ⅸ度较为接近. 选取宝兴和芦山为特征计算点, 构建动态复合震源模型, 对近断层区域内宝兴和芦山两个特征点进行了模拟计算. 模拟结果显示, 近断层区域强地面运动呈现持续时间短、 高频成分多等特征.Abstract: A MS7.0 earthquake occurred in Lushan County, Sichuan Province of China on 20 April 2013, and the maximum intensity is up to Ⅷ to Ⅸ at Baoxing and Lushan Counties, which are located in the meizoseismal area. This study analyzed the dynamic source process with the source mechanism parameters and empirical relationships, estimated the strong ground motion in the near-fault field based on the Brune's circle model. A dynamical composite source model (DCSM) has been developed to simulate the near-fault strong ground motion with associated fault rupture properties at Baoxing and Lushan, respectively. The results indicate that the frictional undershoot behavior in the dynamic source process of Lushan MS7.0 earthquake is actually different from the overshoot activity of the Wenchuan MS8.0 earthquake. Moreover, the predictions of broadband synthetic seismogram for Lushan and Baoxing shows that the strong ground motion simulation is characterized by large peak values, shorter duartions and more hige-frequency contents, which is affected by higer value of effective stess drop and asperity slip distribution on the fault plane.
-
引言
2013年4月20日8时2分在我国四川省雅安市芦山县发生了MS7.0地震, 震中位置为30.3°N、 103.0°E. 芦山MS7.0地震距2008年5月12日汶川MS8.0地震初始破裂震中约85 km, 距汶川地震余震密集分布区南端约60 km. 芦山MS7.0地震震中位于龙门山断裂带南段的前山断裂附近, 主震破裂过程呈北北东向的挤压逆冲变形特征, 与龙门山断裂带总体走向和运动性质一致(龙门山断裂带走向主要为近北东向). 初步分析认为, 芦山MS7.0地震与汶川MS8.0地震均为巴颜喀拉地块向东运动遇到华南地块阻挡, 应力积累和释放的结果(刘杰等, 2013). 龙门山断裂带全长约500 km, 宽约30—40 km. 其横向主要由中央断裂带、 山后断裂带、 山前断裂带及推覆构造带组成; 纵向可以分为3段: 北川—宁强、 勉县为东北段; 北川—都江堰为中段; 都江堰—泸定、 康定附近为西南段. 这次芦山MS7.0地震发生在西南段, 2008年汶川MS8.0地震则发生在中北段, 汶川地震的发生使得龙门山断裂带整体由震中—东北方向破裂了约300 km.
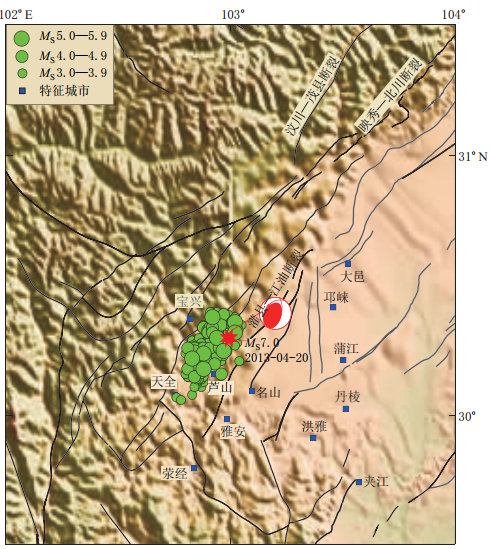
芦山MS7.0地震震中附近100 km范围内, 1900年以来共发生MS≥5.0地震12次, 其中MS6.0—6.9地震3次, 最大地震为2008年汶川MS8.0地震①. 截止到2013年4月26日, 芦山MS7.0地震造成196人遇难, 21人失踪, 逾万人受伤. 其中破坏最严重的发生在震中附近的芦山、 宝兴等地区. 震区余震不断, 截止到4月26日12时, 芦山地震余震区已记 录MS≥3.0余震110次. 其中MS≥5.0余震4次, 最大余震为4月21日17时5分MS5.4 地震, 震中位于芦山县与邛崃市交界(图1).
本研究旨在分析和讨论芦山MS7.0地震的震源参数特征, 进而估计其近断层区域强地面运动的特征和大小. 基于已知的震源参数计算地震视应力等震源参数, 明确芦山MS7.0地震为震源动态模型中的应力下调模式; 结合断层面上滑动集中区的分布, 进一步构建动态复合震源模型(dynamical composite source model, 简写为DCSM), 选取极震区宝兴和芦山两个特征点模拟计算其强地面运动参数. 初步结果显示, 芦山MS7.0地震的近断层区域强地面运动受有效应力降及断层面上滑动集中区的影响较为明显.
1. 震源参数及强地面运动特征
Wyss和Brune(1968)提出视应力σa的概念, 视应力是与地震辐射能量直接相关的物理量. 其物理意义在于, 发震断层单位面积发生单位错动辐射的地震波能量的大小, 即

式中, M0为地震矩, 单位为N · m; μ为介质的剪切模量, 通常取值为μ=3×104 N·m. ES为地震波辐射能, 美国地质调查局(USGS)最新公布的测定结果为(2.3 —2.8)×1014 J. 结合式(1)和表1, 可以求得芦山MS7.0地震的视应力σa约为0.49—0.84 MPa.
陈学忠等(2003)指出, 视应力σa与余震强度存在着一定的统计关系, 即通常一次主震后高视应力的地震一般对应后续较大的余震产生. 基于对造成视应力取值大小的震源力学过程及断层破裂过程中动摩擦机制影响的考虑, 以及单一σa取值大小对余震危险性进行评估存在一定的不确定性, 本研究引入地震发生时动态破裂过程模型, 结合视应力σa 的取值, 对芦山Ms7.0地震断层破裂过程进行分析. 在不考虑破裂能(Er)的前提下,可以将震源动态模型过程分为3种主要的模型: 完全应力降模型(Orowan, 1960; Brune, 1970)、 应力上调模型(Savage,Wood, 1971)和应力下调模型(Brune, 1970, 1976; Smith et al, 1991; Zúniga, 1993). 这3种模型分别对应摩擦应力等于、 大于和小于断层面上的终止剪切应力的情况. 结合断层破裂过程中静态应力降(Δσs), 可以表示为: 当2σa=Δσs时, 为完全应力降模型; 当2σa <Δσs时, 为应力上调模型; 当2σa>Δσs时, 为应力下调模型.
对于已知断层面上滑动位移, 静态应力降(Δσs)可表示为(Starr, 1928; Knopoff, 1958; Keilis,Borok, 1959)

式中,D为断层面上的平均滑动位移, W为断层宽度. 结合表1, 取D≈1.0 m,W ≈ 30 km. 参照式(2)和式(3), Δσs约为0.6—0.8 MPa.结合已知断层面上滑动位移的分布情况来估计芦山MS7.0地震的有效破裂面积. 首先应用矩震级与断层破裂面积对数之间的双线性经验关系, 估算发震断层破裂面积(Hanks,Bakun, 2002)

式中,MW为矩震级,A为断层破裂面积. 式(5)在Hanks和Bakun(2002)原文中为分段函数, 即以A取537 km2为分段点, 当A=537 km 2时,MW≈6.71. 由于本文涉及的芦山 MS7.0地震矩震级小于6.71(表1), 因此我们在验算该地震的破裂面积时, 仅采用式(5)中给出的这一部分, 进一步可以推算出芦山 MS7.0地震的有效破裂面积约为389—447 km 2. 对比图2与表1, 图2a中滑动位移大于0.2 m的有效破裂面积约为450 km 2, 图2b中滑动位移大于0.3 m的有效破裂面积约为400—500 km 2. 事实上, 断层面上滑动位移的反演结果并不具备唯一性(表1), 式(5)的推算结果与图2中的结果具备相对一致性. 由于芦山地震断层面上滑动分布集中且相对单一, 研究过程中可以将其近似为圆盘模型进行理论计算. 令圆盘模型半径R≈11 km, 结合式(4)则Δσs约为 0.36 MPa.
表 1 芦山MS7.0地震震源及断层参数Table 1. Source and fault parameters of the Lushan MS7.0 earthquake
基于式(2)—(4)的计算结果, 已知Δσs取值范围约为0.36—0.8 MPa, 结合σa的估计范围为0.49—0.84 MPa, 可以得出芦山地震为2σa>Δσs情况下的应力下调模式的初步结论. Brune(1970)认为, 应力下调模式对应着地震时断层错动会突然受阻而可能发生的被突然锁住的情况. 对比2008年汶川MS8.0地震, 基于USGS给出的震源参数及式(2), 可以计算得到汶川MS8.0地震的σa仅为0.55 MPa, 属于应力上调模式. 该模式对应地震时的断层错动过头情况. 尽管2008年汶川MS8.0地震与2013年芦山MS7.0地震同发生在龙门山断裂带上, 但二者σa大小存在较大差异, 且断层破裂过程中对应的两种错动模式完全不同.
截止到2013年4月19日, 汶川MS8.0地震余震区共发生MS ≥5.0余震50次, 最大余震为MS6.4; 截止到4月26日, 芦山MS7.0地震余震区已记录MS≥5.0余震4次, 最大余震为MS5.4. 汶川地震与芦山地震余震的时空分布特征明显不同: 汶川地震具备明显的分段性, 尽管其主震发震位置在龙门山断裂带南西段的汶川—映秀一段, 但其余震展布则呈明显的沿该断裂带北东段的青川一段分布, 长达300 km; 芦山地震断层破裂长度较短, 震后余震展布较汶川地震明显集中程度较高.
1.1 估算近断层区域强地面运动的理论值
Andrews(1986)对地震强地面运动的频谱响应进行分析时给出

式中, σB为Brune圆盘模型下的有效应力降; AFS为S波辐射图型因子, 其在震源球面上的均方根为AFS= 2/5 . 由前面已给出的计算结果σa≈0.49—0.84 MPa, 则σB≈2.1—3.6 MPa. 进一步采取Brune(1970, 1971)圆盘模型下给出的近场强震质点运动速度的估算方法, 即

This page contains the following errors:
error on line 1 at column 1: Start tag expected, '<' not foundBelow is a rendering of the page up to the first error.
芦山MS7.0地震发生后, 中国地震局于4月27日给出了实测烈度分布图, 极震区最大烈度为Ⅸ度. 烈度通常是通过对震区实际调查获取的震害资料, 由于地震发生后的影响区域很大, 往往是震后一段时间才能给出现场震害调查的烈度分布图. 然而在地震应急救援中, 为快速可靠地估计极震区的烈度值, 可以利用烈度与强地面运动参数之间的转换关系(Wald et al, 1999)

式中, PGA单位为cm/s2, PGV单位为cm/s, IMM为场地烈度. 将基于式(7)得到的近场强地面运动的理论估计值, 近似为峰值加速度(PGA)和峰值速度(PGV), 代入式(8)中, IMM≈7.0—9.9. 该结果与实测的极震区最大烈度Ⅸ较为接近.
1.2 构建动态复合震源模型计算近断层区域强地面运动
针对芦山MS7.0地震构建动态复合震源模型(DCSM)(孟令媛,史保平, 2011), 模型参数的设定综合考虑前面提到的反演结果(表1、 图2a). 作者在2011年针对汶川MS8.0地震的研究中, 修正了复合震源模型, 提出可以根据已有反演数据建立动态化的复合震源模型(DCSM), 即断层面上的走向、 倾向和滑动角参数不再单一取值, 而是可以动态化地进行赋值. 此外, DCSM模型修正了原有的试错算法, 应用地震矩和地震波辐射能(有效应力降或视应力)两个条件同时约束模型. 尽管目前尚无查到有关芦山MS7.0地震的速度结构文献, 由于芦山MS7.0地震与汶川MS8.0地震同处龙门山断裂带, 因此, 本文针对芦山MS7.0地震建立DCSM的相关速度结构主要参照汶川MS8.0地震(刘启元等, 2009), 其断层面上滑动位移分布见图2b.
应用已构建的DCSM模型, 对近断层区域的宝兴和芦山两个特征点进行了模拟计算, 并分别给出了加速度和速度的模拟时程曲线图(图3、 图4). 挑选宝兴和芦山两个特征点的主要原因在于这两个特征点位处Ⅷ— Ⅸ度烈度的极震区, 距离芦山地震的震中位置及主断层均较近. 宝兴和芦山两个特征点距离主断层的最短距离分别为 7和15 km, 即均为近断层区域( <30 km), 二者的震中距分别为19和17 km. 此外, 由于宝兴和芦山两地为震后人员伤亡的集中地区, 因此本研究确定两个特征点的经纬度位置时主要参考了两个地区人口集中点的经纬度. 国家强震动台网中心针对芦山MS7.0地震公布的强震数据统计情况, 其初步获取的95组三分量加速度记录中, 震中距范围为27.7—769 km. 获取的PGA最大为400.7 cm/s2, 对应震中距为27.7 km. 已获取记录中PGA大于200 cm/s2 的记录共8条.
图3给出了宝兴特征点地表质点加速度、 速度三分量数值模拟计算结果. 图中给出的分别为地表质点运动NS、 EW及UD三分量加速度和速度模拟结果的时程曲线图. 由图3可以看出, 模拟结果的加速度和速度的各自三分量时程曲线图均呈现波形集中和高频成分偏多的特点. 波形集中即时程曲线图的持续时间相对较短, 仅约为5—10 s, 这一点与宝兴台站距离震中位置较近而接收到的地震波成分中高频成分较多是趋于一致的. 宝兴特征点模拟的NS、 EW及UD三分量的PGA分别为389, 500和331 cm/s2, PGV模拟结果分别为25, 43和31 cm/s. 由于现有DCSM模型近似采用了汶川MS8.0地震的速度结构(刘启元等, 2009), 针对宝兴特征点的模拟结果是基于基岩上获得的, 并未添加土层的速度数据, 因此图3中强地面运动参数模拟结果中高频的成分相对较多, 尤其在加速度时程曲线图中更为明显.
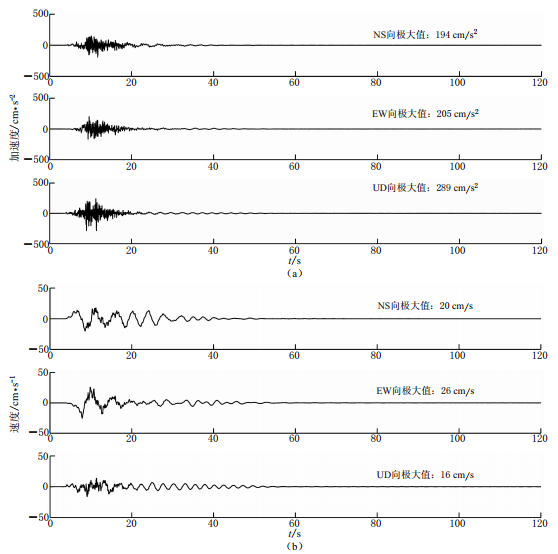
图4给出了芦山特征点地表质点加速度、 速度NS、 EW及UD三分量模拟结果的时程曲线图. 芦山特征点模拟的NS、 EW及UD三分量PGA分别为194, 205和289 cm/s2, PGV模拟结果分别为20, 26和16 cm/s. 图4给出的芦山特征点加速度和速度的三分量时程曲线的模拟结果相较于图3呈现出部分低频成分, 尤其是速度三分量的时程曲线, 且持续时间约为10 s. 芦山特征点PGA和PGV均比宝兴特征点小. 国家强震动台网在已公布PGA的三分量加速度记录中, PGA第二高值出现在距离震中32.6 km的芦山飞仙台, 该台站实测的NS、 EW及UD三分量PGA分别为357.0, 387.4和267.4 cm/s2. 由于目前尚未公布相关PGV实测记录及相关时程曲线图, 且本研究选取的芦山特征点与芦山飞仙台站位置有所差别, 因此, 图4中给出的模拟结果与芦山飞仙台的实测记录并不具有完全的可比性. 尽管如此, 仍可以依据芦山飞仙台的PGA实测记录, 判断本研究基于DCSM模型针对所选取特征点强地面运动的模拟结果具有较好的合理性.
本研究给出的强地面运动模拟结果不包含仪器响应差异的影响, 相关程序计算地表运动三分量的过程主要为选定速度结构、 给出滑动模型、 输入相关计算参数后, DCSM模型即为确定. 实际上, 模型一旦确定, 针对不同特征点(某地点)计算得到三分量的时程曲线图即为一次性计算得到. 由于格林函数的计算结果需要在球坐标系与笛卡尔坐标系中进行转换, 程序设定的默认方向即为NS、 EW和UD三个方向, 因此一次性的计算结果被分解为这三个方向. DCSM的优势之一即可以给出含有高频成分的地震到模拟结果. 与同样能给出含高频成分的有限断层随机振动模型不同, DCSM模型考虑应力降、 地震波辐射能的影响, 并且能够给出垂直分量的时程曲线图.
2. 讨论与结论
2013年4月20日芦山地震发生后, 关于芦山MS7.0地震与汶川MS8.0地震的关联性问题立即引起了学术界的广泛讨论. 从构造背景的角度考虑, 芦山地震与汶川地震的发震位置均为巴颜喀拉块体的边界上, 芦山地震与汶川地震的震中位置距离约85 km, 且芦山地震与汶川地震均发生在龙门山断裂带上, 受到龙门山断裂带总体走向和运动特征的影响, 两次地震的震源机制解也较为一致, 均为逆冲型的地震. 前面也提到, 芦山MS7.0地震为2σa>Δσs情况下的应力下调模式, 对应着地震时断层错动会突然受阻而可能发生被突然锁住的情况; 而汶川地震则属于应力上调模式, 对应地震时断层错动过头的情况. 由于二者σa大小存在较大差异, 且断层破裂过程中对应两种完全不同的错动模式, 不同的错动模式反映了断层面上应力变化的不同情况, 对强地面运动地震学意义重大, 因其决定了高频辐射能的相对数量, 进而决定了给定应力降之后的峰值加速度和峰值速度模拟结果的差异性.
芦山MS7.0地震具备一个特征, 即其震源过程中有效应力降与汶川MS8.0地震的差异性并不大. 主要原因在于两次地震的σa差异较小, 芦山MS7.0地震σa为0.49—0.84 MPa, 汶川MS8.0地震σa为0.55 MPa, 有效应力降 σB的差异性也不明显. 由此基于Brune圆盘模型对芦山地震近场质点加速度和速度进行估算可以发现, 尽管芦山地震断层破裂尺度相对于汶川地震明显偏小, 但其近场强地面运动的理论估算值仍相对较高, 这一点可以利用极震区烈度值的大小得到验证.
关于发震断层破裂过程的模拟, 本文基于断层面上的滑动位移分布的反演结果约束断层面上滑动集中区的分布位置(图2a), 基于大小不同地震破裂过程具有自相似的假定(Frankel, 1991), 即主震断层面可由多个随机分布的大小尺度不同的子源叠加而成, 随机叠加而成的断层面上的滑移分布遵从k-2模型(Zeng,Anderson, 1996), 进而完成对断层破裂过程的运动学描述(图2b). 现阶段DCSM的改进程度仍然存在一定的局限性, 主要在于对最大一二个子源位置的约束. 实际上, 如果DCSM模型构建过程中不约束子源位置, 完全随机分配, 对模拟结果整体PGA和PGV的平均水平不会有大的影响, 但对近断层区域强地面运动的模拟会影响很大, 尤其是对最大子源位置附近区域特征点模拟结果的PGA和PGV影响很大.
关于DCSM模型相关程序计算三分量的具体过程, 主要为选定速度结构、 给出滑动模型和输入相关计算参数三个步骤. 模型一旦确定, 针对不同特征点的计算需要调整的参数只有特征点的经纬度参数. 根据不同的经纬度参数, 会针对该特征点重新计算一次格林函数. 同样地, 一旦确定某一个特征点, 计算得到三分量的时程曲线图即为一次性计算得到. DCSM模型计算程序设定的默认方向即为NS、 EW和UD三个方向, 因此一次性的计算结果被分解为这三个方向.
DCSM的前身为复合震源模型, 创新性地采用了随机子源分配的方式, 解决了地震波时程曲线图模拟结果中的高频成分问题. 同样地, DCSM的优势之一即可以给出含有高频成分的地震动模拟结果. DCSM模型考虑应力降、 地震波辐射能的影响, 能够分别给出水平和垂直分量的时程曲线图. 原始的复合震源模型通常针对小尺度的走滑型断层进行模拟, 而DCSM模型改进后不仅可以针对走滑型断层进行模拟, 也可以针对逆冲型断层模型进行模拟. 除考虑应力降、 地震波辐射能的影响外, 还实现了分段断层走向、 倾向的滑动角的动态化设定. 但现有DCSM模型所给出的强地面运动模拟结果并未包含仪器响应的差异. 随着芦山MS7.0地震强震观测数据和震区速度结构的研究的不断完善, 未来还可以对已构建的DCSM模型进行逐步地修正和改进, 以求获取适用于龙门山断裂带强震地表运动预测的有效模型.
2011年2月21日发生在新西兰克莱斯特彻奇的MW 6.1地震, 造成200多人遇难. 相对该地区半年前发生的MW7.0地震, 这次地震给克莱斯特彻奇城造成了更为严重的建筑物损毁和人员伤亡. 一个重要的原因就在于这次MW6.1地震造成的近断层强地面运动强且震中位处城市中心附近, 加之半年前MW7.0地震对城市建筑物的损害, 克莱斯特彻奇城内很多建筑物仍在重建, 尚未完全修复, 经不起二次打击(孟令媛,史保平, 2012). 因此, 未来的研究应对可能发生的、 距离城市较近的大中型地震给予足够的重视, 避免城市直下型地震的加强型破坏; 需要加强地震发生后对城市内建筑物可能产生强地面运动影响的判断, 尤其是人口密集的城市以及曾经受过地震破坏的城市建筑, 重视震后及时、 快速、 高标准修复, 以便应对未来地震可能对人口密集城市造成的破坏.
本文在撰稿过程中, 史保平教授、 蒋海昆研究员和张永仙研究员给予了有益的指导与帮助, 作者在此一并表示诚挚的谢意.
-
表 1 芦山MS7.0地震震源及断层参数
Table 1 Source and fault parameters of the Lushan MS7.0 earthquake

-
陈学忠, 王小平, 王林瑛, 张天中. 2003. 地震视应力用于震后趋势快速判定的可能性[J]. 国际地震动态, (7): 1-3. 刘杰, 易桂喜, 张致伟, 官致君, 阮祥, 龙锋, 杜方. 2013. 2013年4月20日四川芦山M7.0级地震介绍[J]. 地球物理学报, 56(4): 1404-1407. 刘启元, 李昱, 陈九辉, 郭彪, 李顺成. 2009. 汶川MS8.0地震: 地壳上地幔S波速度结构的初步研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 52(2): 309-319. 孟令媛, 史保平. 2011. 应用动态复合震源模型模拟汶川MW7.9地震强地面运动[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(4): 1010-1027. 孟令媛, 史保平. 2012. 2011年新西兰MW6.1地震震源过程及强地面运动特征初步分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 55(5): 1601-1612. 王卫民, 郝金来, 姚振兴. 2013. 2013年4月20日四川芦山地震震源破裂过程反演初步结果[J]. 地球物理学报, 56(4): 1412-1417. 张勇, 许力生, 陈运泰. 2013. 芦山4·20地震破裂过程及其致灾特征初步分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 56(4): 1408-1411. Andrews D J. 1986. Objective determination of source parameters and similarity of earthquakes of different size[C]//Das S, Boatwright J, Scholz C H eds. Earthquake Source Mechanics. Washington: AGU: 259-267.
Brune J N. 1970. Tectonic stress and spectra of seismic shear waves from earthquakes[J]. J Geophys Res, 75(26): 4997-5009.
Brune J N. 1971. Correction of "tectonic stress and spectra of seismic shear waves from earthquakes"[J]. J Geophys Res, 76(20): 5002.
Brune J N. 1976. The physics of earthquake strong motion[C]//Lomnitz C, Rosenblueth E eds. Seismic Risk and Engineering Decisions. New York: Elsevier Sci Publ Co: 141-177.
Frankel A. 1991. High-frequency spectral falloff for earthquakes, fractal dimension of strength on faults[J]. J Geophys Res, 96(B4): 6291-6302.
Hanks T C, Bakun W H. 2002. A bilinear source-scaling model for M-logA observations of continental earthquakes[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 92(5): 1841-1846.
Keilis-Borok V I. 1959. On estimation of the displacement in an earthquake source and source dimension[J]. Annali di Geofisica, 12(2): 205-214.
Knopoff L. 1958. Energy release in earthquake[J]. Geophys J Inter, 1(1): 44-52.
Orowan E. 1960. Mechanism of seismic faulting in rock deformation: A symposium[J]. Geol Soc Am Mem, 79: 323-345.
Savage J C, Wood M D. 1971. The relation between apparent stress and stress drop[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 61(5): 1381-1388.
Smith K D, Brune J N, Priestly K F. 1991. The seismic spectrum, radiated energy, and the Savage and Wood inequality for complex earthquake[J]. Tectonophysics, 188(3/4): 303-320.
Starr A T. 1928. Slip in a crystal and rupture in a solid due to shear[J]. Proc Camb Phil Soc, 24(4): 489-500.
Wald D J, Quitoriano V, Heaton T H, Thomas H, Kanamori H. 1999. Relationships between peak ground acceleration, peak ground velocity, and modified Mercalli intensity in California[J]. Earthquake Spectra, 15(3): 557-564.
Wyss M, Brune J N. 1968. Seismic moment, stress, and source dimensions for earthquakes in the California-Nevada region[J]. J Geophys Res, 73(14): 4681-4694.
Zeng Y, Anderson J G. 1996. A composite source modeling of the 1994 Northridge earthquake using genetic algorithm[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 86(1B): 71-83.
Zúñiga F R. 1993. Fractional overshoot and partial stress drop. Which one?[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 83(3): 939-944.
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 罗恒之,曾宪伟,李文君,罗国富. 宁夏地区地震视应力时空变化特征分析. 地震工程学报. 2025(01): 178-188+198 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 臧阳,孟令媛,周龙泉. 2016年新西兰M_S8.0地震震源及强地面运动特征分析. 地震学报. 2017(01): 1-12+155 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 王俊,郑定昌,郑江蓉,詹小艳,江昊琳,李正楷,张金川. 利用背景噪声自相关研究芦山M7.0地震震源区地壳相对波速的时空变化特征. 地震地质. 2016(01): 152-168 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 白玉柱,徐锡伟,李铁明,周本刚. 芦山地震强地面运动频谱特征及致灾相关性分析. 地震工程学报. 2016(04): 570-580 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. Meng Lingyuan,Zhou Longquan,Shi Haixia. A Study on the Characteristics of the Yutian, Xinjiang M_S7.3 Earthquake, February 12, 2014. Earthquake Research in China. 2015(01): 47-56 .  必应学术
必应学术
6. 孟令媛,周龙泉,刘杰. 2013年巴基斯坦M_W7.7地震震源参数特征及烈度分布估计. 地震. 2014(04): 12-19 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 赵烽帆,史海霞,周志华. 2008年汶川M_S8.0地震和2013年芦山M_S7.0地震震源特征比较分析. 中国地震. 2014(04): 604-610 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: