Characteristics of shear-wave splitting in the crust in Shanxi region
-
摘要: 通过对山西数字地震台网2000年6月—2012年12月的波形记录资料的分析, 使用剪切波分裂系统分析方法, 即SAM综合分析方法, 获得了山西地区18个数字地震台站的快剪切波偏振结果. 结果表明: 位于活动断裂上的台站的快剪切波偏振优势方向与活动断裂的走向基本一致; 个别距离断裂较远的台站的快剪切波偏振优势方向与震源机制解及GPS主压应变方向完全一致; 少数位于几条断裂交汇处的台站的快剪切波偏振优势方向则较为复杂, 与活动断裂的走向和GPS主压应变方向均不一致, 反映了该地区断裂背景和应力分布特征的复杂性.Abstract: Based on the analysis of seismic waveform data recorded by the Shanxi Digital Seismic Network from June 2000 to December 2012, the dominant polarization directions of fast shear-waves at 18 stations are obtained by use of the systematic analysis method (SAM) of shear-wave splitting in this study. The results show that for the stations located on active faults, the dominant polarization directions of fast shear-waves are mainly consistent with the strike of active faults; for individual stations further away from active faults, the dominant polarization directions are completely consistent with focal mechanism solutions and directions of regional principal compressive strains inferred from GPS data. While for a few stations located at the junction of several faults, the polarization of fast shear-wave is inconsistent with both the strike of active faults and the direction of principal compressive strain from GPS, indicating that faulting background and distribution characteristics of regional stress field are complex in Shanxi region.
-
Keywords:
- Shanxi region /
- fast shear-wave /
- polarization /
- principal compressive stress /
- active fault
-
引言
地震波也称体波,分为纵波(压缩波)和横波(剪切波). 在均匀(各向同性)介质中传播时,纵波和横波的偏振都是线性的. 但是在地球内部非均匀(各向异性)特性的影响下,其偏振表现为不规律的质点运动,这种运动现象反映了波的偏振特性. 当剪切波在各向异性介质中传播时,由于传播速度和偏振特性的不同会产生分裂现象,即分裂为快剪切波和慢剪切波. 这两列波分别以不同的速度和振动方向沿正交方向偏振. 研究表明,地震各向异性是地球内部普遍存在的一种本能现象,广泛存在于地壳和上地幔中(Crampin, 1978,1981; 姚陈等,1992; 高原等, 1995,1999).
自Crampin(1978,1981)提出横波分裂理论以来,关于地震各向异性的研究备受关注. 国内的大量研究结果(姚陈等,1992; 孙勇,郑斯华,1993; 高原等, 1995,1996; 钱晓东等,2002; 华卫等,2006; 赖院根等,2006; 王新岭等,2006; 太龄雪等,2008)表明,快剪切波的偏振方向与裂隙的走向和区域主压应力方向一致; 但也有研究表明,快剪切波的偏振优势方向与震源应力场主压应力方向相差甚远(李白基等,2002); 慢剪切波的分裂时间延迟能够反映介质的各向异性程度,与应力环境的变化密切相关(Gao et al,1998; Crampin et al,1999); 因此,通过剪切波分裂可以研究地壳介质的地震各向异性特征和地壳应力状态的变化(高原等,1999; 石玉涛等,2006; 吴晶等,2007). 最新的研究表明,剪切波分裂参数反映了震前的应力积累和临震前的应力释放过程,可将其用于地震预测研究(Crampin et al,2003; Gao,Crampin,2004; 高原,滕吉文,2005; Wu et al,2006). 相关研究进一步表明,位于活动断裂上的台站记录的快剪切波偏振优势方向与活动断裂的走向一致(Peng,Ben-Zion,2004; 石玉涛等,2006; 吴晶等,2007),快剪切波的偏振优势方向受到区域应力场和断裂分布等多种因素的控制,复杂地质构造会造成剪切波偏振方向的不同,反映出区域应力场的复杂性(高原等, 1995,1999; 雷军等,1997; 石玉涛等,2006; 吴晶等,2007).
山西地区是我国地质构造较为复杂、 破坏性地震多发的区域. 有史料记载以来(公元前2222—公元2012年)共发生破坏性地震(M≥4.7)112次,且大部分发生在盆地地区. 山西盆地带主要由大同、 忻定、 太原、 临汾、 运城等5大盆地组成,构成了山西构造活动的主体,其边缘受活动断裂控制. 盆地内地震密集成带,呈NE向或NNE向排列分布,并集中于断陷盆地及盆地边缘,是未来强震活动的主要场所(张玲等,2011).
关于山西地区的地质特征和地球物理特征的研究,一直是地球物理研究的重要内容. 本研究将采用剪切波分裂系统分析方法,利用山西地区2000年6月—2012年12月的数字地震波形资料,对山西地区地壳介质的各向异性进行初步研究,并结合该区域内复杂的地质构造,进一步讨论该区域内剪切波的分裂特性及其与应力分布和断裂分布的关系.
1. 区域背景与资料
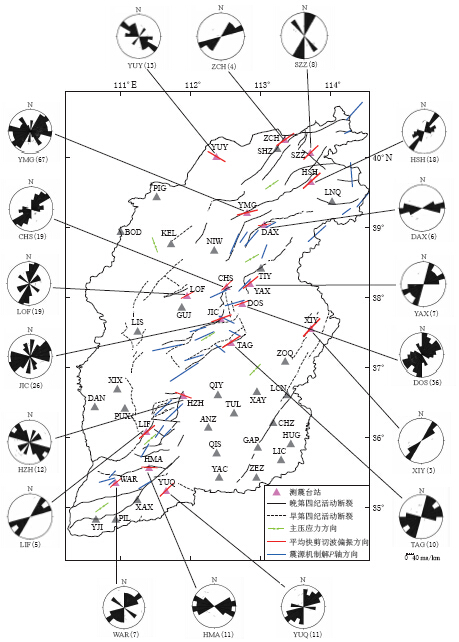
山西地区地处汾渭断陷带,位于鄂尔多斯地块东缘,总体呈“S”形,走向为NNE向,由5个大的断陷盆地组成,自北向南依次为大同盆地、 忻定盆地、 太原盆地、 临汾盆地和运城盆地(图 1). 这几个断陷盆地间以横向隆起相隔,各隆起自北向南依次为恒山隆起、
![]() 图 1 山西地区测震台站与断裂分布图① 口泉断裂; ② 六棱山北麓断裂; ③ 恒山北麓断裂; ④ 恒山南麓断裂; ⑤ 云中山山前断裂; ⑥ 五台山北麓断裂; ⑦ 系舟山北麓断裂; ⑧ 交城断裂; ⑨ 太谷断裂; ⑩ 霍山山前断裂; ⑪ 罗云山山前断裂; ⑫ 峨嵋台地北缘断裂; ⑬ 中条山北麓断裂Figure 1. Distribution of seismic stations and faults in the Shanxi region① Kouquan fault; ② Liulengshan northern piedmont fault; ③ Hengshan northern piedmont fault; ④ Hengshan southern piedmont fault; ⑤ Yunzhongshan piedmont fault; ⑥ Wutaishan northern piedmont fault; ⑦ Xizhoushan northern piedmont fault; ⑧ Jiaocheng fault; ⑨ Taigu fault; ⑩ Huoshan piedmont fault; ⑪ Luoyunshan piedmont fault; ⑫ Northern margin fault of Emei terrace; ⑬ Zhongtiaoshan northern piedmont fault
图 1 山西地区测震台站与断裂分布图① 口泉断裂; ② 六棱山北麓断裂; ③ 恒山北麓断裂; ④ 恒山南麓断裂; ⑤ 云中山山前断裂; ⑥ 五台山北麓断裂; ⑦ 系舟山北麓断裂; ⑧ 交城断裂; ⑨ 太谷断裂; ⑩ 霍山山前断裂; ⑪ 罗云山山前断裂; ⑫ 峨嵋台地北缘断裂; ⑬ 中条山北麓断裂Figure 1. Distribution of seismic stations and faults in the Shanxi region① Kouquan fault; ② Liulengshan northern piedmont fault; ③ Hengshan northern piedmont fault; ④ Hengshan southern piedmont fault; ⑤ Yunzhongshan piedmont fault; ⑥ Wutaishan northern piedmont fault; ⑦ Xizhoushan northern piedmont fault; ⑧ Jiaocheng fault; ⑨ Taigu fault; ⑩ Huoshan piedmont fault; ⑪ Luoyunshan piedmont fault; ⑫ Northern margin fault of Emei terrace; ⑬ Zhongtiaoshan northern piedmont fault石岭关隆起、 灵石隆起和峨嵋台地. 断陷带内各盆地均不对称,表现为一侧深而另一侧浅,在盆地的两侧均发育有深大断裂.
大同盆地及其东南侧的山地均向东南倾斜,其西侧主控断裂为口泉断裂,东南侧主控断裂为六棱山北麓断裂和恒山北麓断裂. 忻定盆地由两个半地堑盆地组成,均向东南倾斜,盆地东南侧的主控断裂分别为五台山北麓断裂、 系舟山北麓断裂和系舟山西麓断裂; 盆地另一侧的主控断裂则为恒山南麓断裂和云中山山前断裂. 太原盆地的沉降中心靠近盆地西部,其西侧的主控断裂为交城断裂,东侧主控断裂为太谷断裂. 临汾盆地内部结构复杂,发育有一系列NNE向和WNW向断裂,并有几个沉降中心. 其中罗云山山前断裂中段控制着盆地西侧临汾凹陷的沉降中心,霍山山前断裂控制着洪洞凹陷的沉降中心. 临汾盆地南部的侯马凹陷,其沉降中心在侯马一带,主要受罗云山山前断裂的南段和峨嵋台地北缘断裂控制. 运城盆地南侧是控制沉降中心的中条山北麓断裂.
山西地区历史上地震活动强烈,主要分布于断陷带及其两侧,有时呈震群形式出现,如太谷、 平遥等震群,这些地震均属壳内浅源地震. 震源机制解、 地应力测量等均显示该地区现今构造运动总体上仍然表现为NE-ENE向挤压、 NW向拉张的应力场作用下的运动,这表明现今断裂活动继承着新生代以来的运动方式,与地堑-裂谷的形成应力状况是一致的(杨国华等,1999).
山西数字测震台网建设于“九五”期间,2002年开始正式运行,由21个遥测地震台站组成,以JVC-100短周期地震计为主,配以16位数据采集器; 采样率为50 sps. “十五”期间对山西数字测震台网进行了升级改造,加大了原台网的台站密度,升级了短周期地震计和数据采集器. 改扩建后的山西数字测震台网共有台站32个,全部使用24位IP数据采集器; 采样率为100 sps; 地震计的有效动态范围大于120 dB; 频带宽度为60 s—40 Hz. 另外,“十五”期间山西省相继建成了晋城、 长治、 运城、 太原等地方台网,这些地方台网的纳入使山西数字测震台网的台站达到46个,对山西数字台网的监测能力给予了一定的补充(图 1). 根据台网分布特征,山西数字地震台网南北跨度大,两台直线距离最大约60 km,造成山西测震台网台站数量相对偏少,分布不够均匀的状况,特别是山西中部和南部的地震台站更为稀疏,因而为山西地区剪切波分裂参数分析提供的数据非常有限.
本文利用2000年6月—2012年12月山西数字测震台网12余年的波形记录共356次,依据剪切波分裂方法原理,得到剪切波窗口内ML≥1.0的波形数据共283个. 在此基础上,对窗口内的三分向波形记录进行优选,最终得到用于剪切波分裂计算的248次地震,其震中分布如图 1所示. 本文根据每个台站的数据记录情况,对数据较多的台站进行了筛选,最后获得有计算结果的台站共18个.
2. 计算方法与数据处理
本研究采用剪切波分裂系统分析方法(systematic analysis method of shear-wave splitting,简写为SAM综合分析方法)(高原等,2004; 石玉涛等,2006),研究山西地区地壳介质的各向异性特征. SAM综合分析方法是在相关函数的基础上提出的一种分析方法,包含3个主要内容,即相关函数计算、 时间延迟校正和偏振分析检验,且此系统具有自我检验的特点(高原,郑斯华,1994).
为避免地表界面S-P转换波对剪切波分裂的影响,应选择剪切波窗口内的波形记录. 对于泊松比为0.25的介质,剪切波窗理论入射角的临界值为35°,即入射角≤35°范围内的剪切波记录才能使用. 考虑到地表沉积层的存在,在实际计算和数据处理中剪切波窗口可增大至40°—45°(Shih,Meyer,1990; Cochran et al,2003; Peng,Ben-Zion,2004).
快剪切波偏振方向和慢剪切波时间延迟是剪切波分裂的两个主要参数. 计算剪切波分裂参数,就是对两个水平分量的剪切波波形沿顺时针方向在0°—180°内旋转,步长为1°; 然后根据质点运动的变化轨迹,判断快剪切波到达线段与正北方向的夹角,在“旋转角度”对话框里输入该角度值,通过质点运动轨迹的突然变化,可以确定快、 慢剪切波的初动; 最后改变相对时间移动点数,直至运动轨迹成线性时为止,此时的“旋转角度”就是偏振方向,相对时间移动即为慢波延迟时间,这样便可获得所需的剪切波分裂参数(高原等, 1995,2004).
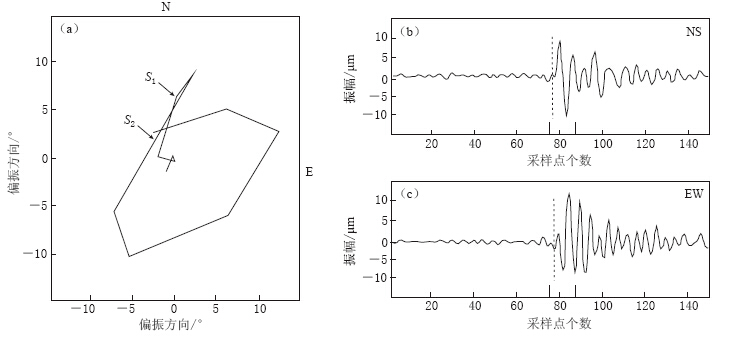
图 2给出了娄烦台(LOF)记录的2012年3月15日发生的一次ML1.2地震的两水平方向剪切波偏振图. 依据张学民等(2003)利用区域人工地震测深剖面得到的拟合速度结构,计算得到该地震事件的入射角为13.6°,快剪切波的偏振方向为18°,慢剪切波的延迟时间为0.86 ms/km.
![]() 图 2 两水平方向剪切波偏振图(a) 剪切波质点运动轨迹(偏振图), S1, S2分别表示快、 慢剪切波震动的起始位置, 以箭头示出; (b) 南北(NS)分量的剪切波波形; (c) 东西(EW)分量的剪切波波形. 横坐标上两条短竖线给出了 偏振图中剪切波的波形范围, 虚线段为剪切波的开始位置Figure 2. Two horizontal shear-wave polarization diagrams(a) Particle motion traces of shear-waves where S1 and S2 indicate the start points of fast shear-wave and slow shear-wave, respectively; (b) Shear waveform in NS direction; (c) Shear waveform in EW direction. In figs. (b) and (c), two vertical short bars indicate the range of shear waveforms, and vertical dotted lines indicate the start points of shear-waves
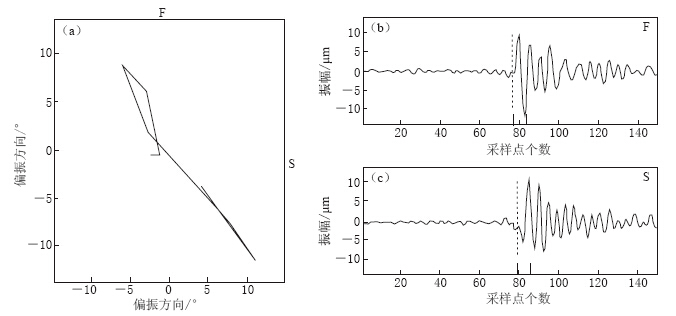
图 2 两水平方向剪切波偏振图(a) 剪切波质点运动轨迹(偏振图), S1, S2分别表示快、 慢剪切波震动的起始位置, 以箭头示出; (b) 南北(NS)分量的剪切波波形; (c) 东西(EW)分量的剪切波波形. 横坐标上两条短竖线给出了 偏振图中剪切波的波形范围, 虚线段为剪切波的开始位置Figure 2. Two horizontal shear-wave polarization diagrams(a) Particle motion traces of shear-waves where S1 and S2 indicate the start points of fast shear-wave and slow shear-wave, respectively; (b) Shear waveform in NS direction; (c) Shear waveform in EW direction. In figs. (b) and (c), two vertical short bars indicate the range of shear waveforms, and vertical dotted lines indicate the start points of shear-waves图 2a为没有经过时间延迟校正的剪切波偏振图,图 2b和图 2c分别为原始两水平向的剪切波波形. 从图 2a中可以看出,其质点运动轨迹并不是线性的. 图 3a给出了偏振分析检验图,这里将剪切波通过波形旋转得到快剪切波(图 3b)和慢剪切波(图 3c),然后进行时间延迟校正. 经波形旋转和时间延迟校正后的剪切波偏振图已呈线性特征,因此可以确定上述计算得到的剪切波分裂结果是比较可靠的.
![]() 图 3 偏振分析检验(a) 快剪切波(F)和慢剪切波(S)经过时间延迟校正后的偏振图; (b) 快剪切波(F)波形; (c) 慢剪切波 (S)波形. 横坐标上两条短竖线表示偏振图中剪切波的波形范围, 虚线段分别表示快、 慢剪切波的初至Figure 3. Polarization analysis and check(a) Diagram of particle motion traces of fast shear-wave (F) and slow shear-wave (S), in which the effect of time delay has been removed. (b) Waveform of fast shear-wave; (c) Waveform of slow shear-wave. In Figs. (b) and (c), two vertical short bars indicate the range of shear waveforms, which are equivalent to move the slow shear wave ahead of one time-delay unit, and the effect of time delay is removed. Two dashed lines indicate the first arrival of fast and slow shear waves, respectively
图 3 偏振分析检验(a) 快剪切波(F)和慢剪切波(S)经过时间延迟校正后的偏振图; (b) 快剪切波(F)波形; (c) 慢剪切波 (S)波形. 横坐标上两条短竖线表示偏振图中剪切波的波形范围, 虚线段分别表示快、 慢剪切波的初至Figure 3. Polarization analysis and check(a) Diagram of particle motion traces of fast shear-wave (F) and slow shear-wave (S), in which the effect of time delay has been removed. (b) Waveform of fast shear-wave; (c) Waveform of slow shear-wave. In Figs. (b) and (c), two vertical short bars indicate the range of shear waveforms, which are equivalent to move the slow shear wave ahead of one time-delay unit, and the effect of time delay is removed. Two dashed lines indicate the first arrival of fast and slow shear waves, respectively3. 计算结果
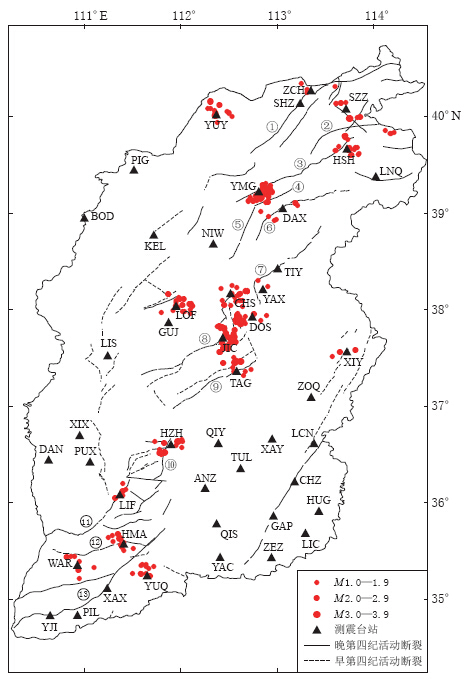
本文根据SAM综合分析方法对山西数字测震台网2000年6月—2012年12月的全部数据进行了剪切波分裂分析,获得剪切波窗口内共18个台站的计算结果,具体如图 4和表 1所示,其中所选分析台站至少有3条以上的有效波形记录.
![]() 图 4 山西地区18个台站快剪切波偏振方向的空间分布及其等面积投影玫瑰图红色线段表示地震台下方的平均快剪切波偏振方向,其长度代表慢波相对延迟时间的大小; 蓝色线段表示 2001年11月至2008年5月期间山西地区地震震源机制的最大主压应力方向(王凯英等,2012); 玫瑰图中台站代码后面括号中的数字为用于分析的地震事件个数; 灰色三角形表示无有效观测数据的台站Figure 4. Spatial distribution of average fast shear-wave polarization directions and their homolographic projection rose graphs beneath 18 stations in the Shanxi regionThe red lines show the average fast shear-wave polarization directions beneath the stations,the length of each line indicates the value of the slow shear-wave time-delay. The blue lines show the direction of maximum principal compressive stress axis of focal mechanism in Shanxi region during November 2001 to May 2008(after Wang et al,2012). The number in parenthesis after the station code in the rose graphs is the number of seismic events used for analysis, and the gray triangles denote the stations without effective observation data表 1 山西数字测震台网18个台站的剪切波分裂参数Table 1. Parameters of shear-wave splitting for 18 seismic stations of the Shanxi Digital Seismic Network
图 4 山西地区18个台站快剪切波偏振方向的空间分布及其等面积投影玫瑰图红色线段表示地震台下方的平均快剪切波偏振方向,其长度代表慢波相对延迟时间的大小; 蓝色线段表示 2001年11月至2008年5月期间山西地区地震震源机制的最大主压应力方向(王凯英等,2012); 玫瑰图中台站代码后面括号中的数字为用于分析的地震事件个数; 灰色三角形表示无有效观测数据的台站Figure 4. Spatial distribution of average fast shear-wave polarization directions and their homolographic projection rose graphs beneath 18 stations in the Shanxi regionThe red lines show the average fast shear-wave polarization directions beneath the stations,the length of each line indicates the value of the slow shear-wave time-delay. The blue lines show the direction of maximum principal compressive stress axis of focal mechanism in Shanxi region during November 2001 to May 2008(after Wang et al,2012). The number in parenthesis after the station code in the rose graphs is the number of seismic events used for analysis, and the gray triangles denote the stations without effective observation data表 1 山西数字测震台网18个台站的剪切波分裂参数Table 1. Parameters of shear-wave splitting for 18 seismic stations of the Shanxi Digital Seismic Network
山西数字测震台网中有28个台站无有效观测数据,主要是由于山西特殊的构造环境所致. 山西现今地震活动主要发生在汾渭断陷带内的五大断陷盆地,其两侧的隆起区除右玉、 娄烦、 昔阳、 垣曲一带外,其余地方地震分布相对较少. 另外,由于山西数字测震台网的建设历时较长,跨越了“九五”、 “十五”长达10年的时间,个别建成较晚的台站有效数据较少或无有效数据.
快剪切波偏振方向与台站的原地主压应力方向一致,由于受区域应力场的控制,其偏振方向与断裂分布和地质构造等有关. 由图 4中给出的山西地区18个台站快剪切波平均偏振方向的空间分布可以看出,18个台站中有10个台站(CHS,WAR,HSH,YMG,TAG,YUQ,LIF,XIY,ZCH,YAX)显示出快剪切波偏振方向为NE向,1个台站(YUY)显示为NW向,1个台站(LOF)显示为NNE向,2个台站(HMA,DAX)显示为近EW向; 另外4个台站(JIC,DOS,HZH,SZZ)显示出复杂的快剪切波偏振分布,有两个或多个偏振优势方向.
4. 讨论与结论
山西地区取得有效观测数据的18个台站,由于其所处的构造部位不同,其快剪切偏振波优势方向受到活动断裂的影响以及区域与局部应力场的影响,表现出复杂的分布特征.
右玉台(YUY)位于山西西部鄂尔多斯隆起区内,根据小震综合断面解推断这一地区的平均应力场为: 主压应力轴取向160°,近似水平; 主张应力轴取向250°—275°,仰角很大. 应力场以NNW-SSE向的水平挤压作用为主(刘巍等,1993). 本文得到的右玉台快剪切波偏振方向为NW的结果(图 4),与刘巍等(1993)的结果基本一致; 与GPS测量导出的该区域附近主压应变方向为NW(郭良迁等,2010)这一结果相吻合.
岔上台(CHS)位于太原盆地西北边界的控制断裂山根底断裂西北侧1.9 km处(图 4). 该断裂为全新世活动断裂,走向为NE向. 岔上台的快剪切波偏振优势方向为NE向,与断裂的走向近乎一致. 根据对较大规模的活动断裂研究结果认为,活动断裂上的台站的快剪切波偏振方向与周围台站的结果不一致,往往与断裂走向一致(Crampin et al,2003; 吴晶等,2007). 岔上台的结果支持了这个结论.
娄烦台(LOF)位于山西西部鄂尔多斯隆起区内娄烦断裂的南侧,距离娄烦断裂9.1 km. 娄烦台的快剪切波偏振优势方向为NNE向,与小震综合断面解推断的这一地区平均应力场取向为160°(刘巍等,1993)是不一致的,与娄烦断裂NE走向也是不一致的. 说明在这一局部地区其应力场既受到鄂尔多斯隆起区整体应力场的作用,也受到娄烦断裂对应力场局部调整的影响. 娄烦台的结果进一步证明了快剪切波偏振方向有很强的局部区域性.
晋祠台(JIC)位于太原盆地西侧的控制断裂即交城断裂与田庄断裂的交汇处(图 4),两断裂分别为全新世活动断裂与晚更新世活动断裂,在晋祠台附近的走向分别为NE向与近EW向. 晋祠台的快剪切波偏振优势方向为NNE向(近似为NS)和ENE向. 由此看来,两个优势方向与两条断裂的走向均不一致,反映了断裂背景和应力分布特征的复杂性.
侯马台(HMA)位于临汾盆地侯马凹陷南侧控制断裂峨嵋台地北缘断裂南侧1.6 km处(图 4). 该断裂为晚更新世活动断裂,在侯马台附近的走向为近EW向. 考虑到断裂的宽度,可以认为侯马台位于该断裂带上. 侯马台的快剪切波偏振优势方向为WNW向,近EW向,与断裂的走向近乎一致.
万荣台(WAR)位于临汾盆地与运城盆地之间的横向隆起,即峨嵋台地,台地内构造相对简单. 该台的快剪切波偏振优势方向为NE向和NW向. 根据王凯英等(2012)对2001年昆仑山口西MS8.1地震前后山西构造带应力状态变化的研究可知,在昆仑山口西地震前后山西构造带的最大主压应力轴方向发生了明显的变化. 该地震前山西构造带最大主压应力轴方向以NW向分布为主; 地震后转变为以NE向分布为主. 万荣台快剪切波的两个偏振优势方向正好与该构造带最大主压应力轴变化前后的两个优势方向一致,因此推测出现这种结果,与计算时同时选取了2001年昆仑山口西地震前后的地震有关.
恒山北麓断裂是大同盆地东南侧的主控边界断裂,控制着大同盆地马营庄凹陷的形成和发展,属全新活动断裂,且为正倾滑断裂. 恒山台(HSH)距离恒山北麓断裂1.6 km,与雁门关台(YMG)(距离恒山北麓断裂1.9 km)几乎同在该断裂带上. 从图 4可看出恒山台的快剪切波偏振优势方向为NE向,与恒山北麓断裂在该区域的走向一致. 雁门关台的快剪切波偏振优势方向为ENE,亦与恒山北麓断裂在该区域的走向一致. 距离相近的两个台由于地处同一条断裂带上的不同段,仅仅是因为断裂各段的走向差异造成快剪切波偏振优势方向的不同,更进一步验证了活动断裂上的台站的快剪切波偏振方向往往与该断裂走向一致的结论.
太谷台(TAG)位于太原盆地东侧控制断裂太谷断裂东侧0.9 km处(图 4). 该断裂为全新世活动断裂,在太谷台附近的走向为NE向. 太谷台的快剪切波偏振优势方向为NE向,与太谷断裂的走向近乎一致,且与王凯英等(2012)运用应力状态定量化参数反演方法得到的该区域最大主压应力轴以NE向分布为主的结论相吻合. 这种主压应力与断层方向的一致性,有利于断层的走滑运动; 与由GPS资料得到的太原盆地相对两侧山地具有走滑运动的观点(郭良迁等,2010)是一致的.
霍州台(HZH)位于临汾盆地的东侧,地处霍山断裂、 什林断裂、 贾村断裂的交汇处,其构造部位相对复杂. 该台快剪切波偏振优势方向为NW向,与附近断裂的走向均不一致,与王凯英等(2012)运用应力状态定量化参数反演方法得到的该区域最大主压应力轴以NE向分布为主的结论也不一致. 进一步验证了在断裂交汇处,应力场方向的变化也很复杂(石玉涛等,2006). 这种特殊的位置导致霍州台的快剪切波偏振优势方向与附近断裂的走向均不一致.
东山台(DOS)位于山西东部太行山隆起区内系舟山西麓断裂与田庄断裂延长线的交汇处. 该台快剪切波偏振优势方向为近SN向和NE向(图 4). NE向优势方向与小震综合断面解推断的这一地区主压应力场方向为40°—50°(刘巍等,1993)完全一致; SN向优势方向与两条断裂延长线的走向ENE几乎一致. 说明在这一局部地区其应力场既受到太行山隆起区整体应力场的作用,也受到断裂对应力场局部调整的影响. 东山台结果也证明了快剪切波偏振方向有很强的局部区域性.
垣曲台(YUQ)位于山西东部太行山隆起区内. 刘巍等(1993)根据小震综合断面解推断,这一地区的平均应力场为: 主压应力轴平均取向40°—50°,仰角小于10°; 主张应力轴平均取向130°—150°,仰角为30°—40°; 应力场以NE向水平挤压作用为主. 垣曲台快剪切波偏振优势方向为NE向(图 4),与刘巍等(1993)得到的该地区主压应力场方向的结果完全一致.
杨兴台(YAX)位于忻州盆地东部太行山隆起区内,紧邻忻定盆地. 根据小震综合断面解推断的这一地区的平均应力场为: 主压应力轴平均取向为50°—70°,仰角稳定在40°左右; 主张应力轴平均取向为140°—160°,仰角小于10°; 平均应力场以水平拉张作用为主(刘巍等,1993). 杨兴台快剪切波偏振优势方向为NE向(图 4),与刘巍等(1993)得到的该地区的主压应力场方向完全一致.
山自皂台(SZZ)位于大同盆地内的横向隆起区. 根据小震综合断面解推断的这一地区的平均应力场为: 主压应力轴平均取向为50°—60°,仰角变化很大,最大可达60°; 主张应力轴平均取向为130°—150°,仰角在10°—40°之间变化; 平均应力场以水平或近水平的拉张作用为主(刘巍等,1993). 山自皂台快剪切波偏振优势方向为NE向(图 4),与刘巍等(1993)得到的该地区主压应力场方向完全一致. 此外,山自皂台的快剪切波偏振还有一组优势方向为NW向(图 4),这可能与2001年11月14日昆仑山口西MS8.1地震前后山西构造带的最大主压应力轴方向发生变化有关(王凯英等,2012).
另外,临汾台(LIF)位于罗云山山前断裂西侧0.2 km处,代县台(DAX)位于五台山北麓断裂南侧1.1 km处,昔阳台(XIY)位于井陉—左权断裂东侧0.9 km处,镇川(ZCH)台位于口泉断裂西侧0.8 km处. 由图 4可见,这4个台站的快剪切波偏振优势方向与距离台站最近断裂的走向基本一致,再次证明了活动断裂上的台站的快剪切波偏振方向往往与断裂走向一致的观点.
快剪切波偏振优势方向代表了观测台站及其附近的主压应力方向. 尽管其会受到局部断裂和活动构造的影响,但本文研究表明山西地区的快剪切波偏振优势方向与震源机制解以及GPS测量获得的区域主压应变方向基本一致,与山西地区的区域主压应力方向也有很强的关联性.
位于活动断裂上的台站,例如,HSH、 YMG、 CHS、 TAG、 HMA、 LIF、 DAX、 XIY和ZCH等台,其快剪切波偏振优势方向与活动断裂走向基本一致. 根据快剪切波偏振优势方向的分布可以判断地下断层是否为活动断层,这一结果与吴晶等(2007)的研究结果相一致. 距离活动断裂较远的台站(即位于隆起区内的地震台站),例如YUY、 WAR、 SZZ、 YAX和YUQ台,由于受区域应力场的作用,其快剪切波偏振优势方向显示出很好的一致性,与区域主压应力方向以及GPS主压应变方向一致. 处于断裂附近的台站,例如DOS和LOF台,快剪切波偏振优势方向由于受到区域应力场和断裂的共同作用,其平均快剪切波偏振方向与区域主压应力方向以及断裂方向均不一致.
局部复杂的地质构造会影响台站的快剪切波偏振优势方向,导致与主要活动断裂走向不一致,或与相邻台站的结果相差较大的现象. 复杂的地质结构也会造成快剪切波偏振优势方向较为离散或出现多个优势方向的现象,反映了地震活动与区域构造密切相关的分布特征,例如JIC和HZH台.
山西地区构造复杂,断裂带多,仍需要利用较多的资料分时段对该地区进行更加精细的地震学研究.
感谢中国地震局地震预测研究所高原研究员课题组提供的软件支持.
-
图 1 山西地区测震台站与断裂分布图
① 口泉断裂; ② 六棱山北麓断裂; ③ 恒山北麓断裂; ④ 恒山南麓断裂; ⑤ 云中山山前断裂; ⑥ 五台山北麓断裂; ⑦ 系舟山北麓断裂; ⑧ 交城断裂; ⑨ 太谷断裂; ⑩ 霍山山前断裂; ⑪ 罗云山山前断裂; ⑫ 峨嵋台地北缘断裂; ⑬ 中条山北麓断裂
Figure 1. Distribution of seismic stations and faults in the Shanxi region
① Kouquan fault; ② Liulengshan northern piedmont fault; ③ Hengshan northern piedmont fault; ④ Hengshan southern piedmont fault; ⑤ Yunzhongshan piedmont fault; ⑥ Wutaishan northern piedmont fault; ⑦ Xizhoushan northern piedmont fault; ⑧ Jiaocheng fault; ⑨ Taigu fault; ⑩ Huoshan piedmont fault; ⑪ Luoyunshan piedmont fault; ⑫ Northern margin fault of Emei terrace; ⑬ Zhongtiaoshan northern piedmont fault
图 2 两水平方向剪切波偏振图
(a) 剪切波质点运动轨迹(偏振图), S1, S2分别表示快、 慢剪切波震动的起始位置, 以箭头示出; (b) 南北(NS)分量的剪切波波形; (c) 东西(EW)分量的剪切波波形. 横坐标上两条短竖线给出了 偏振图中剪切波的波形范围, 虚线段为剪切波的开始位置
Figure 2. Two horizontal shear-wave polarization diagrams
(a) Particle motion traces of shear-waves where S1 and S2 indicate the start points of fast shear-wave and slow shear-wave, respectively; (b) Shear waveform in NS direction; (c) Shear waveform in EW direction. In figs. (b) and (c), two vertical short bars indicate the range of shear waveforms, and vertical dotted lines indicate the start points of shear-waves
图 3 偏振分析检验
(a) 快剪切波(F)和慢剪切波(S)经过时间延迟校正后的偏振图; (b) 快剪切波(F)波形; (c) 慢剪切波 (S)波形. 横坐标上两条短竖线表示偏振图中剪切波的波形范围, 虚线段分别表示快、 慢剪切波的初至
Figure 3. Polarization analysis and check
(a) Diagram of particle motion traces of fast shear-wave (F) and slow shear-wave (S), in which the effect of time delay has been removed. (b) Waveform of fast shear-wave; (c) Waveform of slow shear-wave. In Figs. (b) and (c), two vertical short bars indicate the range of shear waveforms, which are equivalent to move the slow shear wave ahead of one time-delay unit, and the effect of time delay is removed. Two dashed lines indicate the first arrival of fast and slow shear waves, respectively
图 4 山西地区18个台站快剪切波偏振方向的空间分布及其等面积投影玫瑰图
红色线段表示地震台下方的平均快剪切波偏振方向,其长度代表慢波相对延迟时间的大小; 蓝色线段表示 2001年11月至2008年5月期间山西地区地震震源机制的最大主压应力方向(王凯英等,2012); 玫瑰图中台站代码后面括号中的数字为用于分析的地震事件个数; 灰色三角形表示无有效观测数据的台站
Figure 4. Spatial distribution of average fast shear-wave polarization directions and their homolographic projection rose graphs beneath 18 stations in the Shanxi region
The red lines show the average fast shear-wave polarization directions beneath the stations,the length of each line indicates the value of the slow shear-wave time-delay. The blue lines show the direction of maximum principal compressive stress axis of focal mechanism in Shanxi region during November 2001 to May 2008(after Wang et al,2012). The number in parenthesis after the station code in the rose graphs is the number of seismic events used for analysis, and the gray triangles denote the stations without effective observation data
表 1 山西数字测震台网18个台站的剪切波分裂参数
Table 1 Parameters of shear-wave splitting for 18 seismic stations of the Shanxi Digital Seismic Network

-
高原, 滕吉文. 2005. 中国大陆地壳与上地幔地震各向异性研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 20(1): 180-185. Gao Y, Teng J W. 2005. Studies on seismic anisotropy in the crust and mantle on Chinese mainland[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 20(1): 180-185 (in Chinese).
高原, 郑斯华. 1994. 唐山地区剪切波分裂研究(Ⅱ): 相关函数分析法[J]. 中国地震, 10(增刊): 22-32. Gao Y, Zheng S H. 1994. On shear wave splitting in Tangshan region (Ⅱ): Correlation function analysis method[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 10(Suppl.): 22-32 (in Chinese).
高原, 郑斯华, 孙勇. 1995. 唐山地区地壳裂隙各向异性[J]. 地震学报, 17(3): 283-293. Gao Y, Zheng S H, Sun Y. 1995. Crustal crack anisotropy in Tangshan[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 17(3): 283-293 (in Chinese).
高原, 郑斯华, 王培德. 1996. 海南省东方地区1992年小震群剪切波分裂研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 39(2): 221-232. Gao Y, Zheng S H, Wang P D. 1996. Shear wave splitting study on small earthquake swarm of 1992 in Dongfang of Hainan, South China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 39(2): 221-232 (in Chinese).
高原, 郑斯华, 周蕙兰. 1999. 唐山地区快剪切波偏振图象及其变化[J]. 地球物理学报, 42(2): 228-232. Gao Y, Zheng S H, Zhou H L. 1999. Polarization patterns of fast shear wave in Tangshan region and their variations[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 42(2): 228-232 (in Chinese).
高原, 刘希强, 梁维, 郝平. 2004. 剪切波分裂系统分析方法(SAM)软件系统[J] . 中国地震, 20(1): 101-107. Gao Y, Liu X Q, Liang W, Hao P. 2004.Systemtic analysis method of shear-wave splitting: SAM software system[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 20(1): 101-107 (in Chinese).
郭良迁, 占伟, 杨国华, 薄万举. 2010. 山西断陷带的近期位移和应变率特征[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 30(4): 36-42. Guo L Q, Zhan W, Yang G H, Bo W J. 2010. Short-term displacement and characteristics of strain rate of Shanxi fault subsidence zone[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 30(4): 36-42 (in Chinese).
华卫, 刘杰, 陈章立, 郑斯华. 2006. 2003年云南大姚6.2级、 6.1级地震序列S波分裂研究[J]. 地震学报, 28(4): 357-371. Hua W, Liu J, Chen Z L, Zheng S H. 2006. Study on S wave splitting in Dayao earthquake sequence with M=6.2 and M=6.1 in Yunnan in 2003[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 28(4): 357-371 (in Chinese).
赖院根, 刘启元, 陈九辉, 刘洁, 李顺成, 郭飙, 黄志斌. 2006. 首都圈地区横波分裂与地壳应力场特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 49(1): 189-196. Lai Y G, Liu Q Y, Chen J H, Liu J, Li S C, Guo B, Huang Z B. 2006. Shear wave splitting and the features of the crustal stress field in the Capital Circle[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 49(1): 189-196 (in Chinese).
雷军, 王培德, 姚陈, 陈运泰. 1997. 云南剑川近场横波特征及其与构造的关系[J]. 地球物理学报, 40(6): 791-801. Lei J, Wang P D, Yao C, Chen Y T. 1997. The near-field shear wave splitting and its relation with structure in Jianchuan, Yunnan Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 40(6): 791-801 (in Chinese).
李白基, 秦嘉政, 钱晓东. 2002. 1995年武定6.5级地震余震的S波分裂[J]. 地震研究, 25(1): 108-114. Li B J, Qin J Z, Qian X D. 2002. Shear-wave splitting of the aftershocks for the 1995 earthquake of Yunnan Wuding[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 25(1): 108-114 (in Chinese).
刘巍, 赵新平, 安卫平, 张开建. 1993. 山西地区的地壳应力场[J]. 山西地震, (3): 3-11. Liu W, Zhao X P, An W P, Zhang K J. 1993. The crustal stress field in Shanxi Province[J]. Earthquake Research in Shanxi, (3): 3-11 (in Chinese).
钱晓东, 李白基, 秦嘉政. 2002. 2000年云南姚安MS6.5地震余震序列S波分裂研究[J]. 中国地震, 18(2): 157-165. Qian X D, Li B J, Qin J Z. 2002. Study on shear wave splitting for sequence of the aftershocks of Yao'an MS6.5 earthquake in Yunnan[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 18(2): 157-165 (in Chinese).
石玉涛, 高原, 吴晶, 罗艳, 苏有锦. 2006. 云南地区地壳介质各向异性: 快剪切波偏振特性[J]. 地震学报, 28(6): 574-585. Shi Y T, Gao Y, Wu J, Luo Y, Su Y J. 2006. Seiemic anisotropy of the crust in Yunnan, China: Polarizations of fast shear-waves[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 28(6): 574-585 (in Chinese).
孙勇, 郑斯华. 1993. 唐山地区剪切波分裂研究[J]. 中国地震, 9(1): 61-67. Sun Y, Zheng S H. 1993. On shear wave splitting in Tangshan region[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 9(1): 61-67 (in Chinese).
太龄雪, 高原, 曹凤娟, 石玉涛, 吴晶, 焦明若. 2008. 辽宁1999年岫岩地震的剪切波分裂特征[J]. 地震学报, 30(4): 340-354. Tai L X, Gao Y, Cao F J, Shi Y T, Wu J, Jiao M R. 2008. Shear-wave splitting before and after the 1999 Xiuyan earthquake in Liaoning, China[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 30(4): 340-354 (in Chinese).
王凯英, 马瑾, 刁桂苓, Yu Rebetsky, 王晓山, 闫小兵. 2012. 2001年昆仑山口西地震前后山西构造带的应力状态变化[J]. 地震地质, 34(4): 597-605. Wang K Y, Ma J, Diao G L, Rebetsky Y, Wang X S, Yan X B. 2012. Stress change of Shanxi tectonic belt related to the 2001 MS8.1 Kunlun earthquake[J]. Seismology and Geology, 34(4): 597-605 (in Chinese).
王新岭, 刘杰, 张国民, 马宏生, 王辉. 2006. 2000年姚安地震余震序列的剪切波分裂研究[J]. 地震学报, 28(2): 119-131. Wang X L, Liu J, Zhang G M, Ma H S, Wang H. 2006. Study on shear wave splitting in the aftershock region of the Yao'an earthquake in 2000[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 28(2): 119-131 (in Chinese).
吴晶, 高原, 陈运泰, 黄金莉. 2007. 首都圈西北部地区地壳介质地震各向异性特征初步研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 50(1): 209-220. Wu J, Gao Y, Chen Y T, Huang J L. 2007. Seismic anisotropy in the crust in northwestern capital area of China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 50(1): 209-220 (in Chinese).
杨国华, 王敏, 韩月萍, 杨春花, 王秀文, 郭跃宏. 1999. 山西地震带近期水平运动状态及活动性[J]. 地壳形变与地震, 19(4): 50-55. Yang G H, Wang M, Han Y P, Yang C H, Wang X W, Guo Y H. 1999. Present crustal horizontal movement and activity of Shanxi fault belt determined by GPS[J]. Crustal Deformation and Earthquake, 19(4): 50-55 (in Chinese).
姚陈, 王培德, 陈运泰. 1992. 卢龙地区S波偏振与上地壳裂隙各向异性[J]. 地球物理学报, 35(3): 305-315. Yao C, Wang P D, Chen Y T. 1992. Shear-wave polarization and crack induced anisotropy of upper crust in Lulong, North China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 35(3): 305-315 (in Chinese).
张玲, 梁向军, 赵晋泉, 董春丽, 张蕙. 2011. 山西数字测震台网监测能力及其构造意义[J]. 山西地震, (4): 21-24. Zhang L, Liang X J, Zhao J Q, Dong C L, Zhang H. 2011. Monitoring ability and tectonic significance of Shanxi Digital Seismic Network[J]. Earthquake Research in Shanxi, (4): 21-24 (in Chinese).
张学民, 束沛镒, 刁桂苓. 2003. 山西省部分台站下方S波速度结构研究及与地震关系探讨[J]. 地震学报, 25(4): 341-350. Zhang X M, Shu P Y, Diao G L. 2003. Study on S wave velocity structure under part stations in Shanxi Province[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 25(4): 341-350 (in Chinese).
Cochran E S, Vidale J E, Li Y G. 2003. Near-fault anisotropy following the Hector Mine earthquake[J]. J Geophys Res, 108(B9): 2436-2447.
Crampin S. 1978. Seismic-wave propagation through a cracked solid: Polarization as a possible dilatancy diagnostic[J]. Geophys J R astr Soc, 53(3): 467-496.
Crampin S. 1981. A review of wave motion in anisotropic and cracked elastic-media[J]. Wave Motion, 3(4): 343-391.
Crampin S, Volti T, Stefánsson R. 1999. A successfully stress-forecast earthquake[J]. Geophys J Int, 138(1): F1-F5.
Crampin S, Chastin S, Gao Y. 2003. Shear-wave splitting in a critical crust: Ⅲ. Preliminary report of multi-variable measurements in active tectonics[J]. J Appl Geophys, 54(3): 265-277.
Gao Y, Crampin S. 2004. Observations of stress relaxation before earthquakes[J]. Geophys J Int, 157(2): 578-582.
Gao Y, Wang P, Zheng S H, Wang M, Chen Y T, Zhou H. 1998. Temporal changes in shear-wave splitting at an isolated swarm of small earthquakes in 1992 near Dongfang, Hainan Island, southern China[J]. Geophys J Int, 135(1): 102-112.
Peng Z, Ben-Zion Y. 2004. Systematic analysis of crustal anisotropy along the Karadere-Duzce branch of the North Anatolian fault[J]. Geophys J Int, 159(1): 253-274.
Shih X R, Meyer R P. 1990. Observation of shear wave splitting from natural events: South Moat of Long Valley Caldera, California, June 29 to August 12, 1982[J]. J Geophys Res, 95(B7): 11179-11195.
Wu J, Crampin S, Gao Y, Hao P, Volti T, Chen Y T. 2006. Smaller source earthquakes and improved measuring techniques allow the largest earthquakes in Iceland to be stress forecast (with hindsight)[J]. Geophys J Int, 166(3): 1293-1298.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 张玲,王睿敏,李丽,王想. 太原盆地及邻区上地壳各向异性研究. 山西地震. 2025(01): 1-6+12 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王想,高原,吴鹏,周依,王时. 剪切波分裂揭示的华北克拉通中部造山带上地壳地震各向异性. 地球物理学报. 2022(07): 2503-2517 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 郭祥云,蒋长胜,王晓山,田鑫. 鄂尔多斯块体周缘中小地震震源机制及应力场特征. 大地测量与地球动力学. 2017(07): 675-685 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: