Study on crustal deformation characteristics before Xinjiang Yutian MS7.3 earthquake in 2014
-
摘要: 利用1999—2007年和2009—2013年两期GPS速度场资料, 采用最小二乘配置方法分别计算了2008年和2014年新疆两次于田MS7.3地震前新疆及周边地区的主应变率、 面应变率及最大剪应变率, 分析了该区域的变形动态特征, 并结合速度剖面分析方法给出了震源区的构造变形特征. 速度场及应变率场动态结果表明: 新疆天山地区的地壳变形特征整体表现为由南向北缩短, 相对运动速率表现为由南向北、 由西向东逐渐减小; 震源区东侧的左旋剪切变形明显大于西侧; 2008年与2014年两次于田MS7.3地震的震源区均处于拉张与挤压变形的过渡地带, 易于强地震的发生; 2008年于田MS7.3地震的张性兼有少量剪性破裂的发生使得阿尔金断裂的左旋剪切变形增强. GPS速度场剖面分析结果表明, 2014年于田MS7.3地震前震源区西侧的变形宽度大于东侧, 剪切应变积累程度西侧高于东侧. 综合分析认为, 震源周边构造区应变积累的差异性有利于强震的孕育, 2008年于田MS7.3地震对2014年于田MS7.3地震可能有促进作用.Abstract: This paper calculates the principal strain rate, plane strain rate and maximum shear strain rate in Xinjiang and its vicinity by using the least squares method with GPS data set during 1999—2007 and 2009—2013. The crustal tectonic deformation characteristics in this area before 2008 and 2014 Yutian MS7.3 earthquakes are also analyzed comprehensively. The dynamic results of velocity field and strain rate field indicate that the crust shortening decreases gradually from south to north and from west to east, suggesting that the sinistral shear deformation in the eastern side is significantly greater than that in the western side around focal area. The source areas of 2008 and 2014 MS7.3 Yutian earthquakes are located in the transitional zone of the tensile and compressive deformation, which is prone to occurrence of a great earthquake. The surface rupture in 2008 Yutian earthquake, which is mainly tensile with little shear component, strengthened the sinistral shear deformation of Altyn Tagh fault. The GPS velocity profiles show that the deformation width of western side is greater than that of the east in the hypocentral region before 2014 Yutian MS7.3 earthquake, consistent with the degree of shear strain accumulation. In conclusion, this difference between two sides in strain accumulation are easy for the nucleation process of 2014 Yutian earthquake. And it is inferred that the 2008 Yutian MS7.3 earthquake may play a role in promoting the 2014 Yutian MS7.3 earthquake.
-
Keywords:
- GPS /
- crustal deformation /
- GPS profile /
- strain accumulation
-
-
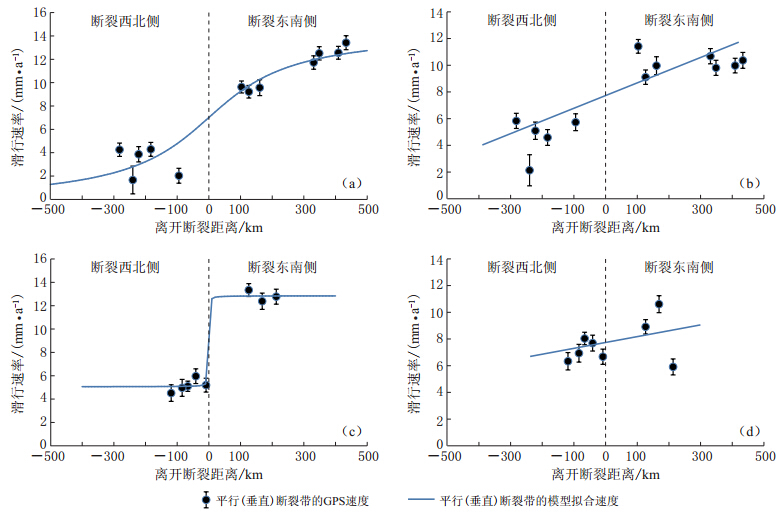
图 4 横跨断裂带的2009—2013年GPS站速度剖面和拟合结果(a)剖面A平行断裂带结果;(b)剖面A垂直断裂带结果;(c)剖面B平行断裂带结果;(d)剖面B垂直断裂带结果
Figure 4. GPS velocity profiles cross fault during 2009—2013, and model fitting results(a)Results of profile A(parallel component);(b)Results of profile A(vertical component);(c)Results of profile B(parallel component);(d)Results of profile B(vertical component)
-
洪顺英, 申旭辉, 单新建, 刘智荣, 戴娅琼, 荆凤. 2010. 基于升降轨ASAR的于田MS7.3级地震同震形变场信息提取与分析[J]. 国土资源遥感, 4(3): 98-102. Hong S Y, Shen X H, Shan X J, Liu Z R, Dai Y Q, Jing F. 2010. The calculation and analysis of the co-seismic deformation field of Yutian MS7.3 earthquake basing on the ascending and descending orbit ASAR data[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 4(3): 98-102 (in Chinese).
江在森, 刘经南. 2010. 应用最小二乘配置建立地壳运动速度场与应变场的方法[J]. 地球物理学报, 53(5): 1109-1117. Jiang Z S, Liu J N. 2010. The method in establishing strain field and velocity field of crustal movement using least squares collocation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 53(5): 1109-1117 (in Chinese).
江在森, 马宗晋, 牛安福, 张晓亮, 王双绪, 陈兵. 2003. GPS技术应用于中国地壳运动研究的方法及初步结果[J]. 地学前缘, 10(1): 71-79. Jiang Z S, Ma Z J, Niu A F, Zhang X L, Wang S X, Chen B. 2003. Approaches and preliminary results of crust movement researches based on the GPS in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 10(1): 71-79 (in Chinese).
李志海, 马宏生, 曲延军. 2009. 2008年3月21日新疆于田7.3级地震发震构造与震前地震活动特征研究[J]. 中国地震, 25(2): 199-205. Li Z H, Ma H S, Qu Y J. 2009. Study on seismogenic structure and seismic activity characteristics before the Yutian M7.3 earthquake on March 21, 2008, Xinjiang[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 25(2): 199-205 (in Chinese).
牛之俊, 游新兆, 杨少敏. 2007. 利用GPS分析天山现今地壳形变特征[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 27(2): 1-9. Niu Z J, You X Z, Yang S M. 2007. Analysis of contemporary crustal deformation characteristics with GPS data of Tianshan mountain[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 27(2): 1-9 (in Chinese).
王琪, 丁国瑜, 乔学军, 王晓强, 游新兆. 2000. 天山现今地壳快速缩短与南北地块的相对运动[J]. 科学通报, 45(14): 1543-1547. Wang Q, Ding G Y, Qiao X J, Wang X Q, You X Z. 2000. Crustal shortening in Tianshan area and relatively movement of north and south block[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 45(14): 1543-1547 (in Chinese).
王晓强, 李杰, 王琪, Alexander Z. 2005. 天山现今地壳运动的形变场分析[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 25(3): 63-68. Wang X Q, Li J, Wang Q, Alexander Z. 2005. Analysis of present-day crustal deformation of Tianshan[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 25(3): 63-68 (in Chinese).
魏文薪, 江在森, 武艳强, 赵静. 2012. 利用GPS数据研究川滇块体东边界主要断裂带运动特性[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 37(9): 1041-1044. Wei W X, Jiang Z S, Wu Y Q, Zhao J. 2012. Motion characteristics of major faults in east boundary of Sichuan-Yunnan Block obtained with GPS data[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 37(9): 1041-1044 (in Chinese).
武艳强, 江在森, 杨国华, 方颖, 王武星. 2009. 利用最小二乘配置球面上整体解算GPS应变场的方法及应用[J]. 地球物理学报, 52(7): 1707-1714. Wu Y Q, Jiang Z S, Yang G H, Fang Y, Wang W X. 2009. The application and method of GPS strain calculation in whole mode using least square collocation in sphere surface[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 52(7): 1707-1714 (in Chinese).
武艳强, 江在森, 杨国华, 赵静. 2012. 南北地震带北段近期地壳变形特征研究[J].武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 37(9): 1045-1048. Wu Y Q, Jiang Z S, Yang G H, Zhao J. 2012. Deformation characteristics of north section of North-South Seismic Zone in recent period [J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 37(9): 1045-1048 (in Chinese).
徐锡伟, 谭锡斌, 吴国栋, 陈建波, 沈军, 方伟, 宋和平. 2011. 2008年于田MS7.3地震地表破裂带特征及其构造属性讨论[J]. 地震地质, 33(2): 462-471. Xu X W, Tan X B, Wu G D, Chen J B, Shen J, Fang W, Song H P. 2011. Surface rupture features of the 2008 Yutian MS7.3 earthquake and its tectonic nature[J]. Seismology and Geology, 33(2): 462-471 (in Chinese).
徐锡伟, 于贵华. 2014. 新疆维吾尔自治区和田地区于田县(北纬36.1度, 东经82.5度)7.3级地震构造图[EB/OL]. [2014-03-01]. http://www.eq-igl.ac.cn/admin/upload/files/%E5%8F%91%E9%9C%87%E6%9E%84%E9%80%A0%E5%9B%BE(1).jpg. Xu X W, Yu G H. 2014. Yutian County, Hotan Prefecture, Xinjiang (latitude 36.1 degree, longitude 82.5 degree) 7.3 earthquake seismogenic structure diagram[EB/OL]. [2014-03-01]. http://www.eq-igl.ac.cn/admin/upload/files/%E5%8F%91%E9%9C%87%E6%9E%84%E9%80%A0%E5%9B%BE(1).jpg (in Chinese).
杨少敏, 李杰, 王琪. 2008. GPS研究天山现今变形与断层活动[J]. 中国科学: D辑, 38(7): 872-880. Yang S M, Li J, Wang Q. 2008. The deformation pattern and fault rate in the Tianshan Mountains inferred from GPS observations[J]. Science in China: Series D, 38(7): 872-880 (in Chinese).
Dong D, Herring T A, King R W. 1998. Estimating regional deformation from a combination of space and terrestrial geodetic data[J]. J Geophys Res, 72(4): 200-214.
Global Centroid Moment Tensor. 2008. Global CMT Catalog: Southern Xinjiang, China[EB/OL]. [2008-04-01]. http://www.globalcmt.org/cgi-bin/globalcmt-cgi-bin/CMT4/form? itype=ymd&yr=2008&mo=3&day=1&oyr=2008&omo=3&oday=30&jyr=1976&jday=1&ojyr=1976 &ojday=1&otype=nd&nday=30&lmw=6&umw=10&lms=6&ums=10&lmb=6&umb=10&llat=-90&ulat=90 &llon=-180&ulon=180&lhd=0&uhd=1000<s=-9999&uts=9999&lpe1=0&upe1=90&lpe2=0&upe2=90&list=0.
Herring T A, King R W, McClusky S C. 2006a. GAMIT Reference Manual, Release 10.3.Massa Chussetts Institute[CP/OL]. [2014-03-02]. http://www-gpsg.mit.edu/-simon/gtgk/docs.htm.
Herring T A, King R W, McClusky S C. 2006b. GLOBK Reference Manual, Release 10.3.Massa Chussetts Institute[CP/OL]. [2014-03-02]. http://www-gpsg.mit.edu/-simon/gtgk/docs.htm.
Meade B J, Hager B H. 2005. Block models of crustal motion in southern California constrained by GPS measurements[J]. J Geophys Res, 110(B3): B03403. doi:10.1029/2004JB003209.
USGS. 2008. M7.2-Xinjiang-Xizang border region (BETA)[EB/OL]. [2008-03-22]. http://comcat.cr.usgs.gov/earthquakes/eventpage/pde20080320223257930_10#scientific_moment-tensor.
USGS. 2014. M6.9-272 km ESE of Hotan, China (BETA)[EB/OL]. [2014-02-20]. http://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/eventpage/usc000mnvj#scientific_moment-tensor.
Wu Y Q, Jiang Z S, Yang G H, Wei W X, Liu X X. 2011. Comparison of GPS strain rate computing methods and their reliability[J]. Geophys J Int, 185(2): 703-717.





 下载:
下载: