Broadband ambient noise tomography in Yunnan Province
-
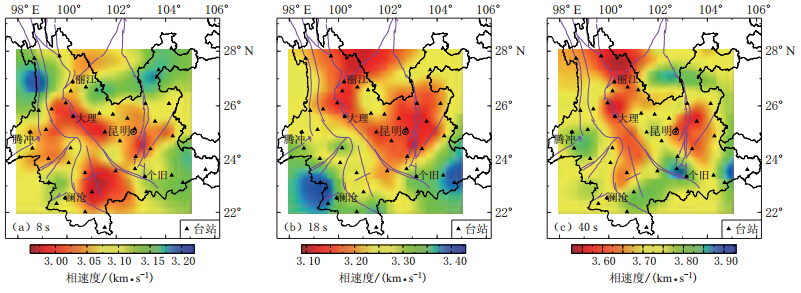
摘要: 选取云南省区域台网46个地震台从2007年11月—2009年10月的宽频带噪声数据, 通过互相关方法获得经验格林函数, 采用自适应时频分析方法获取相速度频散曲线, 并且反演得到8—40 s的相速度分布图. 研究结果表明: 云南地区短周期相速度低速异常与地表断裂带分布和沉积层厚度密切相关; 在短周期相速度分布图上, 红河断裂南北段呈现差异, 表明红河断裂南北段周边介质存在物性差异, 这可能是造成地震活动南北差异的主要原因; 长周期相速度分布图显示, 红河断裂和小江断裂带存在低速异常, 可能是切穿地壳的超壳断裂, 该低速异常可能与深部热作用有关; 红河断裂和小江断裂带交汇地区存在高速异常, 该高速异常体对川滇块体深部介质向南运动可能起到了阻挡的作用. 本文结果为下一步反演云南地区的三维剪切波速度结构奠定了基础.Abstract: In this paper, the Rayleigh wave empirical Green’s functions are retrieved from cross-correlation of the ambient noise data recorded by the 46 permanent stations of Yunnan Regional Seismic Network from November 2007 to October 2009. The regional phase velocities with periods from 8 s to 40 s are then inverted using the generalized Backus-Gilbert method. The results show that low-velocity anomalies at shorter periods associate with the faulting area and sedimentary basins. The difference between north and south across Honghe fault due to substantial variations at shorter period phase velocity maps coincides with distribution of earthquakes. As the period becomes longer, low-velocity anomalies around the Honghe fault and Xiaojiang fault are still visible, which suggests that they are probably correlated with the high heat flow from the deeper area and the faults have cut through the crust. The phase velocities at the junction of the Xiaojiang fault and Honghe fault exhibit high-velocity anomalies that maybe, to an extent, hinder the materials of Sichuan--Yunnan block moving towards the south. These phase velocity dispersion maps provide necessary information to construct a 3-D shear velocity model of the crust in Yunnan Province.
-
Keywords:
- ambient noise /
- phase velocity /
- surface wave tomography /
- crustal structure /
- Yunnan Province
-
-
图 1 云南地区区域构造略图(阚荣举,韩源,1992)及台站和地震分布图
F1: 怒江断裂; F2: 北澜沧江—昌宁—双江断裂; F3: 金沙江断裂; F4: 红河断裂; F5: 剑川断裂;F6: 程海断裂; F7: 元谋—绿汁江断裂; F8: 普渡河断裂; F9: 小江断裂带; F10: 畹町断裂; F11: 南汀河断裂; F12: 弥勒断裂; F13: 南澜沧江断裂. ① 滇缅泰板块; ② 印支板块; ③ 扬子板块; ④ 华南亚板块. Tc: 腾冲块体; Ba: 保山块体; Ls: 兰坪—思茅弧后盆地
Figure 1. Regional tectonic map of Yunnan area(after Kan,Han,1992) as well as locations of stations and earthquakes
F1: Nujiang fault; F2: Northern Lancangjiang- -Changning- -Shuangjiang fault; F3: Jinshajiang fault; F4: Honghe fault; F5: Jianchuan fault; F6: Chenghai fault; F7: Yuanmou- -Lüzhijiang fault; F8: Puduhe fault; F9: Xiaojiang fault zone; F10: W and ing fault; F11: Nantinghe fault; F12: Mile fault; F13: Southern Lancangjiang fault. ① Yunnan- -Myanmar- -Thail and block; ② Indo-China block; ③ Yangtze block; ④ South China block. Tc: Tengchong block; Ba: Baoshan block; Ls: Lanping- -Simao back arc basin. The triangle in the right panel indicates the station and the circle indicates the earthquake M≥5.0 occurred since the year AD 1500
图 3 台站对FUN-TNC的经验格林函数(a)及群速度频散曲线测量示意图(b)(台站FUN和TNC的位置分布见图 1)
Figure 3. Example of the empirical Green’s functions and dispersion analysis of the station pair FUN-TNC(locations of stations FUN and TNC,see Fig. 1)(a)The empirical Green’s functions of station pair FUN-TNC;(b)Group velocity dispersion curve measurements
表 1 相速度值的初始参考模型
Table 1 The initial reference phase velocity model at different periods

-
白志明, 王椿镛. 2003. 云南地区上部地壳结构和地震构造环境的层析成像研究[J]. 地震学报, 25(2): 117-127. Bai Z M, Wang C Y. 2003. Structure of the upper crust and tomography of seismic tectonic condition in Yunnan[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 25(2): 117-127 (in Chinese).
白志明, 王椿镛. 2004. 云南遮放-宾川和孟连-马龙宽角地震剖面的层析成像研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 47(2): 257-267. Bai Z M, Wang C Y. 2004. Tomography research of the Zhefang-Binchuan and Menglian-Malong wide-angle seismic profiles in Yunnan Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 47(2): 257-267 (in Chinese).
房立华, 吴建平, 吕作勇. 2009. 华北地区基于噪声的瑞利面波群速度层析成像[J]. 地球物理学报, 52(3): 663-671. Fang L H, Wu J P, Lü Z Y. 2009. Rayleigh wave group velocity tomography from ambient seismic noise in North China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 52(3): 663-671 (in Chinese).
高东辉, 陈永顺, 孟宪森, 张永刚, 唐有彩. 2011. 黑龙江地区背景噪声面波群速度层析成像[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(4): 1043-1051. Gao D H, Chen John Y, Meng X S, Zhang Y G, Tang Y C. 2011. Crustal and uppermost mantle structure of the Heilongjiang region from ambient noise tomography[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(4): 1043-1051 (in Chinese).
何正勤, 苏伟, 叶太兰. 2004a. 云南地区地壳中上部横波速度结构研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 47(5): 838-844. He Z Q, Su W, Ye T L. 2004a. S-wave velocity structure of the middle and upper crust in the Yunnan region[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 47(5): 838-844 (in Chinese).
何正勤, 苏伟, 叶太兰. 2004b. 云南地区的短周期面波相速度层析成像研究[J]. 地震学报, 26(6): 583-590. He Z Q, Su W, Ye T L. 2004b. Seismic tomography of Yunnan region using short period surface wave phase velocity[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 26(6): 583-590 (in Chinese).
胡鸿翔, 陆涵行, 王椿镛, 何正勤, 朱良保, 颜其中, 樊跃新, 张国庆, 邓英娥. 1986. 滇西地区地壳结构的爆破地震研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 29(2): 133-144. Hu H X, Lu H X, Wang C Y, He Z Q, Zhu L B, Yan Q Z, Fan Y X, Zhang G Q, Deng Y E. 1986. Explosion investigation of the crustal structure in western Yunnan Province[J]. Acta Geophysica Sinica, 29(2): 133-144 (in Chinese).
胡家富, 苏有锦, 朱雄关, 陈赟. 2003. 云南的地壳S波速度与泊松比结构及其意义[J]. 中国科学: D辑, 33(8): 714-722. Hu J F, Su Y J , Zhu X G, Chen Y. 2005. S-wave velocity of the crust and the structure of Poisson ratio in Yunnan and meanings[J]. Science in China: Series D, 48(2): 210-218.
阚荣举, 林中洋. 1986. 云南地壳上地幔构造的初步研究[J]. 中国地震, 2(4): 50-61. Kan R J, Lin Z Y. 1986. A preliminary study on crustal and upper mantle structures in Yunnan[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 2(4) : 50-61 (in Chinese).
阚荣举, 韩源. 1992. 云南遮放至马龙地学断面说明书[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 1-20. Kan R J, Han Y. 1992. The Specification of Geoscience Transect from Zhefang to Malong, Yunnan Province[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press: 1-20 (in Chinese).
李昱, 姚华建, 刘启元, 陈九辉, van der Hilst R D, 李顺成, 黄慧, 郭飚, 王峻, 齐少华. 2010. 川西地区台阵环境噪声瑞利波相速度层析成像[J]. 地球物理学报, 53(4): 842-852. Li Y, Yao H J, Liu Q Y, Chen J H, van der Hilst R D, Li S C, Huang H, Guo B, Wang J, Qi S H. 2010. Phase velocity array tomography of Rayleigh waves in western Sichuan from ambient seismic noise[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 53(4): 842-852 (in Chinese).
林中洋, 胡鸿翔, 张文彬, 章惠芬, 何正勤, 林真明, 邱陶兴. 1993. 滇西地区地壳上地幔速度结构特征的研究[J]. 地震学报, 15(4): 427-440. Lin Z Y, Hu H X, Zhang W B, Zhang H F, He Z Q, Lin Z M, Qiu T X. 1993. A study on velocity structure of the crust and upper mantle in western Yunnan region[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 15(4): 427-440 (in Chinese).
楼海, 王椿镛, 皇甫岗, 秦嘉政. 2002. 云南腾冲火山区上部地壳三维地震速度层析成像[J]. 地震学报, 24(3): 243-251. Lou H, Wang C Y, Huangfu G, Qin J Z. 2002. Three-dimensional seismic velocity tomography of the upper crust in Tengchong volcanic area, Yunnan Province[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 24(3): 243-251 (in Chinese).
毛玉平, 韩新民. 2003. 云南地区强震(M≥6)研究[M]. 昆明: 云南科技出版社: 1-10. Mao Y P, Han X M. 2003. The Research of Strong Earthquakes (M≥6) in Yunnan[M]. Kunming: Yunnan Science & Technology Press: 1-10 (in Chinese).
潘佳铁, 吴庆举, 李永华, 张风雪, 张广成. 2011. 华北地区瑞雷面波相速度层析成像[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(1): 67-76. Pan J T , Wu Q J, Li Y H, Zhang F X, Zhang G C. 2011. Rayleigh wave tomography of the phase velocity in North China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(1): 67-76 (in Chinese).
王椿镛, W D Mooney, 王溪莉, 吴建平, 楼海, 王飞. 2002. 川滇地区地壳上地幔三维速度结构研究[J]. 地震学报, 24(1): 1-16. Wang C Y, Mooney W D, Wang X L, Wu J P, Lou H, Wang F. 2002. Study on velocity structure of crust and upper mantle in Sichuan-Yunnan region, China[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 24(1): 1-16 (in Chinese).
吴建平, 明跃红, 王椿镛. 2001. 云南数字地震台站下方的S波速度结构研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 44(2): 228-237. Wu J P, Ming Y H, Wang C Y. 2001. The S wave velocity structure beneath digital seismic stations of Yunnan Province inferred from teleseismic receiver function modeling[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 44(2): 228-237 (in Chinese).
吴建平, 杨婷, 王未来, 明跃红, 张天中. 2013. 小江断裂带周边地区三维P波速度结构及其构造意义[J]. 地球物理学报, 56(7): 2257-2267. Wu J P, Yang T, Wang W L, Ming Y H, Zhang T Z. 2013. Three dimensional P-wave velocity structure around Xiaojiang fault system and its tectonic implications[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 56(7): 2257-2267 (in Chinese).
熊绍柏, 滕吉文, 尹周勋, 赖明惠, 黄一平. 1986. 攀西构造带南部地壳上地幔结构的爆炸地震研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 29(3): 235-244. Xiong S B, Teng J W, Yin Z X, Lai M H, Huang Y P. 1986. Explosion seismological study of the structure of the crust and upper mantle at southern part of the Panxi tectonic belt[J]. Acta Geophysica Sinica, 29(3): 235-244 (in Chinese).
胥颐, 刘建华, 刘福田, 宋海斌, 郝天珧, 江为为. 2003. 哀牢山-红河断裂带及其邻区的地壳上地幔结构[J]. 中国科学: D辑, 33(12): 1201-1208. Xu Y, Liu J H, Liu F T, Song H B, Hao T Y, Jiang W W. 2005. Crust and upper mantle structure of the Ailaoshan-Red River fault zone and adjacent regions[J]. Science in China: Series D, 48(2): 156-164.
曾融生, 孙为国. 1992. 青藏高原岩石圈及其东部邻区的地震活动性和震源机制以及高原物质东流的讨论[J]. 地震学报, 14(增刊): 523-533. Zeng R S, Sun W G. 1993. Seismicity and focal mechanism in Tibetan Plateau and its implications to lithospheric flow[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 6(2): 261-287.
张智, 赵兵, 张晰, 刘财. 2006. 云南思茅-中甸地震剖面的地壳结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 49(5): 1377-1384. Zhang Z, Zhao B, Zhang X, Liu C. 2006. Crustal structure beneath the wide angle seismic profile between Simao and Zhongdian in Yunnan[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 49(5): 1377-1384 (in Chinese).
张智, 陈赟, 李飞. 2008. 利用地震面波频散重建川滇地区壳幔S波速度[J]. 地球物理学报, 51(4): 1114-1122. Zhang Z, Chen Y, Li F. 2008. Reconstruction of the S-wave velocity structure of crust and mantle from seismic surface wave dispersion in Sichuan-Yunnan region[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 51(4): 1114-1122 (in Chinese).
张晓曼, 胡家富, 胡毅力, 杨海燕, 陈佳, 彭恒初, 文丽敏. 2011. 云南壳幔S波速度结构与强震的构造背景[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(5): 1222-1232. Zhang X M, Hu J F, Hu Y L, Yang H Y, Chen J, Peng H C, Wen L M. 2011. The S-wave velocity structure in the crust and upper mantle as well as the tectonic setting of strong earthquake beneath Yunnan region[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(5): 1222-1232 (in Chinese).
张中杰, 白志明, 王椿镛, 滕吉文, 吕庆田, 李继亮, 刘一峰, 刘振宽. 2005a. 三江地区地壳结构及动力学意义: 云南遮放-宾川地震反射/折射剖面的启示[J]. 中国科学: D辑, 35(4): 314-319. Zhang Z J, Bai Z M, Wang C Y, Teng J W, Lü Q T, Li J L, Liu Y F, Liu Z K. 2005a. The crustal structure under Sanjiang and its dynamic implications: Revealed by seismic reflection/refraction profile between Zhefang and Binchuan, Yunnan[J]. Science in China: Series D, 48(9): 1329-1336.
张中杰, 白志明, 王椿镛, 吕庆田, 滕吉文, 李继亮, 孙善学, 王新征. 2005b. 冈瓦纳型和扬子型地块地壳结构: 以滇西孟连-马龙宽角反射剖面为例[J]. 中国科学: D辑, 35(5): 387-392. Zhang Z J, Bai Z M, Wang C Y, Teng J W, Lü Q T, Li J L, Sun S X, Wang X Z. 2005b. Crustal structure of Gondwana- and Yangtze-typed blocks: An example by wide-angle seismic profile from Menglian to Malong in western Yunnan[J]. Science in China: Series D, 48(11): 1828-1836.
周龙泉, 刘杰, 苏有锦, 马宏生, 周俊杰. 2009. 利用S波高频衰减参数对云南地区地壳Q值成像[J]. 地球物理学报, 52(6): 1500-1507. Zhou L Q, Liu J, Su Y J, Ma H S, Zhou J J. 2009. Tomography for Q of Yunnan region from high-frequency attenuation of S wave[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 52(6): 1500-1507 (in Chinese).
Backus G, Gilbert F. 1968. Resolving power of gross earth data[J]. Geophys J R astr Soc, 16(2): 169-205.
Bensen G D, Ritzwoller M H, Shapiro N M. 2007a. Broad-band ambient noise surface wave tomography across the United States[J]. J Geophys Res, 113(B5): B05306.
Bensen G D, Ritzwoller M H, Barmin M P, Levshin A L, Lin F, Moschetti M P, Shapiro N M, Yang Y. 2007b. Processing seismic ambient noise data to obtain reliable broad-band surface wave dispersion measurements[J]. Geophys J Int, 169(3): 1239-1260.
Bensen G D, Ritzwoller M H, Yang Y. 2009. A 3D velocity model of the crust and uppermost mantle beneath the United States from ambient seismic noise[J]. Geophys J Int, 177(3): 1177-1196.
Cho K H, Herrmann R B, Ammon C J, Lee K. 2007. Imaging the upper crust of the Korean Peninsula by surface-wave tomography[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 97(18): 198-207.
Ditmar P G, Yanovskaya T B. 1987. Generalization of Backus-Gilbert method for estimation of lateral variations of surface wave velocities[J]. Phys Solid Earth, Izvestia Acad Sci USSR, 23(6): 470-477.
Guo Z, Gao X, Yao H J, Li J, Wang W M. 2009. Midcrustal low-velocity layer beneath the central Himalaya and southern Tibet revealed by ambient noise array tomography[J]. Geochem Geophy Geosyst,10(5): Q05007. doi:10.1029/2009GC002458.
Huang J L, Zhao D P, Zheng S H. 2002. Lithospheric structure and its relationship to seismic and volcanic activity in southwest China[J]. J Geophys Res, 107(B10): 2255.
Lei J S, Zhao D P, Su Y J. 2009. Insight into the origin of the Tengchong intraplate volcano and seismotectonics in southwest China from local and teleseismic data[J]. J Geophys Res, 114(B5): B05302.
Lev E, Long M D, van der Hilst R D. 2006. Seismic anisotropy in eastern Tibet from shear-wave splitting reveals changes in lithosphere deformation[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 251(3): 293-304.
Levshin A L, Ritzwoller M H. 2001. Automated detection, extraction, and measurement of regional surface waves[J]. Pure Appl Geophys, 158(8): 1531-1545.
Li H Y, Su W, Wang C Y, Huang Z X. 2009. Ambient noise Rayleigh wave tomography in western Sichuan and eastern Tibet[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 282(1/2/3/4): 201-211.
Lin F, Moschetti M P, Ritzwoller M H. 2008. Surface wave tomography of the western United States from ambient seismic noise: Rayleigh and Love wave phase velocity maps[J]. Geophys J Int, 173(1): 281-298.
Lin F C, Ritzwoller M H, Townend J, Bannister S, Savage M K. 2007. Ambient noise Rayleigh wave tomography of New Zealand[J]. Geophys J Int, 170(2): 649-666.
Lobkis O I, Weaver R L. 2001. On the emergence of the Green's function in the correlations of a diffuse field[J]. J Acoust Soc Am, 110(6): 3011-3017.
Royden L H, Burchfiel B C, King R W, Wang E, Chen Z L, Shen F, Liu Y P. 1997. Surface deformation and lower crustal flow in eastern Tibet[J]. Science, 276(5313): 788-790.
Saygin E, Kennett B L N. 2010. Ambient seismic noise tomography of Australian continent[J]. Tectonophysics, 481(1/2/3/4): 116-125.
Shapiro N M, Campillo M, Stehly L, Ritzwoller M H. 2005. High resolution surface wave tomography from ambient seismic noise[J]. Science, 307(5715): 1615-1618.
Shen Z K, Lü J N, Wang M, Bürgmann R. 2005. Contemporary crustal deformation around the southeast borderland of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. J Geophys Res, 110(B11): B11409.
Wang C Y, Huangfu G. 2004. Crustal structure in Tengchong volcanic-geothermal area, western Yunnan, China[J]. Tectonophysics, 380(1/2): 69-87.
Wapenaar K. 2004. Retrieving the elastodynamic Green's function of an arbitrary inhomogeneous medium by cross correlation[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 93(25): 254301.
Wei W, Sun R M, Shi Y L. 2010. P-wave tomographic images beneath southeastern Tibet: Investigating the mechanism of the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 53(9): 1252-1259.
Yang Y J, Ritzwoller M H, Levshin A L, Shapiro N M. 2007. Ambient noise Rayleigh wave tomography across Europe[J]. Geophys J Int, 168(1): 259-274.
Yang Y J, Li A B, Ritzwoller M H. 2008. Crustal and uppermost mantle structure in southern Africa revealed from ambient noise and teleseismic tomography[J]. Geophys J Int, 174(1): 235-248.
Yanovskaya T B, Ditmar P G. 1990. Smoothness criteria in surface wave tomography[J]. Geophys J Int, 102(1): 63-72.
Yao H J, van der Hilst R D, de Hoop M V. 2006. Surface-wave tomography in SE Tibet from ambient seismic noise and two-station analysis: Ⅰ .Phase velocity maps[J]. Geophys J Int, 166(2): 732-744.
Yao H J, Beghein C, van der Hilst R D. 2008. Surface-wave tomography in SE Tibet from ambient seismic noise and two-station analysis: Ⅱ .Crustal and upper-mantle[J]. Geophys J Int, 173(1): 205-219.
Zheng S H, Sun X L, Song X D, Yang Y, Ritzwoller M H. 2008. Surface wave tomography of China from ambient seismic noise correlation[J]. Geochem Geophy Geosyst, 9(5): Q05020. doi:10.1029/2008GC001981.
Zheng Y, Shen W, Zhou L, Yang Y, Xie Z, Ritzwoller M H. 2011. Crust and uppermost mantle beneath the North China Craton, northeastern China, and the Sea of Japan from ambient noise tomography[J]. J Geophys Res, 116(B12): B12312.
Zhou L, Xie J, Shen W, Zheng Y, Yang Y, Shi H, Ritzwoller M H. 2012. The structure of the crust and uppermost mantle beneath South China from ambient noise and earthquake tomography[J]. Geophys J Int, 189(3): 1565-1583.





 下载:
下载: