Reliability research of earthquake early warning information
-
摘要: 提出了一种地震预警信息可靠度检验方法. 针对地震预警系统对信息的高度时效性及准确性要求, 并结合其应用特点, 从地震动记录信噪比、 特征参数相容性、 特征参数协调性及地震预警定位结果可靠性等4个方面对地震预警信息的综合可靠度进行探讨, 并分别提出了相应的可靠度定量计算方法. 利用日本KiK-net台网记录的444个地震事件共4737条三分向加速度记录对上述4个指标参数及综合可靠度指标参数的验证结果表明, 采用本方法有助于提高地震预警信息发布的准确性和可靠性, 减少“漏报”及“误报”事件的发生.Abstract: The earthquake early warning system (EEWs) has highly requirements for information’s timeliness and accuracy. In this paper, we proposed an information reliability test method for EEWs. Based on the EEWs’ application features, this paper proposed four information reliability tests, which are signal to noise ratio (SNR) test, characteristic parameters (such as τc and Pd) compatibility test, characteristic parameters coordination test and EEW location reliability test. For each test, a quantitative calculation formula is defined, and then the reliability of the entire information can be calculated. 4737 three-component acceleration records of 444 seismic events from KiK-net in Japan were used in order to test and verify the applicability of our method. The results show that, by taking the reliability tests method proposed in this paper, the accuracy and reliability of the EEW information are improved, and then “missed alarms” or “false alarms” are reduced.
-
Keywords:
- earthquake early warning /
- signal to noise ratio /
- compatibility /
- coordination
-
-
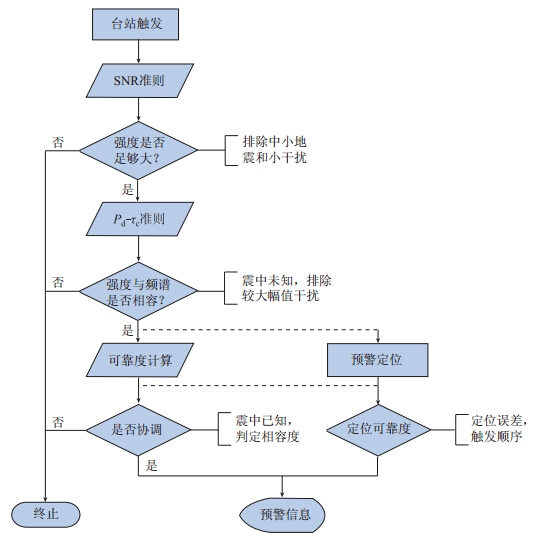
图 3 地震预警信息可靠度检验方法示意图
Figure 3. Schematic diagram of reliability test method for earthquake early warning information used in this paper SNR means the signal to noise ratio,τc and Pd are the ground-motion period and the high-pass filtered displacement amplitude from the initial 3 s of the P waveforms,respectively
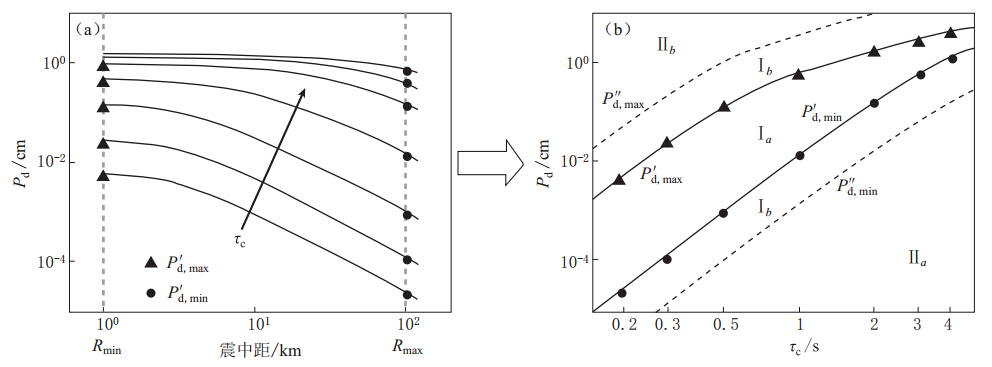
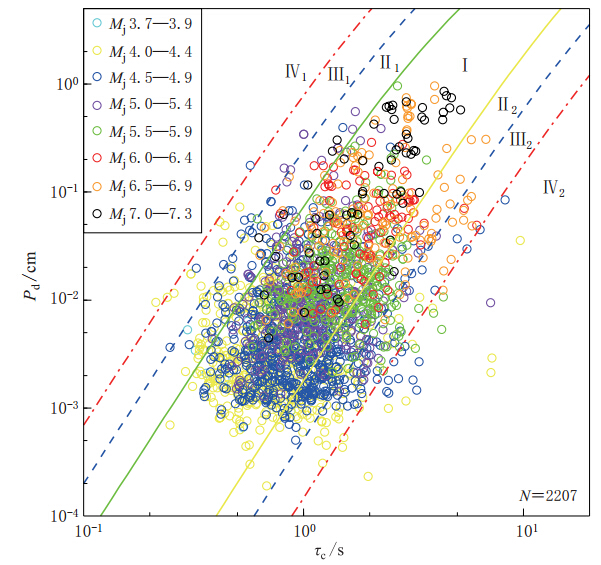
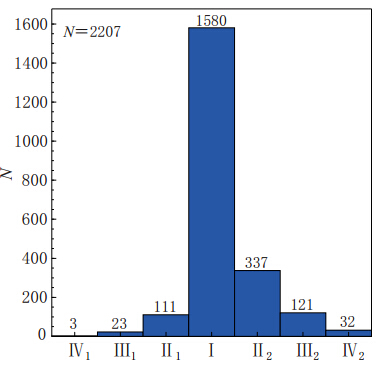
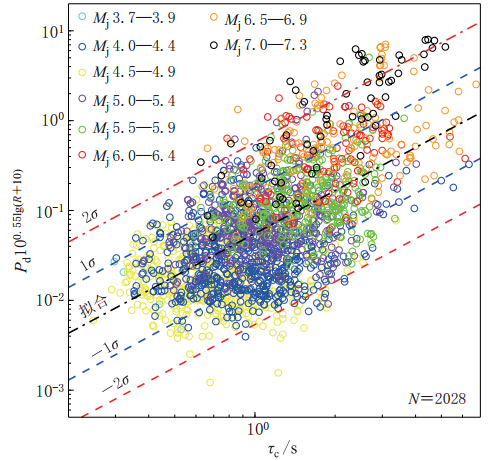
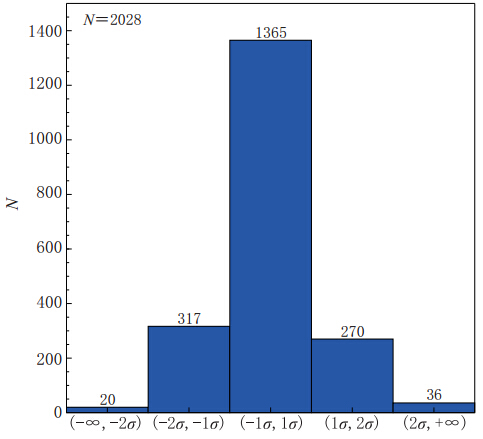
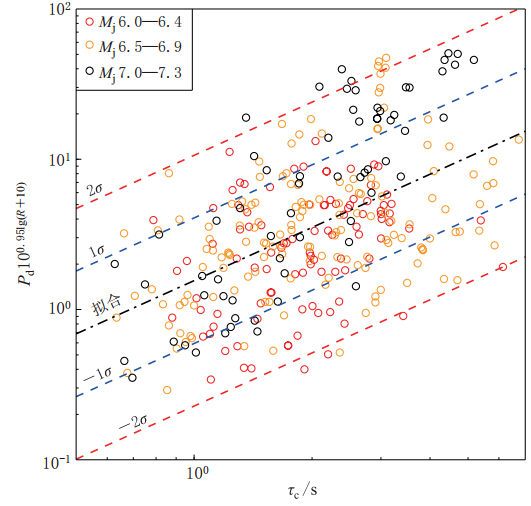
图 9 τc-Pd准则推导过程示意图(引自Böse等,2009)(a)由PGA衰减关系转换得到的Pd随震级和震中距的衰减关系;(b)由PGA衰减关系转换得到的Pd与τc的相容性检验关系
Figure 9. Schematic diagram of derivation of τc-Pd criteria(after Böse et al,2009)(a)Attenuation relationship of Pd with magnitude and epicentral distance based on PGV attenuation relationship;(b)Compatibility test relationship between Pd and τc based on PGV attenuation relationship
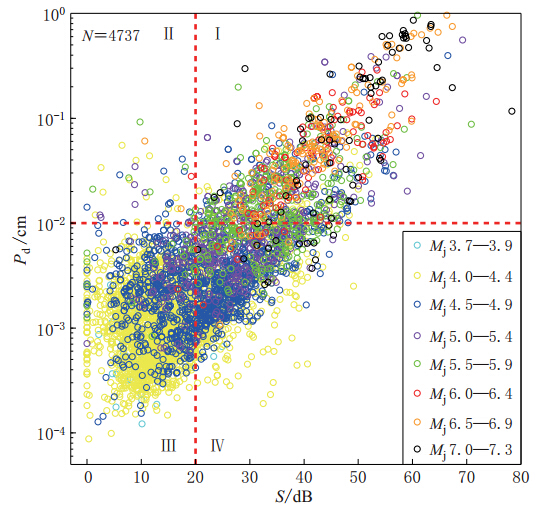
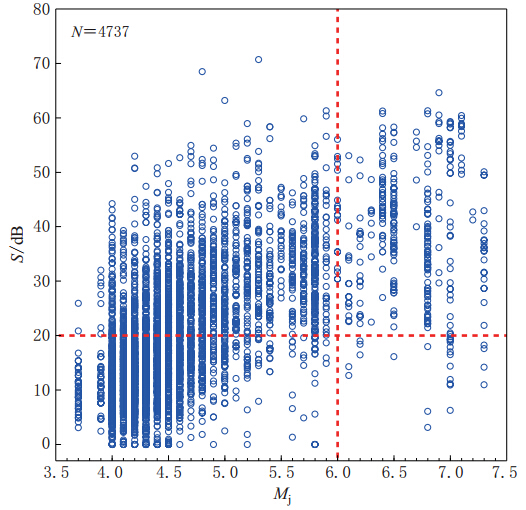
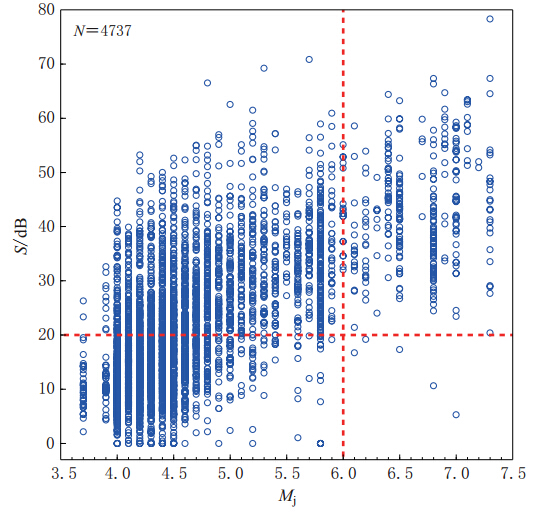
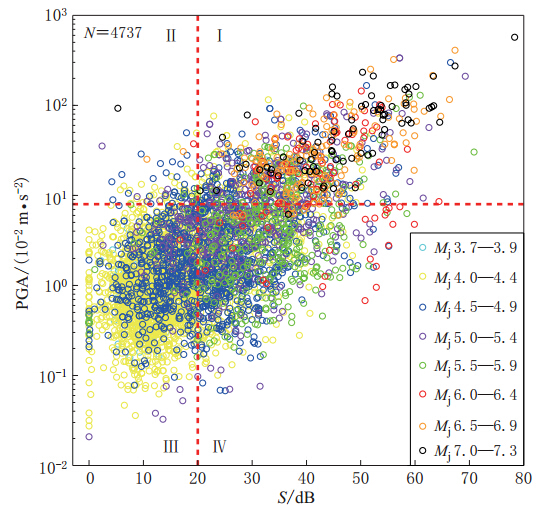
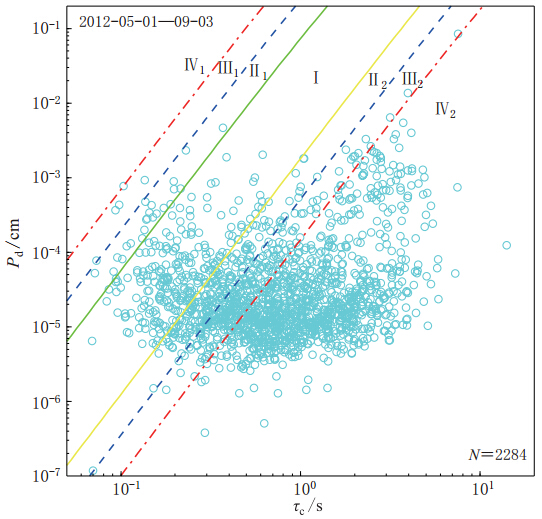
图 10 τc-Pd准则可靠度检验结果图中绿色实线和黄色实线分别表示由本文所用记录确定的震中距为0 km和100 km的两条控制界线,蓝色虚线和红色虚线分别表示±1σ和±2σ的扩展界线
Figure 10. Test result of reliability by using τc-Pd criteria The green and yellow solid lines represent boundary lines for the epicentral distance of 0 km and 100 km,respectively,which were determined by the data used in this paper. Blue and red dashed lines are extended lines with a st and ard deviation of ±1σ and ±2σ,respectively
-
金星, 张红才, 李军, 韦永祥, 马强. 2012a. 地震预警连续定位方法研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 55(3): 925-936. Jin X, Zhang H C, Li J, Wei Y X, Ma Q. 2012a. Research on continuous location method used in earthquake early warning system[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 55(3): 925-936 (in Chinese).
金星, 张红才, 李军, 韦永祥, 马强. 2012b. 地震预警震级确定方法研究[J]. 地震学报, 34(5): 593-610. Jin X, Zhang H C, Li J, Wei Y X, Ma Q. 2012b. Research on earthquake early warning magnitude estimation[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 34(5): 593-610 (in Chinese).
李山有, 马强, 金星, 宋晋东. 2004. 地震预警系统与智能应急控制系统研究[J]. 世界地震工程, 20(4): 21-26. Li S Y, Ma Q, Jin X, Song J D. 2004. Study on earthquake early warning system and intelligent emergency controlling system[J]. World Earthquake Engineering, 20(4): 21-26 (in Chinese).
马强. 2008. 地震预警技术研究与应用[D]. 哈尔滨: 中国地震局工程力学研究所: 80-121. Ma Q. 2008. Study and Application on Earthquake Early Warning[D]. Harbin: Institute of Engineering Mechanics, China Earthquake Administration: 80-121 (in Chinese).
万柯松, 倪四道, 曾祥方, Paul Sommerville. 2009. 汶川大地震中的应急地震学[J]. 中国科学: D辑, 39(1): 1-10. Wan K S, Ni S D, Zeng X F, Paul S. 2009. Real-time seismology in great Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Science in China: Series D, 39(1): 1-10 (in Chinese).
袁志祥, 单修政, 徐世芳, 李金正, 李娟, 乔迎春. 2007. 地震预警技术综述[J].自然灾害学报, 16(6): 216-223. Yuan Z X, Shan X Z, Xu S F, Li J Z, Li J, Qiao Y C. 2007. An overview of earthquake early warning technology[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 16(6): 216-223 (in Chinese).
张红才. 2013. 地震预警系统关键技术研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 中国地震局工程力学研究所: 21-70. Zhang H C. 2013. Study of Key Technologies in Earthquake Early Warning System[D]. Harbin: Institute of Engineering Mechanics, China Earthquake Administration: 21-70 (in Chinese).
张红才, 金星, 李军, 韦永祥. 2011. 地震预警定位方法研究[J]. 地震工程与工程振动, 31(3): 168-176. Zhang H C, Jin X, Li J, Wei Y X. 2011. Research on earthquake early warning location methods[J]. Journal of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 31(3): 168-176 (in Chinese).
张红才, 金星, 李军, 韦永祥, 马强. 2012. 地震预警震级计算方法研究综述[J]. 地球物理学进展, 27(2): 464-474. Zhang H C, Jin X, Li J, Wei Y X, Ma Q. 2012. Review on magnitude estimation methods applied to earthquake early warning systems[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 27(2): 464-474 (in Chinese).
张红才, 金星, 李军, 韦永祥, 朱海燕. 2013. 地震预警系统研究及应用进展综述[J]. 地球物理学进展, 28(2): 706-719. Zhang H C, Jin X, Li J, Wei Y X, Zhu H Y. 2013. Progress of research and application of earthquake early warning system (EEWs)[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 28(2): 706-719 (in Chinese).
Alcik H, Ozel O, Apaydin N, Erdik M. 2009. A study on warning algorithms for Istanbul earthquake early warning system[J]. Geophys Res Lett, 36(5): L00B05. doi:10.1029/2008GL036659.
Allen R M, Gasparini P, Kamigaichi O, Böse M. 2009. The status of earthquake early warning around the world: An introductory overview[J]. Seismol Res Lett, 80(5): 682-695.
Böse M, Hauksson E, Solanki K, Kanamori H, Wu Y M, Heaton T. 2009. A new trigger criterion for improved real-time performance of onsite earthquake early warning in southern California[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 99(2A): 897-905.
Cua G, Fischer M, Heaton T, Wiemer S. 2009. Real-time performance of the Virtual Seismologist earthquake early warning algorithm in southern California[J]. Seismol Res Lett, 80(5): 740-747.
Erdik M, Fahjan Y, Ozel O, Alcik H, Mert A, Gul M. 2003. Istanbul earthquake rapid response and the early warning system[J]. Bull Earthq Eng, 1(1): 157-163.
Espinosa-Aranda J M, Jiménez A, Contreras O, Ibarrola G, Ortega R. 1995. Mexico city seismic alert system[J]. Seismol Res Lett, 66(6): 42-53.
Goltz J D, Flores P J. 1997. Real-time earthquake early warning and public policy: A report on Mexico City's Sistema de Alerta Sísmica[J]. Seismol Res Lett, 68(5): 727-733.
Hsiao N C, Wu Y M, Shin T C, Zhao L, Teng T L. 2009. Development of earthquake early warning system in Taiwan[J]. Geophys Res Lett, 36(5): L00B02. doi:10.1029/2008GL036596.
Iannaccone G, Zollo A, Elia L, Convertito V, Satriano C, Martino C, Festa G, Lancieri M, Bobbio A, Stabile T A, Vassallo M, Emolo A. 2010. A prototype system for earthquake early-warning and alert management in southern Italy[J]. Bull Earthq Eng, 8(5): 1105-1129.
Iglesias A, Singh S K, Santoyo M A, Pacheco J, Ordaz M. 2007. The seismic alert system for Mexico city: An evaluation of its performance and a strategy for its improvement[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 97(5): 1718-1729.
Kamigaichi O. 2004. JMA earthquake early warning[J]. Journal of JAEE, 4(3): 134-137.
Kamigaichi O, Saito M, Doi K, Matsumori T, Tsukada S, Takeda K, Shimoyama T, Nakamura K, Kiyomoto M, Watanabe Y. 2009. Earthquake early warning in Japan: Warning the general public and future prospects[J]. Seismol Res Lett, 80(5): 717-726.
Kanno T, Narita A, Morikawa N, Fujiwara H, Fukushima Y. 2006. A new attenuation relation for strong ground motion in Japan based on recorded data[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 96(3): 879-897.
Nakamura Y, Saita J. 2007. UrEDAS, the earthquake warning system: Today and tomorrow[G]//Earthquake Early Warning Systems. Heidelberg: Springer: 249-281.
Peng H S, Wu Z L, Wu Y M, Yu S M, Zhang D N, Huang W H. 2011. Developing a prototype earthquake early warning system in the Beijing capital region[J]. Seismol Res Lett, 82(3): 394-403.
Shieh J T, Wu Y M, Allen R M. 2008. A comparison of τc and τPmax for magnitude estimation in earthquake early warning[J]. Geophys Res Lett, 35(20): L20301. doi:10.1029/2008GL035611.
Suárez G, Novelo D, Mansilla E. 2009. Performance evaluation of the seismic alert system (SAS) in Mexico city: A seismological and a social perspective[J]. Seismol Res Lett, 80(5): 707-716.
Voronoi G.1908.Nouvelles applications des paramètres continus à la théorie des formes quadratiques.Deuxième mémoire. Recherches sur les parallélloèdres primitifs[J]. Journal für die Reine und Angewandte Mathematik, 134: 198-287.
Wen K L, Shin T Z, Wu Y M, Hsiao N C, Wu B R. 2009. Earthquake early warning technology progress in Taiwan[J]. Journal of Disaster Research, 4(4): 202-210.
Wenzel F, Oncescu M C, Baur M, Fiedrich F. 1999. An early warning system for Bucharest[J]. Seismol Res Lett, 70(2): 161-169.
Wu Y M, Kanamori H. 2005a. Rapid assessment of damage potential of earthquakes in Taiwan from the beginning of P waves[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 95(3): 1181-1185.
Wu Y M, Kanamori H. 2005b. Experiment on an onsite early warning method for the Taiwan early warning system[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 95(1): 347-353.
Wu Y M, Zhao L. 2006. Magnitude estimation using the first three seconds P-wave amplitude in earthquake early warning[J]. Geophys Res Lett, 33(16): L16312. doi:10.1029/2006GL026871.
Wu Y M, Yen H Y, Zhao L, Huang B S, Liang W T. 2006. Magnitude determination using initial P waves: A single-station approach[J]. Geophys Res Lett, 33(5): L05306. doi:10.1029/2005GL025395.
Wu Y M, Kanamori H, Allen R M, Hauksson E. 2007. Determination of earthquake early warning parameters, τc and Pd, for southern California[J]. Geophys J Int, 170(2): 711-717.
Wurman G, Allen R M, Lombard P. 2007. Toward earthquake early warning in northern California[J]. J Geophys Res, 112(B8): B08311. doi:10.1029/2006JB004830.
Zollo A, Lancieri M, Nielsen S. 2006. Earthquake magnitude estimation from peak amplitudes of very early seismic signals on strong motion records[J]. Geophys Res Lett, 33(23): L23312. doi:10.1029/2006GL027795.
Zollo A, Iannaccone G, Lancieri M, Cantore L, Convertito V, Emolo A, Festa G, Gallovi F, Vassallo M, Martino C, Satriano C, Gasparini P. 2009. Earthquake early warning system in southern Italy: Methodologies and performance evaluation[J]. Geophys Res Lett, 36(5): L00B07. doi:10.1029/2008GL036689.




 下载:
下载: