Spatio-temporal variation of non-dipole magnetic fields with different degree in China
-
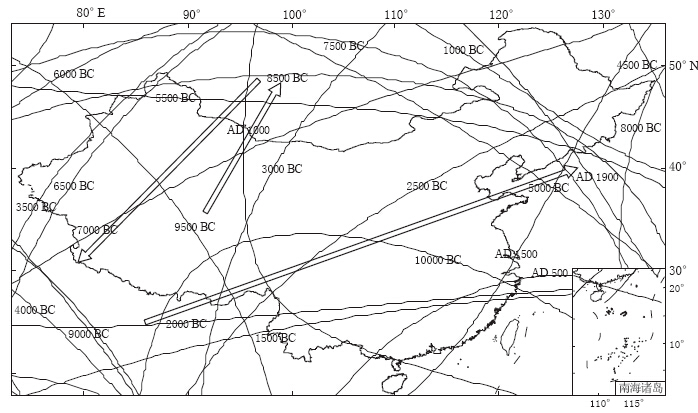
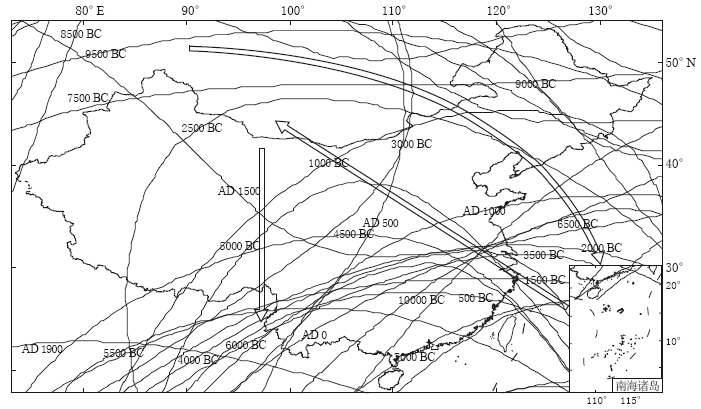
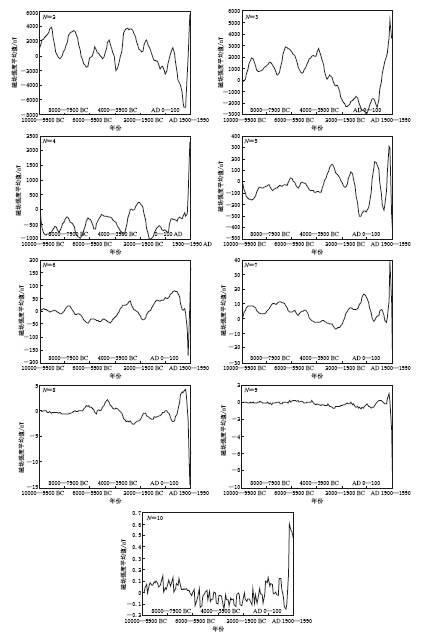
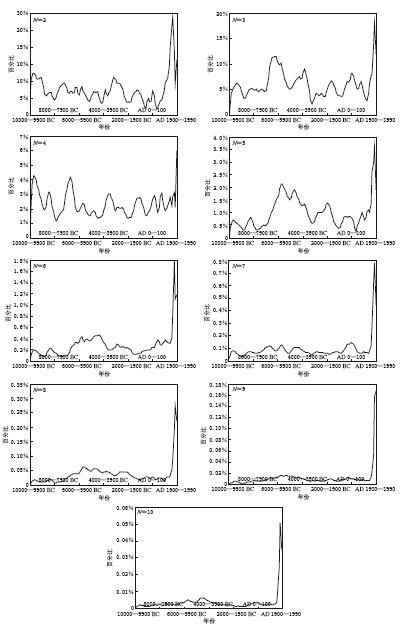
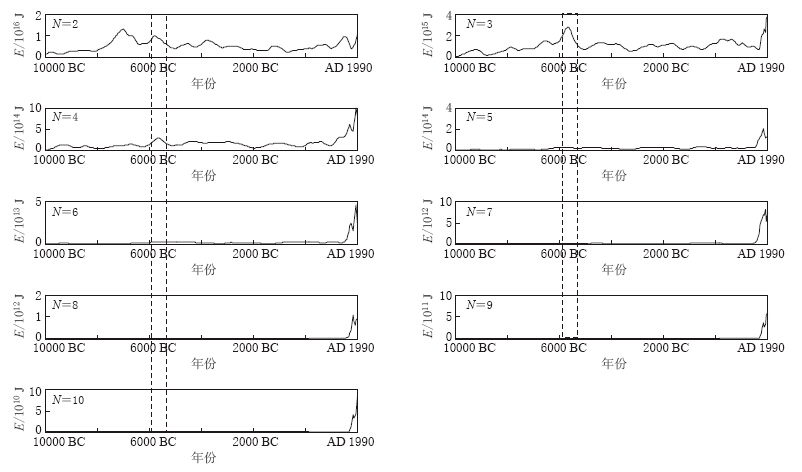
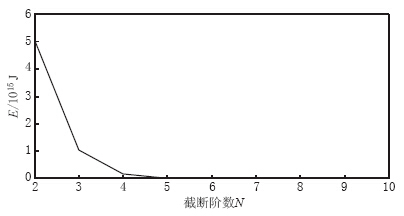
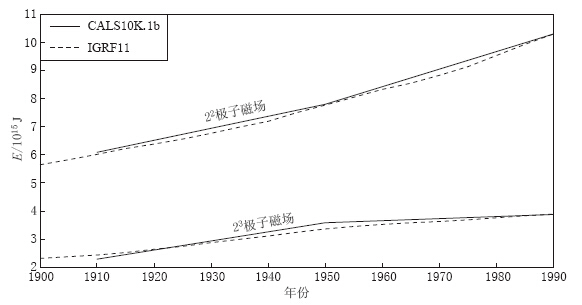
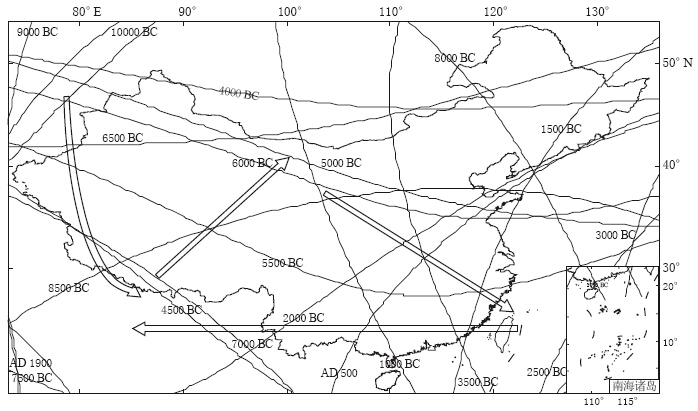
摘要: 为了研究中国境内各阶非偶极子(ND)磁场,通过最新的地磁场模型CALS10K.1b计算了10000 BC—AD 1990年ND磁场在中国境内的时空及能量变化;22,23和24极子磁场零值线主要呈现出从我国中北部向东南部移动,从北部向东部移动,以及从东南部向西北部移动的趋势;除了26极子磁场,其余ND磁场在1500年以后均有“翘尾”现象,其所占主磁场的比值在10000 BC—AD 1500年呈震荡变化,从1500年开始快速上升;除了22极子磁场,其它各阶ND磁场能量随时间变化的趋势基本一致. 在5650 BC年左右,各阶ND磁场能量值均出现高值并随阶数的增大而衰减,反映了在该时间点通过地核发电机产生的磁场能量随径向距离而近似线性衰减,地磁场能量主要源自地球液态外核. 将CALS10K.1b模型结果与IGRF11模型对比后,得出CALS10K.1b模型所计算的ND磁场及能量值较为可靠,而两者差异主要源于数据和建模方法的不同.
-
关键词:
- 非偶极磁场 /
- 时空变化 /
- CALS10K.1b /
- IGRF11
Abstract: In order to systematically study all non-dipole (ND) magnetic fields (truncation level N=2—10) in China, we studied the spatio-temporal variation of ND magnetic fields with different degree and their energies during the period of 10000 BC—1990 AD based on the newest time-based global model CALS10K.1b. The latest version of IGRF, i.e., IGRF11, was also adopted to compare and verify. Results show that the zero lines of 22, 23 and 24 pole fields mainly moved from middle-northern region to southeastern region of China, from northern to eastern China, and moved from southeastern to northwestern region of China. Except the 26 pole field, all ND fields exhibited “tail raise”. The percentage of ND field accounting for main field oscillated during 10000 BC—1500 AD, and then rapidly increased. The energies of all ND fields changed following almost same trend except the 22 pole field. Around the year 5650 BC, the energy reached high value, and then attenuated with the degree increasing, which indicates that the energy resulting from the Earth core’s dynamo attenuates linearly alone with radial distance. The energy of geomagnetic field mainly originates from the Earth’s fluid outer core. Comparison of the result based on CALS10K.1b with that from IGRF11 showed that CALS10K.1b’s results in this study are more reliable, and their differences mainly result from different data used and modeling methods.-
Keywords:
- non-dipole magnetic field /
- spatio-temporal variation /
- CALS10K.1b /
- IGRF11
-
-
表 1 2N(N=2,3,…,10)极子磁场所占主磁场的平均百分比值
Table 1 Mean percentage of 2N(N=2,3,…,10)pole fields accounting for main field

-
安振昌, 王月华. 1999. 1900-2000年非偶极子磁场的全球变化[J]. 地球物理学报, 42(2): 169-177. An Z C, Wang Y H. 1999. Global changes of the non-dipole magnetic fields for 1900-2000[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 42(2): 169-177 (in Chinese).
康国发, 徐慧, 张永忠. 1995. 东亚地磁非偶极场的变化特征研究[J]. 云南大学学报, 17(4): 358-362. Kang G F, Xu H, Zhang Y Z. 1995. Change characteristics of geomagnetic non-dipole field in East Asia[J]. Journal of Yunnan University, 17(4): 358-362 (in Chinese).
林云芳, 曾小平, 郭启华. 1985. 东亚地区地磁非偶极场长期变化的分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 28(5): 482-496. Lin Y F, Zeng X P, Guo Q H. 1985. Analysis of secular variations of non-dipole geomagnetic field in East Asia[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 28(5): 482-496 (in Chinese).
王亶文. 2004. 20世纪地磁长期变化场分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 47(3): 423-427. Wang D W. 2004. The analysis of the geomagnetic secular variation in the 20th century[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 47(3): 423-427 (in Chinese).
徐文耀. 2001. 地磁场能量在地球内部的分布及其长期变化[J]. 地球物理学报, 44(6): 747-753. Xu W Y. 2001. Distribution of geomagnetic energy in the earth's interior and its secular variation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 44(6): 747-753 (in Chinese).
Baag C G, Helsley C E. 1974. Geomagnetic secular variation model E[J]. J Geophys Res, 79(32): 4918-4922.
Bauer L A, Hazard D L. 1900. The physical decomposition of the earth's permanent magnetic field: No.1. The assumed normal magnetization and the characteristics of the resulting residual field[J]. J Geophys Res, 5(1): 1-4.
Bloxham J, Jackson A. 1992. Time-dependent mapping of the magnetic field at the core-mantle boundary [J]. J Geophys Res, 97(B13): 19537-19563.
Constable C G, Johnson C L, Lund S P. 2000. Global geomagnetic field models for the past 3000 years: Transient or permanent flux lobes?[J]. Phil Trans R Soc A, 358(1768): 991-1008.
Daly L, Le Goff M. 1996. An updated and homogeneous world secular variation data base. 1. Smoothing of the archaeomagnetic results[J]. Phys Earth Planet Inter, 93(3/4): 159-190.
Donadini F, Korte M, Constable C. 2009. Geomagnetic field for 0-3 ka: 1. New data sets for global modeling[J]. Geochem Geophys Geosyst, 10(6). doi:10.1029/2008GC002295.
Finlay C C, Maus S, Beggan C D, Bondar T D, Chambodut A, Chernova T A, Chulliat A, Golovkov V P, Hamilton B, Hamoudi M, Holme R, Hülot G, Kuang W, Langlais B, Lesur V, Lowes F J, Luhr H, Macmillan S, Mandea M, Mclean S, Manoj C, Menvielle M, Michaelis I, Olsen N, Rauberg J, Rother M, Sabaka T J, Tangborn A W P, Tøffner-Clausen L, Thébault E, Thomson A, Wardinski I, Wei Z, Zvereva T. 2010. International geomagnetic reference field: The eleventh generation[J]. Geophys J Int, 183(3): 1216-1230.
Gubbins D. 1975. Can the Earth's magnetic field be sustained by core oscillations?[J]. Geophys Res Lett, 2(9): 409-412.
Gubbins D, Herrero-Bervera E. 2007. Encyclopedia of Geomagnetism and Paleomagnetism[M]. Dordrecht: Springer: 1-1054.
Hongre L, Hulot G, Khokhlov A. 1998. An analysis of the geomagnetic field over the past 2000 years[J]. Phys Earth Planet Inter, 106(3/4): 311-335.
Jackson A, Jonkers A R T, Walker M R. 2000. Four centuries of geomagnetic secular variation from historical records[J]. Phil Trans R Soc A, 358(1768): 957-990.
Johnson C L, Constable C G. 1998. Persistently anomalous Pacific geomagnetic fields[J]. Geophys Res Lett, 25(7): 1011-1014.
Korte M, Constable C G. 2003. Continuous global geomagnetic field models for the past 3000 years[J]. Phys Earth Planet Inter, 140(1/2/3): 73-89.
Korte M, Constable C G. 2005. Continuous geomagnetic field models for the past 7 millennia: 2. CALS7K[J]. Geochem Geophys Geosyst, 6(2). doi:10.1029/2004GC000801.
Korte M, Constable C. 2011. Improving geomagnetic field reconstructions for 0-3 ka[J]. Phys Earth Planet Inter, 188(3/4): 247-259.
Korte M, Donadini F, Constable C G. 2009. Geomagnetic field for 0-3 ka: 2. A new series of time-verying global models[J]. Geochem Geophys Geosyst, 10(6). doi:10.1029/2008GC002297.
Korte M, Constable C, Donadini F, Holme R. 2011. Reconstructing the Holocene geomagnetic field[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 312(3/4): 497-505.
Langel R A, Sabaka T J, Baldwin R T, Conrad J A. 1996. The near-Earth magnetic field from magnetospheric and quiet-day ionospheric sources and how it is modeled[J]. Phys Earth Planet Inter, 98(3/4): 235-267.
Maus S, Macmillan S, Chernova T, Choi S, Dater D, Golovkov V, Lesur V, Lowes F, Luhr H, Mai W, Mclean S, Olsen N, Rother M, Sabaka T, Thomson A, Zvereva T. 2005. The 10th-generation international geomagnetic reference field[J]. Phys Earth Planet Inter, 151(3/4): 320-322.
Olsen N, Mandea M. 2008. Rapidly changing flows in the Earth's core[J]. Nature Geosciences, 1(6): 390-394.
Olsen N, Lühr H, Sabaka T J, Mandea M, Rother M, Tøffner-Clause L, Choi S. 2006. CHAOS: A model of earth's magnetic field derived from CHAMP, Øersted, and SAC-C magnetic satellite data[J]. Geophys J Int, 166(1): 67-75.
Olsen N, Mandea M, Sabaka T J, Tøffner-Clause L. 2009. CHAOS-2: A geomagnetic field model derived from one decade of continuous satellite data[J]. Geophys J Int, 179(3): 1477-1487.
Olsen N, Mandea M, Sabaka T J, Tøffner-Clause L. 2010. The CHAOS-3 geomagnetic field model and candidates for the 11th generation IGRF[J]. Earth Planets Space, 62(10): 719-727.
Sabaka T J, Olsen N, Langel R A. 2002. A comprehensive model of the quiet-time, near-Earth magnetic field: Phase 3[J]. Geophys J Int, 151(1): 32-68.
Sabaka T J, Olsen N, Purucker M E. 2004. Extending comprehensive models of the Earth's magnetic field with Oersted and CHAMP data[J]. Geophys J Int, 159(2): 521-547.
Vestine E H, Kahle A B. 1968. The westward drift and geomagnetic secular change[J]. Geophys J Int, 15(1/2): 29-37.
Walker A D, Backus G E. 1997. A six-parameter statistical model of the Earth's magnetic field[J]. Geophys J Int, 130(3): 693-700.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 周思远,段颖,尤伟,赵育飞,张勇. 地磁三分量测量中磁偏角仪器差的改正问题. 华南地震. 2023(02): 97-103 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: