Effect of parameters on near-fault ground-motion simulations for moderate-strong earthquakes by stochastic finite-fault method
-
摘要: 介绍了模拟地震动时程的随机有限断层法及近年来对该方法的改进,改进后的随机有限断层法适合模拟中强地震;比较了不同场地方位角的中强地震近场地震动时程与平均伪加速度反应谱(PSA);定量分析了中强地震近场地震动模拟结果的参数敏感性. 结果表明:不同场地方位角的中强地震近场PSA在短周期部分差别较大;应力降是模型中最重要的参数,其对反应谱短周期部分影响最大;几何扩散系数对PSA的整体影响也较为明显. 将随机有限断层法应用到工程安全性评价工作中时,应当重点关注对反应谱短周期部分影响较大的应力降和该区域的几何扩散系数,同时要调查该区域优势场地方位角的分布,更加合理地控制中强地震近场强震动的模拟.Abstract: This paper described stochastic finite-fault method and related improvements which have been widely used in simulating acceleration time histories. The improved method is more suitable for the simulation of moderate-strong earthquakes. And then we compared the time histories and average PSA (pseudo-acceleration response spectra) of near-fault moderate-strong earthquakes for different site azimuths so as to analyze parametric sensitivity quantitatively to near-fault ground-motion simulations for moderate-strong earthquakes using the revised program. The results show that PSA values are apparenly different at short period for different site azimuths, and stress drop is the most important model parameter, which controls response spectra at short period. In addition, the geometric-spreading coefficient has a significant impact on PSA. Therefore, in order to get more accurate simulations for the near-fault moderate-strong earthquakes we should focus on stress drop and geometric-spreading coefficient which have great influence on PSA values at short period when applying stochastic finite-fault method to the seismic safety evaluation of moderate earthquakes. And the distribution of dominating site azimuths is another factor which should also be considered in this situation.
-
引言
随机法是模拟地震动加速度时程的一个重要工具,包括随机点源法和随机有限断层法(Boore,1983,2009;Atkinson,Boore,1995;Beresnev,Atkinson,1998;Motazedian,Atkinson,2005; 李启成,景立平,2009). 为了弥补点源法不适合模拟近场地震动的缺陷,Beresnev和Atkinson(1998)在随机点源法(Boore,1983,2003)的基础上提出了考虑断层几何信息的随机有限断层法. 在该方法中,断层破裂面被分为N个子断层,每个子断层都被看作一个点源(Hartzell,1978),利用随机点源模型计算地震动,然后在时域中附加适当的延迟时间之后进行求和,进而得到整个断层产生的地震动加速度时程(Beresnev,Atkinson,1997,1998).
随机有限断层法在历经10多年的研究后,目前已经发展得比较成熟. 最初的随机有限断层法(FINSIM模型)不适合模拟中小地震;Motazedian和Atkinson(2005)提出含有动力学拐角频率的震源谱,在高频部分引入保证远场高频辐射能守恒的标度因子Hij,并引入了脉冲子断层百分比(Ppuls)的概念;Boore(2009)将震源持时改用子断层拐角频率的倒数1/0ij来表示,在低频部分引入了滤波器函数S()来保证远场低频傅里叶谱的一致性,从而使随机有限断层法(EXSIM模型)适用于较宽的震级范围,适合模拟5级甚至更小震级的地震动.
随机有限断层法可以直接生成地震动时程,并且计算快速、 高效且高频部分表现良好. 该方法在强震地震动模拟方面已得到一些应用. 例如:石玉成等(2005)利用随机有限断层法的FINSIM模型模拟分析了马衔山北缘活动断裂M7.0地震发震时在坝址区产生的地震动特征;王晓荣等(2011)利用FINSIM模型计算了海河断裂M6.5地震的地震动;Atkinson等(2011)对比了分别使用随机有限断层法和混合宽频带法模拟MW7.5地震断层距为2 km和10 km处的加速度反应谱,结果表明两种方法的模拟结果相似. 这些应用大多属于对强震地震动的模拟,该类地震发震构造特征相对清晰,断层几何信息明确,因而会大大减小随机有限断层模型震源参数的不确定性,并且相似规模地震的强震记录较丰富,有利于控制强震时程的模拟效果. 而中强地震影响地区则需要考虑这类地震近场强震动影响特征的工程安全性评价(例如核电工程弥散地震的安全性评价),对中强地震近场强震动模拟提出了更高要求. 为此,本文着眼于将随机有限断层法应用于中强地震近场强震动的模拟研究.
由于中强地震的发震构造不明确,因此在采用随机有限断层法模拟其近场强震动时,会面临断层几何信息、 应力降和断层破裂传播速度等震源参数以及路径、 场地参数的较大不确定性,从而对计算地震动峰值、 反应谱以及地震动时程产生较大的影响(高阳等,2013). 为了更好地模拟中强地震的近场地震动,需要对这些参数的影响进行定量分析. 其中,影响最大的参数有哪些,场地方位角不同时近场地震动的模拟结果如何等,这些都是我们需要关注的问题.
1. 方法概述
1.1 随机有限断层模型
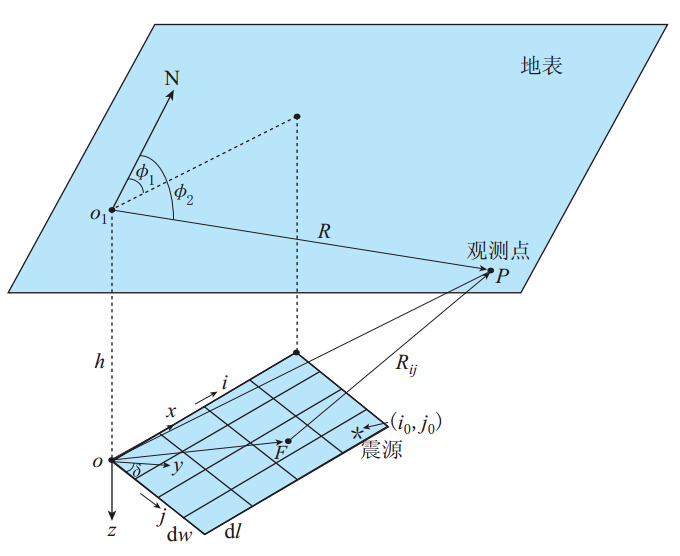
随机有限断层模型是预测近场地震动的重要工具. 图1给出了随机有限断层模型的示意图. 图中,o是断层起点,δ是断层倾角,1是断层走向,2是观测点方位角,dl和dw是子断层的长和宽,h是断层上边界深度,F是子断层中心,Rij是第ij个子断层到观测点的距离. 每个子断层相当于一个点源,其震源谱使用标准Brune震源模型,即ω2模型. 其中,第ij个子断层在观测点处剪切波的加速度傅里叶谱Aij()为

This page contains the following errors:
error on line 1 at column 1: Start tag expected, '<' not foundBelow is a rendering of the page up to the first error.
![]() 图 1 随机有限断层模型示意图 (引自 Beresnev,Atkinson,1997)Figure 1. Sketch of stochastic finite-fault model(after Beresnev,Atkinson,1997)
图 1 随机有限断层模型示意图 (引自 Beresnev,Atkinson,1997)Figure 1. Sketch of stochastic finite-fault model(after Beresnev,Atkinson,1997)为了生成点源的加速度时程,首先需要给定地震动持时,并用窗函数调整均值为零、 方差为1的高斯白噪声的形状;然后将调整后的白噪声变换到频域并进行归一化处理,再乘以式(1)计算出的第ij个子断层加速度谱Aij(),从而得到加速度频谱;之后将该加速度频谱变换到时域,得到所要求的第ij个子断层的加速度时程aij(t);最后将这个观测点的子断层加速度时程在时域附加一定的延迟时间后进行求和,即为整个断层在观测点的地震动加速度时程a(t):

式中,nl和nw分别是沿断层走向和倾向方向的子断层数,nl×nw为子断层总数,Δtij是破裂传播到第ij个子源的时间滞后与从第ij个子源到场地由于传播距离不同引起的时间滞后的叠加.
This page contains the following errors:
error on line 1 at column 1: Start tag expected, '<' not foundBelow is a rendering of the page up to the first error.
1.2 随机有限断层法的改进
从最初不适合模拟中小地震的FINSIM模型到最新的EXSIM12模型,这些针对随机有限断层法的改进主要集中在对震源项的修改上(Beresnev,Atkinson,1998;Motazedian,Atkinson,2005;Boore,2009). 本文采用目前最新的EXSIM12模型模拟地震动. 该模型较为重要的改进主要表现在以下几个方面.
1)FINSIM模型为了保证总地震矩M0守恒,子源要求触发多次子震,这在物理上难以给出合理的解释,而EXSIM模型中,子震只触发一次,更符合实际情况.
2)FINSIM模型模拟的地震动结果对子断层尺寸较为敏感. 为了减小子断层尺寸对合成地震动的影响,Beresnev和Atkinson(1998)建议划分的子断层尺寸应该在5—15 km范围内,因此FINSIM模型难以模拟中小地震地震动. 为了解决这个问题,Motazedian和Atkinson(2005)发展了含有动力学拐角频率的震源谱,即后破裂的子源比先破裂的子源具有更低的拐角频率,子源拐角频率随破裂面增大而下降.
3)子断层动力学拐角频率随着破裂的传播不断减小,导致子源辐射能随之减小而不能保持守恒. 因此,在高频部分引入了保证远场高频辐射能守恒的标度因子Hij,Hij通过对加速度谱平方的积分来进行计算;在低频部分引入了滤波器函数S()来保证远场低频傅里叶谱的一致性,这样合成的地震动幅值不再依赖于子断层的尺寸. 没有了子断层大小的限制,EXSIM12模型就能够适用于较宽的震级范围,可以模拟5级甚至更小震级的地震动.
4)Motazedian和Atkinson(2005)引入脉冲子断层百分比的概念,以此来描述在破裂发生的任一时刻,滑动只发生在部分断层上. 例如50%的脉冲面积表示在子断层破裂过程中最多有50%的子断层是活动的,只有这部分活动脉冲子断层对动力学拐角频率产生贡献,而其它子断层对动力学拐角频率则没有贡献. 活动的子断层随着破裂的传播而沿着断层移动,显然这种结果更符合有限断层模型生成地震动的实际情况. 脉冲子断层概念的提出有助于解决随机有限断层法模拟地震动在低频部分幅值偏大的问题.
This page contains the following errors:
error on line 1 at column 1: Start tag expected, '<' not foundBelow is a rendering of the page up to the first error.
6)删除子断层时间序列窗函数的截头,以保证位移时间序列不再发生长周期偏移.
This page contains the following errors:
error on line 1 at column 1: Start tag expected, '<' not foundBelow is a rendering of the page up to the first error.
国内一些学者也对随机有限断层法进行了部分改进. 例如:王国新(2001)通过对强地震动加速度傅里叶位移幅值谱的研究,提出了新的震源谱模型;孙晓丹等(2009)基于该震源谱模型研究了相关的动力学拐角频率,避免了地震动随机合成结果对子源尺寸的依赖;陶夏新等(2012)引入了震源谱的标度因子,用于补偿震源谱参数随破裂面扩展调整引起的能量损失.
1.3 模型参数
随机有限断层模型包括震源、 路径和场地等众多输入参数. 由于中强地震发震构造不明确,从而导致了断层尺寸、 倾角和深度(这里指断层上边界到地表的距离)难以确定. 此外,子断层应力降、 破裂传播速度、 几何扩散系数b和κ等参数在一定区域具有偶然不确定性(应力降是Brune震源模型定义的与高频谱水平有关的值,几何扩散系数b表示由地震波传播和散射引起的几何衰减快慢,κ表示场地的高频损失). 任一时刻活动脉冲子断层百分比也难以估计. 本文就这些具有较大不确定性的参数进行了地震动敏感性分析. 由于剪切波速和介质密度等震源参数较为确定,路径滞弹性衰减函数中的品质因子在一定区域内有确定的值,场地放大系数也可以根据场地的具体情况而确定,故这些参数均不在本文讨论范围之内.
中强地震的断层走向和倾向难以确定,致使工程场地相对断层的方位角难以确定,因而不同场地方位角的模拟结果在近场的差别可能会比较明显. 因此,首先在所有模型参数保持不变的情况下考察不同场地方位角近场强震动的差异性,然后在场地方位角一定的情况下研究应力降、 破裂速度、 脉冲百分比、 断层尺寸、 倾角、 深度、 几何扩散系数以及κ等参数对中强地震近场强震动模拟结果的影响.
2. 不同场地方位角的地震动模拟结果
本文采用随机有限断层法模拟中强地震近场基岩(V30=760 m/s)上的地震动. 李明等(2009)研究了MW5.0—6.0地震在近断层区域的临界断层距范围约为19—31 km. 由于核电工程比较关心的是中强地震10 km断层距范围内的地震动,因此本文以MW5.5地震在断层距10 km处为例,研究随机有限断层法各个参数对地震动模拟结果的影响,以及不同场地方位角的地震动模拟结果. 为了排除震源位置和断层滑动分布的影响,本研究对滑动分布随机取值,并随机选取10个震源,每个震源随机模拟10次,最后对随机震源的伪加速度反应谱(PSA)取几何平均值.
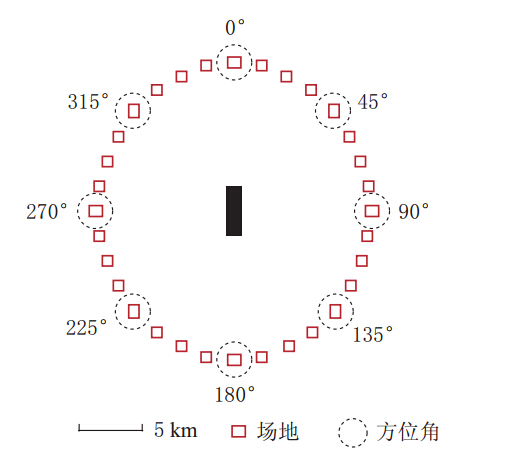
采用随机有限断层模型模拟地震动时,在相同断层距的情况下,如果方位角不同,地震动峰值、 持时和反应谱也会不同. 本文模拟了相同断层距(Rrup=10 km)下8个不同场地方位角的地震动时程和平均PSA. 断层走向为正北向,并分别设定倾角为50°的逆断层(倾向朝东)和倾角为90°的走滑断层,二者上边界在地表的投影如图2所示. 剪切波速、 介质、 密度和品质因子等部分输入参数采用北美东部基岩场地参数值(Atkinson,Boore,2006),详见表1. 反应谱阻尼取为5%.
表 1 模拟地震动使用的参数Table 1. Parameters used in ground motion simulations
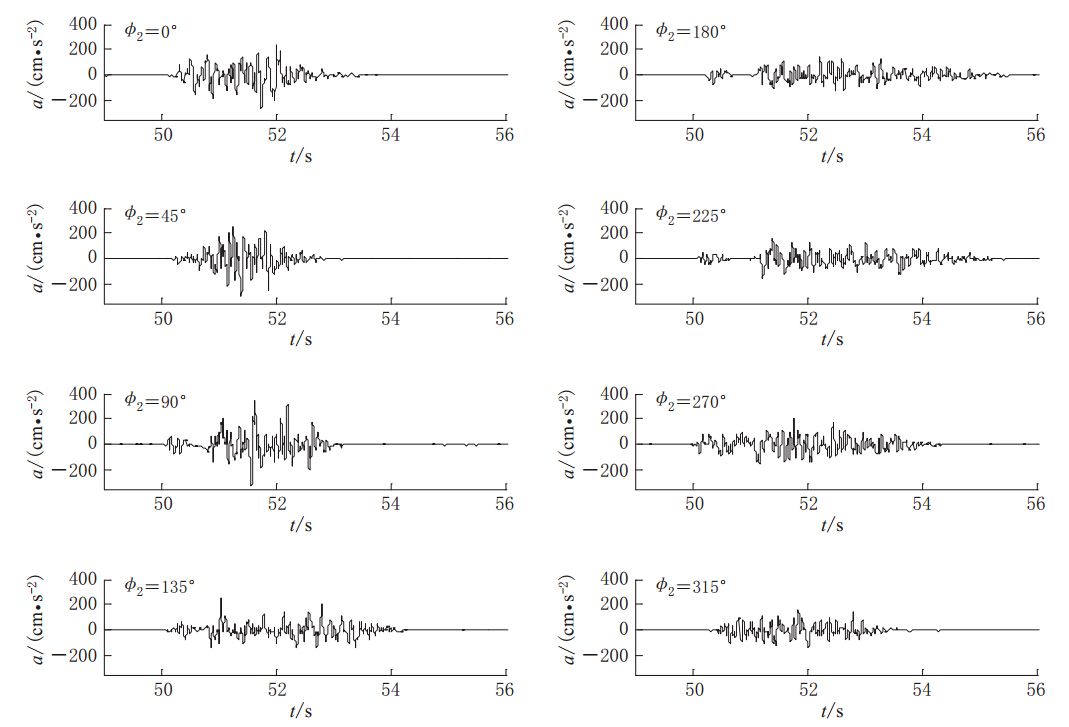
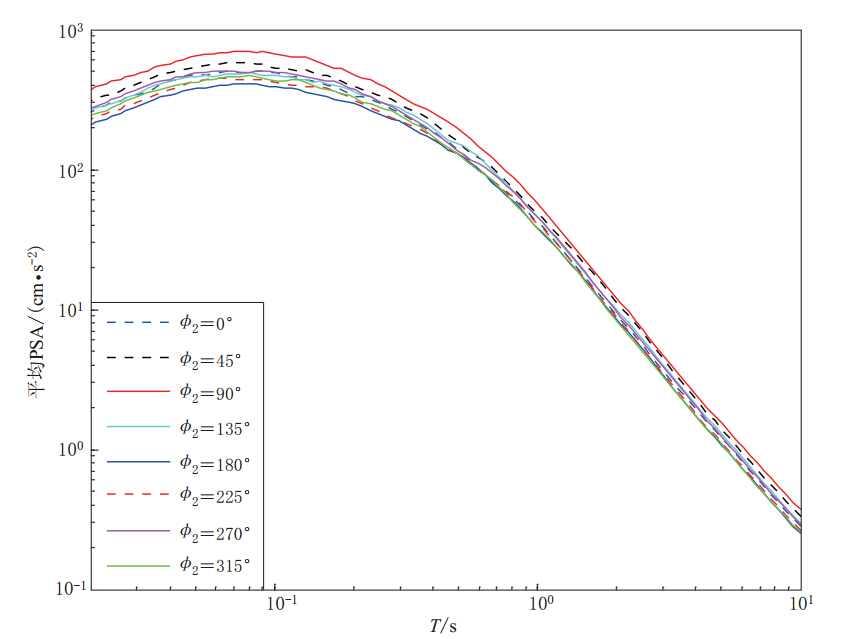
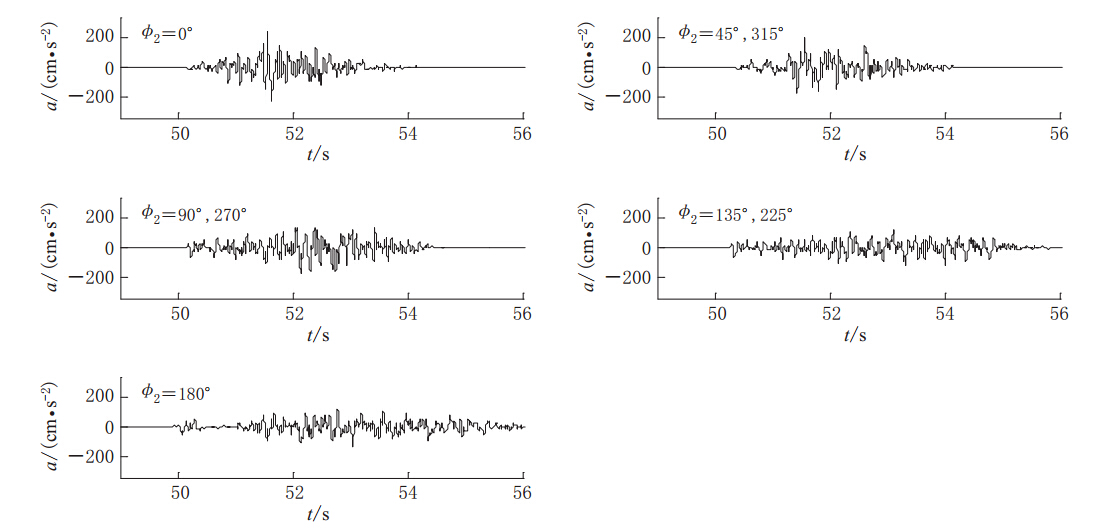
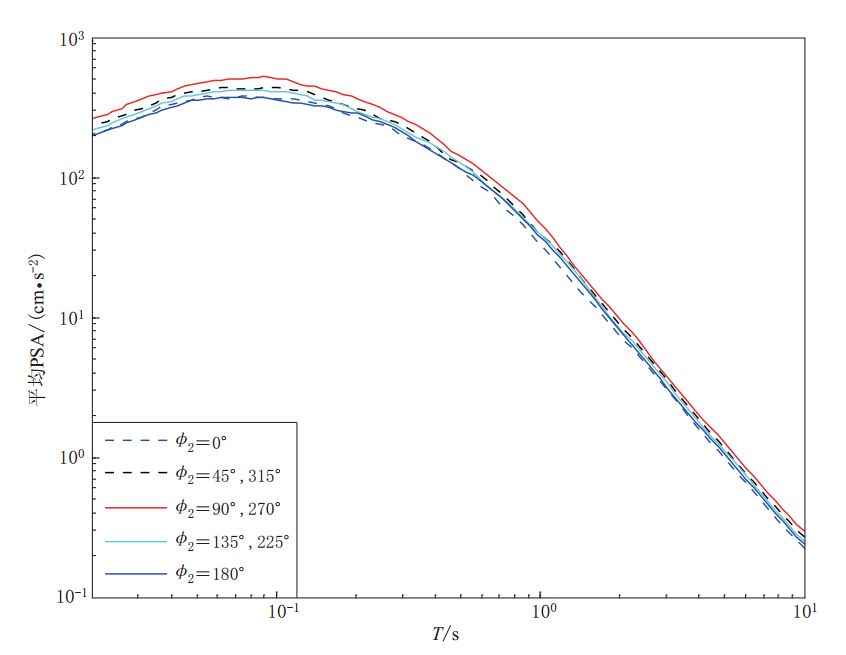
当第ij(i=1,j=1)个子断层为震源(该子断层位于走向反方向的断层上边界顶点处)时得到的倾角为50°和90°的地震动时程分别如图3和图5所示,相应地所有随机震源的平均PSA分别如图4和图6所示.
当倾角为50°时,不同方位角的加速度时程模拟结果(图3)表明:在约45°—90°方位角时峰值加速度最大,持时最短;在约180°—225°方位角时峰值加速度较小,持时最长. 该结果反映了断层上盘效应和一定的破裂方向性效应. 从图4可以看出,在90°方位角时平均PSA最大,短周期部分在180°方位角时平均PSA最小,长周期部分在315°方位角时平均PSA最小.
当倾角为90°时,该方法模拟的断层两侧的加速度时程与反应谱是对称的(图5,图6). 从图5可以看出,在0°方位角时峰值加速度最大,持时最短;在180°方位角时峰值加速度较小,持时最长. 该结果反映了断层破裂的方向性效应. 从图6可知,90°和270°方位角的平均反应谱值较大.
倾角为50°和90°时不同场地方位角的平均PSA分别如图4和图6所示. 其总体趋势表现为短周期部分的模拟反应谱值离散程度较大,而长周期部分的离散程度较小.
由于不同场地方位角的反应谱结果差别较大,尤其是在短周期部分. 因此,在使用随机有限断层法进行中强地震安全性评价时,应当通过调查一个区域内中强地震发震构造的优势走向和倾向分布情况,尽量获取场地方位角的信息,从而合理地控制中强地震近场地震动的模拟.
3. 参数敏感性研究
随机有限断层模型包括震级、 应力降、 破裂传播速度、 脉冲百分比、 断层走向、 倾角、 断层尺寸、 滑动分布、 震源深度、 震源附近介质的密度和平均剪切波速等震源参数,几何扩散项、 Q值等路径参数,以及不同频率的场地放大因子和高频损失κ等场地参数. 此外还要考虑地震动持时参数(包括震源持时和路径持时). 对于中强地震,脉冲百分比、 断层尺寸、 倾角和深度等参数往往是未知的,而应力降、 破裂传播速度、 几何扩散系数和κ在一定区域内具有偶然不确定性,我们可以通过调试这些参数来研究其对中强地震近场强震动的影响.
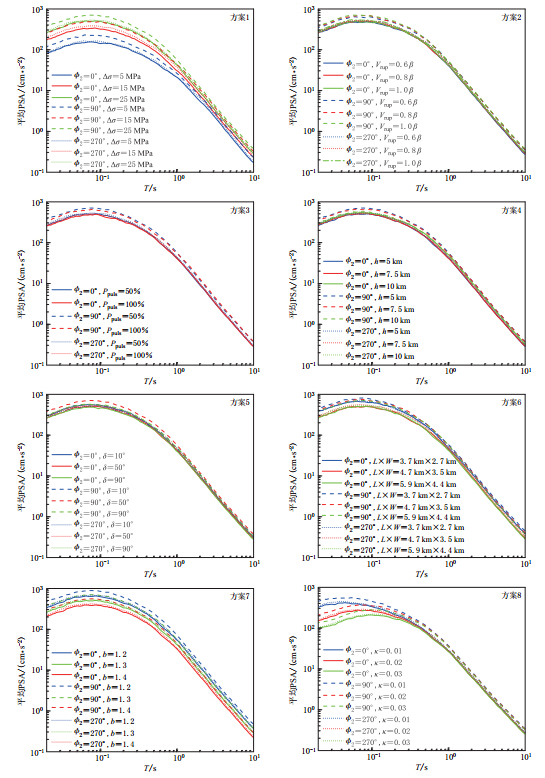
表2给出了这些参数的取值范围. 应力降Δσ和破裂速度Vrup都是了解断层破裂物理机制的重要参数(Kanamori,Rivera,2004). 破裂速度可以采用其与平均剪切波速β的比值来确定,该值可变范围相对较小,为0.6—1.0,一般取0.8(Beresnev,Atkinson,1997). 剪切波速设为3.7 km/s. 由于脉冲长度不能小于子断层长度,因此MW5.5地震脉冲面积百分比的范围设定为50%—100%. 断层尺寸采用Wells和Coppersmith(1994)关于震级与断层长宽的公式来计算,还可以在该计算结果的基础上乘以一定的断层长宽修正因子Fstr,图7中的方案6即为乘以相应修正因子后的断层长宽. 高频损失κ考虑了近地表衰减效应,这部分固有衰减与频率无关,而是由场地和区域地壳结构决定的(Hough,Anderson,1988;Roverlli et al,1988),本文设定基岩上κ在0.01—0.03之间.
表 2 参数变化方案Table 2. Parameters variation scenarios
为了分离各个参数对地震动结果的影响,在每个方案中我们只设定其中一个参数在一定范围内变化,其它参数均采用表1给出的期望值,以此计算出断层距10 km处的地震动平均PSA,结果如图7所示. 其中,断层走向为正北向,倾向朝东,断层上边界深度为5 km,场地方位角分别取0°,90°和270°,断层距10 km以内路径持时设为1 s.
从方案1可知,子断层应力降增大时,相对长周期而言,平均PSA在短周期增大的幅度较大,并且随着应力降的增大,反应谱的增幅会有所减小. 从方案2—6可知,在同一场地方位角下,破裂速度、 脉冲百分比、 断层深度、 倾角和断层长宽修正因子对平均PSA影响较小(而根据以往的研究,强震断层长宽修正因子对平均PSA的影响较为明显). 从方案7可知,虽然几何扩散系数b只上下浮动了0.1个单位,但其对反应谱短周期和长周期部分的影响均较为明显. 从方案8可知,平均PSA在短周期部分对κ的变化略敏感,而在长周期部分不敏感. 研究结果表明,其它场地方位角的平均PSA均会得到类似的结果,此处不再赘述.
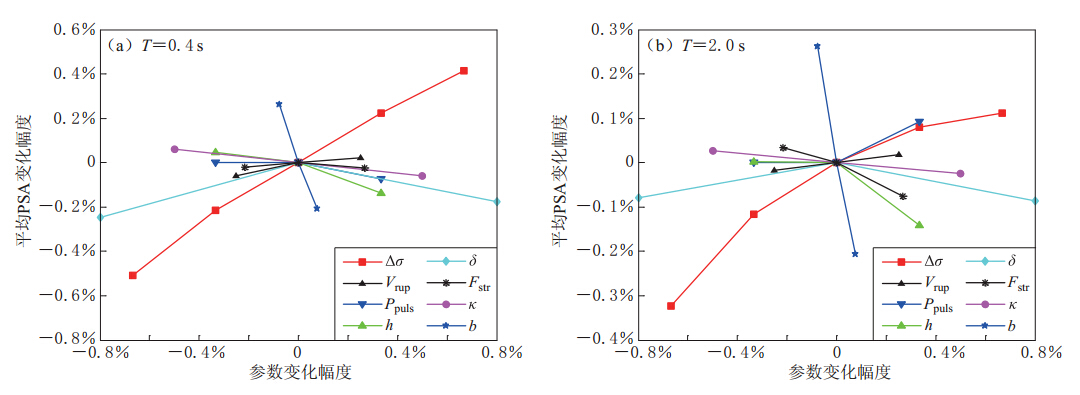
为了进一步分析参数变化在短周期和长周期时对中强地震近场强震动的影响程度,我们将方位角为90°时各参数的取值区间相对基准参数值的变化幅度,以及反应谱变化幅度进行统计(表3),并给出了周期为0.4 s和2.0 s时的参数变化幅度和平均PSA变化幅度对应图(图8). 通过比较不难发现:子断层应力降控制了平均PSA的短周期部分,是随机有限断层模型中最重要的参数;几何扩散系数和κ对短周期部分的影响也较为明显;在长周期部分,应力降和几何扩散系数均对平均PSA影响较大,而其它参数对其影响相对较小.
表 3 参数与平均PSA变化幅度对应表(ϕ2=90°)Table 3. Variation amplitude of parameters and corresponding average PSA values(ϕ2=90°)
由于中强地震安全性评价工作关注最多的是近场地震动的高频特征,因此采用随机有限断层法模拟时需要更加关注对反应谱短周期段影响较大的参数的合理取值.
4. 讨论与结论
本文详细介绍了随机有限断层模型模拟地震动的方法及相关改进,改进后的方法适用于模拟中强地震. 针对MW5.5地震在断层距10 km处的地震动,采用最新的EXSIM12模型进行了模拟. 结果表明,由于受破裂的方向性效应和上盘效应的影响,不同场地方位角下近场平均PSA在短周期时差别明显,这正是中强地震安全性评价工作中最为关注的. 因此,在应用随机有限断层方法模拟中强地震近场强震动时,应当通过调查该区域中强地震发震构造的优势走向和倾向分布情况,尽量获取场地的方位角信息,从而更加合理地控制中强地震近场地震动的模拟.
本文研究了随机有限断层法模拟中强地震近场强震动时的参数敏感性问题. 结果表明:应力降是随机有限断层模型中最关键的参数,它控制了PSA的短周期部分;几何扩散系数尽管只上下浮动0.1个单位,但它对近场反应谱短周期部分和长周期部分的影响均较为明显. 由于中强地震安全性评价工作关注最多的是近场地震动的高频特征,因此,采用随机有限断层法模拟时需要更加关注对反应谱高频段影响较大的参数的合理取值,重点考察一定区域应力降和几何扩散系数的偶然不确定性. 以往研究表明,通过拟合一个区域记录较好的地震动的PSA来确定该区域的应力降是较为合适的方法.
在应用随机有限断层法模拟中强地震近场强震动时,尽管断层几何情况未知,但由于与之相关的参数对地震动模拟结果影响较小,故而并不影响我们使用随机有限断层法模拟中强地震. 我们应当重点关注应力降和该区域的几何扩散系数,同时要注意优势场地方位角的分布等. 本文结果为在安全性评价工作中更合理地采用随机有限断层法模拟中强地震近场强震动提供了参考.
审稿专家对本文提出了诸多宝贵的修改意见和建议,作者在此表示衷心的感谢.
-
图 1 随机有限断层模型示意图 (引自 Beresnev,Atkinson,1997)
Figure 1. Sketch of stochastic finite-fault model(after Beresnev,Atkinson,1997)
表 1 模拟地震动使用的参数
Table 1 Parameters used in ground motion simulations

表 2 参数变化方案
Table 2 Parameters variation scenarios

表 3 参数与平均PSA变化幅度对应表(ϕ2=90°)
Table 3 Variation amplitude of parameters and corresponding average PSA values(ϕ2=90°)

-
高阳 , 潘华, 汪素云. 2013. 中强地震近场强震动的随机有限断层模型参数影响研究[J]. 国际地震动态, (11): 45-46. Gao Y, Pan H, Wang S Y. 2013. Parameters sensitivity of stochastic finite-fault model for moderate earthquakes near-fault ground motions[J]. Recent Development in World Seismology, (11): 45-46 (in Chinese).
李明, 谢礼立, 翟长海, 杨永强. 2009. 近断层地震动区域的划分[J]. 地震工程与工程振动, 29 (5): 20-25. Li M, Xie L L, Zhai C H, Yang Y Q. 2009. Scope division of near-fault ground motion[J]. Journal of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 29 (5): 20-25 (in Chinese).
李启成, 景立平. 2009. 随机点源方法和随机有限断层方法模拟地震动的比较[J]. 世界地震工程, 25 (1): 6-11. Li Q C, Jing L P. 2009. The comparison between stochastic point-source method and stochastic finite-fault method[J]. World Earthquake Engineering, 25 (1): 6-11 (in Chinese).
石玉成, 陈厚群, 李敏, 卢育霞. 2005. 随机有限断层法合成地震动的研究与应用[J]. 地震工程与工程振动, 25 (4): 18-23. Shi Y C, Chen H Q, Li M, Lu Y X. 2005. The study and application of stochastic finite faults method in ground motion synthesizing[J]. Journal of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 25 (4): 18-23 (in Chinese).
孙晓丹, 陶夏新, 王国新, 刘陶钧. 2009. 地震动随机合成中与震源谱相关的动力学拐角频率[J]. 地震学报, 31 (5): 537-543. Sun X D, Tao X X, Wang G X, Liu T J. 2009. Dynamic corner frequency in source spectral model for stochastic synthesis of ground motion[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 31 (5): 537-543 (in Chinese).
陶夏新, 陈富, 孙晓丹. 2012. 强地震动随机合成中震源谱模型的改进[J]. 岩土工程学报, 34 (3): 504-507. Tao X X, Chen F, Sun X D. 2012. Improvement of source spectrum model for synthesis of strong ground motion[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 34 (3): 504-507 (in Chinese).
王国新. 2001. 强地震动衰减研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 中国地震局工程力学研究所: 64-77. Wang G X. 2001. Study on Strong Ground Motion Attenuation[D]. Harbin: Institute of Engineering Mechanics, China Earthquake Administration: 64-77 (in Chinese).
王晓荣, 易立新, 李鹏. 2011. 利用随机有限断层法计算海河断裂的地震动[J]. 地震研究, 34 (2): 188-193. Wang X R, Yi L X, Li P. 2011. Computing the ground motion of the Haihe fault with stochastic finite fault model[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 34 (2): 188-193 (in Chinese).
Anderson J G, Hough S E. 1984. A model for the shape of the Fourier amplitude spectrum of acceleration at high frequencies[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 74 (5): 1969-1993.
Atkinson G M, Boore D. 1995. New ground motion relations for eastern North America[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 85 (1): 17-30.
Atkinson G M, Boore D. 2006. Earthquake ground-motion prediction equation for eastern North America[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 96 (6): 2181-2205.
Atkinson G M, Goda K, Assatourians K. 2011. Comparison of nonlinear structural responses for accelerograms simulated from the stochastic finite-fault approach versus the hybrid broadband approach[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 101 (6): 2967-2980.
Beresnev I A, Atkinson G M. 1997. Modeling finite-fault radiation from the spectrum[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 87 (1): 67-84.
Beresnev I A, Atkinson G M. 1998. FINSIM: A FORTRAN program for simulating stochastic acceleration time histories from finite faults[J]. Seism Res Lett, 69 (1): 27-32.
Boore D. 1983. Stochastic simulation of high-frequency ground motion based on seismological models of the radiated spectra[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 73 (6): 1865-1894.
Boore D. 2003. Simulation of ground motion using the stochastic method[J]. Pure Appl Geophys, 160 (3/4): 635-676.
Boore D. 2009. Comparing stochastic point-source and finite-source ground-motion simulations: SMSIM and EXSIM[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 99 (6): 3202-3216.
Hartzell S. 1978. Earthquake aftershocks as Green's functions[J]. Geophys Res Lett, 5 (1): 1-14.
Hough S E, Anderson J G. 1988. High frequency spectra observed at Anza California: Implications for Q structure[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 78 (2): 692-707.
Kanamori H, Rivera L. 2004. Static and dynamic scaling relations for earthquakes and their implications for rupture speed and stress drop[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 94 (1): 314-319.
Motazedian D, Atkinson G M. 2005. Stochastic finite-fault modeling based on a dynamic corner frequency[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 95 (3): 995-1010.
Roverlli A, Bonamassa O, Cocco M, Dibona M, Mazza S. 1988. Scaling laws and spectral parameters of the ground motion in active extensional areas in Italy[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 78 (2): 530-560.
Wells D, Coppersmith K. 1994. New empirical relationships among magnitude, rupture length, rupture width, rupture area, and surface displacement[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 84 (4): 974-1002.
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 陈凯,潘华. 基于机器学习的区域地震动模拟——以2022年泸定M_S6.8地震为例. 地震学报. 2025(02): 242-253 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 贾晓辉,曹秀玲,王晓山. 考虑地形效应的随机有限断层法地震动模拟研究. 地震研究. 2024(04): 619-626 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 党鹏飞,刘启方,马完君,王冲. 参数对地震动随机模拟结果的影响分析. 防灾减灾工程学报. 2022(04): 768-777+818 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 梁俊伟,钟菊芳,吴海波,陈功. 基于能量的随机有限断层法研究. 南昌航空大学学报(自然科学版). 2015(02): 10-15+69 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 高阳,潘华,汪素云. 中强地震随机有限断层模型应力降参数的确定方法. 震灾防御技术. 2014(04): 733-747 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(14)




 下载:
下载: