Assessment of the automatic centroid moment tensor inversion system for global strong earthquakes (MW≥6.5) based on the W-phase method
-
摘要: 使用最近构建的虚拟全球地震台网记录的波形数据,采用OpenMP的并行编程技术优化原有算法, 研制了基于W震相技术的全球强震(MW≥6.5)矩心矩张量自动反演系统.为了评估该系统的准确度和时效性,将离线自动测定的2008年1月—2013年7月全球140次地震(MW6.5—9.0)的矩心矩张量与全球矩心矩张量工作组(GCMT)的结果进行了比较.结果表明:该系统可准确测定全球MW≥6.5地震的矩张量,绝大多数地震矩震级与GCMT给出的矩震级呈现出良好的线性趋势,两者之差ΔMW的标准方差约0.13,ΔMW位于区间(-0.2,0.2)的地震占总数的96%;地震矩6个分量分别与GCMT相应的结果沿对角线近线性分布,多数地震矩心水平位置与GCMT给出的矩心水平位置比较接近,两者间大圆弧距离位于区间(0,50km)的地震次数占总数的84%;在台站覆盖较均匀的条件下,该系统能够实现震后25—40分钟自动准确测定全球MW≥6.5地震的矩心矩张量.Abstract: We develop an automatic centroid moment tensor (CMT) inversion system for large earthquakes (MW≥6.5) at global scale based on the W-phase method. We use seismic waveforms observed by global virtual seismic networks including Chinese stations, which have been recently set up. To speed up the calculation of moment tensor solutions, the W-phase method is parallelized using openMP. In order to assess the accuracy and timeliness of this implementation, automatic moment tensor solutions for 140 global events (MW6.5—9.0) are determined offline. Compared with the global CMT (GCMT) solutions, the result indicates that this system mentioned is able to precisely retrieve CMT solutions of global events with MW≥6.5. There is remarkably good linear relationship between the moment magnitude of W-phase CMT and GCMT. The standard deviation of the magnitude difference ΔMW is about 0.13, and 96 percent of the inversions yield a MW within MW-GCMT from the GCMT ±0.2. In comparison with the GCMT solutions, six elements of moment tensors derived show nearly linear distribution along the diagonal, respectively. 84 percent of inversions yield a great-circle distance smaller than 50 km between the CMT and GCMT centroids. As shown above, majority of the centroids are very similar with the GCMT centroids. When the data coverage is sufficient, this system can thus automatically determine the CMT of global earthquakes with MW≥6.5 in between 25 min and 40 min after the origin time.
-
Keywords:
- W phase /
- automatic centroid moment tensor inversion /
- assessment
-
引言
地震矩心矩张量自动反演系统能在震后第一时间获取地震矩心时间、矩心位置、标量地震矩以及断层面几何参数等地震工作者所关心的重要震源信息,直观地反映了地震破裂面的几何形状和震源运动学特征,因此该系统对大地震本身的研究、地震灾害的快速评估、海啸预警及震后应力分布研究等方面都具有重要的意义.
自2008年5月12日汶川大地震以来,中国地震台网中心地震应急数据产品产出工作组在中国地震局监测预报司支持下,开展了地震矩张量常规人工测定工作,较准确地反演了国内外约327次地震矩张量,但结果一般在震后30—120分钟获取.为了进一步提高地震矩张量测定的准确度和时效性,工作组采用最近构建的虚拟全球地震台网宽频带台站记录的地震波形,根据Kanamori和Rivera(2008)提出的基于W震相测定地震矩张量的方法,研制出了全球强震矩心矩张量自动反演系统.该系统现已上线试运行,将能够实现25—40分钟自动准确测定全球MW≥6.5地震的矩张量.
W震相是在S波之前到达的一种较明显的长周期波(100—1 000 s),最早在1992年日本记录的尼加拉瓜海啸地震的位移波形中被辨识出(Kanamori,1993).根据地震射线理论,在选定初至P波开始至15Δ s(Δ表示震中距,单位为度)的时窗中,W震相所携带的能量可解释为P、PP、SP和S等多个震相的叠加.对于MW≥6.5强震,本文使用的W震相测定地震矩张量法采用全球一维速度模型PREM,基于简振正型叠加法计算理论波形.
为了评估该系统的准确度和时效性,离线自动测定了2008年1月—2013年7月全球140次地震(MW6.5—9.0)的矩张量解,并采用国际通行做法,以美国哥伦比亚大学全球矩心矩张量(global centroid moment teasor,简写为GCMT)工作组给出的地震矩张量为标准,对测定的矩震级、矩张量6个分量、矩心位置等参量进行比较,并初步分析了结果误差产生的原因.该系统自动测定的矩震级等震源参量,可为未来全球强震矩震级发布、地震海啸预警以及地震灾情预判等提供科学的参考依据.
1. 数据
为了充分使用已有的地震波形,尽可能地减少台站分布不均匀对测定国内外地震矩张量结果的影响,通过对多个历史震例理论波形与实际观测记录进行比较分析,最终从中国数字测震台网中选取211个高质量记录的台站,联合台网代码II,IU,GE,G,MN,TW,JP,KR,KZ,KG共10个国际台网,建立了虚拟全球地震台网.考虑到宽频带速度型地震计的幅频特性以及强震激发的地震波所包含主要能量的频段范围,选取的国内台站地震计类型多为JCZ-1,JCZ-1T,CTS-1,CMG-3ESPC或BBVS-120;国际台站地震计类型多为STS-1或STS-2.
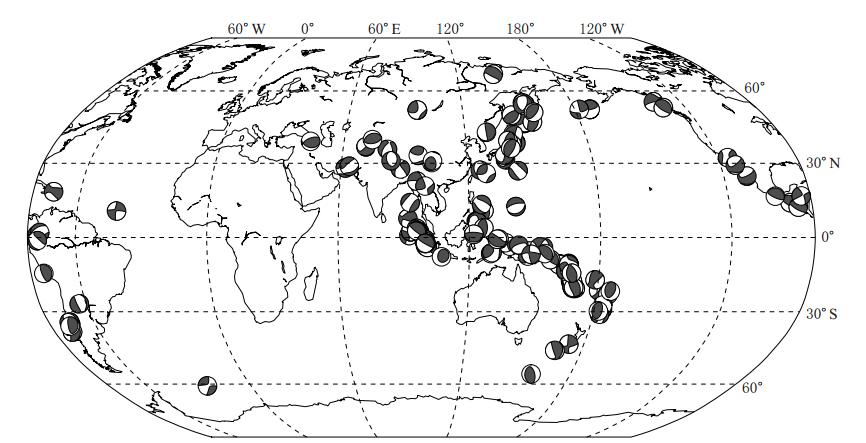
本文根据中国地震台网中心发布的地震速报目录,选用2008年1月—2013年7月全球140次地震(MW6.5—9.0),分别从中国地震台网中心和IRIS收集或下载震中距5°—85°范围内上述虚拟台网记录的地震波形.
自动化数据预处理的主要步骤为:①波形质量控制,舍去信噪比不高的和断点等“坏”波形;②时间域反卷积,将原始的速度地震记录转化为位移记录;③采用4阶巴特沃斯(Butterworth)滤波器带通滤波,使用依赖于震级大小的不同滤波频段(表 1),滤波频段的选取主要考虑用于计算理论波形的一维速度模型分辨率和不同大小的地震所激发出的包含主要能量的地震波波长,滤波频段在反演开始时基于速报震级M的选取,但在计算过程中会根据反演的矩震级不断地进行修正;④选用W震相时间窗:当震中距Δ≤12°时,选用初至P波后180 s;当12°<Δ≤85°时,选用初至P波开始至15Δ s.
表 1 选用的滤波频段Table 1. Corner frequency-bands used for b and pass filtering
2. 方法
2.1 反演方法
W震相矩张量反演采用的主要技术思路类似于Dziewonski等(1981)和Ekström2005等(2005)提出的标准矩心矩张量(centroid moment tensor,简写为CMT)反演方法,但两种方法存在以下不同:①选用的地震波时窗;②W震相矩张量反演所使用的长周期地震波形;③前者采用时间域反卷积方法提取位移波形,能对时间序列每个抽样点进行实时处理,使得W震相可在限幅记录中无失真恢复,从而可充分使用强震近震(震中距5°—30°)波形,而后者则主要使用频率域反卷积方法提取位移波形;④确定矩心水平位置和矩心深度的反演算法.
W震相反演未知震源参数向量m为

式中:地震矩张量f=[Mrr,Mpp,Mtt,Mrp,Mrt,Mpt]T;表征矩心时空坐标ηc=[θc,φc,hc,τc]T,其中θc,φc,hc,τc分别表示矩心余纬度、矩心经度、矩心深度及矩心时间.
为了确定最佳的矩心时空坐标ηc,可通过网格搜索法使定义的误差函数

最小.式中,向量sW表示W震相的理论波形,向量dW表示W震相的实际观测波形.
由于使用W震相,在测定强震震源参数时具有以下优势:①W震相传播速度明显高于面波,因此相对于传统的面波波形反演方法,一般在震后22—35分钟即可完成震源参数的测定,更适合大地震快速响应;②对于远震台,W震相主要在地幔中传播,因而W震相传播受浅层大陆地壳和洋壳结构强烈不均匀性的影响并不大.因此,该方法也逐渐被美国国家地震信息中心、美国太平洋海啸警报中心、日本气象厅等国外多所科研机构所使用(Hayes et al,2009;Duputel et al,2012).
2.2 实时处理流程
中国地震台网中心研发的基于W震相技术的矩心矩张量反演系统实时处理流程主要分为以下步骤:
第一步,系统近实时获取本单位自动地震速报系统测定的地震震源位置和震级M,基于Kanamori和Rivera(2008)方法,可通过震级M估算出矩心时间偏移td.反演得到初步矩张量解.
第二步,在假定自动速报给定的震源位置为矩心位置前提的条件下,基于一维网格搜索在矩心时间偏移td解空间中求出最佳解,使误差函数χ(m)最小; 使用最佳解td,再次迭代计算,修订第一步求得的矩张量解.
第三步,在满足遴选后波形道数N≥15及与台站方位间隙角γ≤270°的条件下,水平向搜索间隔开始时设为0.4°,尔后在局部最小值附近进一步细化网格为0.2°和0.1°;在深度上搜索间隔一般设为2km.基于三维网格搜索,使误差函数χ(m)最小,求出最佳矩心水平位置和矩心深度.最后使用优化的矩心水平位置和矩心深度再次计算,得到最佳矩张量解.该解亦即最后发布结果.
由于网格搜索带来巨大的计算量,时间消耗多,因此在需要满足地震应急的背景下,应采取合适的计算机并行技术以减少计算时间.该系统采用OpenMP的并行编程技术,优化了原有算法,充分利用多核处理器所带来的性能提升,使得计算效率大大提高.目前该系统数据预处理和上述流程中3步反演所需总时间可控制在1—2分钟内.
3. 结果分析
采用最近构建的虚拟全球地震台网记录的波形数据(5°≤Δ≤85°),利用依赖于震级大小的滤波频段,离线自动测定2008年1月—2013年7月全球140次地震(MW6.5—9.0)的矩张量解(图 1).采用国际通行的做法,以美国哥伦比亚大学GCMT工作组给出的地震矩张量为标准,从以下6个方面评估结果的准确度和时效性.
3.1 矩震级MW与MW-GCMT的比较
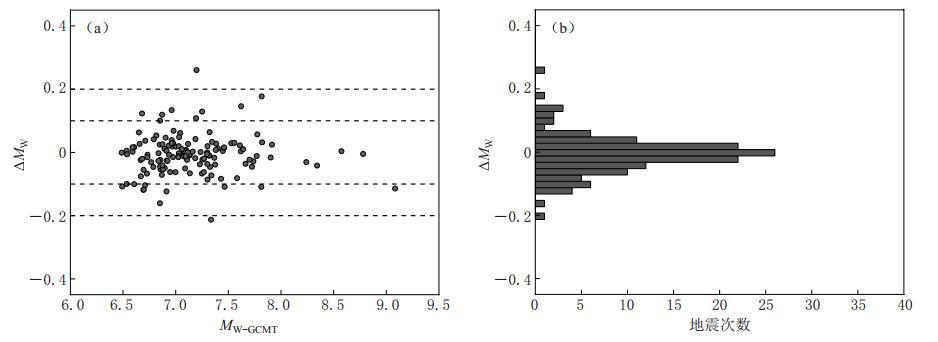
为比较本文测定的矩震级MW与GCMT的矩震级MW-GCMT的差异,计算了两者之差ΔMW,其中ΔMW= MW-MW-GCMT.从图 2和表 2可以看出,绝大多数矩震级MW与MW-GCMT吻合较好.两者之差ΔMW位于区间(-0.1,0.1)的地震占总数的83%,而位于区间(-0.2,0.2)的地震占总数的百分比则高达96%,ΔMW的标准方差仅为0.13.表明采用该方法,基于虚拟全球地震台网记录的波形所测定强震(MW≥6.5)的矩震级很准确.由图 2可见,不同大小地震测定的矩震级是比较稳定的,其中包括:最小地震为2008年2月24日22时印尼苏门答腊以西MW6.4地震,最大地震为2011年3月11日13时日本东北部MW9.0地震等,其中24次MW7.5以上地震测定的矩震级吻合都较好.仅有一次地震(2013年6月25日52时)的矩震级偏差较大,该地震是日本MW9.0巨震后1小时12分在主震震源区附近发生的又一次较大余震.由于主震尾波强烈干扰,使得此次地震测定的矩震级比MW-GCMT7.6偏大0.4.对于此类地震,通常称为“被干扰型地震”,可先计算主震的理论波形,后在实际观测波形中扣除主震的影响来准确计算“被干扰型地震”的矩张量.另外还有3次地震(MW-GCMT6.5—7.0)的矩震级偏差大于0.2,造成此现象的原因可能有:①波形质量较好的台站较少,或者所使用的台站分布很不均匀,在此情形下,进行第二步反演,结果会出现偏差;②个别台站因环境噪声、仪器噪声、地震计方位角偏差,以及地震仪器响应参数不正确等因素造成记录数据失真.
表 2 矩震级偏差ΔMW的统计分析Table 2. Statistical analyses of the magnitude difference ΔMW=MW-MW-GCMT
3.2 矩震级MW与速报震级M的比较
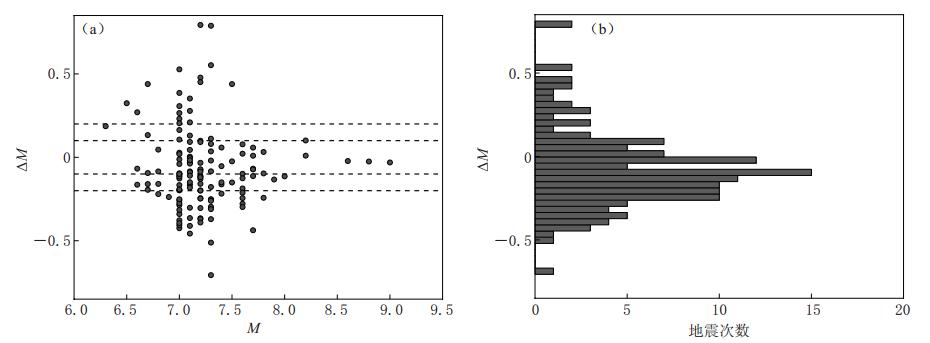
为比较本文测定的矩震级MW与中国地震台网中心速报正式发布震级M的差异,计算了两者之差ΔM=MW-M.由于矩震级与速报震级M在地震大小不同度量类型上其物理意义存在较大差别,因此,本文只作简单比较.从图 3和表 3可以看出,大多数矩震级MW与震级M存在一定偏差.两者间的残差ΔM位于区间(-0.2,0.2)的地震占总数的59%,位于区间(-0.3,0.3)的地震占总数的77%,两者间残差ΔM的标准方差约为0.26.根据统计的均值和中位数可知,大多数矩震级MW比震级M稍偏小.
表 3 矩震级偏差ΔM统计分析Table 3. Statistical analyses of the magnitude difference ΔM=MW-M
3.3 地震矩张量与GCMT的比较
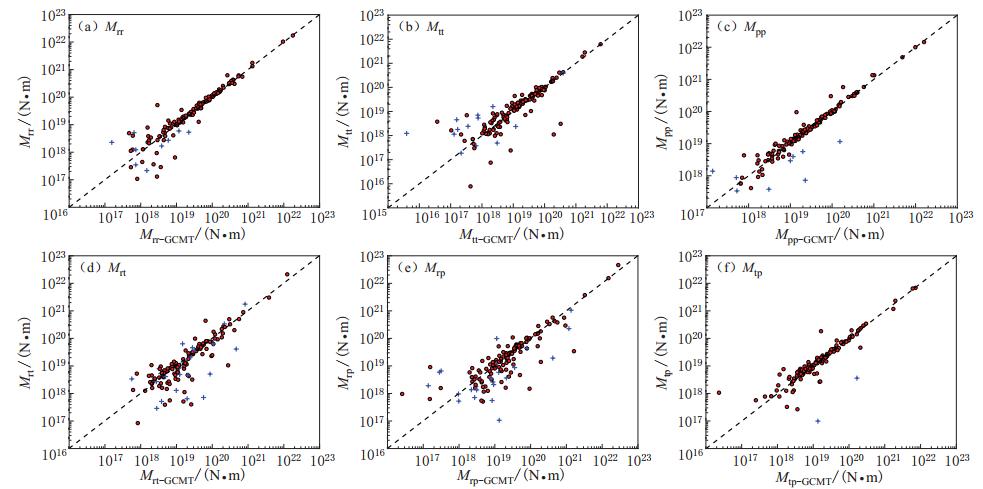
我们把测定的地震矩6个分量(Mrr,Mtt,Mpp,Mrt,Mrp,Mtp)分别与GCMT进行比较,得到图 4所示的结果.可以明显看出,随着各分量的绝对值大于1019 N·m,6个分量与GCMT间的相似性均变得更好.这说明在满足波形道数不小于15个以及台站方位间隙角不大于270°的前提条件下,基于W震相技术,能够准确测定大震甚至巨震的矩张量.特别是,在面波震级完全饱和的情况下,使用此方法能在地震快速响应方面发挥重要作用.一般来讲,利用长周期波形反演浅源地震矩张量解时,分量Mrt和Mrp的收敛性会相对较低(Kanamori,Given,1981).由图 4d和图 4e也不难发现,分量Mrt和Mrp较其它4个分量更为发散.这已成为国内外地震工作者在测定地震矩张量时遇到的一个熟知问题:对于浅源的纯逆冲型事件或纯正断层型事件,虽然M0sin2δ能较好约束,但地震矩M0和断层面倾角δ单独确定会比较困难,两者存在相互耦合的关系.对于巨震,这种耦合效应带来的影响更显著(Tsai et al,2011).另外,结果中各分量也出现了一些符号相反的情况,这也在一定程度上说明了对于少数复杂地震基于波形拟合方法反演矩张量6个分量结果的不唯一性.
![]() 图 4 本文测定的地震矩6个分量(Mrr,Mtt,Mpp,Mrt,Mrp,Mtp)与GCMT相应分量的比较.红色圆圈表示两者符号相同,蓝色十字表示两者符号相反Figure 4. Comparisons of the moment tensor elements of CMT measured in this study and GCMT for Mrr(a), Mtt(b), Mpp(c), Mrt(d), Mrp(e) and Mtp(f). Red circles denote that the moment tensor components of CMT and GCMT are of same sign, while blue crosses denote the opposite sign
图 4 本文测定的地震矩6个分量(Mrr,Mtt,Mpp,Mrt,Mrp,Mtp)与GCMT相应分量的比较.红色圆圈表示两者符号相同,蓝色十字表示两者符号相反Figure 4. Comparisons of the moment tensor elements of CMT measured in this study and GCMT for Mrr(a), Mtt(b), Mpp(c), Mrt(d), Mrp(e) and Mtp(f). Red circles denote that the moment tensor components of CMT and GCMT are of same sign, while blue crosses denote the opposite sign3.4 矩心水平位置分别与地震速报目录测定的震中位置以及GCMT给出的矩心水平位置的比较
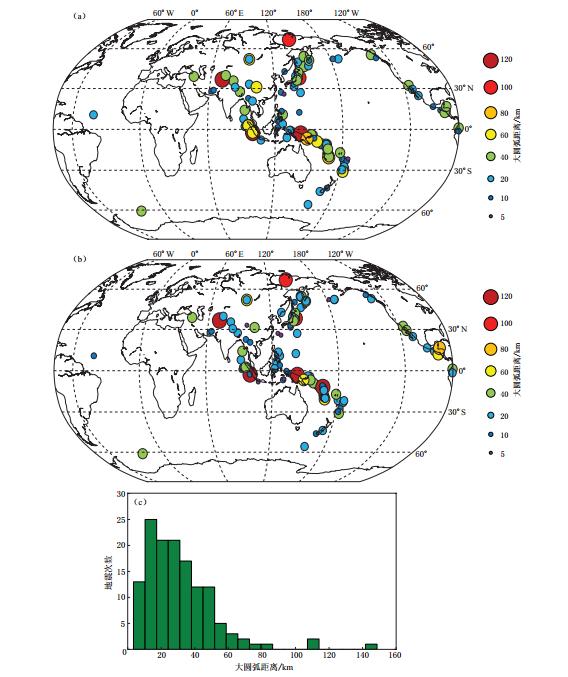
将矩心水平位置分别与地震速报目录测定的震中位置、GCMT给出的矩心水平位置比较,绘制出图 5.可以看出,相对于矩心水平位置与地震速报给出的震中位置间的大圆弧距离D1,矩心水平位置与GCMT给出的矩心水平位置间的大圆弧距离D2更小,后者吻合度更高.大圆弧距离D2的平均值为39.1 km,中位数为27.2 km,标准方差约49.8km,位于区间(0,50 km)的地震次数占总数的83%.说明测定的矩心水平位置结果与GCMT给出的结果基本一致,但也存在多次地震大圆弧距离D2大于50 km的情况.造成此现象的主要原因,可能是大震或巨震震源破裂过程复杂,当破裂长度多达数百公里时,若测定此类地震基于点源模型,系统则不能简单假设矩心时间偏移(centroid time shift)表征震源破裂持续时间(rupture duration)的1/2.对于这种情况可采用类似GCMT工作组的技术思路,即基于网格搜索技术,同时反演矩心时间偏移、破裂持续时间及矩心的水平位置,这样势必会使其中多次地震大圆弧距离D2进一步减小.但由于反演时新增了未知参数,将会带来大量的时间消耗,以致于降低此方法的时效性.
![]() 图 5 (a) 本文测定的矩心水平位置与地震速报给出的震中位置间大圆弧距离D1;(b)本文测定的矩心水平位置与GCMT给出的矩心水平位置间大圆弧距离D2;(c)本文测定的矩心水平位置与GCMT给出的矩心水平位置间大圆弧距离的频次直方分布图Figure 5. (a)The great-circle distances(D1)between horizontal centroid locations in this study and the epicenter locations given by the earthquake release; (b)The great-circle distances (D2)between horizontal centroid locations in this study and those obtained by GCMT; (c)Histogram of D2 distribution
图 5 (a) 本文测定的矩心水平位置与地震速报给出的震中位置间大圆弧距离D1;(b)本文测定的矩心水平位置与GCMT给出的矩心水平位置间大圆弧距离D2;(c)本文测定的矩心水平位置与GCMT给出的矩心水平位置间大圆弧距离的频次直方分布图Figure 5. (a)The great-circle distances(D1)between horizontal centroid locations in this study and the epicenter locations given by the earthquake release; (b)The great-circle distances (D2)between horizontal centroid locations in this study and those obtained by GCMT; (c)Histogram of D2 distribution3.5 矩心深度与GCMT给出的矩心深度的比较
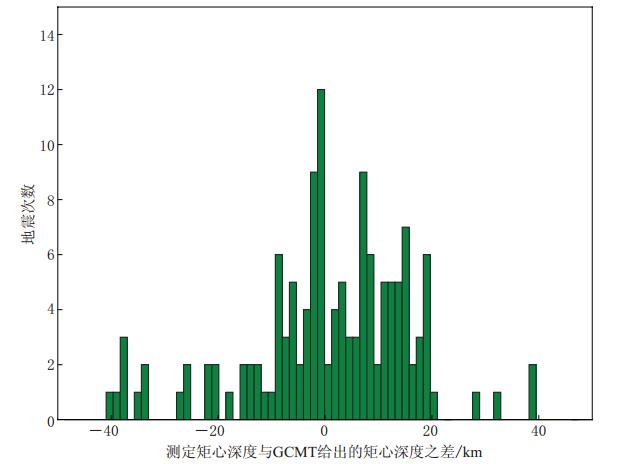
由于采用了较长周期的W震相,此方法对浅源地震深度(h≤11.5 km)的约束能力有限.采用类似GCMT工作组的技术思路,系统设定深度初始值为11.5 km,网格搜索间隔为2 km.将矩心深度与GCMT给出的矩心深度比较后绘制出图 6.据图 6可知,测定的矩心深度与GCMT给出的矩心深度之差位于区间(-10,10 km)的地震占总数的53.6%,标准方差约为17.8 km.
3.6 测定时间
在满足遴选后波形道数不小于15个及台站方位间隙角不大于270°的条件下,若采用震中距小于50°内台站的波形记录,约25分钟内即可完成测定.如需进一步提高结果的稳定性,则采用震中距小于85°内更多台站记录的波形数据,约40分钟内可准确测定(Hayes et al,2009;Duputel et al,2012).自2013年7月,该系统在中国地震台网中心部署并上线试运行以来,在预计的时间内自动测定了多次地震矩张量,结果与GCMT基本一致.例如,2013年9月24日巴基斯坦M7.8地震发生后约37分钟,自动系统将矩震级MW7.8(MW-GCMT7.7)通过短信发送给相关领导; 2013年10月1日11时38分鄂霍次克海M6.7地震在震后35分钟即测定矩震级为MW6.7(MW-GCMT为6.7).由于该系统目前处于上线试运行阶段,所以尚需以后更多的震例加以佐证,以统计出较准确的实际用时.
4. 讨论与结论
本文基于最近构建的虚拟全球地震台网记录的波形数据,采用OpenMP的并行编程技术优化原有算法,研制了基于W震相技术的全球强震(MW≥6.5)矩心矩张量自动反演系统,且评估其准确度和时效性,得到以下几点结论:
1) 采用虚拟全球地震台网,基于W震相技术的全球强震矩心矩张量自动反演系统,可准确测定全球MW≥6.5地震的矩张量解.而且绝大多数地震矩震级与GCMT给出的矩震级呈现出良好的线性趋势.两者之差(ΔMW)的标准方差约0.13.ΔMW位于区间(-0.2,0.2)的地震占总数的96%.测定的地震矩6个分量分别与GCMT相比其相似性均较好.多数地震矩心水平位置与GCMT给出的矩心水平位置也比较接近,两者间大圆弧距离位于区间(0,50 km)的地震占总数的84%.
2) 在满足遴选后波形道数不小于15及台站方位间隙角不大于270°的条件下,若采用震中距小于50°内台站的波形记录,约25分钟内即完成测定.如需进一步提高结果的稳定性,则采用震中距小于85°内更多台站记录的波形数据,可在约40分钟内准确测定.
3) 基于W震相技术,该系统能够准确测定大震的矩张量.特别是在面波震级完全饱和的情况下,使用此方法能在地震快速响应中发挥重要作用.而对于大震,更需要注意地震M0与断层面倾角δ两者间的耦合效应.
4) 该系统对连续余震矩张量反演会出现偏差现象.由于复杂的震源破裂过程、简化的一维速度模型以及个别台站记录失真等因素,可能会在一定程度上影响到矩张量反演结果的准确度.
评审专家对本文提出了宝贵意见;中国地震台网中心地震台网部数据管理组提供了高质量数据波形;全球台网数据从IRIS DMC下载.在此一并表示感谢!
-
图 4 本文测定的地震矩6个分量(Mrr,Mtt,Mpp,Mrt,Mrp,Mtp)与GCMT相应分量的比较.红色圆圈表示两者符号相同,蓝色十字表示两者符号相反
Figure 4. Comparisons of the moment tensor elements of CMT measured in this study and GCMT for Mrr(a), Mtt(b), Mpp(c), Mrt(d), Mrp(e) and Mtp(f). Red circles denote that the moment tensor components of CMT and GCMT are of same sign, while blue crosses denote the opposite sign
图 5 (a) 本文测定的矩心水平位置与地震速报给出的震中位置间大圆弧距离D1;(b)本文测定的矩心水平位置与GCMT给出的矩心水平位置间大圆弧距离D2;(c)本文测定的矩心水平位置与GCMT给出的矩心水平位置间大圆弧距离的频次直方分布图
Figure 5. (a)The great-circle distances(D1)between horizontal centroid locations in this study and the epicenter locations given by the earthquake release; (b)The great-circle distances (D2)between horizontal centroid locations in this study and those obtained by GCMT; (c)Histogram of D2 distribution
表 1 选用的滤波频段
Table 1 Corner frequency-bands used for b and pass filtering

表 2 矩震级偏差ΔMW的统计分析
Table 2 Statistical analyses of the magnitude difference ΔMW=MW-MW-GCMT

表 3 矩震级偏差ΔM统计分析
Table 3 Statistical analyses of the magnitude difference ΔM=MW-M

-




 下载:
下载: