Crustal structure in China from teleseismic receiver function
-
摘要: 利用中国数字地震台网30个台站的高质量宽频带远震数据,采用H-k叠加搜索法对中国境内的地壳结构进行研究,获得了研究区内的地壳厚度和vP/vS分布特征.结果表明, 中国境内的vP/vS值介于1.6—1.9之间,地壳厚度变化剧烈,在29—81 km之间.100°—110°E之间存在一个地壳厚度陡变带, 将中国分为东西两个部分.东部地壳厚度相对均匀,为31—36 km, 西部地区地壳厚度相对较厚且变化较大,中部地区地壳厚度为34—49 km.总的看来,青藏高原地区地壳最厚,可达81 km;天山、准噶尔盆地和内蒙古地区地壳厚度次之;华南地区地壳最薄.另外,中国大陆地壳平均波速比为1.738(σ=0.253),比全球大陆平均波速比1.78(σ=0.269)低.较低的波速比可能暗示中国境内地壳低速层的存在或者铁镁质成分的缺失.Abstract: This paper selects broadband teleseismic waveform data recorded by the China Digital Seismography Network to study the crustal structure in China.The crustal thickness and vP/vS ratio are estimated by the grid-search method.The result shows that the vP/vS ratio is between 1.6 and 1.9, and the crustal thickness ranges 29—81 km in China.The gradient belt between 100°E and 110°E divided China into eastern and western parts.The crustal thickness beneath eastern China smoothly ranges from 31 km to 36 km, while the crustal thickness in the western part is relatively thick and changed greatly.Crustal thickness ranges from 34 km to 49 km in the middle of China.In general, the crust in Tibetan Plateau is the thickest, reaching 81 km; crustal thickness decreases in Tianshan, Junggar basin and Inner Mongolia and thins out in South China coastal.The average vP/vS ratio over China crust is about 1.738 (σ=0.253), which is significantly lower than the average 1.78 (σ=0.269) of global continental crust.The lower vP/vS ratio may imply the existence of low velocity zone in the crust or the absence of mafic in China.
-
Keywords:
- receiver function /
- H-k stacking method /
- crustal thickness /
- vP/vS ratio /
- Poisson’s ratio
-
引言
地壳作为岩石圈的重要组成部分,对其物质组成和性质差异的了解程度决定着我们进一步研究地球深部特性的进程.地壳与上地幔的分界面即莫霍面两侧存在着地震波速、物质化学组成以及岩石性质的剧烈变化,是研究地球结构的一个重要间断面,在测地学、地球动力学和地震学中均对其有着广泛的研究.例如:曾融生等(1995)利用深震测深剖面得到了中国莫霍界面的深度图;方剑(1999)利用卫星重力资料反演得到了全球的地壳厚度和岩石圈厚度;黄建平等(2008)利用布格重力数据和地形数据反演计算了中国及邻区的地壳厚度; Chen等(2010)利用接收函数研究了中国大陆的地壳厚度和泊松比分布.
地壳厚度和构成在研究地壳起源和演化中有着紧密的约束关系,而地壳的构成则与地壳泊松比σ紧密相关.实验表明,温度和压力对泊松比影响很小(Christensen,1996).就普通岩石而言,泊松比为0.20—0.35,而岩石的矿物成分对其泊松比则有着很大的影响,硅石成分的减少或者铁镁质成分的增加都会使岩石的泊松比升高.对于下地壳而言,低泊松比(σ<0.26)、中等泊松比(0.26<σ<0.28)以及高泊松比(σ>0.28)分别由长英质、中间级混合矿物和铁镁质主导(Zandt,Ammon,1995).一般认为,地幔物质的侵入是地壳增生的主要途径,而地幔中富含铁镁质,这个过程往往伴随着泊松比的增大,较小的泊松比与地壳运动的后期改造有关.另外,局部熔融对泊松比的影响也很大,泊松比会随着流体成分的增加而升高(Watanabe,1993).
从古老的华北克拉通、 扬子克拉通到印度-欧亚大陆碰撞形成的年轻活跃的青藏高原,我国的地质构造具有很大的横向差异.而且我国也是地震多发的国家,近几十年来的唐山MS7.8大地震、汶川MS8.0大地震以及玉树MS7.0地震都给人们的生命和财产造成了巨大的损失.因此,研究中国的地壳结构对了解地壳演化、地震定位和大地震机制等方面具有极其重要的意义.
已有很多研究者作过中国地壳结构方面的研究,例如,Pn和Sn波走时层析成像(Liang et al,2004; 裴顺平等,2004; Sun et al,2004; Sun,Toksöz,2006),人工地震测深(曾融生等,1995; Wang et al,2000,2007; Zhang et al,2005; Li et al,2006; Zhao et al,2006),地震反射剖面(王椿镛等,2001,2003),以及莫霍面Ps转换波(Mangino et al,1999; 高星等,2005;黄建平等,2008; Chen et al,2010)等.Pn和Sn波走时成像表明,我国境内Sn波速度分布表现为东低西高,而且高速Sn波通常处于塔里木、准噶尔、柴达木、鄂尔多斯这样稳定的盆地和克拉通内.根据人工地震测深得到的剖面,Li等(2006)将中国大陆划分为14个主要构造带.Ps转换波研究表明中国地壳厚度分布从东到西依次增厚.尽管走时成像提供了一种研究地壳和地幔横向变化的高效手段,但其分辨比较低,通常在10 km左右(Sun et al,2004).人工地震测深和地震反射剖面虽然可以获得所期望深度的地壳分辨,但高昂的花费使其不能获取大范围的覆盖.而且人工地震测深的激发源缺少剪切波的能量,使其对S波速度的约束很差.
近些年来,随着宽频带数字地震仪的投入使用,接收函数已经成为一种研究台站下方地壳和上地幔结构的常见方法,而且已经被应用于全球各大版块的研究中.Sheehan等(1995)利用接收函数得到了科罗拉多山的地壳厚度分布;Zhu和Kanamori(2000)提出了接收函数的H-k方法,并且获得了洛杉矶盆地的地壳厚度和波速比分布.随后Zhu等(2006)利用接收函数方法研究了爱琴海地区的地壳厚度分布,得到了大陆地壳的延伸证据.在国内,高星等(2005)利用转换函数和波形反演的方法得到了中国及邻近地区的地壳结构,许卫卫和郑天愉(2005)利用壳幔转换波能量的叠加搜索方法得到了渤海湾盆地的地壳速度结构和泊松比分布,黄海波等(2011)利用P波接收函数研究获得了南海西沙群岛下方的地壳结构,武岩等(2011)采用接收函数共转换点叠加方法得到了华北地区的地壳结构,任枭等(2012)采用接收函数的H-k方法研究了鄂尔多斯地块东南地带的莫霍面深度变化特征,胡家富等(2003)及查小惠和雷建设(2013)研究获得了云南地区的地壳结构和泊松比分布.
本文将根据我国境内的31个宽频带数字地震台站记录到的远震资料,采用时间域迭代反褶积(Ligorría,Ammon,1999)提取P波接收函数,然后通过接收函数叠加搜索法(H-k方法)获取这31个台站下方的地壳厚度和波速比分布.
1. 方法与资料
1.1 方法
远震体波波形包含着震源、传播路径和接收区介质结构的丰富信息.接收函数就是通过去除远震体波中的震源、传播路径和仪器等影响后,得到反映台站下方地壳上地幔结构的时间序列.当给定地壳的初始P波速度vP,在水平层状均匀地壳模型下,由Ps波相对于P波的倒时差便可以求得地壳的厚度H.但是这种方法受vP不确定性的影响很大.研究表明,0.1 km/s的P波速度变化便可以引起地壳厚度4 km的误差(Zhu,Kanamori,2000).为此,引入P波在莫霍界面多次反射转换波PpPs及PsPs+PpSs震相,同时对地壳厚度和泊松比进行约束.直达P波以及Ps和PpPs震相的走时可以表示如下:

则Ps和PsPs震相相对直达波的到时可以表示为


式中,H为地壳厚度,vP和vS分别代表P波和S波速度,i和j分别表示P波和S波在地壳内的出射角.假设地层为水平,则各反射转换波的转换点距离很近,可以作近似计算TPsPs+PpSs-TPpPs≈TPs-TP,则

由上述公式可知,当给定一对H和vP/vS值,就可以求出对应的Ps,PpPs,PsPs+PpSs震相与P波的到时差.Zhu和Kanamori(2000)提出了同时利用Ps,PpPs,PsPs+PpSs震相对H和vP/vS进行约束的H-k域网格搜索方法,解决了单独使用Ps震相时H和k存在折衷的问题:

式中,r(t)为径向接收函数; tPs,tPpPs,tPsPs+PpSs分别表示所预测的Ps,PpPs,PsPs+PpSs震相相对直达波的到时;wi为这3个震相的权重,Σwi=1.扫描H,k域,当H和k对应真实的地壳厚度和泊松比时,s(H,k)达到极大值,从而也就得到所求的地壳厚度和波速比.波速比与地壳弹性系数泊松比σ之间存在确定的转换关系,即

这种方法无需人工对震相进行识别,可以对大批量记录进行处理,并且是对不同震中距和不同方位角的接收函数进行叠加,从而抑制了横向不均匀性的影响,得到的是一个平均的地壳模型.
1.2 资料
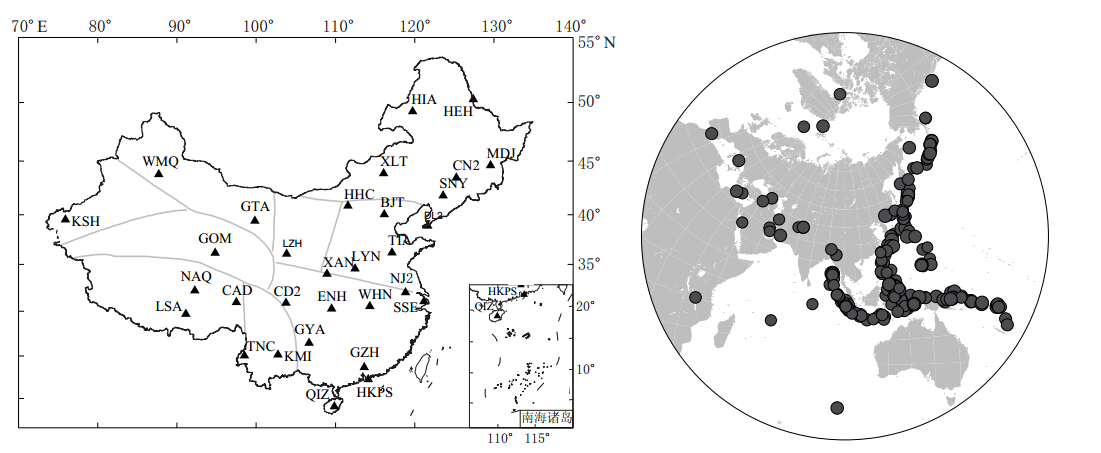
选取中国数字地震台网IC(10个台站)和CB(20个台站)以及香港地区HKPS台站等共31个台站2009—2012年的远震波形数据,所用台站较好地覆盖了中国大陆的主要地区.图1为所用台站分布和所选地震的震中分布.在接收函数研究中,为了减小410 km和660 km间断面的影响以及避免P波绕射波的出现,选取地震震中距范围为30°—90°;为了获取P波初动清晰、信噪比高的数据,选取MS5.5—7.0的远震数据.
2. 数据处理
2.1 接收函数的提取及H-k叠加
原始数据经去倾斜、去线性趋势及0.05—2 Hz的带通滤波后,为了确保最深界面多次反射波出现以及所选地震波形能量的一致性,我们首先选取P波初至前50 s和初至后150 s,在长度为200 s的时窗内截取P波波形;然后将ZNE三分量地震波形数据旋转到ZRT坐标系; 最后用垂向分量分别对径向分量和切向分量在时间域作迭代反褶积(Ligorría,Ammon,1999)提取P波接收函数.计算中迭代次数为200,并且使用系数分别为1.5(拐角频率约为0.7 Hz)和2.5(拐角频率约为1.25 Hz)的高斯滤波器对接收函数作高斯低通滤波,以获取不同频带宽度范围的接收函数.最后结合自相关计算和人工肉眼识别的方法从中挑选出震相清晰、信噪比高的接收函数.
进行接收函H-k叠加搜索时,将Ps,PpPs和PsPs+PpSs震相的权重分别设为0.7,0.2和0.1.H和k的搜索步长分别为0.1km和0.001.关于P波速度的选取,我们参考了Crust1.0模型(Laske et al,2013).该模型是基于人工地震测深得到的全球1°×1°地壳模型,具有很高的可信度.所有台站测量结果如表1所示.
表 1 台站相关信息及其下方地壳厚度H、波速比k和泊松比σTable 1. Stationsin formation and results of the Moho depth(H),vP/vS ratio(k)and Poisson’sratio(σ)
2.2 单台处理实例
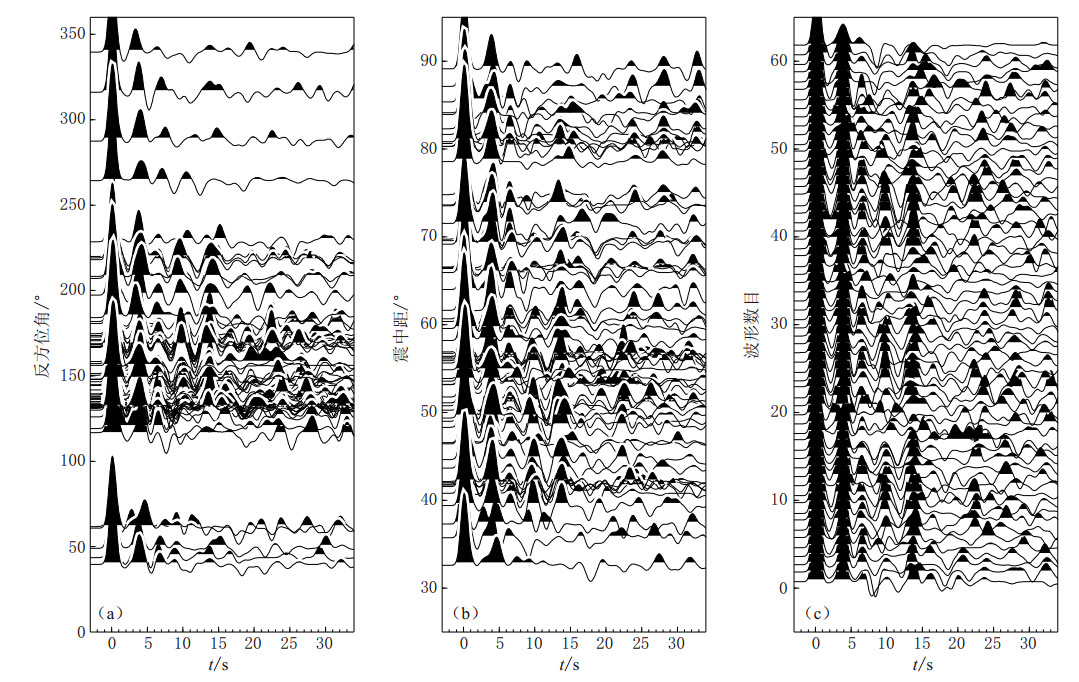
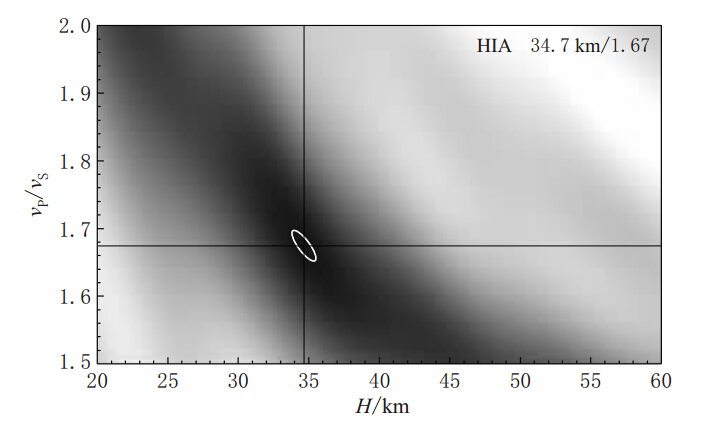
以从HIA台提取到的接收函数为例,图2a,b分别给出了HIA台接收函数随反方位角和震中距的空间分布.由该图可以看出,该台的接收函数随反方位角的分布主要集中在120°—230°之间,震中距范围则具有较好的分布.为了更清晰地展示Ps转换波和多次波震相,图2c给出了接收函数按地震时间的排列.我们可以看到,Ps波和多次波震相清晰明显且具有很好的一致性.图3为HIA台H-k扫描结果.图中十字交叉的地方即为搜索得到的最佳点,白色椭圆为置信区间.由该图可知,H-k扫描得到的HIA台下方地壳厚度和波速比分别为(34.68±2.8)km和1.674± 0.072(σ=0.223).
3. 地壳厚度和泊松比分布
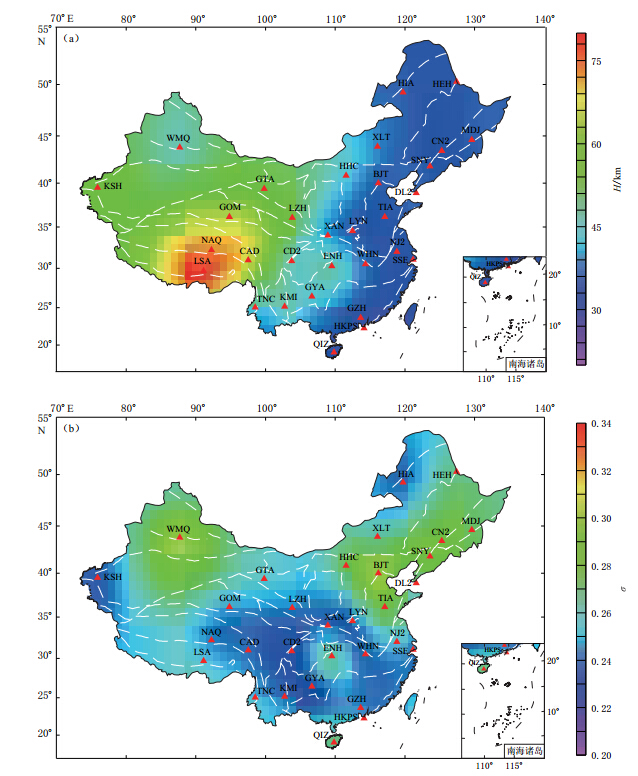
通过对中国境内31个台站接收函数的研究,得到了这31个台站下方的地壳厚度和泊松比(图4).结果表明: 我国东北地区地壳厚度为31—38 km,泊松比除了HIA台下方较小(0.220)外,其余均为0.258—0.274;华北平原地壳厚度比较均匀,为33—35 km;华南地区除了ENH台,地壳厚度均为28—39 km;西北地区除WMQ台处于天山北麓和准噶尔盆地南缘地壳厚度较薄,为45.29 km外,其余均为50 km以上;青藏高原地壳厚度较厚,为65—81 km.总体上,中国地壳厚度表现为东南较薄、西北较厚、青藏高原地区最厚的特征.
通过一种改良的标准最小曲率算法,将中国境内31个台站得到的地壳厚度和泊松比以1°×1°的网格插值,得到了中国地壳厚度和泊松比分布图(图4).需要指出的是,这种图仅仅是为了展示中国地壳厚度和泊松比的横向变化.由于数据密度有限,在离数据点太远的地方会出现极值,那并不能代表真实的地壳厚度和泊松比.
从图4中我们可以看出地壳厚度的分布有着明显的界线,大约在100°—110°E之间,这与中国的南北地震带及重力异常带是非常一致的.这个分界带将中国分为东西两个部分.东部地壳厚度较薄,平均厚度为35.51 km;越往西越厚,西部平均地壳厚度可达59.79 km.在中国,地壳最薄的地区在南部沿海和扬子克拉通上;东北部地壳比南部厚几千米,比较均匀.而越往西,地壳厚度急剧增厚,青藏高原地区地壳厚度可达80 km.本次测量所有台站的平均vP/vS均为1.738,低于世界大陆的平均值1.78(Zandt,Ammon,1995).这也暗示着中国大陆地壳富含长硅质或者缺少铁镁质.
4. 讨论
通过地理上的划分,我们按台站位置将其分为5个部分来进行分析讨论.
在东北的5个台站中,我们通过H-k方法得到的平均地壳厚度和vP/vS分别为34.88 km和1.750(σ=0.256).HIA台地处呼伦贝尔高原,有着相对低的vP/vS,如果剔除HIA台的数据,那么该地区vP/vS值为1.770(σ=0.265).这与Li等(2006)在中国进行的人工地震测深中得到的σ=0.266是相当一致的.而Li等得到的东北地区地壳厚度为32—40 km,本文接收函数得到的结果为29.9—39.1 km(表2).在该地区进行的主动震源地震波折射探测得出的结果为:蒙古—海拉尔褶皱带的地壳厚度为36—40 km,松辽盆地的地壳厚度为32—34 km(Yuan et al,1986;Li et al,2006).蒙古—海拉尔褶皱带和松辽盆地分别位于东北地区的西北部和东南部.位于东北地区西北部的HIA和XLT台接收函数得出的地壳厚度与深地震测深数据非常吻合;位于东北地区东南部的CN2和MDJ台结果也与松辽盆地深地震测深结果吻合得较好.
表 2 接收函数结果与深地震测深结果(Li等,2006)比较Table 2. Comparison of crustal thickness(H) and vP/vS ratios(k)from receiver function with those from deep seismic sounding(Li et al,2006)
华北地区西部的鄂尔多斯地块、中部的造山带及东部的华北平原为其主要构造单元.该地区的6个台站接收函数都给出了清晰的Ps震相,测量结果除了西部的HHC台站,其余5个台站得到的地壳厚度均在33—37 km之间,平均为35.05 km.这5个台站都位于东部的华北平原.而西部的HHC台站测得的地壳厚度为43.69 km,比东部的平均厚度厚8.6 km.华北地区东部地壳变薄与中生代华北块体盆地扩张导致的地壳变薄有关(Wang et al,2005).该地区6个台站测量得到的vP/vS值从LYN台的1.720(σ=0.245)到BJT台的1.910(σ=0.311),平均值为1.771(σ=0.264).该值比全球地盾和地台的平均波速比值(1.81±0.04)要低.在Zandt和Ammon(1995)对华北克拉通的研究中,BJT台下方的vP/vS 值也较高,本文结果与其相符.这表明该台站下的地壳富含镁铁质,或者下地壳存在着长英质成分的剥离.
华南地区板块相对稳定,主要由扬子克拉通和华夏块体组成.地壳整体上表现为东南薄、西北厚的特点.地壳较薄的地区分布在华夏块体沿海的台站(GZH和QIZ台)及扬子克拉通东南的台站(SSE和NJ2台)上,平均地壳厚度为31.88 km.WHN台和ENH台分别位于扬子板块的东西两侧,地壳厚度都较大,WNH台地壳厚度为37 km,ENH台因靠近扬子板块西缘地壳厚度陡变带,地壳厚度达49 km.ENH台下方vP/vS出现一个较大值1.800(σ=0.277).Chen等(2010)在利用接收函数研究中国境内台站下方地壳厚度和波速比的过程中也发现在ENH台下方存在一个H=35.9 km,k=1.996的极大波速比值,不过因vP/vS值过大而选择了另一峰值作为结果.而在本文中,扫描结果中只出现了一个峰值,并且与黄建平等(2008)所得的vP/vS值1.89相差不多,因此我们认为这一结果是可以接受的.整个华南地区vP/vS的平均值为1.71(σ=0.239),相对变化较大,但与深地震测深结果相比偏小.在华南东南部地区台站下方得到的vP/vS为1.68—1.72,处在一个低值.Wang等(2000)在对该地区的深震测深剖面研究中,得出该地区的vP/vS从上地壳的1.71上升到下地壳的1.78.一般认为扬子克拉通在岩石圈构造上一直保持稳定,其陆壳岩石组成以闪长石为主(邱瑞照等,2006).而闪长石的泊松比约为0.237(vP/vS=1.71)(Christensen,1996),因此,在华南地区得到的泊松比偏小,在地质解释上是完全说得通的.但是与深地震测深结果相比偏差较大,其主要原因是两种方法的差异引起的: 其一,接收函数反映的是台站下方的地壳结构,而深地震测深反映的是几百千米长的剖面上的平均地壳结构;其二,深地震测深是采用P波进行约束,接收函数则是利用P波和S波同时对地壳平均结构进行约束,而vP/vS会随着深度的变化而变化,因此两者在对地壳波速比的反映上存在差异.但是通常在地壳厚度的反映上两者差异较小,一般为3—4 km(李永华等,2009).
中国西北地区包括塔里木盆地和准噶尔盆地两个稳定的克拉通地块,这两个盆地被天山和祁连山所分隔.本文研究的台站在西北地区只有4个,从东往西依次为LZH,GTA,WMQ和KSH台.LZH和GTA台沿祁连山布设,WMQ和KSH台沿天山布设.整个地区地壳平均厚度为52.7 km,平均vP/vS为1.775(σ=0.268),均比华东地区高很多.但是因这4个台站都位于两个克拉通外围,所得到的结果并不能反映出准噶尔盆地和塔里木盆地的地壳结构.
作为全世界海拔最高的高原,青藏高原形成于印度板块与欧亚板块的碰撞,其构造远比克拉通构造复杂.受喀喇昆仑和喜马拉雅两条地壳厚度陡变带控制,青藏高原地区中心厚度都在65 km以上(LSA,NAQ和CAD台),为整个中国台站中得到的最大地壳厚度.边缘地区地壳厚度则陡然变薄.东部CD2和KMI台地壳厚度分别为45 km和47 km.该地区的平均vP/vS为1.722(σ=0.246).另外需指出的是,我们在TNC台测量的结果与其它台站相差甚远,仅为(41.95±3.2)km,vP/vS值也仅为1.634(σ=0.201).在进行测量时我们发现该台站接收函数多次反射波震相不明显且复杂,因此并没有将其结果绘于图5中.在研究TNC台时,李永华等(2009)得到的地壳厚度和波速比分别为35 km和1.87,而Chen等(2010)得到的结果分别为39 km和1.568,前者波速比高而后者波速比低.我们认为TNC台所处的腾冲火山地区地壳结构较为复杂,需要进一步研究再确定.
5. 讨论与结论
由于台站数量的限制,本文结果只是对研究区域地壳厚度和泊松比的一种空间采样,但是仍能很清晰地反映中国大陆的主要构造单元及其接触带,并且接收函数结果与人工地震测深结果有着较好的一致性.根据本文得到的结果,可以看出中国境内地壳厚度从东到西逐渐增厚.
中国东部地区地壳厚度相对较薄,并且分布比较均匀,最薄的地壳出现在华夏板块沿海地区以及扬子克拉通东部的一些台站.往西部地区,地壳厚度急剧增厚,从青藏高原边缘的45 km(CD2台)增加到板块中心的81 km(LSA台).在整个中国地壳厚度变化中,大约100°—110°E之间存在着一个近南北走向的地壳厚度陡变带,这个陡变带即为与很多浅源地震相关的南北地震带,在此过渡带上不仅地震活动强,并且存在着很大的重力异常.
青藏高原和华南地区vP/vS值均偏低,而西北、华北地区的vP/vS值相对高一些,低的vP/vS值意味着地壳富含长英质且缺少铁镁质成分,或者是地壳有大量缺少铁质和超铁质成分的变质沉积岩和硅质岩的侵入.根据Zandt和Ammon(1995)的研究结果,新生代和中生代地壳中长英质成分占主导地位,前寒武纪时期形成的克拉通有着双层的地壳结构: 上地壳以长英质中间混合岩石为主,下地壳主要为铁镁质成分.青藏高原属于新生代印度与欧亚板块碰撞的产物,因此地壳以长英质为主导致波速比偏低;而华北克拉通形成于前寒武纪时期,具有双层地壳的特性,其下地壳以铁镁质成分为主.
在TNC台得到的接收函数结果与该地区其它台相差较大,我们认为可能是台站下方存在局部熔融所致,具体原因尚需进一步研究.
-
表 1 台站相关信息及其下方地壳厚度H、波速比k和泊松比σ
Table 1 Stationsin formation and results of the Moho depth(H),vP/vS ratio(k)and Poisson’sratio(σ)

表 2 接收函数结果与深地震测深结果(Li等,2006)比较
Table 2 Comparison of crustal thickness(H) and vP/vS ratios(k)from receiver function with those from deep seismic sounding(Li et al,2006)

-
方剑 . 1999. 利用卫星重力资料反演地壳及岩石圈厚度[J]. 地壳形变与地震, 19 (1): 26-31. Fang J. 1999. Global crustal and lithospheric thickness inversed by using satellite gravity data[J]. Crustal Deformation and Earthquake,19 (1): 26-31 (in Chinese).
高星, 王卫民, 姚振兴. 2005. 中国及邻近地区地壳结构[J]. 地球物理学报,48 (3): 591-601. Gao X, Wang W M, Yao Z X. 2005. Crustal structure of China mainland and its adjacent regions[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,48 (3): 591-601 (in Chinese).
黄海波, 丘学林, 胥颐, 曾钢平. 2011. 利用远震接收函数方法研究南海西沙群岛下方地壳结构[J]. 地球物理学报,54 (11): 2788-2798. Huang H B, Qiu X L, Xu Y, Zeng G P. 2011. Crustal structure beneath the Xisha Islands of the South China Sea simulated by the teleseismic receiver function method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,54 (11): 2788-2798 (in Chinese).
黄建平, 崇加军, 倪四道. 2008. 利用H-Kappa方法反演中国地区台站下地壳厚度[J]. 中国科学技术大学学报,38 (1): 33-40. Huang J P, Chong J J, Ni S D. 2008. Inversing the crustal thickness under the stations of China via H-Kappa method[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology of China,38 (1): 33-40 (in Chinese).
胡家富, 苏有锦, 朱雄关, 陈赟. 2003. 云南的地壳S波速度与泊松比结构及其意义[J]. 中国科学: D辑,33 (8): 714-722. Hu J F, Su Y J, Zhu X G, Chen Y. 2005. S-wave velocity and Poisson's ratio structure of crust in Yunnan and its implication[J]. Science in China: Series D,33 (8): 714-722 (in Chinese).
李永华, 吴庆举, 田小波, 张瑞青, 潘佳铁, 曾融生. 2009. 用接收函数方法研究云南及其邻区地壳上地幔结构[J]. 地球物理学报,52 (1): 67-80 Li Y H, Wu Q J, Tian X B, Zhang R Q, Pan J T, Zeng R S. 2009. Crustal structure in the Yunnan region determined by modeling receiver functions[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,52 (1): 67-80 (in Chinese).
裴顺平, 许忠淮, 汪素云. 2004. 中国大陆及邻近地区上地幔顶部Sn波速度层析成像[J]. 地球物理学报,47 (2): 250-256. Pei S P, Xu Z H, Wang S Y. 2004. Sn wave tomography in the uppermost mantle beneath the China continent and adjacent regions[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,47 (2): 250-256 (in Chinese).
邱瑞照, 邓晋福, 李廷栋. 2006. 中国大陆岩石圈物质组成及演化[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 1-288. Qiu R Z, Deng J F, Li T D. 2006. The Composition and Evolution of the Lithosphere in China Continent[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 1-288 (in Chinese).
任枭, 徐志国, 杨辉, 陈宏峰, 邹立晔. 2012. 鄂尔多斯地块东南缘地带Moho深度变化特征研究[J]. 地球物理学报,55 (12): 4089-4096. Ren X, Xu Z G, Yang H, Chen H F, Zou L Y. 2012. Moho depth distribution character beneath the Ordos block's southeastern margin areas[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,55 (12): 4089-4096 (in Chinese).
王椿镛, 楼海, 魏修成, 吴庆举. 2001. 天山北缘的地壳结构和1906年玛纳斯地震的地震构造[J]. 地震学报,23 (5): 460-470. Wang C Y, Lou H, Wei X C, Wu Q J. 2001. Crustal structure in northern margin of Tianshan mountains and seismotectonics of 1906 Manas earthquake[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,23 (5): 460-470 (in Chinese).
王椿镛, 吴建平, 楼海, 周民都, 白志明. 2003. 川西藏东地区的地壳P波速度结构[J]. 中国科学: D辑,33 (S1): 181- 189. Wang C Y, Wu J P, Lou H, Zhou M D, Bai Z M. 2003. Crustal P wave velocity structure of western Sichuan and eastern Tibet[J]. Science in China: Series D,33 (S1): 181-189 (in Chinese).
武岩, 丁志峰, 朱露培. 2011. 利用共转换点叠加方法研究华北地区地壳结构[J]. 地球物理学报,54 (10): 2528-2537. Wu Y, Ding Z F, Zhu L P. 2011. Crustal structure of the North China Craton from teleseismic receiver function by the Common Conversion Point stacking method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,54 (10): 2528-2537 (in Chinese).
许卫卫, 郑天愉. 2005. 渤海湾盆地北西盆山边界地区泊松比分布[J]. 地球物理学报,48 (5): 1077-1084. Xu W W, Zheng T Y. 2005. Distribution of Poisson's ratios in the northwestern basin-mountain boundary of the Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,48 (5): 1077-1084 (in Chinese).
曾融生, 孙为国, 毛桐恩, 林中洋, 胡鸿翔, 陈光英. 1995. 中国大陆莫霍界面深度图[J]. 地震学报,17 (3): 322-327. Zeng R S, Sun W G, Mao T E, Lin Z Y, Hu H X, Chen G Y. 1995. Moho depth distribution of China mainland[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,17 (3): 322-327 (in Chinese).
查小惠, 雷建设. 2013. 云南地区地壳厚度和泊松比研究[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学,43 (3): 446-456. Zha X H, Lei J S. 2013. Crustal thickness and Poisson's ratio beneath the Yunnan region[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences,56 (4): 693-702.
Chen Y L, Niu F L, Liu R F, Huang Z B, Tkal ic ′ H, Sun L, Chan W. 2010. Crustal structure beneath China from receiver function analysis[J]. J Geophys Res,115 (B3): B03307. doi:10.1029/2009JB006386.
Christensen N I. 1996. Poisson's ratio and crustal seismology[J]. J Geophys Res,101 (B2): 3139-3156.
Laske G, Masters G, Ma Z, Pasyanos M. 2013. Update on CRUST 1.0: A 1-degree global model of Earth's crust[J]. Geophys Res Abstracts,15 : 2658.
Li S L, Mooney W D, Fan J. 2006. Crustal structures of mainland China from deep seismic sounding data[J]. Tectonophysics,420 (1/2): 239-252
Liang C T, Song X D, Huang J L. 2004. Tomographic inversion of Pn travel times in China[J]. J Geophys Res,109 (B11): B11304. doi:10.1029/2003JB002789.
Ligorría J P, Ammon C J. 1999. Iterative deconvolution and receiver-function estimation[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,89 (5): 1395-1400.
Mangino S, Priestley K, Ebel J. 1999. The receiver structure beneath the China digital seismograph network stations[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,89 (4): 1053-1076.
Sheehan A F, Abers G A, Jones C H, Lerner-Lam A L. 1995. Crustal thickness variations across the Colorado Rocky Mountains from teleseismic receiver functions[J]. J Geophys Res,100 (B10): 20391-20404.
Sun Y S, Toksz M N. 2006. Crustal structure of China and surrounding regions from P wave traveltime tomography[J]. J Geophys Res,111 (B3): B03310. doi:10.1029/2005JB003962.
Sun Y S, Li X, Kuleli S, Morgan F D, Toksöz M N. 2004. Adaptive moving window method for 3-D P-velocity tomography and its application in China[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,94 (2): 740-746.
Wang C Y, Zeng R S, Mooney W D, Hacker B R. 2000. A crustal model of the ultrahigh-pressure Dabie Shan orogenic belt, China, derived from deep seismic refraction profiling[J]. J Geophys Res,105 (B5): 10857-10869.
Wang C Y, Han W B, Wu J P, Lou H, Chan W W. 2007. Crustal structure beneath the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau and its tectonic implications[J]. J Geophys Res,112 (B7): B07307. doi:10.1029/2005JB003873.
Wang Y, Houseman G A, Lin G, Guo F, Wang Y J, Fan W M, Chang X. 2005. Mesozoic lithospheric deformation in the North China block: Numerical simulation of evolution from orogenic belt to extensional basin system[J]. Tectonophysics,405 (1/2/3/4): 47-63.
Watanabe T. 1993. Effects of water and melt on seismic velocities and their application to characterization of seismic reflectors[J]. Geophys Res Lett,20 (24): 2933-2936.
Yuan X C, Wang S, Li L, Zhu J S. 1986. A geophysical investigation of deep structure in China[G]//Reflection Seismology: A Global Perspective. Washington D.C. : AGU, 13 : 151-160..
Zandt G, Ammon C J. 1995. Continental crust composition constrained by measurements of crustal Poisson's ratio[J]. Nature,374 (6518): 152-154.
Zhang Z, Badal J, Li Y, Chen Y, Yang L, Teng J. 2005. Crust upper mantle seismic velocity structure across southeastern China[J]. Tectonophysics,395 (1/2): 137-157.
Zhao J, Mooney W D, Zhang X, Li Z, Jin Z, Okaya N. 2006. Crustal structure across the Altyn Tagh Range at the northern margin of the Tibetan Plateau and tectonic implications[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett,241 (3/4): 804-814.
Zhu L P, Kanamori H. 2000. Moho depth variation in southern California from teleseismic receiver functions[J]. J Geophys Res,105 (B2): 2969-2980.
Zhu L P, Mitchell B J, Akyol N, Cemen I, Kekovali K. 2006. Crustal thickness variations in the Aegean region and implications for the extension of continental crust[J]. J Geophys Res,111 (B1): B01301. doi:10.1029/2005JB003770.
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 柳建新,Syed muzyan SHAHZAD,孙娅,Asim SHAHZAD,李川,Meryem FANIDI,Ishfaque MUHAMMAD. 基于接收函数的中国东南部区域深部成矿机制(英文). Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China. 2022(01): 273-284 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李海艳,蔡辉腾,金星,姚华建,李培,徐嘉隽,林琛,任丛荣. 利用远震P波接收函数研究中国福建地区地壳厚度和泊松比. 地球物理学报. 2021(03): 805-822 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 程先琼,蒋科植. 基于深度降噪自编码神经网络的中国大陆地壳厚度反演. 地震学报. 2021(01): 34-47+136 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 韩如冰,李秋生,徐义贤,张洪双,陈昊,郎超,吴庆宇,王晓冉. 南岭—武夷交汇区的深部背景及地壳泊松比. 地球物理学报. 2019(07): 2477-2489 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 琚长辉,王伟,王祥春,高星. 基于波场分离的接收函数正演及偏移. 地球物理学进展. 2015(06): 2676-2682 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: