Modeling the dynamic process of slab subduction based on temperature-dependent thermal coefficients
-
摘要: 热传导系数和热膨胀系数是影响板块俯冲动力学过程的两个重要参数. 由于地球介质的不均匀性,热系数也会随深度发生变化.然而,这种变化在地球动力学模拟研究中往往被忽略.本文针对随温度变化的热传导系数和热膨胀系数, 模拟板块俯冲的动力学过程,分析热系数、黏度对板块俯冲形态的影响及其对应的地幔对流特征.结果表明,依温度变化的热传导系数和热膨胀系数会影响地幔温度及黏度分布,进而改变板块的俯冲角度;黏度是控制板块俯冲动力学演化过程的重要因素;地幔对流受黏度结构的影响,呈现分层对流及局部多个对流环等多种不同形态的对流场特征.Abstract: The thermal conductivity and expansion coefficients are two significant parameters that have influence on the dynamic process of slab subduction. Due to the heterogeneity of Earth medium, these two coefficients are usually variable with depth. Unfortunately, such variations are often ignored in current modeling studies of geodynamics. The present study refers to the temperature-dependent thermal conductivity and expansion to simulate the dynamic process of slab subduction. The impact of thermal parameters and viscosity on slab geometry and the corresponding characteristics of mantle convection are analyzed. The modeling results show that the temperature-dependent thermal conductivity and expansion affect the subduction angle by changing the thermal and viscosity structure. The viscosity plays a critical role in controlling the slab dynamic evolution. The mantle convection is affected by viscosity structure and exhibits different patterns, such as layered convection and local multiple convection loops, etc.
-
Keywords:
- slab subduction /
- viscosity structure /
- mantle convection /
- numerical modeling
-
引言
地幔是一个复杂的热动力系统,板块俯冲与地幔对流作用密切相关(Dubuffet et al,2000; 傅容珊等,2005).地球动力学家普遍认为俯冲板块的负浮力为地幔对流提供了驱动力(Kincaid,Sacks,1997; Bercovici,2003),俯冲板块可以通过俯冲作用促进地幔中的物质流动,而地幔对流又会反过来影响俯冲板块的形态及俯冲作用的形成演化(Zhong,Gurnis,1997; Rodríguez-González et al,2009).利用板块俯冲与地幔对流之间的相互作用和相互影响,研究俯冲板块的动力学过程,有助于深入理解板块动力学机制及壳幔相互作用.
地幔内部存在多形态和多尺度的对流体系,由于缺乏直接的地幔对流观测数据,仅依靠地球物理(van der Hilst et al,1997; Monnereau,Quere,2001)、地球化学(Allègre et al,1986)、地球动力学(Hager,Curnis,1987; Yamaji,1992)等间接观测或实验结果来分析理解板块俯冲过程显得十分困难.如何量化板块俯冲与地幔对流之间的作用,分析不同俯冲板块的俯冲形态及其对应的地幔对流模式无疑是研究板块俯冲动力学过程的重要发展方向之一.
前人主要通过数值模拟研究了影响板块俯冲形态的主要因素,结果表明板块俯冲受板块密度、地幔黏度等诸多因素控制(Zhong et al,2000; Billen,Hirth,2005,2007; Rodríguez-González et al,2012).然而,目前的研究通常将热传导系数和热膨胀系数取为常数作近似简化处理(Zhong et al,2000; Billen,Hirth,2005,2007; 朱桂芝等,2009; 高翔等,2012; Rodríguez-González et al,2012).实验结果表明,热传导系数和热膨胀系数都是随温度变化的(Bouhifd et al,1996; Xu et al,2004).忽略温度对热系数的影响,势必会改变板块俯冲的热结构,制约板块俯冲的动力学演化,以致于影响到对壳幔动力结构的深入探讨.
为此,本文针对随温度变化的热系数,使用COMSOL Multiphysics 4. 2a软件,模拟板块俯冲的动力学过程,分析热系数及黏度对板块俯冲形态的影响,以及不同的俯冲形态所对应的地幔对流特征.计算中采用Hirth和Kohlstedt(2003)实验得到的依赖压力和温度变化的黏度结构.
1. 数值模拟
1.1 控制方程
将地幔视为不可压缩的黏性流体介质,采取Boussinesq近似,考虑重力作用及绝热压缩生热的影响,板块俯冲与地幔对流过程满足以下质量、动量及能量守恒方程:

式中,u 为速度,η为黏度,P为压力,ρ为密度,g为重力加速度,CP为常压热容,T为温度,t为时间,k为热传导系数,α为热膨胀系数,vz为垂向速度分量.
计算过程中,仅考虑由温度引起密度变化所产生的浮力效应,则密度表示为

式中,ρ0为参考密度,T0为地表温度.
1.2 建立模型
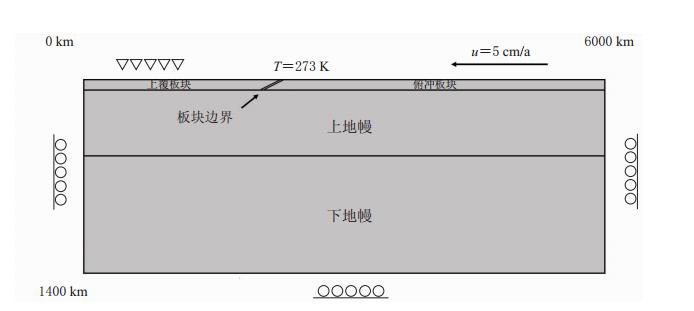
本文选取一个6 000 km×1 400 km的剖面作为计算区域(图1).俯冲板块厚95 km;板块年龄Asub由板块宽度和俯冲速度控制(Rodríguez-González et al,2012),即Asub=D/u,式中D为模型右侧边界到板块边界的水平距离,u为俯冲速度.这里,我们将俯冲速度取为定值u=5 cm/a,得到恒定的板块年龄Asub=80 Ma,以排除板块参数对俯冲形态的影响.
板块边界设置了一个狭长的低黏度剪切带.研究表明,该剪切带的黏度大小及几何形态会对板块俯冲的动力学过程造成较大的影响(Manea,Gurnis,2007).鉴于由大量观测统计得到的岩石圈范围的板块边界平均倾角为32°±9°(Lallemand et al,2005),本文采用剪切带倾角为30°,宽15 km,与Rodríguez-González等(2012)的设置类似.
模型初始温度分布根据Stein和Stein(1992)给出的基于全球深度和热流(global depth and heat)的温度模型计算得出.其上边界设为恒温边界条件,取值为273K;侧边界、底边界均为绝热边界条件.对于力学边界条件,上覆板块的表面固定,其余边界自由滑动,以板块汇聚速率作为板块运动的主要约束,模拟俯冲板块在25Ma间的动态演化过程.其中计算步长为5 Ma,模型所采用的固定参数见表1.
表 1 模型固定参数Table 1. Fixed model parameters
1.3 关键参数
1.3.1 热传导与热膨胀系数
热传导系数k和热膨胀系数α是制约俯冲板块热结构的两个重要参数.由于地球介质的不均匀性(van der Hilst,Karason,1999),热系数也应是变化的.Xu等(2004)的研究表明,橄榄石的热传导系数随温度升高呈指数递减.热传导系数与温度的关系为

Bouhifd等(1996)对镁橄榄石热膨胀系数的实验结果表明,热膨胀系数随温度升高线性增加,其经验关系式为

式(5)和(6)中的T均为绝对温度.
本文基于Xu等(2004)和Bouhifd等(1996)的实验结果,采用随温度变化的热传导系数(式(5))和热膨胀系数(式(6)),分析其对模型温度及黏度结构的影响.
1.3.2 黏度结构
黏度结构是确定俯冲板块形态的关键参数之一(Gurnis,Hager,1988; Billen,Hirth,2007).长期以来地幔黏度都是一个热门话题.目前对于地幔黏度的分布,尽管不同地球物理反演结果不尽相同,但普遍认为其范围大致在1020—1022Pa·s之间,地幔黏度大致表现为径向分层(Forte et al,1991; King,Masters,1992; Mitrovica,Peltier,1993).实验及理论研究均表明,温度和压力是影响地幔黏度的重要因素(Hirth,Kohlstedt,2003),因此考虑随温度、压力变化的地幔黏度来分析板块俯冲的动力学过程会更接近真实地球地幔的情况. 在地幔中,形变与扩散蠕变(diffusion creep)和位错蠕变(dislocation creep)相关(Karato,Wu,1993; Karato,Jung,2003).对于上地幔,流变性质表现为这两种形变机制的综合影响,可以用有效黏度来表示(Billen,Hirth,2007; Rodríguez-González et al,2012),即

式中,ηdif为扩散蠕变黏度,ηdis为位错蠕变黏度,由下式计算(Hirth,Kohlstedt,2003):

This page contains the following errors:
error on line 1 at column 1: Start tag expected, '<' not foundBelow is a rendering of the page up to the first error.
表 2 黏度相关参数Table 2. Viscosity parameters
下地幔主要由钙钛矿组成,地震各向异性研究及实验研究表明,其形变主要由扩散蠕变控制(Ritsema,2000),其黏度可能是上地幔的10倍(Peltier,1989; Stacey et al,1989)甚至100倍(Hager,Clayton,1989).本文选取不同的下地幔与上地幔黏度之比ηl/ηu,计算地幔黏度结构对俯冲形态的影响.
2. 结果与分析
本文选取了几组不同的模型研究板块俯冲的动力学过程,计算中所使用的参数如表3所示. 通过改变热系数(k和α)(模型1,2)、上下地幔黏度差异(ηl/ηu)(模型1,3,4)及板块边界剪切带黏度(ηsz)(模型1,5,6),分析其对俯冲板块几何形态的影响.
表 3 模型参数Table 3. Model parameters
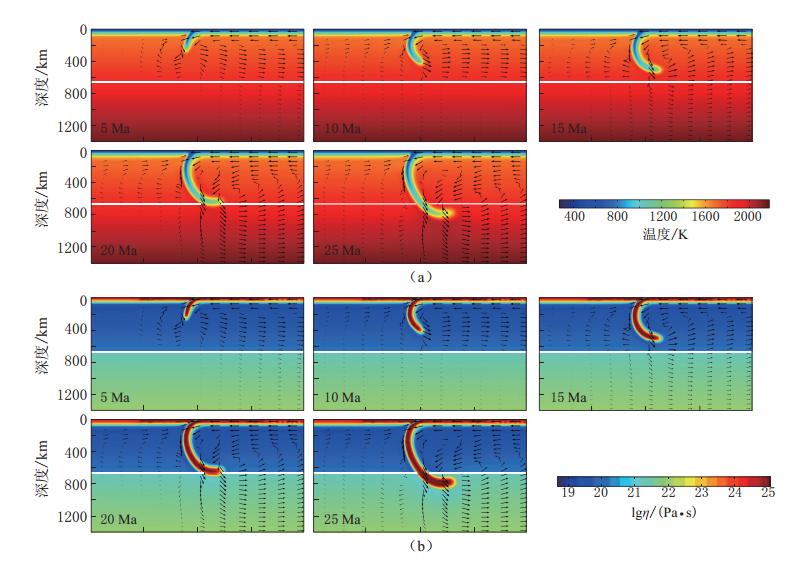
2.1 俯冲板块热结构及黏度演化
图2给出了模型1的俯冲动力学演化过程.在俯冲开始阶段,由于板块温度明显低于周围地幔温度,其密度相对较大,板块因受负浮力的影响而俯冲进入地幔.在板块俯冲的驱动下,地幔物质随之流入上覆板块与俯冲板块之间的地幔楔.在上地幔范围内,随着俯冲深度的加深,由于作用在板块上的负浮力增加,板块的俯冲倾角逐渐增大,上下地幔的对流活动增强.且由式(7)、(8)可知,上地幔黏度随深度增加而增大,造成板块在上地幔俯冲过程中随俯冲深度的加深而逐渐向后弯曲.至板块俯冲进入下地幔时,因下地幔黏度是上地幔黏度的10倍,板块所受黏滞阻力增加,俯冲速度减小,俯冲板块在800 km深度之上趋于平缓.
2.1.1 热系数的影响
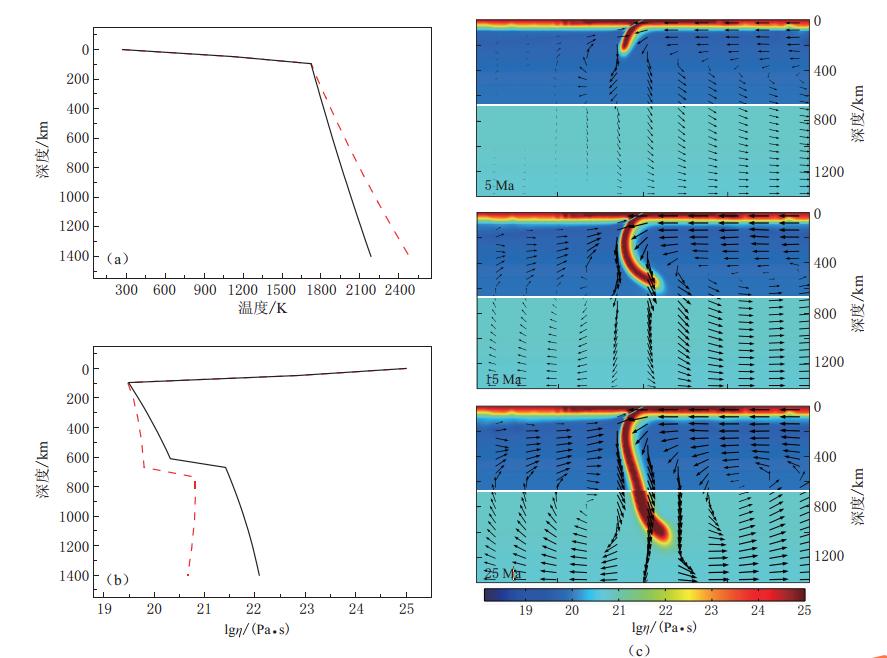
为了探讨随温度变化的热传导系数和热摩擦系数对板块俯冲演化的影响,我们比较了模型1与模型2的结果(图3).模型2为热传导系数和热膨胀系数均取定值的情况.由模型的初始温度和黏度结构(图3a,b)可知,模型2的初始温度(图3a中红虚线)要高于模型1的温度(图3a中黑实线),且温度增量随深度增加逐渐加大.由于黏度与温度成反比(式(8)),故不考虑温度对热系数影响时,模型2中上、下地幔平均黏度(图3b中红虚线)均比模型1(图3b中黑实线)小一个数量级.
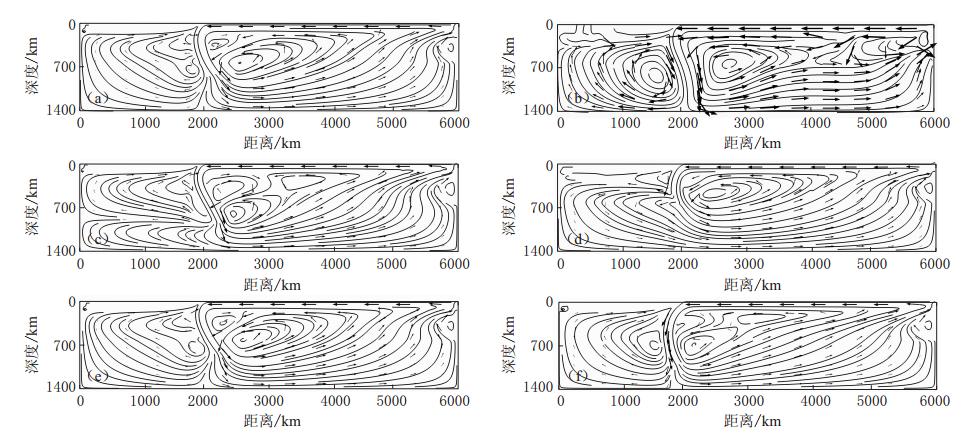
![]() 图 3 热系数对板块俯冲演化的影响(a)、(b)分别为模型1(黑色实线)和模型2(红色虚线)的热结构和黏度结构,(c)为俯冲经历5,15和25 Ma后模型2的黏度演化. 图中白色实线表示上、下地幔的分界线,箭头表示流速Figure 3. Influence of thermal coefficients on slab subduction evolution (a)-(b)Temperature and viscosity depth profiles for model 1(black solid line) and model 2(red dashed line);(c)Viscosity profiles for model 2 after 5,15 and 25 Ma evolution. The white line denotes the boundary of upper and lower mantle,and the arrows represent fluid velocities
图 3 热系数对板块俯冲演化的影响(a)、(b)分别为模型1(黑色实线)和模型2(红色虚线)的热结构和黏度结构,(c)为俯冲经历5,15和25 Ma后模型2的黏度演化. 图中白色实线表示上、下地幔的分界线,箭头表示流速Figure 3. Influence of thermal coefficients on slab subduction evolution (a)-(b)Temperature and viscosity depth profiles for model 1(black solid line) and model 2(red dashed line);(c)Viscosity profiles for model 2 after 5,15 and 25 Ma evolution. The white line denotes the boundary of upper and lower mantle,and the arrows represent fluid velocities地幔黏度的变化直接影响到板块俯冲的演化过程.由图3c可以看出:在俯冲开始的5Ma,模型2的俯冲形态与模型1基本一致,热参数对浅部俯冲角度的影响较小;随着俯冲深度的增加,因模型2中地幔平均黏度较小,地幔对流速度与模型1相比较快,带动了更多地幔热物质流入地幔楔;同时,板块所受黏滞阻力较小,故板块在上地幔的俯冲角度小于模型1的结果,进入下地幔时,其角度接近于垂直.
2.1.2 地幔黏度结构的影响
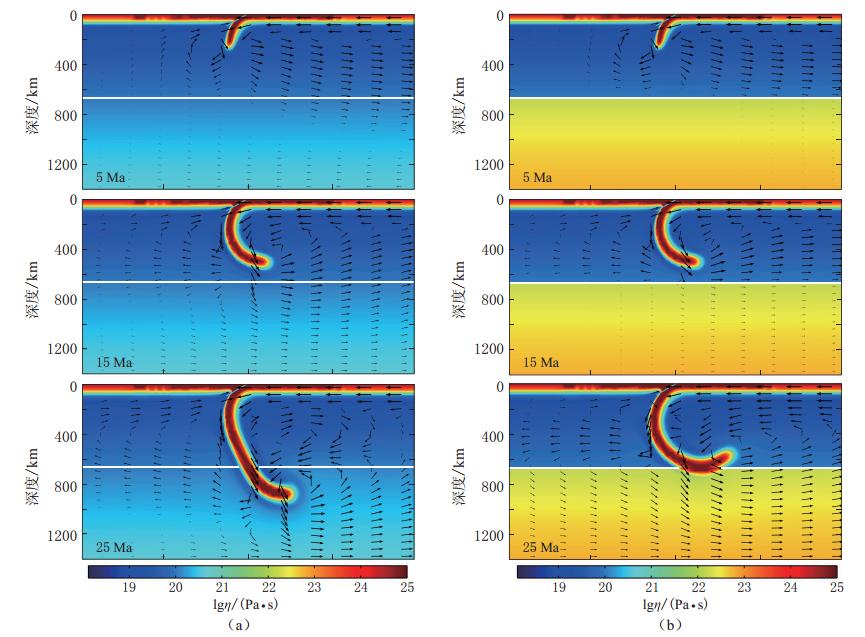
通过改变上下地幔黏度差异使下地幔与上地幔的黏度之比ηl/ηu=1(模型3)或ηl/ηu=100(模型4),以此来研究地幔黏度结构对板块俯冲过程的影响,结果如图4所示.由于上地幔黏度保持不变,在开始的15Ma内板块俯冲形态在模型1、模型3和模型4中是一致的;随着板块向下地幔俯冲,因模型3中下地幔黏度与上地幔相差较小,板块俯冲速度较快,俯冲深度达到约950km.模型4中当上下地幔黏度相差两个数量级时,俯冲板块的前端向后弯曲并停滞在670km深度之上.由此可见,上下地幔黏度差异越小,板块俯冲深度越深; 黏度差异越大,板块弯曲程度越明显.这与Billen和Hirth(2007)的模拟结果具有较为一致的趋势.需要说明的是,本文采用的热传导系数和热膨胀系数是随温度变化的,在下地幔与上地幔黏度之比相同的情况下,地幔黏度均值会整体偏大,因而当板块俯冲至下地幔后,其几何形态与同等情况下Billen和Hirth(2007)的结果相比会显得更加弯曲.
![]() 图 3 地幔黏度结构对板块俯冲演化的影响(a)模型3,ηl/ηu=1;(b)模型4,ηl/ηu=100.白色实线表示上、下地幔的分界线,箭头表示流速Figure 3. Influence of mantle viscosity structure on slab subduction evolution(a)Model 3 with ηl/ηu=1;(b)Model 4 with ηl/ηu=100. The white line denotes the boundary of upper and lower mantle,and the arrows represent fluid velocities
图 3 地幔黏度结构对板块俯冲演化的影响(a)模型3,ηl/ηu=1;(b)模型4,ηl/ηu=100.白色实线表示上、下地幔的分界线,箭头表示流速Figure 3. Influence of mantle viscosity structure on slab subduction evolution(a)Model 3 with ηl/ηu=1;(b)Model 4 with ηl/ηu=100. The white line denotes the boundary of upper and lower mantle,and the arrows represent fluid velocities2.1.3 板块边界剪切带黏度的影响
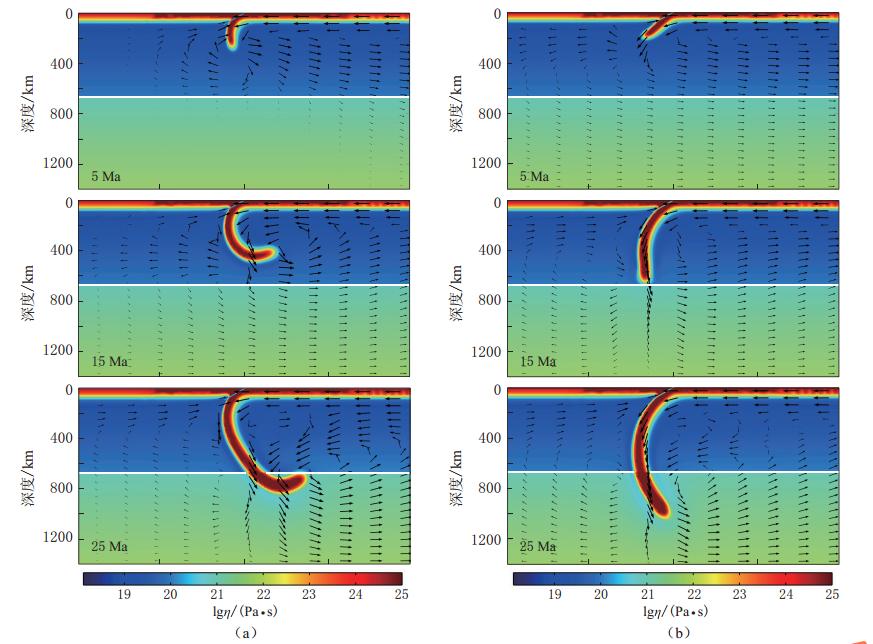
板块边界处剪切带的黏度特性与俯冲板块与上覆板块的耦合程度有关,其对俯冲过程的影响如图5所示.比较模型1,5和6可知:模型5中板块边界剪切带的黏度相对较小,其板块耦合程度低于模型1和6,板块以较大的倾角(~90°)进入上地幔并逐渐向后弯曲,到达下地幔后其弯曲程度与模型1相比更为明显;模型6中因剪切带黏度大,板块耦合程度相对较高,在开始的5 Ma板块以较低角度(~40°)俯冲,之后在负浮力作用下俯冲角度逐渐增加并垂直进入下地幔,板块整体弯曲程度较小. 上述结果与Billen和Hirth(2007)及Rodríguez-González等(2012)的研究结果相类似.
![]() 图 5 板块边界剪切带黏度对板块俯冲演化的影响(a)模型5,ηsz=5×1020 Pa · s,(b)模型6,ηsz=3×1021 Pa · s. 白色实线表示上、 下地幔的分界线,箭头表示流速Figure 5. Influence of the shear zone viscosity at the plate boundary on slab subduction evolution(a)Model 5 with ηsz=5×1020 Pa · s;(b)Model 6 with ηsz=3×1021 Pa · s. The white line denotes the boundary of upper and lower mantle,and the arrows represent fluid velocities
图 5 板块边界剪切带黏度对板块俯冲演化的影响(a)模型5,ηsz=5×1020 Pa · s,(b)模型6,ηsz=3×1021 Pa · s. 白色实线表示上、 下地幔的分界线,箭头表示流速Figure 5. Influence of the shear zone viscosity at the plate boundary on slab subduction evolution(a)Model 5 with ηsz=5×1020 Pa · s;(b)Model 6 with ηsz=3×1021 Pa · s. The white line denotes the boundary of upper and lower mantle,and the arrows represent fluid velocities2.2 俯冲板块引起的地幔对流特征比较
图6给出了不同模型对应的地幔对流场.由图6可以看出,地幔对流格局主要受黏度结构的影响.对于模型2,因热传导系数和热膨胀系数取为常数,地幔平均黏度是几个模型中最低的,因而俯冲板块进入下地幔后所达到的深度最深,地幔对流整体表现为单层环状,即全地幔对流的格局(图6b).当考虑温度对热系数的影响时(模型1,5,6),下地幔与上地幔的黏度比保持不变,地幔对流格局与模型2大致相同,但由于地幔平均黏度增大,板块虽俯冲进入下地幔,但地幔流速相对较小,在俯冲板块左侧区域环流显著减弱,局部有小范围的对流环出现(图6a,e,f).改变上下地幔的黏度差异,使下地幔与上地幔黏度 之比为1时(模型3),地幔对流格局较为复杂,在俯冲板块左侧区域地幔对流出现以900km 为界分层对流的现象,右侧区域局部存在多个对流环(图6c).对于模型4,因下地幔黏度比上地幔大两个数量级,俯冲板块停留在上下地幔分界面之上,故除了地幔楔处的角落流,地幔在较大范围内表现为单层环状对流的格局(图6d).对于不同的模型,地幔对流呈现出多种形态,其与板块俯冲之间的关系极为复杂,对于这一部分今后还将作更为详尽的研究之比为1时(模型3),地幔对流格局较为复杂,在俯冲板块左侧区域地幔对流出现以900 km为界分层对流的现象,右侧区域局部存在多个对流环(图6c).对于模型4,因下地幔黏度比上地幔大两个数量级,俯冲板块停留在上下地幔分界面之上,故除了地幔楔处的角落流,地幔在较大范围内表现为单层环状对流的格局(图6d).对于不同的模型,地幔对流呈现出多种形态,其与板块俯冲之间的关系极为复杂,对于这一部分今后还将作更为详尽的研究.
3. 讨论与结论
板块俯冲过程涉及地球内部复杂的物质与能量交换,是地球动力学研究领域的一项重要内容.本文通过对板块俯冲动力学过程的模拟计算,得到如下结论:
1)依赖温度变化的热传导和热膨胀系数会影响温度及黏度分布,进而影响板块的俯冲形态. 热系数对板块浅部俯冲角度影响较小,对板块深部影响较大.
2)黏度是制约板块俯冲动力学演化的重要因素上下地幔之间较大的黏度差异能够阻止或延迟俯冲板块穿透至下地幔;板块边界处剪切带的黏度决定着俯冲板块与上覆板块的耦合程度,黏度越小,耦合程度越低;俯冲角度越大,板块越弯曲.
3)地幔对流依赖于不同的黏度结构,在地幔中会出现区域性分层对流及局部多个对流环等对流场.
热传导系数和热膨胀系数通过对流和扩散作用控制着地球内部的能量交换,其变化直接影响到地幔热状态与板块俯冲的动力学演化.最新的研究结果表明,热传导系数和热膨胀系数并不仅仅随温度单调变化,而且还受温度、压力和矿物组成的共同作用,呈现出较为复杂的变化(Tosi et al,2013; Hofmeister et al,2014).这种变化对于板块俯冲及地幔对流的影响值得进一步研究.
俯冲板块能否穿透660 km间断面一直是地球动力学研究关注的热点问题之一,同时也是确定地幔对流模式的关键因素.地震震源分布及层析成像结果显示俯冲板块的形态各异(Fukao et al,2001),有些可穿透660km间断面到达下地幔,形成全地幔对流模式;有些则停滞于660km间断面附近,表现为双层地幔对流模式.本文基于不同的地幔黏度结构及板块边界剪切带黏度,得到的板块俯冲形态多呈现为垂直穿透或向后弯曲.对于类似日本海地区西太平洋俯冲板块向前水平延伸并停滞于660 km间断面之上的形态,可能与相变过程中的亚稳态橄榄石分布(Kirby et al,1996)、660km相变负克拉伯龙斜率(Torii,Yoshioka,2007),以及海沟后撤作用(Christensen,1996)有关,这些均需在今后的模拟研究中加以验证.
-
图 3 热系数对板块俯冲演化的影响(a)、(b)分别为模型1(黑色实线)和模型2(红色虚线)的热结构和黏度结构,(c)为俯冲经历5,15和25 Ma后模型2的黏度演化. 图中白色实线表示上、下地幔的分界线,箭头表示流速
Figure 3. Influence of thermal coefficients on slab subduction evolution (a)-(b)Temperature and viscosity depth profiles for model 1(black solid line) and model 2(red dashed line);(c)Viscosity profiles for model 2 after 5,15 and 25 Ma evolution. The white line denotes the boundary of upper and lower mantle,and the arrows represent fluid velocities
图 3 地幔黏度结构对板块俯冲演化的影响(a)模型3,ηl/ηu=1;(b)模型4,ηl/ηu=100.白色实线表示上、下地幔的分界线,箭头表示流速
Figure 3. Influence of mantle viscosity structure on slab subduction evolution(a)Model 3 with ηl/ηu=1;(b)Model 4 with ηl/ηu=100. The white line denotes the boundary of upper and lower mantle,and the arrows represent fluid velocities
图 5 板块边界剪切带黏度对板块俯冲演化的影响(a)模型5,ηsz=5×1020 Pa · s,(b)模型6,ηsz=3×1021 Pa · s. 白色实线表示上、 下地幔的分界线,箭头表示流速
Figure 5. Influence of the shear zone viscosity at the plate boundary on slab subduction evolution(a)Model 5 with ηsz=5×1020 Pa · s;(b)Model 6 with ηsz=3×1021 Pa · s. The white line denotes the boundary of upper and lower mantle,and the arrows represent fluid velocities
表 1 模型固定参数
Table 1 Fixed model parameters

表 2 黏度相关参数
Table 2 Viscosity parameters

表 3 模型参数
Table 3 Model parameters

-
傅容珊, 冷伟, 常筱华. 2005. 地幔对流与深部物质运移研究的新进展[J]. 地球物理学进展, 20(1): 170-179. Fu R S, Leng W, Chang X H. 2005. Advancements in the study of mantle convection and the material movements in deep Earth interior[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 20(1): 170-179 (in Chinese).
高翔, 张健, 孙玉军, 吴时国. 2012. 马尼拉海沟俯冲带热结构的模拟研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 55(1): 117-125. Gao X, Zhang J, Sun Y J, Wu S G. 2012. A simulation study on the thermal structure of Manila trench subduction zone[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 55(1): 117-125 (in Chinese).
朱桂芝, 石耀霖, 陈石, 张怀. 2009. 西太平洋板块向东北地区深部俯冲的数值模拟[J]. 地球物理学报, 52(4): 950-957. Zhu G Z, Shi Y L, Chen S, Zhang H. 2009. Numerical simulations on deep subduction of western Pacific Plate to NE China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 52(4): 950-957 (in Chinese).
Allègre C J, Staudacher T, Sarda P. 1986. Rare gas systematics: Formation of the atmosphere, evolution and structure of the Earth's mantle[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 81(2): 127-150.
Bercovici D. 2003. The generation of plate tectonics from mantle convection[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 205(3): 107-121.
Billen M I, Hirth G. 2005. Newtonian versus non-Newtonian upper mantle viscosity: Implications for subduction initiation[J]. Geophys Res Lett, 32(19): L19304. doi:10.1029/2005GL023457.
Billen M I, Hirth G. 2007. Rheologic controls on slab dynamics[J]. Geochem Geophys Geosyst, 8(8): Q08012. doi:10.1029/2007GC001597.
Bouhifd M A, Andrault D, Fiquet G, Richet P. 1996. Thermal expansion of forsterite up to the melting point[J]. Geophys Res Lett, 23(10): 1143-1146.
Christensen U R. 1996. The influence of trench migration on slab penetration into the lower mantle[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 140(1): 27-39.
Dubuffet F, Rabinowicz M, Monnereau M. 2000. Multiple scales in mantle convection[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 178(3): 351-366.
Forte A M, Peltier W R, Dziewonski A M. 1991. Inferences of mantle viscosity from tectonic plate velocities[J]. Geophys Res Lett, 18(9): 1747-1750.
Fukao Y, Widiyantoro S, Obayashi M. 2001. Stagnant slabs in the upper and lower mantle transition region[J]. Rev Geophys, 39(3): 291-323.
Gurnis M, Hager B H. 1988. Controls of the structure of subducted slabs[J]. Nature, 335: 317-321.
Hager B H, Curnis M. 1987. Mantle convection and the state on the Earth's interior[J]. Rev Geophys, 25(6): 1277-1285.
Hager B H, Clayton R W. 1989. Constraints on the structure of mantle convection using seismic observations, flow models, and the geoid[G]//Mantle Convection: Plate Tectonics and Global Dynamics. New York: Gordon and Breach Science Publisher: 657-763.
Hirth G, Kohlstedt D. 2003. Rheology of the upper mantle and the mantle wedge: A view from the experimentalists, in inside the subduction factory[J]. Geophysical Monograph, 138: 83-105.
Hofmeister A M, Dong J, Branlund J M. 2014. Thermal diffusivity of electrical insulators at high temperatures: Evidence for diffusion of bulk phonon-polaritons at infrared frequencies augmenting phonon heat conduction[J]. J Appl Phys, 115(16): 163517.
Karato S, Wu P. 1993. Rheology of the upper mantle: A synthesis[J]. Science, 260(5109): 771-778.
Karato S, Jung H. 2003. Effects of pressure on high-temperature dislocation creep in olivine[J]. Philos Mag, 83(3): 401-414.
Kincaid C, Sacks I S. 1997. Thermal and dynamical evolution of the upper mantle in subduction zones[J]. J Geophys Res, 102(B6): 12295-12315.
King S D, Masters G. 1992. An inversion for radial viscosity structure using seismic tomography[J]. Geophys Res Lett, 19(15): 1551-1554.
Lallemand S, Heuret A, Boutelier D. 2005. On the relationships between slab dip, back-arc stress, upper plate absolute motion, and crustal nature in subduction zones[J]. Geochem Geophys Geosyst, 6(9): Q09006. doi:10.1029/2005GC000917.
Manea V, Gurnis M. 2007. Subduction zone evolution and low viscosity wedges and channels[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 264(1): 22-45.
Kirby S H, Stein S, Okal E A, Rubie D C. 1996. Metastable mantle phase transformations and deep earthquakes in subducting oceanic lithosphere[J]. Rev Geophys, 34(2): 261-306.
Mitrovica J X, Peltier W R. 1993. The inference of mantle viscosity from an inversion of the Fennoscandian relaxation spectrum[J]. Geophys J Int, 114(1): 45-62.
Monnereau M, Quere S. 2001. Spherical shell models of mantle convection with tectonic plates[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 184(3): 575-587.
Peltier W R. 1989. Mantle viscosity[G]//Mantle Convection: Plate Tectonics and Global Dynamics. New York: Gordon and Breach Science Publisher: 389-475.
Ritsema J. 2000. Evidence for shear velocity anisotropy in the lowermost mantle beneath the Indian Ocean[J]. Geophys Res Lett, 27(7): 1041-1044.
Rodríguez-González J, Negredo A M, Petricca P, Carminati E. 2009. Modeling with COMSOL the interaction between subducting plates and mantle flow[C]. COMSOL User's Conference. Milan, October 14-16, 2009.
Rodríguez-González J, Negredo A M, Billen M I. 2012. The role of the overriding plate thermal state on slab dip variability and on the occurrence of flat subduction[J]. Geochem Geophys Geosyst, 13(1): Q01002. doi:10.1029/2011GC003859.
Stacey F D, Fu R S, Spiliopoulos S. 1989. Viscosity structure implied by mantle convection[J]. Phys Earth Planet Inter, 55(1): 1-9.
Stein C A, Stein S. 1992. A model for the global variation in oceanic depth and heat flow with lithospheric age[J]. Nature, 359(6391): 123-129.
Torii Y, Yoshioka S. 2007. Physical conditions producing slab stagnation: Constraints of the Clapeyron slope, mantle viscosity, trench retreat, and dip angles[J]. Tectonophysics, 445(3): 200-209.
Tosi N, Yuen D A, de Koker N, Wentzcovitch R M. 2013. Mantle dynamics with pressure- and temperature-dependent thermal expansivity and conductivity[J]. Phys Earth Planet Inter, 217: 48-58.
van der Hilst R D, Widiyantoro S, Engdahl E R. 1997. Evidence for deep mantle circulation from global tomography[J]. Nature, 386(6625): 578-584.
van der Hilst R D, Karason H. 1999. Compositional heterogeneity in the bottom 1000 kilometers of Earth's mantle: Toward a hybrid convection model[J]. Science, 283(5409): 1885-1888.
Xu Y S, Shankland T J, Linhardt S, Rubie D C, Langenhorst F, Klasinski K. 2004. Thermal diffusivity and conductivity of olivine, wadsleyite and ringwoodite to 20 GPa and 1373 K[J]. Phys Earth Planet Int, 143/144: 321-336.
Yamaji A. 1992. Periodic hotspot distribution and small-scale convection in the upper mantle[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 109(1): 107-116.
Zhong S, Gurnis M. 1997. Dynamic interaction between tectonic plates, subducting slabs, and the mantle[J]. Earth Interactions, 1(3): 1-18.
Zhong S, Zuber M T, Moresi L, Gurnis M. 2000. Role of temperature-dependent viscosity and surface plates in spherical shell models of mantle convection[J]. J Geophys Res, 105(B5): 11063-11082.
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: