The seismo-ionospheric monitoring technologies and their application research development
-
摘要: 2017年即将发射的中国电磁监测试验卫星将填补地震电离层立体监测体系中不可或缺的空白区域,也将为天地一体化地震电磁对比校验及圈层耦合机理认识提供重要的科学支撑.针对近期地震电离层立体监测体系发展的需求,本文主要介绍了目前国内用于地震研究的地基及空基电离层探测技术,包括电离层垂测/斜测、甚低频(VLF)电波观测、舒曼谐振观测、GPS及空间卫星电磁等,并总结了各种探测技术在国内外地震应用研究中的进展; 最后结合不同探测手段的优势,探讨了地震电磁立体探测系统的构建,并就未来的多手段综合应用发展提出了建议.Abstract: China Seismo-Electromagnetic Satellite (CSES) will be launched in 2017, which will fill in the gap in the stereo seismo-ionospheric monitoring system, and provide the scientific support for integrated space-ground comparison and validation in seismo-electromagnetic field, and for further understanding geosphere coupling mechanism. In order to meet the development requirements in stereo seismo-ionospheric monitoring system and fully understand each tool, this paper introduces the major ground-based and space-borne ionospheric monitoring technologies in China, including vertical/slant ionosounding, VLF (very low frequency) electromagnetic wave observation, Shumann resonance detection, GPS TEC (total electron content), and space electromagnetic satellite. Meanwhile, the application achievements in earthquake research are summarized, especially the developing status in China. Finally based on the integration of advantages for each technology, the basic framework of stereo electromagnetic monitoring system is discussed, and future comprehensive research fields are also suggested based on multi-source observation data from this system.
-
-
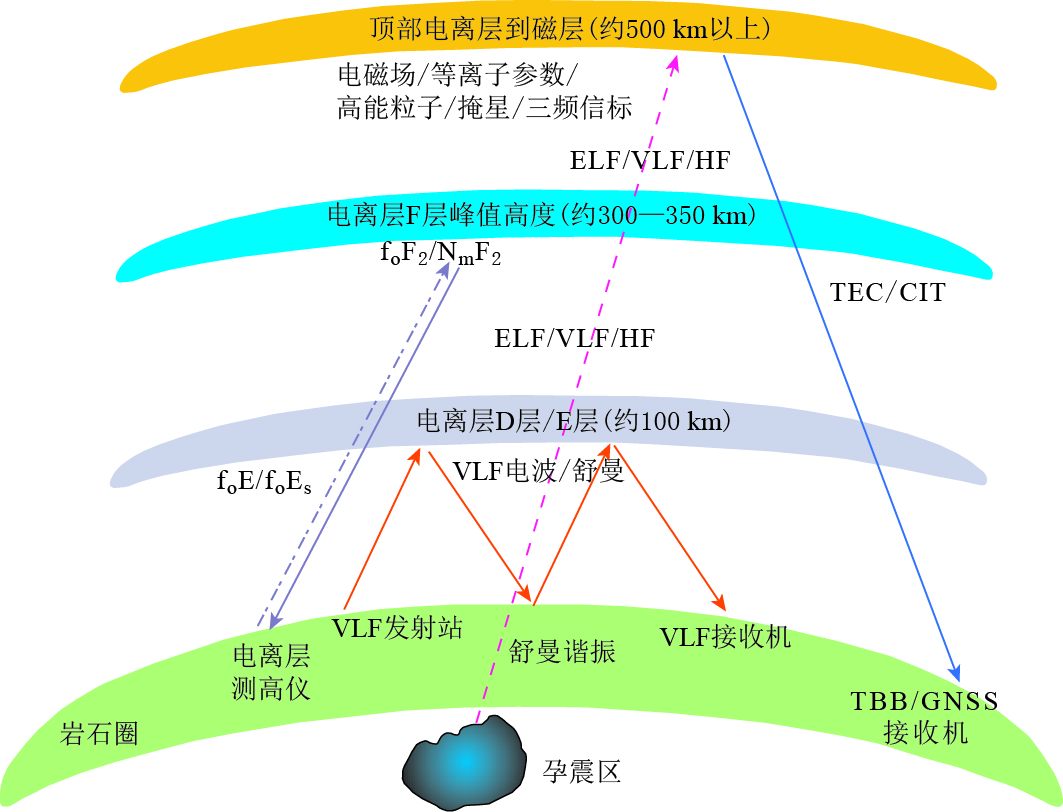
表 1 电离层探测技术各项指标对比
Table 1 Comparison of indices for several ionospheric monitoring technologies
探测技术 主要探测参量 敏感层位 优势 缺点 电离层测高 foF2 F2层,D层,E层峰值 时间连续,观测精度高 受限于台站数目和台站分布 GPS TEC TEC 电离层峰值高度300—350 km 时间连续,接收台站数目较多,全球覆盖性较好 多高度积分效应 VLF电波 VLF电磁波信号强度和相位 电离层底界面 时间连续,有固定信号源 只能记录到发射站至接收站链路上所产生的扰动 舒曼谐振 电磁场矢量变化 地—电离层波导尺寸 时间连续,信号强度和频率基本稳定 扰动信号来源难以定义 卫星观测电磁场 电磁场波形及频谱 卫星高度 全球覆盖,宽频带 同一研究区域观测时间间隔较长 原位等离子体参量 电子离子密度温度、能量粒子通量等 卫星高度 全球覆盖,高度单一 同一研究区域观测时间间隔较长 电离层结构探测掩星观测 TEC,电子密度剖面 卫星高度以下 全天候、全球覆盖、高垂直分辨率 事件发生具有很大随机性,时空均不连续 三频信标 相对TEC,绝对TEC, 电子密度剖面 卫星高度以下 区域性高时空分辨率 受限于地面接收站分布 -
李建勇. 2010. 利用GPS数据研究地震电离层TEC异常[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地震预测研究所: 1-107. Li J Y. 2010. Research on Seismic Ionospheric Anomalies Based on GPS Data[D]. Beijing: Institute of Earthquake Science, China Earthquake Administration: 1-107 (in Chinese).
夏淳亮. 2004. GPS台网观测中电离层TEC的解算方法及TEC现报系统的初步研制[D]. 武汉: 中国科学院武汉物理与数学研究所: 1-61. Xia C L. 2004. TEC Ionospheric Computing Technique and Initial Development of TEC Nowcasting System in GPS Observational Network[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan Institute of Physics and Mathematics, Chinese Academy of Sciences: 1-61 (in Chinese).
中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所. 2015. DPS4D digisonde[EB/OL]. [2015-11-25]. http://space.iggcas.ac.cn/SYIonogram.html. Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences. 2015. DPS4D digisonde[EB/OL]. [2015-11-25]. http://space.iggcas.ac.cn/SYIonogram.html (in Chinese).
Wikipedia. 2015. List_of_VLF-transmitters[EB/OL]. [2015-11-25]. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_VLF-transmitters.
Zeren Z M, Zhang X M, Shen X H, Sun W H, Ning D M, Ruzhin Y. 2014. VLF radio signal anomalies associated with strong earthquakes[C]//Proceedings of the 2014 XXXIth URSI IEEE General Assembly and Scientific Symposium. Beijing: IEEE: 1-4.




 下载:
下载:
