Reliability tests of shear wave velocity structure from joint inversion of multiple types of seismic data
-
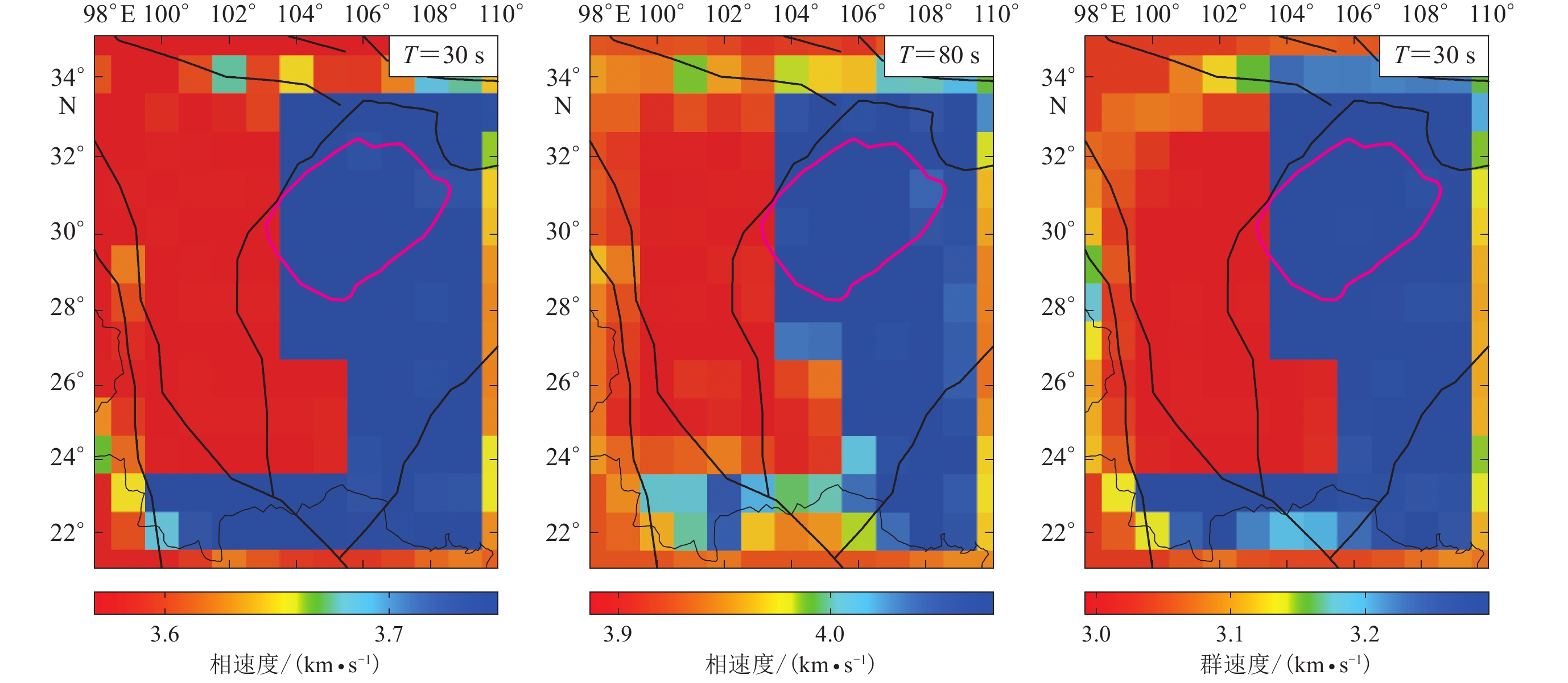
摘要: 本文模拟使用青藏高原东南缘区域台网及国家台网的170个宽频台站基于背景噪声、天然地震面波、P波接收函数反演时的实际数据,对青藏高原东南缘假定的初始模型进行恢复,通过计算初始模型台站下方纯路径频散、提取各台站对间的瑞雷波频散曲线、计算理论接收函数以及反演剪切波速度结构来测试使用不同单项数据与联合使用多种数据反演对初始模型的恢复程度。结果表明,同时使用接收函数、基于噪声经验格林函数的群速度、相速度频散以及基于天然地震面波的相速度频散联合反演的剪切波速度结构,充分利用了几种数据的分辨率优势,清晰地分辨出中下地壳及上地幔顶部的低速层。此外,本文也分析了实际数据处理中出现的计算误差、随机噪声干扰对计算结果稳定性的影响。结果显示:对于面波频散,加入1%的误差后,联合反演的结果仍可很好地反映低速层的形态,但是当误差提升至5%后,对最终结果则产生了一定程度的影响;而在接收函数中加入4%的随机噪声时,虽然地幔低速层的上界面和下界面会略微受到随机噪声的影响,但是低速层的深度范围和速度值均得到了较好的恢复。Abstract: Based on the real data from joint inversion of ambient noise, surface wave data, and P wave receiver functions of 170 broad-band seismic stations of national and regional networks of the southeastern margin of Tibetan Plateau and its adjacent areas, we preformed the recovering tests to the presumed initial model of southeastern margin of Tibetan Plateau. We calculated pure path dispersion curves on the basis of the initial model, then retrieved the Rayleigh wave dispersion curves between station pairs and receiver functions beneath each station. Finally, the recovering tests were taken to measure the recovery ability to the initial model based on different seismic data alone and joint inversion of multiple types of seismic data. Our result reveals that joint inversion of receiver function, dispersion cures based on empirical Green’s functions (EGFs) of ambient noise and on teleseismic surface wave data can take full advantage of the resolution of each seismic data, and can resolve the crustal and upper mantle LVZs perfectly. Additionally, we analyzed the resulting reliability on the condition of adding calculation error or random noise. From these tests, surface wave dispersions with 1% error in joint inversion can resolve the low velocity zone (LVZ) commendably, while with 5% error can cause some differences from the initial model. Though receiver functions with 4% random noise in joint inversion can reduce the resolution of the upper and lower boundaries of the mantle LVZ, they can commendably recover the LVZs in terms of occurrence depth and velocities.
-
-
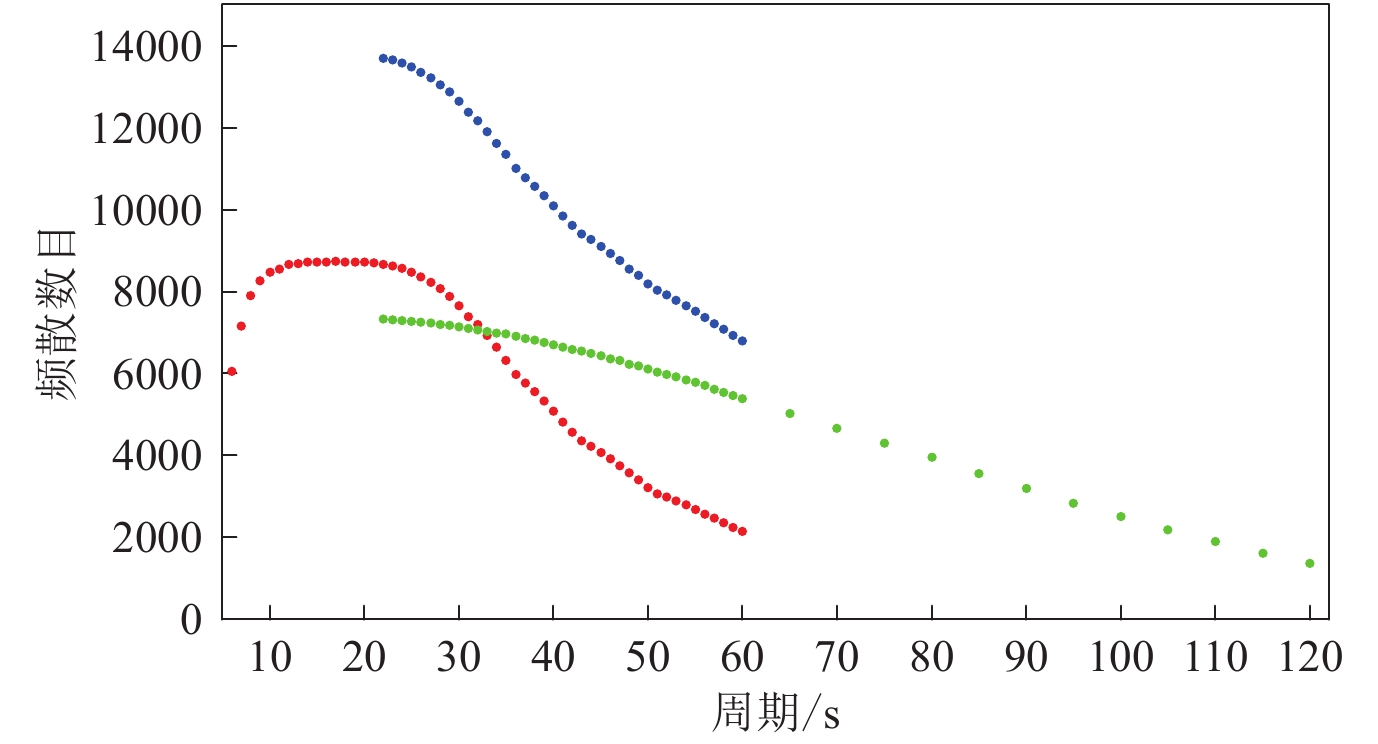
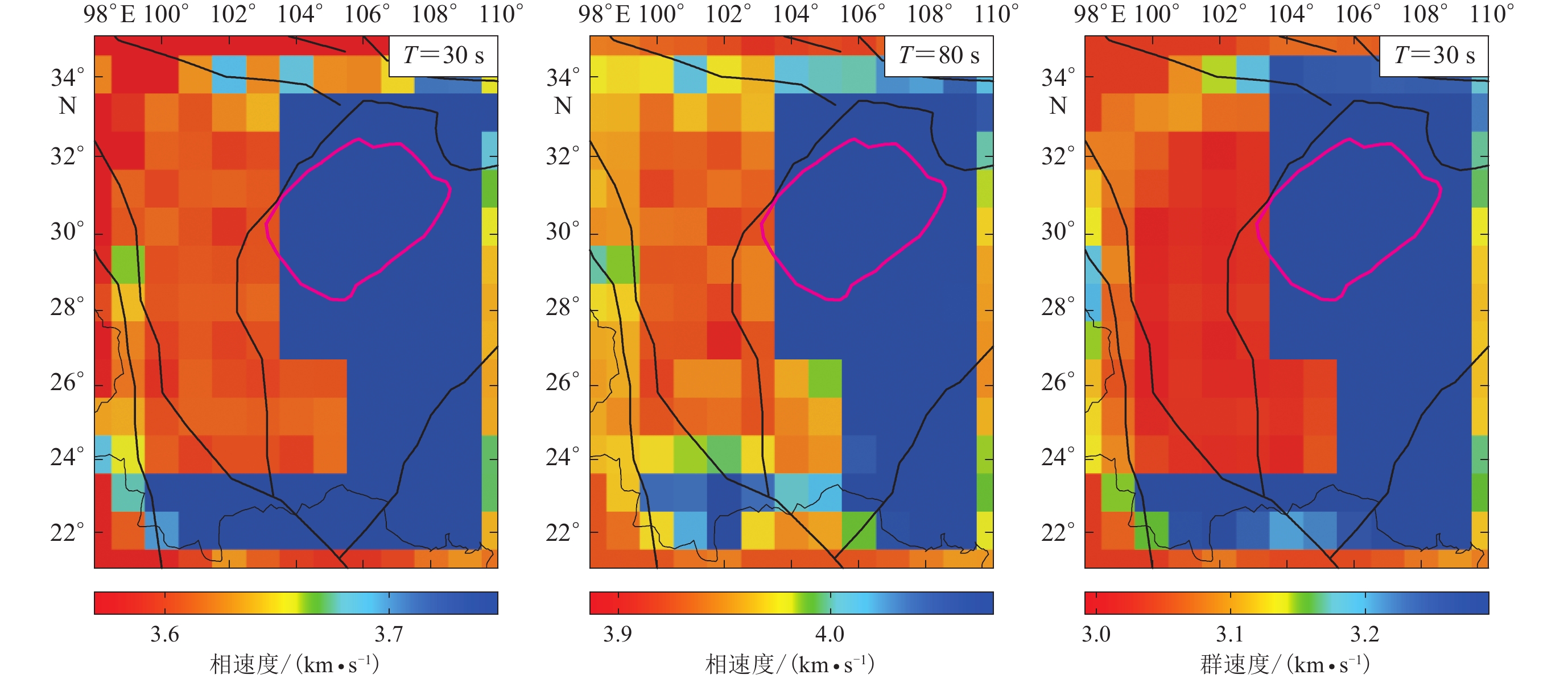
图 2 成像分辨率检测试验中各周期实际使用的频散数目
红色圆点与绿色圆点分别表示基于背景噪声经验格林函数和基于天然地震面波的频散数目;蓝色圆点表示在重叠周期21—60 s内基于两种数据最终提取的频散数目
Figure 2. Number of dispersion measurements used in resolution test at each periods
The red dots and green dots represent the number of dispersion measurements retrieved from empirical Green’s functions based on ambient noise,two-station analysis using teleseismic sur-face wave data,respectively;blue dots represent the number of final dispersion measurements retrieved from the two types of data in the overlapping periods (21−60 s)
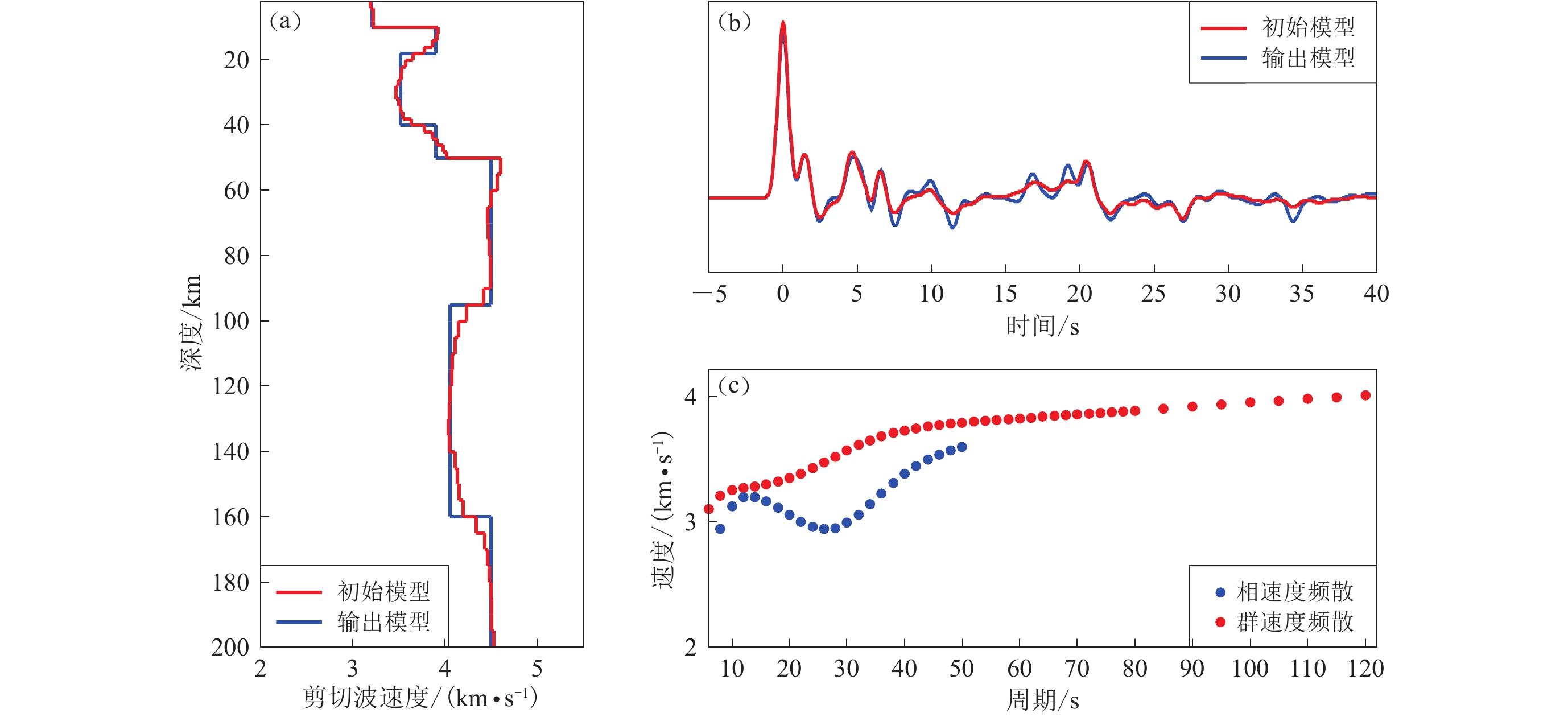
图 3 格点(102°E,25°N)下方的联合反演结果
(a) 初始模型和由面波频散曲线及接收函数联合反演的输出模型;(b) 根据图(a)中模型计算的P波接收函数;(c) 基于初始模型的瑞雷波相速度、群速度频散曲线
Figure 3. Joint inversion results beneath the grid (102°E,25°N)
(a) The initial model and output model after joint inversion of surface wave dispersion measurements and receiver function; (b) The P wave receiver functions calculated according to the initial models in Fig.(a); (c) Rayleigh wave phase velocity and group velocity dispersion measurements calculated according to the initial model respectively
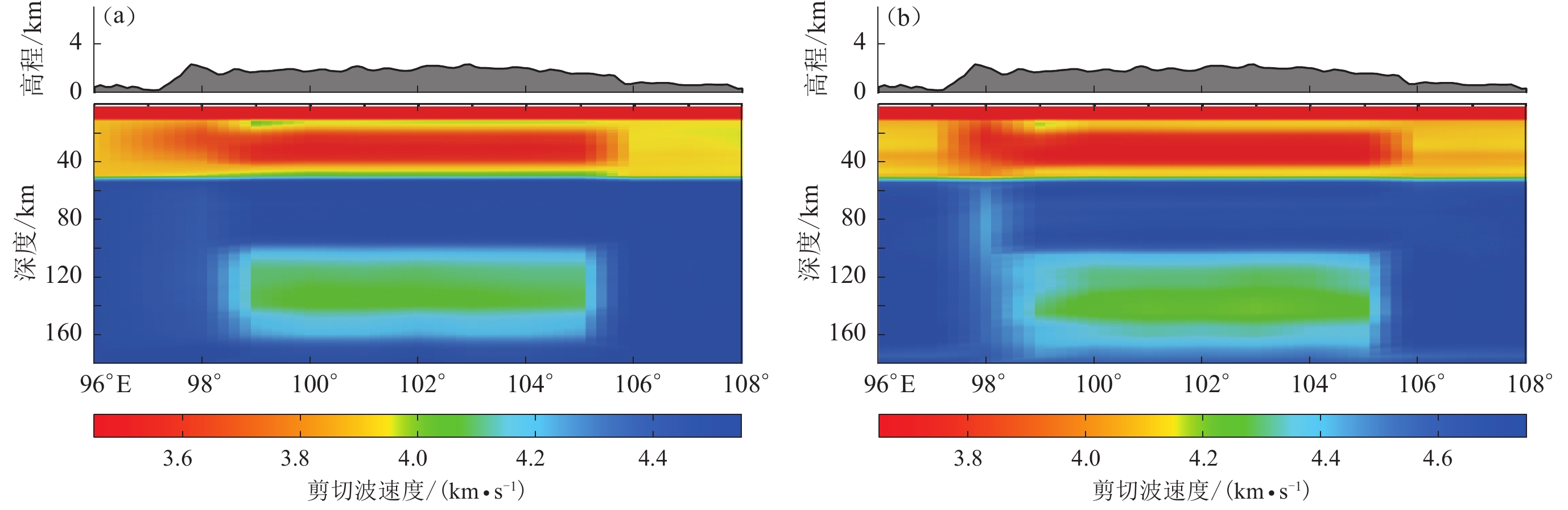
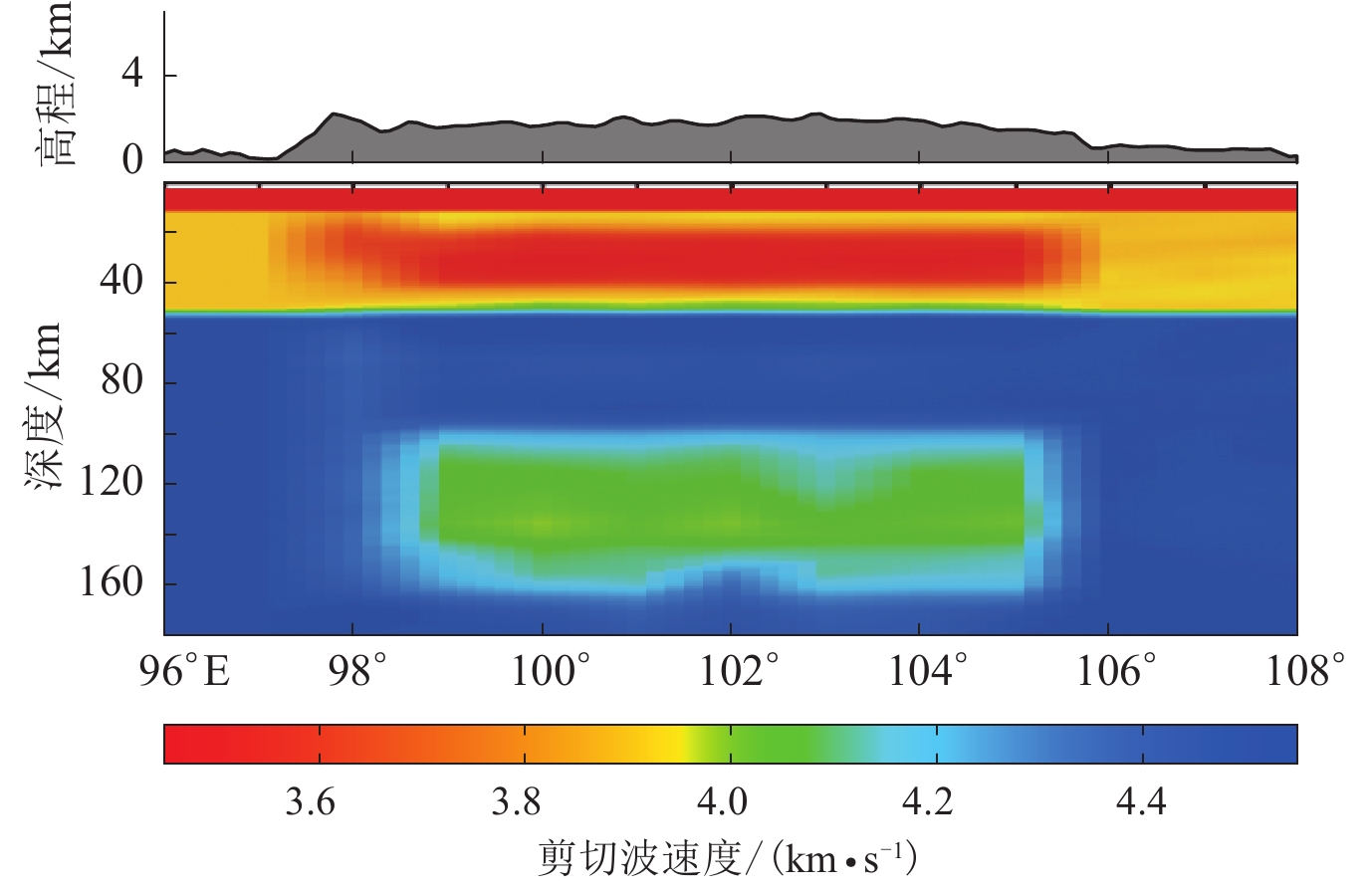
图 5 使用不同数据反演所得沿25°N剖面的剪切波速度结构
(a) 仅使用基于背景噪声的瑞雷波群速度频散反演;(b) 仅使用基于天然地震面波的瑞雷波相速度频散反演;(c) 同时使用基于背景噪声及天然地震面波的瑞雷波群速度、相速度频散反演;(d) 仅使用接收函数反演;(e) 同时使用3种数据联合反演
Figure 5. Cross sections of shear wave velocity structure along 25°N from inversion by using different seismic data
(a) The output model inverted from Rayleigh wave group velocity dispersions based on ambient noise;(b) The output model inverted from Rayleigh wave phase velocity dispersions based on teleseismic wave;(c) The output model jointly inverted from Rayleigh wave group velocity and phase velocity dispersions based on ambient noise and teleseismic wave;(d) The output model inverted from receiver function;(e) The output model jointly inverted from three types of seismic wave data
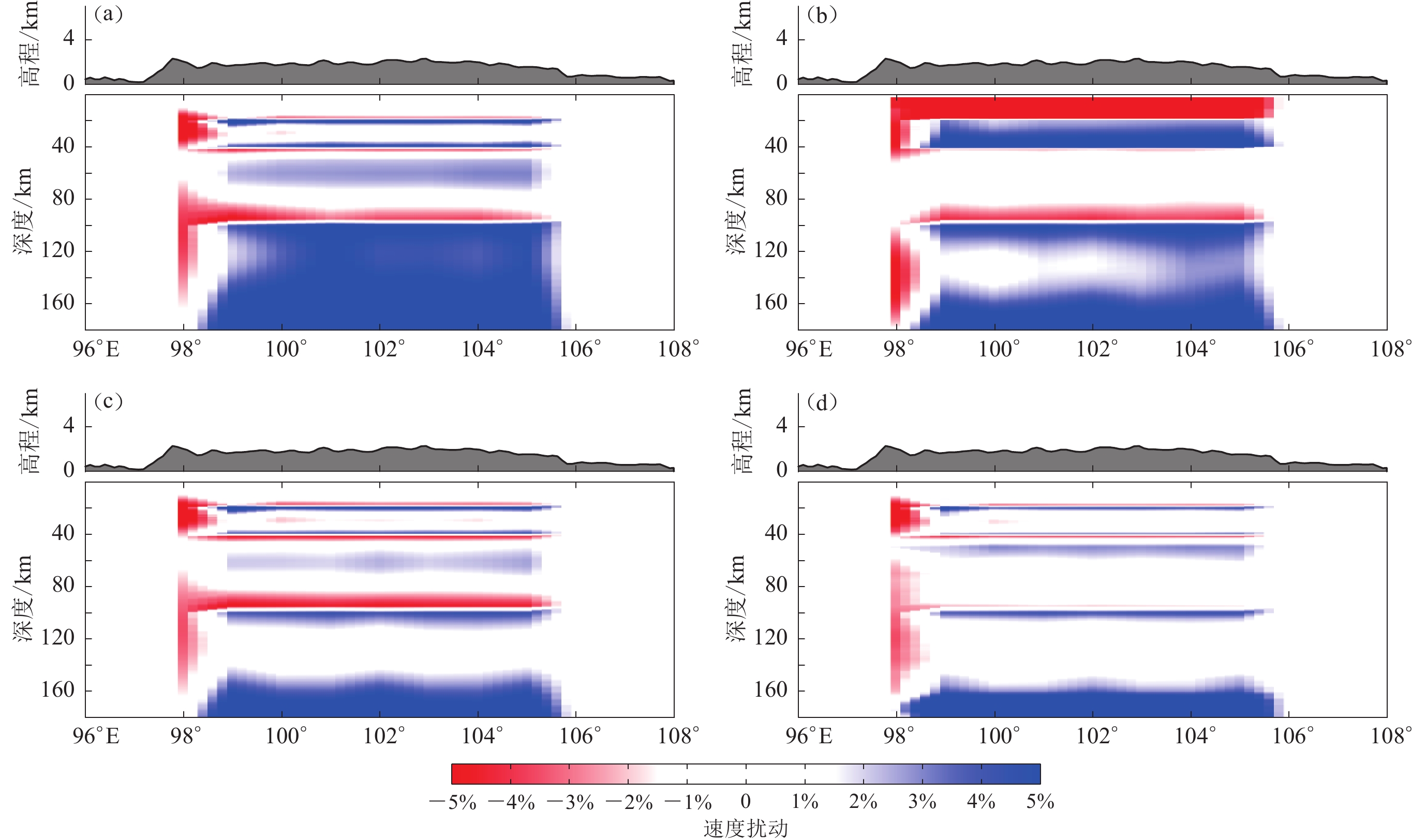
图 6 沿25°N剖面使用不同数据反演后模型与初始模型的速度扰动分布
(a) 仅使用基于背景噪声的瑞雷波群速度频散反演;(b) 仅使用基于天然地震面波的瑞雷波相速度频散反演;(c) 同时使用基于背景噪声及天然地震面波的瑞雷波群速度、相速度频散反演;(d) 同时使用3种数据联合反演
Figure 6. Cross sections of shear wave velocity perturbation along 25°N using different types of seismic data
(a) Cross sections of shear wave velocity perturbation calculated based on Rayleigh wave group velocity dispersion measurements;(b) Similar to Fig.(a) but calculated based on Rayleigh wave phase velocity dispersion measurements from teleseismic wave;(c) Similar to Fig.(a) but calculated based on both Rayleigh wave group velocity and phase velocity dispersion measurements from ambient noise and tele-seismic wave;(d) Similar to Fig.(a) but calculated based on three types of seismic data
图 9 格点(102°E,25°N)下方100组基于加入随机噪声的接收函数联合反演的结果
(a) 初始模型和联合反演输出模型;(b) 联合反演使用的P波接收函数;(c) 瑞雷波相速度、群速度频散曲线
Figure 9. The 100 joint inversion results beneath the grid (102°E, 25°N) based on receiver functions with different random noise
(a) The initial model and the output models based on joint inversion;(b) The P wave receiver functions used in joint inversions;(c) The Rayleigh wave phase velocity and group velocity dispersion measurements used in joint inversions
-
胡家富,朱雄关,夏静瑜,陈赟. 2005. 利用面波和接收函数联合反演滇西地区壳幔速度结构[J]. 地球物理学报,48(5):1069–1076. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2005.05.013 Hu J F,Zhu X G,Xia J Y,Chen Y. 2005. Using surface wave and receiver function to jointly inverse the crust-mantle velocity structure in the west Yunnan area[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,48(5):1069–1076 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1002/cjg2.750
刘启元,李昱,陈九辉,van der Hilst R D,郭飚,王峻,齐少华,李顺成. 2010. 基于贝叶斯理论的接收函数与环境噪声联合反演[J]. 地球物理学报,53(11):2603–2612. Liu Q Y,Li Y,Chen J H,van der Hilst R D,Guo B,Wang J,Qi S H,Li S C. 2010. Joint inversion of receiver function and ambient noise based on Bayesian theory[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,53(11):2603–2612 (in Chinese).
Bao X W,Sun X X,Xu M J,Eaton D W,Song X D,Wang L S,Ding Z F,Mi N,Li H,Yu D Y,Huang Z C,Wang P. 2015. Two crustal low-velocity channels beneath SE Tibet revealed by joint inversion of Rayleigh wave dispersion and receiver functions[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett,415:16–24.
Bensen G B,Ritzwoller M H,Barmin M P,Levshin A L,Lin F,Moschetti M P,Shapiro N M,Yang Y. 2007. Processing seismic ambient noise data to obtain reliable broad-band surface wave dispersion measurements[J]. Geophys J Int,169(3):1239–1260. doi: 10.1111/gji.2007.169.issue-3
Bensen G B,Ritzwoller M H,Shapiro N M. 2008. Broadband ambient noise surface wave tomography across the United States[J]. J Geophys Res,113(B5):B5306. doi: 10.1029/2007JB005248
Bodin T,Sambridge M,TkalčIć H,Arroucau P,Gallagher K,Rawlinson N. 2012. Transdimensional inversion of receiver functions and surface wave dispersion[J]. J Geophys Res,117(B2):B02301.
Campillo M,Paul A. 2003. Long-range correlations in the diffuse seismic coda[J]. Science,299(5606):547–549. doi: 10.1126/science.1078551
Chang S J,Baag C E,Langston C A. 2004. Joint analysis of teleseismic receiver functions and surface wave dispersion using the genetic algorithm[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,94(2):691–704. doi: 10.1785/0120030110
Fang H J,Zhang H J,Yao H J,Allam A,Zigone D,Ben-Zion Y,Thurber C,van der Hilst R D. 2016. A new algorithm for three-dimensional joint inversion of body wave and surface wave data and its application to the Southern California Plate boundary region[J]. J Geophys Res,121(5):3557–3569. doi: 10.1002/2015JB012702
Julià J,Ammon C J,Herrmann R B,Correig A M. 2000. Joint inversion of receiver function and surface wave dispersion observations[J]. Geophys J Int,143(1):99–112. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-246x.2000.00217.x
Kang D,Shen W S,Ning J Y,Ritzwoller M H. 2016. Seismic evidence for lithospheric modification associated with intracontinental volcanism in northeastern China[J]. Geophys J Int,204(1):215–235.
Lawrence J F,Wiens D A. 2004. Combined receiver-function and surface wave phase-velocity inversion using a niching genetic algorithm:Application to Patagonia[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,94(3):977–987. doi: 10.1785/0120030172
Li Y H,Wu Q J,Zhang R Q,Tian X B,Zeng R S. 2008. The crust and upper mantle structure beneath Yunnan from joint inversion of receiver functions and Rayleigh wave dispersion data[J]. Phy Earth Planet Inter,170(1/2):134–146.
Lin F C,Ritzwoller M H,Townend J,Bannister S,Savage M K. 2007. Ambient noise Rayleigh wave tomography of New Zea-land[J]. Geophys J Int,170(2):649–666. doi: 10.1111/gji.2007.170.issue-2
Lin F C,Moschetti M P,Ritzwoller M H. 2008. Surface wave tomography of the western United States from ambient seismic noise:Rayleigh and Love wave phase velocity maps[J]. Geophys J Int,173(1):281–298. doi: 10.1111/gji.2008.173.issue-1
Liu Q Y,van der Hilst R D,Li Y,Yao H J,Chen J H,Guo B,Qi S H,Wang J,Huang H,Li S C. 2014. Eastward expansion of the Tibetan Plateau by crustal flow and strain partitioning across faults[J]. Nat Geosci,7(5):361–365. doi: 10.1038/ngeo2130
Love A E H. 1911. Some Problems of Geodynamics[M]. New York: Cambridge University Press: 1–210.
Moschetti M P,Ritzwoller M H,Lin F C,Yang Y. 2010. Crustal shear wave velocity structure of the western United States inferred from ambient seismic noise and earthquake data[J]. J Geophs Res,115(B10):B10306. doi: 10.1029/2010JB007448
Obrebski M,Allen R M,Zhang F X,Pan J T,Wu Q J,Hung S H. 2012. Shear wave tomography of China using joint inversion of body and surface wave constraints[J]. J Geophys Res,117(B1):B01311.
Paige C C,Saunders M A. 1982a. LSQR:An algorithm for sparse linear equations and sparse least squares[J]. ACM Trans Math Software,8(1):43–71. doi: 10.1145/355984.355989
Paige C C,Saunders M A. 1982b. LSQR:Sparse linear equations and least squares problems[J]. ACM Trans Math Software,8(2):195–209. doi: 10.1145/355993.356000
Press F. 1956. Determination of crustal structure from phase velocity of Rayleigh waves part I:Southern California[J]. GSA Bull,67(12):1647–1658. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1956)67[1647:DOCSFP]2.0.CO;2
Saint Louis University. 2013. Computer programs in seismology[CP/OL]. [2018−05−01]. http://www.eas.slu.edu/eqc/eqccps.html.
Shapiro N M,Ritzwoller M H. 2002. Monte-Carlo inversion for a global shear-velocity model of the crust and upper mantle[J]. Geophys J Int,151(1):88–105. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-246X.2002.01742.x
Shapiro N M,Campillo M. 2004. Emergence of broadband Rayleigh waves from correlations of the ambient seismic noise[J]. Geophys Res Lett,31(7):L07614.
Shapiro N M,Campillo M,Stehly L,Ritzwoller M H. 2005. High-resolution surface-wave tomography from ambient seismic noise[J]. Science,307(5715):1615–1618. doi: 10.1126/science.1108339
Stoneley R. 1926. The effect of the ocean on Rayleigh waves[J]. Geophys Suppl Mon Not Roy Astronom Soc,1(7):349–356.
Sun X L,Song X D,Zheng S H,Yang Y J,Michiael H R. 2010. Three dimensional shear wave velocity structure of the crust and upper mantle beneath China from ambient noise surface wave tomography[J]. Earthquake Science,23(5):449–463. doi: 10.1007/s11589-010-0744-4
Sun X X,Bao X W,Xu M J,Eaton D W,Song X D,Wang L S,Ding Z F,Mi N,Yu D Y,Li H. 2014. Crustal structure beneath SE Tibet from joint analysis of receiver functions and Rayleigh wave dispersion[J]. Geophys Res Lett,402(5):1479–1484.
Tokam A P K,Tabod C T,Nyblade A A,Julià J,Wiens D A,Pasyanos M E. 2010. Structure of the crust beneath Cameroon,West Africa,from the joint inversion of Rayleigh wave group velocities and receiver functions[J]. Geophys J Int,183(2):1061–1076. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2010.04776.x
Wang W L,Wu J P,Fang L H,Lai G J,Yang T,Cai Y. 2014. S wave velocity structure in southwest China from surface wave tomography and receiver functions[J]. J Geophys Res,119(2):1061–1078. doi: 10.1002/2013JB010317
Wessel P,Smith W H F. 1998. New,improved version of generic mapping tools released[J]. Eos Trans AGU,79(47):579. doi: 10.1029/98EO00426
Yang Y J,Ritzwoller M H,Levshin A L,Shapiro N M. 2007. Ambient noise Rayleigh wave tomography across Europe[J]. Geophys J Int,168(1):259–274. doi: 10.1111/gji.2007.168.issue-1
Yang Y J,Zheng Y,Chen J,Zhou S Y,Celyan S,Sandvol E,Tilmann F,Priestley K,Hearn T M,Ni J F,Brown L D,Ritzwoller M H. 2010. Rayleigh wave phase velocity maps of Tibet and the surrounding regions from ambient seismic noise tomography[J]. Geochem Geophys Geosyst,11(8):Q08010.
Yao H J,van der Hilst R D,de Hoop M V. 2006. Surface-wave array tomography in SE Tibet from ambient seismic noise and two-station analysis: I . Phase velocity maps[J]. Geophys J Int,166(2):732–744. doi: 10.1111/gji.2006.166.issue-2
Yao H J,Beghein C,van der Hilst R D. 2008. Surface-wave array tomography in SE Tibet from ambient seismic noise and two-station analysis: Ⅱ . Crust and upper-mantle structure[J]. Geophys J Int,173(1):205–219. doi: 10.1111/gji.2008.173.issue-1
Zhang P,Yao H J. 2017. Stepwise joint inversion of surface wave dispersion,Rayleigh wave ZH ratio,and receiver function data for 1D crustal shear wave velocity structure[J]. Earthquake Science,30(5/6):229–238. doi: 10.1007/s11589-017-0197-0
Zheng S H,Sun X L,Song X D,Yang Y J,Ritzwoller M H. 2008. Surface wave tomography of China from ambient seismic noise correlation[J]. Geochem Geophys Geosyst,9(5):Q05020.
Zheng X,Zhao C P,Zhou L Q,Zheng S H. 2019. Crustal and upper mantle structure beneath SE Tibetan Plateau from joint inversion of multiple types of seismic data[J]. Geophys J Int,217:331–345. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggz027
Zhou L Q,Xie J Y,Shen W S,Zheng Y,Yang Y J,Shi H X,Ritzwoller M H. 2012. The structure of the crust and uppermost mantle beneath South China from ambient noise and earthquake tomography[J]. Geophys J Int,189(3):1565–1583. doi: 10.1111/gji.2012.189.issue-3





 下载:
下载: