Coseismic deformation and fault slip inversion of the 2017 MW7.3 Halabjah, Iraq, earthquake based on Sentinel-1A data
-
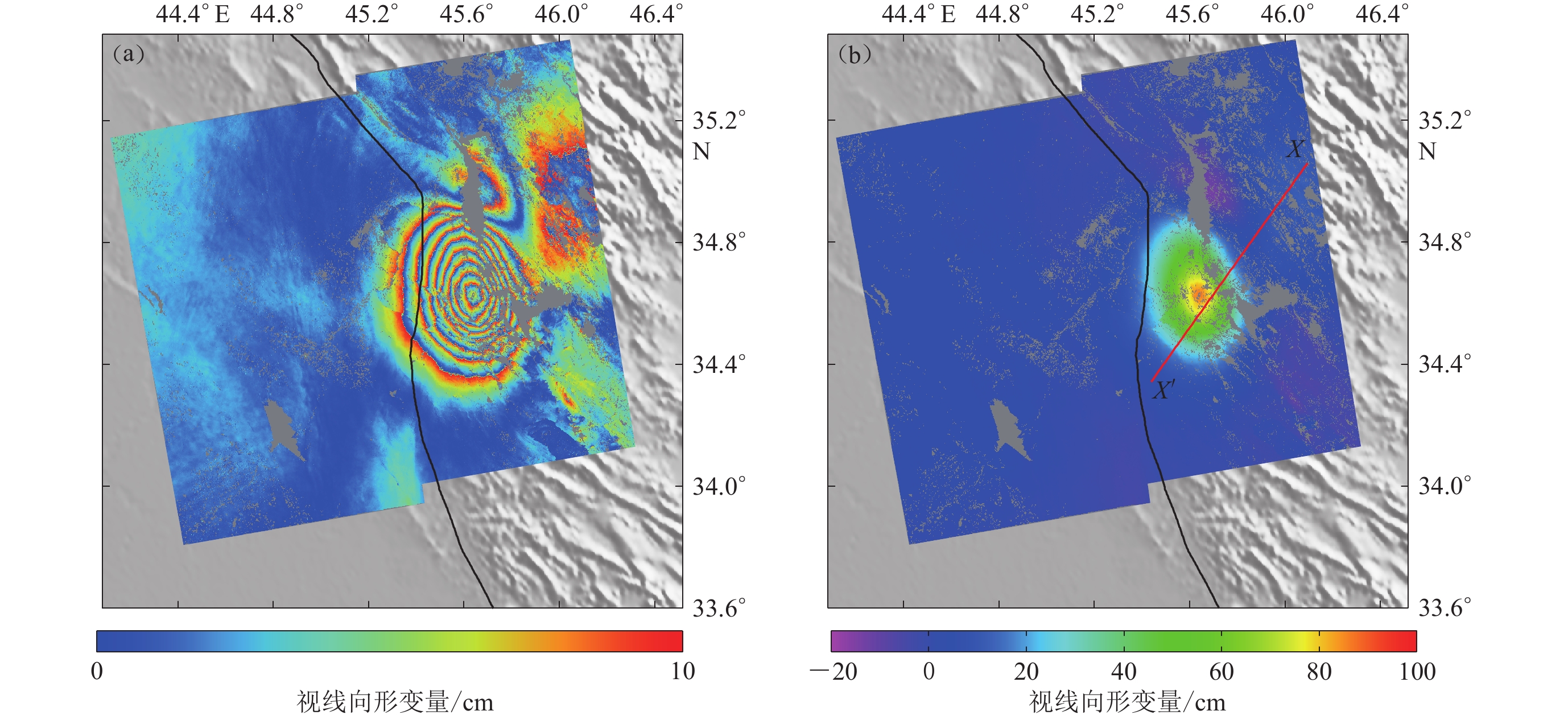
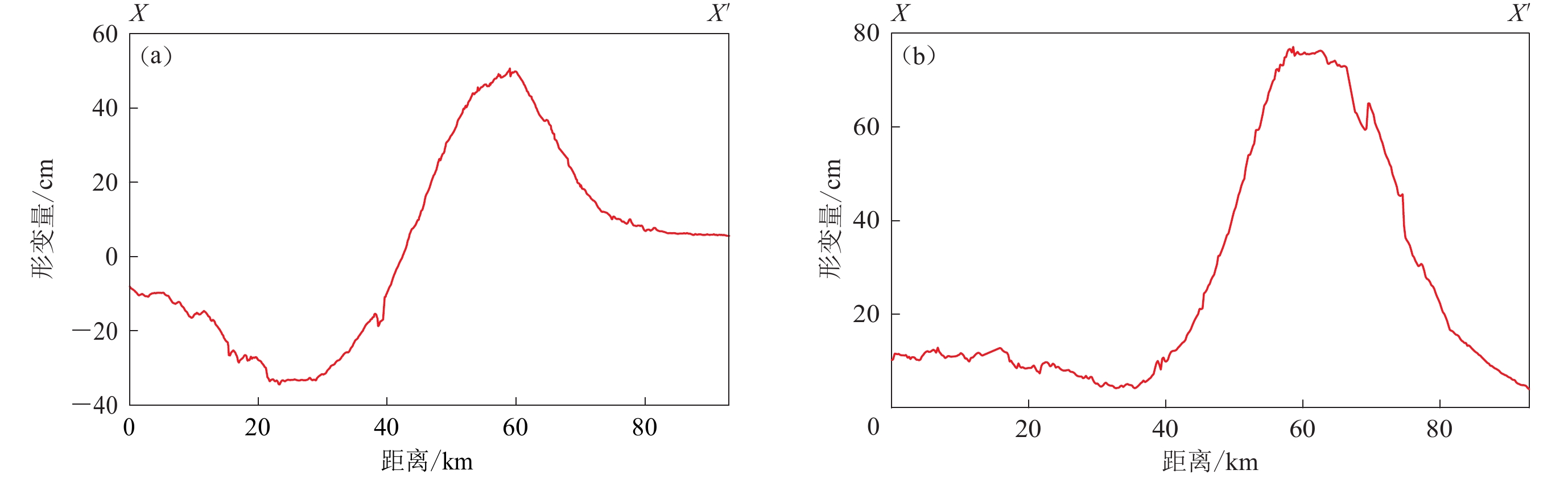
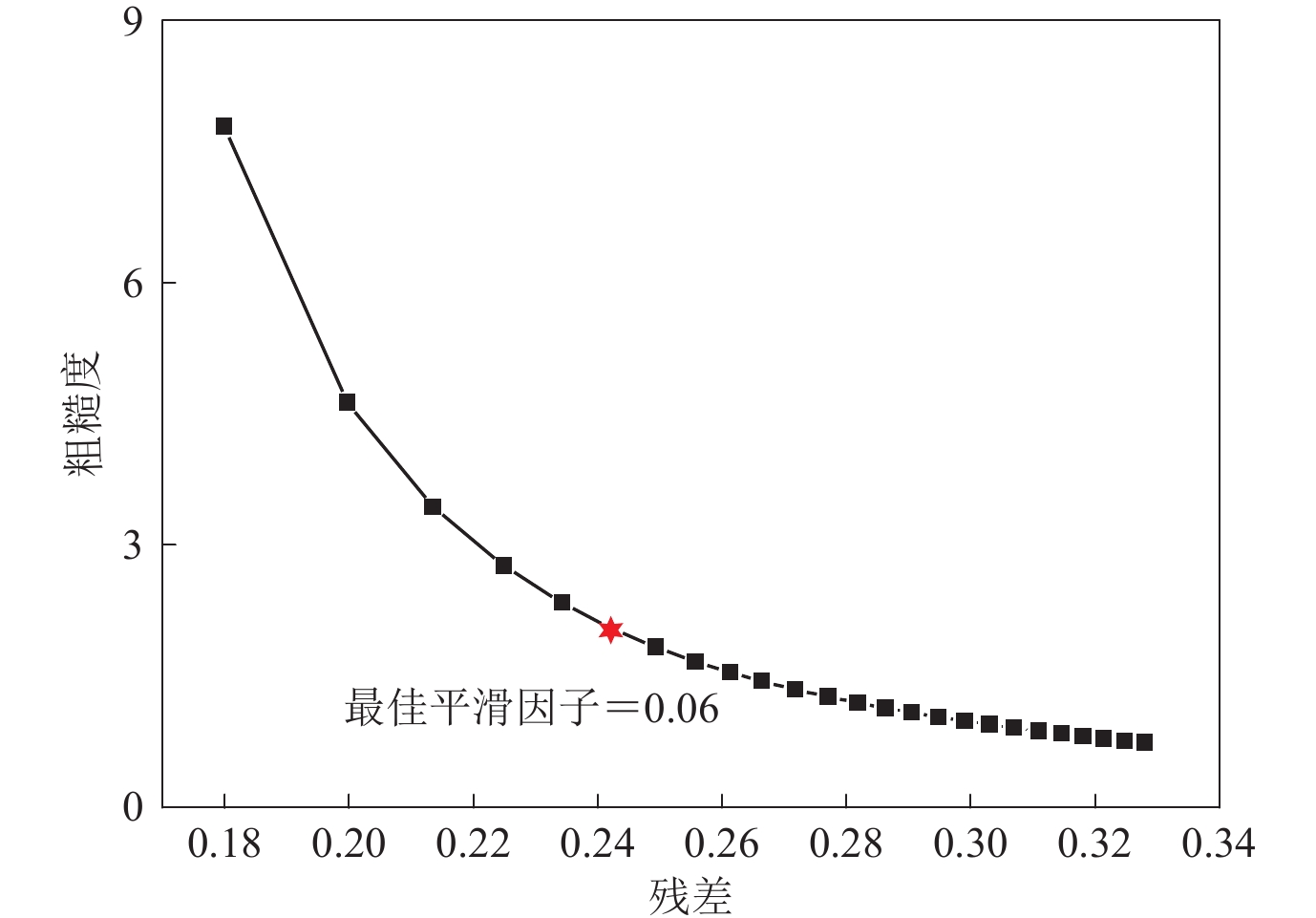
摘要: 本文首先利用二轨法对欧洲空间局Sentinel-1A雷达卫星影像进行差分干涉处理,获取了覆盖2017年伊拉克哈莱卜杰(Halabjah)MW7.3地震震区的同震形变场,结果表明:哈莱卜杰地震造成的地表形变影响范围约为60 km×70 km,形变场基本沿扎格罗斯主前缘断层展布;形变场的西南盘呈现隆升趋势,最大视线向形变值为88 cm,东北盘呈现下降趋势,最大视线向形变值为37 cm;隆升形变值远大于沉降值,反映出发震断层以逆冲运动为主的特征。然后基于弹性半平面空间矩形位错模型,分别采用多峰值粒子群算法和最速下降法确定了发震断层的几何参数和滑动分布结果。反演结果显示发震断层以逆冲运动为主,兼少量右旋走滑运动,最大滑动量为3.34 m,释放的地震矩为1.68×1020 N·m (MW7.4),与地震学的研究结果一致。
-
关键词:
- 伊拉克哈莱卜杰地震 /
- Sentinel-1A雷达数据 /
- 同震形变 /
- 滑动分布
Abstract: In this study, firstly, based on Sentinel-1A radar satellite images of Europe Space Agency, the coseismic deformation field covering the whole 2017 MW7.3 Halabjah, Iraq, earthquake region was obtained by using two-pass interferometry technique. The result shows that the main deformation region caused by the Halabjah earthquake is about 60 km×70 km, which distributes along the Zagros main front fault. Uplift occurred in the southwestern part with 88 cm at most along the line of sight, while in the northeastern subsidence occurred with 37 cm at most along the line of sight, the displacement indicates that the seismogenic fault is characterized by thrusting movement. Then nonlinear multi-peak particle swarm optimization algorithm and linear steepest descent method with rectangular dislocation model in elastic half-space are used to estimate the fault geometric parameters and coseismic slip distribution. The inversion results suggest that the seismogenic fault is dominated by thrust movement with a little right-lateral strike-slip component, and the maximum slip is about 3.34 m. The seismic moment from inversion is 1.68×1020 N·m (MW7.4), which is consistent with the result of seismology. -
-
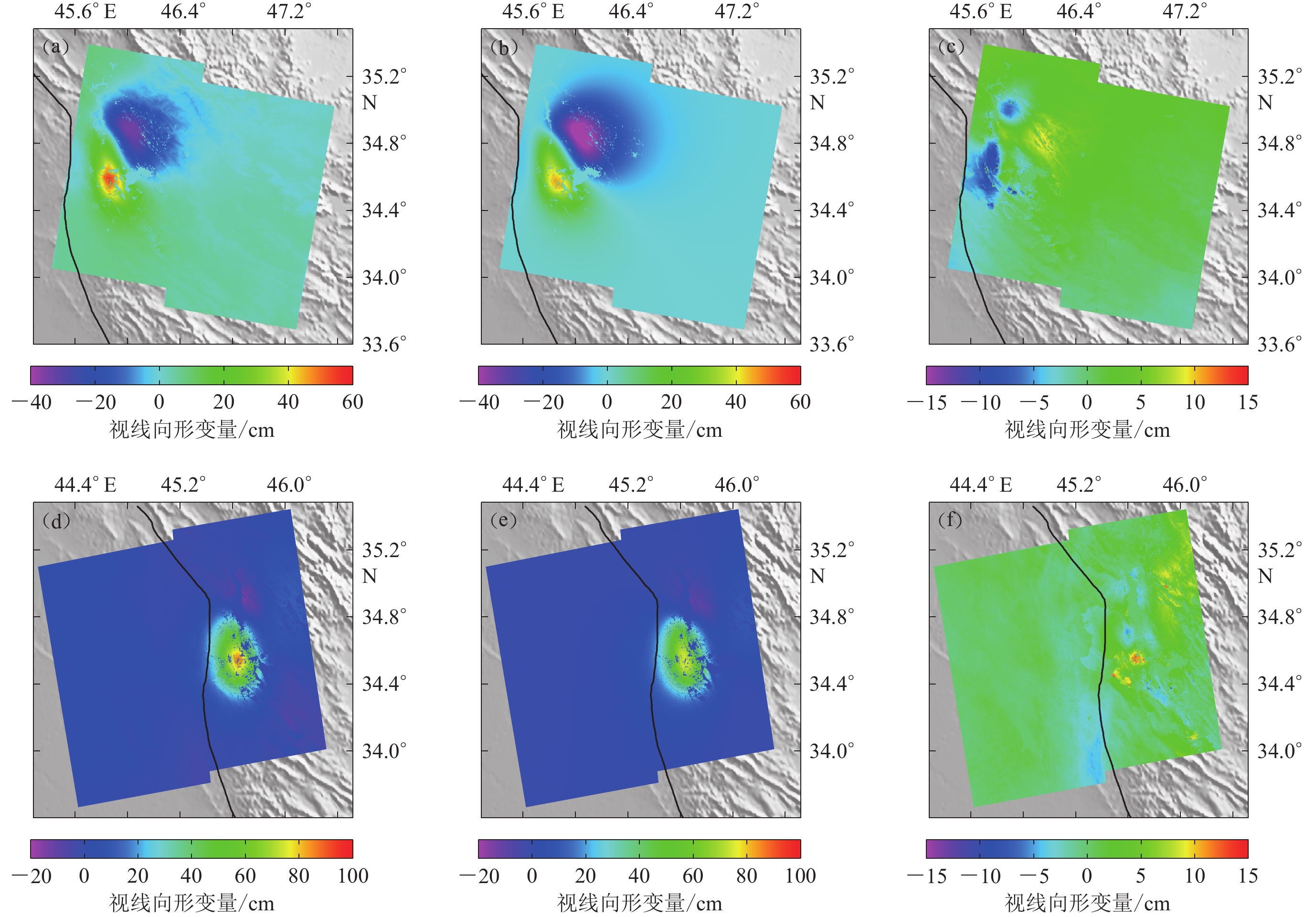
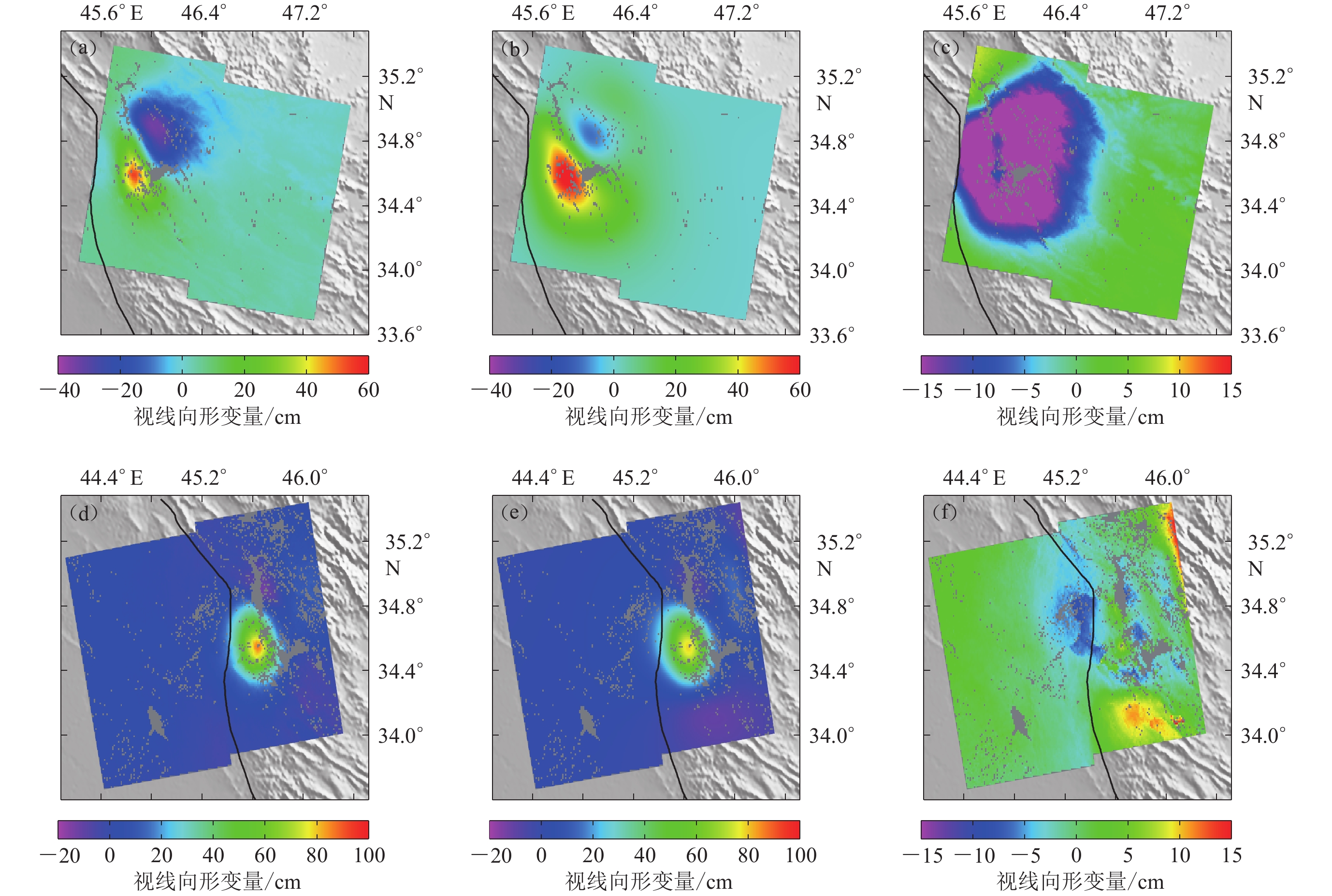
图 5 均匀滑动模型拟合的形变图和残差图
(a) 降轨形变;(b) 降轨拟合形变;(c) 降轨残差;(d) 升轨形变;(e) 升轨拟合形变;(f) 升轨残差
Figure 5. The fitted and residual displacement diagram based on the uniform slip model
(a) The displacement diagram for descending;(b) The fitted displacement diagram for descending;(c) The residual displacement diagram for descending;(d) The displacement diagram for ascending;(e) The fitted displacement diagram for ascending;(f) The residual displacement diagram for ascending
图 9 滑动分布模型拟合的形变图和残差图
(a) 降轨形变;(b) 降轨拟合形变;(c) 降轨残差;(d) 升轨形变;(e) 升轨拟合形变;(f) 升轨残差
Figure 9. The fitted and residual displacement diagram based on the slip distribution model
(a) The displacement diagram for descending;(b) The fitted displacement diagram for descending;(c) The residual displacement diagram for descending;(d) The displacement diagram for ascending;(e) The fitted displacement diagram for ascending;(f) The residual displacement diagram for ascending
表 1 2017年11月12日伊拉克哈莱卜杰MW7.3地震的震源机制解
Table 1 The focal mechanism solutions of the MW7.3 Halabjah,Iraq,earthquake on November 12,2017
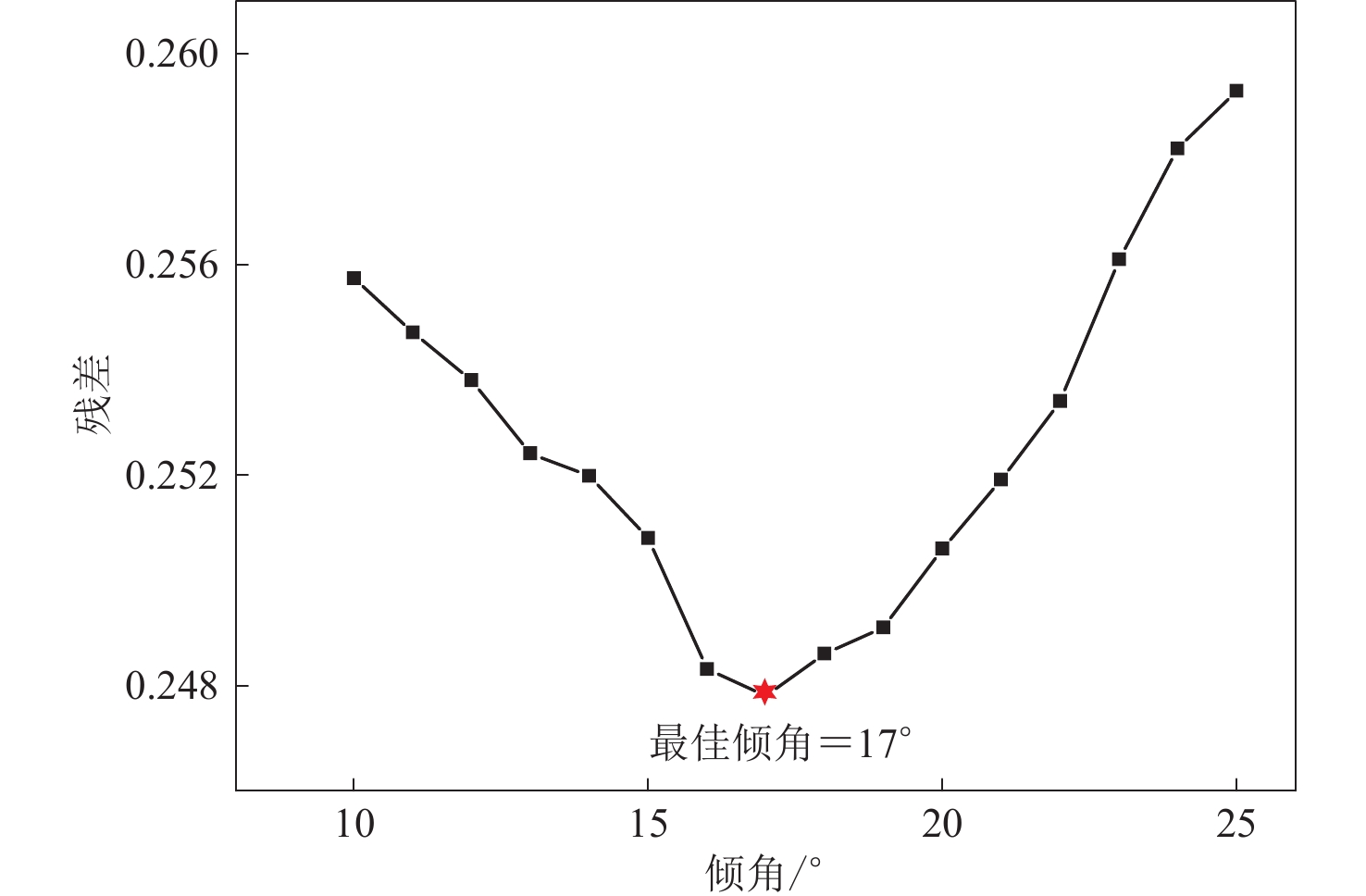
机构 MW 东经/° 北纬/° 走向/° 倾角/° 滑动角/° 深度/km USGS (2017) 7.3 45.959 34.911 351 16 137 19.0 GCMT (2017) 7.4 45.840 34.830 351 11 140 17.9 表 2 雷达影像对参数
Table 2 Parameters of SAR image pair
卫星 震前日期 震后日期 时间间隔/d 垂直基/m 轨道 模式 Sentinel-1A 2017−11−07 2017−11−19 12 36 6 升轨 Sentinel-1A 2017−11−11 2017−11−23 12 −52 72 降轨 -
冯万鹏,李振洪. 2010. InSAR资料约束下震源参数的PSO混合算法反演策略[J]. 地球物理学进展,25(4):1189–1196. Feng W P,Li Z H. 2010. A novel hybrid PSO/simplex algorithm for determining earthquake source parameters using InSAR data observations[J]. Progress in Geophysics,25(4):1189–1196 (in Chinese).
单新建,屈春燕,龚文瑜,赵德政,张迎峰,张国宏,宋小刚,刘云华,张桂芳. 2017. 2017年8月8日四川九寨沟7.0级地震InSAR同震形变场及断层滑动分布反演[J]. 地球物理学报,60(12):4527–4536. Shan X J,Qu C Y,Gong W Y,Zhao D Z,Zhang Y F,Zhang G H,Song X G,Liu Y H,Zhang G F. 2017. Coseismic deformation field of the Jiuzhaigou MS7.0 earthquake from Sentinel-1A InSAR data and fault slip inversion[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,60(12):4527–4536 (in Chinese).
许才军,何平,温扬茂,张磊. 2012. 日本2011 Tohoku-Oki MW9.0级地震的同震形变及其滑动分布反演: GPS和InSAR约束[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),37(12):1387–1391. Xu C J,He P,Wen Y M,Zhang L. 2012. Coseismic deformation and slip distribution for 2011 Tohoku-Oki MW9.0 earthquake:Constrained by GPS and InSAR[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,37(12):1387–1391 (in Chinese).
张国宏,屈春燕,单新建,张桂芳,宋小刚,汪荣江,李振洪,胡植庆. 2011. 2008年MS7.1于田地震InSAR同震形变场及其震源滑动反演[J]. 地球物理学报,54(11):2753–2760. Zhang G H,Qu C Y,Shan X J,Zhang G F,Song X G,Wang R J,Li Z H,Hu Z Q. 2011. The coseismic InSAR measurements of 2008 Yutian earthquake and its inversion for the fault slip[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,54(11):2753–2760 (in Chinese).
张洪瑞,侯增谦. 2015. 大陆碰撞造山样式与过程: 来自特提斯碰撞造山带的实例[J]. 地质学报,89(9):1539–1559. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2015.09.001 Zhang H R,Hou Z Q. 2015. Pattern and process of continent-continent collision orogeny: A case study of the Tethys collisional orogen[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,89(9):1539–1559 (in Chinese).
赵强,王双绪,蒋锋云,李宁. 2017. 利用InSAR技术研究2016年青海门源MW5.9地震同震形变场及断层滑动分布[J]. 地震,37(2):95–105. Zhao Q,Wang S X,Jiang F Y,Li N. 2017. Coseismic deformation field and fault slip distribution of the 2016 Qinghai Menyuan MW5.9 earthquake from InSAR measurement[J]. Earthquake,37(2):95–105 (in Chinese).
Agard P,Monié P,Gerber W,Omrani J,Molinaro M,Meyer B,Labrousse L,Vrielynck B,Jolivet L,Yamato P. 2006. Transient,synobduction exhumation of Zagros blueschists inferred from P-T,deformation,time,and kinematic constraints: Implications for Neotethyan wedge dynamics[J]. J Geophys Res,111:B11401.
Elliott J R,Copley A C,Holley R,Scharer K,Parsons B. 2013. The 2011 MW7.1 Van (Eastern Turkey) earthquake[J]. J Geophys Res,118(4):1619–1637. doi: 10.1002/jgrb.50117
Farr T G,Rosen P A,Caro E,Crippen R,Duren R,Hensley S,Kobrick M,Paller M,Rodriguez E,Roth L,Seal D,Shaffer S,Shimada J,Umland J,Werner M,Oskin M,Burbank D,Alsdorf D. 2007. The shuttle radar topography mission[J]. Rev Geophys,45(2):RG2004.
Feng W P,Li Z H,Elliott J R,Fukushima Y,Hoey T,Singleton A,Cook R,Xu Z H. 2013. The 2011 MW6.8 Burma earthquake: Fault constraints provided by multiple SAR techniques[J]. Geophys J Int,195(1):650–660.
Feng W P,Li Z H,Hoey T,Zhang Y,Wang R J,Samsonov S,Li Y S,Xu Z H. 2014. Patterns and mechanisms of coseismic and postseismic slips of the 2011 MW7.1 Van (Turkey) earthquake revealed by multi-platform synthetic aperture radar interferometry[J]. Tectonophysics,632:188–198.
GCMT. 2017. 201711121818A Iran-Iraq border region[EB/OL]. [2018−05−18]. http://www.globalcmt.org/CMTsearch.html. Goldstein R M,Werner C L. 1998. Radar interferogram filtering for geophysical applications[J]. Geophys Res Lett,25(21):4035–4038. doi: 10.1029/1998GL900033
Hetland E A,Musé P,Simons M,Lin Y N,Agram P S,DiCaprio C J. 2012. Multiscale InSAR time series (MInTS) analysis of surface deformation[J]. J Geophys Res,117:B02404.
Lohman R B,Simons M. 2013. Some thoughts on the use of InSAR data to constrain models of surface deformation: Noise stru-cture and data down sampling[J]. Geochem Geophy Geosy,6(1):Q01007.
Madanipour S,Ehlers T A,Yassaghi A,Rezaeian M,Enkelman E,Bahroudi A. 2013. Synchronous deformation on orogenic plateau margins: Insights from the Arabia-Eurasia collision[J]. Tectonophysics,608(6):440–451.
Okada Y. 1985. Surface deformation due to shear and tensile faults in a half-space[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,75(42):1135–1154.
Pepe A,Lanari R. 2006. On the extension of the minimum cost flow algorithm for phase unwrapping of multitemporal differential SAR interferograms[J]. IEEE T Geosci Remote,44(9):2374–2383.
Tavani S,Parente M,Puzone F,Puzone1 F,Corradetti1 A,Gharabeigli G,Valinejad M,Morsalnejad D,Mazzoli S. 2018. The seismogenic fault system of the 2017 MW7.3 Iran-Iraq earthquake: Constraints from surface and subsurface data,cross-section balancing,and restoration[J]. J Geophys Res,9(3):821–831.
USGS. 2017. M7.3: 29 km S of Halabjar, Iraq[EB/OL]. [2018−05−18]. https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/eventpage/ us2000bmcg#executive. Wang R, Diao F, Hoechner A. 2013. SDM: A geodetic inversion code incorporating with layered crust structure and curved fault geometry[C]//European Geosciences Union Conference. Vienna: EGU General Assembly 2013: Number EGU2013-2411-1.





 下载:
下载: