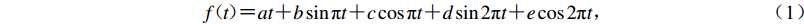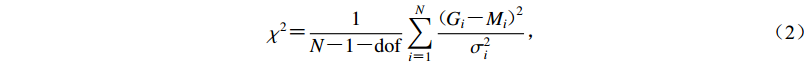3D numerical model for viscoelastic postseismic deformation following the Maule MW8.8 earthquake in 2010
-
摘要: 2010年智利马乌莱MW8.8地震发生在纳斯卡板块与南美板块的板块边界处,引起了显著的同震和震后效应。GPS台网数据显示记录到的同震海向位移最大约5 m,垂向沉降最大约50 cm。在经过对俯冲效应、季节变化等效应的校正后,震后6年的海向最大位移约68 cm,垂向抬升最大约20 cm。马乌莱地震显著的震后形变对该区域的地下三维黏弹性结构有良好的约束。本文建立了智利中南部俯冲带区域的三维有限元模型,黏弹性的地幔楔及海洋地幔均使用伯格斯体材料,并在断层面上设置2 km厚的软弱层以模拟震后余滑。在与GPS台站震后位移数据进行比较后,模拟结果表明,大洋地幔顶部存在约120 km厚,黏度为1×1019 Pa·s的软流圈。模拟震后余滑效应的软弱层黏度为5×1017 Pa·s,其等效震后余滑的最大值在震后前两年接近2 m,且随着时间的增长而快速衰减。Abstract: The 2010 MW8.8 Maule earthquake occurred near the plate boundary between the Nazca plate and the South American plate. The earthquake produced significant coseismic and postseismic deformation. The maximum coseismic motion is about 5 m in the horizontal direction and about 5 cm subsidence. After correcting the GPS data for secular, seasonal and annual trends, the postseismic cumulative motion within the first 6 years after the earthquake include up to about 68 cm in the horizontal direction and up to 20 cm uplift. The three-dimensional (3D) viscoelastic structure can be constrained by the postseismic deformation of the 2010 earthquake. We have constructed a 3D finite element model to study the effects of the rheological structure on the postseismic deformation of the 2010 earthquake. We assume the viscoelasticrelaxation of the upper mantle to be represented by the Burgers rheology. And in the paper, a 2 km thick weak shear zone attached to the megathrust is used to simulate the afterslip. Based on the comparison with the GPS observation data, the preferred model determined that a 120 km thick asthenosphere with a viscosity of 1×1019 Pa·s at the top of the oceanic upper mantle is required to fit the data. The afterslip simulated by shear zone with a viscosity of 5×107 Pa·s is up to 2 m in the first 2 years and decays rapidly with time.
-
引言
在俯冲带发生大地震后,GPS等大地测量手段可在地表观测到相应的同震及震后地壳形变,这些观测数据为研究上地幔的流变学结构和性质提供了良好的机会。Wang等(2012)通过研究处于不同地震周期的三个俯冲带,苏门答腊,智利以及卡斯凯迪亚,总结得出控制地震周期运动的三个主要的动力学过程分别为:① 震后余滑。地震发生后,断层面主破裂区域附近产生持续无震滑动。震后余滑量与主破裂区域的距离成反比,同时随时间呈指数衰减。震后余滑导致上覆板块持续朝海沟方向运动。② 上地幔的黏弹性松弛效应。地震发生后,其导致的应力扰动场在上地幔产生黏弹性应力松弛效应,在弧前及弧后大范围区域产生较长时间的海沟方向的运动。③ 断层面的闭锁效应。断层面的重新闭锁导致上覆板块向大陆方向运动。
Hu等(2004)在研究1960年智利MW9.5大地震时,观察到长达数十年时间尺度的震后变形,主要由上地幔的黏弹性松弛效应及断层闭锁效应控制,并给出南美板块地幔楔的黏滞系数为3×1019 Pa·s。在2012年印度洋MW8.6地震的震后形变研究中(Hu et al,2016a),需要在大洋上地幔顶部增加一层黏度较小的软流圈地幔才能更好地拟合观测数据。地震层析成像(Chen,2017)和大地电磁(Utada,Kiyoshi,2014)等相关研究已证实软流圈存在的可能性。本文利用最新的2010年马乌莱MW8.8地震引发的震后形变观测数据,对纳斯卡—南美俯冲带的三维黏弹性结构进行深入研究,期望对本区域的流变学结构和性质提供进一步约束。
如图1所示,纳斯卡板块以66 mm/a的速率向南美板块下俯冲,在俯冲带区域积累了巨大的应力。智利中部的地震空区自1835年以来一直在积累应力(Ruegg et al,2009),直到最后的应力释放引发了主要破裂区域长达500 km的2010年马乌莱MW8.8地震。陆地GPS台网记录到一致的海向位移场,最大同震水平位移约为5 m。在垂向上多数台站表现为沉降,最大同震沉降值约为50 cm,但仍有在海岛上靠近海沟的GPS台站同震表现出抬升。许多研究使用同震GPS台网和InSAR数据(Tong et al,2010;Moreno et al,2012)或加入远震、海啸数据(Yue et al,2014)等进行运动学反演,得到了破裂模式较为一致的断层面同震破裂模型。黄禄渊等(2017)和林鑫等(2017)讨论了本次地震的同震效应和库仑应力对本地区其它地震的影响,并认为其产生的库仑应力变化对2015年伊拉佩尔(Illapel)MW8.3地震等本地区地震的发生起到了促进作用。此后也有许多对此次地震震后效应的研究。这些研究有的使用单一的黏弹性松弛效应解释震后形变(Li et al,2017,2018;Sun et al,2018),但未考虑震后余滑等效应,解释上可能放大了黏弹性松弛效应;有的研究在数据处理阶段利用震后余滑和黏弹性松弛效应的方向性与时间衰减速率不同,试图将震后余滑效应与黏弹性松弛效应分开进行研究(Bedford et al,2013,2016),但由于震后余滑和黏弹性松弛效应并非简单的线性叠加关系,显然不能分别模拟;有的研究在模拟黏弹性松弛效应时同时施加运动学的震后余滑(Klein et al,2016),但建模时将海洋岩石圈厚度设置为90 km,其底部温度较高,黏度较低,可能低估了海洋侧的软流圈黏弹性效应;有的研究将地下物质分块,使用卡尔曼滤波和格林函数法共同反演震后余滑和黏弹性参数(Weiss et al,2019)。本研究拟在模型中添加近期研究中定量约束的海洋软流圈模型,并使用断层面上2 km厚的软弱层模拟震后余滑,以期通过正演的方法,使得震后余滑与相互耦合的黏弹性松弛效应能在同一个模型模拟得出,并预通过此模型研究2010年马乌莱MW8.8地震震后形变的主要影响因素。
1. 数据处理
本文从内华达州大地测量实验室(Nevada Geodetic Laboratory,缩写为NGL)(Blewitt et al,2018)共获取了82个台站的GPS三分量时间序列数据,并对其进行了拟合降噪处理,以获得主要受到2010年马乌莱地震影响的震后形变量。首先,选取GPS震前有连续记录的时间窗口,并用式(1)拟合线性的长期板块俯冲效应和由潮汐、降水等作用引起的季节和年际变化,即
$$ f{\text{(}} t {\text{)}} {\text{=}} at {\text{+}} b\sin \pi t {\text{+}} c\cos \pi t {\text{+}} d\sin 2\pi t {\text{+}} e\cos 2\pi t{\text{,}} $$ (1) 式中,a,b,c,d,e为待拟合参数,t为GPS仪器观测时间。其次,在得到拟合函数参数后,可将这一部分代表长期线性及季节性变化的形变量在2010年地震发生后的数据中减去,其中有一部分台站为震后短期内建设,这些台站的震前拟合数据由临近台站插值获得。为了对研究区域有更好的台网覆盖,我们还加入了Wang等(2007)和Klotz等(2001)研究中的部分台站震间数据。与图1的同震位移不同,从图2a中可以看到,震间GPS速度场水平方向上大多一致向陆,在海岸线附近每年大约有4 cm的陆向位移,且速度的大小随着距海岸线距离的增加而逐渐衰减至趋于零值。智利俯冲带南部在中远场内陆部分区域表现出海向运动的特征,体现了1960年地震震后效应的长期影响(Hu et al,2004)。在垂向上,近海岸处表现出沉降,在中远场表现为抬升,且随相对海岸线距离的增加而衰减。垂向速率明显小于水平运动速率,最大约为1 cm/a。
再次,使用指数及对数函数的组合来拟合已消除震前趋势量的震后数据。最后,震后拟合曲线的两个点之间作差即可得到该时间范围内的台站震后位移量。通过拟合曲线计算出的震后形变,可以较好地避免从观测数据直接测量引起的来自数据本身的误差。在图2b中,震后6年的GPS数据表明,水平方向上有与同震方向(图1)较为一致的海向运动,最大海向累积位移在距离主破裂区域100—200 km的中场,约为68 cm,在距离主破裂区域200 km以上的远场随距海沟距离的增加而衰减;垂向上在海岸线附近表现为沉降,最大累积沉降约为15 cm,在中场表现为抬升,最大累积抬升约为20 cm,在远场又表现为逐渐减小的沉降。
2. 有限元模型
本文使用基于已发表的俯冲带动力学模型及研究区地震学、层析成像等相关地球物理数据(Hu et al,2016a,b),建立了本次研究的三维有限元黏弹性模型(图3)。模型包括弹性的上板片和海洋板片,以及黏弹性的地幔楔、软流圈和深部海洋地幔,并有一个上覆在模型俯冲带板块界面的2 km厚的黏弹性软弱层。模型黏弹性部分均为伯格斯体,且开尔文黏度ηK与麦克斯韦黏度ηM之间存在ηK=0.1ηM的关系。模型东西、南北、垂向长分别为4000 km×2000 km×2000 km,使得同震主要破裂区域距离边界800 km以上,以消除边界效应。模型上表面为自由边界,其余五个面为滚筒支撑。依据slab1.0 (Hayes et al,2012)三维俯冲带几何模型,我们从25°S—42°S每一纬度确定一条剖面,并将其延拓至模型底部1000 km深处,组合得到断层面几何模型。在发震时刻将同震滑动量施加到断层面上,断层面两侧相对错动,产生扰动的应力应变场。地震后断层面上的软弱层应力产生黏弹性松弛效应,其作用等效于震后余滑效应。
根据Oncken等(2006)的综述,模型研究区域的海洋岩石圈年龄为25—35 Ma。若认为温度低于600 ℃的海洋板片为弹性的(Watts,Zhong,2000),则由半空间冷却模型可以算出弹性海洋板片的厚度约为30 km,这与Hu等(2004)的模型相符。对于大陆弹性上板片,Hicks等(2014)的成像研究将莫霍面深度定为45—50 km,本文采用50 km作为模型的大陆弹性上板片厚度,相较Hu等(2004)的模型厚了10 km,这也与地表安第斯山脉的地形隆起相符合。经过测试,具有40 km厚的大陆弹性上板片的模型相较于50 km厚的模型,主要差异在于40 km厚的上板片使得地幔楔更接近地表,其在靠近海沟处黏弹性松弛效应明显较大,但由于我们的模型中最靠近海沟的海岸线附近的GPS台站处模拟得到的震后位移差距在10%以内,远场两者几乎没有差异,进一步的研究需要更靠近海沟的海洋GPS台站数据作支撑。
模型的材料性质参考Hu等(2016b)的研究给出。模型所有部分的材料密度均为3 300 kg/m3,泊松比为0.25。假定弹性板片的剪切模量为48 GPa,黏弹性部分的剪切模量为64 GPa,而软弱层的剪切模量又要低一个数量级,为6.4 GPa。
模型的黏弹性部分使用伯格斯(Burgers)体模拟,这种流变学结构能更好地同时模拟短期效应和长期效应。伯格斯体的开尔文体部分剪切模量与麦克斯韦部分相同,开尔文黏度比麦克斯韦黏度低一个数量级。在Hu等(2004)的研究中,地幔楔、海洋地幔的黏度分别被定为3×1019 Pa·s和1×1020 Pa·s。由于本次地震距1960年智利MW9.5地震已超过半个世纪,震后余滑等短期效应已衰减至可忽略的程度,其研究得到的黏度值能较为准确地反映长期的上地幔黏弹性松弛效应,因此在本文的模型中同样设定地幔楔、海洋地幔黏度分为3×1019 Pa·s和1×1020 Pa·s。本研究主要关注软流圈的黏度ηa和厚度,以及软弱层的黏度ηs,我们对这三个参数进行了网格搜索。软流圈黏度ηa的范围为1×1018—5×1019 Pa·s,软流圈厚度的取值范围为20—300 km,软弱层黏度的取值范围为3×1017—1×1019 Pa·s,测试模型共有353个。对每一个模型参数下的模拟结果均按式(2)进行卡方检验,即
$$ {\chi ^2} {\text{=}} \frac{1}{{N {\text{-}} 1 {\text{-}} {\rm{dof}}}}\mathop \sum \limits_{i {\text{=}} 1}^N \frac{{{{{\text{(}} {{G_i} {\text{-}} {M_i}} {\text{)}}}^2}}}{{\sigma _i^2}}{\text{,}} $$ (2) 式中,G为台站观测值,M为模型预测值,σ为台站观测标准差,i为观测值标号,N为总观测值数,dof为模型自由度。如使用三分量数据时,dof为3。定义最优模型为拥有最小误差的模型。
本文的有限元网格包含约20万个四面体单元,90万个节点。有限元模型使用PyLith-2.2.2软件(Aagaard et al,2017)在Intel志强8164平台上进行模拟需要约1个小时。
3. 模拟结果
3.1 同震模拟结果检验
在研究震后效应之前,需要先验证同震模拟结果的正确性。在Moreno等(2012)的研究中,与本文相似,也考虑了断层面几何,因此选用其同震破裂模型进行模拟。
如图4所示,同震模拟结果在水平方向上,在近场和远场都较好地拟合了GPS观测数据,符合其近场最大约5 m的同震水平位移量和空间衰减特征,垂向上模拟结果也与观测上沉降的特征相一致,拟合了最大约50 cm的沉降值。与观测值略有不同的是,在同震破裂带边缘的一些台站,模拟值虽然方向一致,但在水平和垂向上都有一定的亏损。这是由于本文主要关注震后效应,模拟震后余滑时,我们将主要破裂区域上覆软弱层设置为弹性,其余部分为黏弹性。若在黏弹性部分的软弱层下施加同震破裂,在数值上会有偏差,所以在模拟时会将同震破裂较小(小于5 m)的断层面上的同震破裂值假设为0。近场台站主要受附近的主要破裂影响,远场台站受总地震矩影响,两者数值都没有大的变化,只有在同震破裂边缘的台站会有所亏损。在远场也有个别台站的模拟值与观测值方向不同,由于该个别台站附近的台站观测值与总体海向水平位移模式相一致,这些个别台站可能是受到了局部地质条件的影响发生了不同方向的位移。综上,该同震破裂模型可以支撑进一步的研究。
3.2 敏感性测试
虽然模型的总效应不全是各部分效应的线性叠加,但不同部分对地表形变贡献的多少、影响区域的大小等均有所不同。了解各自的效应有助于我们理解总体模拟结果,因此我们对模型各部分效应进行了敏感性测试。在模拟单独效应时,将模型其它部分均设置为纯弹性以消除其黏弹性效应,黏弹性模型参数设置为最优模型参数(图3)。
在图5所示的敏感性测试中,震后余滑效应在近岸处水平方向上表现为强烈的海向水平运动,在靠近海沟处两年最大累积位移约为85 cm,且随着与海沟距离的增加,衰减迅速;垂向上在海岸处表现为抬升,最大累积抬升量约为30 cm,在远场表现为沉降,最大沉降量约为6 cm。
![]() 图 5 震后两年震后余滑与各部分黏弹性松弛效应的独立模拟及其综合效应(a) 软弱层模拟的震后余滑效应;(b) 地幔楔应力松弛效应;(c) 大洋地幔软流圈应力松弛效应;(d) 深部大洋地幔应力松弛效应;(e) 图(a)−(d)的综合效应Figure 5. Independent simulation of afterslip viscoelastic relaxation effect of each part and its combined effect in 2 years after earthquake(a) Afterslip effects simulated by weak shear zone;(b) Stress relaxation effects of mantle wedge;(c) Stress relaxation effects of oceanic asthenosphere;(d) Stress relaxation effects of deep oceanic mantle;(e) Combined effects of figs.(a)−(d)
图 5 震后两年震后余滑与各部分黏弹性松弛效应的独立模拟及其综合效应(a) 软弱层模拟的震后余滑效应;(b) 地幔楔应力松弛效应;(c) 大洋地幔软流圈应力松弛效应;(d) 深部大洋地幔应力松弛效应;(e) 图(a)−(d)的综合效应Figure 5. Independent simulation of afterslip viscoelastic relaxation effect of each part and its combined effect in 2 years after earthquake(a) Afterslip effects simulated by weak shear zone;(b) Stress relaxation effects of mantle wedge;(c) Stress relaxation effects of oceanic asthenosphere;(d) Stress relaxation effects of deep oceanic mantle;(e) Combined effects of figs.(a)−(d)地幔楔黏弹性松弛效应非常显著,水平方向上也表现为海向运动,相较于震后余滑效应,最大累积水平位移值位于海岸线附近,约为25 cm,这是由于地幔楔的前缘在海岸线附近区域的下方。垂向整体表现为抬升,最大累积抬升量约为15 cm,也在海岸线附近。震后余滑效应和地幔楔黏弹性效应主导了中远场的陆上震后形变场,但地幔楔黏弹性松弛效应随空间的衰减作用小于震后余滑效应,所以陆地侧远场形变主要由地幔楔黏弹性松弛效应控制。
软流圈效应在水平方向表现为陆向,且随着与海沟距离的增加衰减地非常迅速。在陆地上的最大累积位移位于海岸附近,两年最大累积水平位移约为30 cm。垂向上在海岸附近表现为沉降,最大累积沉降量约为30 cm,远场表现为较小的抬升,最大累积抬升量约为4 cm。这与震后余滑效应相反。相较于其它效应,软流圈效应对GPS观测区域的影响主要在于近场。
深部海洋地幔影响非常小,两年最大累积水平位移和垂向位移都小于5 cm,对震后效应的贡献有限,但也表现为水平方向上的陆向和垂向上陆侧的沉降。
综合效应,在陆地GPS台网范围内,水平方向仍主要是海向,两年最大累积水平位移位于距离海岸约100—200 km的中场处,约为35 cm。垂向在近岸和远场抬升,最大累积抬升位于近岸处,约为15 cm,中间有一个沉降的过度带,最大累积沉降约为10 cm。
3.3 最小误差模型
如图6,在仅考虑水平分量数据拟合的情况下,网格搜索得到的最优模型参数中软流圈黏度ηa为8×1018 Pa·s,软流圈厚度为120 km,软弱层黏度ηs为3×1017 Pa·s;而如果仅考虑垂直分量的拟合情况,最优模型为软流圈黏度ηa为2×1018 Pa·s,软流圈厚度为20 km,软弱层黏度ηs为1×1019 Pa·s。从这两个结果可以看出,相较于水平分量的最优模型,垂直分量的最优模型的模型参数要求一个更薄更软的软流圈和更小的震后余滑量。
根据之前敏感性测试的结果,软流圈效应和震后余滑效应在垂向上方向大致相反,但大小相近,特别是在海岸附近。两者两年垂向累积沉降和抬升绝对值都约为30 cm,而GPS台站观测到的抬升只有约5 cm。模型预测值与观测值较大的偏差可能是由于如下原因:近场对软流圈效应和震后余滑效应的大小会有较大的敏感度,导致结果不稳定;由于模型在考虑震后余滑时,使用的软弱层黏度均一,不能很好地反映震后余滑的各向异性,而海岸附近的台站位于同震主要破裂区域上方,受到各向异性的影响会较大;在同震形变比较大的地方,在震后短期内可能有显著的孔隙回弹效应,而本论文没有考虑相关影响。
如果同时考虑三分量数据,最优模型为软流圈黏度ηa为1019 Pa·s,软流圈厚度为120 km,软弱层黏度ηs为5×1017 Pa·s。由于水平方向位移值较垂向位移值更大,而垂向数据不确定度又较水平方向位移大,所以由三分量数据得到的最优模型参数与最符合水平方向数据的模型参数在同一数量级。
在三分量数据的最优模型参数下,图7给出了震后6年每两年的模型预测值与台站记录值的比较结果。在0—2年的水平位移图中,给出了与GPS观测一致以海向为主的运动模式,并且在同震区域两侧模拟得到的与海岸平行的运动也与台站观测相符。中远场的模拟值与台站拟合数值吻合较好,近场数据略有误差,主要是海岸附近在同震主破裂上方的台站的模拟值相对于观测值有5—10 cm的亏损。同样的,垂向上台站模拟值相对于观测到的抬升也小5—10 cm,甚至发生反向,这可能是上文提到的震后余滑的各向异性和孔隙回弹等效应导致的,但也反映了水平方向数据由于观测值大,更具有稳定性。而在2—4年、4—6年的水平位移图中,我们可以看到水平分量上模拟值与观测值的运动模式仍然保持一致,拟合度在多数台站上都很高。近海岸台站的水平亏损和台站垂向上的误差发生了减小,这可能是由震后余滑随时间衰减较黏弹性松弛效应快,孔隙回弹效应衰弱等因素导致的。
综上,联合考虑三分量因素后,在水平方向变形占主导的情况下,本次研究得出的最优模型为软流圈黏度ηa为1019 Pa·s,软流圈厚度为120 km,软弱层黏度ηs为5×1017 Pa·s。
3.4 震后余滑分布
在本次研究中,我们使用一个2 km厚的软弱层模拟震后余滑,得到的震后余滑分布在同震区域的四周,符合应力驱动下的滑动分布。
从图8中可以看到,震后余滑在空间上在接近同震破裂区域的位置处最大,深部震后余滑随深度的增加而减小;在时间上,前两年最大震后余滑量接近2 m,而2—4年的最大值约为0.5 m,4—6年最大值约为0.4 m,表现出震后余滑量随时间增长而快速衰减的趋势。
将本文的震后余滑分布与前人的研究结果(Bedford et al,2013;Klein et al,2016;Weiss et al,2019)作比较可以看出:相同点在于主要余滑量都分布在主震破裂带也即主要的余震分布区域周围,且余滑量均随时间快速衰减;不同点在于,在Bedford等(2013)的研究中,震后短期(约100天)内同震主要破裂带仍存在较大的震后余滑,而本文的模型设置即使在同震主要破裂带震后余滑需为零,但若作进一步的研究可以将该区域的黏度设定为有梯度的递减以使得在该区域进行余滑。在Weiss等(2019)的研究中,在同震区域下方6年累积余滑量平均为2—3 m,与本次研究的结果相似,但在同震区域上方6年累积余滑量最大有8 m。震后余滑的分布有较大的各向异性,在浅部接近海沟处的巨大位移量,可以通过进一步的地球物理探测方法确认。这些研究有一个共同点,即震后余滑的分布不连续,这是反演方法所决定的,而本次研究中的震后余滑是连续的,连续的震后余滑分布可能更能代表实际物理过程。
综上,本次研究得到的震后余滑分布与前人的研究结果基本一致,能够体现出震后余滑的一阶效应。
4. 讨论与结论
本次研究建立了一个用来研究2010年MW8.8马乌莱地震的三维黏弹性有限元模型,模型包括50 km厚的弹性上板片和30 km厚的弹性海洋板片,以及黏弹性的地幔楔、软流圈和海洋地幔,并使用一个2 km厚的软弱层模拟应力驱动的震后余滑。固定地幔楔黏度为3×1019 Pa·s,深部海洋地幔黏度为1×1020 Pa·s,在353个参数模型中进行了网格搜索,得到的最优模型中,软流圈黏度、厚度以及软弱层黏度分别为1×1019 Pa·s,120 km和5×1017 Pa·s。
使用最优模型参数模拟得到的结果与实际GPS观测值相比,水平方向上的运动模式有一致的拟合,一阶效应能够吻合,说明基本的物理机制是正确的。在近海岸处模拟值的亏损,以及垂向上的误差可能与震后余滑的各向异性和孔隙回弹等二阶效应有关,可分别将软弱带分为不同黏度的块,以及设置弹性板块的泊松比来进行模拟,但由于自由度变多,有限元网格搜索的计算量会呈数量级的增加,对于二阶效应的模拟需要建立在对一阶效应的建模上。
模拟得到的震后余滑分布在同震主要区域周围,最大值在震后前两年可达到近2 m,在2—4年减小为0.5 m,在4—6年减小为0.4 m,有随着时间增长快速衰减的趋势。与其它的研究相比,本次研究得到的震后余滑分布是连续的,但可能没有很好地反映各向异性。可以根据进一步的地震学研究成果对震后余滑的空间分布进行约束,例如Hu等(2016b)在对2011年东日本大地震的研究中,利用重复地震研究(Igarashi et al,2003;Uchida,Matsuzawa,2013),以50 km深度为界将软弱层分为了黏度不同的两块。在有上述根据的支持下,可将软弱层分块,并以本文的模型作为基础,固定其它参数以减小计算量,设置不同区块的黏度进行网格搜索,可得到最优模型下的各向异性的震后余滑分布。进一步考虑软弱层的各向异性效应可以更好地拟合部分海岸附近的观测数据,但是不会改变本文得出的软弱层有效黏滞系数。
我们未进一步考虑例如软弱层各向异性等二阶效应是基于如下因素:模型中3个自由参数与需测试参数的排列数量之间为立方关系,现已需要测试300多个模型。若增加两个以上模型参数将需要测试上万个模型,需要的计算时间和资源均不易实现。另一方面,考虑更多的二阶效应可以改善部分台站的数据拟合水平,但是不会改变本文得出的主要结论。对于震后动力学过程的认识还在不断完善中。我们不确定靠近海岸的部分台站处模拟值相对于测量值的偏差是完全由软弱层的各向异性引起的,还是其它模型中尚未考虑的次阶动力学过程,例如孔隙水压弹性效应或者其它尚未认识到的动力学过程。为此,本文重点讨论震后的主要动力学过程。
中国科学技术大学超算中心提供了计算资源,作者在此表示衷心的感谢。
-
图 5 震后两年震后余滑与各部分黏弹性松弛效应的独立模拟及其综合效应
(a) 软弱层模拟的震后余滑效应;(b) 地幔楔应力松弛效应;(c) 大洋地幔软流圈应力松弛效应;(d) 深部大洋地幔应力松弛效应;(e) 图(a)−(d)的综合效应
Figure 5. Independent simulation of afterslip viscoelastic relaxation effect of each part and its combined effect in 2 years after earthquake
(a) Afterslip effects simulated by weak shear zone;(b) Stress relaxation effects of mantle wedge;(c) Stress relaxation effects of oceanic asthenosphere;(d) Stress relaxation effects of deep oceanic mantle;(e) Combined effects of figs.(a)−(d)
-
黄禄渊,张贝,瞿武林,张怀,石耀霖. 2017. 2010智利Maule特大地震的同震效应[J]. 地球物理学报,60(3):972–984. doi: 10.6038/cjg20170312 Huang L Y,Zhang B,Qu W L,Zhang H,Shi Y L. 2017. The co-seismic effects of 2010 Maule earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,60(3):972–984 (in Chinese).
林鑫,郝金来,姚振兴. 2017. 智利MW8.3地震与MW8.8地震的震源过程及其引起的库仑应力特征[J]. 地球物理学报,60(7):2680–2692. Lin X,Hao J L,Yao Z X. 2017. Rupture process and Coulomb stress change of the MW8.3 earthquake and the MW8.8 earthquake,Chile[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,60(7):2680–2692 (in Chinese).
Aagaard B, Williams C, Knepley M, Williams C. 2017. Computational infrastructure for geodynamics: Software[CP/OL]. [2019-08-05]. https://geodynamics.org/cig/software/pylith.
Bedford J,Moreno M,Baez J C,Lange D,Tilmann F,Rosenau M,Heidbach O,Oncken O,Bartsch M,Rietbrock A,Tassara A,Bevis M,Vigny C. 2013. A high-resolution,time-variable afterslip model for the 2010 Maule MW8.8,Chile megathrust earthquake[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett,383:26–36. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2013.09.020
Bedford J,Moreno M,Li S Y,Oncken O,Baez J C,Bevis M,Heidbach O,Lange D. 2016. Separating rapid relocking,afterslip,and viscoelastic relaxation:An application of the postseismic straightening method to the Maule 2010 cGPS[J]. J Geophys Res:Solid Earth,121(10):7618–7638. doi: 10.1002/2016JB013093
Blewitt G,Hammond W C,Kreemer Corné K. 2018. Harnessing the GPS data explosion for interdisciplinary science[J]. Eos,99:1–2.
Chen L. 2017. Layering of subcontinental lithospheric mantle[J]. Science Bulletin,62(14):1030–1034. doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2017.06.003
Hayes G P,Wald D J,Johnson R L. 2012. Slab1.0:A three-dimensional model of global subduction zone geometries[J]. J Geophys Res:Solid Earth,117(B1):B01302.
Hicks S P,Rietbrock A,Ryder I M,Lee C S,Miller M. 2014. Anatomy of a megathrust:The 2010 M8.8 Maule,Chile earthquake rupture zone imaged using seismic tomography[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett,405:142–155. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2014.08.028
Hu Y,Wang K L,He J H,Klotz J,Khazaradze G. 2004. Three-dimensional viscoelastic finite element model for postseismic deformation of the great 1960 Chile earthquake[J]. J Geophys Res:Solid Earth,109(B12):B12403. doi: 10.1029/2004JB003163
Hu Y,Bürgmann R,Banerjee P,Feng L J,Hill E M,Ito T,Tabei T,Wang K L. 2016a. Asthenosphere rheology inferred from observations of the 2012 Indian Ocean earthquake[J]. Nature,538(7625):368–372. doi: 10.1038/nature19787
Hu Y,Bürgmann R,Uchida N,Banerjee P,Freymueller J T. 2016b. Stress-driven relaxation of heterogeneous upper mantle and time-dependent afterslip following the 2011 Tohoku earthquake[J]. J Geophys Res:Solid Earth,121(1):385–411. doi: 10.1002/2015JB012508
Igarashi T,Matsuzawa T,Hasegawa A. 2003. Repeating earthquakes and interplate aseismic slip in the northeastern Japan subduction zone[J]. J Geophys Res:Solid Earth,108(B5):2249.
Klein E,Fleitout L,Vigny C,Garaud J D. 2016. Afterslip and viscoelastic relaxation model inferred from the large-scale post-seismic deformation following the 2010 MW8.8 Maule earthquake (Chile)[J]. Geophys J Int,205(3):1455–1472. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggw086
Klotz J,Khazaradze G,Angermann D,Reigber C,Perdomo R,Cifuentes O. 2001. Earthquake cycle dominates contemporary crustal deformation in Central and Southern Andes[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett,193(3/4):437–446.
Li S Y,Moreno M,Bedford J,Rosenau M,Heidbach O,Melnick D,Oncken O. 2017. Postseismic uplift of the Andes following the 2010 Maule earthquake:Implications for mantle rheology[J]. Geophys Res Lett,44(4):1768–1776.
Li S Y,Bedford J,Moreno M,Barnhart W D,Rosenau M,Oncken O. 2018. Spatio-temporal variation of mantle viscosity and the presence of cratonic mantle inferred from 8 years of postseismic deformation following the 2010 Maule,Chile,earthquake[J]. Geochem,Geophys,Geosyst,19(9):3272–3285.
Moreno M,Melnick D,Rosenau M,Baez J,Klotz J,Oncken O,Tassara A,Chen J,Bataille K,Bevis M,Socquet A,Bolte J,Vigny C,Brooks B,Ryder I,Grund V,Smalley B,Carrizo D,Bartsch M,Hase H. 2012. Toward understanding tectonic control on the MW8.8 2010 Maule Chile earthquake[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett,321-322:152–165. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2012.01.006
Oncken O, Chong G, Franz G, Giese P, Götze H J, Ramos V A, Strecker M R, Wigger P. 2006. The Andes: Active Subduction Orogeny[M]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Science & Business Media: 443–457.
Ruegg J C,Rudloff A,Vigny C,Madariaga R,de Chabalier J B,Campos J,Kausel E,Barrientos S,Dimitrov D. 2009. Interseismic strain accumulation measured by GPS in the seismic gap between Constitución and Concepción in Chile[J]. Phys Earth Planet Inter,175(1/2):78–85.
Sun T H,Wang K L,He J H. 2018. Crustal deformation following great subduction earthquakes controlled by earthquake size and mantle rheology[J]. J Geophys Res:Solid Earth,123(6):5323–5345. doi: 10.1029/2017JB015242
Tong X P,Sandwell D,Luttrell K,Brooks B,Bevis M,Shimada M,Foster J,Smalley Jr R,Parra H,Soto J C B,Blanco M,Kendrick E,Genrich J,Caccamise II D J. 2010. The 2010 Maule,Chile earthquake:Downdip rupture limit revealed by space geodesy[J]. Geophys Res Lett,37(24):L24311.
Uchida N,Matsuzawa T. 2013. Pre- and postseismic slow slip surrounding the 2011 Tohoku-Oki earthquake rupture[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett,374:81–91. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2013.05.021
Utada H,Kiyoshi B. 2014. Estimating the electrical conductivity of the melt phase of a partially molten asthenosphere from seafloor magnetotelluric sounding data[J]. Phys Earth Planet Inter,227:41–47. doi: 10.1016/j.pepi.2013.12.004
Wang K L,Hu Y,Bevis M,Kendrick E,Smalley Jr R,Vargas R B,Lauría E. 2007. Crustal motion in the zone of the 1960 Chile earthquake:Detangling earthquake-cycle deformation and forearc-sliver translation[J]. Geochem,Geophys,Geosyst,8(10):Q10010.
Wang K L,Hu Y,He J H. 2012. Deformation cycles of subduction earthquakes in a viscoelastic Earth[J]. Nature,484(7394):327–332. doi: 10.1038/nature11032
Watts A B,Zhong S. 2000. Observations of flexure and the rheology of oceanic lithosphere[J]. Geophys J Int,142(3):855–875. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-246x.2000.00189.x
Weiss J R,Qiu Q,Barbot S,Wright T J,Foster J H,Saunders A,Brooks B A,Bevis M,Kendrick E,Ericksen T L,Avery J,Smalley Jr R,Cimbaro S R,Lenzano L E,Barón J,Báez J C,Echalar A. 2019. Illuminating subduction zone rheological properties in the wake of a giant earthquake[J]. Sci Adv,5(12):eaax6720. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aax6720
Yue H,Lay T,Rivera L,An C,Vigny C,Tong X P,Soto J C B. 2014. Localized fault slip to the trench in the 2010 Maule,Chile MW8.8 earthquake from joint inversion of high-rate GPS,teleseismic body waves,InSAR,campaign GPS,and tsunami observations[J]. J Geophys Res:Solid Earth,119(10):7786–7804. doi: 10.1002/2014JB011340





 下载:
下载: