Paleoearthquakes and the latest active age of Jinghe segment of Bolokenu-Aqikekuduk fault
-
摘要: 博罗可努—阿齐克库都克断裂是西天山北西向右旋走滑断裂系中最北端的一条活动断裂,其在中国境内延伸最长。本文在艾比湖西侧及精河县东南侧最新地表形变上开挖两条探槽,进行该断裂古地震的初步研究。根据活动性质差异和断裂截切关系将该断裂分为艾比湖段和精河以东段,在对沉积物光释光年代和地震关系分析的基础上,确定了此两段断裂的最新活动时代均为全新世,初步确定其古地震期次,最新地震事件距今3.7—4.86 ka之间;根据冲沟位错和洪积扇年代测定结果,确定精河以东段的活动速率大于4 mm/a;根据探槽错动至地表,及地表破裂带位置及长度,推测艾比湖段可能为1765年精河M61/2的发震构造,且其震级很有可能被低估,因为艾比湖段的破裂总长度超过60 km,震级极有可能达到M7.0以上。Abstract: Bolokenu-Aqikekuduk fault is located at the northernmost end of the NW-trending dextral strike-slip fault system in the west Tianshan mountain, and is also the longest active fault extending in China. The latest active ages of both faults are determined to be Holocene based on the relation between the optically stimulated luminescence age of sediments and earthquake colluvial wedges. In this paper, two trenches were excavated on the latest surface deformation in the west of Aibi lake and southeast of Jinghe county. According to activity difference, the fault can be divided into the Aibi lake segment and the east Jinghe segment. The results show that the latest active times of the two segments are determined to be Holocene, and the latest earthquake events occurred on 3.7−4.86 ka BP respectively. According to the results of gully dislocation and pluvial fan dating, the activity rate in the east Jinghe segment is more than 4 mm/a. Furthermore, it is deduced that the Aibi Lake segment may be the seismogenic structure of M61/2 Jinghe earthquake in 1765, and its magnitude is likely to be underestimated. According to the rupture length of Aibi lake segment more than 60 km, the magnitude is likely to be more than M7.0.
-
-
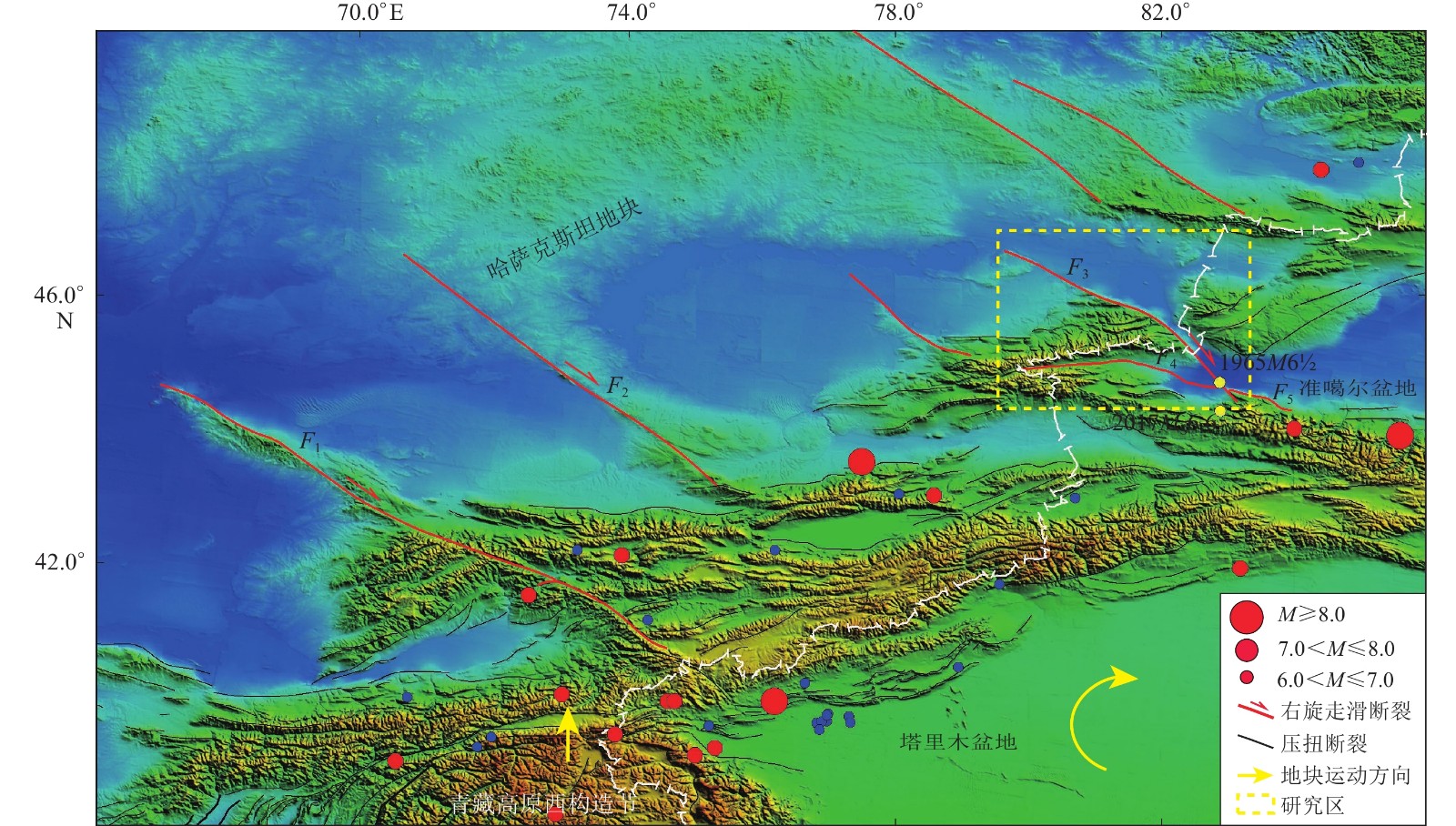
图 1 青藏高原西构造结节和天山地区的构造及强震分布图
F1: 塔拉斯—费尔干纳断裂; F2: 肯迪克塔什断裂; F3: 博罗可努-阿齐克库都克断裂;F4:温泉—博乐断裂;F5:四棵树—古尔图南断裂
Figure 1. Structure of western Syntaxis of Tibet Plateau and Tianshan area and distribution of earthquakes
F1:Talas-Fergana fault; F2:Kindyktash fault; F3:Bolokenu-Aqikekuduk fault; F4:Wenquan-Bole fault;F5:Sikeshu-Guertunan fault
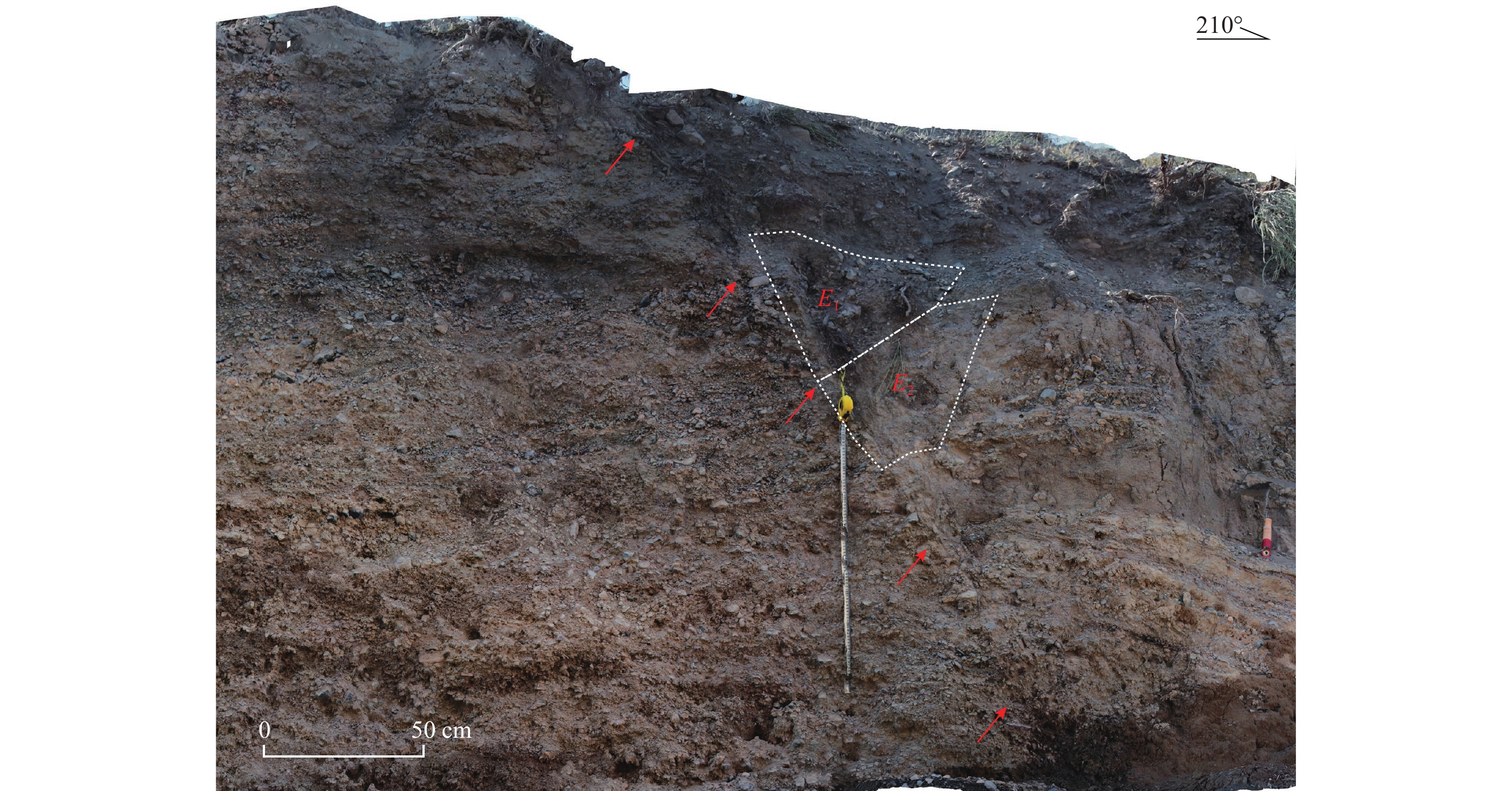
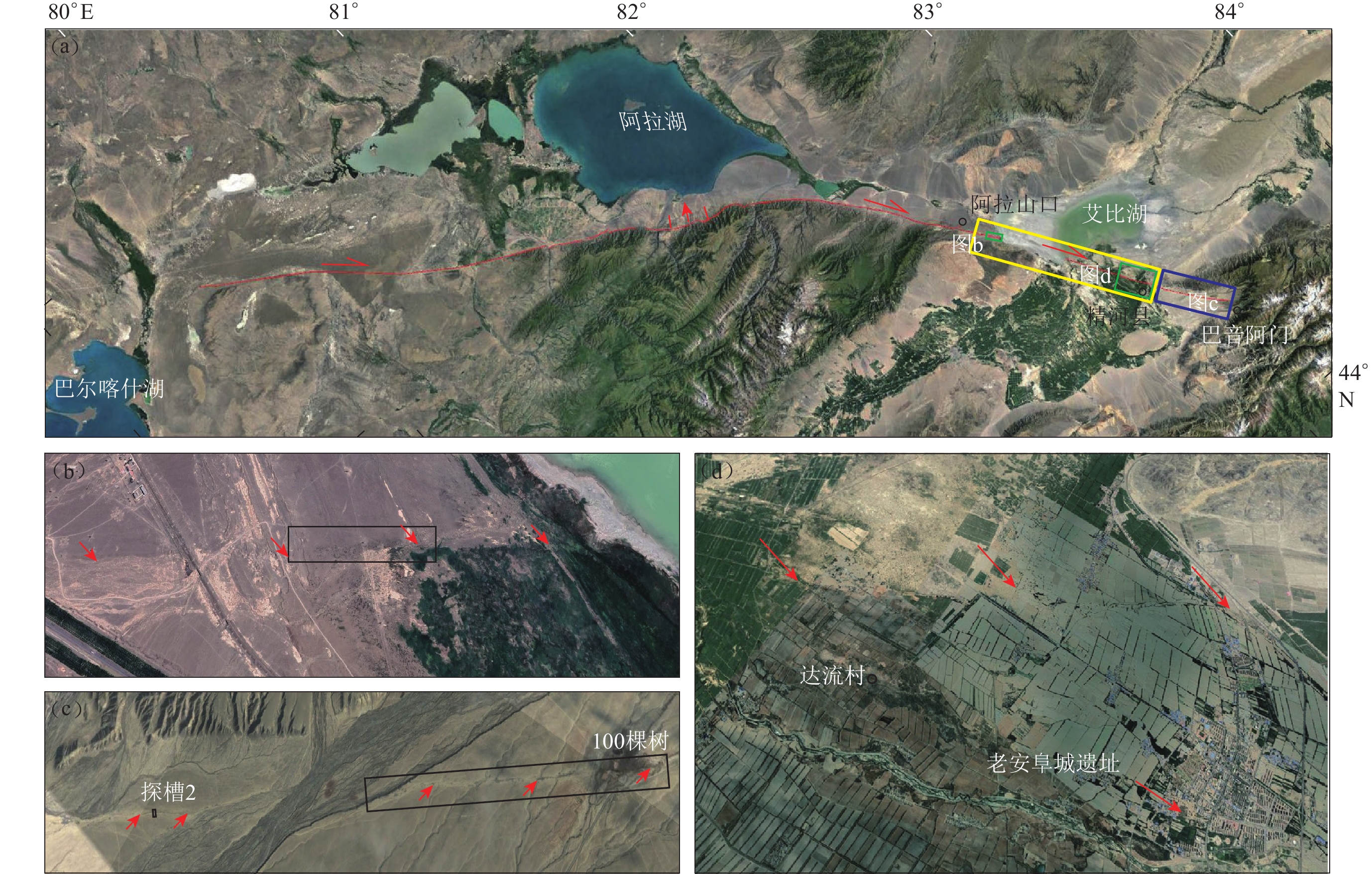
图 2 博阿断裂天山以北段的展布影像解译及活动性质
(a) 博阿断裂总体展布图;(b) 艾比湖西岸断裂影像;(c) 100棵树附近断裂影像;(d) 精河县城断裂影像。图中黄色框为艾比湖段;蓝色框为精河以东段;红色剪头指示形变带。影像来自Google Earth
Figure 2. The distribution and activity of the northern Tianshan mountain segment of Bolokenu-Aqikekuduk fault
(a) The trace of Bolokenu−Aqikekuduk fault;(b) The trace of Aibi lake segment;(c) The trace of 100 trees segment;(d) The trace of Jinghe county. The yellow frame is Aibi lake segment,blue frame is east Jinghe segment,red arrows indicate deformation trace of the fault. The figures are from Google Earth
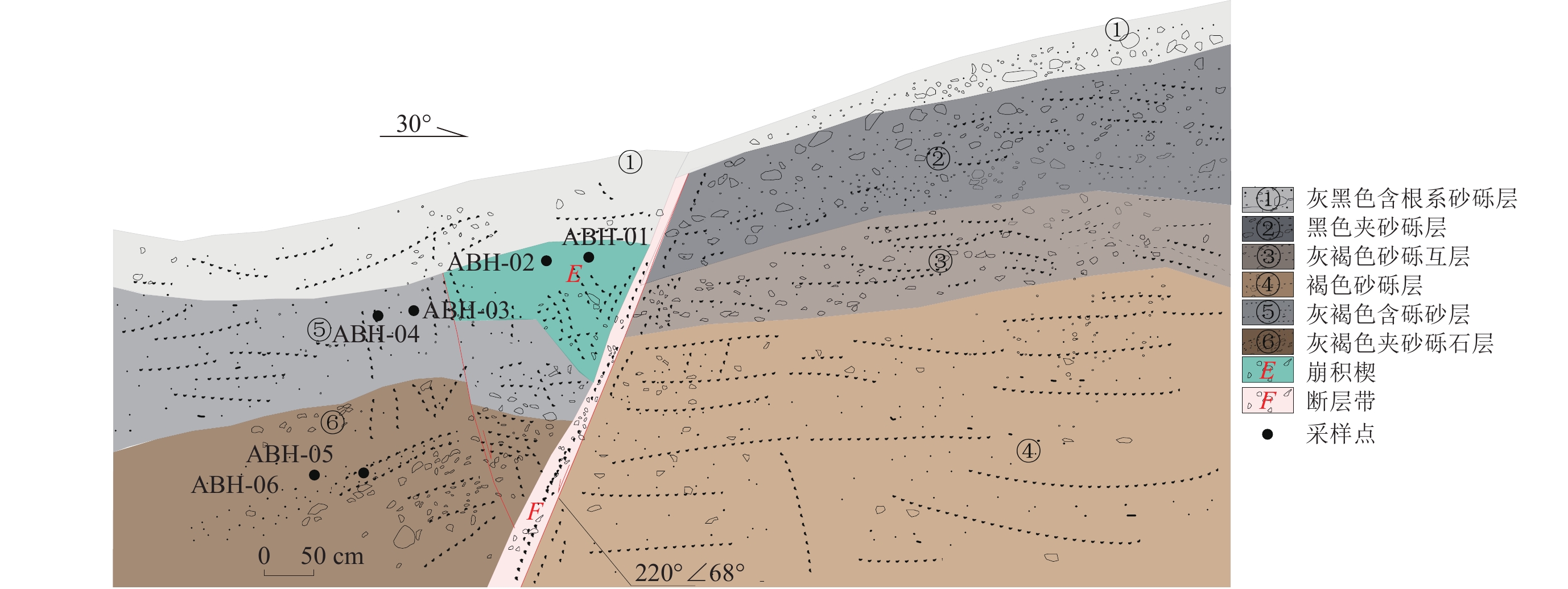
表 1 艾比湖探槽光释光年代测试结果
Table 1 Optically stimulated luminescence dating results of Aibi lake trench
原始编号 埋藏深度/m 剂量率/(Gy·ka−1) 等效剂量/Gy 年龄/ka ABH-01 0.2 5.09±0.26 11.14±0.35 2.19±0.13 ABH-02 0.2 5.31±0.27 10.53±0.37 1.98±0.12 ABH-03 0.5 5.78±0.33 12.65±0.41 2.19±0.14 ABH-04 0.5 4.77±0.12 9.53±0.15 2.00±0.06 ABH-05 1.2 4.34±0.13 13.21±0.19 3.04±0.10 ABH−06 1.2 4.49±0.13 8.73±0.45 1.95±0.12 注:样品由北京光释光实验室测定 表 2 探槽2样品测试结果
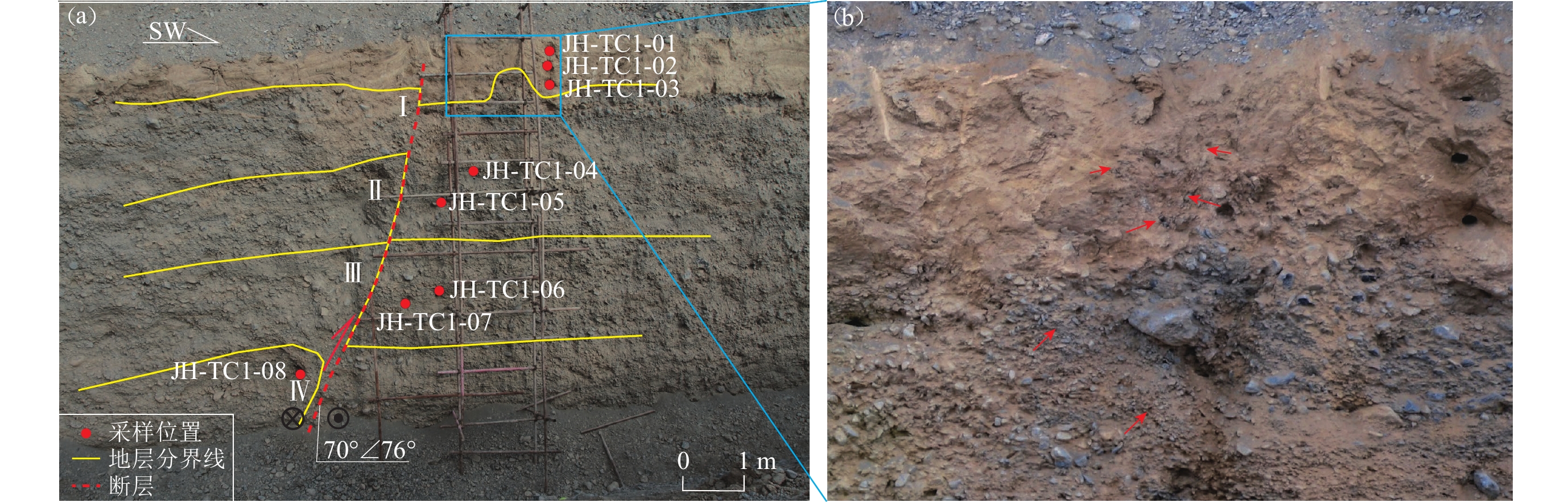
Table 2 Test results of trench 2 sample
原始编号 埋藏深度/m 含水率 剂量率/(Gy·ka−1) 等效剂量/Gy 年龄/ka JH-TC1-01 0.3 15%±5% 5.22±0.34 19.30±0.70 3.70±0.28 JH-TC1-02 0.6 16%±5% 5.16±0.34 25.09±0.65 4.86±0.35 JH-TC1-03 0.9 13%±5% 5.50±0.38 39.37±0.98 7.16±0.53 JH-TC1-04 2.0 6%±3% 3.44±0.10 36.72±0.69 10.67±0.38 JH-TC1-05 2.3 6%±3% 3.37±0.10 34.58±0.45 10.26±0.32 JH-TC1-06 5.0 6%±3% 3.64±0.12 64.53±0.70 17.75±0.61 JH-TC1-07 7.0 6%±3% 4.09±0.21 74.68±2.99 18.27±1.20 JH-TC1-08 7.9 6%±3% 3.28±0.09 58.70±0.53 17.88±0.53 注:样品由北京光释光实验室测定 -
邓起东, 冯先岳, 张培震, 徐锡伟, 杨晓平, 彭斯震, 李军. 2000. 天山活动构造[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 373–387. Deng Q D, Feng X Y, Zhang P Z, Xu X W, Yang X P, Peng S Z, Li J. 2000. Active Tectonics of the Tianshan Mountain[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press: 373–387 (in Chinese).
胡宗凯,杨晓平,杨海波,李军,吴国栋,黄伟亮. 2019. 博罗可努—阿齐克库都克断裂精河段晚更新世以来的断错地貌和走滑速率[J]. 地震地质,41(2):266–280. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2019.02.002 Hu Z K,Yang X P,Yang H B,Li J,Wu G D,Huang W L. 2019. Faulted landform and slip rate of the Jinghe section of the Bolokenu-Aqikekuduke fault since the Late Pleistocene[J]. Seismology and Geology,41(2):266–280 (in Chinese).
胡宗凯,杨晓平,杨海波,吴国栋,李军,周本刚. 2020. 北天山博罗可努—阿齐克库都克断裂精河段的古地震事件[J]. 地震地质,42(4):773–790. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2020.04.001 Hu Z K,Yang X P,Yang H B,Wu G D,Li J,Zhou B G. 2020. Study on paleoearthquakes along the Jinghe section of Bolokenu-Aqikekuduke fault[J]. Seismology and Geology,42(4):773–790 (in Chinese).
李杰,王晓强,谭凯,刘代芹,帕尔哈提,蒋靖祥,方伟. 2010. 北天山现今活动构造的运动特征[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学,30(6):1–5. Li J,Wang X Q,Tan K,Liu D Q,Paerhati,Jiang J X,Fang W. 2010. Analysis of movement characters of present-day active tectonics of northern Tianshan region[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics,30(6):1–5 (in Chinese).
毛昶熙. 2009. 堤防工程手册(设计−施工−管理−科研)[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社: 126–128. Mao C X. 2009. Dikes Engineering Manual (Design-Construction-Management-Researches)[M]. Beijing: China Water & Power Press: 126–128 (in Chinese).
沈军,杨晓平. 1998. 博罗科努断裂西北段古地震形变带初步研究[J]. 内陆地震,12(3):248–255. Shen J,Yang X P. 1998. A preliminary study on the paleoearthquake rupture belt on the northwestern section of Bolohkenu fault[J]. Inland Earthquake,12(3):248–255 (in Chinese).
吴敬禄. 1995. 新疆艾比湖全新世沉积特征及古环境演化[J]. 地理科学,15(1):39–46. Wu J L. 1995. Characters of the evolution of climate and environment during the last 10 ka years in Aibi lake basin,Xinjiang[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica,15(1):39–46 (in Chinese).
谢毓寿, 蔡美彪. 1987. 中国地震历史资料汇编第三卷[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 632–633. Xie Y S, Cai M B. 1987. Summary of the Chinese Historical Earthquake Records[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 632–333 (in Chinese).
新疆维吾尔自治区地震局. 1981. 新疆维吾尔自治区地震资料汇编[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 2–158. Earthquake Agency of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. 1981. Summary of the Chinese Historical Earthquake Records of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press: 2–158 (in Chinese).
杨少敏,李杰,王琪. 2008. GPS研究天山现今变形与断层活动[J]. 中国科学:D辑,38(7):872–880. Yang S M,Li J,Wang Q. 2008. The deformation pattern and fault rate in the Tianshan mountains inferred from GPS observations[J]. Science in China:Series D,51(8):1064–1080. doi: 10.1007/s11430-008-0090-8
杨晓平,沈军. 2000. 天山内部博罗科努断裂精河:阿拉山口段晚更新世以来的活动特征[J]. 地震地质,22(3):305–315. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2000.03.011 Yang X P,Shen J. 2000. Late quaternary activity of Jinghe:Alashankou section of the Boluokenu fault,Interior Tianshan[J]. Seismology and Geology,22(3):305–315 (in Chinese).
赵世勇. 2015. 精河安阜城史话[J]. 新疆地方志,(1):51–57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1826.2015.01.014 Zhao S Y. 2015. Historical talks on Anfu city in Jinghe county[J]. Xinjiang Local Chronicles,(1):51–57 (in Chinese).
Allen M B,Windley B F,Zhang C. 1993. Palaeozoic collisional tectonics and magmatism of the Chinese Tien Shan,central Asia[J]. Tectonophysics,220(1/2/3/4):89–115.
Burtman V S,Skobelev S F,Molnar P. 1996. Late Cenozoic slip on the Talas-Ferghana fault,the Tien Shan,central Asia[J]. GSA Bull,108(8):1004–1021. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1996)108<1004:LCSOTT>2.3.CO;2
Campbell G E,Walker R T,Abdrakhmatov K,Schwenninger J L,Jackson J,Elliott J R,Copley A. 2013. The Dzhungarian fault:Late Quaternary tectonics and slip rate of a major right-lateral strike-slip fault in the northern Tien Shan region[J]. J Geophys Res:Solid Earth,118(10):5681–5698. doi: 10.1002/jgrb.50367
Korjenkov A M,Bobrovskii A V,Mamyrov E M. 2010. Evidence for strong paleoearthquakes along the Talas-Fergana fault near the Kök-Bel Pass,Kyrgyzstan[J]. Geotectonics,44(3):262–270. doi: 10.1134/S0016852110030040
Shen J,Wang Y P,Li Y Z. 2011. Characteristics of the Late Quaternary right-lateral strike-slip movement of Bolokenu-Aqikekuduk fault in northern Tianshan mountains,NW China[J]. Geoscience Frontiers,2(4):519–527. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2011.05.004
Wells D L,Coppersmith K J. 1994. New empirical relationships among magnitude,rupture length, rupture width,rupture area,and surface displacement[J]. Bulletin of the seismological Society of America,84(4):974–1002.
Zubovich A V,Wang X Q,Scherba Y G,Schelochkov G G,Reilinger R,Reigber C,Mosienko O I,Molnar P,Michajljow W,Makarov V I,Li J,Kuzikov S I,Herring T A,Hamburger M W,Hager B H,Dang Y M,Bragin V D,Beisenbaev R T. 2010. GPS velocity field for the Tien Shan and surrounding regions[J]. Tectonics,29(6):TC6014.
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(7)




 下载:
下载: