Joint inversion of the lithospheric structure of the central North China Craton from ambient noise and seismic surface wave
-
摘要: 基于ChinArray三期项目布设于华北克拉通中部的流动台阵观测数据,利用背景噪声互相关和地震面波层析成像获取了研究区内6—140 s周期的瑞雷面波频散,使用蒙特卡罗非线性反演方法获得了华北克拉通中部岩石圈的高分辨率三维S波速度结构。结果显示华北克拉通不同地块的岩石圈速度结构存在显著的横向差异:其中鄂尔多斯盆地腹地整体表现为高速特征,延伸至200 km以下,但其东南缘存在小范围的低速异常;东部的华北盆地整体表现为低速特征,具有较薄的地壳和岩石圈厚度;中部造山带南北两端以及南北重力梯度线下方存在相连接的低速区域,在深处延伸至华北盆地下方;在下地壳和上地幔顶部,大同火山群区域的低速体逐渐向西偏移至鄂尔多斯盆地东北角下方;而在上地幔中,该区域的低速异常随深度增加而逐渐减弱,低速体延伸至东南方向的华北盆地下方。基于本研究获得的S波速度模型,我们认为:鄂尔多斯盆地腹地保持了克拉通特性,但其东南缘存在局部的岩石圈改造作用;华北盆地发生了强烈的岩石圈破坏减薄和地壳伸展变形;中部造山带南北端以及南北重力梯度线下方的岩石圈发生了局部的改造减薄,其机制可能都来源于华北盆地下方地幔热物质的上涌;大同火山群下方上涌的热物质从鄂尔多斯盆地东北角下方侵入下地壳,在地壳内上升过程中受到上地壳的阻挡,向东流动至大同火山群下方,形成了大同火山群的岩浆活动,其深部来源可能与西向俯冲的太平洋停滞板块有关。Abstract: Based on the observation data of the ChinArray Phase Ⅲ deployed in the central North China Craton, the Rayleigh surface wave dispersion with period range of 6 s to 140 s in the studied area is obtained using cross-correlation of ambient noise and seismic surface wave tomography. The high-resolution 3-D S-wave velocity structure of the lithosphere in the central North China Craton is further obtained with the Monte Carlo nonlinear inversion method. The results exhibit significant lateral differences in the lithospheric structure of different blocks of the North China Craton. The central part of the Ordos basin is characterized by high velocity overall, extending below 200 km, but there is a small range of low-velocity anomalies on the southeast margin. The North China basin in the east is characterized by low-velocity with thin crust and lithospheric thickness. Connected low-velocity zones at the northern and southern ends of the central orogenic belt and below the north-south gravity gradient line are observed, which extends below the North China basin. In the lower crust and uppermost mantle, the low-velocity zone in the Datong volcanic group area gradually shifts westward to the northeast corner of the Ordos basin. While in the upper mantle, the low-velocity anomalies in this area gradually fade off as the depth increased. And the low-velocity zone extended below the North China basin in the southeast. Based on the S-wave velocity model obtained in this study, we believe that the heart of the Ordos basin maintains the cratonic characteristics overall, but there is a local lithospheric modification at the southeast margin; the North China basin has experienced strong lithospheric destruction and thinning and crustal extensional deformation; the lithosphere at the northern and southern ends of the central orogenic belt and the north-south gravity gradient line has undergone partial modification and thinning. The mechanism may be the same and due to the upwelling of hot material in the mantle below the North China basin; the upwelling hot material below the Datong volcanic group intrudes into the lower crust below the northeast corner of the Ordos basin. Then it is blocked by the upper crust when rising in the crust and flows eastward to the bottom of the Datong volcanic group, forming the magmatic activity of the Datong volcanic group. The deep source may be related to the stagnant Pacific slab.
-
-
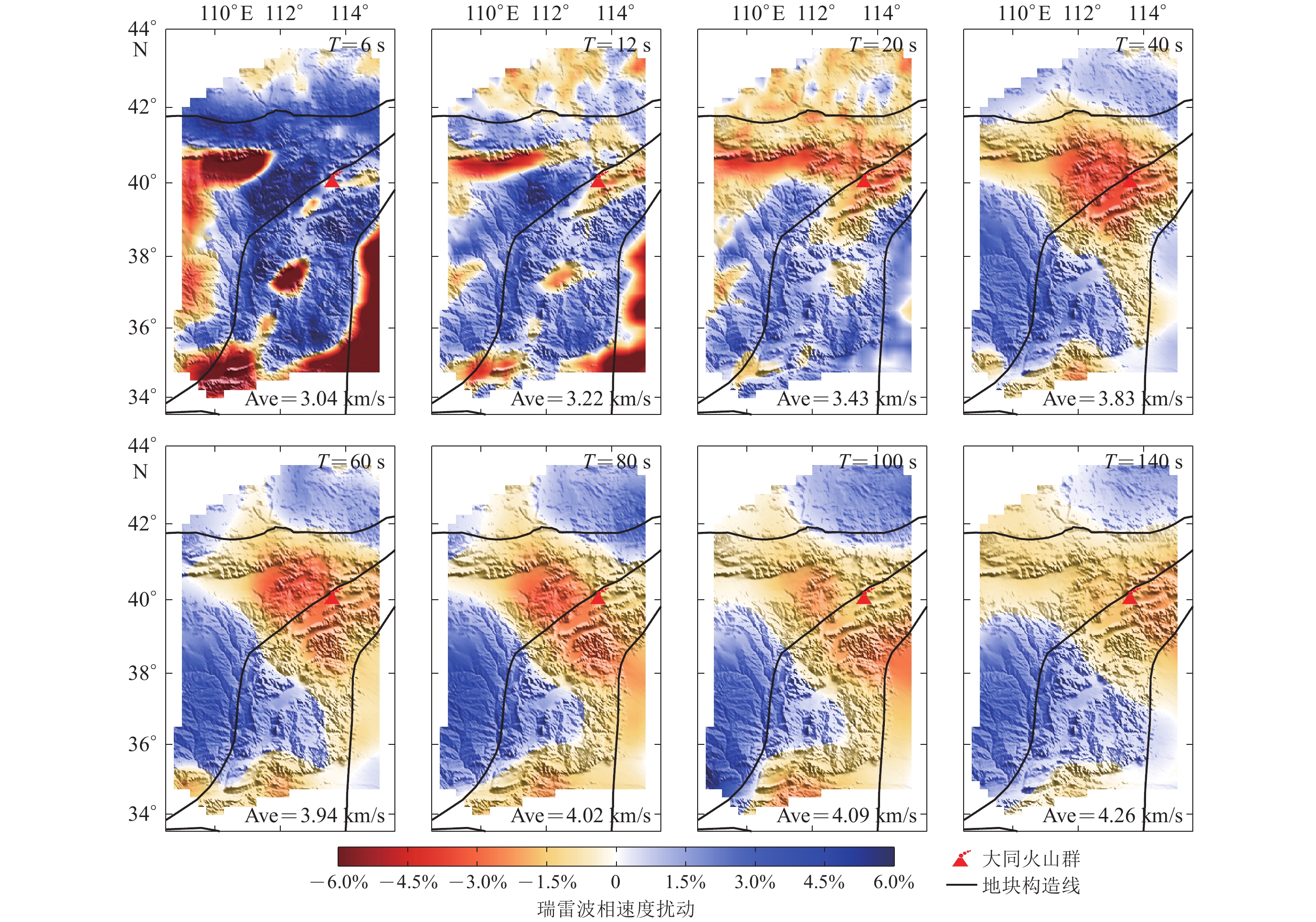
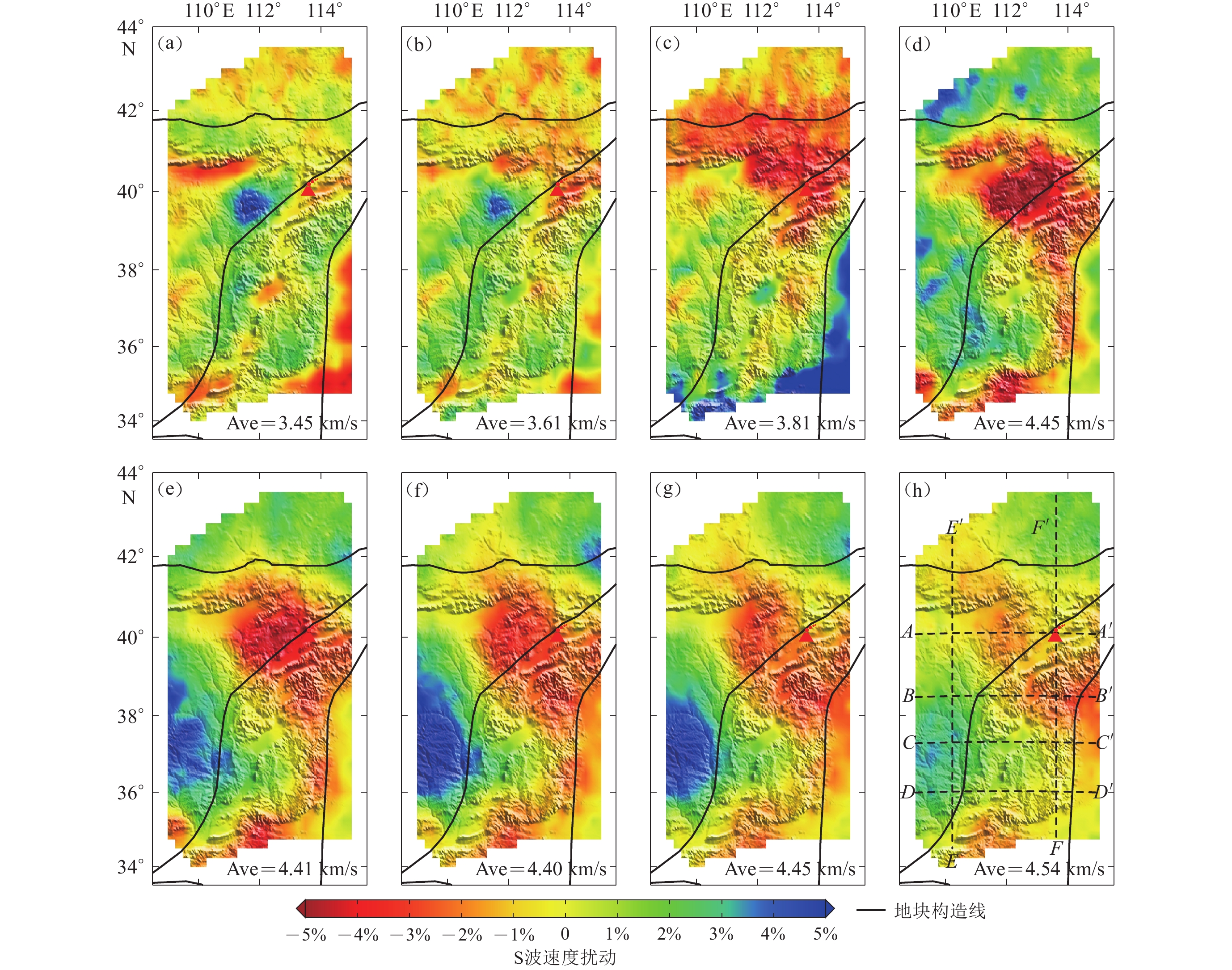
图 8 华北克拉通中部不同深度的S波速度水平切片(图中Ave表示每个深度h对应的S波平均速度)
Figure 8. Horizontal slices of S-wave velocities at different depths in the central North China Craton. The average S wave velocity Ave of each depth is shown in the lower right corner
(a) h=5 km; (b) h=15 km;(c) h=30 km;(d) h=50 km;(e) h=70 km;(f) h=100 km;(g) h=140 km;(h) h=200 km
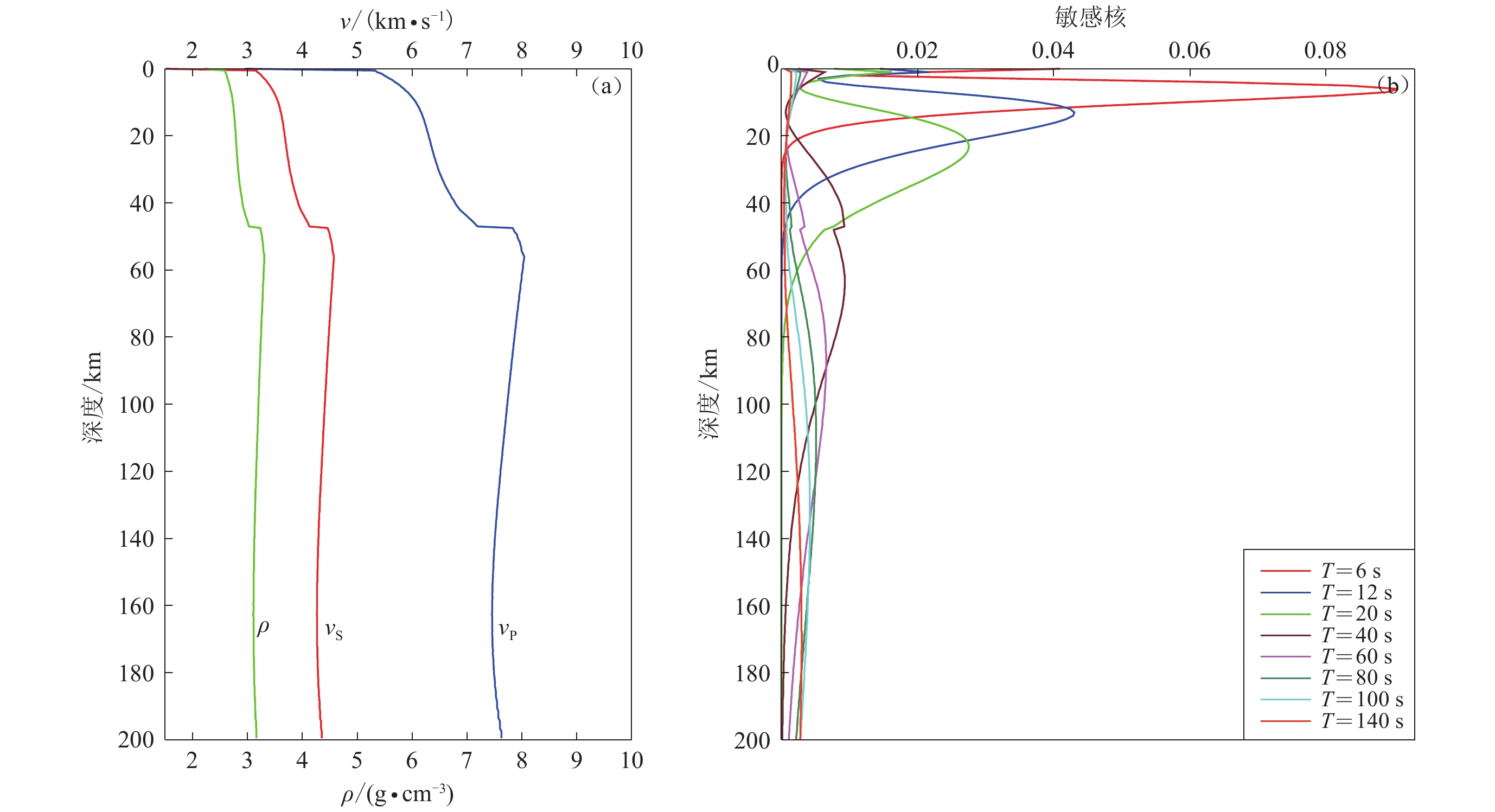
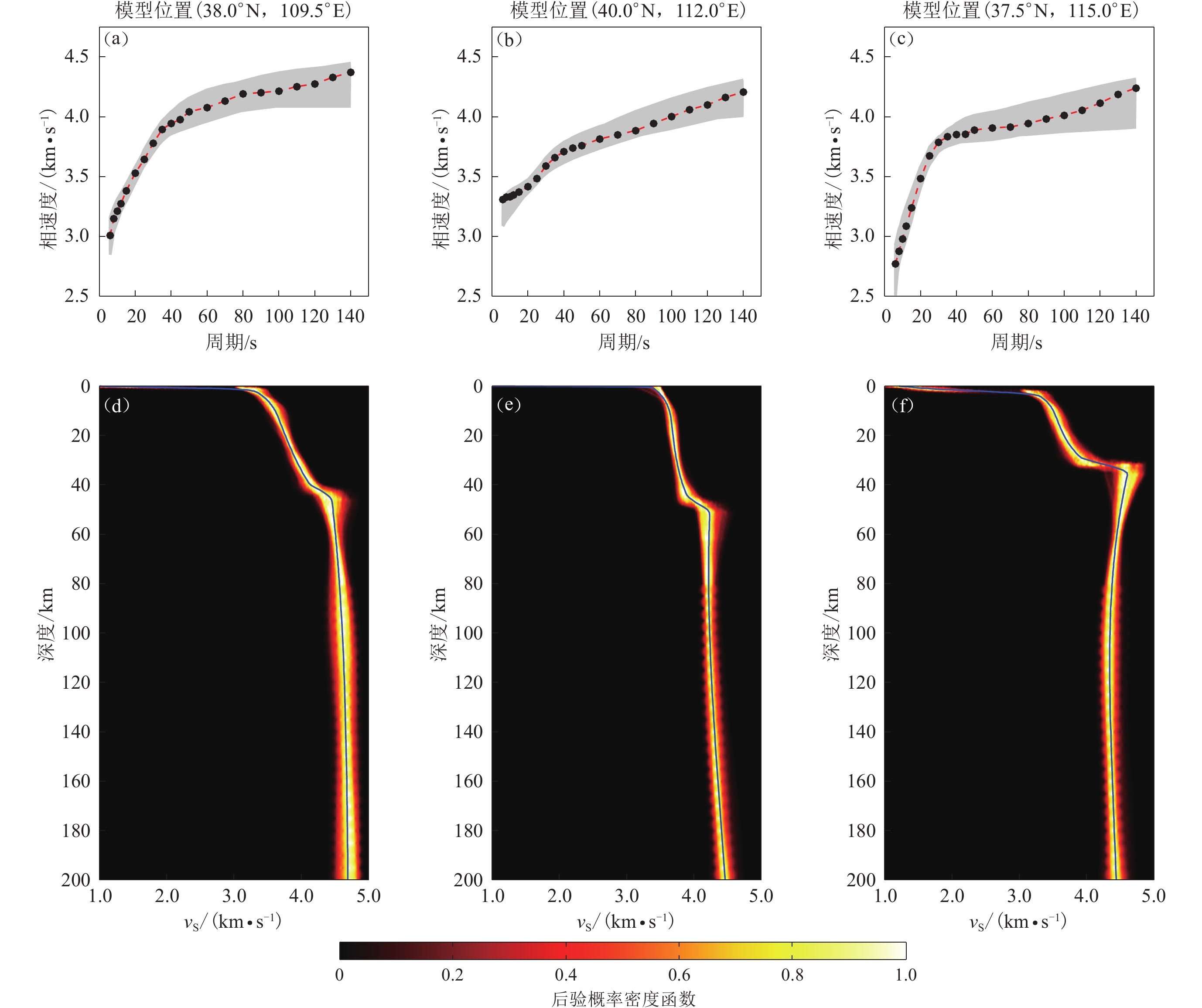
图 7 一维S波速度模型反演举例,其位置在图1中以蓝色圆点表示
(a−c) 瑞雷波相速度频散;(d−f) 一维S波速度模型。黑色圆点代表观测的频散曲线,灰色线条代表计算的频散曲线,蓝色曲线代表最终的平均S波速度模型
Figure 7. Examples of 1-D S-wave velocity model inversion. Their positions are represented by blue dots in Fig. 1
(a−c) Rayleigh wave phase velocity dispersions;(d−f) 1-D S wave velocity models. The black dots represent the observed dispersion curves,and the gray lines represent the calculated dispersion curves,and the blue curve represents the final average S-wave velocity model
图 9 S波速度模型垂直剖面,其位置以黑色虚线标注在图8h中,图中黑色粗实线代表莫霍面深度
Figure 9. Vertical sections of the S-wave velocity model,the positions of which are marked with black dotted lines in Fig. 8h,the thick black lines denote the Moho depth
-
陈凌,程骋,危自根. 2010a. 华北克拉通边界带区域深部结构的特征差异性及其构造意义[J]. 地球科学进展,25(6):571–581. Chen L,Cheng C,Wei Z G. 2010a. Contrasting structural features at different boundary areas of the North China Craton and its tectonic implications[J]. Advances in Earth Science,25(6):571–581 (in Chinese).
陈凌,危自根,程骋. 2010b. 从华北克拉通中、西部结构的区域差异性探讨克拉通破坏[J]. 地学前缘,17(1):212–228. Chen L,Wei Z G,Cheng C. 2010b. Significant structural variations in the central and western North China Craton and its implications for the craton destruction[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,17(1):212–228 (in Chinese).
陈文寄, 李大明, 戴潼漠. 1992. 大同第四纪玄武岩的K–Ar年龄及过剩氩[M]// 中国新生代火山岩年代学与地球化学. 北京: 地震出版社: 81–92. Chen W J, Li D M, Dai T M. 1992. The K–Ar age and excess Ar of Quaternary basalt in Datong[M]// The Age and Geochemistry of Cenozoic Volcanic Rock in China. Beijing: Seismology Press: 81–92 (in Chinese).
李自红,刘保金,袁洪克,酆少英,陈文,李稳,寇昆朋. 2014. 临汾盆地地壳精细结构和构造:地震反射剖面结果[J]. 地球物理学报,57(5):1487–1497. doi: 10.6038/cjg20140513 Li Z H,Liu B J,Yuan H K,Feng S Y,Chen W,Li W,Kou K P. 2014. Fine crustal structure and tectonics of Linfen basin:From the results of seismic reflection profile[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,57(5):1487–1497 (in Chinese).
汪洋,程素华. 2011. 中国东部岩石圈热状态与流变学强度特征[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,35(1):12–23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2011.01.002 Wang Y,Cheng S H. 2011. Thermal state and rheological strength of the lithosphere beneath the eastern China[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia,35(1):12–23 (in Chinese).
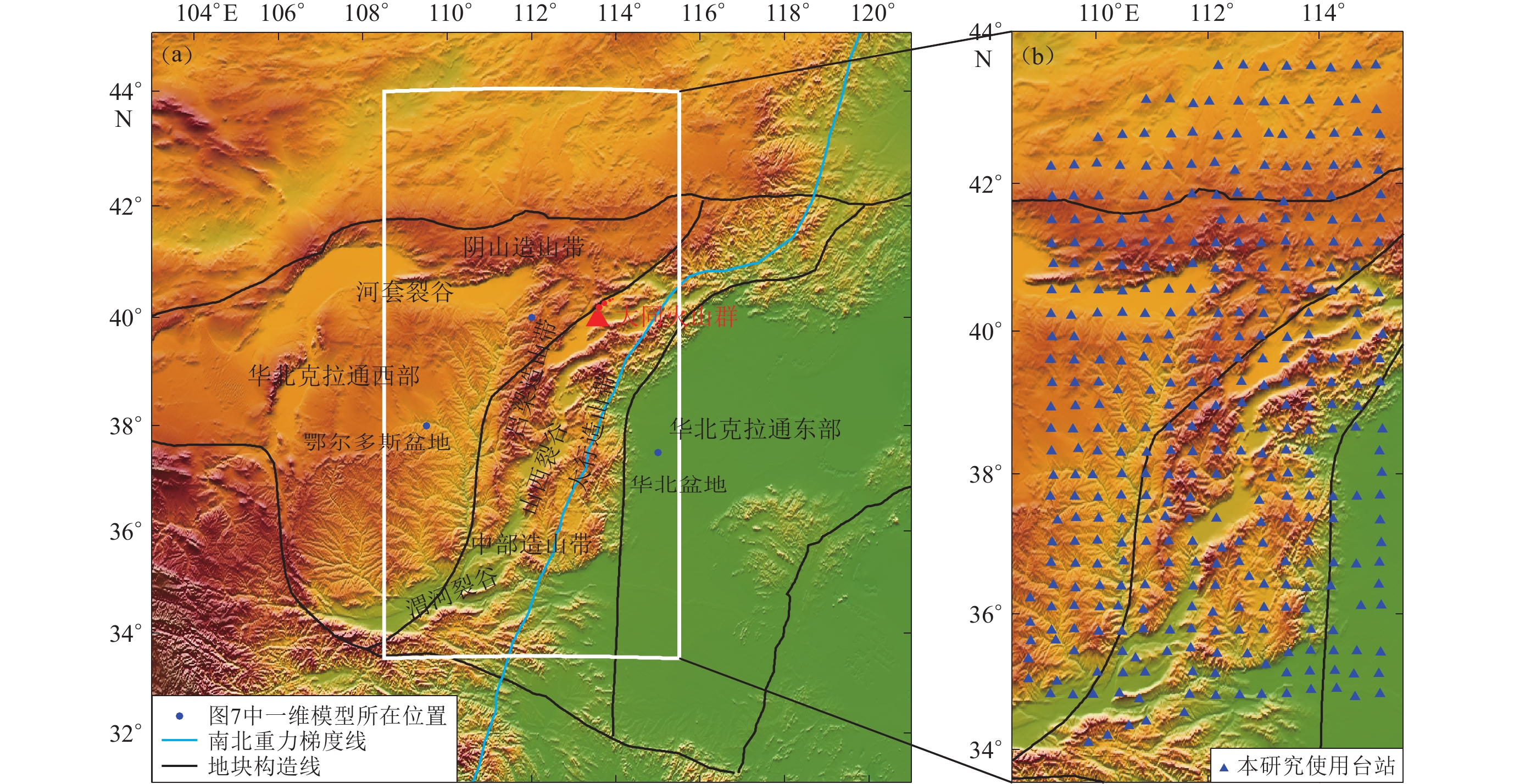
中国地震科学探测台阵数据中心. 2011. 中国地震科学探测台阵波形数据: 喜马拉雅计划[DB/OL]. [2020-06-12]. http://www.chinarraydmc.cn/map/station/distribution. China Seismic Array Data Management Center. 2011. China Seismic Array waveform data of Himalaya project[DB/OL]. [2020-06-12]. http://www.chinarraydmc.cn/map/station/distribution (in Chinese).
钟世军,吴建平,房立华,王未来,范莉苹,王怀富. 2017. 青藏高原东北缘及周边地区基于程函方程的面波层析成像[J]. 地球物理学报,60(6):2304–2314. doi: 10.6038/cjg20170622 Zhong S J,Wu J P,Fang L H,Wang W L,Fan L P,Wang H F. 2017. Surface wave Eikonal tomography in and around the northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,60(6):2304–2314 (in Chinese).
朱日祥,郑天愉. 2009. 华北克拉通破坏机制与古元古代板块构造体系[J]. 科学通报,54(14):1950–1961. Zhu R X,Zheng T Y. 2009. Destruction geodynamics of the North China Craton and its Paleoproterozoic plate tectonics[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,54(19):3354–3366.
朱日祥,陈凌,吴福元,刘俊来. 2011. 华北克拉通破坏的时间、范围与机制[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,41(5):583–592. Zhu R X,Chen L,Wu F Y,Liu J L. 2011. Timing,scale and mechanism of the destruction of the North China Craton[J]. Science China Earth Sciences,54(6):789–797.
朱日祥,徐义刚,朱光,张宏福,夏群科,郑天愉. 2012. 华北克拉通破坏[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,42(8):1135–1159. Zhu R X,Xu Y G,Zhu G,Zhang H F,Xia Q K,Zheng T Y. 2012. Destruction of the North China Craton[J]. Science China Earth Sciences,55(10):1565–1587.
Afonso J C,Fullea J,Griffin W L,Yang Y,Jones A G,Connolly J A D,O’Reilly S Y. 2013. 3-D multiobservable probabilistic inversion for the compositional and thermal structure of the lithosphere and upper mantle. I:A priori petrological information and geophysical observables[J]. J Geophys Res:Solid Earth,118(5):2586–2617. doi: 10.1002/jgrb.50124
Ai S X,Zheng Y,He L P,Song M Q. 2019. Joint inversion of ambient noise and earthquake data in the Trans-North China Orogen:On-going lithospheric modification and its impact on the Cenozoic continental rifting[J]. Tectonophysics,763:73–85. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2019.05.003
An M J,Shi Y L. 2006. Lithospheric thickness of the Chinese continent[J]. Phys Earth Planet Inter,159(3/4):257–266.
Bao X W,Song X D,Xu M J,Wang L S,Sun X X,Mi N,Yu D Y,Li H. 2013. Crust and upper mantle structure of the North China Craton and the NE Tibetan Plateau and its tectonic implications[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett,369/370:129–137. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2013.03.015
Barmin M P,Ritzwoller M H,Levshin A L. 2001. A fast and reliable method for surface wave tomography[J]. Pure Appl Geophys,158(8):1351–1375. doi: 10.1007/PL00001225
Bensen G D,Ritzwoller M H,Barmin M P,Levshin A L,Lin F,Moschetti M P,Shapiro N M,Yang Y. 2007. Processing seismic ambient noise data to obtain reliable broad-band surface wave dispersion measurements[J]. Geophys J Int,169(3):1239–1260. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2007.03374.x
Bodin T,Sambridge M,Tkalčić H,Arroucau P,Gallagher K,Rawlinson N. 2012. Transdimensional inversion of receiver functions and surface wave dispersion[J]. J Geophys Res:Solid Earth,117(B2):B02301.
Chen L,Cheng C,Wei Z G. 2009. Seismic evidence for significant lateral variations in lithospheric thickness beneath the central and western North China Craton[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett,286(1/2):171–183.
Chen L. 2010. Concordant structural variations from the surface to the base of the upper mantle in the North China Craton and its tectonic implications[J]. Lithos,120(1/2):96–115.
Dong H,Wei W B,Ye G F,Jin S,Jones A G,Jing J N,Zhang L T,Xie C L,Zhang F,Wang H. 2014. Three-dimensional electrical structure of the crust and upper mantle in Ordos block and adjacent area:Evidence of regional lithospheric modification[J]. Geochem Geophys Geosyst,15(6):2414–2425. doi: 10.1002/2014GC005270
Dziewonski A M,Anderson D L. 1981. Preliminary reference Earth model[J]. Phys Earth Planet Inter,25(4):297–356. doi: 10.1016/0031-9201(81)90046-7
Fadel I,Paulssen H,van der Meijde M,Kwadiba M,Ntibinyane O,Nyblade A,Durrheim R. 2020. Crustal and upper mantle shear wave velocity structure of Botswana:The 3 April 2017 central Botswana earthquake linked to the East African Rift System[J]. Geophys Res Lett,47(4):e2019GL085598.
Fan W M,Zhang H F,Baker J,Jarvis K E,Mason P R D,Menzies M A. 2000. On and off the North China Craton:Where is the Archaean keel?[J]. J Petrol,41(7):933–950. doi: 10.1093/petrology/41.7.933
Fukao Y,Obayashi M,Inoue H,Nenbai M. 1992. Subducting slabs stagnant in the mantle transition zone[J]. J Geophys Res:Solid Earth,97(B4):4809–4822. doi: 10.1029/91JB02749
Goes S,Govers R,Vacher P. 2000. Shallow mantle temperatures under Europe from P and S wave tomography[J]. J Geophys Res:Solid Earth,105(B5):11153–11169. doi: 10.1029/1999JB900300
Griffin W L, Zhang A D, O’Reilly S Y, Ryan C G. 1998. Phanerozoic evolution of the lithosphere beneath the Sino-Korean Craton[G]//Mantle Dynamics and Plate Interactions in East Asia.Washington D C: American Geophysical Union: 107–126.
Guo Z,Chen Y J. 2017. Mountain building at northeastern boundary of Tibetan Plateau and craton reworking at Ordos block from joint inversion of ambient noise tomography and receiver functions[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett,463:232–242. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2017.01.026
Huang J L,Zhao D P. 2006. High-resolution mantle tomography of China and surrounding regions[J]. J Geophys Res:Solid Earth,111(B9):B09305.
Huang Z X,Li H Y,Zheng Y J,Peng Y J. 2009. The lithosphere of North China Craton from surface wave tomography[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett,288(1/2):164–173.
Jiang M M,Ai Y S,Chen L,Yang Y J. 2013. Local modification of the lithosphere beneath the central and western North China Craton:3-D constraints from Rayleigh wave tomography[J]. Gondwana Res,24(3/4):849–864.
Jin G,Gaherty J B. 2015. Surface wave phase-velocity tomography based on multichannel cross-correlation[J]. Geophys J Int,201(3):1383–1398. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggv079
Laske G, Masters G, Ma Z T, Pasyanos M. 2013. Update on CRUST1.0: A 1-degree global model of Earth’s crust[C]//EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts. Vienna, Austria: EGU: 2658.
Lei J S,Zhao D P. 2006. Global P-wave tomography:On the effect of various mantle and core phases[J]. Phys Earth Planet Inter,154(1):44–69. doi: 10.1016/j.pepi.2005.09.001
Lei J S. 2012. Upper-mantle tomography and dynamics beneath the North China Craton[J]. J Geophys Res:Solid Earth,117(B6):B06313.
Levshin A L,Ritzwoller M H. 2001. Automated detection,extraction,and measurement of regional surface waves[J]. Pure Appl Geophys,158(8):1531–1545. doi: 10.1007/PL00001233
Li G L,Niu F L,Yang Y J,Xie J. 2018. An investigation of time-frequency domain phase-weighted stacking and its application to phase-velocity extraction from ambient noise’s empirical Green’s functions[J]. Geophys J Int,212(2):1143–1156. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggx448
Li G L,Niu F L,Yang Y J,Tao K. 2019. Joint inversion of Rayleigh wave phase velocity,particle motion,and teleseismic body wave data for sedimentary structures[J]. Geophys Res Lett,46(12):6469–6478. doi: 10.1029/2019GL082746
Li S L,Guo Z,Chen Y J,Yang Y J,Huang Q H. 2018. Lithospheric structure of the Northern Ordos from ambient noise and teleseismic surface wave tomography[J]. J Geophys Res:Solid Earth,123(8):6940–6957.
Lin F C,Ritzwoller M H,Snieder R. 2009. Eikonal tomography:Surface wave tomography by phase front tracking across a regional broad-band seismic array[J]. Geophys J Int,177(3):1091–1110. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2009.04105.x
Menzies M A,Fan W M,Zhang M. 1993. Palaeozoic and Cenozoic lithoprobes and the loss of >120 km of Archaean lithosphere,Sino-Korean Craton,China[J]. Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ,76(1):71–81. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1993.076.01.04
Menzies M,Xu Y G,Zhang H F,Fan W M. 2007. Integration of geology,geophysics and geochemistry:A key to understanding the North China Craton[J]. Lithos,96(1/2):1–21.
Shen W S,Ritzwoller M H,Schulte-Pelkum V,Lin F C. 2013. Joint inversion of surface wave dispersion and receiver functions:A Bayesian Monte-Carlo approach[J]. Geophys J Int,192(2):807–836. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggs050
Tang Y C,Chen Y J,Zhou S Y,Ning J Y,Ding Z F. 2013. Lithosphere structure and thickness beneath the North China Craton from joint inversion of ambient noise and surface wave tomography[J]. J Geophys Res:Solid Earth,118(5):2333–2346. doi: 10.1002/jgrb.50191
Wang W L,Wu J P,Fang L H,Lai G J,Cai Y. 2017. Sedimentary and crustal thicknesses and Poisson’s ratios for the NE Tibetan Plateau and its adjacent regions based on dense seismic arrays[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett,462:76–85. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2016.12.040
Xu X W,Ma X Y. 1992. Geodynamics of the Shanxi rift system,China[J]. Tectonophysics,208(1/2/3):325–340.
Xu Y G,Ma J L,Frey F A,Feigenson M D,Liu J F. 2005. Role of lithosphere-asthenosphere interaction in the genesis of Quaternary alkali and tholeiitic basalts from Datong,western North China Craton[J]. Chem Geol,224(4):247–271. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2005.08.004
Yin Y T,Jin S,Wei W B,Ye G F,Jing J E,Zhang L T,Dong H,Xie C L,Liang H D. 2017. Lithospheric rheological heterogeneity across an intraplate rift basin (Linfen Basin,North China) constrained from magnetotelluric data:Implications for seismicity and rift evolution[J]. Tectonophysics,717:1–15. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2017.07.014
Zhang Y Q,Mercier J L,Vergély P. 1998. Extension in the graben systems around the Ordos (China),and its contribution to the extrusion tectonics of South China with respect to Gobi-Mongolia[J]. Tectonophysics,285(1/2):41–75.
Zhao D P. 2004. Global tomographic images of mantle plumes and subducting slabs:Insight into deep Earth dynamics[J]. Phys Earth Planet Inter,146(1/2):3–34.
Zhao G C,Sun M,Wilde S A,Li S Z. 2005. Late Archean to Paleoproterozoic evolution of the North China Craton:Key issues revisited[J]. Precambrian Res,136(2):177–202. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2004.10.002
Zhu R X,Chen L,Wu F Y,Liu J L. 2011. Timing,scale and mechanism of the destruction of the North China Craton[J]. Science China Earth Science,54(6):789–797. doi: 10.1007/s11430-011-4203-4
Zhu R X,Xu Y G,Zhu G,Zhang H F,Xia Q K,Zheng T Y. 2012. Destruction of the North China Craton[J]. Science China Earth Science,55(10):1565–1587. doi: 10.1007/s11430-012-4516-y




 下载:
下载: