Characteristics of subway stray current in geoelectrical resistivity observation
-
摘要: 在对地铁杂散电流产生机理的讨论的基础上,定量计算了地铁运行时杂散电流在地电阻率观测中所呈现的影响幅度,结果表明地铁杂散电流传播范围可以达到几十甚至上百千米。通过对城市周边的北京通州、天津青光、宝坻、塘沽、江苏江宁和辽宁新城子等六个地电阻率观测台站观测到的该类信号的研究,分析了其幅值、主要频率范围以及空间分布特征,结果表明该类信号的幅值从几mV至几十mV不等,与源距关系密切,周期主要集中在50—200 s范围内,在分析地震异常前兆信号时该类信号可使信噪比降低10—30 dB左右,其相对方差最大超出标准20倍左右。根据地铁运行时杂散电流传播的特征,本文提出了几种压制该类信号的措施,为识别地震前地电阻率异常信息及排除噪声提供依据。Abstract: The geoelectrical resistivity observation is one of the most important methods in the study of earthquake precursor, and the characteristics of the stray current during subway operation in the geoelectrical resistivity observation are useful for analyzing the geoelectric observation data and the anomaly variation before earthquakes. Based on the study on the generation mechanism, the quantitatively results of the influence of stray current on geoelectrical resistivity observation were given in this paper. The result shows that the effect distance can reach dozens or even a hundred kilometers. Through monitoring the stray current in some geoelectrical resistivity observation stations around cities, such as Tongzhou station in Beijing, Qingguang, Baodi and Tanggu stations in Tianjin, Jiangning station in Jiangsu and Xinchengzi station in Liaoning, the amplitude and frequency range of the stray current signal as well as its spatial distribution characteristics were analyzed. It shows that the amplitude of the signal ranges from several to tens millivolt, and the period range is mainly from 50 s to 200 s. Due to the influence of stray current, the signal-to-noise ratio is decreased by 10 to 30 dB, and the accuracy of the observation data is more than 20 times worse than the specified requirement. According to the characteristics of the stray current propagation, several methods which can be used to suppress the signal were proposed in this paper, and it will provide a foundation for the identification of anomaly information from the observation data and anti-interference technology study.
-
地震短临预报是世界难题,而有效的短临预报会在防震减灾中发挥巨大作用。1975年海城MS7.3大地震的成功预报,避免了十几万人的生命和财产损失。我国科学家在近二十年对国内发生的二十多次地震作出了比较成功的短临预报(张晓东等,2011;马钦忠,2014),这其中地震电磁学也起到了重要作用,而地电阻率观测方法是地震电磁学研究中一个很重要的方法。我国的地震地电阻率观测采用多方向地表四极对称装置的直流观测方法,供电极距一般在1 km左右,其观测目的是研究与地震孕育和发生相关的地电阻率变化。在长期的观测实践中,地电阻率方法同样发挥了重要作用,先后记录到了地电阻率台网内部及其周边地区(300 km左右范围内)几十个中强以上地震异常,特别是记录到了几乎所有的MS7.0以上强震的异常信息,包括1976年7月28日河北唐山MS7.8地震、1988年11月6日云南澜沧—耿马MS7.6地震、2008年5月12日四川汶川MS8.0地震等。这些震例的研究结果表明,地电阻率在震前的变化具有明显特点,表现为:在大震发生前,近震中台站的地电阻率趋势下降,下降幅度约为百分之几到百分之十几,异常分布范围为200—300 km,持续时间2—3年;震后,趋势下降现象发生转折,主要表现为缓慢回升、恢复或者下降趋势停止,具有明显的可重复性(钱复业等,1982;桂燮泰等,1989;钱家栋,1993;杜学彬等,2006;钱家栋等,2013;马钦忠,2014;Lu et al,2016)。
为了有效地监测与地震孕震和发生过程相关的地电阻率异常变化,按照地震地电阻率观测规范要求(中国地震局,2009),其观测数据日均值精度(相对方差)应优于0.3%。这就要求在长期观测过程中,不仅要求观测系统长期稳定性好,观测精度高,同时对测区环境也有着较高的要求。我国现有地电阻率观测台站82个,这些台站在建设时大多选择远离城区且周边环境对观测的影响很小的位置,但随着经济的发展,各种环境因素的变化对地电阻率观测造成了一定的影响,导致观测精度降低,这其中以地铁、轻轨等城市轨道交通(以下统称为地铁)运行造成的影响最为严重。因此,正确认识地铁运行时入地电流(即地铁杂散电流)在地电阻率观测中的响应特征就显得十分重要。
地铁运行的动力系统是直流供电,在运行过程中对地有较大的泄露漏电,而地电阻率测量的也是直流电压信号,因此就目前的地电阻率观测仪器和观测方式来说,很难克服杂散电流的影响,造成地电阻率观测数据精度明显降低。地铁杂散电流信号幅度大,传播距离远,可以达到几十甚至上百千米,严重影响了城市周边的地电阻率观测(张世中等,2013;王兰炜等,2019)。
对于地铁杂散电流干扰的研究,大部分文献集中于杂散电流对地下管线腐蚀的研究(王猛,2005,刘文权,2014;董亮等,2021),但是在我国地震前兆观测中,结合现有地电阻率观测方法和仪器,讨论杂散电流特征以及如何对地电阻率观测造成影响的研究,文献则几乎未见。为此,本文拟在讨论地铁运行对地电阻率观测影响机理的基础上,通过对北京通州、天津青光、塘沽、宝坻、江苏江宁和辽宁新城子等地电阻率观测台站周边地铁杂散电流影响的实际测试,分析地铁杂散电流信号的幅度、信号频率范围等特征,研究其对地电阻率观测的影响程度,并提出了几种压制地铁杂散电流影响的措施,以期为地电阻率观测中能够准确识别和提取震前异常信息以及相应的抗干扰技术研究奠定基础。
1. 地铁杂散电流的产生及影响
1.1 产生机理
城市轨道交通车包括地铁、轻轨都以直流电力牵引系统为动力,列车通过接触网(轨)接受由变电所提供的电流,通过走行轨回流,这样列车与牵引变电所间形成闭合的电气连接回路。图1给出了变电所供电、列车单车运行时的电流示意图及简化等效电路图(王猛,2005;王崇林等,2007;刘文权,2014)。
如图1所示,在地铁实际运行中,地铁列车通过架空接触网接受来自变电所的电流I1,由于各种因素的限制,走行轨不可能完全绝缘于道床结构,不可避免地向道床泄漏电流,这样就导致少部分电流是通过大地回流的方式返回牵引变电所的,称为杂散电流,用IS表示。通过走行轨回流的电流为I2。杂散电流IS可以按照基尔霍夫电流定律计算得到,即
$$ {I}_{{\rm{S}}}={I}_{1}\frac{{R}_{{\rm{N}}}}{{R}_{{\rm{L}}}+{R}_{{\rm{S}}}+{R}_{{\rm{N}}}} \text{,} $$ (1) 式中,RN为负导体(钢轨)的电阻,RP为正导体(架空接触线)的电阻,RL为负载端的对地电阻,RS为电站端的对地电阻。从式(1)可以看出,杂散电流的大小与走行轨对地的绝缘电阻有关,绝缘性能越好,杂散电流越小,绝缘性能越差,杂散电流就越大。虽然在地铁建设中,走行轨与道床之间采取了绝缘措施,但是随着地铁运营时间的推移,受到的如潮湿、污染等环境因素的影响,使地铁车站以及区间隧道中的钢轨对地绝缘性能降低或先期防护措施失效,故而较大的杂散电流泄漏到大地中。实际上,地铁供电系统是一个非常复杂的系统,在同一条线路的某个时刻,会有多辆列车运行,也会有多个牵引变电所向运行的列车供电,杂散电流大小受多种因素的影响,其产生的机理和模型更为复杂(王猛,2005;王崇林等,2007;梅进武,林国松,2017;朱峰等,2018;澹台乐琰等,2020),但正是这种流入大地的杂散电流影响了地电阻率的正常观测。
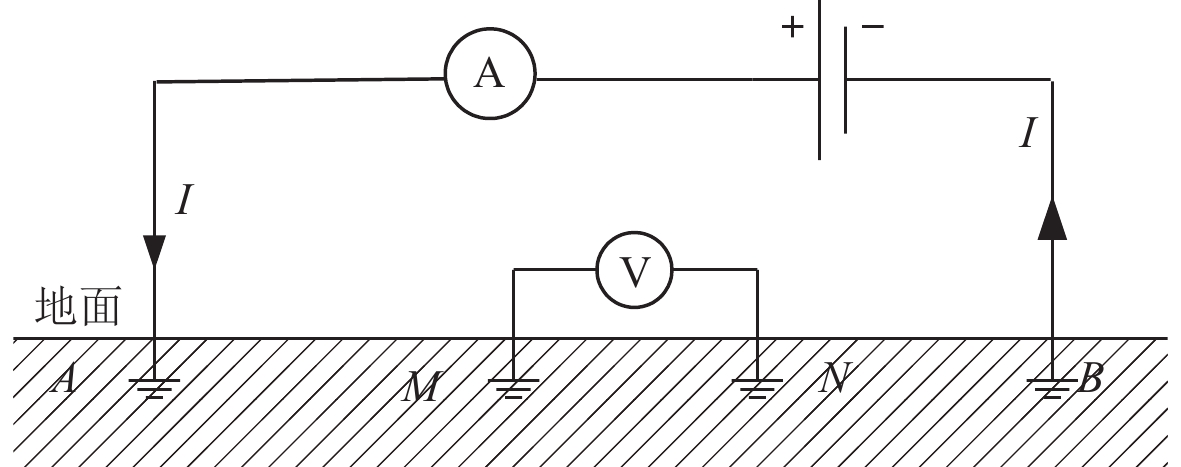
图2给出了地电阻率测量原理示意图。图中A,M,N,B是埋设于地表下2—3 m的四个电极,其中A,B是供电极,M,N是测量极。
在地电阻率测量时,通过电极A,B向地下介质供入一定强度的电流I,并测量M,N之间的人工供电电位差ΔV,利用式(2)计算得到地电阻率ρ,即
$$ \rho =K\frac{\Delta V}{I} \text{,} $$ (2) 式中K为装置系数,仅与四个观测电极的几何位置相关。在四极对称装置下,装置系数K为
$$ K=\frac{\pi d_{AM} d_{AN}}{d_{MN}} \text{,} $$ (3) 式中,dAM,dAN,dMN为相应电极间的距离。
在地电阻率实际测量中,对人工供电电流I的测量是通过对标准电阻的电压测量得到,不受外界因素的影响。因此人工电位差ΔV的测量误差也就是地电阻率的测量误差。对人工供电电位差ΔV的测量采用多次测量取均值的方式,一般为5—10次。
当地铁列车运行时,产生的杂散电流流入大地后,会造成测量过程中测量电极间附加的电位波动。假设单次测量的附加电位波动为VDi,对于多次测量,由其引起的人工电位差测量误差e为
$$ e=\frac{1}{N}\sum\limits _{i=1}^{N}{V}_{{\rm{D}}i}\qquad i=\mathrm{1, 2}, 3\text{,} \cdots \text{,} N \text{,} $$ (4) 式中:$ N $为测量次数;VDi为附加电位波动,与地铁运行有关,在各次测量时间内随机变化,且均值不为0,从而导致人工电位差ΔV的波动,使测量随机误差变大。
我国地铁采用DC750V或DC1500V直流供电系统,北京地铁采用DC750V供电系统,实际的测试结果表明,地铁在启动和运行时,泄露入地的杂散电流值一般要大于100 A。而上海地铁、广州地铁、深圳地铁均采用额定电压为DC1500V的直流供电系统,额定牵引电流可高达3000 A,按5%的杂散电流泄漏计算,泄露入地的杂散电流可高达150 A (林江等,2002),由于其信号幅度大,传播范围广,因此严重影响了地铁周边的地电阻率台站的正常观测。
1.2 影响范围
地电阻率测量时,假设人工供电电流为$ {I}_{1} $,地下介质电阻率为ρ1,根据式(2)和式(4),地铁杂散电流造成的地电阻率测量的相对误差δ则为
$$ \delta =\frac{e}{\Delta V}=\frac{K {V}_{{\rm{D}}}}{{I}_{1} {\rho }_{1}}{\text{×}} 100\mathrm{\%} {\text{.}} $$ (5) 地铁漏电点可以看作一个点电源。假设地铁到台站之间的地表介质均匀,电阻率为ρ2,则入地的杂散电流IS在距离地铁r1和r2处的两个测量极M,N之间产生的电位差为(李金铭,2005;刘国兴,2005;胡先茂,2011)
$$ {V}_{{\rm{D}}}=\frac{{I}_{{\rm{S}}} {\rho }_{2}}{2\pi }\left(\frac{1}{{r}_{1}}-\frac{1}{{r}_{2}}\right) {\text{.}} $$ (6) 将式(6)带入式(5),可得地铁杂散电流引起的电阻率测量相对误差为
$$ \delta =\frac{K}{2\pi } \frac{{I}_{{\rm{S}}}}{{I}_{1}} \frac{{\rho }_{2}}{{\rho }_{1}} \left(\frac{1}{{r}_{1}}-\frac{1}{{r}_{2}}\right){\text{×}} 100{\text{%}} ,$$ (7) 令${P}_{1}=\dfrac{{I}_{{\rm{S}}}}{{I}_{1}}$,${P}_{2}=\dfrac{{\rho }_{2}}{{\rho }_{1}}$,则有
$$ \delta =\frac{K}{2\pi } {P}_{1} {P}_{2} \frac{{r}_{2}-{r}_{1}}{{r}_{1} {r}_{2}}{\text{×}} 100{\text{%}} {\text{.}} $$ (8) 对于四极对称装置,在装置确定后,测量极距dMN与供电极距dAB之间的比例就是确定的,有$d_{AB}=C{d_{MN}}$,C为一常数。根据式(3)可得$ K={\pi ( {C}^{2}-1 ) d_{AB}}/{4C} $,带入式(8)可得
$$ \delta =\frac{{C}^{2}-1}{8C} d_{AB} {P}_{1} {P}_{2} \frac{{r}_{2}-{r}_{1}}{{r}_{1} {r}_{2}}{\text{×}} 100{\text{%}} {\text{.}} $$ (9) 实际上,由于观测台站距离地铁至少几千米,也就是r1和r2均至少为几千米,而测量极距dMN只有300—500 m,因此r1和r2远远大于r2-r1,且r2≈r1,dMN≈r2-r1。假设r2≈r1=r,则式(9)变为
$$ \delta \approx \frac{{C}^{2}-1}{8{C}^{2}} {d_{AB}^{2}} \frac{{P}_{1} {P}_{2}}{{r}^{2}}{\text{×}} 100{\text{%}} {\text{.}} $$ (10) 由式(10)可见,当供电极距与测量极距的比例为常数C时,地铁杂散电流对地电阻率观测影响大小与地铁距台站的距离、供电极距、地铁杂散电流IS与人工供电电流I1的比值P1以及杂散电流传播路径上的地表土壤电阻率与测区介质电阻率的比值P2等因素有关。其影响与台站至地铁的距离平方成反比,距离越远,影响越小;与供电极距平方成正比,供电极距越大,影响越大;与P1和P2成正比,P1和P2越大,影响越大。实际上,P1代表了地电阻率测量时噪声与信号的比值,噪声越大,P1越大,对观测结果的影响越大。在观测台站位置确定后,P2是一个确定值。
在现有台站的观测中,C的取值范围为3—5之间,也就是式(10)中第一项的变化在0.11—0.12之间,可见C的变化对测量结果的影响很小,这也就意味着当供电极距确定后,改变测量极距对观测结果影响不大。
表1给出了四极对称观测装置在P1=75 (人工供电电流I1=2 A,地铁杂散电流IS=150 A),P2=1,C=3.33,测区至地铁不同距离、不同供电极距条件下,地铁杂散电流对观测的影响。
表 1 地铁杂散电流导致的地电阻率测量相对误差δ随距离的变化(P1=75,P2=1,C=3.33)Table 1. The influence of stray current on geoelectrical resistivity varies with distance (P1=75,P2=1,C=3.33)测区至地铁
距离r1/kmδ dAB=1000 m dAB=500 m dAB=200 m 10 8.530% 2.132% 0.341% 20 2.132% 0.533% 0.085% 30 0.948% 0.237% 0.038% 40 0.533% 0.133% 0.021% 50 0.341% 0.085% 0.014% 60 0.237% 0.059% 0.009% 70 0.174% 0.044% 0.007% 80 0.133% 0.033% 0.005% 90 0.105% 0.026% 0.004% 100 0.085% 0.021% 0.003% 根据地震监测的要求,地电阻率观测数据的相对方差应小于0.3%。从表1可以看出,在P1=75,P2=1,C=3.33的条件下,当供电极距dAB=1000 m时,要求台站距离地铁达到60 km以上,相对方差才可以降到0.3%以内,而要使相对方差降低到0.1%的范围内,则距离至少应达到90—100 km左右。而在dAB=500 m和dAB=200 m时,要求台站与地铁距离分别为30 km和15 km左右。
以上的分析是基于单车运行并假设介质均匀的条件下,给出的地铁对观测数据影响的理论结果。实际上,由于地铁线路至台站之间地质条件的复杂性,在一定范围内对杂散电流的分布有较大影响(李雷等,2019)。同时正如前文所述,地铁供电系统是一个非常复杂的系统,在同一条线路的某个时刻,会有多辆列车同时运行,也会有多个牵引变电所向运行的列车供电,再者由于各个城市地铁列车运行发车间隔(密度)不同、各个列车运行方向不同,入地的杂散电流大小就会不同,对地电阻率观测的影响也就不同。因此,为了研究地电阻率观测中地铁杂散电流的特征,选择了几个不同的地电阻率台站,对地铁杂散电流进行了实际测试和分析。
2. 地铁杂散电流实际测试与分析
2.1 地铁杂散电流信号幅度
为了研究地铁杂散电流的特征以及对地电阻率观测造成的实际影响,在北京通州台、天津青光台、塘沽台、宝坻台、江苏江宁台和辽宁新城子台等地电阻率观测台对地铁杂散电流信号进行了24小时左右的连续测试。测试时直接测量电极M与N之间的电位差变化情况,采样率为10 Hz。表2是各个台站距地铁线路的最近距离和地电阻率观测装置情况。
表 2 各个台站观测装置及与地铁最近距离Table 2. The configuration in geoelectrical resistivity observation station and its distance from the subway序号 台站名称 与地铁最近距离/km 观测装置 测道方向 供电极距/m 测量极距/m 装置系数/m 1 北京通州台 11.0 南北、东西 1 760 320 7 351 2 天津青光台 7.6 南北、东西 1 000 316 2 237 3 天津塘沽台 城区线:40.0
九号线:7.0南北、东西
南北、东西南北:1 500
东西:1 000南北:500
东西:3003 141
2 3824 天津宝坻台 52.0 南北、东西 1 000 200 3 769 5 江苏江宁台 城区线:30.0
机场线:3.0南北、东西
南北、东西1 000
1 000300
3002 382
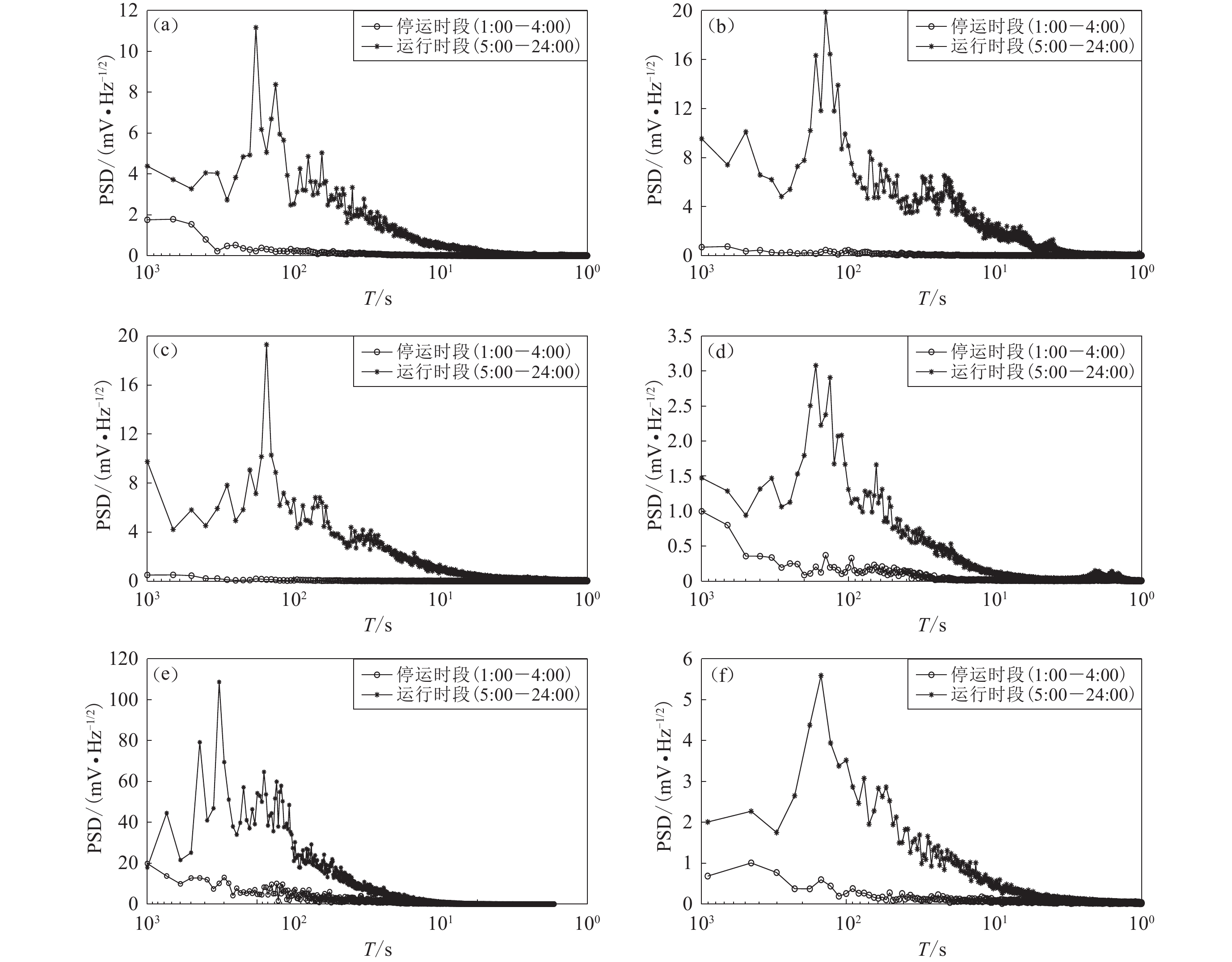
2 3826 辽宁新城子台 19.4 南北、东西 1 000 300 2 382 图3给出了文中六个台站实际记录的地铁杂散电流信号的时序图。从图3可以看出:在每天的0时至4时的地铁停运时段,只记录到各个台站的场地背景噪声信号,该信号幅度较小,变化比较平稳,幅度小于1 mV;在5时至24时的地铁运行时段,记录到明显的地铁杂散电流信号,其变化比较剧烈。这种现象在各个台站相同,但由于每个台站与地铁线路距离不同,杂散电流信号的幅度也不同。
![]() 图 3 各观测台南北(左)、东西(右)测道记录的地铁杂散电流信号(a) 北京通州台 (2014-04-21 13:00开始);(b) 天津青光台 (2014-05-16 16:00开始);(c) 天津塘沽台(2014-05-13 17:00开始);(d) 天津宝坻台 (2014-05-12 11:00开始)Figure 3. The stray current signals recorded from north-south (left) and east-west (right) channel at different observations(a) Tongzhou station in Beijing (from 13:00,April 21,2014);(b) Qingguang station in Tianjin (from 16:00,May 16,2014);(c) Tanggu station in Tianjin (from 17:00,May 13,2014);(d) Baodi station in Tianjin (from 11:00,May 12,2014)
图 3 各观测台南北(左)、东西(右)测道记录的地铁杂散电流信号(a) 北京通州台 (2014-04-21 13:00开始);(b) 天津青光台 (2014-05-16 16:00开始);(c) 天津塘沽台(2014-05-13 17:00开始);(d) 天津宝坻台 (2014-05-12 11:00开始)Figure 3. The stray current signals recorded from north-south (left) and east-west (right) channel at different observations(a) Tongzhou station in Beijing (from 13:00,April 21,2014);(b) Qingguang station in Tianjin (from 16:00,May 16,2014);(c) Tanggu station in Tianjin (from 17:00,May 13,2014);(d) Baodi station in Tianjin (from 11:00,May 12,2014)![]() 图 3 各观测台南北(左)、东西(右)测道记录的地铁杂散电流信号(e) 江苏江宁台 (2014-10-13 15:00开始);(f) 辽宁新城子台 (2014-07-30 17:00开始)Figure 3. The stray current signals recorded from north-south (left) and east-west (right) channe at different observations(e) Jiangning station in Jiangsu (from 15:00,October 13,2014);(f) Xinchengzi station in Liaoning (from 17:00,July 30,2014)
图 3 各观测台南北(左)、东西(右)测道记录的地铁杂散电流信号(e) 江苏江宁台 (2014-10-13 15:00开始);(f) 辽宁新城子台 (2014-07-30 17:00开始)Figure 3. The stray current signals recorded from north-south (left) and east-west (right) channe at different observations(e) Jiangning station in Jiangsu (from 15:00,October 13,2014);(f) Xinchengzi station in Liaoning (from 17:00,July 30,2014)从杂散电流信号的幅度来看:北京通州台南北、东西测道的幅度均大于3 mV;天津青光台南北、东西测道的幅度均大于6 mV;天津塘沽台南北、东西测道的幅度分别大于4 mV和2 mV;天津宝坻台南北、东西测道的幅度分别大于1 mV和0.5 mV;江苏江宁台南北、东西测道的幅度分别大于10 mV和30 mV;辽宁新城子台南北、东西测道的幅度分别大于2 mV和1 mV。由此可以看到,在不同地电阻率台站观测到的地铁杂散电流信号幅度不同,这不仅与当地地铁运行时入地杂散电流的大小有关,还与台站与地铁线路的距离有关。几个台站中,天津宝坻台距离地铁最远,信号幅度最小,江苏江宁台距离地铁最近,信号幅度最大。天津青光和宝坻台受天津城区多条地铁线路的影响,青光台由于距离地铁线路更近,信号幅度明显大于宝坻台。塘沽台距离轻轨9号线的距离约7 km,但是距离城区超过40 km,受城区地铁线路影响较小,其信号幅度比青光台略小。
2.2 地铁杂散电流信号周期
地铁杂散电流信号存在着明显的周期性变化,且其中含有多种周期成分,这主要是由于地铁运行的时间间隔以及杂散电流不稳定造成的(董亮等,2021)。为了确定地铁杂散电流信号的频率分布范围,利用离散傅里叶变换(discrete Fourier transformation,缩写为DFT)方法对测试数据进行了频谱分析。在进行频谱分析时,每个台站的测试数据按照地铁运行时段和停运时段分别进行分析,便于对场地固有背景噪声频谱和地铁杂散电流信号频谱进行对比。
对于各个台站的测试数据,以1小时的测试数据x(k)为一个数据段,按照式(11)计算其功率谱密度,即
$$ {\rm{PS}} {\rm{D}} ( K ) =\sqrt{\frac{{\left|X ( K ) \right|}^{2}}{N {f}_{{\rm{s}}}}} \text{,} $$ (11) 式中,X(K)为x(k)的傅里叶变换,N为一个数据段的总点数,fs为采样频率。
按照式(11)分别计算地铁停运时段和运行时段功率谱密度的平均值。图4给出了各个台站地铁停运时段与运行时段的功率谱密度的对比。
![]() 图 4 地铁运行时段和停运时段功率谱密度PSD对比(a) 北京通州台;(b) 天津青光台;(c) 天津塘沽台;(d) 天津宝坻台;(e) 江苏江宁台;(f) 辽宁新城子台Figure 4. Comparison of PSDs in subway operation with those in non-operation time period(a) Tongzhou station in Beijing;(b) Qingguang station in Tianjin;(c) Tanggu station in Tianjin;(d) Baodi station in Tianjin;(e) Jiangning station in Jiangsu;(f) Xinchengzi station in Liaoning
图 4 地铁运行时段和停运时段功率谱密度PSD对比(a) 北京通州台;(b) 天津青光台;(c) 天津塘沽台;(d) 天津宝坻台;(e) 江苏江宁台;(f) 辽宁新城子台Figure 4. Comparison of PSDs in subway operation with those in non-operation time period(a) Tongzhou station in Beijing;(b) Qingguang station in Tianjin;(c) Tanggu station in Tianjin;(d) Baodi station in Tianjin;(e) Jiangning station in Jiangsu;(f) Xinchengzi station in Liaoning从图4可以看出,在地铁运行时段,各个台站记录的地铁杂散电流信号功率谱形态基本一致,信号周期主要集中在50—300 s范围之间,但又略有不同,这主要与各城市地铁的运行密度有关,其中:北京通州台的信号周期范围主要集中在50—250 s之间,幅度最大的五个信号周期在100—200 s之间;天津青光台的信号周期范围主要集中在50—200 s之间,幅度最大的五个信号周期在120—180 s之间;天津宝坻台的信号周期范围主要集中在50—200 s之间,幅度最大的五个信号周期在120—180 s之间;天津塘沽台的信号周期范围主要集中在50—200 s之间,幅度最大的五个信号周期在120—200 s之间,特别是在150 s周期左右明显高出其它周期成分,这与塘沽台距离城区地铁较远,距离天津轻轨9号线仅有7 km,受这条线路的影响大有关,天津9号线的发车间隔为2—3 min,也与此周期吻合;江苏江宁台的信号周期主要集中在50—330 s之间,幅度最大的五个周期信号在70—333 s之间;辽宁新城子台的信号周期范围主要集中在50—220 s之间,幅度最大的五个周期在100—180 s之间。
将各个台站记录的地铁运行时段的功率按照50 s周期等间隔分段,分别计算50—100 s,100—150 s,150—200 s,200—250 s,250—300 s,300—350 s各个分段的功率在50—350 s周期范围内功率中所占比例,结果列于表3。
表 3 不同台站地铁运行时杂散电流不同周期功率占比Table 3. The distribution of power in different periods at different stations during subway operation周期范围/s 北京通州台 天津青光台 天津塘沽台 天津宝坻台 江苏江宁台 辽宁新城子台 50—100 10.17% 19.02% 8.74% 14.78% 33.34% 24.26% 100—150 29.56% 60.50% 11.66% 54.55% 6.77% 57.57% 150—200 56.87% 18.13% 76.35% 27.00% 9.13% 15.67% 200—250 2.38% 1.68% 0.85% 1.12% 39.28% 2.10% 250—300 0.17% 0.20% 1.81% 0.57% 0.77% 0.00% 300—350 0.83% 0.47% 0.59% 1.97% 10.71% 0.40% 从表3可以看出:各个台站记录到的杂散电流信号的主要周期分布范围基本一致,主要集中在50—200 s范围内;除江苏江宁台外,其它各台在这个周期范围内的功率占比达到了95%以上,200—350 s周期占比仅不到5%;而江苏江宁台在50—200 s和200—350 s周期段占比几乎相同,都达到50%左右,这是由于江宁台受南京城区和机场线共同影响,且机场线地铁运行密度较低。
3. 对地电阻率观测的影响及抑制
3.1 对测量信噪比的影响
从第二节的讨论可见,地铁运行主要影响了地电阻率观测中的人工电位差的测量,导致测量信噪比降低,测量方差变大。表4给出了不同台站地铁杂散电流信号幅度及其对测量信噪比的影响,其中,地铁停运时段和运行时段的背景噪声幅度是按照噪声的有效值(即噪声均方差)来计算。
表 4 六个台站记录的地铁杂散电流信号幅度及测量信噪比Table 4. The stray current signal amplitude and the SNR for the six stations台站名称 测道
方向人工电位差/mV 噪声幅度/mV 测量信噪比/dB 信噪比降低
/dB停运时段 运行时段 停运时段 运行时段 北京通州 南北 7 0.14 1.33 34.0 14.4 19.6 东西 7 0.17 1.16 32.3 15.6 16.7 天津青光 南北 9 0.09 4.96 40.0 5.2 34.8 东西 9 0.36 2.25 28.0 12.0 15.9 天津塘沽 南北 7 0.06 1.94 41.3 11.1 30.2 东西 10 0.40 0.79 28.0 22.0 5.9 天津宝坻 南北 41 0.07 0.48 55.4 38.6 16.7 东西 41 0.06 0.25 56.7 44.3 12.4 江苏江宁 南北 93 0.19 3.60 53.8 28.2 25.6 东西 73 0.56 13.86 42.3 14.4 27.9 辽宁新城子 南北 26 0.13 1.02 34.0 14.4 19.6 东西 26 0.10 0.46 32.3 15.6 16.7 从表4中可以看出,受地铁杂散电流的影响,各个台站的地电阻率测量信噪比降低了10—30 dB,其中天津塘沽台东西测道信噪比降低最小,为5.9 dB,天津青光台南北测道信噪比降低最多,达到34.8 dB。
3.2 对测量数据的影响
地铁运行时产生的杂散电流对地电阻率观测造成了严重的干扰,图5和图6分别给出了天津青光台和江苏江宁台受地铁杂散电流影响的地电阻率小时观测数据曲线。
从图5和图6可以明显看出:在地铁停运时段,两个台站的地电阻率观测数据稳定,测量均方差较小,观测数据精度符合规范要求;而在地铁运行时段,两个台站地电阻率测值出现较大幅度的跳动,观测数据精度也不符合规范要求。天津青光台南北方向地电阻率测值在地铁停运时段稳定在10.02 Ω•m左右,而在地铁运行时段则在9.85—10.25 Ω•m之间剧烈变化,相对变幅达到4%左右。由此可知青光台的测量均方差在地铁停运时段不到0.02 Ω•m,而在地铁运行时段最大达到0.6 Ω•m,增大了30倍左右,观测数据的相对均方差也超过了3%,最大达到5%左右。江苏江宁台东西方向地电阻率测值在地铁停运时段稳定在101.5 Ω•m左右,而在地铁运行时段便呈现为98—104 Ω•m之间的剧烈跳动变化,相对变幅达到6%左右,因此江宁台的测量均方差在地铁停运时段不到0.2 Ω•m,而在地铁运行时段最大为10 Ω•m,增大了50倍左右,观测数据的相对均方差也超过了5%,最大达到10%。
通过对几个台站连续30天观测数据的统计,分析了地铁运行时段的地电阻率最大变幅和测量的相对均方差,具体结果列于表5。此处地电阻率最大变幅指每天地电阻率最大测值与最小测值之差的30天平均值,相对均方差为每天小时测量值相对方差的30天平均值。
表 5 六个台站的地电阻率变幅与相对方差Table 5. The maximum variation and relative RMS value of geoelectrical resistivity for six stations台站 电阻率最大变幅/Ω·m 相对均方差 南北 东西 南北 东西 北京通州 1.83 3.99 0.65% 1.75% 天津青光 1.29 0.48 3.73% 1.72% 天津塘沽 1.72 0.59 7.57% 2.55% 天津宝坻 0.32 0.22 0.36% 0.20% 江苏江宁 1.50 5.22 1.13% 5.37% 辽宁新城子 0.09 0.05 0.15% 0.08% 从表5中可以看出,几个台站观测数据的相对均方差除辽宁新城子台外,均超出了观测规范的要求,最大为天津塘沽台南北测道,达到7.6%,其次为江苏江宁台东西测道,达到5.37%,天津青光台南北测道达到3.73%,北京通州台东西测道达到1.75%,超出了规范要求的5—20倍左右。
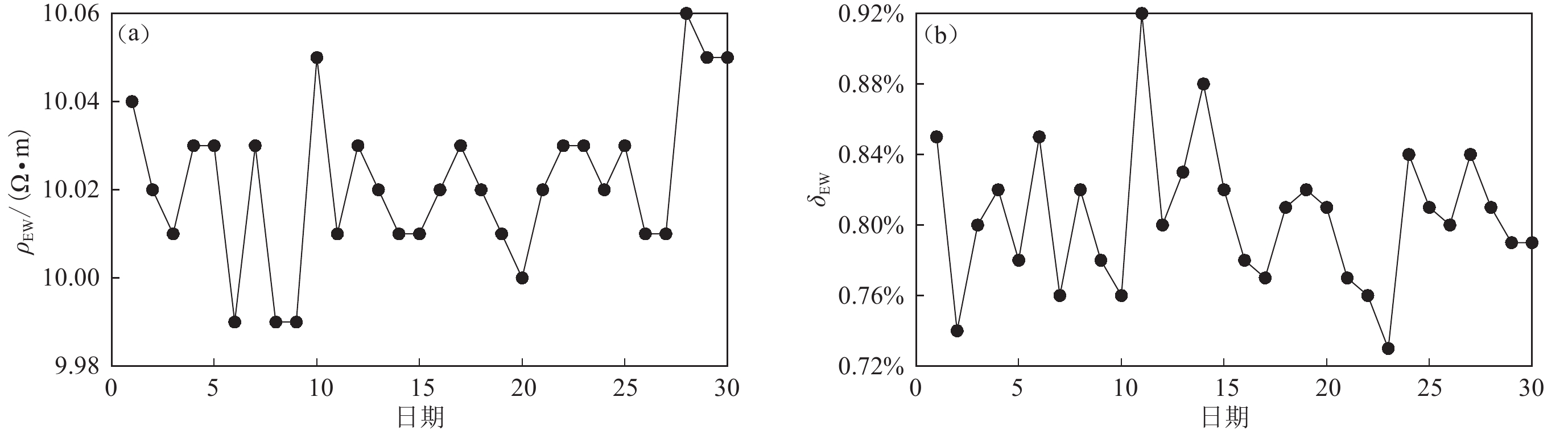
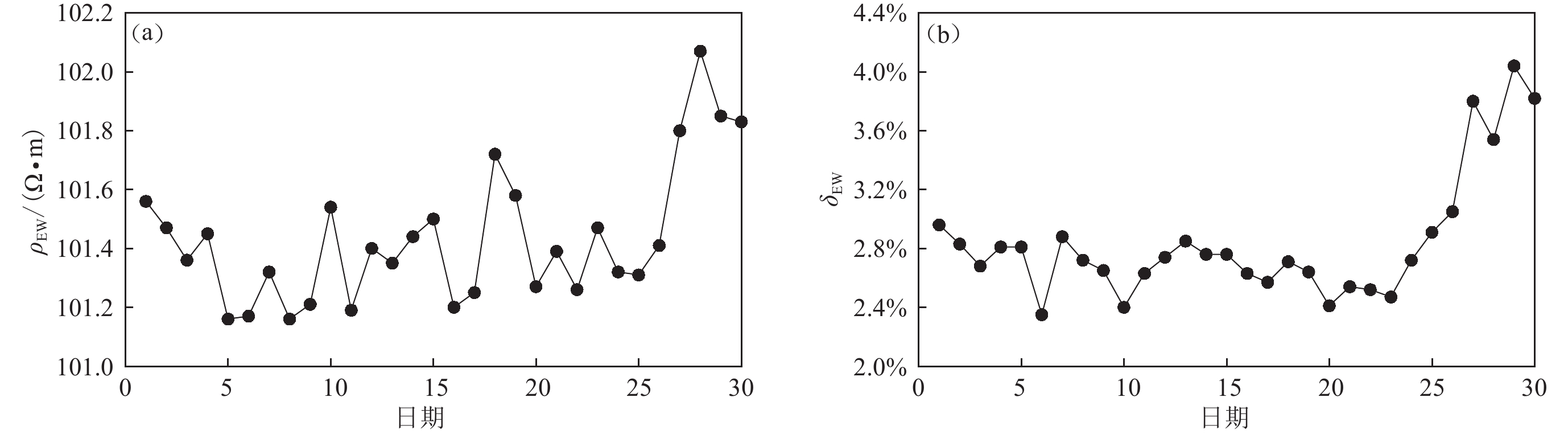
在分析地震地电阻率数据趋势性变化中,一般应用日均值较多。图7和图8分别以天津青光和江苏江宁台为例,给出了连续30天地电阻率日均值和相对方差的变化情况。
从图7和图8中可以看出,受地铁杂散电流的影响,地电阻率的日均值存在明显波动变化,相对均方差也远远超出观测规范要求的0.3%。在30天中,青光台地电阻率日均值最大波动幅度为0.07 Ω•m左右,相对变化0.7%左右,相对方差最大达到0.92%,最小为0.73%左右,超出规范要求2—3倍多;而江宁台地电阻率日均值最大波动幅度为0.9 Ω•m,相对变化0.9%左右,相对方差最大为4%,最小为2.4%,超出规范要求的8—10倍多。
可见受地铁杂散电流的影响,日均值数据精度也远远不能满足地震监测预测研究的要求,导致观测数据质量降低,观测数据不可用,给日常的数据分析、应用造成很大的困难。
3.3 地铁杂散电流信号的抑制措施
由于地铁杂散电流的影响,一些城市周边的电阻率观测台站选择搬迁重建,使台站远离城区以避免城市地铁杂散电流的干扰,例如江苏南京台、安徽合肥台、甘肃兰州台等。表6给出了在现有条件不变的情况下,要使地铁杂散电流影响$ \delta $小于0.3%,根据式(10)计算的以上几个台站理论上的最小避让距离。
表 6 六个台站的理论避让距离(P1=75,P2=1,δ=0.3%)Table 6. The minimum distance between observation station and subway for the six stations (P1=75,P2=1,δ=0.3%)台站名称 供电极距/m 测量极距/m C=dAB/dMN 最小避让距离/km 北京通州台 1 760 320 5.50 97 天津青光台 1 000 316 3.16 53 天津塘沽台 1 500 500 3.00 79 天津宝坻台 1 000 200 5.00 55 江苏江宁台 1 000 300 3.33 53 辽宁新城子 1 000 300 3.33 53 注:P1为地电阻率测量时噪声与信号之比,P2为地铁到台站电阻率与台站电阻率之比,δ为相对均方差。 由表6可以看出,在实际中由于地铁杂散电流影响范围较大,通常在供电极距为1 km的情况下,避让距离至少在55 km左右(天津宝坻台、江苏江宁台、天津青光台和辽宁新城子台),而对于较大的供电极距来说,避让距离则要达到80 km (天津塘沽台)至100 km左右(北京通州台)。但对于城市周边的地电阻率监测来说,搬迁已经不太现实,且即使搬迁,监测台站均远离城市几十甚至上百千米,不仅会由于台站距离较远使监测效能降低,而且也会造成已有观测数据的中断和不连续,这对需要较长时间连续观测数据作为变化背景的地电阻率观测来说极为不利。
实际上,从地铁杂散电流信号的特征可以看出,地铁杂散电流信号幅度大、传播距离远,且信号能量集中在特定的频率范围以内,这就为抑制地铁杂散电流的影响提供了相应的思路和方法,只要针对其信号特点,采取技术措施设法提高测量的信噪比,就可以有效地提高观测精度。具体来说,可以通过增大供电电流、增加测量时间,缩小观测极距以及采用交流观测等方法来压制地铁杂散电流的影响。
3.3.1 增大供电电流
在地铁杂散电流基本稳定的条件下,相应地在地电阻率台站观测到的信号幅度也就基本确定,这样就可以通过增大人工供电流的方式来提高测量的信噪比,降低地铁杂散电流对观测的影响。这种方法对于距离地铁较远,受地铁杂散电流影响不大的台站比较有效。例如天津宝坻台,由于距离地铁相对较远、即使在地铁运行时段,其观测的信噪比仍然达到40 dB左右,这样就可以通过增大人工供电电流,进一步提高测量信噪比,以有效改善观测数据精度。在其它条件不变时,供电电流每增大一倍,信噪比可以增加6 dB。但是受供电电源性能等因素的限制,这种方法对信噪比的提高是有限度的,而且对于杂散电流信号幅度较大的台站,该方法不适用。
3.3.2 增加测量次数
根据式(3),受地铁杂散电流影响,地电阻率观测误差与测量次数有关,只要增加测量次数,误差就会减小。同时地铁杂散电流信号是有一定周期范围的,对于周期信号来说,当测量时间刚好是杂散电流信号周期的整倍数时,所有采样点的平均值就是0。也就是说,在地电阻率测量时,只要测量的时间足够长,且是杂散电流信号周期的整数倍,或者即使测量时间不完全是杂散电流信号周期的整数倍,该信号在测量中的均值也会接近为0,对观测结果的影响也就会大大降低。实际上,由于地铁杂散电流的主要周期范围最大为300 s左右,为了达到抑制干扰的效果,每次测量至少应该需要五个周期左右,这也就意味着一个通道的测量时间至少需要25 min左右,三个通道就需要75 min,这在实际的观测中是不允许的。
3.3.3 缩小观测极距
从式(10)可以看出,地铁杂散电流的影响程度与供电极距相关,与供电极距的平方成正比。因此在供电极距与测量极距比例一定的条件下,只要缩小供电极距,就能有效地降低杂散电流的影响。在其它条件不变时,供电极距每缩小一倍,相对误差可减小到原来的1/4。目前,部分台站采用该方法进行观测试验,并取得了一定的效果,例如江宁台地表100 m供电极距观测,观测数据精度提高很多,基本在0.02 Ω•m以下。
但是随着供电极距的缩小,探测范围相应缩小,介质局部不均匀影响加大,不利于地震孕震信息的监测。为了有效监测地震,弥补极距缩小带来的探测范围的损失,可以将电极埋设到地下一定深度,但要特别注意电极埋深和观测极距的合理设计(聂永安等,2010;毛先进等,2014;王兰炜等,2015)。目前采用缩小极距的井下观测(一些台站将供电极距缩小到100 m左右)在干扰抑制方面取得了一定效果,观测数据精度也满足观测规范要求,但是由于缺乏震例的研究结果,其监测效能还有待进一步的检验。
3.3.4 地电阻率交流观测
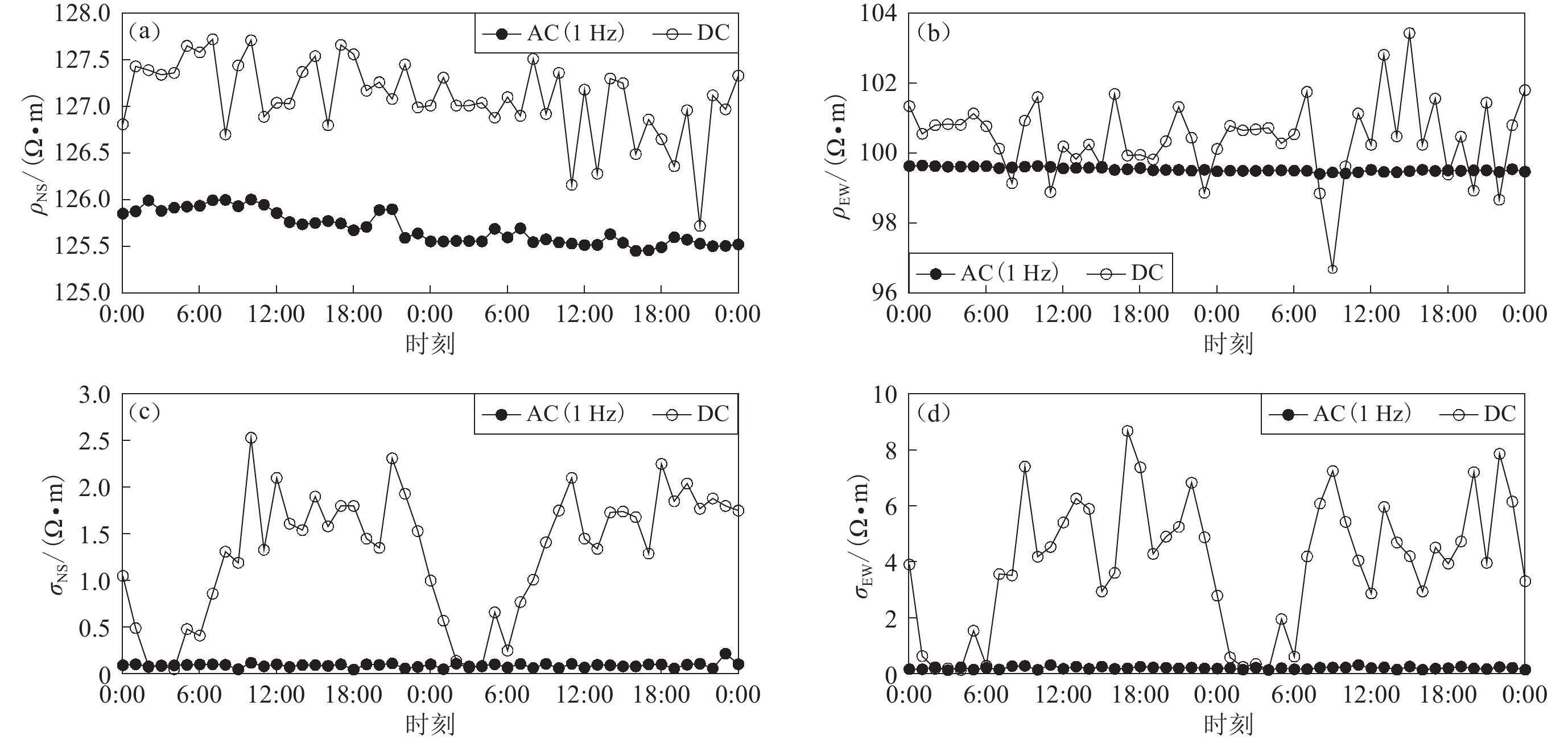
地电阻率交流观测方法的原理与现有的直流观测相同,仅仅是将人工供电信号由直流改为低频交流信号。由于采用特定频率的信号进行观测,可以选择避开地铁杂散电流信号频率范围,从而有效抑制其影响,大幅度提高了观测数据的精度(张宇等,2016)。图9给出了在同一观测装置下,江苏江宁台直流与交流观测结果的对比。
![]() 图 9 江苏江宁台地电阻率交、直流小时观测数据曲线(2016年9月29日至30日)(a) 南北方向地电阻率;(b) 东西方向地电阻率;(c) 南北方向测量均方差;(d) 东西方向测量均方差Figure 9. Comparison of AC & DC hourly geoelectrical resistivity observation data of Jiangning station(a) Geoelectrical resistivity of NS direction;(b) Geoelectrical resistivity of EW direction;(c) RMS value of NS direction;(d) RMS value of EW direction
图 9 江苏江宁台地电阻率交、直流小时观测数据曲线(2016年9月29日至30日)(a) 南北方向地电阻率;(b) 东西方向地电阻率;(c) 南北方向测量均方差;(d) 东西方向测量均方差Figure 9. Comparison of AC & DC hourly geoelectrical resistivity observation data of Jiangning station(a) Geoelectrical resistivity of NS direction;(b) Geoelectrical resistivity of EW direction;(c) RMS value of NS direction;(d) RMS value of EW direction从图9可以看出,在交流观测全天的观测数据中,南北方向测值稳定在125.5—126.0 Ω•m,测量均方差小于0.2 Ω•m,相对均方差小于0.15%,东西方向测值稳定在99.5 Ω•m左右,测量均方差小于0.25 Ω•m,相对均方差小于0.25%。与直流观测结果相比,观测数据波动明显减小,测量精度达到规范要求。
4. 讨论与结论
地铁运行时入地的杂散电流呈现信号幅度大、传播范围广的特点。随着城市轨道交通的快速发展,越来越多的城市地铁开通运行,对城市周边地电阻率观测的影响问题日益突出,造成观测数据剧烈起伏变化和测量方差变大,导致观测数据质量不符合地震监测预测研究的需求。
理论分析表明地铁杂散电流信号幅度大小与台站距地铁的距离、观测极距、测区电阻率、杂散电流大小等因素相关,由地铁杂散电流造成的地电阻率测量相对误差大小与距离平方成反比、与供电极距平方成正比。在现有观测技术条件和观测装置条件下,要使观测数精度达到0.3%,地电阻率台站测区至地铁的距离通州台要达到97 km,塘沽台为80 km,其余几个台也在55 km左右。对于供电极距为1 km的观测装置来说,当地铁至地电阻率台站测区的距离达到90 km左右时,地铁杂散电流影响为0.1%左右,可以忽略不计。
实际上,受各城市地铁列车运行发车间隔(密度)、运行时杂散电流大小以及介质不均匀等因素的影响,地铁对地电阻率观测的影响非常复杂。通过在六个地电阻率台站对地铁杂散电流信号的实际测试和分析,其信号的频谱范围主要在50—200 s周期之间,但各台稍有差别,而且不同台站记录的信号幅度也不尽相同,这与各城市地铁运行的密度以及台站与地铁的距离有关。
为应对地铁杂散电流的影响,继续发挥地电阻率观测方法在城市及周边区域地震监测预测的效能,根据地铁杂散电流信号的特征,提出了几种抑制地铁杂散电流影响的方法。在不改变现有观测条件的情况下,地电阻率交流观测方法是从根本上解决地铁杂散电流影响的最有效的途径。
总之,虽然地铁杂散电流对地电阻率观测造成了影响,但是通过采用新的观测技术和方法可以达到有效抑制、减小其影响的目的,从而为震前地电阻率异常变化的识别和提取奠定良好基础。
-
图 3 各观测台南北(左)、东西(右)测道记录的地铁杂散电流信号
(a) 北京通州台 (2014-04-21 13:00开始);(b) 天津青光台 (2014-05-16 16:00开始);(c) 天津塘沽台(2014-05-13 17:00开始);(d) 天津宝坻台 (2014-05-12 11:00开始)
Figure 3. The stray current signals recorded from north-south (left) and east-west (right) channel at different observations
(a) Tongzhou station in Beijing (from 13:00,April 21,2014);(b) Qingguang station in Tianjin (from 16:00,May 16,2014);(c) Tanggu station in Tianjin (from 17:00,May 13,2014);(d) Baodi station in Tianjin (from 11:00,May 12,2014)
图 3 各观测台南北(左)、东西(右)测道记录的地铁杂散电流信号
(e) 江苏江宁台 (2014-10-13 15:00开始);(f) 辽宁新城子台 (2014-07-30 17:00开始)
Figure 3. The stray current signals recorded from north-south (left) and east-west (right) channe at different observations
(e) Jiangning station in Jiangsu (from 15:00,October 13,2014);(f) Xinchengzi station in Liaoning (from 17:00,July 30,2014)
图 4 地铁运行时段和停运时段功率谱密度PSD对比
(a) 北京通州台;(b) 天津青光台;(c) 天津塘沽台;(d) 天津宝坻台;(e) 江苏江宁台;(f) 辽宁新城子台
Figure 4. Comparison of PSDs in subway operation with those in non-operation time period
(a) Tongzhou station in Beijing;(b) Qingguang station in Tianjin;(c) Tanggu station in Tianjin;(d) Baodi station in Tianjin;(e) Jiangning station in Jiangsu;(f) Xinchengzi station in Liaoning
图 9 江苏江宁台地电阻率交、直流小时观测数据曲线(2016年9月29日至30日)
(a) 南北方向地电阻率;(b) 东西方向地电阻率;(c) 南北方向测量均方差;(d) 东西方向测量均方差
Figure 9. Comparison of AC & DC hourly geoelectrical resistivity observation data of Jiangning station
(a) Geoelectrical resistivity of NS direction;(b) Geoelectrical resistivity of EW direction;(c) RMS value of NS direction;(d) RMS value of EW direction
表 1 地铁杂散电流导致的地电阻率测量相对误差δ随距离的变化(P1=75,P2=1,C=3.33)
Table 1 The influence of stray current on geoelectrical resistivity varies with distance (P1=75,P2=1,C=3.33)
测区至地铁
距离r1/kmδ dAB=1000 m dAB=500 m dAB=200 m 10 8.530% 2.132% 0.341% 20 2.132% 0.533% 0.085% 30 0.948% 0.237% 0.038% 40 0.533% 0.133% 0.021% 50 0.341% 0.085% 0.014% 60 0.237% 0.059% 0.009% 70 0.174% 0.044% 0.007% 80 0.133% 0.033% 0.005% 90 0.105% 0.026% 0.004% 100 0.085% 0.021% 0.003% 表 2 各个台站观测装置及与地铁最近距离
Table 2 The configuration in geoelectrical resistivity observation station and its distance from the subway
序号 台站名称 与地铁最近距离/km 观测装置 测道方向 供电极距/m 测量极距/m 装置系数/m 1 北京通州台 11.0 南北、东西 1 760 320 7 351 2 天津青光台 7.6 南北、东西 1 000 316 2 237 3 天津塘沽台 城区线:40.0
九号线:7.0南北、东西
南北、东西南北:1 500
东西:1 000南北:500
东西:3003 141
2 3824 天津宝坻台 52.0 南北、东西 1 000 200 3 769 5 江苏江宁台 城区线:30.0
机场线:3.0南北、东西
南北、东西1 000
1 000300
3002 382
2 3826 辽宁新城子台 19.4 南北、东西 1 000 300 2 382 表 3 不同台站地铁运行时杂散电流不同周期功率占比
Table 3 The distribution of power in different periods at different stations during subway operation
周期范围/s 北京通州台 天津青光台 天津塘沽台 天津宝坻台 江苏江宁台 辽宁新城子台 50—100 10.17% 19.02% 8.74% 14.78% 33.34% 24.26% 100—150 29.56% 60.50% 11.66% 54.55% 6.77% 57.57% 150—200 56.87% 18.13% 76.35% 27.00% 9.13% 15.67% 200—250 2.38% 1.68% 0.85% 1.12% 39.28% 2.10% 250—300 0.17% 0.20% 1.81% 0.57% 0.77% 0.00% 300—350 0.83% 0.47% 0.59% 1.97% 10.71% 0.40% 表 4 六个台站记录的地铁杂散电流信号幅度及测量信噪比
Table 4 The stray current signal amplitude and the SNR for the six stations
台站名称 测道
方向人工电位差/mV 噪声幅度/mV 测量信噪比/dB 信噪比降低
/dB停运时段 运行时段 停运时段 运行时段 北京通州 南北 7 0.14 1.33 34.0 14.4 19.6 东西 7 0.17 1.16 32.3 15.6 16.7 天津青光 南北 9 0.09 4.96 40.0 5.2 34.8 东西 9 0.36 2.25 28.0 12.0 15.9 天津塘沽 南北 7 0.06 1.94 41.3 11.1 30.2 东西 10 0.40 0.79 28.0 22.0 5.9 天津宝坻 南北 41 0.07 0.48 55.4 38.6 16.7 东西 41 0.06 0.25 56.7 44.3 12.4 江苏江宁 南北 93 0.19 3.60 53.8 28.2 25.6 东西 73 0.56 13.86 42.3 14.4 27.9 辽宁新城子 南北 26 0.13 1.02 34.0 14.4 19.6 东西 26 0.10 0.46 32.3 15.6 16.7 表 5 六个台站的地电阻率变幅与相对方差
Table 5 The maximum variation and relative RMS value of geoelectrical resistivity for six stations
台站 电阻率最大变幅/Ω·m 相对均方差 南北 东西 南北 东西 北京通州 1.83 3.99 0.65% 1.75% 天津青光 1.29 0.48 3.73% 1.72% 天津塘沽 1.72 0.59 7.57% 2.55% 天津宝坻 0.32 0.22 0.36% 0.20% 江苏江宁 1.50 5.22 1.13% 5.37% 辽宁新城子 0.09 0.05 0.15% 0.08% 表 6 六个台站的理论避让距离(P1=75,P2=1,δ=0.3%)
Table 6 The minimum distance between observation station and subway for the six stations (P1=75,P2=1,δ=0.3%)
台站名称 供电极距/m 测量极距/m C=dAB/dMN 最小避让距离/km 北京通州台 1 760 320 5.50 97 天津青光台 1 000 316 3.16 53 天津塘沽台 1 500 500 3.00 79 天津宝坻台 1 000 200 5.00 55 江苏江宁台 1 000 300 3.33 53 辽宁新城子 1 000 300 3.33 53 注:P1为地电阻率测量时噪声与信号之比,P2为地铁到台站电阻率与台站电阻率之比,δ为相对均方差。 -
董亮,姚知林,葛彩刚,石超杰,陈金泽. 2021. 地铁杂散电流干扰下管地电位波动特征的傅里叶分析[J]. 表面技术,50(2):294–303. doi: 10.16490/j.cnki.issn.1001-3660.2021.02.031 Dong L,Yao Z L,Ge C G,Shi C J,Chen J Z. 2021. Fourier analysis of the fluctuation characteristics of pipe-to-soil potential under metro stray current interference[J]. Surface Technology,50(2):294–303 (in Chinese).
杜学彬,马占虎,叶青,谭大诚,陈军营. 2006. 与强地震有关的视电阻率各向异性变化[J]. 地球物理学进展,21(1):93–100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2006.01.015 Du X B,Ma Z H,Ye Q,Tan D C,Chen J Y. 2006. Anisotropic changes in apparent resistivity associated with strong earthquakes[J]. Progress in Geophysics,21(1):93–100 (in Chinese).
桂燮泰,关华平,戴经安. 1989. 唐山、松潘地震前视电阻率短临异常图象重现性[J]. 西北地震学报,11(4):71–75. Gui X T,Guan H P,Dai J A. 1989. The short-term and immediate anomalous pattern recurrences of the apparent resistivity before the Tangshan and Songpan earthquakes of 1976[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal,11(4):71–75 (in Chinese).
胡先茂. 2011. 城市轨道交通对埋地管线影响范围的分析[J]. 现代城市轨道交通,(3):74–76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7533.2011.03.024 Hu X M. 2011. Analysis on influence scope of urban rail transit on buried pipelines[J]. Modern Urban Transit,(3):74–76 (in Chinese).
李金铭. 2005. 地电场与电法勘探[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 60–67. Li J M. 2005. Geoelectric Field and Electrical Exploration[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 60–67 (in Chinese).
李雷,刘楠康,曾文,邵华锋. 2019. 轨道交通杂散电流在复杂地质条件下的分布[J]. 广东电力,32(8):133–140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-290X.2019.008.017 Li L,Liu N K,Zeng W,Shao H F. 2019. Distribution of stray current in rail transit under complex geological conditions[J]. Guangdong Electric Power,32(8):133–140 (in Chinese).
林江,唐华,于海学. 2002. 地铁迷流腐蚀及其防护技术[J]. 建筑材料学报,5(1):72–76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2002.01.014 Lin J,Tang H,Yu H X. 2002. Protection of stray current corrosion in metro[J]. Journal of Building Materials,5(1):72–76 (in Chinese).
刘国兴. 2005. 电法勘探原理与方法[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 7–13. Liu G X. 2005. The Principle and Method of Electrical Exploration[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 7–13 (in Chinese).
刘文权. 2014. 城市地铁杂散电流对埋地输油管道的危害[J]. 全面腐蚀控制,28(11):29–32. doi: 10.13726/j.cnki.11-2706/tq.2014.11.029.04 Liu W Q. 2014. Interference corrosion hazards of subway stray currents on buried jet fuel metal pipeline[J]. Total Corrosion Control,28(11):29–32 (in Chinese).
马钦忠. 2014. 中外几次重要地震预测与预报结果之启示[J]. 地震学报,36(3):500–513. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-3782.2014.03.015 Ma Q Z. 2014. Enlightment of the success or failure prediction for some large earthquakes at home and abroad[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,36(3):500–513 (in Chinese).
毛先进,杨玲英,钱家栋. 2014. 水平层状介质中深埋装置系统地电阻率影响系数特征研究[J]. 地震学报,36(4):678–685. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-3782.2014.04.013 Mao X J,Yang L Y,Qian J D. 2014. Characteristics of the influence coefficient in the cases of deeply-buried configurations for geoelectrical resistivity observation[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,36(4):678–685 (in Chinese).
梅进武,林国松. 2017. 多列车运行情况下的地铁杂散电流分析[J]. 电气化铁道,28(4):68–70. Mei J W,Lin G S. 2017. Analysis of metro stray current under multi-train operation[J]. Electric Railway,28(4):68–70 (in Chinese).
聂永安,巴振宁,聂瑶. 2010. 深埋电极的地电阻率观测研究[J]. 地震学报,32(1):33–40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-3782.2010.01.004 Nie Y A,Ba Z N,Nie Y. 2010. Study on buried electrode resistivity monitoring system[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,32(1):33–40 (in Chinese).
钱复业,赵玉林,于谋明,王志贤,刘小伟,常思敏. 1982. 地震前地电阻率的异常变化[J]. 中国科学:B辑,(9):831–839. Qian F Y,Zhao Y L,Yu M M,Wang Z X,Liu X W,Chang S M. 1982. Geoelectrical resistivity anomalies before earthquake[J]. Science in China:Series B,(9):831–839 (in Chinese).
钱家栋. 1993. 与大震孕育过程有关的地电阻率变化研究[J]. 中国地震,9(4):341–350. Qian J D. 1993. A study on the changes in geoelectrical resistivity associated with preparatory process of great earthquakes in China[J]. Earthquake Research in China,9(4):341–350 (in Chinese).
钱家栋,马钦忠,李劭秾. 2013. 汶川MS8.0地震前成都台NE测线地电阻率异常的进一步研究[J]. 地震学报,35(1):4–17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-3782.2013.01.002 Qian J D,Ma Q Z,Li S N. 2013. Further study on the anomalies in apparent resistivity in the NE configuration at Chengdu station associated with Wenchuan MS8.0 earthquake[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,35(1):4–17 (in Chinese).
澹台乐琰,韩肖清,王磊,袁铁江. 2020. 多列车运行下地铁杂散电流建模仿真[J]. 电测与仪表,57(22):7–16. Tantai L Y,Han X Q,Wang L,Yuan T J. 2020. Modeling and simulation of stray current in subway with multi-train operation[J]. Electrical Measurement &Instrumentation,57(22):7–16 (in Chinese).
王崇林,马草原,王智,潘春德,王雨扬. 2007. 地铁直流牵引供电系统杂散电流分析[J]. 城市轨道交通研究,10(3):51–53. Wang C L,Ma C Y,Wang Z,Pan C D,Wang Y Y. 2007. Analysis of stray current in metro DC traction power system[J]. Urban Mass Transit,10(3):51–53 (in Chinese).
王兰炜,张宇,张世中,颜蕊,王子影,张兴国,胡哲. 2015. 我国井下地电阻率观测技术现状分析[J]. 地震地磁观测与研究,36(2):95–102. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3246.2015.02.018 Wang L W,Zhang Y,Zhang S Z,Yan R,Wang Z Y,Zhang X G,Hu Z. 2015. The status of deep-well geo-electrical resistivity observation in China[J]. Seismological and Geomagnetic Observation and Research,36(2):95–102 (in Chinese).
王兰炜,张宇,张兴国,胡哲,王子影,马小溪. 2019. 地震地电阻率交流观测方法及观测实验[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学,39(7):738–742. Wang L W,Zhang Y,Zhang X G,Hu Z,Wang Z Y,Ma X X. 2019. AC geo-electrical resistivity observation method and experimental observation[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics,39(7):738–742 (in Chinese).
王猛. 2005. 直流牵引供电系统钢轨电位与杂散电流分析[J]. 城市轨道交通研究,8(3):24–26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-869X.2005.03.008 Wang M. 2005. Rail potential and stray current of DC traction power system[J]. Urban Mass Transit,8(3):24–26 (in Chinese).
张世中,石航,王兰炜,胡哲,刘大鹏,魏连生,鞠永. 2013. 地电台站受城市轨道交通干扰的测试分析与抗干扰措施研究[J]. 地震学报,35(1):117–124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-3782.2013.01.012 Zhang S Z,Shi H,Wang L W,Hu Z,Liu D P,Wei L S,Ju Y. 2013. Test analysis on disturbances caused by urban rail transit at geoelectric stations and measures to reduce its influence[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,35(1):117–124 (in Chinese).
张晓东,蒋海昆,李正媛,卢显,安艳茹. 2011. 汶川地震对地震预报工作的一些启示[J]. 工程研究:跨学科视野中的工程,3(4):309–320. Zhang X D,Jiang H K,Li Z Y,Lu X,An Y R. 2011. The revelation of Wenchuan earthquake for earthquake forecast[J]. Journal of Engineering Studies,3(4):309–320 (in Chinese).
张宇,张兴国,王兰炜,马小溪,赵庆福,袁慎杰,王子影. 2016. 新型地电阻率交流观测系统研究及江宁台观测试验[J]. 地震学报,38(5):807–810. doi: 10.11939/jass.2016.05.015 Zhang Y,Zhang X G,Wang L W,Ma X X,Zhao Q F,Yuan S J,Wang Z Y. 2016. A new AC geo-electrical resistivity observation system and experimental observation in Jiangning seismic station[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,38(5):807–810 (in Chinese).
中国地震局. 2009. DB/T 33.1-2009地震地电观测方法地电阻率观测第1部分: 单极距观测[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社: 3. China Earthquake Administration. 2009. DB/T 33.1−2009 The Method of Earthquake-Related Geoelectrical Monitoring: Geoelectrical Resistivity Observation: Part 1: Single Separation Configuration[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China: 3 (in Chinese).
朱峰,李嘉成,曾海波,邱日强. 2018. 城市轨道交通轨地过渡电阻对杂散电流分布特性的影响[J]. 高电压技术,44(8):2738–2745. Zhu F,Li J C,Zeng H B,Qiu R Q. 2018. Influence of rail-to-ground resistance of urban transit systems on distribution characteristics of stray current[J]. High Voltage Engineering,44(8):2738–2745 (in Chinese).
Lu J,Xie T,Li M,Wang Y L,Ren Y X,Gao S D,Wang L W,Zhao J L. 2016. Monitoring shallow resistivity changes prior to the 12 May 2008 MS8.0 Wenchuan earthquake on the Longmen Shan tectonic zone,China[J]. Tectonophysics,675:244–257. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2016.03.006
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 张志宏,侯作亮,杨士超,李梦莹,黄明威. 基于AMT的地电阻率观测场地优化选择研究——以辽宁新城子深井地电阻场地为例. 大地测量与地球动力学. 2025(04): 436-440 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王丽,李伟,沈红会,孙君嵩,李鸿宇. 地电阻率受高压输电线路架线施工干扰的判定. 华北地震科学. 2024(02): 102-108 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 曹原. 高导电率地质区间地铁杂散电流控制技术研究. 机电信息. 2024(11): 85-89 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 张宇,王兰炜,胡哲,张世中,张兴国,娄晓宇. 加权平均算法在地电阻率日均值计算中的应用. 地震. 2023(02): 25-37 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李雪浩,何思源,李国超,刘华姣,廖绍欢,赵乃千. 成都地震监测中心站地电阻率交、直流观测系统对比分析. 地震地磁观测与研究. 2023(05): 118-124 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 刘建波,雷生学,张明东,刘文兵,刘金城,马义山. 用自然电位估算地铁干扰大小——以天津塘沽地震台为例. 地震地磁观测与研究. 2023(05): 107-117 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载: