Earthquake damage assessment for building group considering dynamic interaction between buildings and sedimentary basin
-
摘要:
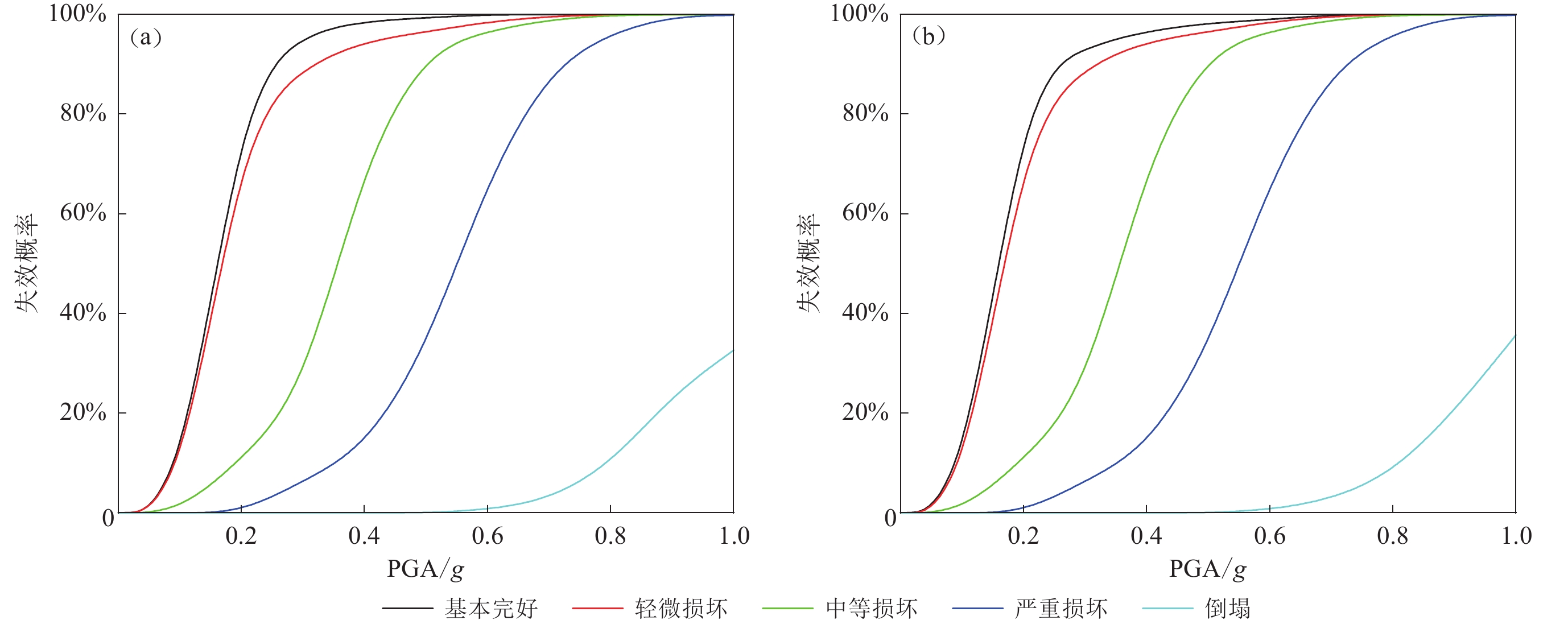
我国大量城镇位于沉积盆地,沉积盆地对地震动具有显著的幅值放大和持时增长效应,同时沉积盆地与建筑群间的动力相互作用将导致地震动空间重分布。针对此问题,本文提出了一种考虑建筑群-沉积盆地动力相互作用的建筑群震害评估方法:首先,以剪切层模型、弯剪耦合模型等简化力学模型模拟建筑结构,计算建筑群-沉积盆地动力相互作用,获得建筑群的基础顶面地震动;然后,基于精细化有限元模型分析典型单体建筑的地震易损性;最后,结合所求建筑群基础顶面地震动、易损性曲线进行建筑群震害评估。结果表明:采用简化力学模型、精细化有限元模型模拟建筑结构时,上部建筑对基础顶面地震动的影响具有等效性,因此所建方法适用于考虑建筑群-沉积盆地动力相互作用的建筑群震害评估;建筑群-沉积盆地动力相互作用主要导致盆地内地表地震动峰值降低,但局部位置会在盆地效应基础上产生附加放大效应;建筑群-沉积盆地动力相互作用导致不同地表点地震动加速度反应谱峰值相差3倍,同时放大邻近建筑出现相同等级震害的概率差异,所分析算例中,在是否考虑建筑群-沉积盆地动力相互作用的情况下,邻近四栋相同框架结构发生中等损坏的概率范围分别为66%—92%和87%—93%,此结果与实际震害中建筑结构交替破坏的现象一致。
Abstract:Building clusters as “scatterers” and “secondary sources” will change the seismic wave propagation in the site under earthquakes. Seismic damage investigation results of the 1976 Friuli earthquake and the 1985 Mexico earthquake revealed that the building damages had the spatial distribution of alternating destruction. Additionally, many cities and towns in China are located in sedimentary basins. Sedimentary basins have significant amplitude-amplifying and duration-increasing effects on ground motion. The dynamic interaction between the sedimentary basin and buildings leads to spatial redistribution and significant spatial variation of ground motions. Thus, this paper proposes a framework for earthquake damage assessment of buildings considering the dynamic interaction between buildings and the sedimentary basin. Firstly, simplified mechanical models including the shear layer model and flexural-shear model are used to simulate building structures; and the dynamic interaction between buildings and the sedimentary basin is calculated to obtain the ground motions on the top surface of the building foundations. Then, the seismic vulnerability of a typical single building is analyzed based on a refined finite element model with fiber-beam and layered shell elements. Finally, combined with the ground motions of foundations and vulnerability curves of buildings, earthquake damage assessment of buildings is realized rapidly. The results show that the influence of the superstructures on ground motions on the top of the foundations is equivalent when the simplified mechanical model and the refined finite element model are used to simulate building structures. The proposed method is suitable for earthquake damage assessment of building groups considering the dynamic interaction between buildings and basins. However, there are significant differences in solving the seismic response of building clusters using simple mechanical models and refined finite element models. Therefore, it is necessary to comprehensively consider the size of building clusters, and the importance and complexity of buildings in urban areas in seismic damage assessment. A multi-scale method is suitable. The dynamic interaction between buildings and basins mainly reduces the peak value of the surface ground motion in the basin, however, the local location will produce additional amplification based on the basin effect. The interaction between the buildings and the basin causes a three-time difference in the peak values of the acceleration response spectrum at different surface locations. At the same time, the difference in the probability of earthquake damage of the same level in neighboring buildings is magnified. In the analyzed example, when the interaction of building group and basin is considered or not considered, the medium damage probability ranges of the same four adjacent buildings are 66%−92% and 87%−93%, respectively, which is consistent with the earthquake damage phenomenon of building structures in the previous earthquakes. The proposed method takes the failure probability of building structures as the assessment index, which can be solved through seismic vulnerability analysis of individual building structures or directly extracted from the seismic vulnerability database. Compared with dynamic time-history analysis results of building clusters, this index is more suitable for predicting unfavorable locations or buildings before earthquakes, especially for communities with relatively unitary building-types. The failure probability of the entire community can be obtained by combining the seismic vulnerability of typical building structures with the peak ground acceleration at the building foundations.
-
Keywords:
- basin effect /
- site-city interaction /
- vulnerability /
- earthquake damage assessment
-
-
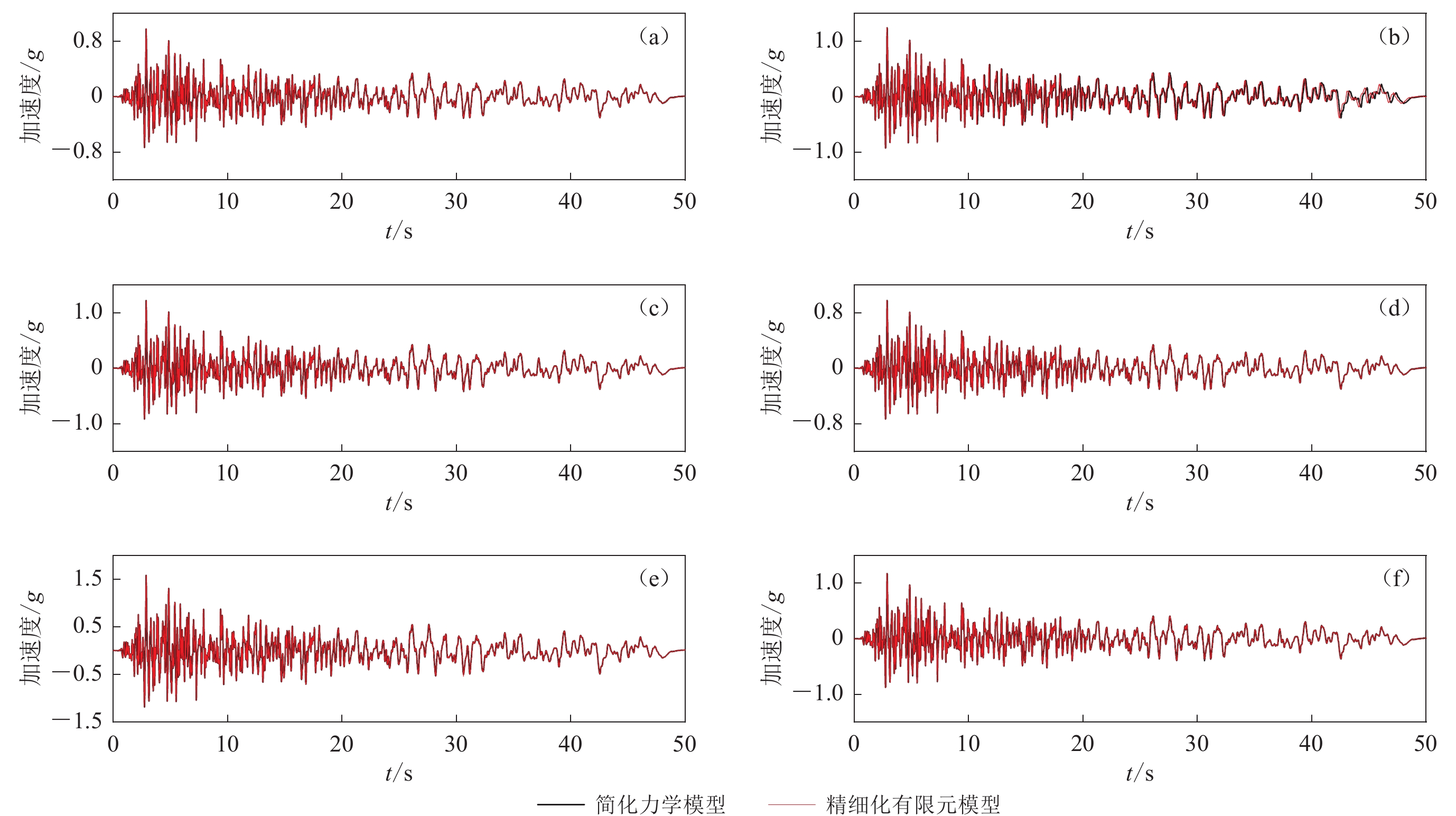
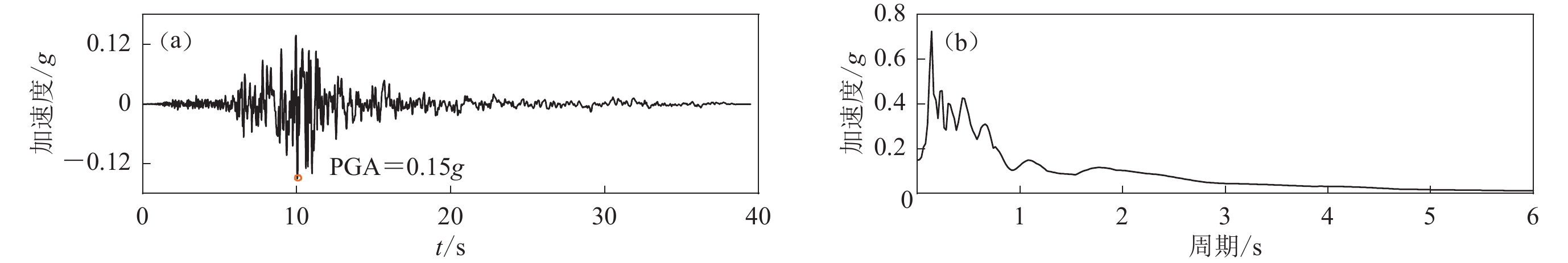
图 3 地震作用下简化力学模型和精细化有限元模型对应的基础顶面地震动
(a) 3层框架结构,基频为3.2 Hz;(b) 10层框剪结构,基频为2.1 Hz;(c) 4层框架结构,基频为2.3 Hz;(d) 15层框剪结构,基频为1.3 Hz;(e) 5层框架结构,基频为2.0 Hz;(f) 20层框剪结构,基频为1.0 Hz
Figure 3. Ground motions of foundation top surfaces of refined finite element and simplified mechanical models under earthquakes
(a) 3-layered frame structure,fundamental frequency is 3.2 Hz;(b) 10-layered frame-shear wall structure,fundamental frequency is 2.1 Hz;(c) 4-layered frame structure,fundamental frequency is 2.3 Hz;(d) 15-layered frame-shear wall structure,fundamental frequency is 1.3 Hz;(e) 5-layered frame structure,fundamental frequency is 2.0 Hz;(f) 20-layered frame-shear wall structure,fundamental frequency is 1.0 Hz
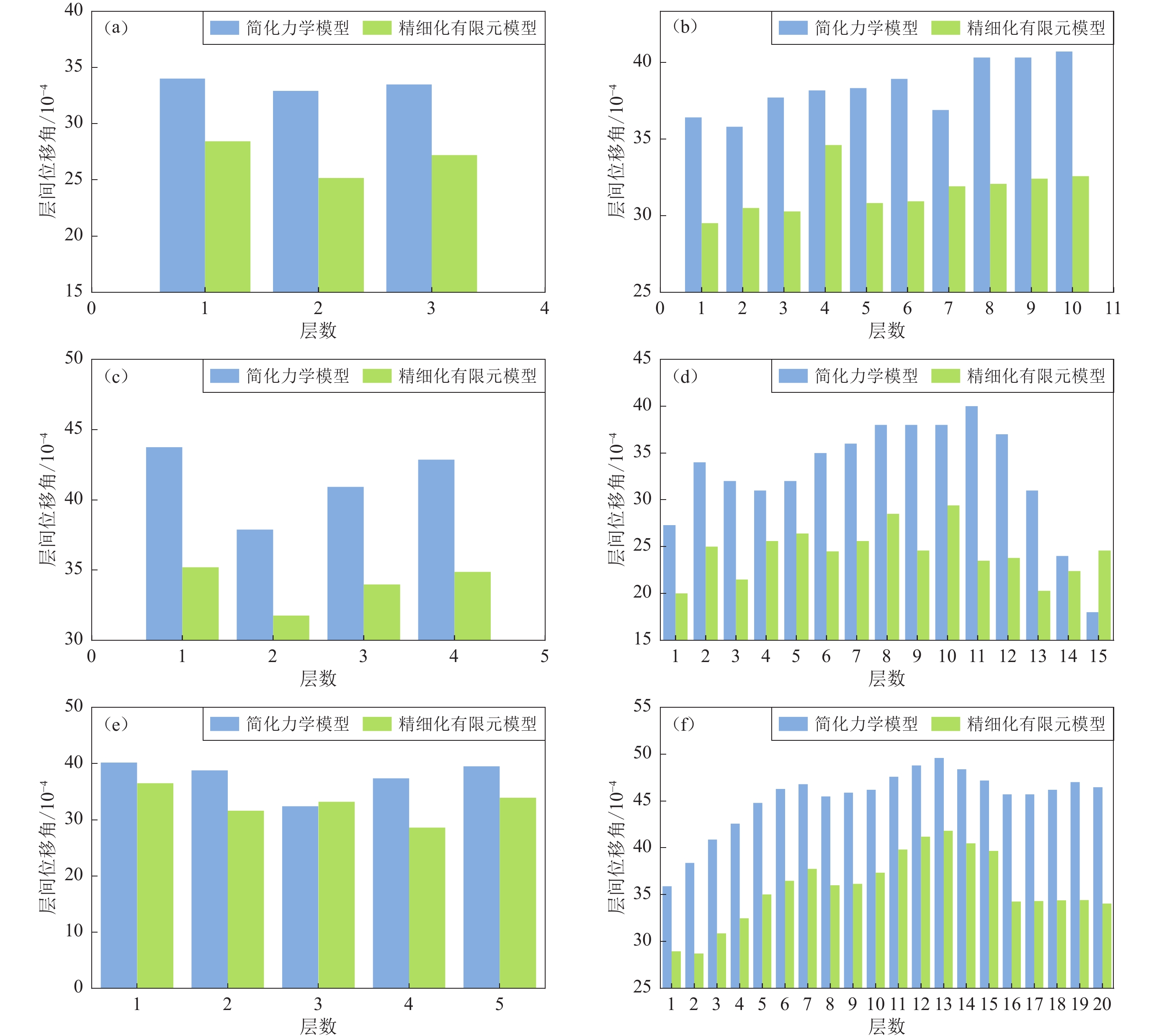
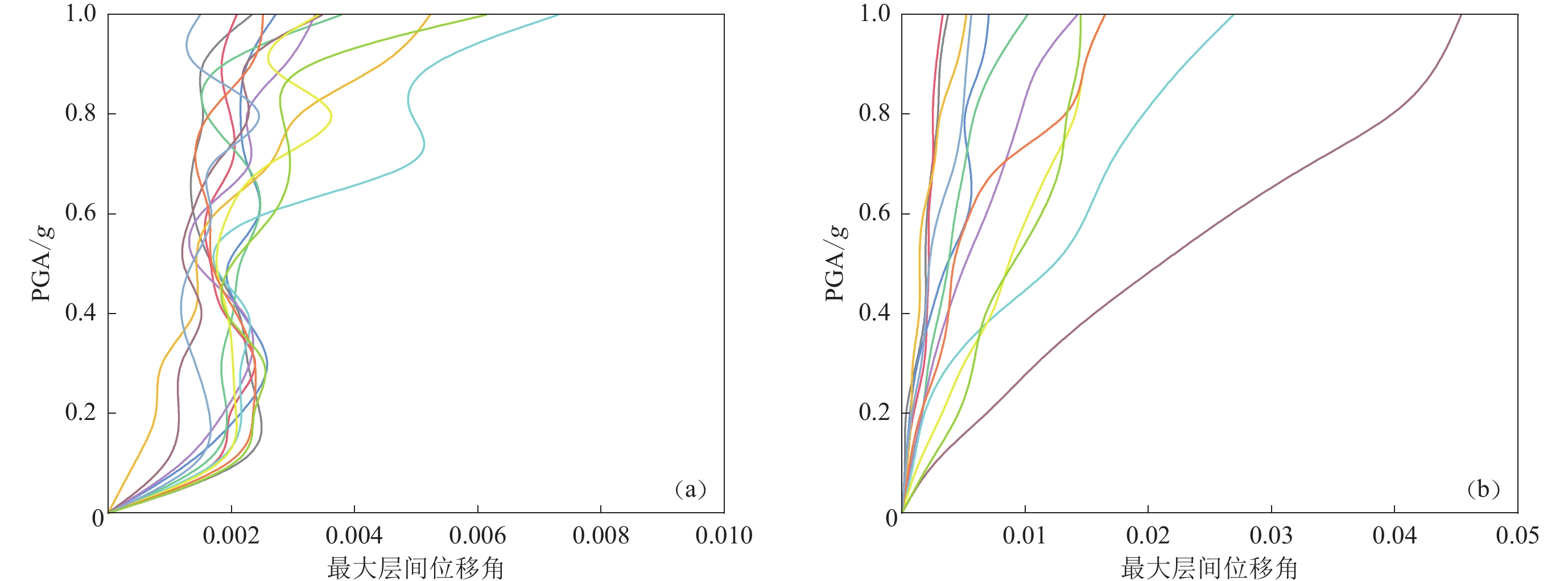
图 4 框架、框剪结构的精细化有限元模型和简化力学模型各层的最大层间位移角对比
(a) 3层框架结构,基频为3.2 Hz;(b) 10层框剪结构,基频为2.1 Hz;(c) 4层框架结构,基频为2.3 Hz;(d) 15层框剪结构,基频为1.3 Hz;(e) 5层框架结构,基频为2.0 Hz;(f) 20层框剪结构,基频为1.0 Hz
Figure 4. Comparison of maximum interlayer displacement angles between refined finite element and simplified mechanical models of frame and frame-shear wall structures
(a) 3-layered frame structure,fundamental frequency is 3.2 Hz;(b) 10-layered frame-shear wall structure,fundamental frequency is 2.1 Hz;(c) 4-layered frame structure,fundamental frequency is 2.3 Hz;(d) 15-layered frame-shear wall structure,fundamental frequency is 1.3 Hz;(e) 5-layered frame structure,fundamental frequency is 2.0 Hz;(f) 20-layered frame-shear wall structure,fundamental frequency is 1.0 Hz
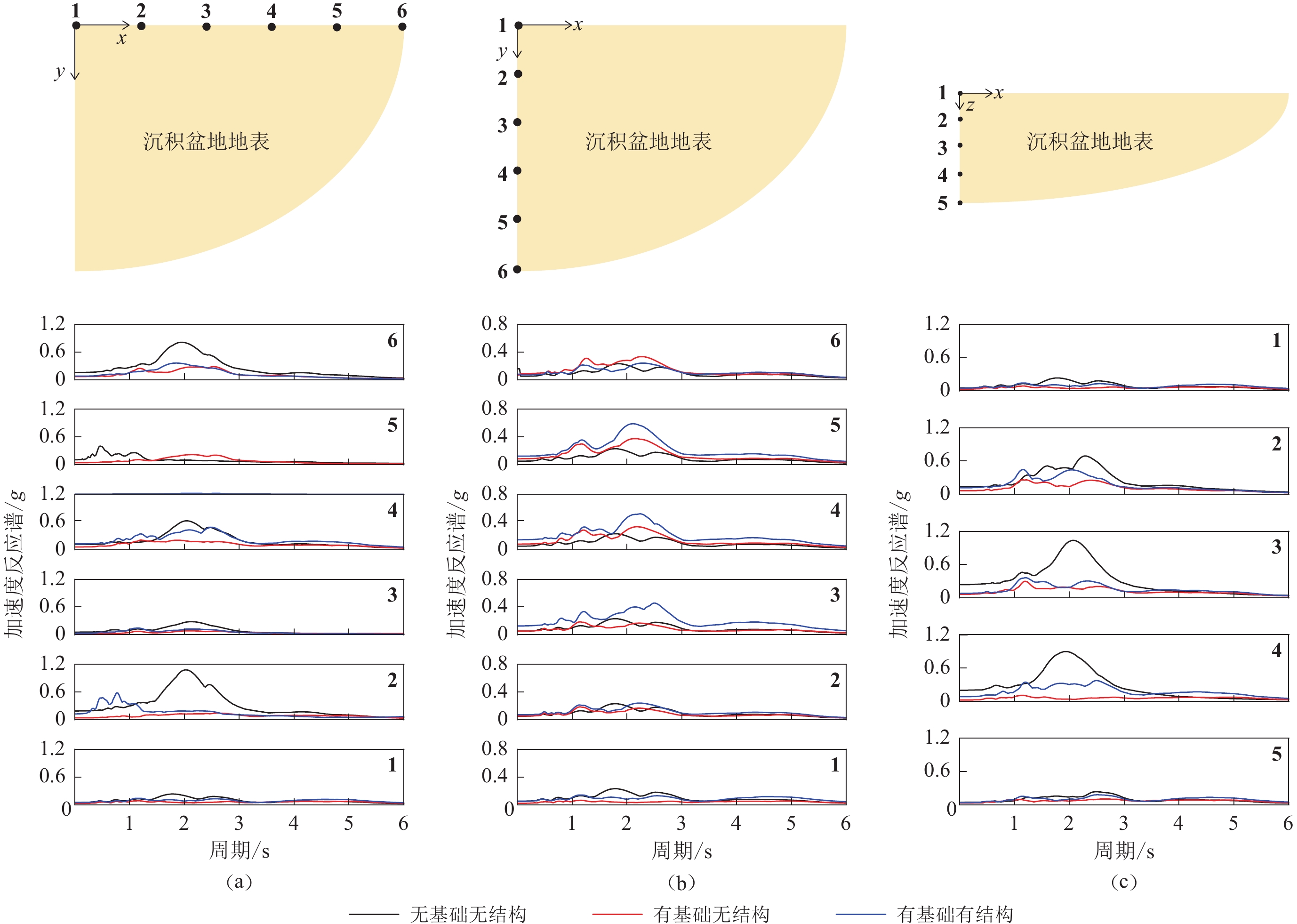
图 11 建筑群、建筑群基础对沉积盆地地震动加速度反应谱的影响
(a) x向地表点及其加速度反应谱;(b) y向地表点及其加速度反应谱;(c) z向地表点及其加速度反应谱
Figure 11. Effect of buildings and foundations on the acceleration response spectrum of the sedimentary basin
(a) Surface points in x-direction and their acceleration response spectrum;(b) Surface points in y-direction and their acceleration response spectrum;(c) Surface points in z-direction and their acceleration response spectrum
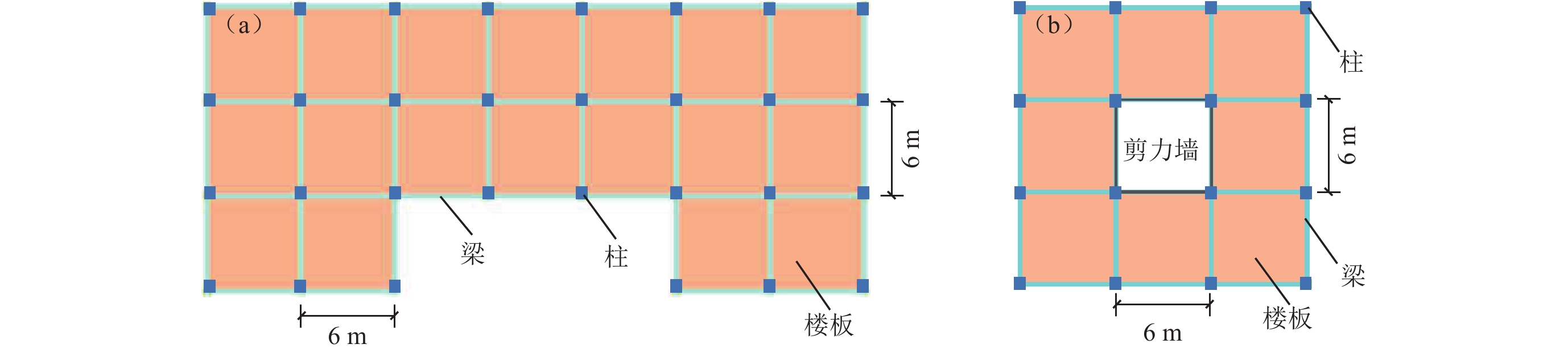
表 1 框架结构和框剪结构的材料本构模型参数
Table 1 Material constitutive model parameters of frame and frame-shear wall structures
材料 密度/(kg·m−3) 弹性模量/GPa 屈服应力 /MPa 硬化刚度系数 轴向抗压强度/MPa 峰值压应变 极限压应变 钢筋 7 800 200 235 0.001 − − − 混凝土 2 500 25.6 − − 21.8 0.001 7 0.003 8 表 2 框架结构和框剪结构的模型参数
Table 2 Model parameters of frame and frame-shear wall structures
结构
类型结构
层数结构
高度/m结构基频/Hz 精细化有限元模型 简化力学模型 框架 3 9.9 3.24 3.24 4 13.2 2.31 2.31 5 17.2 2.02 2.02 框剪 10 36 2.11 2.11 15 54 1.33 1.33 20 72 1.00 0.99 表 3 盆地和半空间域的介质参数
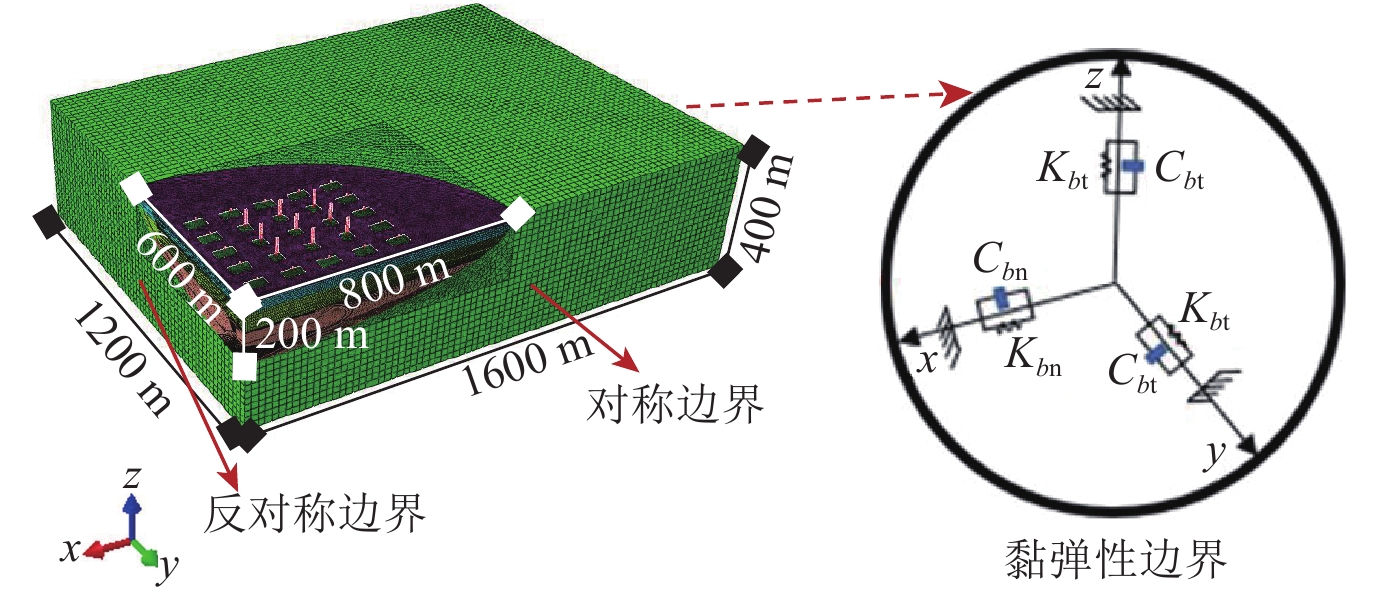
Table 3 Media parameters of the basin and half-space
区域 厚度/m 密度/(kg·m−3) 弹性模量/MPa 泊松比 剪切波速/(m·s−1) 阻尼比 第一层盆地 20 1 800 187.2 0.4 200 0.04 第二层盆地 30 1 800 421.2 0.35 300 0.04 第三层盆地 50 1 800 748.8 0.33 400 0.04 第四层盆地 100 1 900 916.5 0.33 600 0.03 半空间 400 2 200 3520 0.3 800 0.02 表 4 框架、框剪结构极限状态对应的最大层间位移角限值(季静等,2022)
Table 4 Limit states corresponding to the maximum interlayer displacement angle of frame and frame-shear structures (Ji et al,2022)
结构类型 不同极限状态对应的最大层间位移角限值 基本完好 轻微破坏 中等破坏 严重破坏 倒塌 框架结构 0.000 8 0.002 0.006 0.015 0.025 框剪结构 0.001 0 0.003 0.008 0.016 0.030 -
巴振宁,赵靖轩,吴孟桃,梁建文. 2022. 基于CPU-GPU异构并行的复杂场地近断层地震动谱元法模拟[J]. 地震学报,44(1):182–193. doi: 10.11939/jass.20210076 Ba Z N,Zhao J X,Wu M T,Liang J W. 2022. Simulation of near-fault ground motions in complex sites based on CPU-GPU heterogeneous parallelism by spectral element method[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,44(1):182–193 (in Chinese).
陈少林,张莉莉,李山有. 2014. 半圆柱型沉积盆地对SH波散射的数值分析[J]. 工程力学,31(4):218–224. Chen S L,Zhang L L,Li S Y. 2014. Numerical analysis of the plane SH waves scattering by semi-cylindrical alluvial valley[J]. Engineering Mechanics,31(4):218–224 (in Chinese).
杜永峰,黄小宁,李慧. 2018. 基于性能的基础隔震钢筋混凝土框剪结构的倒塌可靠度分析[J]. 地震工程学报,40(5):879–882. Du Y F,Huang X N,Li H. 2018. Performance-based collapse reliability analysis of base-isolated frame-wall structures[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal,40(5):879–882 (in Chinese).
高玉峰,代登辉,张宁. 2022. 翡翠河谷地震动地形效应解析分析[J]. 地震学报,44(1):40–49. doi: 10.11939/jass.20210099 Gao Y F,Dai D H,Zhang N. 2022. Analytical study on the topographic effect on ground motion of Feitsui canyon[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,44(1):40–49 (in Chinese).
季静,陈珊珊,王雨,韩小雷. 2022. 改进拉丁超立方抽样选波法对RC框架结构地震易损性影响研究[J]. 土木工程学报,55(3):18–26. Ji J,Chen S S,Wang Y,Han X L. 2022. Influence of ground motion selection method based on improved Latin hypercube sampling on seismic fragility of RC frame structure[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal,55(3):18–26 (in Chinese).
李孟达. 2016. 框架-剪力墙结构地震易损性分析与抗震性能评估[D]. 哈尔滨:中国地震局工程力学研究所:42−43. Li M D. 2016. Seismic Vulnerability Analysis and Earthquake Resistant Capability Evaluation of Frame-Shear Wall Structure[D]. Harbin:Institute of Engineering Mechanics,China Earthquake Administration:42−43 (in Chinese).
李正,朱炳寅,李宁. 2011. 基于ABAQUS的钢筋混凝土框架结构地震损伤分析[J]. 建筑结构,41(增刊):249–252. Li Z,Zhu B Y,Li N. 2011. Seismic damage analysis of reinforced concrete frame structures based on ABAQUS[J]. Building Structure,41(S1):249–252 (in Chinese).
刘晶波,谷音,杜义欣. 2006. 一致粘弹性人工边界及粘弹性边界单元[J]. 岩土工程学报,28(9):1070–1075. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2006.09.004 Liu J B,Gu Y,Du Y X. 2006. Consistent viscous-spring artificial boundaries and viscous-spring boundary elements[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,28(9):1070–1075 (in Chinese).
刘中宪,齐欣,王冬,柴寿喜,姚殊. 2018. 沉积河谷-建筑群地震动力相互作用的二维IBEM模拟[J]. 岩土力学,39(10):3803–3811. Liu Z X,Qi X,Wang D,Chai S X,Yao S. 2018. Simulation of dynamic interaction between sedimentary valley and buildings under seismic loading by 2D IBEM[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,39(10):3803–3811 (in Chinese).
陆新征. 2015. 工程地震灾变模拟:从高层建筑到城市区域[M]. 第二版. 北京:科学出版社:127−158. Lu X Z. 2015. Earthquake Disaster Simulation of Civil Infrastructures:From High Buildings to City Region[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing:Science Press:127−158 (in Chinese).
罗俊. 2012. 框剪结构强震破坏模式研究[D]. 重庆:重庆大学:10−12. Luo J. 2012. Failure Mode Study of Frame-Shear Wall Structure Subject to Strong Earthquake Loads[D]. Chongqing:Chongqing University:10−12 (in Chinese).
强生银,刘启方,温瑞智,王宏伟. 2021. 基于二维数值模拟的盆地地震动放大系数[J]. 地震工程与工程振动,41(4):131–144. Qiang S Y,Liu Q F,Wen R Z,Wang H W. 2021. Basin amplification effect of seismic ground motion based on seismic wave numerical simulation in two-dimensional model[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Dynamics,41(4):131–144 (in Chinese).
项梦洁,陈隽. 2021. 考虑场地效应的建筑群动力可靠度PDEM评估[J]. 工程力学,38(8):85–96. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2020.08.0549 Xiang M J,Chen J. 2021. Dynamic reliability evaluation of building cluster considering site effect based on PDEM[J]. Engineering Mechanics,38(8):85–96 (in Chinese).
于彦彦,田浩,韩天成,丁海平. 2022. 断层位置对三维盆地地震效应的影响[J]. 地震学报,44(1):87–95. doi: 10.11939/jass.20210095 Yu Y Y,Tian H,Han T C,Ding H P. 2022. Influence of the finite fault location on the three-dimensional basin seismic effect[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,44(1):87–95 (in Chinese).
张博文,翟盼盼,吕洋,熊峰. 2020. 考虑SSSI效应的城市区域建筑群地震响应分析[J]. 地震工程与工程振动,40(5):187–192. Zhang B W,Zhai P P,Lü Y,Xiong F. 2020. Seismic response analysis of urban building clusters on a regional scale considering structure-soil-structure interaction[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Dynamics,40(5):187–192 (in Chinese).
Applied Technology Council. 2007. Recommended Methodology for Quantification of Building System Performance and Response Parameters[R]. Redwood City,CA:Applied Technology Council:115−128.
Chávez-García F J,Bard P Y. 1994. Site effects in Mexico City eight years after the September 1985 Michoacan earthquakes[J]. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng,13(4):229–247. doi: 10.1016/0267-7261(94)90028-0
Chen S P,Liu Q F,Zhai C H,Wen W P. 2022. Influence of building-site resonance and building properties on site-city interaction:A numerical investigation[J]. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng,158:107307. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2022.107307
Guéguen P,Bard P Y,Chávez-García F J. 2002. Site-city seismic interaction in Mexico City-like environments:An analytical study[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,92(2):794–811. doi: 10.1785/0120000306
Guidotti R,Mazzieri I,Stupazzini M,Dagna P. 2012. 3D numerical simulation of the site-city interaction during the 22 February 2011 MW6.2 Christchurch earthquake[C/OL]//Proceedings of the 15th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering. Lisboa:Sociedade Portuguesa de Engenharia Sismica. [2022-02-16]. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:162175840.
Kato B,Wang G. 2021. Regional seismic responses of shallow basins incorporating site-city interaction analyses on high-rise building clusters[J]. Earthq Eng Struct Dyn,50(1):214–236. doi: 10.1002/eqe.3363
Kham M,Semblat J F,Bard P Y,Dangla P. 2006. Seismic site-city interaction:Main governing phenomena through simplified numerical models[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,96(5):1934–1951. doi: 10.1785/0120050143
Sahar D,Narayan J P. 2016. Quantification of modification of ground motion due to urbanization in a 3D basin using viscoelastic finite-difference modelling[J]. Nat Hazards,81(2):779–806. doi: 10.1007/s11069-015-2105-z
Schwan L,Boutin C,Padrón L A,Dietz M S,Bard P Y,Taylor C. 2016. Site-city interaction:Theoretical,numerical and experimental crossed-analysis[J]. Geophys J Int,205(2):1006–1031. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggw049
Tian Y,Sun C J,Lu X Z,Huang Y L. 2022. Quantitative analysis of site-city interaction effects on regional seismic damage of buildings[J]. J Earthq Eng,26(8):4365–4385. doi: 10.1080/13632469.2020.1828199
Tsogka C,Wirgin A. 2003. Simulation of seismic response in an idealized city[J]. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng,23(5):391–402. doi: 10.1016/S0267-7261(03)00017-4
Uenishi K. 2010. The town effect:Dynamic interaction between a group of structures and waves in the ground[J]. Rock Mech Rock Eng,43(6):811–819. doi: 10.1007/s00603-010-0102-9
Zhang X L,Peng X B,Chen S L,Li X J,Dou Z,He X L,Xu C. 2021. Rapid prediction of strong ground motions from major earthquakes:An example in the Wudu basin,Sichuan,China[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,111(5):2635–2660. doi: 10.1785/0120210066




 下载:
下载: