Analysis of monitoring capability of strong motion sation based on the probability interval of ambient noise
-
摘要:
本文以珠江三角洲地震监测和预警系统粤东密集台网的强震日常记录数据为基础,利用强震台站背景噪声有效值密度函数,研究强震动台站背景噪声频谱的统计规律,建立强震台站背景噪声有效值平均模型、最小模型以及噪声有效值概率分布区间,通过利用强震台站背景噪声有效值概率分布区间与区域地震事件的频率-加速度幅值分布曲线互比的强震台站监测能力分析方法,得到了不同台站每日背景噪声加速度有效值,并估算了强震台站记录不同震级区域地震事件的概率,来评价台站的监测能力。强震台站背景噪声有效值概率分布区间分析方法是背景噪声有效值概率密度分布分析的延伸和拓展,有助于工程地震学中频率域去噪低端截止频率的讨论。由于仪器自噪声和环境噪声的相互作用不同而导致台站的噪声下限不同,强震台站背景噪声最小模型可以作为该台最优监测能力的估计,是强震仪及观测环境的综合指标。
Abstract:This study is based on the strong motion daily records from the dense network of seismic monitoring and early warning systems of the Pearl River Delta in eastern Guangdong. By utilizing the RMS density function of background noise at strong motion stations, we investigate the statistical characteristics of the background noise spectrum at these stations. We establish the average model, minimum model, and probability distribution interval for the RMS of background noise. This forms the basis for a method to analyze the monitoring capabilities of strong motion stations by comparing the probability distribution intervals of background noise RMS with the frequency-acceleration amplitude distribution curves of regional earthquake events.Using this method, we obtain the daily background noise acceleration RMS for different stations and estimate the probability of recording regional seismic events of various magnitudes, thereby evaluating the monitoring capabilities of the stations. The lower noise limits for different stations vary due to the interaction between instrument self-noise and environmental noise. The minimum model of background noise RMS can be used as an estimate of the optimal monitoring capability of a station, serving as a comprehensive indicator of both the strong motion instrument and the observation environment. This also contributes to discussions on the low-end cut-off frequency for denoising in the frequency domain within engineering seismology. The probability distribution interval analysis method for background noise RMS is an extension and expansion of the probability density distribution analysis of background noise RMS.
-
引言
随着实时数据传输的数字强震加速度仪的广泛运用,强震观测网络的应用领域由地震工程学、近场地震学、地震区划图编制与工程结构抗震设计扩展到烈度速报、地震预警、震害的快速评估等实时应用领域(周雍年,2006;卢大伟,李小军,2010)。强震观测数据是震灾预防与地震应急的重要基础,作为其主要组成部分的背景噪声因携带丰富场地、地脉动源等关键信息备受国内外学者关注。
实际上,台站背景噪声分析常用于微震观测领域,包括功率谱密度分析、背景噪声层析成像等方法。其中:功率谱密度分析用于了解台站背景噪声频谱特性、估算背景噪声的频率成分及各成分的相对强弱;概率密度方法是对背景噪声功率谱进行统计分析,可直观地判断观测数据的质量(Bormann,2002;Stehly et al,2006;Abd et al,2013;El Fellah et al,2017)。在功率谱密度分析基础上,设立对比观测实验,将一台经实验室校准过的地震仪,作为参考地震仪与另外一台或两台地震仪安装于同一台基,使用相关分析方法从两或三台地震仪的同步观测数据中扣除相关分量获得非相关分量,并将非相关分量作为地震仪自身噪声的估计值,即利用了参考地震仪来估算被测地震仪的灵敏度、自噪声(Sleeman,2006;Gerner,Bokelmann,2013)及方位角(Holcomb,2002;吕永清等,2007;Tasič,Runovc,2013;Xie et al,2018)等。此外,还可利用台站背景噪声分形特征分析得到宽频带地震台背景噪声在特定尺度下时域波形特征(丁莉莎等,2021)。
国内外学者对强震台站背景噪声也进行了各种分析和利用,2009年Hutt等就Geotech公司的 PA-23,Guralp 公司的CMG-5TC,Kinemetrics公司的ES-T,Nanometrics 公司的Titan以及RefTek 公司的RT-47-01/3五种加速度计的偏移、线性度、自噪声及动态范围等进行测试,认为位于人口稠密地区、道路沿线、旋转机械附近、高射频干扰或电磁干扰环境中的观测墩,或位于软质沉积物上的观测墩,因环境噪声较强不能进行加速度计自噪声测试(Hutt et al,2010);2013年Cauzzi和Clinton (2013)利用瑞士及南加州高质量强震台站建立了强震台站背景低噪声模型(accelerometric low-noise models,缩写为ALNM)和强震台站背景高噪声模型(accelerometric high-noise models,缩写为 AHNM),并指出ALNM主要受传感器及数据采集器自身噪声影响,AHNM的高频段受台站所处城市环境噪声干扰,中频段噪声受微动峰值影响,低频段检测噪声能力受台站安装质量和环境的限制;丁莉莎(2014)在进行高温加速度计研制过程中分别对常温及高温环境下加速度计噪声进行了分析,结果显示高温状态下加速度计噪声明显高于常温工作状态时;江汶乡(2015)在地震预警强震数据处理技术的研究中,得到直接观测的强震加速度仪噪声与相干方法估计的自噪声在量级上的近似性,自噪声可用于判断仪器是否适用于地震预警,针对环境噪声易造成预警系统误触发,提出单台站抗干扰误触发算法。上述研究表明强震台站最小背景噪声功率谱值会受仪器自噪声的影响,而实际监测能力会受观测环境的影响。
强震台站监测能力分析在设计原理及实际应用上与微震观测台站存在差异:首先,利用背景噪声功率谱评估微震观测台站对地震波观测能力的方法是通过建立台站背景噪声水平与可监测的最小地震震级及其震中距之间关系来实现(Welch,1967)。由于微震观测台站主要依赖地震波震相到时进行地震定位,而初动震相检测决定了震级计算的可靠性(Havskov,Alguacil,2007),Schultz等(2015)认为当地震信号功率谱是微震观测台站日常记录的噪声信号功率谱的10倍以上时,P波震相的拾取才不受噪声影响。也有学者通过以往震例数据建立了每个台站监测能力与震级、震中距的函数用以合成特定震级地震监测概率图(Schorlemmer,Woessner,2008)。与微震观测台站不同,强震台站观测更注重天然地震和非天然地震引起的场地或工程结构的强烈震动在某一时刻的最大震动强度。强震台站监测能力受台站背景噪声的限制,对于一定大小的地震,只有当震中距在一定范围之内,地震波到达台站时的振幅高出台站背景噪声时才能被监测仪器记录。为了实现强震台站运行状态在线监控及监测数据质量评价,本文尝试利用强震台站日常记录中的背景噪声进行分析,选择台站对区域地震事件的监测能力作为一项评价标准,从强震台站背景噪声频谱及其统计特征入手,对台站数据进行评价;并结合不同震级区域地震事件的频率-加速度幅值分布进行台站监测能力分析,完成实时强震观测台站数据质量评价及运行状态评估。
1. 数据
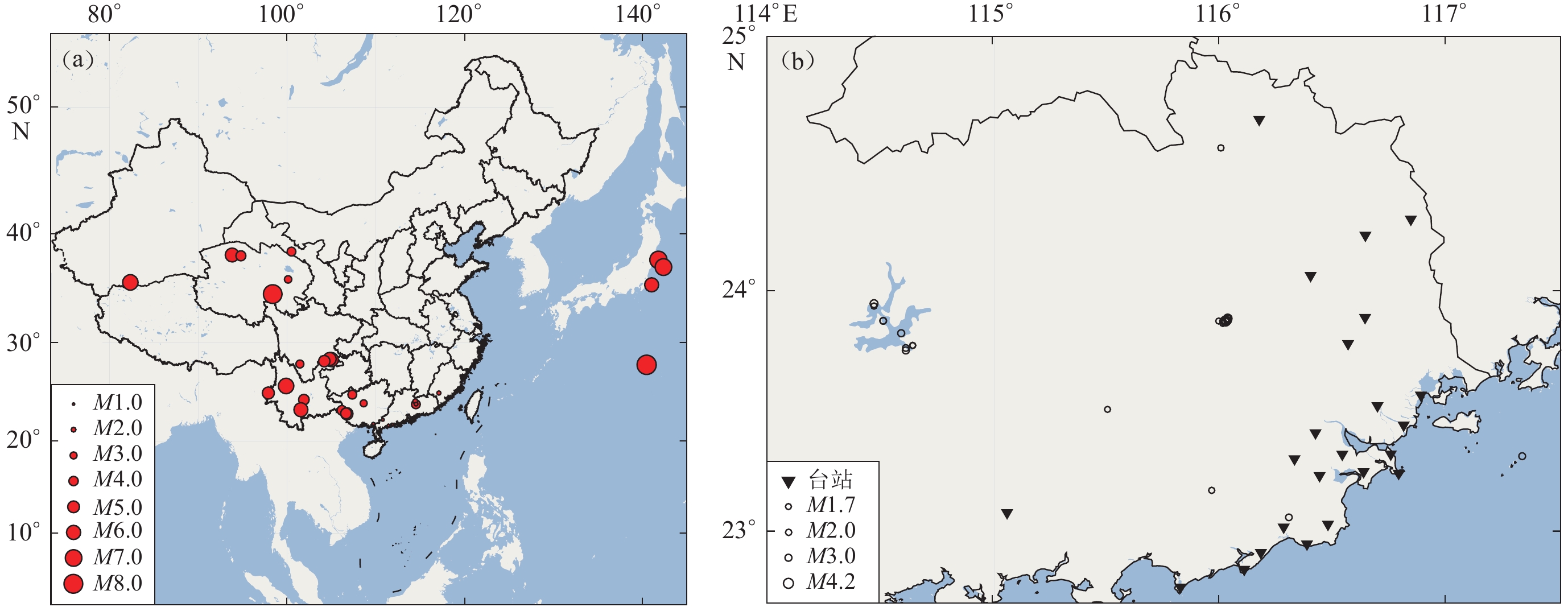
本文收集国内外震中距约在100 km、震级为M1.0—7.0的区域地震事件,区域强震数据来自中国强震动台网中心及日本地球科学和抗灾研究所的K-NET,KiK-net观测网络(NIED,2019),区域地震数据及用于背景噪声分析的日常记录数据来自广东地震台。其中区域强震数据和区域地震事件用于频率-加速度幅值分布模型的建立(图1a),详细信息列于附表1。
![]() 图 1 珠江三角洲地震监测和预警系统粤东密集台网强震观测台站布局及相关地震事件(a) 区域地震频率-加速度幅值分布模型的地震分布;(b) 台站布局及测试地震分布图Figure 1. Layout of strong motion observation stations and related seismic events in the eastern Guangdong dense network of the Pearl River Delta seismic monitoring and early warning system(a) Distribution of earthquakes used to establish the regional earthquake frequency-acceleration amplitude distribution model;(b) Station layout and distribution of test earthquakes
图 1 珠江三角洲地震监测和预警系统粤东密集台网强震观测台站布局及相关地震事件(a) 区域地震频率-加速度幅值分布模型的地震分布;(b) 台站布局及测试地震分布图Figure 1. Layout of strong motion observation stations and related seismic events in the eastern Guangdong dense network of the Pearl River Delta seismic monitoring and early warning system(a) Distribution of earthquakes used to establish the regional earthquake frequency-acceleration amplitude distribution model;(b) Station layout and distribution of test earthquakes广东强震观测从2013年起由事件触发式存储转换为实时传输,至今积累了大量的连续记录,特别是珠江三角洲地震监测和预警系统中的粤东密集台网,该台网结合粤东地区活动断裂构造及地貌特征,共建设75个井下短周期测震站(其中30站增设地面强震加速度计),布设成以间距约为15 km接近正交的北东向、北西向的观测网格和部分依粤东北山区及莲花山脉以北盆地地形条件不规则形状的观测网络,实现了速度及加速度同时记录,为强震台站背景噪声分析提供了数据基础。本文共收集2020年24台强震加速度日常记录数据及59次地震事件进行分析(图1b)。
2. 方法
强震台站背景噪声频谱、频谱统计特征及台站监测能力分析包含以下几个步骤:
2.1 强震台站背景噪声功率谱分析
采用改进周期图法(Welch方法)对强震台站的背景噪声功率谱密度(power spectral density,缩写为PSD)进行分析(Welch,1967;Howard,2002;Havskov,Alguacil,2007):首先,对观测数据据进行去直流和去趋势项、分段以及选择窗函数;然后,估计每段数据的噪声功率谱并转换为加速度功率谱;最后,对所有分段数据的加速度功率谱结果取平均。本文采用的力平衡加速度计平坦响应范围为DC—80 Hz,采样率为100 Hz,研究频带选为DC—40 Hz,不再进行传递函数扣除。
2.2 强震台站噪声有效值概率密度分析
1) 选取连续数天或数周乃至数月的强震日常观测数据,用改进周期图法估计固定长度观测数据的加速度功率谱;
2) 采用1/3倍频程带宽将上述功率谱的有效频带划分为若干子频带(也可使用1/8或1/6倍频程带宽),各子频带的中心频率为:
$$ {f}_{{\rm{c}}}={G}^{\tfrac{{2n+1}}{{2b}}} \text{,} $$ (1) 式中:G为倍频程系数,其值为2或$10^{{{3}}/{{10}} }$;n为使子频带集合与需统计功率谱频带相符合的任意整数;b为倍频程带宽分数的分母,上下限频率如下:
$$ \begin{split}\\ \left\{\begin{array}{c} f_{\rm{h}}=G^{\frac{1}{2b}}f_{\rm{c}}, \\ f_{\rm{l}}=G^{-\frac{1}{2b}}f_{\rm{c}}.\end{array}\right.\end{split} $$ (2) 3) 噪声加速度有效值估算。对各子频带内的台基噪声功率谱进行积分后开方得到各子频带的背景噪声加速度有效值(Bormann,2002),并转换为dB值表示。
4) 统计计算。以2)中选定的子频带与1 dB的有效值为间隔,将从0 Hz到奈奎斯特频率的全频带及−200—0 dB的有效值区间划分为网格。再利用1)中每个固定长度背景噪声有效值结果估算各中心频率有效值占数据总样本的概率密度,并使用不同颜色绘制在频率-加速度图上得到有效值概率密度分布。
5) 最后,分别找出台站背景噪声有效值概率密度分布中每个子频带的最大概率密度值所对应的噪声有效值以及最小噪声有效值作为平均模型和最小模型,并以不同颜色虚线标注。
2.3 强震台站背景噪声有效值概率分布区间
考虑到单一的平均模型不能准确描绘背景噪声概率密度分布较为离散的台站,在此提出台站背景噪声有效值概率分布区间的分析方法。
已知台站背景噪声概率密度分布:
$$P\left\{{f={f}_{i}|{\rm{rms}}={\rm{RMS}}}_{j}\right\}={p}_{ij},{f}_{i}\in {f}_{m},i\in m,{{\rm{RMS}}}_{j}\in [ -\mathrm{200,0} ] ,j\in {N} \text{,} N=201 \text{,} $$ (3) 式中:$ {f}_{m} $为子频带的中心频率集合,m为子频带的个数;$ {{\rm{RMS}}}_{j} $为−200—0 dB有效值区间的任意一个子区间;N为有效值区间总数;$ {p}_{ij} $表示中心频率为$ {f}_{i} $,有效值取值为${{\rm{RMS}}} _{j}$的概率。
跟据分布函数定义(陈魁,2000)可知当中心频率为${f}_{{\rm{c}}},{f}_{{\rm{c}}}\in {f}_{m}$,背景噪声有效值小于${{\rm{RMS}}} _{j}$时的分布函数为:
$$ \varGamma {f}_{{\rm{c}}} ( {{\rm{RMS}}}_{j} ) =P\left\{{f=f}_{ {\rm{c}}}|{\rm{Min}}\_{\rm{model}}\ll {\rm{rms}}{\text{≤}} {{\rm{RMS}}}_{j}\right\}\text{,} $$ (4) $$ \varGamma {f}_{{\mathrm{c}}} ( {\mathrm{RMS}} ) =P\left\{{f=f}_{ {\mathrm{c}}}|{\mathrm{rms}}{\text{≤}} {{\mathrm{RMS}}} _{j}\right\}-P\left\{f={f}_{{\mathrm{c}}}|{\mathrm{rms}} < {\mathrm{Min}}\_{\mathrm{model}}\right\} \text{,} $$ (5) 因为最小模型为仪器本底噪声模型,所以$P\left\{{f=f}_{ {\rm{c}}}|{\rm{rms}} < {\rm{Min}}\_{\rm{model}}\right\}=0$,则:
$$ \varGamma {f}_{{\rm{c}}} ( {\rm{RMS}} ) =P\left\{{f=f}_{ {\rm{c}}}|{\rm{rms}}{\text{≤}} {{\rm{RMS}}}_{j}\right\}=\sum _{j}{p}_{{i}_{c}j} .$$ (6) 此时,$ \varGamma {f}_{{\mathrm{c}}} ( {\mathrm{RMS}} ) $表明中心频率为$ {f}_{{\mathrm{c}}} $时,其背景噪声有效值落在 [ Min_model,$ \mathrm{RMS} $ ] 上的概率,如当$ \varGamma {f}_{{\mathrm{c}}} ( {\mathrm{RMS}} ) =95\text{%} $时,背景噪声有效值落在 [ Min_model,${\mathrm{ RMS }}$95 ] 的概率为95%。
2.4 地震事件汇集及其频率-加速度幅值分布模型
参考Clinton和Heaton (2002)的方法,对收集到的国内外距各台站震中距约为100 km、震级在M1.0—7.0的区域地震事件估算地震事件经过倍频程滤波后各中心频点加速度绝对最大值;然后通过平均各地震记录中不同中心频率绝对最大值得到该震级的频率-加速度幅值分布曲线。
2.5 强震台站监测能力分析
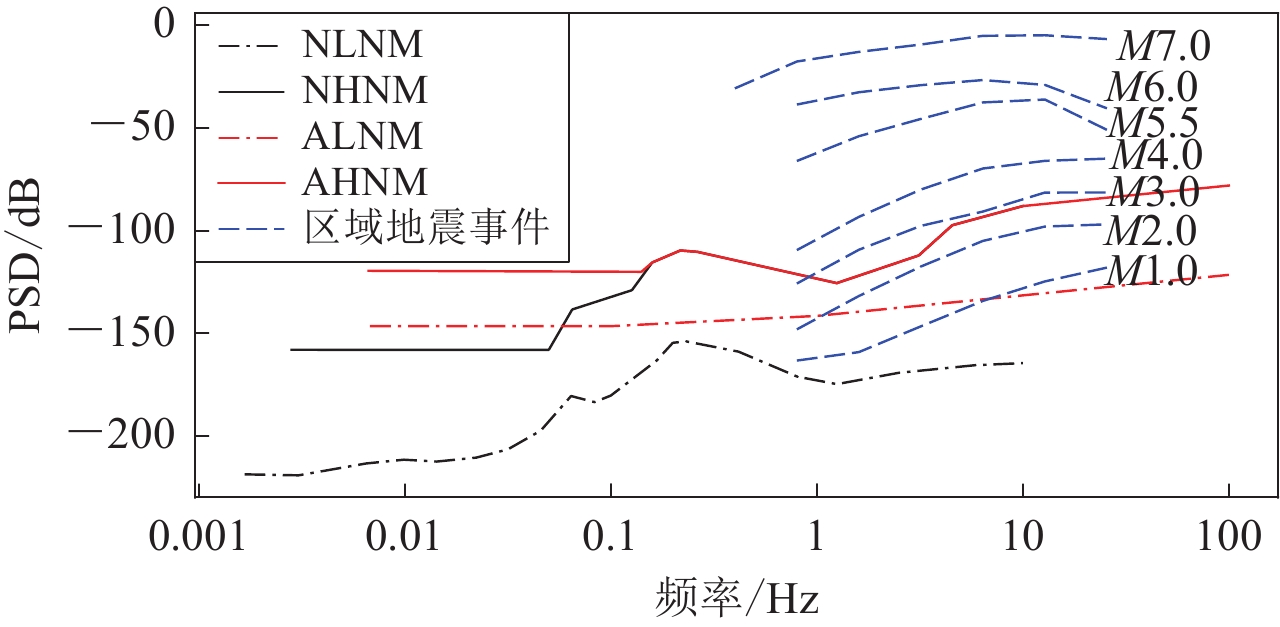
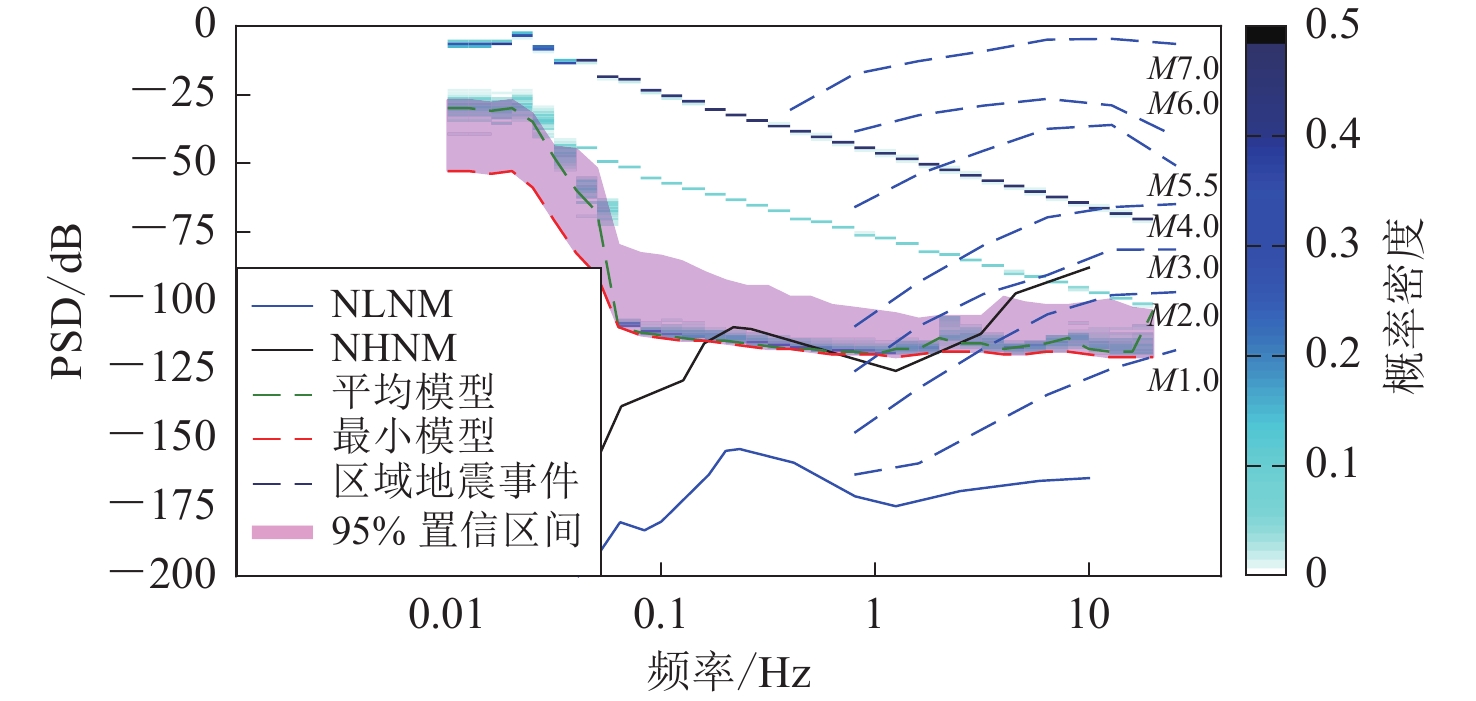
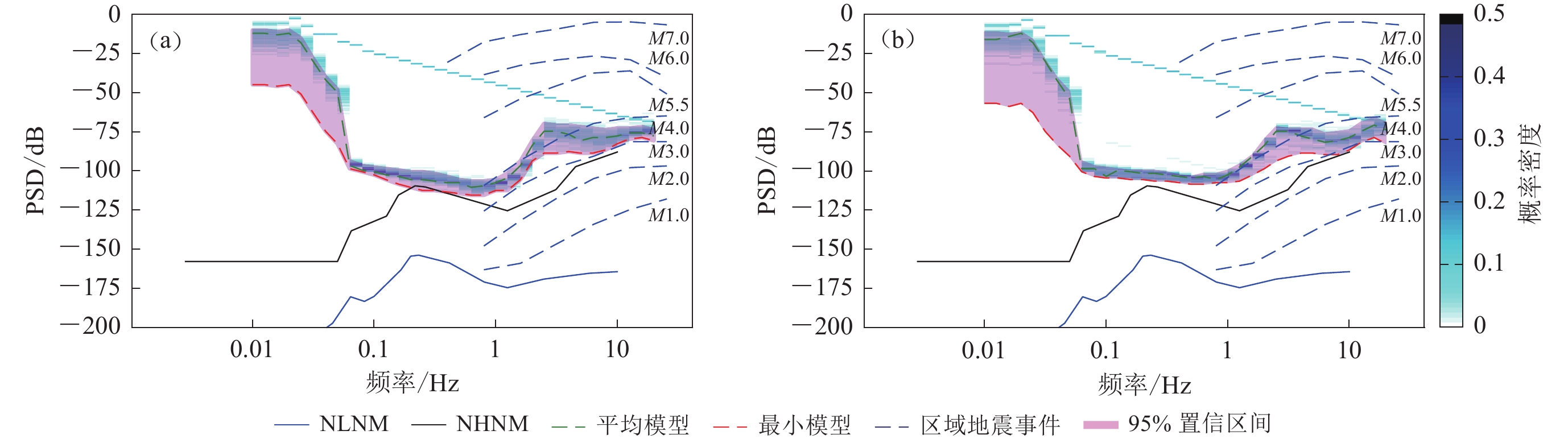
本文将2.1和2.2节中台站连续时间背景噪声有效值概率密度分布与2.4节不同震级频率-加速度幅值曲线、新一代高噪声模型(new high-noise models ,缩写为NLNM)和新一代低噪声模型(new low-noise models ,缩写为NHNM)(Peterson,1993)及高质量强震台站背景噪声模型(AHNM及ALNM)(Cauzzi et al,2013)进行对比;通过对比不同概率下台站背景噪声有效值概率密度分布区间上限与不同震级频率-加速度幅值曲线(图2)的接近程度实现台站监测能力评估。
![]() 图 2 噪声加速度模型与区域地震事件频率-幅度分布曲线 (Clinton,Heaton,2002) 对比Figure 2. Comparison of the noise acceleration model with the frequency-amplitude distribution curve of regional earthquake events (modified fromClinton, Heaton,2002)
图 2 噪声加速度模型与区域地震事件频率-幅度分布曲线 (Clinton,Heaton,2002) 对比Figure 2. Comparison of the noise acceleration model with the frequency-amplitude distribution curve of regional earthquake events (modified fromClinton, Heaton,2002)3. 强震台站监测能力分析
利用强震台站背景噪声有效值的平均模型、最小模型及概率分布区间结合区域地震事件的频率-加速度幅值曲线评估台站的监测能力。其中:背景噪声平均模型能有效地反映背景噪声随频率分布的趋势;背景噪声有效值概率分布区间能揭示背景噪声分布的离散度。但上述统计规律会被台站频繁地功能测试所影响,所以建立平均模型和概率分布区间前需对功能测试信号进行识别和分离以排除其影响。
3.1 功能测试信号的影响和处理
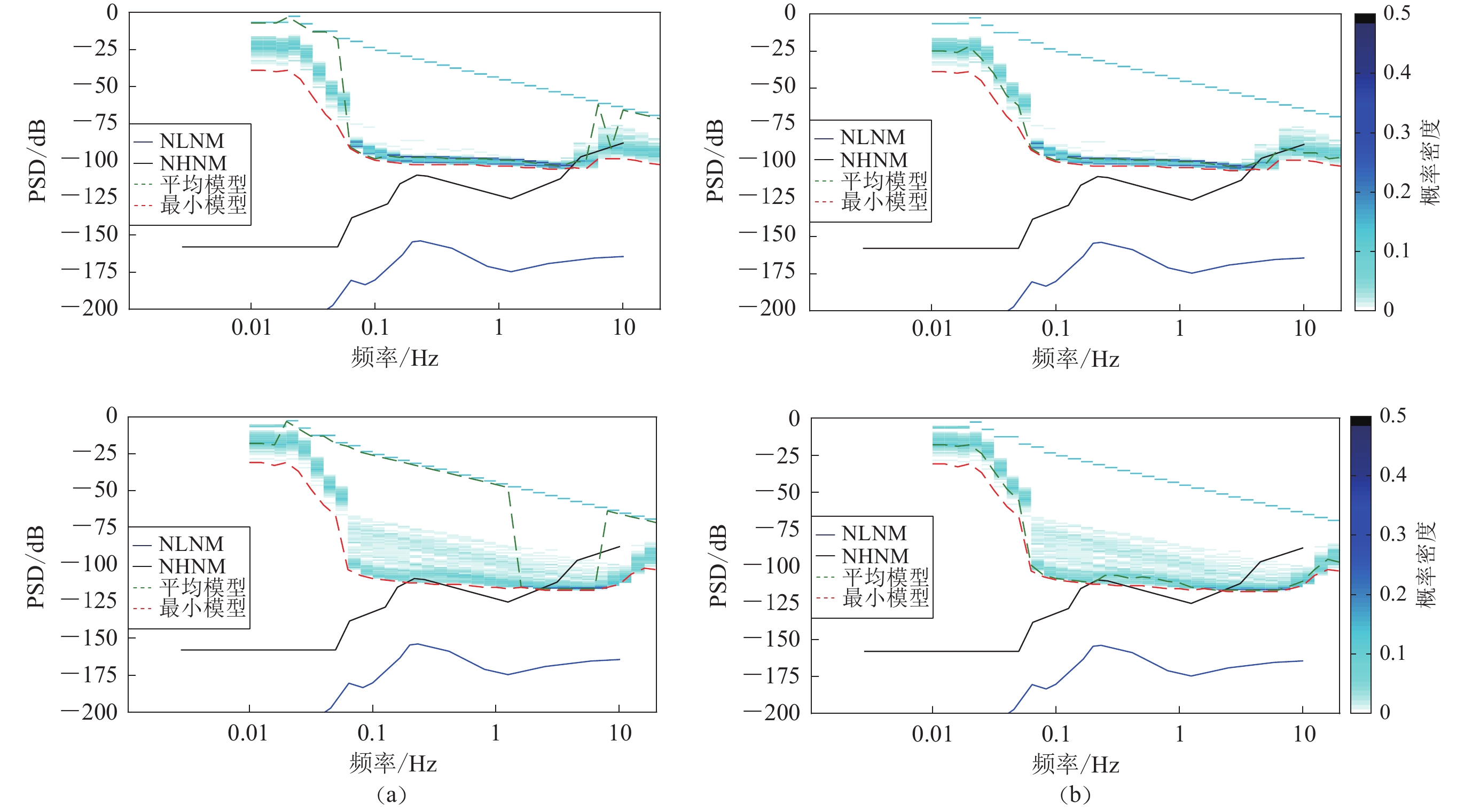
依据国家地震行业标准《强震动观测技术规程》(中国地震局,2017)的要求,各强震台网中心应定期对在运行设备进行功能测试,即通过数据采集器向加速度计发送阶跃标定信号。为保证标定信号的信噪比,标定信号能量应远大于台站背景噪声,因此标定信号对台站背景噪声平均模型的计算有很大影响。如图3所示,HLQZ台因频繁进行功能测试,大部分背景噪声有效值概率密度分布在频带0.01—50 Hz内,噪声平均模型呈跳变形态(见图3a上);而HLZT台受观测环境及多次功能测试影响,背景噪声平均模型出现跳变(见图3a下)。本文需对阶跃标定信号有效值分布及概率分布规律进行如下分析处理。
方波信号时域表达(王广福,1986):
$$ \begin{split}& i ( t ) ={I}_{0} [ {u}_{0} ( t ) -{u}_{0} ( t-\tau ) + {u}_{0} ( t-2\tau ) -{u}_{0} ( t-3\tau ) ] , \end{split}$$ (7) 式中,$ {u}_{0} $为单位阶跃函数,$ \tau $为阶跃标定宽度,$ {I}_{0} $为标定电流。
方波信号频域表达:
$$ I ( {\mathrm{j}}\omega ) ={I}_{0}\left({\int }_{0}^{\tau }{{\rm{e}}}^{-{\mathrm{j}}\omega t}{\mathrm{d}}t+{\int }_{2\tau }^{3\tau }{{\rm{e}}}^{-{\mathrm{j}}\omega t}{\rm{d}}t\right), $$ (8) $$ I ( {\mathrm{j}}\omega ) ={I}_{0}{\tau }^{2}\left|\frac{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\left(\dfrac{\omega \tau }{2}\right)}{\dfrac{\omega \tau }{2}}\right|{ ( {\rm{e}}}^{-{\mathrm{j}}\frac{\omega \tau }{2}}+{{\rm{e}}}^{-{\mathrm{j}}\frac{5\omega \tau }{2}} ) , $$ (9) 式中,$ I ( {\mathrm{j}}\omega ) $为$i ( t ) $的频率特性,j为虚数单位,$ \omega$为角频率。
方波信号谱的模为:
$$ \left|I ( {\mathrm{j}}\omega ) \right|={I}_{0}{\tau }^{2}\left|\frac{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\left(\dfrac{\omega \tau }{2}\right)}{\dfrac{\omega \tau }{2}}\right| \sqrt{{\left[\mathrm{c}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{s}\left(\frac{\omega \tau }{2}\right)+\mathrm{c}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{s}\left(\frac{5\omega \tau }{2}\right)\right]}^{2}+{\left[\mathrm{s}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\left(\frac{\omega \tau }{2}\right)+\mathrm{s}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\left(\frac{5\omega \tau }{2}\right)\right]}^{2}}. $$ (10) 根据IEEE对噪声功率谱定义和Parseval定理(Howard,2002):信号$i ( t ) $在区间$ [ 0,T ] $内存在${\displaystyle\int }_{0}^{T}{i ( t ) }^{2}{\rm{d}}t={\displaystyle\int }_{-\infty }^{\infty }\varphi ( {\mathrm{j}}\omega ) {\rm{d}}\omega ={\displaystyle\int }_{-\infty }^{\infty }{\left|I ( {\mathrm{j}}\omega ) \right|}^{2}{\rm{d}}\omega$,能量谱密度为$ \varphi ( {\mathrm{j}}\omega ) ={\left|I ( {\mathrm{j}}\omega ) \right|}^{2} $;又因为在区间$ [ 0,T ] $上信号平均功率$\overline{P} ( T ) ={1}/{T}{\displaystyle\int }_{0}^{T}{i ( t ) }^{2}{\rm{d}}t={\displaystyle\int }_{-\infty }^{\infty }X ( {\mathrm{j}}\omega ) {\rm{d}}\omega$,故信号的功率谱密度$X ( {\mathrm{j}}\omega ) = {1}/{T}\varphi ( {\mathrm{j}}\omega ) ={{1}/{T}\left|I ( {\mathrm{j}}\omega ) \right|}^{{\rm{2}}}$,此时:
$$\begin{split}& 10{\rm{lg}}X ( {\mathrm{j}}\omega ) -20{\rm{lg}} ( \left|I ( {\mathrm{j}}\omega ) \right| ) -10{\rm{lg}}T=-20{\rm{lg}}\omega +20{\rm{lg}}{I}_{0}+20{\rm{lg}}2+20{\rm{lg}}\tau +\\& 10{\rm{lg}}\left\{{\left[\mathrm{c}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{s}\left(\frac{\omega \tau }{2}\right)+\mathrm{c}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{s}\left(\frac{5\omega \tau }{2}\right)\right]}^{2}+{\left[\mathrm{s}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\left(\frac{\omega \tau }{2}\right)+\mathrm{s}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\left(\frac{5\omega \tau }{2}\right)\right]}^{2}\right\}+20{\rm{lg}}\left(\left|\mathrm{s}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\left(\frac{\omega \tau }{2}\right)\right|\right) - 10{\rm{lg}}T=\\& -20{\rm{lg}}\omega +20{\rm{lg}}{I}_{0}+20{\rm{lg}}2+20{\rm{lg}}\tau +10{\rm{lg}} [ 2+2\mathrm{cos} ( 2\omega \tau ) ] +20{\rm{lg}}\left|\mathrm{sin}\left(\frac{\omega \tau }{2}\right)\right|-10{\rm{lg}}T \text{,} \end{split}$$ (11) 式中,$20{\mathrm{lg}}{{I}}_{0}+20{\rm{lg}}2+20{\mathrm{lg}}\mathrm{\tau }$及$ 10\lg T $为常数项,$10{\mathrm{lg}} [ 2+2\mathrm{c}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{s} ( 2\mathrm{\omega }\mathrm{\tau } ) ] \in ( -\mathrm{\infty },6.020\;6 ] $并呈$ \pi/\tau $周期变化,$20{\rm{lg}}\left(\left|\mathrm{s}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\left({\mathrm{\omega }\mathrm{\tau }}/{2}\right)\right|\right)\in ( -\mathrm{\infty },0 ] $并呈$ 4\pi/\tau $周期变化,因此,随$ \mathrm{\omega } $的增加$ -20\lg \mathrm{\omega } $逐渐成为标定信号功率谱的优势项。
最后,在整个频率范围内以恒定的相对带宽(RBW)从信号功率谱密度中计算有效值振幅,其中:$\omega=2\pi f,\mathrm{R}\mathrm{B}\mathrm{W}={G}^{{1}/{2b}}-{G}^{-{1}/{2b}},{f}_{{\mathrm{c}}}={G}^{ ( 2n+1 ) /2b}$;此时,中心频率${f}_{{\rm{c}}}$的噪声功率谱密度为${X ( f}_{ {\rm{c}}} ) =\displaystyle\sum\limits _{{f}_{{\rm{l}}}}^{{f}_{{\rm{h}}}}X ( f ) $;当f>0.1 Hz,阶跃标定信号功率谱密度$10{\rm{lg}}{X ( f}_{ {\rm{c}}} ) $与${\rm{lg}}{f}_{{\rm{c}}}$之间随${f}_{{\rm{c}}}$增加呈现强线性关系,斜率为−20。
而信号有效值为:
$$\begin{split} {N}_{\mathrm{r}\mathrm{m}\mathrm{s}}{|}_{{f}_{{\rm{c}}}}= \sqrt{\displaystyle\sum _{{f}_{l}}^{{f}_{h}}X ( f ) \cdot{f}_{{\rm{c}}}\cdot \mathrm{R}\mathrm{B}\mathrm{W}}\,\, \text{,} \end{split}$$ (12) $$ \begin{split}20{\rm{lg}} ( {N}_{\mathrm{r}\mathrm{m}\mathrm{s}}{|}_{{f}_{{\rm{c}}}} ) =10{\rm{lg}}\left(\sum _{{f}_{{\rm{l}}}}^{{f}_{{\rm{h}}}}X ( f ) \cdot{f}_{{\rm{c}}} \cdot \mathrm{R}\mathrm{B}\mathrm{W}\right) =10{\rm{lg}}\left(\sum _{{f}_{{\rm{l}}}}^{{f}_{{\rm{h}}}}X ( f ) \right)+10{\rm{lg}}{f}_{{\rm{c}}}+10{\rm{lg}}\mathrm{R}\mathrm{B}\mathrm{W} \text{,} \end{split}$$ (13) 因此,当f>0.1 Hz时:
$$ 10{\rm{lg}}\left(\sum _{{f}_{{\rm{l}}}}^{{f}_{{\rm{h}}}}X ( f ) \right)=10{\rm{lg}}{X ( f}_{{\rm{c}}} ) \to -20{\rm{lg}}{f}_{{\rm{c}}} \text{,} $$ (14) $$ 20{\rm{lg}} ( {N}_{\mathrm{r}\mathrm{m}\mathrm{s}}{|}_{{f}_{{\rm{c}}}} ) \to -10{\rm{lg}}{f}_{{\rm{c}}} .$$ (15) 据此可直接将阶跃标定信号的有效值分布从台站背景噪声有效值概率密度分布结果中识别出来,如HLQZ台和HLZT台的背景噪声平均模型从阶跃标定信号有效值概率密度分布中分离出,真实反映台站背景噪声频谱分布(图3b)。此外从目前数据结果来看,高信噪比的标定信号严重影响台站对地震事件的监测能力,且存在大震误触发的危险。
3.2 强震台站背景噪声有效值概率分布区间
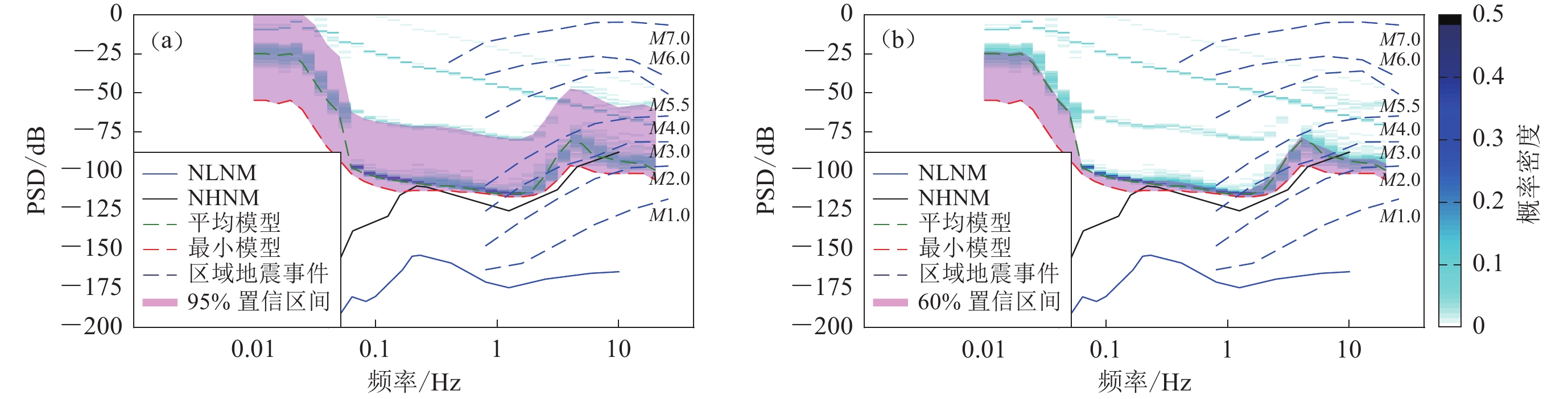
强震台站背景噪声有效值概率分布区间综合最小模型和背景噪声分布概率统计特征,更全面地反映强震台站背景噪声分布。排除功能测试影响后,HLQZ台最小噪声模型及平均模型均高于HLZT台,但是HLQZ台95%背景噪声有效值分布区间范围远小于HLZT台;换言之,HLZT台最优监测能力优于HLQZ台,但是观测环境一致性较HLQZ台差,低频段监测能力也差于HLQZ台,监测能力整体评估难度高于HLQZ台 (图4)。
3.3 强震台站监测能力评估
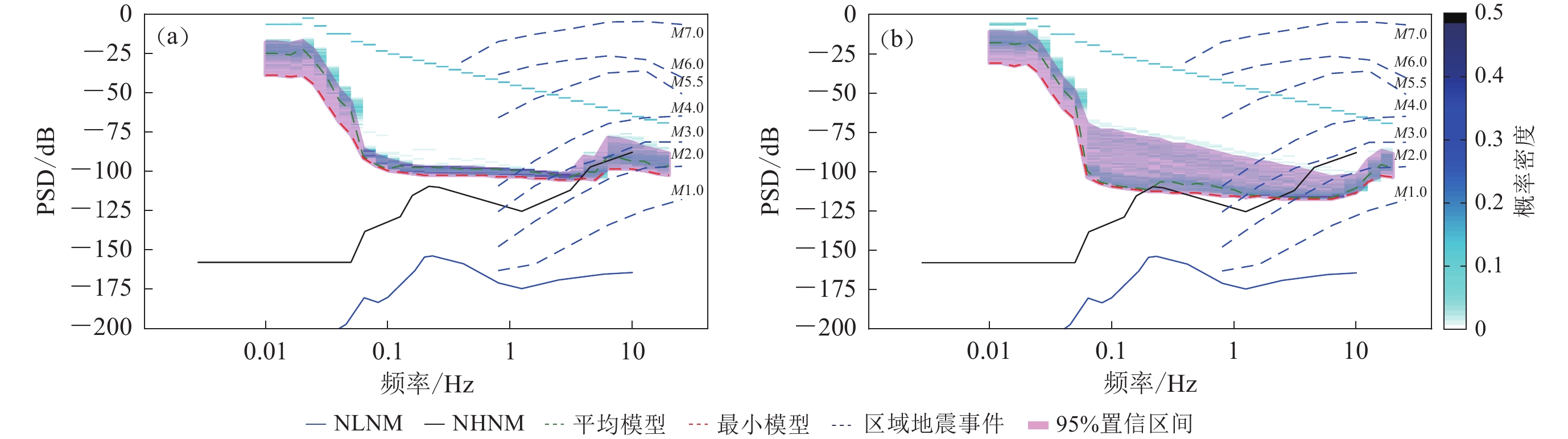
观测环境对强震台站背景噪声的影响主要分布在1—20 Hz频带范围内(Peterson,1993),能量过大时也往往会辐射到低频段,从24台背景噪声有效值概率密度分布结果中发现观测环境较好的台站(如CAGHD等)的最小噪声模型与Hutt等(2010)对The Albuquerque Seismological Laboratory 加速度仪的自噪声模型测试结果接近(图5),且远大于ASL观测山洞环境噪声。Cauzzi和Clinton (2013)利用高质量强震台研究结果也指出强震台站低背景噪声模型主要受传感器及数据采集器自身噪声影响。因此,强震台站背景噪声最小模型可作为强震仪及观测环境的综合指标刻画台站最优监测能力,如HLZT台最优监测能力明显优于HLQZ台(图4)。
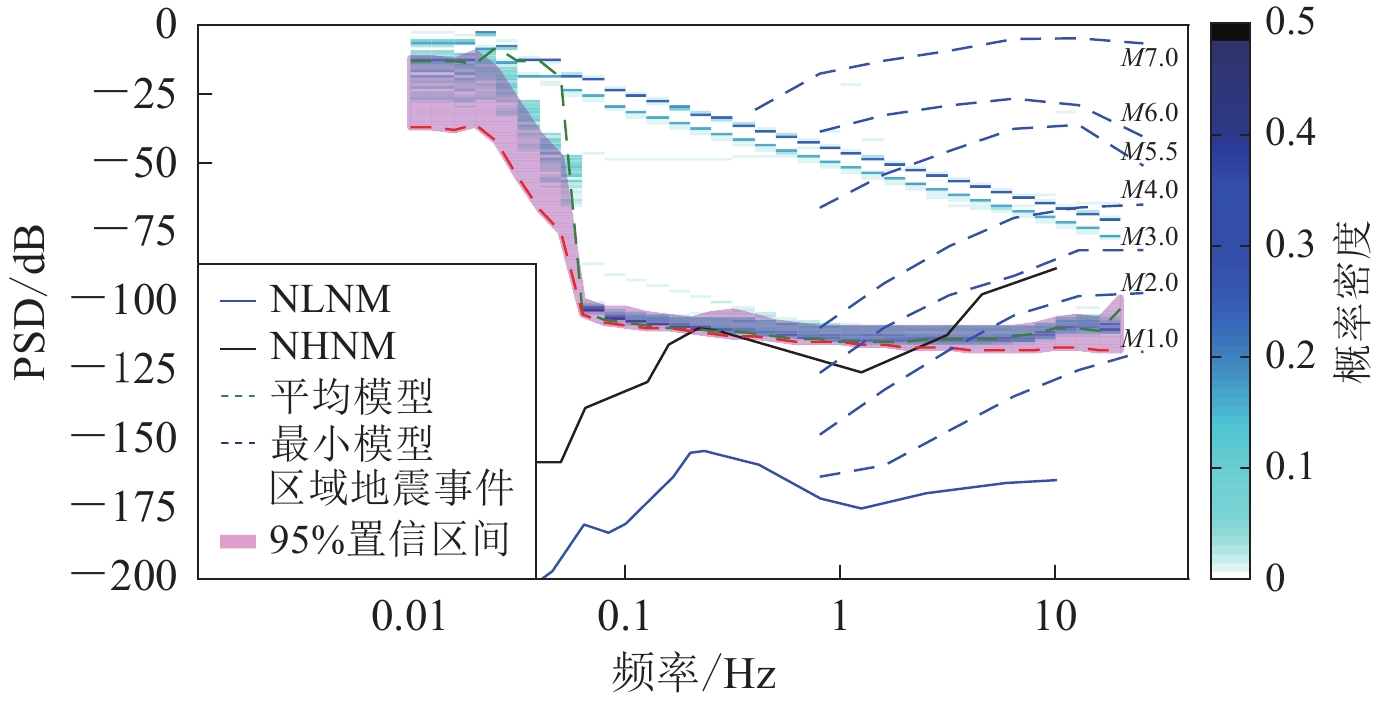
结合背景噪声有效值概率分布区间和区域地震事件的频率−加速度幅值分布,低于不同震级下的区域地震事件加速度分布曲线的背景噪声有效值分布区间的最大概率表示该台站记录到不同震级地震事件的概率.如受观测环境影响,CNLG台利用单一平均模型评估该台监测能力的误差远高于其它台站,引入概率区间后可认为CAGHD台能记录到震中距为70—150 km范围内大于M2.0地震的概率接近99%,CAGHD台能记录震中距为70—150 km范围内M≤1.0地震的概率为0 (图5)。CNLG台能记录到距离台站震中距为70—150 km范围内M>4.0地震的概率接近95%;记录到距离台站震中距为70—150 km范围内M>3.0地震的概率约为60%;记录到台站震中距为70—150 km范围内约M2.0地震的概率接近为0 (图6)。
4. 结果及分析
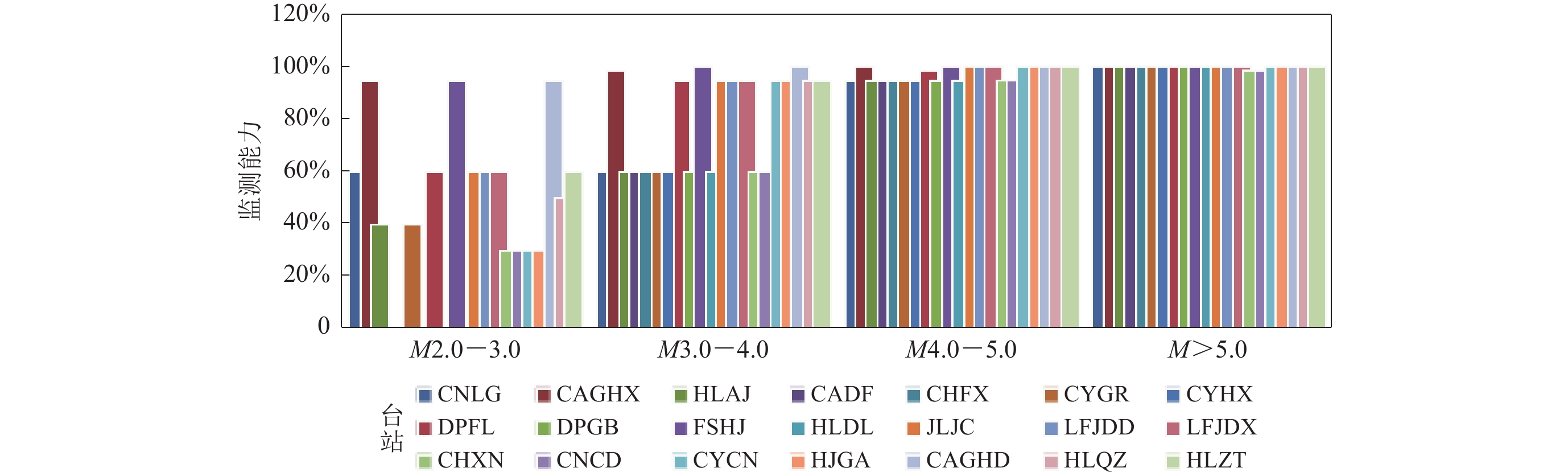
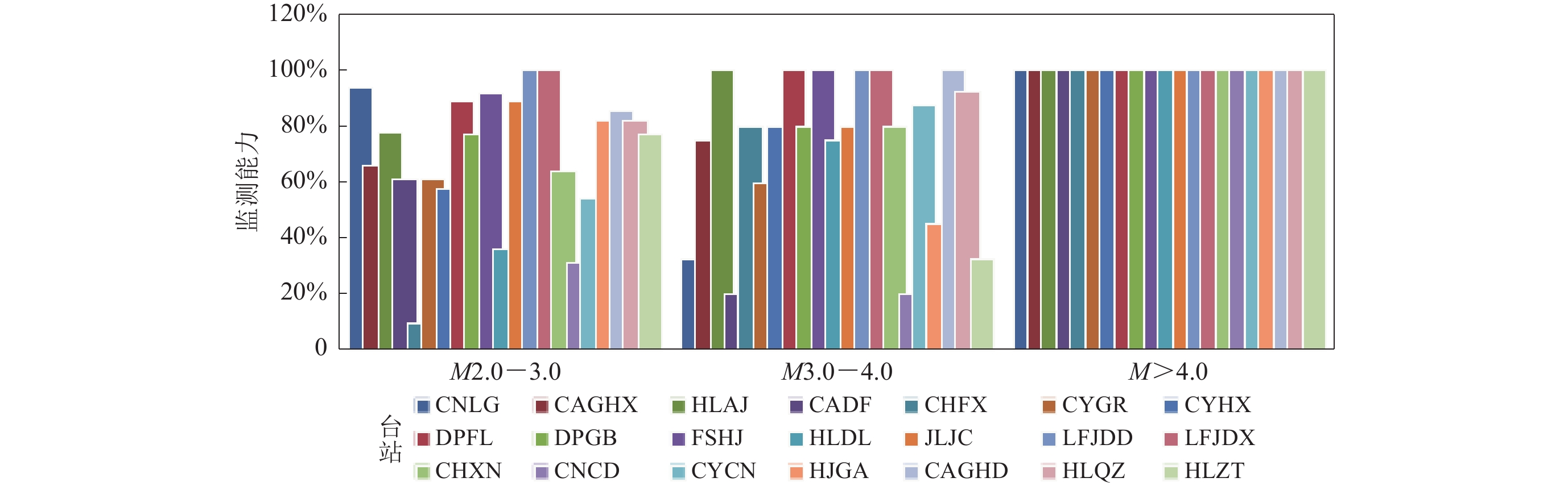
利用2020年24个强震台站日常记录数据分析各台监测能力,我们发现珠江三角洲地震监测和预警系统粤东密集台网中多数强震台站能记录到距离台站震中距为70—150 km范围内M>4.0地震的概率为95%,部分台站有95%概率记录到M≥2.0区域地震;其余台站受观测环境影响,仅能记录M≥5.5的地震(图7)。这是由于同处于人口密集地区的台站实际社会活动的类型、强度及密集程度不同,故台站背景噪声概率密度分布不同,平均噪声模型及最小噪声模型也不尽相同,因而导致各台的监测能力存在差异(表1)。
表 1 台站监测能力评估表Table 1. Evaluation table of monitoring capability for typical stations台站 区域地震最优
监测能力区域地震监测
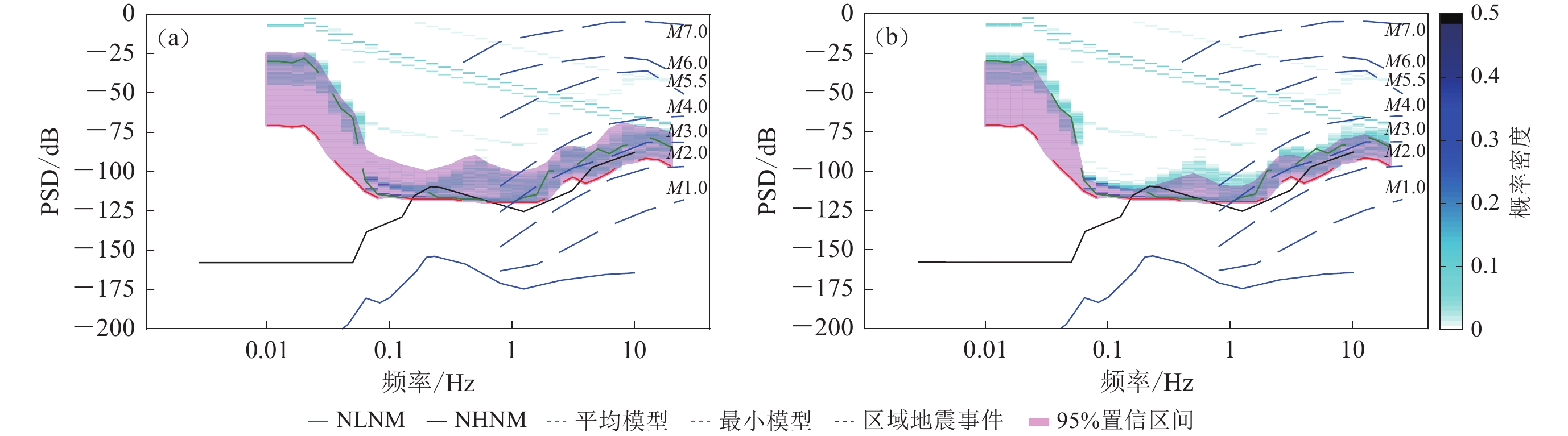
能力 (≥95%)观测环境 台站位置 观测环境影响因素 CNLG 约M2.0 M>4.0 学校教学楼间绿化带内 师生课间活动 CAGHX M>1.0 M>2.0 学校教学楼后面人迹罕至的空地 鲜少人流 HLAJ M>2.0 M≥5.5 村委办公室内 师生课间活动,村委办公活动 CADF M>3.0 M>4.0 学校围墙附近 师生课间活动,校外车辆和人流 CHFX M>3.0 M>4.0 学校围墙附近 师生课间活动,校外车辆和人流 CYGR M>2.0 M≥4.0 学校内,距教学楼3 m 师生课间活动 CYHX M>3.0 M>4.0 潮阳区河溪邮政支局内 工作人员办公活动 DPFL 约M2.0 M≥3.0 学校内,距离教学楼约30 m 师生课间活动 DPGB 约M3.0 M>4.0 学校内,距离垃圾池6 m,距离围墙1 m 师生课间活动 FSHJ M>1.0 M>2.0 学校内篮球场外侧 鲜少人流 HLDL M>3.0 M≥4.0 学校体育馆左侧 师生课间活动 JLJC 约M2.0 M>2.0 学校科技馆内一角,距离围墙1.5 m 师生课间活动 LFJDD 约M2.0 M>2.0 村委办公楼外右侧后方,靠近前边村委围墙旁 工作人员办公活动 LFJDX M>2.0 M≥3.0 村委进大门后右方空地的一角, 工作人员办公活动 CHXN 约M3.0 约M4.0 六合围管理站院内,海边防洪渠旁 工作人员办公活动 CNCD 约M3.0 M≥4.0 学校内,距围墙3米,距教学楼4 m 师生课间活动 CYCN 约M3.0 M>3.0 学校路边的绿化带内,据教学楼6 m 师生课间活动 HJGA 约M3.0 M>3.0 市区幼儿园内,距教学楼3 m 师生课间活动 CAGHD M>1.0 M>2.0 村委院角落 鲜少人流 HLQZ M>2.0 M>3.0 学校教学楼左侧(食堂后方) 师生课间活动 HLZT 约M2.0 M>3.0 学校内,距离教学楼较远 师生课间活动 HDBPZ 数据异常 HJDH LFJS 同处于学校教学楼附近的CAGHX台站和HLAJ台站因人类活动的频度不同,1—20 Hz频带范围内背景噪声有效值分布完全不同,CAGHX台在1—20 Hz频带范围95%的背景噪声有效值低于−100 dB,接近M2.0区域地震的加速度幅值分布,最小模型接近−120 dB;而HLAJ台在1—20 Hz频带范围内最小模型M2.0区域地震的加速度幅值分布,95%的背景噪声有效值高于−100 dB,且大于M>3.0区域地震的加速度幅值分布。上述分析表明CAGHX台95%概率能记录到M>2.0区域地震;HLAJ台60%概率能记录到M≥4.0区域地震,95%概率能记录到M≥5.5区域地震(图8,9)。
CADF台和CHFX台同处于学校围墙附近,且围墙外为供人流和车辆通行的街道,具有相似的观测环境,故两台1—20 Hz频带范围内背景噪声有效值分布相似程度高,95%的背景噪声有效值均介于M3.0—4.0区域地震加速度幅值分布之间,因此两台均存在95%概率能记录到M4.0及以上区域地震(图10)。
2020年粤东密集台网150 km范围内共发生M>4.0地震1次,M3.0—4.0地震8次,M2.5—3.0地震20次,M2.0—2.5地震30次,得出2020年粤东密集台网实际监测能力示意图(图11);综合考虑台站网络通讯及设备故障等影响后认为利用背景噪声功率谱概率密度方法可有效分析珠江三角洲地震监测和预警系统粤东密集台网强震观测台站的监测能力。
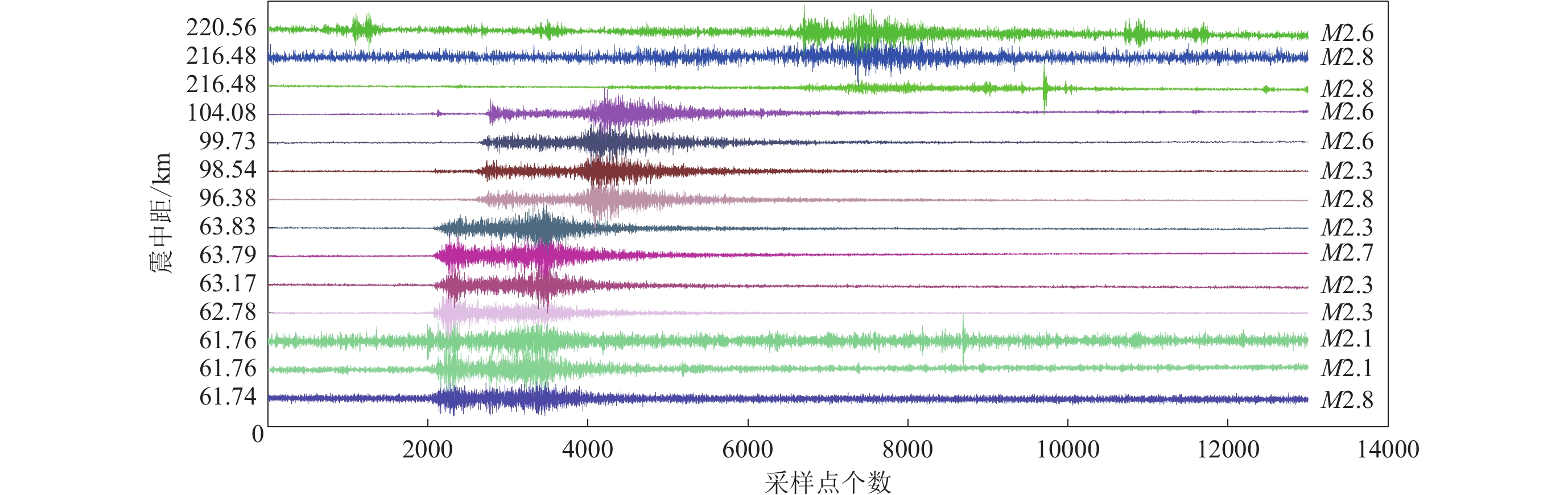
根据背景噪声功率谱概率密度分析预估CAGHD台在2020年95%概率监测到M>2.0地震。实际上,CAGHD台在20次M2.5—3.0地震中有12次因故无数据,其余8次地震中清晰记录到6次,未清晰记录的2次地震震中距大于200 km;30次M2.0—2.5地震中有24次因故无数据,其余6次地震均被清晰记录到(图12),与CAGHD台背景噪声功率谱概率密度分析预评估相吻合。
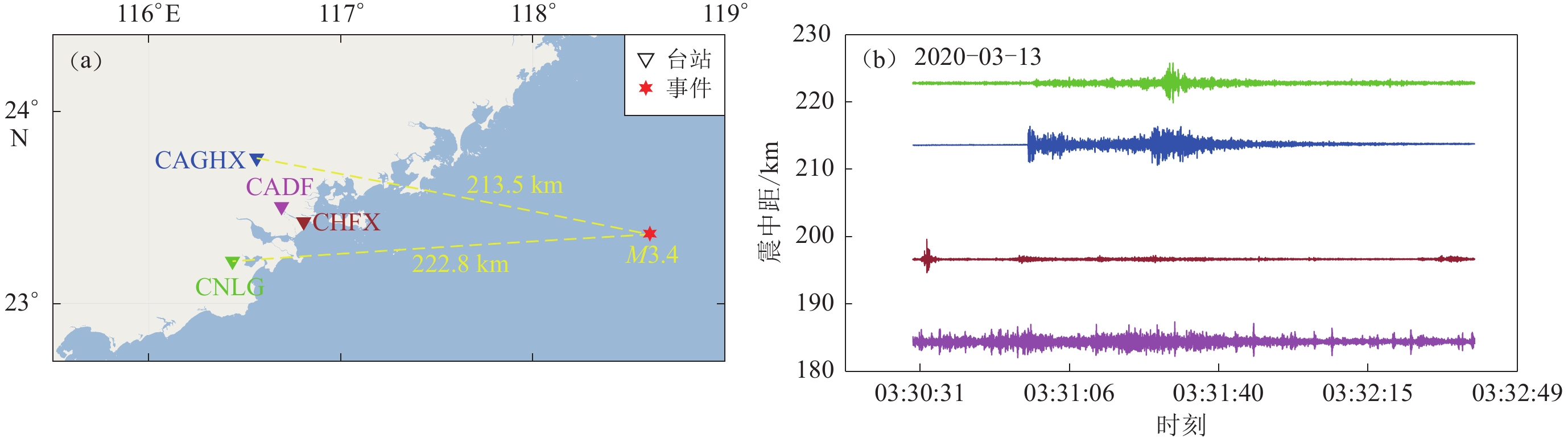
再以2020年3月13日发生在台湾海峡的M3.4地震为检验震例,CAGHX台(距离震中213.5 km)能清晰记录到地震,HLAJ台因仪器故障缺少该段时间记录,CHFX台(距离震中184.1 km)、CADF台(距离震中196.4 km)、CNLG台(距离震中222.8 km)因背景噪声影响识别不出此地震事件,与表1监测能力评价结果一致,验证了本文提出的通过研究台站背景噪声有效值分布评估台站监测能力的方法(图13)。
5. 结论
本文以强震台站背景噪声功率谱分析及概率密度分布分析为基础,提出强震台站背景噪声有效值概率分布区间分析方法,并结合区域地震事件的频率−加速度幅值分布曲线,有效实现强震台站监测能力分析。将方法应用于 珠江三角洲地震监测和预警系统粤东密集台网强震观测台站我们得到:① 强震台站背景噪声有效值概率分布区间分析是背景噪声有效值概率密度分布分析的延伸和拓展;对背景噪声进行长时间有效值概率密度统计,能够定性反映背景噪声在各个频点的幅值分布,而背景噪声有效值概率分布区间明确了噪声幅值分布范围的概率。② 排除阶跃标定信号对有效值概率密度分布估计的影响,优化强震加速度仪监测能力评价方法。③ 不同台站能记录到的噪声下限由于仪器自噪声及环境噪声的相互作用而不同,强震台站背景噪声最小模型可以作为该台最优监测能力,是强震仪及观测环境的综合指标。④ 粤东密集台网中台站多建设在城市主要街道或学校等,受台站环境噪声影响,不同台站监测能力受台站观测环境影响甚大,合理选择建台地址能有效提高台站监测能力。⑤ 利用背景噪声模型与地震事件频率-加速度分布曲线的对比也有助于工程地震学中频率域去噪低端截止频率的讨论。
后续将持续尝试讨论场地类型对背景噪声功率谱的影响,探讨高质量强震台站用于噪声成像的可能性;尝试步进搜索强震台站获取地震记录的概率,探索强震监测网络加速度有效值的二维分布。
中国强震动台网中心和广东省地震局广东地震台为本文提供数据,中国地震局地球物理研究所杨大克研究员和港震公司薛兵研究员对本文的研究提出了宝贵的意见,作者在此一并表示感谢。
1 本文涉及地震事件列表序号 发震时间 M 震中地区 数据类型 目的 年−月−日 时:分 1 2 021−05−21 23:13 3.4 云南漾濞 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 2 2 014−07−12 03:21 7.0 本州东海岸近海 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 3 2 015−05−30 19:23 8.1 小笠原群岛地区 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 4 2 018−09−08 10:31 5.9 云南墨江 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 5 2 019−06−17 22:55 6.0 四川长宁 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 6 2 019−07−04 10:17 5.5 四川珙县 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 7 2 020−01−07 22:09 3.7 甘肃肃南 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 8 2 020−03−24 22:39 4.2 青海海西 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 9 2 020−06−25 03:47 5.9 本州东海岸近海 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 10 2 020−12−24 21:06 3.1 青海兴海 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 11 2 021−01−23 09:59 4.8 云南盐津 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 12 2 021−02−13 22:07 7.3 本州东海岸近海 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 13 2 021−05−21 21:48 6.5 云南漾濞 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 14 2 021−05−21 21:55 5.0 云南漾濞 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 15 2 021−05−21 21:55 5.0 云南漾濞 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 16 2 021−05−21 21:56 4.6 云南漾濞 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 17 2 021−05−21 21:56 4.6 云南漾濞 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 18 2 021−05−21 22:31 5.2 云南漾濞 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 19 2 021−05−21 23:13 3.4 云南漾濞 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 20 2 021−05−21 23:23 4.5 云南漾濞 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 21 2 021−05−22 02:04 7.4 青海玛多 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 22 2 021−05−22 02:28 4.2 云南漾濞 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 23 2 021−05−22 09:48 4.2 云南漾濞 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 24 2 021−05−22 20:14 4.7 云南漾濞 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 25 2 021−05−27 21:06 4.9 青海玛多 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 26 2 021−05−27 19:52 4.0 云南漾濞 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 27 2 021−06−12 18:00 5.1 云南盈江 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 28 2 021−06−16 16:48 5.8 青海茫崖 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 29 2 021−06−28 19:48 4.5 云南双柏 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 30 2 017−07−15 01:41 3.7 广西南丹 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 31 2 017−08−01 06:31 3.0 广西忻城 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 32 2 017−08−13 11:10 3.1 广东东源 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 33 2 017−08−15 13:16 4.1 广西靖西 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 34 2 017−12−08 01:50 1.8 福建龙岩 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 35 2 017−12−20 19:07 1.6 广东东源 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 36 2 017−12−25 14:48 1.0 广东阳江 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 37 2 017−12−29 11:18 1.3 广西博白 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 38 2 017−12−29 18:19 1.2 广东信宜 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 39 2 017−12−30 12:13 3.4 四川盐源 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 40 2 017−12−30 17:06 2.0 广东东源 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 41 2 017−12−30 23:11 1.2 广东茂名 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 42 2 019−11−25 09:18 5.2 广西靖西 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 43 2 019−11−28 07:49 4.6 广西靖西 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 44 2 020−06−26 05:05 6.5 新疆于田 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 45 2 021−04−02 05:40 3.7 广东东源 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 46 2 021−07−02 13:41 2.1 广东连平 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 47 2 021−07−19 12:18 1.6 广东东源 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 48 2 020−01−20 04:17 4.2 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 49 2 020−05−25 11:24 3.6 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 50 2 020−05−22 22:40 3.3 广东东源 强震数据 检验地震 51 2 020−04−01 22:06 3.2 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 52 2 020−01−20 04:28 3.0 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 53 2 020−03−29 19:31 3.0 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 54 2 020−08−15 13:45 3.0 广东东源 强震数据 检验地震 55 2 020−10−14 12:43 3.0 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 56 2 020−11−25 05:10 3.0 广东河源 强震数据 检验地震 57 2 020−03−28 20:59 2.9 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 58 2 020−04−04 05:22 2.9 广东南澳海域 强震数据 检验地震 59 2 020−09−10 22:17 2.9 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 60 2 020−01−23 20:07 2.8 广东惠来 强震数据 检验地震 61 2 020−02−09 07:47 2.8 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 62 2 020−03−24 12:15 2.8 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 63 2 020−04−04 21:40 2.8 广东河源 强震数据 检验地震 64 2 020−05−25 21:50 2.8 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 65 2 020−07−05 20:01 2.8 广东东源 强震数据 检验地震 66 2 020−12−03 09:18 2.8 广东东源 强震数据 检验地震 67 2 020−04−18 13:30 2.7 广东五华 强震数据 检验地震 68 2 020−10−29 04:48 2.7 广东五华 强震数据 检验地震 69 2 020−02−12 17:04 2.6 广东河源 强震数据 检验地震 70 2 020−06−02 13:22 2.6 广东普宁 强震数据 检验地震 71 2 020−06−04 13:43 2.6 广东东源 强震数据 检验地震 72 2 020−09−10 13:34 2.6 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 73 2 020−12−28 01:10 2.6 广东平远 强震数据 检验地震 74 2 020−02−17 18:12 2.5 广东河源 强震数据 检验地震 75 2 020−03−12 08:17 2.5 广东五华 强震数据 检验地震 76 2 020−03−30 19:49 2.5 广东五华 强震数据 检验地震 77 2 020−02−09 15:40 2.4 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 78 2 020−03−30 01:57 2.4 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 79 2 020−07−30 09:17 2.4 广东东源 强震数据 检验地震 80 2 020−12−12 10:46 2.4 广东河源 强震数据 检验地震 81 2 020−12−15 10:51 2.4 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 82 2 020−02−09 21:53 2.3 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 83 2 020−02−26 06:19 2.3 广东河源 强震数据 检验地震 84 2 020−04−04 21:40 2.3 广东河源 强震数据 检验地震 85 2 020−05−06 04:18 2.3 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 86 2 020−05−07 00:43 2.3 广东五华 强震数据 检验地震 87 2 020−05−27 17:35 2.3 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 88 2 020−06−06 06:37 2.3 广东惠来 强震数据 检验地震 89 2 020−08−08 11:31 2.3 广东东源 强震数据 检验地震 90 2 020−11−28 06:01 2.3 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 91 2 020−03−09 02:14 2.2 广东东源 强震数据 检验地震 92 2 020−08−09 15:46 2.2 广东东源 强震数据 检验地震 93 2 020−08−16 23:27 2.2 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 94 2 020−08−29 22:19 2.2 广东东源 强震数据 检验地震 95 2 020−09−29 02:39 2.2 广东河源 强震数据 检验地震 96 2 020−10−29 05:24 2.2 广东东源 强震数据 检验地震 97 2 020−11−01 04:38 2.2 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 98 2 020−11−09 03:13 2.2 广东龙川 强震数据 检验地震 99 2 020−01−04 06:20 2.1 广东惠阳海域 强震数据 检验地震 100 2 020−02−27 20:14 2.1 广东东源 强震数据 检验地震 101 2 020−05−23 08:50 2.1 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 102 2 020−05−29 07:54 2.1 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 103 2 020−07−06 03:05 2.1 广东东源 强震数据 检验地震 104 2 020−10−14 11:17 2.1 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 105 2 020−11−25 05:13 2.1 广东河源 强震数据 检验地震 106 2 020−12−18 05:58 2.1 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 -
图 1 珠江三角洲地震监测和预警系统粤东密集台网强震观测台站布局及相关地震事件
(a) 区域地震频率-加速度幅值分布模型的地震分布;(b) 台站布局及测试地震分布图
Figure 1. Layout of strong motion observation stations and related seismic events in the eastern Guangdong dense network of the Pearl River Delta seismic monitoring and early warning system
(a) Distribution of earthquakes used to establish the regional earthquake frequency-acceleration amplitude distribution model;(b) Station layout and distribution of test earthquakes
图 2 噪声加速度模型与区域地震事件频率-幅度分布曲线 (Clinton,Heaton,2002) 对比
Figure 2. Comparison of the noise acceleration model with the frequency-amplitude distribution curve of regional earthquake events (modified fromClinton, Heaton,2002)
表 1 台站监测能力评估表
Table 1 Evaluation table of monitoring capability for typical stations
台站 区域地震最优
监测能力区域地震监测
能力 (≥95%)观测环境 台站位置 观测环境影响因素 CNLG 约M2.0 M>4.0 学校教学楼间绿化带内 师生课间活动 CAGHX M>1.0 M>2.0 学校教学楼后面人迹罕至的空地 鲜少人流 HLAJ M>2.0 M≥5.5 村委办公室内 师生课间活动,村委办公活动 CADF M>3.0 M>4.0 学校围墙附近 师生课间活动,校外车辆和人流 CHFX M>3.0 M>4.0 学校围墙附近 师生课间活动,校外车辆和人流 CYGR M>2.0 M≥4.0 学校内,距教学楼3 m 师生课间活动 CYHX M>3.0 M>4.0 潮阳区河溪邮政支局内 工作人员办公活动 DPFL 约M2.0 M≥3.0 学校内,距离教学楼约30 m 师生课间活动 DPGB 约M3.0 M>4.0 学校内,距离垃圾池6 m,距离围墙1 m 师生课间活动 FSHJ M>1.0 M>2.0 学校内篮球场外侧 鲜少人流 HLDL M>3.0 M≥4.0 学校体育馆左侧 师生课间活动 JLJC 约M2.0 M>2.0 学校科技馆内一角,距离围墙1.5 m 师生课间活动 LFJDD 约M2.0 M>2.0 村委办公楼外右侧后方,靠近前边村委围墙旁 工作人员办公活动 LFJDX M>2.0 M≥3.0 村委进大门后右方空地的一角, 工作人员办公活动 CHXN 约M3.0 约M4.0 六合围管理站院内,海边防洪渠旁 工作人员办公活动 CNCD 约M3.0 M≥4.0 学校内,距围墙3米,距教学楼4 m 师生课间活动 CYCN 约M3.0 M>3.0 学校路边的绿化带内,据教学楼6 m 师生课间活动 HJGA 约M3.0 M>3.0 市区幼儿园内,距教学楼3 m 师生课间活动 CAGHD M>1.0 M>2.0 村委院角落 鲜少人流 HLQZ M>2.0 M>3.0 学校教学楼左侧(食堂后方) 师生课间活动 HLZT 约M2.0 M>3.0 学校内,距离教学楼较远 师生课间活动 HDBPZ 数据异常 HJDH LFJS 1 本文涉及地震事件列表
序号 发震时间 M 震中地区 数据类型 目的 年−月−日 时:分 1 2 021−05−21 23:13 3.4 云南漾濞 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 2 2 014−07−12 03:21 7.0 本州东海岸近海 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 3 2 015−05−30 19:23 8.1 小笠原群岛地区 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 4 2 018−09−08 10:31 5.9 云南墨江 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 5 2 019−06−17 22:55 6.0 四川长宁 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 6 2 019−07−04 10:17 5.5 四川珙县 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 7 2 020−01−07 22:09 3.7 甘肃肃南 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 8 2 020−03−24 22:39 4.2 青海海西 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 9 2 020−06−25 03:47 5.9 本州东海岸近海 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 10 2 020−12−24 21:06 3.1 青海兴海 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 11 2 021−01−23 09:59 4.8 云南盐津 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 12 2 021−02−13 22:07 7.3 本州东海岸近海 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 13 2 021−05−21 21:48 6.5 云南漾濞 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 14 2 021−05−21 21:55 5.0 云南漾濞 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 15 2 021−05−21 21:55 5.0 云南漾濞 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 16 2 021−05−21 21:56 4.6 云南漾濞 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 17 2 021−05−21 21:56 4.6 云南漾濞 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 18 2 021−05−21 22:31 5.2 云南漾濞 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 19 2 021−05−21 23:13 3.4 云南漾濞 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 20 2 021−05−21 23:23 4.5 云南漾濞 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 21 2 021−05−22 02:04 7.4 青海玛多 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 22 2 021−05−22 02:28 4.2 云南漾濞 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 23 2 021−05−22 09:48 4.2 云南漾濞 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 24 2 021−05−22 20:14 4.7 云南漾濞 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 25 2 021−05−27 21:06 4.9 青海玛多 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 26 2 021−05−27 19:52 4.0 云南漾濞 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 27 2 021−06−12 18:00 5.1 云南盈江 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 28 2 021−06−16 16:48 5.8 青海茫崖 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 29 2 021−06−28 19:48 4.5 云南双柏 强震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 30 2 017−07−15 01:41 3.7 广西南丹 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 31 2 017−08−01 06:31 3.0 广西忻城 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 32 2 017−08−13 11:10 3.1 广东东源 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 33 2 017−08−15 13:16 4.1 广西靖西 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 34 2 017−12−08 01:50 1.8 福建龙岩 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 35 2 017−12−20 19:07 1.6 广东东源 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 36 2 017−12−25 14:48 1.0 广东阳江 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 37 2 017−12−29 11:18 1.3 广西博白 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 38 2 017−12−29 18:19 1.2 广东信宜 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 39 2 017−12−30 12:13 3.4 四川盐源 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 40 2 017−12−30 17:06 2.0 广东东源 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 41 2 017−12−30 23:11 1.2 广东茂名 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 42 2 019−11−25 09:18 5.2 广西靖西 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 43 2 019−11−28 07:49 4.6 广西靖西 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 44 2 020−06−26 05:05 6.5 新疆于田 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 45 2 021−04−02 05:40 3.7 广东东源 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 46 2 021−07−02 13:41 2.1 广东连平 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 47 2 021−07−19 12:18 1.6 广东东源 测震数据 建立地震事件频率-加速度幅值分布模型 48 2 020−01−20 04:17 4.2 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 49 2 020−05−25 11:24 3.6 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 50 2 020−05−22 22:40 3.3 广东东源 强震数据 检验地震 51 2 020−04−01 22:06 3.2 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 52 2 020−01−20 04:28 3.0 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 53 2 020−03−29 19:31 3.0 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 54 2 020−08−15 13:45 3.0 广东东源 强震数据 检验地震 55 2 020−10−14 12:43 3.0 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 56 2 020−11−25 05:10 3.0 广东河源 强震数据 检验地震 57 2 020−03−28 20:59 2.9 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 58 2 020−04−04 05:22 2.9 广东南澳海域 强震数据 检验地震 59 2 020−09−10 22:17 2.9 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 60 2 020−01−23 20:07 2.8 广东惠来 强震数据 检验地震 61 2 020−02−09 07:47 2.8 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 62 2 020−03−24 12:15 2.8 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 63 2 020−04−04 21:40 2.8 广东河源 强震数据 检验地震 64 2 020−05−25 21:50 2.8 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 65 2 020−07−05 20:01 2.8 广东东源 强震数据 检验地震 66 2 020−12−03 09:18 2.8 广东东源 强震数据 检验地震 67 2 020−04−18 13:30 2.7 广东五华 强震数据 检验地震 68 2 020−10−29 04:48 2.7 广东五华 强震数据 检验地震 69 2 020−02−12 17:04 2.6 广东河源 强震数据 检验地震 70 2 020−06−02 13:22 2.6 广东普宁 强震数据 检验地震 71 2 020−06−04 13:43 2.6 广东东源 强震数据 检验地震 72 2 020−09−10 13:34 2.6 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 73 2 020−12−28 01:10 2.6 广东平远 强震数据 检验地震 74 2 020−02−17 18:12 2.5 广东河源 强震数据 检验地震 75 2 020−03−12 08:17 2.5 广东五华 强震数据 检验地震 76 2 020−03−30 19:49 2.5 广东五华 强震数据 检验地震 77 2 020−02−09 15:40 2.4 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 78 2 020−03−30 01:57 2.4 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 79 2 020−07−30 09:17 2.4 广东东源 强震数据 检验地震 80 2 020−12−12 10:46 2.4 广东河源 强震数据 检验地震 81 2 020−12−15 10:51 2.4 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 82 2 020−02−09 21:53 2.3 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 83 2 020−02−26 06:19 2.3 广东河源 强震数据 检验地震 84 2 020−04−04 21:40 2.3 广东河源 强震数据 检验地震 85 2 020−05−06 04:18 2.3 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 86 2 020−05−07 00:43 2.3 广东五华 强震数据 检验地震 87 2 020−05−27 17:35 2.3 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 88 2 020−06−06 06:37 2.3 广东惠来 强震数据 检验地震 89 2 020−08−08 11:31 2.3 广东东源 强震数据 检验地震 90 2 020−11−28 06:01 2.3 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 91 2 020−03−09 02:14 2.2 广东东源 强震数据 检验地震 92 2 020−08−09 15:46 2.2 广东东源 强震数据 检验地震 93 2 020−08−16 23:27 2.2 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 94 2 020−08−29 22:19 2.2 广东东源 强震数据 检验地震 95 2 020−09−29 02:39 2.2 广东河源 强震数据 检验地震 96 2 020−10−29 05:24 2.2 广东东源 强震数据 检验地震 97 2 020−11−01 04:38 2.2 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 98 2 020−11−09 03:13 2.2 广东龙川 强震数据 检验地震 99 2 020−01−04 06:20 2.1 广东惠阳海域 强震数据 检验地震 100 2 020−02−27 20:14 2.1 广东东源 强震数据 检验地震 101 2 020−05−23 08:50 2.1 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 102 2 020−05−29 07:54 2.1 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 103 2 020−07−06 03:05 2.1 广东东源 强震数据 检验地震 104 2 020−10−14 11:17 2.1 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 105 2 020−11−25 05:13 2.1 广东河源 强震数据 检验地震 106 2 020−12−18 05:58 2.1 广东丰顺 强震数据 检验地震 -
陈魁. 2000. 应用概率统计[M]. 北京:清华大学出版社:23−29. Chen K. 2000. Applied Probability and Statistics[M]. Beijing:Tsinghua University Press:23−29 (in Chinese).
丁莉莎. 2014. 应用于高温环境下的地震传感器关键技术研究[D]. 北京:中国地震局地震预测研究所:64−78. Ding L S. 2014. Research of Key Technology of Seismic Sensors Used in High Temperature[D] Beijing:Institute of Earthquake Forecasting,China Earthquake Administration:64−78 (in Chinese).
丁莉莎,马洁美,齐军伟,谢剑波,廖一帆,卢子晋,叶世山,劳谦,吕仲杭. 2021. 利用背景噪声的分形方法监控台站观测系统运行状态[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学,41(4):436−440. Ding L S,Ma J M,Qi J W,Xie J B,Liao Y F,Lu Z J,Ye S S,Lao Q,Lü Z H. 2021. Discussion on monitoring the operating state of seismic station observation system by using fractal method of background noise[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamic,41(4):436−440 (in Chinese).
江汶乡. 2015. 面向地震预警的强震动数据处理技术研究[D]. 哈尔滨:中国地震局工程力学研究所:29−34. Jiang W X. 2015. Research on Strong-Motion Data Processing Technology Oriented to Earthquake Early Warning[D]. Harbin:Institute of Engineering Mechanics,China Earthquake Administration:29−34 (in Chinese).
卢大伟,李小军. 2010. 中国大陆强震动观测发展研究[J]. 国际地震动态,(10):35−42. Lu D W,Li X J. 2010. Study on development of strong motion observation in China[J]. Recent Developments in World Seismology,(10):35−42 (in Chinese).
吕永清,蔡亚先,程骏玲. 2007. 确定地震计安装方位的相干性分析法[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学,27(4):124−127. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5942.2007.04.023 Lü Y Q,Cai Y X,Cheng J L. 2007. Orientation for seismometer with coherence analysing method[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics,27(4):124−127 (in Chinese).
王广福. 1986. 地震观测系统的标定与检查[M]. 北京:地震出版社:117−120. Wang G F. 1986. Calibration and Verification of Seismograph Systems[M]. Beijing:Seismological Press:117−120 (in Chinese).
中国地震局. 2017. DB/T 64-2016 强震动观测技术规程[S]. 北京:地震出版社,5. China Earthquake Administration. 2017. DB/T 64−2016 Technical Regulations for Strong Motion Observation[S]. Beijing:Seismological Press:5 (in Chinese).
周雍年. 2006. 中国大陆的强震动观测[J]. 国际地震动态,(11):1−6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4975.2006.11.001 Zhou Y N. 2006. Strong motion observation in Chinese continent[J]. Recent Developments in World Seismology,(11):1−6 (in Chinese).
Abd El-Aal A E A K,Soliman M S. 2013. New seismic noise models obtained using very broadband stations[J]. Pure Appl Geophys,170(11):1849−1857. doi: 10.1007/s00024-013-0640-7
Bormann P. 2002. New Manual of Seismological Observatory Practice (NMSOP) Volume 1[Z]. Potsdam:GeoForschungsZentrum:838−960.
Cauzzi C,Clinton J. 2013. A high- and low-noise model for high-quality strong-motion accelerometer stations[J]. Earthq Spectra,29(1):85−102. doi: 10.1193/1.4000107
Clinton J F,Heaton T H. 2002. Potential advantages of a strong-motion velocity meter over a strong-motion accelerometer[J]. Seismol Res Lett,73(3):332−342. doi: 10.1785/gssrl.73.3.332
El Fellah Y,Abd El-Aal A E A K,Harnafi M,Villaseñor A. 2017. New comprehensive standard seismic noise models and 3D seismic noise variation for morocco territory,North Africa,obtained using seismic broadband stations[J]. Explor Geophys,48(3):272−283. doi: 10.1071/EG15053
Gerner A,Bokelmann G. 2013. Instrument self-noise and sensor misalignment[J]. Adv Geosci,36:17−20. doi: 10.5194/adgeo-36-17-2013
Havskov J,Alguacil G. 2007. Instrumentation in Earthquake Seismology[M]. Dordrecht:Springer:1−349 .
Holcomb,L G. 2002. Experiments in Seismometer Azimuth Determination by Comparing the Sensor Signal Outputs with The Signal Output of An Oriented Sensor[R]. New Mexico:U. S. Geological Survey:2−183,206 .
Howard R M. 2002. The power spectral density and its application[C]//Principles of Random Signal Analysis and Low Noise Design:The Power Spectral Density and its Applications. Perth:Wiley:59−91.
Hutt C R,Evans J R,Followill F,Nigbor R L,Wielandt E. 2010. Guidelines for Standardized Testing of Broadband Seismometers and Accelerometers[R]. Virginia:U. S. Geological Survey:2009−1295.
NIED. 2019. NIED K−NET,KiK−net[DB/OL]. [2020−02−08].https://www.doi.org/10.17598/NIED.0004.
Peterson J R. 1993. Observations and Modeling of Seismic Background Noise[R]. New Mexico:U. S. Geological Survey:13−35.
Schorlemmer D,Woessner J. 2008. Probability of detecting an earthquake[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,98(5):2103−2117. doi: 10.1785/0120070105
Schultz R,Stern V,Gu Y J,Eaton D. 2015. Detection threshold and location resolution of the alberta geological survey earthquake catalogue[J]. Seismol Res Lett,86(2A):385−397. doi: 10.1785/0220140203
Sleeman R. 2006. Three-channel correlation analysis:A new technique to measure instrumental noise of digitizers and seismic sensors[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,96(1):258−271. doi: 10.1785/0120050032
Stehly L,Campillo M,Shapiro N M. 2006. A study of the seismic noise from its long-range correlation properties[J]. J Geophys Res:Solid Earth,111(B10):B10306.
Tasič I,Runovc F. 2013. Determination of a seismometer’s generator constant,azimuth,and orthogonality in three-dimensional space using a reference seismometer[J]. J Seismol,17(2):807−817. doi: 10.1007/s10950-012-9355-y
Welch P. 1967. The use of fast Fourier transform for the estimation of power spectra:A method based on time averaging over short,modified periodograms[J]. IEEE Trans Audio Electroacoust,15(2):70−73. doi: 10.1109/TAU.1967.1161901
Xie J B,Yang D K,Ding L S,Yuan S Y,Chen J T,Lu Z J,Ye S S,Ma J M,Zhao J H,Li X J. 2018. A comparison of azimuth,misalignment,and orthogonality estimation methods in seismometer testing[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,108(2):1004−1017.




 下载:
下载: