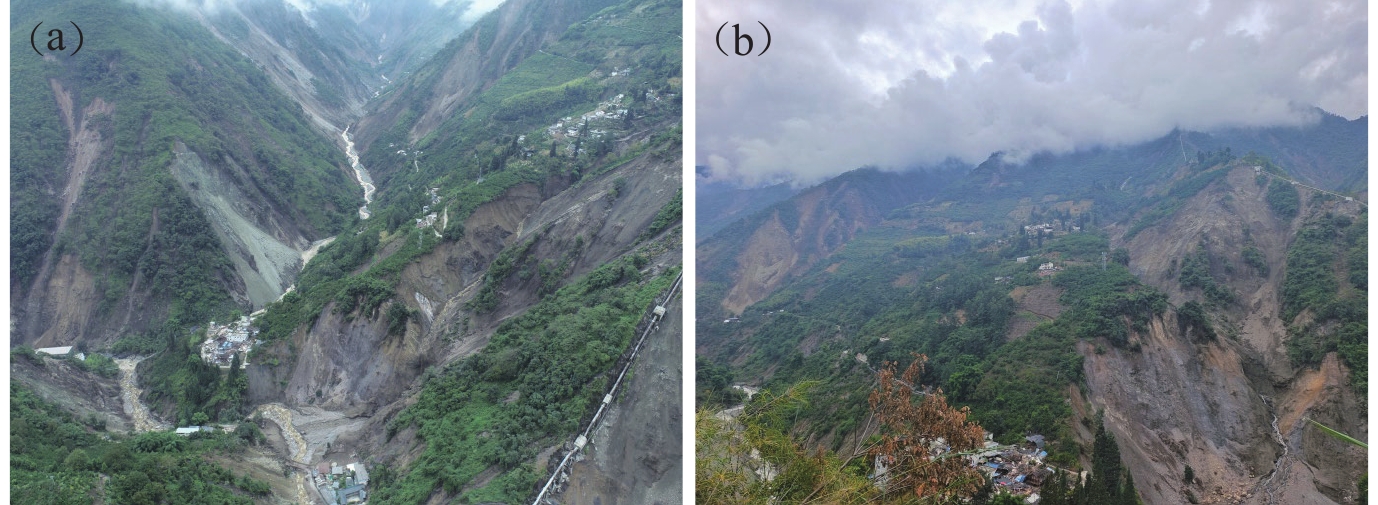
Development characteristics and controlling factors of coseismic geohazards triggered by the Luding MS6.8 earthquake occurred on September 5,2022
-
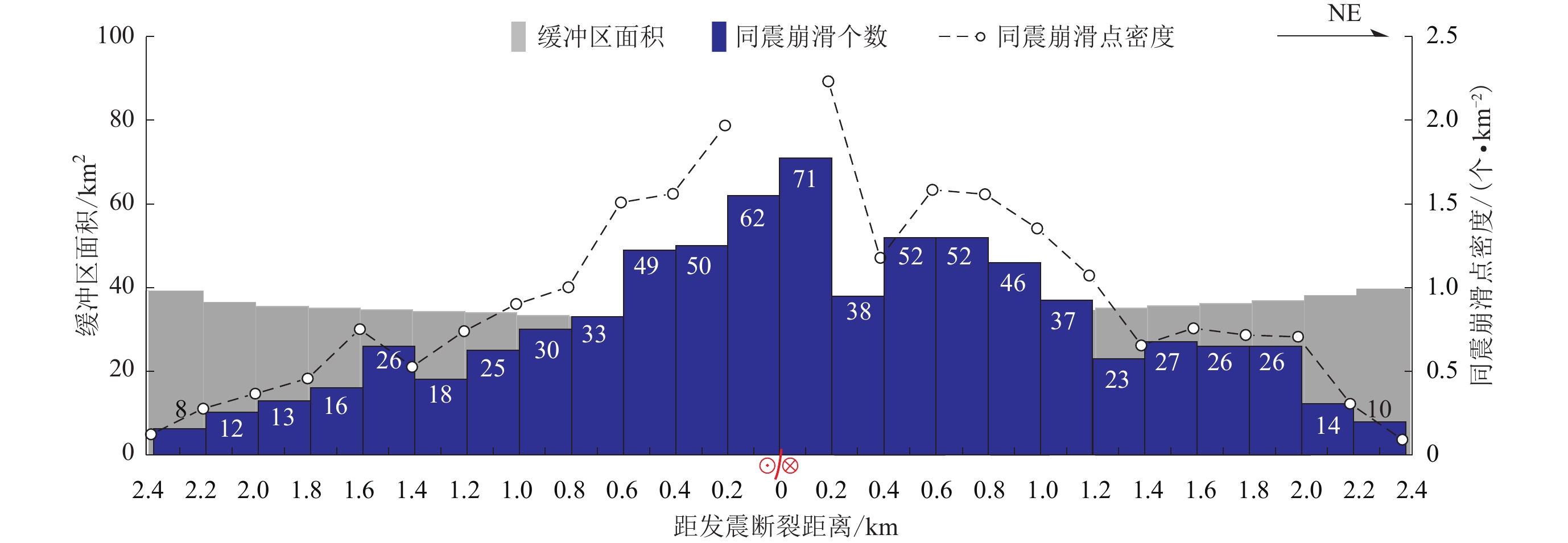
摘要: 基于2022年9月5日泸定MS6.8地震的野外调查,结合遥感解译结果,总结了泸定地震同震地质灾害的发育特征和主控因素,研判了同震地质灾害的演化趋势,并针对同震地质灾害防灾减灾的不同阶段给出了相应的建议。结果显示:泸定地震同震地质灾害整体以小−中型崩塌、滑坡为主,集中分布在磨西镇和海螺沟、得妥镇湾东村、得妥镇大渡河沿岸三个区域;主震和余震、鲜水河活动断裂、地形地貌、特殊岩土体是泸定地震同震崩滑空间分布的主控因素;泸定地震震后地质灾害在未来十年内会极为活跃,需要密切关注磨西河和支沟、大渡河河谷两侧的高陡岸坡、大渡河高阶地、磨西台地边缘区域以及磨西镇、得妥镇同震崩滑密集发育的泥石流沟谷。根据同震地质灾害应急防范的管理逻辑,建议地方政府按照过渡性安置详查阶段、恢复重建阶段、长远规划阶段三个阶段来针对性地开展地质灾害的防灾减灾工作。Abstract: Based on the field investigation of the Luding MS6.8 earthquake occurred on September 5, 2022, combined with the remote sensing interpretation, the development characteristics and controlling factors of coseismic geohazards triggered by the Luding earthquake are summarized, and the evolution trend of coseismic geohazards is studied and judged. According to the different phases of prevention and mitigation of coseismic geohazards, corresponding suggestions are given in order to benefit the prevention and control of geohazards. The results show that the coseismic geohazards of the Luding earthquake are mainly small-medium-sized collapses and landslides, which are concentratedly distributed in three areas: Moxi town and Hailuogou valley, Wandong village of Detuo town and both banks of Daduhe river in Detuo town. Mainshock and aftershocks, Xianshuihe active fault, topography, special rock and sediment mass are the main controlling factors for spatial distribution of coseismic landslides triggered by the Luding earthquake. The geohazards after Luding earthquake will be extremely active in the next 10 years. It is necessary to pay close attention to the high-locality and steep slopes on both banks of the Moxihe river and its tributaries, the Daduhe river, the high-locality terrace along the Daduhe river, the edge area around the Moxi platform, and the debris flows in Moxi town and Detuo town where coseismic landslides are densely developed. Therefore, according to the management logic of emergency prevention of coseismic geohazards, it is suggested that local governments should follow the three phases of detailed investigation, restoration and reconstruction, and long-term planning to carry out geohazard prevention and mitigation work.
-
-
图 8 震区特殊岩土体中的同震崩塌和滑坡
(a) 燕子沟景区公路沿线的冰水堆积崩塌;(b) 海螺沟景区公路沿线坡积碎石土中形成的滑坡;(c) 大渡河沿岸S211公路云母片岩中的顺向坡滑坡;(d) 燕子沟景区公路北侧斜坡花岗岩中的崩塌
Figure 8. Co-seismic landslides occurred in special rock and sediment mass
(a) Collapse occurred in glaciofluvial sediment along road in Yanzigou valley;(b) Landslide occurred in gravel soil along road in Hailuogou valley;(c) Consequent landslide occurred in mica slate along S211 road along Daduhe river; (d) Rockfall occurred in granite along road in Yanzigou valley
表 1 历史地震震后地质灾害活跃期统计
Table 1 Statistics of active period of geohazard after historical earthquakes
地震 MS 震后地质灾害活跃期/a 1923年日本关东地震 7.9 15 1999年台湾集集地震 7.6 5 2005年巴基斯坦克什米尔地震 7.6 5 2008年汶川地震 8.0 20 2013年芦山地震 7.0 10 -
白明坤,Marie-Luce C,李海兵,潘家伟,吴琼,王世广,刘富财,焦利青,张进江,张蕾,龚正. 2022. 鲜水河断裂带乾宁段晚第四纪走滑速率及区域强震危险性研究[J]. 地质学报,96(7):2312–2332. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.07.005 Bai M K,Marie-Luce C,Li H B,Pan J W,Wu Q,Wang S G,Liu F C,Jiao L Q,Zhang J J,Zhang L,Gong Z. 2022. Late Quaternary slip rate and earthquake hazard along the Qianning segment,Xianshuihe fault[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,96(7):2312–2332 (in Chinese).
崔鹏,陈晓清,张建强,杨宗佶,游勇,范建容,苏凤环,孔应德,朱兴华. 2013. “4·20”芦山7.0级地震次生山地灾害活动特征与趋势[J]. 山地学报,31(3):257–265. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2013.03.001 Cui P,Chen X Q,Zhang J Q,Yang Z J,You Y,Fan J R,Su F H,Kong Y D,Zhu X H. 2013. Activities and tendency of mountain hazards induced by the MS7.0 Lushan earthquake,April 20,2013[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,31(3):257–265 (in Chinese).
戴岚欣,许强,范宣梅,常鸣,杨琴,杨帆,任敬. 2017. 2017年8月8日四川九寨沟地震诱发地质灾害空间分布规律及易发性评价初步研究[J]. 工程地质学报,25(4):1151–1164. Dai L X,Xu Q,Fan X M,Chang M,Yang Q,Yang F,Ren J. 2017. A preliminary study on spatial distribution patterns of landslides triggered by Jiuzhaigou earthquake in Sichuan on August 8th,2017 and their susceptibility assessment[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,25(4):1151–1164 (in Chinese).
范宣梅,方成勇,戴岚欣,王欣,罗永红,魏涛,王运生. 2022a. 地震诱发滑坡空间分布概率近实时预测研究:以 2022 年 6 月 1 日四川芦山地震为例[J]. 工程地质学报,30(3):729–739. Fan X M,Fang C Y,Dai L X,Wang X,Luo Y H,Wei T,Wang Y S. 2022a. Near real time prediction of spatial distribution probability of earthquake-induced landslides:Take the Lushan earthquake on June 1,2022 as an example[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,30(3):729–739 (in Chinese).
范宣梅,王欣,戴岚欣,方成勇,邓宇,邹城彬,汤明高,魏振磊,窦向阳,张静,杨帆,陈兰,魏涛,杨银双,张欣欣,夏明垚,倪涛,唐小川,李为乐,戴可人,董秀军,许强. 2022b. 2022年MS6.8级泸定地震诱发地质灾害特征与空间分布规律研究[J]. 工程地质学报,30(5):1504–1516. Fan X M,Wang X,Dai L X,Fang C Y,Deng Y,Zou C B,Tang M G,Wei Z L,Dou X Y,Zhang J,Yang F,Chen L,Wei T,Yang Y S,Zhang X X,Xia M Y,Ni T,Tang X C,Li W L,Dai K R,Dong X J,Xu Q. 2022b. Characteristics and spatial distribution pattern of MS6.8 Luding earthquake occurred on September 5,2022[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,30(5):1504–1516 (in Chinese).
付小方,侯立玮,李海兵,王宗秀,邹付戈. 2008. 汶川大地震(MS8.0)同震变形作用及其与地质灾害的关系[J]. 地质学报,82(12):1733–1746. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.12.009 Fu X F,Hou L W,Li H B,Wang Z X,Zou F G. 2008. Coseismic deformation of the MS8.0 Wenchuan earthquake and its relationship with geological hazards[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,82(12):1733–1746 (in Chinese).
黄润秋. 2011. 汶川地震地质灾害后效应分析[J]. 工程地质学报,19(2):145–151. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2011.02.001 Huang R Q. 2011. After effect of geohazards induced by the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,19(2):145–151 (in Chinese).
黄润秋,李为乐. 2008. “5·12”汶川大地震触发地质灾害的发育分布规律研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,27(12):2585–2592. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.12.028 Huang R Q,Li W L. 2008. Research on development and distribution rules of geohazards induced by Wenchuan earthquake on 12th May,2008[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,27(12):2585–2592 (in Chinese).
李洪梁,黄海,李元灵,张佳佳,王灵,李宝幸. 2022. 川藏铁路沿线板块缝合带地质灾害效应研究[J]. 地球科学,47(12):1–23. Li H L,Huang H,Li Y L,Zhang J J,Wang L,Li B X. 2022. Geohazard effect of plate suture zone along Sichuan-Tibet railway[J]. Earth Science,47(12):1–23 (in Chinese).
倪化勇. 2010. 海螺沟景区典型泥石流流域地貌特征及灾害防治[J]. 水土保持研究,17(1):154–158. Ni H Y. 2010. Geomorphologic characteristics of typical debris-flow basins in Hailuogou scenic spot and disaster prevention[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,17(1):154–158 (in Chinese).
潘家伟,李海兵,Chevalier M L,白明坤,刘富财,刘栋梁,郑勇,卢海建,赵中宝. 2020. 鲜水河断裂带色拉哈—康定段新发现的活动断层:木格措南断裂[J]. 地质学报,94(11):3178–3188. Pan J W,Li H B,Chevalier M L,Bai M K,Liu F C,Liu D L,Zheng Y,Lu H J,Zhao Z B. 2020. A newly discovered active fault on the Selaha-Kangding segment along the SE Xianshuihe fault:The South Mugecuo fault[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,94(11):3178–3188 (in Chinese).
四川省地震局地震地质队鲜水河活动断裂带填图组. 2013. 鲜水河活动断裂带地质图(1 ∶ 50 000)说明书[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 1. Xianshuihe Active Fault Zone Mapping Group, Seismic Geological Team, Sichuan Earthquake Administration. 2013. Manual of Geological Map of Xianshuihe Active Fault Zone (1∶50 000)[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press: 1 (in Chinese).
唐川,梁京涛. 2008. 汶川震区北川9·24暴雨泥石流特征研究[J]. 工程地质学报,16(6):751–758. Tang C,Liang J T. 2008. Characteristics of debris flows in Beichuan epicenter of the Wenchuan earthquake triggered by rainstorm on September 24,2008[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,16(6):751–758 (in Chinese).
铁永波,张宪政,卢佳燕,梁京涛,王东辉,马志刚,李宗亮,鲁拓,石胜伟,刘民生,巴仁基,何龙江,张新克,甘伟,陈凯,高延超,白永健,龚凌枫,曾孝文,徐伟. 2022. 四川省泸定县MS6.8地震地质灾害发育规律与减灾对策[J]. 水文地质工程地质,49(6):1–12. Tie Y B,Zhang X Z,Lu J Y,Liang J T,Wang D H,Ma Z G,Li Z L,Lu T,Shi S W,Liu M S,Ba R J,He L J,Zhang X K,Gan W,Chen K,Gao Y C,Bai Y J,Gong L F,Zeng X W,Xu W. 2022. Characteristics of geological hazards and it’s mitigations of the MS6.8 earthquake in Luding county,Sichuan Province[J]. Hydrogeology &Engineering Geology,49(6):1–12 (in Chinese).
闻学泽,Allen C R,罗灼礼,钱洪,周华伟,黄伟师. 1989. 鲜水河全新世断裂带的分段性、几何特征及其地震构造意义[J]. 地震学报,11(4):362–372. Wen X Z,Allen C R,Luo Z L,Qian H,Zhou H W,Huang W S. 1989. Segmentation,geometric features,and their seismotectonic implications for the Holocene Xianshuihe fault zone[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,11(4):362–372 (in Chinese).
许冲,徐锡伟,吴熙彦,戴福初,姚鑫,姚琪. 2013. 2008年汶川地震滑坡详细编目及其空间分布规律分析[J]. 工程地质学报,21(1):25–44. Xu C,Xu X W,Wu X Y,Dai F C,Yao X,Yao Q. 2013. Detailed catalog of landslides triggered by the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake and statistical analyses of their spatial distribution[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,21(1):25–44 (in Chinese).
许强,李为乐. 2010. 汶川地震诱发大型滑坡分布规律研究[J]. 工程地质学报,18(6):818–826. Xu Q,Li W L. 2010. Distribution of large-scale landslides induced by the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,18(6):818–826 (in Chinese).
殷跃平. 2008. 汶川八级地震地质灾害研究[J]. 工程地质学报,16(4):433–444. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2008.04.001 Yin Y P. 2008. Researches on the geo-hazards triggered by Wenchuan earthquake,Sichuan[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,16(4):433–444 (in Chinese).
殷志强,赵无忌,褚宏亮,孙巍. 2014. “4·20”芦山地震诱发地质灾害基本特征及与“5·12”汶川地震对比分析[J]. 地质学报,88(6):1145–1156. Yin Z Q,Zhao W J,Chu H L,Sun W. 2014. Basic characteristics of geohazards induced by Lushan earthquake and compare to them of Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,88(6):1145–1156 (in Chinese).
张佳佳,李海兵,赵国华,李勇,颜照坤,王焕,云锟. 2015. 2013年四川芦山地震次生山地灾害发育规律[J]. 地质通报,34(5):898–907. Zhang J J,Li H B,Zhao G H,Li Y,Yan Z K,Wang H,Yun K. 2015. Features of secondary mountain hazards triggered by the 2013 Lushan earthquake,Sichuan Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,34(5):898–907 (in Chinese).
赵德军,王道永,吴德超,刘援朝. 2008. 磨西断裂变形与运动学特征研究[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质,28(3):15–20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2008.03.003 Zhao D J,Wang D Y,Wu D C,Liu Y C. 2008. Structural deformation and kinematics of the Moxi fault in western Sichuan[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology,28(3):15–20 (in Chinese).
郑本兴. 2001. 贡嘎山东麓第四纪冰川作用与磨西台地成因探讨[J]. 冰川冻土,23(3):283–291. Zheng B X. 2001. Study on the Quaternary glaciation and the formation of the Moxi platform in the east slopes of the Mount Gongga[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,23(3):283–291 (in Chinese).
中国地震局地球物理研究所. 2022. 2022年9月5日四川甘孜州泸定6.8级地震的震源特征[EB/OL]. [2022-09-06]. http://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzA4MzkxODc5Nw==&mid=2247485850&idx=1&sn=da384b868f35745092495f41e124d4d6&chksm=9fee6338a899ea2eccdfe5c4ca5a8c4ff5fe8aa474f5d1c12d5ad9b16b508f99f915d9d8af8c#rd. Institute of Geophysics, China Earthquake Administration. 2022. The source characteristics of the Luding 6.8 earthquake in Ganzi prefecture, Sichuan Province on September 5, 2022[EB/OL]. [2022-09-06]. http://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzA4MzkxODc5Nw==&mid=2247485850&idx=1&sn=da384b868f35745092495f41e124d4d6&chksm=9fee6338a899ea2eccdfe5c4ca5a8c4ff5fe8aa474f5d1c12d5ad9b16b508f99f915d9d8af8c#rd (in Chinese).
周洪福,韦玉婷,王运生,刘宏. 2017. 1786年磨西地震触发的摩岗岭滑坡演化过程与成因机理[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),44(6):649–658. Zhou H F, Wei Y T, Wang Y S, Liu H. 2017. Discussion on the formation evolution and genetic mechanism of Mogangling landslide triggered by Moxi earthquake, Sichuan, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 44(6): 649–658 (in Chinese).
Bai M K,Chevalier M L,Pan J W,Replumaz A,Leloup P H,Métois M,Li H B. 2018. Southeastward increase of the late Quaternary slip-rate of the Xianshuihe fault,eastern Tibet:Geodynamic and seismic hazard implications[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett,485:19–31. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2017.12.045
Jiang G Y,Xu X W,Chen G H,Liu Y J,Fukahata Y,Wang H,Yu G H,Tan X B,Xu C J. 2015. Geodetic imaging of potential seismogenic asperities on the Xianshuihe-Anninghe-Zemuhe fault system,southwest China,with a new 3-D viscoelastic interseismic coupling model[J]. J Geophys Res:Solid Earth,120(3):1855–1873. doi: 10.1002/2014JB011492
Khan S F,Kamp U,Owen L A. 2013. Documenting five years of landsliding after the 2005 Kashmir earthquake,using repeat photography[J]. Geomorphology,197:45–55. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2013.04.033
Lin C W,Liu S H,Lee S Y,Liu C C. 2006. Impacts of the Chi-Chi earthquake on subsequent rainfall-induced landslides in central Taiwan[J]. Eng Geol,86(2/3):87–101.
Nakamura H, Tsuchiya S, Inoue K, Ishikawa Y. 2000. Sabo Against Earthquakes[M]. Tokyo: Kokon Shoin: 190–220.
Shao Z G,Xu J,Ma H S,Zhang L P. 2016. Coulomb stress evolution over the past 200 years and seismic hazard along the Xianshuihe fault zone of Sichuan,China[J]. Tectonophysics,670:48–65. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2015.12.018
Yin Y P,Wang F W,Sun P. 2009. Landslide hazards triggered by the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake,Sichuan,China[J]. Landslides,6(2):139–152. doi: 10.1007/s10346-009-0148-5





 下载:
下载: